Abstract
The 3′ untranslated region has an important role in gene regulation through microRNAs, and it has been estimated that microRNAs regulate up to 50% of coding genes in mammals. With the aim of allelic variant identification of 3′ untranslated region microRNA seed sites, the 3′ untranslated region was searched for seed sites of four temperament-associated genes (CACNG4, EXOC4, NRXN3, and SLC9A4). The microRNA seed sites were predicted in the four genes, and the CACNG4 gene had the greatest number with 12 predictions. To search for variants affecting the predicted microRNA seed sites, the four 3′ untranslated regions were re-sequenced in a Brahman cattle population. Eleven single nucleotide polymorphisms were identified in the CACNG4, and eleven in the SLC9A4. Rs522648682:T>G of the CACNG4 gene was located at the predicted seed site for bta-miR-191. Rs522648682:T>G evidenced an association with both exit velocity (p = 0.0054) and temperament score (p = 0.0097). The genotype TT had a lower mean exit velocity (2.93 ± 0.4 m/s) compared with the TG and GG genotypes (3.91 ± 0.46 m/s and 3.67 ± 0.46 m/s, respectively). The allele associated with the temperamental phenotype antagonizes the seed site, disrupting the bta-miR-191 recognition. The G allele of CACNG4-rs522648682 has the potential to influence bovine temperament through a mechanism associated with unspecific recognition of bta-miR-191.
1. Introduction
Temperament in cattle is an important trait observed as a response to handling and human-facing activities [1]. There is a growing list of candidate genes associated with temperament traits [2,3], and their complex genetic architecture still needs to be elucidated. Most genetic variations in candidate genes for temperament are based on Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs). These markers are relevant due to their functional implications. For instance, SNPs in coding regions can have amino acid substitution with an effect on protein structure [4], whereas those located in regions such as enhancer, intron, and untranslated regions could be involved in recognition sequences such as transcription factors, splicing, regulatory regions, and sequences of epigenetic modulation [5].
The 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) particularly has an important role in gene regulation through microRNAs (miRNAs). The miRNAs are processed from stem-loop regions of longer RNA transcripts that are ~22 nucleotides (nt) in length [6], and they have a cis-regulatory role in 3′UTR regions [7]. It has been estimated that miRNAs regulate up to 50% of coding genes in mammals [8]. Regulation by miRNAs occurs through recognition of a heptamer of 2–8 nucleotides known as the seed region that binds to messenger RNA (mRNA) at a complementary site located in the 3′UTR sequence. Therefore, the 3′UTR seed site is highly conserved; a change in this site could antagonize the complementary binding of the miRNA-mRNA to a partial binding, with an effect on expression or repression [7].
It has been widely documented that the SNPs could modify the seed site, allowing for changes in gene expression in humans and domestic animal species. Orthologous genes of serotonin receptors associated with temperament have been susceptible to repression by a polymorphism in the 3′UTR of mRNA, affecting aggressive behavior [9]. In contrast, the repression loss for miR-96 by the allelic change in the seed site of the HTR1B gene (A/G) caused a phenotypic change in the aggressiveness of mice [10]. The association of variants in genes of subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels for the treatment of schizophrenia have been identified, and SNP genotypes in the 3′UTR region of CACNA1B gene were associated with an increase in symptoms and allowed for the explanation that the regulation was potentially mediated the modification of the seed site [11]. From the growing list of candidate genes associated with cattle temperament, Paredes-Sánchez et al. [12] found an important association of temperament traits with five intronic SNPs located in the neurexin-3 (NRXN3), calcium voltage-gated channel auxiliary subunit gamma-4 (CACNG4), exocyst complex component-4 (EXOC4), and solute carrier family 9 member A4 (SLC9A4) genes. These candidate genes were implicated in different biological pathways related to the expression of behaviors as a response to stress and fear, supporting their possible role in cattle temperament [12], but their precise implications for gene expression and or regulation requires more study.
Due to the potentially important role of variations in the 3′UTR, this targeted study characterized the 3′UTR in the four candidate genes (CACNG4, EXOC4, NRXN3, and SLC9A4). As a first step, bioinformatic analysis was achieved to detect potential seed sites, and as a second step resequencing each 3′UTR from each gene was accomplished by searching for genetic variation and its effect on regions important for miRNA interactions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Material
The animal data came from a reference population with a pedigree structure, including 242 dams and 12 sires. One hundred sixty-four calves were selected from a population of three hundred fifty-five Brahman calves (one hundred eighty-one males and one hundred seventy-four females) born between 2018 and 2020 at the Texas A&M AgriLife Research and Extension Center in Overton, TX. The selected calves were those with a single dam (n = 148) and dam half-siblings (n = 16). Birth year distribution was: 2018 (n = 91, 41 males and 50 females); 2019 (n = 40, 20 males and 20 females); and 2020 (n = 33, 15 males and 10 females). All calves had data recorded for temperament traits. The temperament tests applied were: exit velocity (EV), an objective test that measures the speed of an animal when traveling 1.8 m after release from a holding chute, measured using an infrared sensor (FarmTek, Inc., North Wylie, TX, USA); pen score (PS), a subjective measurement test through the visual evaluation of animal behavior, assigning scale values where 1 represents a docile animal and 5 points to an aggressive one; temperament score was calculated as the average of the EV and PS values: [TS = (EV + PS)/2] [12,13]. DNA was obtained from ear notches, taken during temperament evaluation, and stored at −80 °C. DNA extraction was performed with the commercial Genelute Mammalian Genomic DNA kit (Cat. G1N350, Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC, St. Louis, MO, USA).
All practices complied with the Guide for the Care and Use of Agricultural Animals in Research and Teaching 2010 and were approved by the Texas A&M University Animal Care and Use Committee AUP 2002-315.
2.2. In Silico Analysis to Locate Seed Sites for miRNAs and their Potential Disrupting of SNPs
The 3′UTR analysis region from CACNG4, EXOC4, NRXN3, and SLC9A4 genes was determined using as a reference the mRNA sequence obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) public database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 15 March 2022)). Using the ARS-UCD 1.3 version of the bovine genome and taking the last position of the final exon defined from the termination codon (TGA) of mRNA, using the Genome Data Viewer tool (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/gdv/ (accessed on 15 March 2022)). The reference sequences were the Bos taurus (L., 1758) genome, so we searched the Bos indicus (L., 1758) genome (version Bos_indicus_1.0) sequences for alignment with the Clustal Omega (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/ (accessed on 18 March 2022)) tool, described by Madeira et al. [14] to ensure a percentage of identity through genomes.
The search of miRNAs homologous sites was carried out in the miRBase v.22.1 database (https://mirbase.org/ (accessed on 23 March 2022)) [15] by taking the previously defined 3′UTR and uploading it into the search engine, specifying for the mature sequence “Mature miRNAs” using the BLASTN method, which allows for searching for homologous miRNAs in long sequences, up to 1000 base pairs (bp), using the “Bos taurus” taxon. The sequences longer than 1000 bp were overlapped with fragments of 250 bp.
Once the miRNA families were identified, the ENSEMBL database (http://ensembl.org/ (accessed on 25 March 2022)) was searched for SNPs, using a search engine for “Cow” and the gene name (e.g., CACNG4). Next, a search was made in the “Genetic Variation” tab, filtering the results by SNP class variations and “Consequences: 3 prime UTR variant”. The sequences were aligned “Pairwise” between miRNAs and 3′UTR with the GenScript tool (https://www.genscript.com/sms2/pairwise_align_dna.html (accessed 30 March 2022)); a perfect complementarity between sequences was sought to have a reliable prediction, locating the seed site and positioning the SNPs.
If an SNP in the seed site was found, the gene sequence with the allelic change was searched in miRBase to determine if there was a loss of homology recognition. We examined for evolutionary conservation between the miRNA and the gene sequence for miRNA search in the microRNAviewer matrix (https://people.csail.mit.edu/akiezun/microRNAviewer/ (accessed on 1 April 2022)) that shows a global view of homologous miRNA genes [16], whereas for the mRNA conservation the 3′UTR of genes was searched among B. taurus, B. indicus, B. mutus, Ovis aries, Capra hircus, Sus scrofa, Equus caballus, and Homo sapiens.
The binding of miRNA-mRNA was evaluated for target site accessibility and free energy through mRNA sequence (3′UTR). The RNAhybrid (https://bibiserv.cebitec.uni-bielefeld.de/rnahybrid/ (accessed on 10 October 2022)) [17] tool finds the minimum free energy (MFE) hybridization between RNA sequences, setting the stringency value at <−20 kcal/mol [18]. To calculate the allelic effect, a change in MFE (ΔMFE) between both variants was calculated with MFEreference − MFEalternative [19].
2.3. Searching for SNPs in 3′UTR and Their Effect on Brahman Cattle Temperament Traits
Samples of 65 calves of the Brahman breed were used as the discovery population. It included animals with docile and temperamental scores selected according to categorical scores for docility, with EV ranges of 0.16–1.82 m/s and 0.4–1.56 m/s for females and males, respectively, and temperamental ranges of 3.13–7.66 m/s and 3.05–10.83 for females and males, respectively [12]. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from these samples were used to amplify the 3′UTR region of CACNG4, EXOC4, NRXN3, and SLC9A4 genes using specific primers (Table 1). All of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products were accomplished using the Nextera Flex protocol from Illumina (Part #15044223 Rev. B).

Table 1.
Primers designed for the amplification of the 3′UTR sequence.
Results of 3′UTR sequencing were analyzed through the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK.3.7) [20], a program group used for variant discovery and genotyping [21]. Reads were aligned with the bovine genome (https://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/bosTau9/bigZips/ (accessed on 8 June 2022)) for total BWA (Burrows–Wheeler alienator) [22], with exact matches that cannot be extended in either direction through Maximal Exact Match for quality control. Once the alignment was performed, step data cleaning was followed by identifying and deleting repeated reads and the selection of major reads with Picar, generating BAI and BAM files. Finally, the outputs were submitted to HaplotypeCaller of GATK to identify variants, extract and filter SNPs, thus generating an output file containing the position of variations, alleles, and quality parameters.
2.4. Effect of CACNG4-3′UTR SNPs on Temperament Traits
DNA samples from 164 Brahman calves were used for SNP genotyping. Samples were amplified with primers (5′-CCATTATCTCCTCTTGGGAA-3′, and 3′-ACCCTTTCTGTGAGCAG-5′) flanking the region of CACNG4-3′UTR that includes the seed site with the rs522648682:T>G SNP. The allelic assignment was achieved once the products were sequenced using SimpleSeq™ (Eurofins Genomics, LLC, Louisville, Kentucky, USA), and the allelic frequency analysis was determined using Cervus 3.0.7 software [23].
2.5. Statistical Association Analysis
A Shapiro–Wilk test was performed on exit velocity, pen score, and temperament score traits, to verify normality. Posteriorly, to estimate the effects of rs522648682:T>G, rs483247086:A>C, and rs109514077:C>T genotypes on the studied temperament traits, a statistical model was fitted using the MIXED procedure in SAS OD for Academics (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) as follows:
where: Yijk = temperament traits (EV, PS, and TS), μ = general mean, Si = random effect common to the progeny of the i-th sire, Dj = random effect common to the progeny of the j-th dam, Gk = fixed effect of k-th genotype of loci, Xl = fixed effect of l-th sex of animal, Ym = fixed effect of m-th year of birth, β1dj = fixed effect of linear covariate for age years of j-th dam, β2dj2 = fixed effect of quadratic covariate for age years of j-th dam, and εijkm = random error.
Least-squares means for the genotypes of the studied loci were estimated and compared using a PDIFF statement considering an alpha = 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. In Silico Analysis of Seed Site and SNP Variants in 3′UTR Sequences
A total of 27 seed sites for miRNAs distributed in the four target genes were found. The CACNG4 and NRXN3 had twelve and eleven predicted seed sites, while EXOC4 and SLC9A4 had one and three seed sites, respectively (Table 2).

Table 2.
Putative seed sites sequences for recognition between miRNAs-mRNA located in candidate genes for temperament.
After the four studied genes were interrogated for database-reported SNPs in their 3ÚTR region, we found that only the CACNG4 gene had 274 reported SNPs, and from those only the transversion T>G (rs522648682) was located at a previously identified miRNA seed site, the bta-miR-191.
The prediction analysis shows that the seed site perfectly complements the bta-miR-191 presence in the 3′UTR-CACNG4 gene, whereas the allelic change T>G induces the loss of bta-miR-191 recognition (Figure 1).
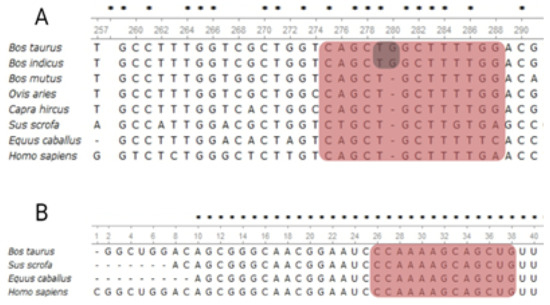
Figure 1.
Characterization of miR-191 as a putative seed site in the 3′UTR-CACNG4. (A) alignment of 3′UTR-CACNG4; the red background displays the putative seed site sequence for miR-191. The SNP is shown in the grey background. The percentage of AT nucleotides for the CACNG4 seed site was 47.67% without considering the SNP, whereas the flanking sequence (30 nucleotides) was 46.67%. (B) miR-191 gene alignment. The alignment shows a hairpin sequence of the positive strand, with a red background for the seed site’s recognition sequence; recognition by miRNA would correspond to an arm 3′ of the miRNA strand (3p). * Conserved position among all the sequences in the alignment.
A homology analysis revealed the seed site for miR-191 located in the bovine CACNG4 gene is conserved in different mammalian species such as sheep, goat, horse, yak, and humans (Figure 1A). The complete seed site is conserved among the Bovidae family species. The homology of the miR-191 gene was also high between the included species, with a 1.0–0.94 conservation value reported in the microRNAviewer matrix (Figure 1B). In addition to the conservation value, the evaluation of binding between mRNA-miRNA shows that the allele T had a MFE = −33.0 kcal/mol, whereas the G allele had a MFE = −28.9 kcal/mol, with a ΔMFE value of 4.1 kcal/mol. Negative ΔMFE displays increased binding, whereas a positive value indicates decreased binding in the variant allele. These results support the importance of this region as a miRNA target recognition in the bovine CACNG4 gene.
3.2. Search for Variants in 3′UTR of the Four Temperament Candidate Genes in Brahman Cattle
The resequencing of the 3′UTR region in the four studied genes shows that the EXOC4 and NRXN3 genes did not have SNP variants, while a total of twenty-two variants were located in the CACNG4 (n = 11) and SLC9A4 (n = 11) genes (Table 3).

Table 3.
Identification of SNP variants in temperament candidate genes in Brahman cattle.
None of the eleven SNPs in the SLC9A4 gene were located at any of the in silico predicted seed site positions; however, the analysis of the CACNG4 SNPs allowed for confirmation in the studied Brahman population, with the presence of SNP rs522648682:T>G previously identified in the in silico analysis as a potential SNP responsible for disrupting a seed site in the 3′UTR of the CACNG4 gene (Figure 1A).
3.3. Association of the SNP rs522648682 Located at 3′UTR of CACNG4 Gene with Temperament Traits in Brahman Cattle
The allelic frequencies in the genotyped Brahman cattle show that only the rs522648682:T>G located at the seed site for bta-miR-191 on the CACNG4 gene was polymorphic (T = 0.3476, G = 0.6524) according to the minor allele frequency >10%.
The results for the association analysis of rs522648682:T>G with three temperament traits (EV, PS, and TS) are shown in Table 4. A significant effect for EV and TS (p < 0.05) was observes; the carriers of the GG genotype had an EV value of 0.74 m/s and a TS value of 1.23 SD, which was greater than the TT genotype. No significant differences were observed between the heterozygous genotype (TG) and GG homozygous genotypes.

Table 4.
Least-squares means and standard errors of the effect for rs522648682 on temperament traits.
4. Discussion
The genotypes of rs522648682-CACNG4 were associated with EV and TS. The genotypes with alternative allele G favored the highest temperamental values, and in silico analysis shows a lost recognition and unstable hybridization for bta-miRNA-191. In contrast, a homozygous genotype (TT) with a reference allele shows docility and stable hybridization in silico between miRNA-mRNA. The GG and TG genotype differences between both temperament tests (0.24 m/s EV and 0.008 SD TS) were similar, whereas among genotypes with significantly different means (TT vs. TG, GG), animals with the G allele were approximately 25% faster in terms of EV. Additionally, the population had a Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium for the rs522648682, supporting the population size effective genotyping; however, the sample number for the association analysis is still limiting for the use of rs522648682-CACNG4 as a marker to assist in cattle temperament selection.
Our in silico search found seed sites for potential miRNA in the four temperament candidate genes analyzed. To our knowledge, none of the predicted miRNAs have been shown to influence the gene expression patterns or temperament traits.
The interaction with miRNAs plays a crucial role in the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression [24]. Therefore, the presence of SNPs in the seed site could create illegitimate sites, interfere with the recognition site, and promote gene expression change [25]. Here, we found in silico and experimental evidence that the miR-191 seed site could be antagonized by the rs522648682 SNP located at the 3′UTR of CACNG4. The seed site comprises a heptamer of 2–8 highly conservated nucleotides for miRNA recognition [6], and it can have a total or partial complementarity between miRNA and mRNA [26].
The rs522648682 was located on position 5, disrupting the architecture of the seed site through allele change. The heptamer had conservated sequences among Bovidae, sheep, goat, horse, and humans. Additionally, the miR-191 gene has conservation and homology between humans, bovine, and horse, according to the matrix comparison performed using microRNAviewer and supported by the experimental evidence of miRBase. However, seed site matches are insufficient as evidence for a putative repression effect, and some additional attributes increase the effectiveness of functional site prediction. Grimson et al. [27] proposed a scoring scheme with a high AU percentage of around 30 nucleotides upstream and downstream from the seed site, while Long et al. [28] found that seed sites with regulatory activity have between 47.8–41.2% AU composition; these last results coincide with the values observed in our study (Figure 1A).
It has been proposed that duplex analysis also supports the prediction of binding between miRNA-mRNA sequences [29]. The RNA duplex is more stable and thermodynamically stronger when MFE is lower, setting an MFE value threshold for the seed site search at MFE ≤ 20 [18]. In addition to the structural recognition of 13 nucleotides between 3′UTR-CACNG4 and bta-miR-191, our hybridization analysis found positive differences when T was replaced by G (ΔMFE = 4.1 kcal/mol). The reference and alternative allele MFE value difference affected hybridization [19], with a positive value increase in MFE having the potential to form a weak RNA duplex [30].
According to the literature, three types of duplex structures can be presented: the canonical with perfect 5′ to 3′ complementarity, the dominant seed sites type with perfect complementarity at the 5′ of the seed site but poor complementarity at the 3′, and compensatory sites with a mismatch at the 5′ end compensated by a complementarity at the 3′ [31]. The SNP could impact the duplex structure type, since the seed site’s reference allele T generates a canonical type and the alternative G is a compensatory site. Non-canonical sites generally do not lead to mRNA modulation by miRNA binding [32,33].
In humans, miR-191 has been extensively studied, and due to its role in the regulation of many diseases, especially different cancer types, it is considered as an important candidate biomarker [34]. Interestingly, miR-191-5p is part of a group of unique circulating miRNAs that are able to distinguish with high precision an Alzheimer’s disease patient from controls [35]; thus, it is also considered as a potential biomarker. In cattle, bta-miR-191 has not been reported as a regulator of CACNG4. Nevertheless, bta-miR-191 has been reported via expression profile analysis in bovine blood serum and plasma [36]. In silico approaches and reporter system information have shown that miR-191 directly represses brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) through binding in 3′UTR in a mouse model [37].
Modulation changes of the CACNG4 gene could contribute to temperament variation since voltage-gated channel genes influence bovine temperament and behavioral activities [38]. Genome-wide association studies in bovine evaluated SNPs for temperament and tenderness traits and found temperament associations in genes with transport, complexes, and activity voltage-gated channels for sodium ions [38]. Voltage-gated channels maintain depolarization, allowing one impulse to be executed [39]. Voltage-gated ion channels allow ions to pass through membranes, forming part of cellular communication in neurons [40]. The nerve impulse could be a possibility for temperament variation studies because it uses voltage-gated channels for faster conduction; it is also an evolutionary advance through subunit unions to form selective channels such as calcium and sodium [41].
Some SNPs located at some calcium channel genes have been reported. In humans, a genotype of rs2229949 on 3′UTR of CACNA1B was associated with adverse behavior symptomatology, predicting that allelic change abolishes a seed site for regulatory miRNA [11].
Additionally, some functions of calcium channels influence physiological responses such as secretion, contraction, and gene transcription. Therefore, mutations can dysregulate their functions and produce a behavior disorder, as the human model indicated by showed neuropsychiatric disease [42]. The genes of subunit gamma are reported to have encoded transmembrane regulators of glutamate receptors [43]. The glutamate receptors (AMPAR) initiate the excitatory neurotransmission and mediate ligand-gated ion channels required to propagate the electrical signal in the brain [44]. AMPAR can increase the reliability of synaptic signals and develop memory formation and learning [44].
Genome association studies have discovered epilepsy disease susceptibility to variations in the CACNA1A gene [45]. Additionally, the GABAA receptor gamma-3 (GABRG3) has a suggestive association with aggressiveness temperament in bovines [46]. Therefore, an imbalance in the propagation of neurotransmitters stimulated by a voltage-gated calcium channel switch that affects the glutamate pathway through AMPA receptors and enriched by changes in GABAA receptors could trigger a variation in regulation, which contributes to the difference in temperament phenotypes, given that it has the potential for activity in a pathway such as excitatory neurotransmission.
5. Conclusions
The 3′UTR of temperament candidate genes is a structural region harboring putative complementary sites for miRNAs with the potential to have an effect on gene expression and therefore aid in the elucidation of complex functional traits. Allelic variations in the 3′UTR could alter the recognition of miRNAs seed sites as it was shown for the CACNG- rs522648682:T>G SNP located at the bta-miR-191 seed site. Further studies are needed to confirm the role of the bta-miR-191 seed site in CACNG4 gene expression and a broadened validation assessment could confirm the SNP rs522648682 as an additional DNA marker for cattle temperament trait selection.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.S.-R.; methodology, G.R.-D.-L.-C., A.M.S.-R., F.A.P.-S., G.M.P.-B., D.G.R., R.D.R. and T.H.W.J.; software, G.R.-D.-L.-C. and F.A.P.-S.; validation, A.M.S.-R.; formal analysis, G.R.-D.-L.-C., A.M.S.-R., F.A.P.-S., E.C. and G.M.P.-B.; investigation, G.R.-D.-L.-C., A.M.S.-R. and R.D.R.; data curation, G.R.-D.-L.-C. and T.H.W.J.; writing—original draft preparation, G.R.-D.-L.-C., F.A.P.-S. and A.M.S.-R.; writing—review and editing, G.R.-D.-L.-C., F.A.P.-S., A.M.S.-R., G.M.P.-B., E.C., D.G.R., T.H.W.J., G.A.P. and R.D.R.; supervision, E.C.; project administration, A.M.S.-R.; funding acquisition, A.M.S.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
CONACyT financing granted through projects 294826 and 299055 and the Instituto Politécnico Nacional via project SIP 20221229.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The present study did not require ethical clearance from the Animal Care and Use Committee because the data were extracted from existing herd books, and the biological samples and genetic materials were obtained from germplasm banks.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
The technical assistance of A. W. Lewis and D. A. Neuendorff and technicians and graduate students in the collection of animal data and samples is acknowledged. David G. Riley acknowledge for project S-1086.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Burrow, H.M.; Dillon, R.D. Relationships between temperament and growth in a feedlot and commercial carcass traits of Bos indicus crossbreds. Aust. J. Exp. Agr. 1997, 37, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifuentes-Rincón, A.M.; Trejo-Tapia, A.G.; Randel, R.D.; Ambriz-Morales, P.; Parra-Bracamonte, G.M. Bovine dopamine receptors DRD1, DRD4, and DRD5: Genetic polymorphisms and diversities among ten cattle breeds. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 15, gmr.15017725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza-Brenner, E.; Sifuentes-Rincón, A.M.; Randel, R.D.; Paredes-Sánchez, F.A.; Parra-Bracamonte, G.M.; Arellano Vera, W.; Rodríguez-Almeida, F.A.; Segura-Cabrera, A. Association of SNP in dopamine and serotonin pathway genes and their interacting genes with temperament traits in Charolais cows. J. Appl. Genet. 2016, 58, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.B.; Chauhan, J.B. Computational analysis of non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphism in the bovine cattle kappa-casein (CSN3) gene. Meta Gene 2018, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thusberg, J.; Vihinen, M. Pathogenic or not? And if so, then how? Studying the effects of missense mutations using bioinformatics methods. Human Mutat. 2009, 30, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Chaparro, M.M.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Zayas-Villanueva, O.A.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L.; Delgado-Enciso, I.; Gomez-Govea, M.A.; Martínez-de-Villarreal, L.E.; Reséndez-Pérez, D.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P. Genetic variants in the 3’UTR of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes and their putative effects on the microRNA mechanism in hereditary breast and ovarian cancer. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, M.J. MicroRNA in the regulation and expression of serotonergic transmission in the brain and other tissues. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2011, 11, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.P.; Covault, J.; Conner, T.S.; Tennen, H.; Kranzler, H.R.; Furneaux, H.M. A common polymorphism in serotonin receptor 1B mRNA moderates regulation by miR-96 and associates with aggressive human behaviors. Mol. Psychiatr. 2008, 14, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, K.S.; McGregor, N.W.; Malhotra, A.; Lencz, T.; Emsley, R.; Warnich, L. Variation within voltage-gated calcium channel genes and antipsychotic treatment response in a South African first episode schizophrenia cohort. Pharmacogenomics J. 2019, 19, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Sánchez, F.A.; Sifuentes-Rincón, A.M.; Casas, E.; Arellano-Vera, W.; Parra-Bracamonte, G.M.; Riley, D.G.; Welsh, T.H., Jr.; Randel, R.D. Novel genes involved in the genetic architecture of temperament in Brahman cattle. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.E.; Neuendorff, D.A.; Riley, D.G.; Vann, R.C.; Willard, S.T.; Welsh, T.H., Jr.; Randel, R.D. Genetic parameters of three methods of temperament evaluation of Brahman calves. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 3082–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Saini, H.K.; Van Dongen, S.; Enright, A.J. miRBase: Tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 36, D154–D158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiezun, A.; Artzi, S.; Modai, S.; Volk, N.; Isakov, O.; Shomron, N. miRviewer: A multispecies microRNA homologous viewer. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmsmeier, M.; Steffen, P.; Höchsmann, M.; Giegerich, R. Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target duplexes. RNA 2004, 10, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrim-Sousa, L.; Freire-Assis, A.; Pezzi, N.; Tanaka, P.P.; Oliveira, E.H.; Passos, G.A. Adhesion between medullary thymic epithelial cells and thymocytes is regulated by miR-181b-5p and miR-30b. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 114, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki-Katagiri, N.; Lin, B.C.; Simon, J.; Hunt, R.C.; Schiller, T.; Russek-Cohen, E.; Komar, A.A.; Bar, H.; Kimchi-Sarfatyet, C. The importance of mRNA structure in determining the pathogenicity of synonymous and non-synonymous mutations in haemophilia. Haemophilia 2017, 23, e8–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouard, J.S.; Schenkel, F.; Marete, A.; Bissonnette, N. The GATK joint genotyping workflow is appropriate for calling variants in RNA-seq experiments. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinowski, S.T.; Taper, M.L.; Marshall, T.C. Revising how the computer program CERVUS accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignone, F.; Gissi, C.; Liuni, S.; Pesole, G. Untranslated regions of mRNAs. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, reviews0004.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clop, A.; Marcq, F.; Takeda, H.; Pirottin, D.; Tordoir, X.; Bibé, B.; Bouix, J.; Caiment, F.; Elsen, J.M.; Eychenne, F.; et al. A mutation creating a potential illegitimate microRNA target site in the myostatin gene affects muscularity in sheep. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, C. What are 3′ UTRs doing? CSH Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a034728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimson, A.; Farh, K.K.H.; Johnston, W.K.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Lim, L.P.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: Determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol. Cell. 2007, 27, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Chan, C.Y.; Ding, Y. Analysis of microRNA-target interactions by a target structure based hybridization model. Biocomp. Ser. 2008, 13, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bug, D.S.; Tishkov, A.V.; Moiseev, I.S.; Petukhova, N.V. Evaluating the effect of 3′-UTR variants in DICER1 and DROSHA on their tissue-specific expression by miRNA target prediction. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaiu, O.; D’amico, S.; Tempora, P.; Lucarini, V.; Fruci, D. Impact of natural occurring ERAP1 single nucleotide polymorphisms within miRNA-Binding Sites on HCMV infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziere, P.; Enright, A.J. Prediction of microRNA targets. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, P.V.; Kreis, S. Integrative approaches for analysis of mRNA and microRNA high-throughput data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, N.; Kulshreshtha, R. miR-191: An emerging player in disease biology. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Dezso, Z.; MacKenzie, C.; Oestreicher, J.; Agoulnik, S.; Byrne, M.; Bernier, F.; Yanagimachi, M.; Aoshima, K.; Oda, Y. Circulating miRNA biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, I.S.; Chung, K.Y.; Yi, J.; Kim, T.I.; Choi, H.S.; Cho, Y.M.; Choi, I.; Kim, S.H. Identification of reference genes for relative quantification of circulating microRNAs in bovine serum. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varendi, K.; Kumar, A.; Härma, M.A.; Andressoo, J.O. miR-1, miR-10b, miR-155, and miR-191 are novel regulators of BDNF. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 4443–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, L.L.H.; Garrick, D.J.; Gill, C.A.; Herring, A.D.; Riggs, P.K.; Miller, R.K.; Sanders, J.O.; Riley, D.G. Genome-wide association study of temperament and tenderness using different Bayesian approaches in a Nellore–Angus crossbred population. Livest. Sci. 2014, 161, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parke, W.C. Neural Networks and Brains. In Biophysics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezanilla, F. Voltage-Gated Ion Channels. In Biological Membrane Ion Channels. Biological and Medical Physics Biomedical Engineering, 5th ed.; Chung, S.H., Andersen, O.S., Krishnamurthy, V., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelfranco, A.M.; Hartline, D.K. Evolution of rapid nerve conduction. Brain Res. 2016, 1641, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanou, E.; Catterall, W.A. Calcium channels, synaptic plasticity, and neuropsychiatric disease. Neuron 2018, 98, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoll, R.A.; Tomita, S.; Bredt, D.S. Auxiliary subunits assist AMPA-type glutamate receptors. Science 2006, 311, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenk, J.; Boudkkazi, S.; Kocylowski, M.K.; Brechet, A.; Zolles, G.; Bus, T.; Costa, K.; Kollewe, A.; Jordan, J.; Bank, J.; et al. An ER assembly line of AMPA-receptors controls excitatory neurotransmission and its plasticity. Neuron 2019, 104, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manickam, A.H.; Ramasamy, S. Mutations in the voltage dependent calcium channel CACNA1A (P/Q type alpha 1A subunit) causing neurological disorders-An overview. Neurol. India 2021, 69, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, D.G.; Gill, C.A.; Boldt, C.R.; Funkhouser, R.R.; Herring, A.D.; Riggs, P.K.; Sawyer, J.E.; Lunt, D.K.; Sanders, J.O. Crossbred Bos indicus steer temperament as yearlings and whole genome association of steer temperament as yearlings and calf temperament post-weaning. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).