RETRACTED: Systemic Retinoids for Generalized Verrucosis Due to Congenital Immunodeficiency: Case Reports and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
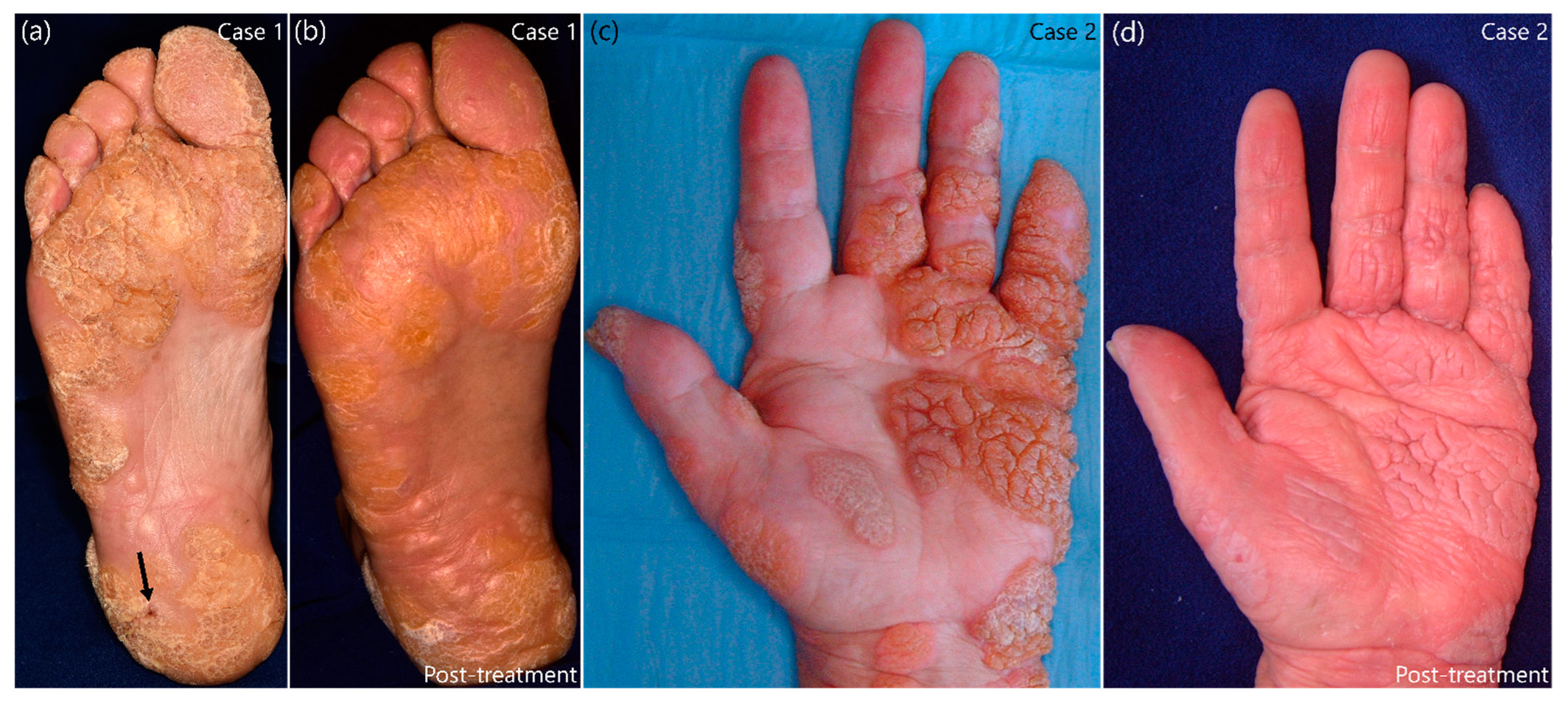
2. Case Presentation
3. Review of the Literature
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEV | acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EV | epidermodysplasia verruciformis |
| GV | generalized verrucosis |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| HPV | human papilloma virus |
| IL | interleukin |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| WES | whole exome sequencing |
References
- zur Hausen, H. Papillomavirus infections—A major cause of human cancers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1288, F55–F78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, H.U.; Burk, R.D.; Chen, Z.; van Doorslaer, K.; zur Hausen, H.; de Villiers, E.M. Classification of papillomaviruses (PVs) based on 189 PV types and proposal of taxonomic amendments. Virology 2010, 401, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadgepatil, S.S.; Gupta, S.; Sharma, Y.K. Clinicoepidemiological Study of Different Types of Warts. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 7989817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrhönen, S.; Johansson, E. Regression of warts. An immunological study. Lancet 1975, 1, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogozinski, T.T.; Jablonska, S.; Jarzabek-Chorzelska, M. Role of cell-mediated immunity in spontaneous regression of plane warts. Int. J. Dermatol. 1988, 27, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri, J.C.; Dubina, M.I.; Kao, G.F.; Rady, P.L.; Tyring, S.K.; Gaspari, A.A. Generalized verrucosis: A review of the associated diseases, evaluation, and treatments. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 66, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, G. Genetics of epidermodysplasia verruciformis: Insights into host defense against papillomaviruses. Semin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, G. Genetics and susceptibility to human papillomaviruses: Epidermodysplasia verruciformis, a disease model. Bull. Acad. Natl. Med. 2010, 194, 923–940. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, H.D.; Macgregor, J.L.; Nord, K.M.; Tyring, S.; Rady, P.; Engler, D.E.; Grossman, M.E. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 60, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Lai, C.H.; Chen, C.B.; Chung, W.H. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis or generalized verrucosis? A clinical and virological comparative study. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, S.; Jablonska, S. Why epidermodysplasia verruciformis—A rare genetic disease—Has raised such great interest. Int. J. Dermatol. 2004, 43, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewirtzman, A.; Bartlett, B.; Tyring, S. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis and human papilloma virus. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 21, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, B.; Itin, P.H. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2014, 45, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekaert, S.M.; Ehrchen, J.; Büttner, R.; Pfister, H.J.; Metze, D. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis in an HIV-infected patient. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2014, 12, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.M.; Katsidzira, L.; Meys, R.; Sterling, J.C.; de Koning, M.; Quint, W.; Nathoo, K.; Munyati, S.; Ndhlovu, C.E.; Salisbury, J.R.; et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis due to multiple and unusual HPV infection among vertically-infected, HIV-positive adolescents in Zimbabwe. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, e119–e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slawsky, L.D.; Gilson, R.T.; Hockley, A.J.; Libow, L.F. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated with severe immunodeficiency, lymphoma, and disseminated molluscum contagiosum. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1992, 27, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stray-Pedersen, A.; Jouanguy, E.; Crequer, A.; Bertuch, A.A.; Brown, B.S.; Jhangiani, S.N.; Muzny, D.M.; Gambin, T.; Sorte, H.; Sasa, G.; et al. Compound heterozygous CORO1A mutations in siblings with a mucocutaneous-immunodeficiency syndrome of epidermodysplasia verruciformis-HPV, molluscum contagiosum and granulomatous tuberculoid leprosy. J. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 34, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Blenes, C.; Pasternak, S.; Issekutz, A.; Gillis, J.; Chowdhury, D.; Finlayson, L. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in lipoid proteinosis: Case report and discussion of pathophysiology. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2015, 32, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, K.H.; Rady, P.; Tyring, S.; Stone, M.S. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis in a child with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014, 31, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cougoul, P.; Tournier, E.; Delavigne, K.; Rauzy, O.B.; Ysebaert, L.; Sibaud, V. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis, a new opportunistic infection related to bendamustine. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, E.S.; Kingsbery, M.Y.; Mintz, E.M.; Hsu, A.P.; Holland, S.M.; Rady, P.L.; Tyring, S.K.; Grossman, M.E. Generalized verrucosis in a patient with GATA2 deficiency. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 170, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagi, T.; Shibaki, A.; Tsuji-Abe, Y.; Yokota, K.; Shimizu, H. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis and generalized verrucosis: The same disease? Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 31, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosumi, H.; Natsuga, K.; Takashima, S.; Miyauchi, T.; Huang, Y.T.; Nomura, T.; Yanagi, T.; Huang, H.Y.; Chiu, F.P.; Chen, P.C.; et al. Two Cases of Interleukin-7-Deficient Generalized Verrucosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1561–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella, G.L. Generalized verrucosis: More emphasis on systemic retinoids. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes Araújo, F.; dos Santos Gon, A.; Sichero, L.; Simão Sobrinho, J. Human papillomavirus type 57 in generalized verrucosis without immunodeficiency. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, e189–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhawan, R.I.; Osei-Tutu, A.; Hugh, J.M. Sustained clinical resolution of acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis in an immunocompromised patient after discontinuation of oral acitretin with topical imiquimod. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2013, 12, 348–349. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniali, D.; Lugão, H.B.; Elias, D.; Bueno Filho, R. Generalized verrucosis in GATA2 deficiency successfully treated with systemic acitretin and trichloroacetic acid. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2021, 38, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, J.C.; Gibbs, S.; Haque Hussain, S.S.; Mohd Mustapa, M.F.; Handfield-Jones, S.E. British Association of Dermatologists’ guidelines for the management of cutaneous warts 2014. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 696–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, I.; Skroza, N.; Bernardini, N.; Nicolucci, F.; Tolino, E.; La Viola, G.; Orsini, D.; Zuber, S.; Potenza, C. Acitretin in management of diffuse common warts: A case report. Dermatol. Ther. 2011, 24, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, C.A.; Perrett, C.M.; Brown, V.L.; Leigh, I.M.; McGregor, J.M.; Proby, C.M. Imiquimod cream 5% for recalcitrant cutaneous warts in immunosuppressed individuals. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallis, E.; Papatheodorou, G.; Bimpakis, E.; Butanska, D.; Menounos, P.; Papadakis, P. Systemic low-dose isotretinoin maintains remission status in epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2008, 22, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iraji, F.; Faghihi, G. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis: Association with isolated IgM deficiency and response to treatment with acitretin. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2000, 25, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anadolu, R.; Oskay, T.; Erdem, C.; Boyvat, A.; Terzi, E.; Gürgey, E. Treatment of epidermodysplasia verruciformis with a combination of acitrecin and interferon alfa-2a. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pt | Diagnosis | Age | Sex | Treatment | Dose | Course | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GV due to IL7 deficiency | 51 | F | etretinate | 10 mg/day | Moderate improvement | [23] (Case 1) |
| 2 | GV due to IL7 deficiency | 63 | M | etretinate | 50 mg/day | Moderate improvement | [22] (Case 2) |
| 3 | EV | 87 | F | acitretin | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | [10] |
| 4 | EV | 60 | F | acitretin | |||
| 5 | GV | 64 | M | acitretin | |||
| 6 | GV | 25 | M | acitretin | |||
| 7 | GV | 87 | M | acitretin | |||
| 8 | GV | 67 | F | acitretin | |||
| 9 | GV due to systemic steroid | 54 | M | acitretin | |||
| 10 | GV due to GATA2 deficiency | 24 | M | acitretin | 25 mg/day | Could not continue the treatment | [21] |
| 11 | GV due to GATA2 deficiency | 12 | M | acitretin | 10 mg/day | Complete improvement after bone marrow transplantation | [24] |
| 12 | EV | 20 | M | isotretinoin | 0.8 mg/kg/day | Complete remission | [26] |
| 13 | EV | 25 | F | acitretin | 0.5–1 mg/kg/day | Moderate improvement | [27] |
| 14 | GV | 16–39 | M | Etretinate for three, acitretin for two | Not mentioned | Good results with rapid disappearance (<1 month) One had complete remission without recurrence after cessation | [28] |
| 15 | GV | F | |||||
| 16 | GV | F | |||||
| 17 | GV | F | |||||
| 18 | GV due to HIV | F | |||||
| 19 | GV | 43 | M | acitretin | 0.7 mg/kg/day | Cosmetic improvement | [29] |
| 20 | Acquired EV due to HIV infection | 46 | M | acitretin | Not mentioned | Successfully maintained with topical imiquimod | [30] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosumi, H.; Natsuga, K.; Yanagi, T.; Ujiie, H. RETRACTED: Systemic Retinoids for Generalized Verrucosis Due to Congenital Immunodeficiency: Case Reports and Review of the Literature. Genes 2023, 14, 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030769
Kosumi H, Natsuga K, Yanagi T, Ujiie H. RETRACTED: Systemic Retinoids for Generalized Verrucosis Due to Congenital Immunodeficiency: Case Reports and Review of the Literature. Genes. 2023; 14(3):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030769
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosumi, Hideyuki, Ken Natsuga, Teruki Yanagi, and Hideyuki Ujiie. 2023. "RETRACTED: Systemic Retinoids for Generalized Verrucosis Due to Congenital Immunodeficiency: Case Reports and Review of the Literature" Genes 14, no. 3: 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030769
APA StyleKosumi, H., Natsuga, K., Yanagi, T., & Ujiie, H. (2023). RETRACTED: Systemic Retinoids for Generalized Verrucosis Due to Congenital Immunodeficiency: Case Reports and Review of the Literature. Genes, 14(3), 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030769







