Biogeography and Genetic Diversity of Terrestrial Mites in the Ross Sea Region, Antarctica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Specimen Collection
2.2. Genetic and Morphological Analyses
2.3. Data Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Convey, P.; Biersma, E.M.; Casanova-Katny, A.; Maturana, C.S. Refuges of Antarctic diversity. In Past Antarctica; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, I.D.; Stevens, M.I.; Wall, D.H. Invertebrates. In Antarctic Terrestrial Microbiology; Cowan, D.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar]
- Hogg, I.D.; Stevens, M.I. Soil fauna of Antarctic Coastal Landscapes. In Geoecology of Antarctic Ice-free Coastal Landscapes. Ecological Studies Analysis and Synthesis; Beyer, L., Boelter, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 154, Chapter 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, T.; Hogg, I.D.; Bargagli, R. Identifying appropriate sampling and modelling approaches for analysing distributional patterns of Antarctic terrestrial arthropods along the Victoria Land latitudinal gradient. Antarct. Sci. 2010, 22, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.I.; Terauds, A.; Smellie, J.; Convey, P.; Chown, S.L. Geothermal activity helps life survive glacial cycles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5634–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyne, J.A.; Orr, H.A. Speciation: A catalogue and critique of species concepts. In Philosophy of Biology: An Anthology; Rosenberg, A., Arp, R., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2004; Chapter 19. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, P. A synonymic catalogue of the Acari from Antarctica, the sub-Antarctic Islands and the Southern Ocean. J. Nat. Hist. 1993, 27, 323–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandtmann, R.W. Terrestrial Prostigmata (trombidiform mites). In Entomology of Antarctica; Antarctic Research Series; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; Volume 10, pp. 51–80. [Google Scholar]
- Strandtmann, R.W. Notes on Nanorchestes. II. Four species from Victoria Land, Antarctica (Acari: Nanorchestidae). Pacific Insects 1982, 24, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, P.J.A.; Convey, P. Surviving out in the cold: Antarctic endemic invertebrates and their refugia. J. Biogeogr. 2008, 35, 2176–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terauds, A.; Chown, S.L.; Morgan, F.; Peat, H.J.; Watts, D.J.; Keys, H.; Convey, P.; Bergstrom, D.M. Conservation biogeography of the A ntarctic. Divers. Distrib. 2012, 18, 726–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terauds, A.; Lee, J. Antarctic biogeography revisited: Updating the Antarctic Conservation Biogeographic Regions. Divers. Distrib. 2016, 22, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.E.; Hogg, I.D.; Convey, P.; Barnes, A.D.; McDonald, I.R. Spatial and Temporal Scales Matter When Assessing the Species and Genetic Diversity of Springtails (Collembola) in Antarctica. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanciulli, P.P.; Summa, D.; Dallai, R.; Frati, F. High levels of genetic variability and population differentiation in Gressittacantha terranova (Collembola, Hexapoda) from Victoria Land, Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 2001, 13, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovenko, N.S.; Smykla, J.; Convey, P.; Kašparová, E.; Kozeretska, I.A.; Trokhymets, V.; Dykyy, I.; Plewka, M.; Devetter, M.; Duriš, Z.; et al. Antarctic bdelloid rotifers: Diversity, endemism and evolution. Hydrobiologia 2015, 761, 5–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagoshima, H.; Imura, S.; Suzuki, A.C. Molecular and morphological analysis of an Antarctic tardigrade, Acutuncus antarcticus. J. Limnol. 2013, 72, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, K.; Sands, C.; McInnes, S.; Pisani, D.; Stevens, M.; Convey, P. An ancient, Antarctic-specific species complex: Large divergences between multiple Antarctic lineages of the tardigrade genus Mesobiotus. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2022, 170, 107429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetras, N.J.; Hogg, I.D.; Banks, J.C.; Adams, B.J. Latitudinal distribution and mitochondrial DNA (COI) variability of Stereotydeus spp. (Acari: Prostigmata) in Victoria Land and the central Transantarctic Mountains. Antarct. Sci. 2010, 22, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vuuren, B.J.; Lee, J.E.; Convey, P.; Chown, S.L. Conservation implications of spatial genetic structure in two species of oribatid mites from the Antarctic Peninsula and the Scotia Arc. Antarct. Sci. 2018, 30, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, K.R.; Hogg, I.D.; Adams, B.J.; Hebert, P.D.N. High levels of intraspecific genetic divergences revealed for Antarctic springtails: Evidence for small-scale isolation during Pleistocene glaciation. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 119, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapelli, A.; Cucini, C.; Fanciulli, P.; Frati, F.; Convey, P.; Nardi, F. Molecular Comparison among Three Antarctic Endemic Springtail Species and Description of the Mitochondrial Genome of Friesea gretae (Hexapoda, Collembola). Diversity 2020, 12, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapelli, A.; Greenslade, P.; Nardi, F.; Leo, C.; Convey, P.; Frati, F.; Fanciulli, P.P. Evidence for Cryptic Diversity in the “Pan-Antarctic” Springtail Friesea antarctica and the Description of Two New Species. Insects 2020, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.I.; Hogg, I.D. Contrasting levels of mitochondrial DNA variability between mites (Penthalodidae) and springtails (Hypogastruridae) from the Trans-Antarctic Mountains suggest long-term effects of glaciation and life history on substitution rates, and speciation processes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 3171–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenslade, P. Collembola from the Scotia Arc and Antarctic Peninsula including descriptions of two new species and notes on biogeography. Polskie Pismo Entomologiczne 1995, 64, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.P.; Duffy, G.A.; Pearman, W.S.; Pertierra, L.R.; Fraser, C.I. Meta-analysis of Antarctic phylogeography reveals strong sampling bias and critical knowledge gaps. Ecography 2022, 2022, e06312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torricelli, G.; Frati, F.; Convey, P.; Telford, M.; Carapelli, A. Population structure of Friesea grisea (Collembola, Neanuridae) in the Antarctic Peninsula and Victoria Land: Evidence for local genetic differentiation of pre-Pleistocene origin. Antarct. Sci. 2010, 22, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenslade, P. An antarctic biogeographical anomaly resolved: The true identity of a widespread species of Collembola. Polar Biol. 2018, 41, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.I.; Greenslade, P.; D’Haese, C.A. Species diversity in Friesea (Neanuridae) reveals similar biogeographic patterns among Antarctic Collembola. Zool. Scr. 2021, 50, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. A DNA-Based Registry for All Animal Species: The Barcode Index Number (BIN) System. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; Dewaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beet, C.R.; Hogg, I.D.; Collins, G.E.; Cowan, D.A.; Wall, D.H.; Adams, B.J. Genetic diversity among populations of Antarctic springtails (Collembola) within the Mackay Glacier ecotone. Genome 2016, 59, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGaughran, A.; Torricelli, G.; Carapelli, A.; Frati, F.; Stevens, M.I.; Convey, P.; Hogg, I.D. Contrasting phylogeographical patterns for springtails reflect different evolutionary histories between the Antarctic Peninsula and continental Antarctica. J. Biogeogr. 2009, 37, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C.; Yuan, X.; Jia, G.; Deng, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; et al. Assessment of four DNA fragments (COI, 16S rDNA, ITS2, 12S rDNA) for species identification of the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, C.; Siepel, H.; Convey, P.; Fanciulli, P.P.; Nardi, F.; Carapelli, A. Overlooked Species Diversity and Distribution in the Antarctic Mite Genus Stereotydeus. Diversity 2021, 13, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaughran, A.; Hogg, I.D.; Stevens, M.I. Patterns of population genetic structure for springtails and mites in southern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2008, 46, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, C.; Siepel, H.; Fanciulli, P.; Nardi, F.; Convey, P.; Carapelli, A. Two New Species of the Mite Genus Stereotydeus Berlese, 1901 (Prostigmata: Penthalodidae) from Victoria Land, and a Key for Identification of Antarctic and Sub-Antarctic Species. Taxonomy 2021, 1, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusitalo, M. Terrestrial species of the genus Nanorchestes (Endeostigmata: Nanorchestidae) in Europe. In Trends in Acarology, Proceedings of the 12th International Congress; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Strandtmann, R.W. Notes on Nanorchestes. V. Two new species of Nanorchestes (Acari: Nanorchestidae) from the Antarctic Peninsula and South Atlantic islands. Pacific Insects 1982, 24, 252–258. [Google Scholar]
- Strandtmann, R.W. Notes on Nanorchestes. IV. Four new species from Macquarie Island, Australia (Acari: Endeostigmatides: Nanorchestidae). Pacific Insects 1982, 24, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, M.I.; Hogg, I.D. Expanded distributional records of Collembola and Acari in southern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Pedobiologia 2002, 46, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaughran, A.; Hogg, I.D.; Convey, P. Extended ecophysiological analysis of Gomphiocephalus hodgsoni (Collembola): Flexibility in life history strategy and population response. Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freckman, D.W.; Virginia, R.A. Extraction of nematodes from Dry Valley Antarctic soils. Polar Biol. 1993, 13, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Penton, E.H.; Burns, J.M.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W. Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the neotropical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14812–14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.Y. ggtree: An r package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.A.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-G.; Lam, T.T.-Y.; Xu, S.; Dai, Z.; Zhou, L.; Feng, T.; Guo, P.; Dunn, C.W.; Jones, B.R.; Bradley, T.; et al. Treeio: An R Package for Phylogenetic Tree Input and Output with Richly Annotated and Associated Data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 37, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, E. pegas: An R package for population genetics with an integrated-modular approach. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 419–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Pei, N.; Mi, X.; Zhang, M.J. Package ‘Phylotools’. Dimension, 12. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/phylotools/phylotools.pdfhttps://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/phylotools/phylotools.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Čandek, K.; Kuntner, M. DNA barcoding gap: Reliable species identification over morphological and geographical scales. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 15, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2018, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.D.J.; Collins, R.A.; Boyer, S.; Lefort, M.; Malumbres-Olarte, J.; Vink, C.; Cruickshank, R.H. Spider: An R package for the analysis of species identity and evolution, with particular reference to DNA barcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dewaard, J.R.; Levesque-Beaudin, V.; Dewaard, S.L.; Ivanova, N.V.; McKeown, J.T.; Miskie, R.; Naik, S.; Perez, K.H.; Ratnasingham, S.; Sobel, C.N.; et al. Expedited assessment of terrestrial arthropod diversity by coupling Malaise traps with DNA barcoding. Genome 2019, 62, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATCM. Annex V to the Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty. Area Protection and Management. Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, Buenos Aires. 1991. Available online: https://ats.aq/documents/keydocs/vol_1/vol1_9_AT_Protocol_Annex_V_e.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Collins, G.E.; Hogg, I.D.; Convey, P.; Sancho, L.G.; Cowan, D.A.; Lyons, W.B.; Adams, B.J.; Wall, D.H.; Green, T.G.A. Genetic diversity of soil invertebrates corroborates timing estimates for past collapses of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22293–22302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeConto, R.M.; Pollard, D. Contribution of Antarctica to past and future sea-level rise. Nature 2016, 531, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, D.; DeConto, R.M. Modelling West Antarctic ice sheet growth and collapse through the past five million years. Nature 2009, 458, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzsimons, J.M. Temperature and three species of Antarctic arthropods. Pac. Insects Monogr. 1971, 25, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hawes, T.C.; Bale, J.S.; Worland, M.R.; Convey, P. Plasticity and superplasticity in the acclimation potential of the Antarctic mite Halozetes belgicae (Michael). J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawes, T.C.; Worland, M.R.; Bale, J.S.; Convey, P. Rafting in Antarctic Collembola. J. Zool. 2007, 274, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.R.; Terauds, A.; Carwardine, J.; Shaw, J.D.; Fuller, R.A.; Possingham, H.P.; Chown, S.L.; Convey, P.; Gilbert, N.; Hughes, K.A.; et al. Threat management priorities for conserving Antarctic biodiversity. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, T.; Hogg, I.D.; Carapelli, A.; Frati, F.; Bargagli, R. Large-scale spatial patterns in the distribution of Collembola (Hexapoda) species in Antarctic terrestrial ecosystems. J. Biogeogr. 2009, 36, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesie, C.; Green, T.G.A.; Türk, R.; Hogg, I.D.; Sancho, L.; Büdel, B. Terrestrial biodiversity along the Ross Sea coastline, Antarctica: Lack of a latitudinal gradient and potential limits of bioclimatic modeling. Polar Biol. 2014, 37, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convey, P.; Quintana, R. The terrestrial arthropod fauna of Cierva Point SSSI, Danco Coast, northern Antarctic Peninsula. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 1997, 33, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, W.B.; Deuerling, K.; Welch, K.A.; Michalski, G.; Walters, W.W.; Nielsen, U.; Wall, D.H.; Hogg, I.; Adams, B.J. The Soil Geochemistry in the Beardmore Glacier Region, Antarctica: Implications for Terrestrial Ecosystem History. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.A.; Gardner, C.B.; Welch, S.A.; Jackson, W.A.; Adams, B.J.; Wall, D.H.; Hogg, I.D.; Fierer, N.; Lyons, W.B. Geochemical zones and environmental gradients for soils from the central Transantarctic Mountains, Antarctica. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 1629–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.L.C.; Adams, B.J.; Diaz, M.A.; Lemoine, N.P.; Dragone, N.B.; Fierer, N.; Lyons, W.B.; Hogg, I.; Wall, D.H. Response of Antarctic soil fauna to climate-driven changes since the Last Glacial Maximum. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 28, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, I.D.; Cary, S.; Convey, P.; Newsham, K.K.; O’Donnell, A.G.; Adams, B.; Aislabie, J.; Frati, F.; Stevens, M.I.; Wall, D.H. Biotic interactions in Antarctic terrestrial ecosystems: Are they a factor? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 3035–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, T.; Hogg, I.D.; Nielsen, U.N.; Bottos, E.M.; Lee, C.K.; Hopkins, D.W.; Cary, S.C.; Barrett, J.E.; Green, T.G.A.; Storey, B.C.; et al. Nematodes in a polar desert reveal the relative role of biotic interactions in the coexistence of soil animals. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.K.; Laughlin, D.C.; Bottos, E.M.; Caruso, T.; Joy, K.; Barrett, J.E.; Brabyn, L.; Nielsen, U.N.; Adams, B.J.; Wall, D.H.; et al. Biotic interactions are an unexpected yet critical control on the complexity of an abiotically driven polar ecosystem. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, J.C.; Wilson, K. Assessment of the usefulness of ribosomal 18S and mitochondrial COI sequences in Prostigmata phylogeny. In Acarology: Proceedings of the 10th International Congress; CSIRO Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2001; Volume 100. [Google Scholar]
- TAM. 2019. Available online: https://tamcamp.org/camp/proposed (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Scientific Committee for Antarctic Research Strategic Plan 2023–2028. Urgent Messages from the South: Antarctic and Southern Ocean Science and Policy. Available online: https://www.scar.org/scar-library/other-publications/strategic-plans/5912-scar-strategic-plan-2023-2028/ (accessed on 26 February 2023).

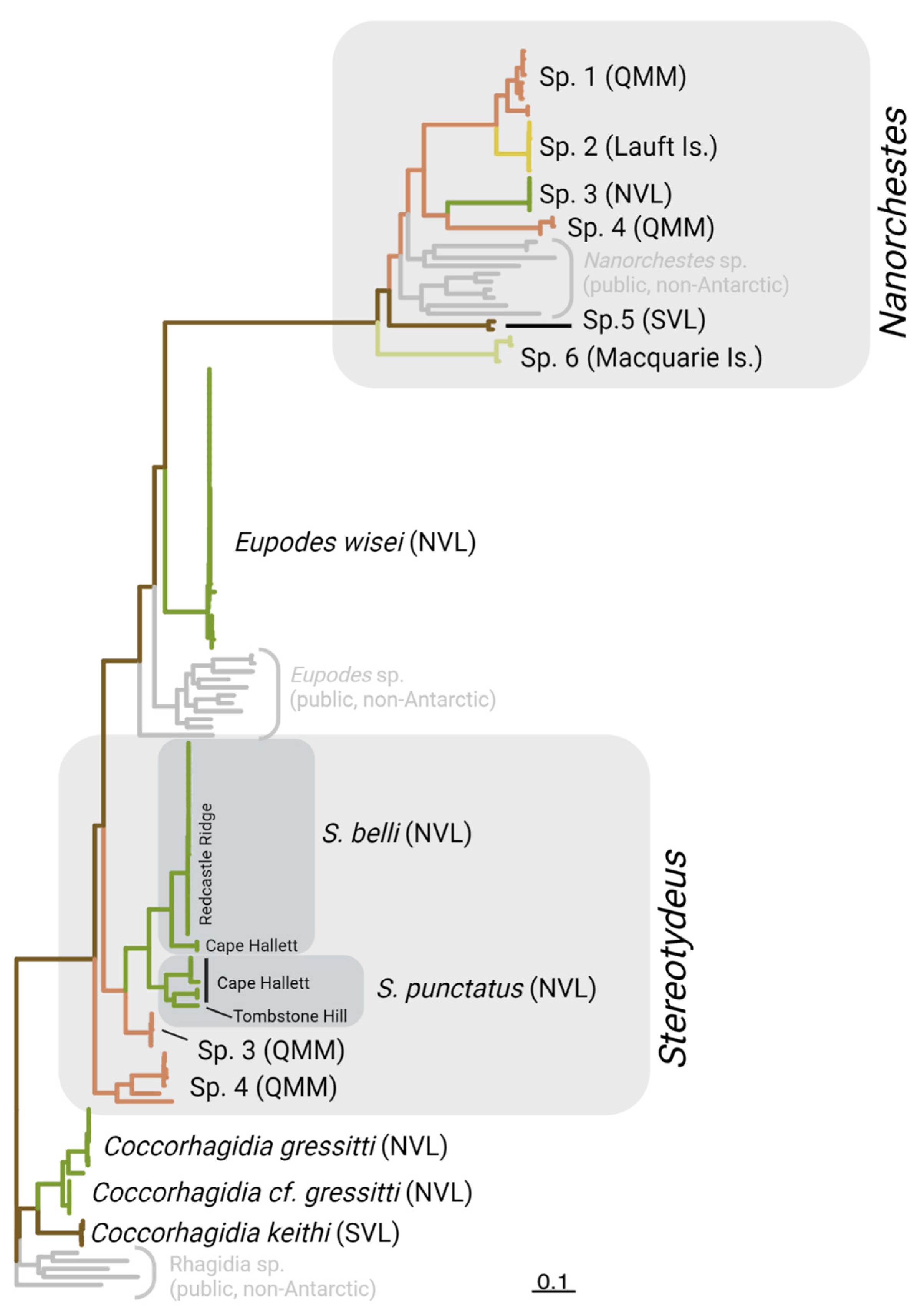
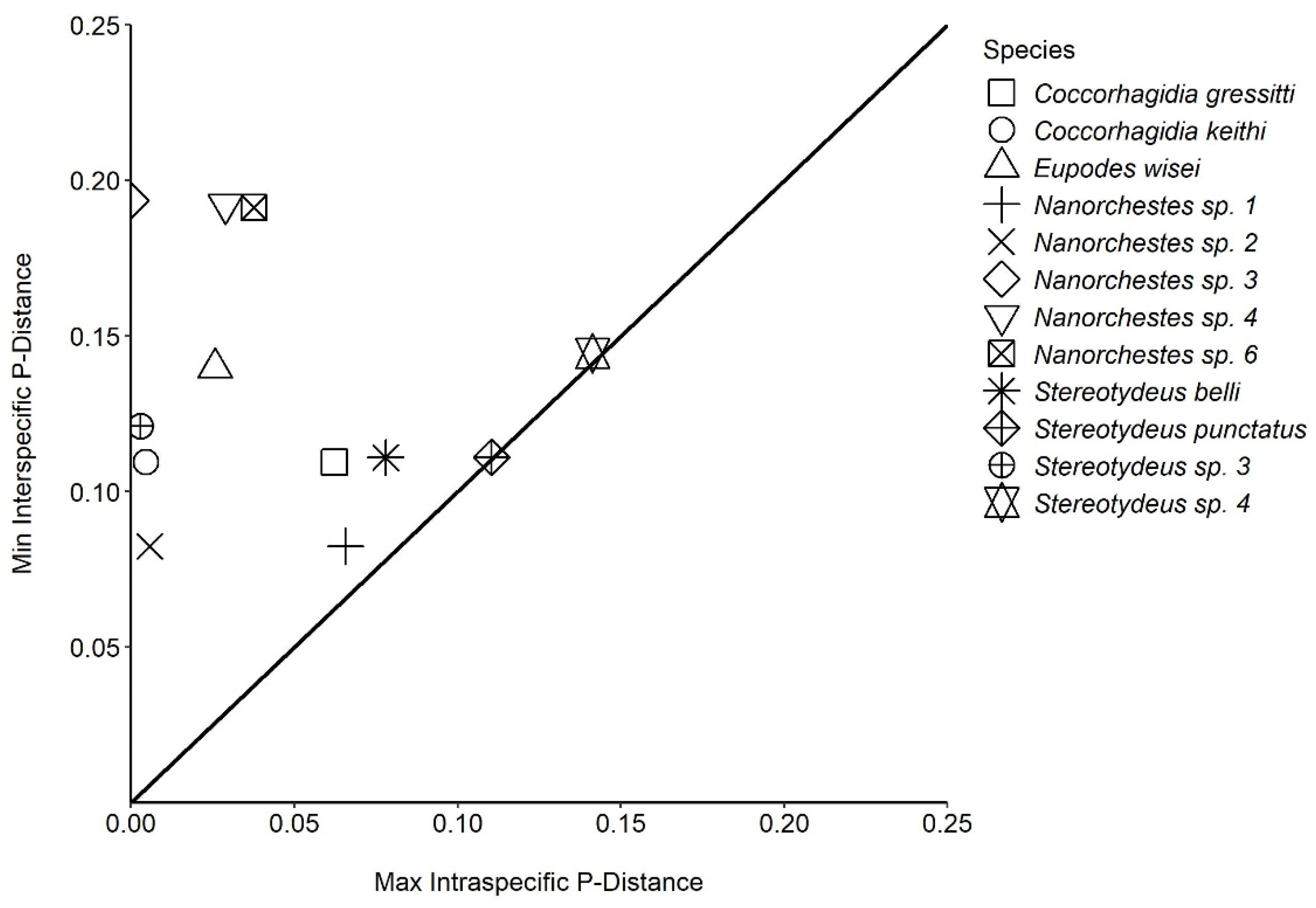
| Genus | Coccorhagidia | Eupodes | Nanorchestes | Stereotydeus | Totals | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Putative Species Clusters | gressitti | keithi | wisei | sp. 1 | sp. 2 | sp. 3 | sp. 4 | sp. 5 | sp. 6 | belli | punctatus | sp. 3 | sp. 4 | 13 | |
| n sequences | 14 | 4 | 36 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 27 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 130 | |
| n BINs | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 23 | |
| Max. intra. | 6.23% | 0.46% | 2.58% | 6.56% | 0.57% | 0.00% | 2.90% | NA | 3.77% | 7.80% | 11.04% | 0.30% | 14.13% | ||
| Min. inter. | 10.94% | 10.94% | 13.97% | 8.24% | 8.24% | 19.35% | 19.21% | NA | 19.13% | 11.09% | 11.09% | 12.10% | 14.44% | ||
| Region | Location | Locations where each putative species cluster was found | Total n clusters per location | ||||||||||||
| Macquarie Is. | [X] ** | ||||||||||||||
| Lauft Island | X * | ||||||||||||||
| NVL | Cape Hallett | X | X | X * | X ** | 4 | |||||||||
| NVL | Christie Peak | [X] | X | 2 | |||||||||||
| NVL | Luther Vale | X | X | 2 | |||||||||||
| NVL | Unnamed Ridge | X | 1 | ||||||||||||
| NVL | Tombstone Hill | X * | X * | 2 | |||||||||||
| NVL | Redcastle Ridge | X * | 1 | ||||||||||||
| SVL | Cliff Nunatak | X | 1 | ||||||||||||
| SVL | Mt. Murray | X | 1 | ||||||||||||
| SVL | Mt. Seuss | X | 1 | ||||||||||||
| SVL | Taylor Valley | X | 1 | ||||||||||||
| QMM (B) | Gateway Spur | X * | 1 | ||||||||||||
| QMM (B) | Ebony Ridge | [X] | X | 2 | |||||||||||
| QMM (B) | Harcourt Spur | X | 1 | ||||||||||||
| QMM (B) | Mt. Kyffin | X | 1 | ||||||||||||
| QMM (S) | Mt. Franke | X | X | X | X * | 4 | |||||||||
| QMM (S) | Mt. Wasko | X | X | X * | 3 | ||||||||||
| Total n locations | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Collins, G.E.; Young, M.R.; Convey, P.; Chown, S.L.; Cary, S.C.; Adams, B.J.; Wall, D.H.; Hogg, I.D. Biogeography and Genetic Diversity of Terrestrial Mites in the Ross Sea Region, Antarctica. Genes 2023, 14, 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030606
Collins GE, Young MR, Convey P, Chown SL, Cary SC, Adams BJ, Wall DH, Hogg ID. Biogeography and Genetic Diversity of Terrestrial Mites in the Ross Sea Region, Antarctica. Genes. 2023; 14(3):606. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030606
Chicago/Turabian StyleCollins, Gemma E., Monica R. Young, Peter Convey, Steven L. Chown, S. Craig Cary, Byron J. Adams, Diana H. Wall, and Ian D. Hogg. 2023. "Biogeography and Genetic Diversity of Terrestrial Mites in the Ross Sea Region, Antarctica" Genes 14, no. 3: 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030606
APA StyleCollins, G. E., Young, M. R., Convey, P., Chown, S. L., Cary, S. C., Adams, B. J., Wall, D. H., & Hogg, I. D. (2023). Biogeography and Genetic Diversity of Terrestrial Mites in the Ross Sea Region, Antarctica. Genes, 14(3), 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030606






