Pleistocene Landscape Dynamics Drives Lineage Divergence of a Temperate Freshwater Fish Gobio rivuloides in Coastal Drainages of Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
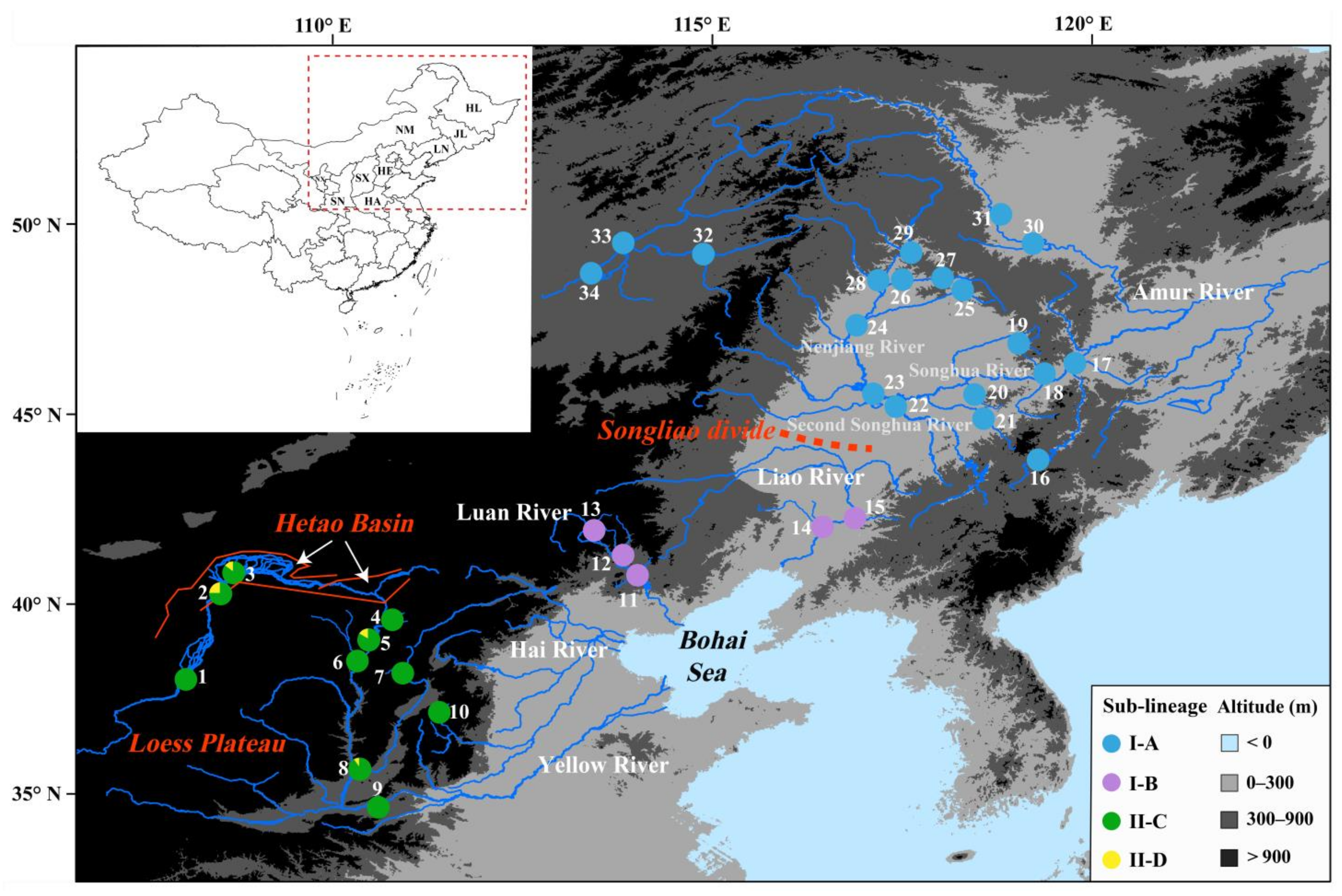
2.1. Specimen Sources
2.2. Acquisition, Processing, and Statistical Analysis of Sequence Data
2.3. Phylogeny and Ancestral Area Reconstruction
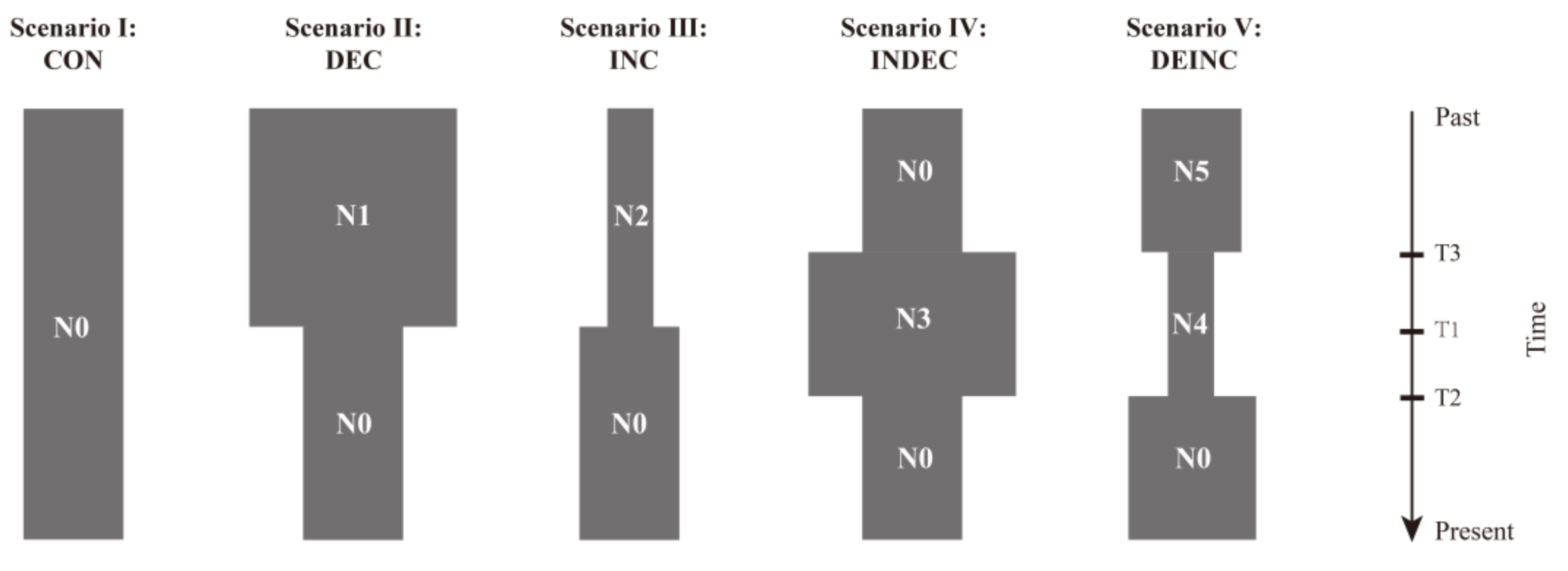
2.4. Genetic Structure and Demographic History
3. Results
3.1. Phylogeny and Ancestral Area Reconstruction
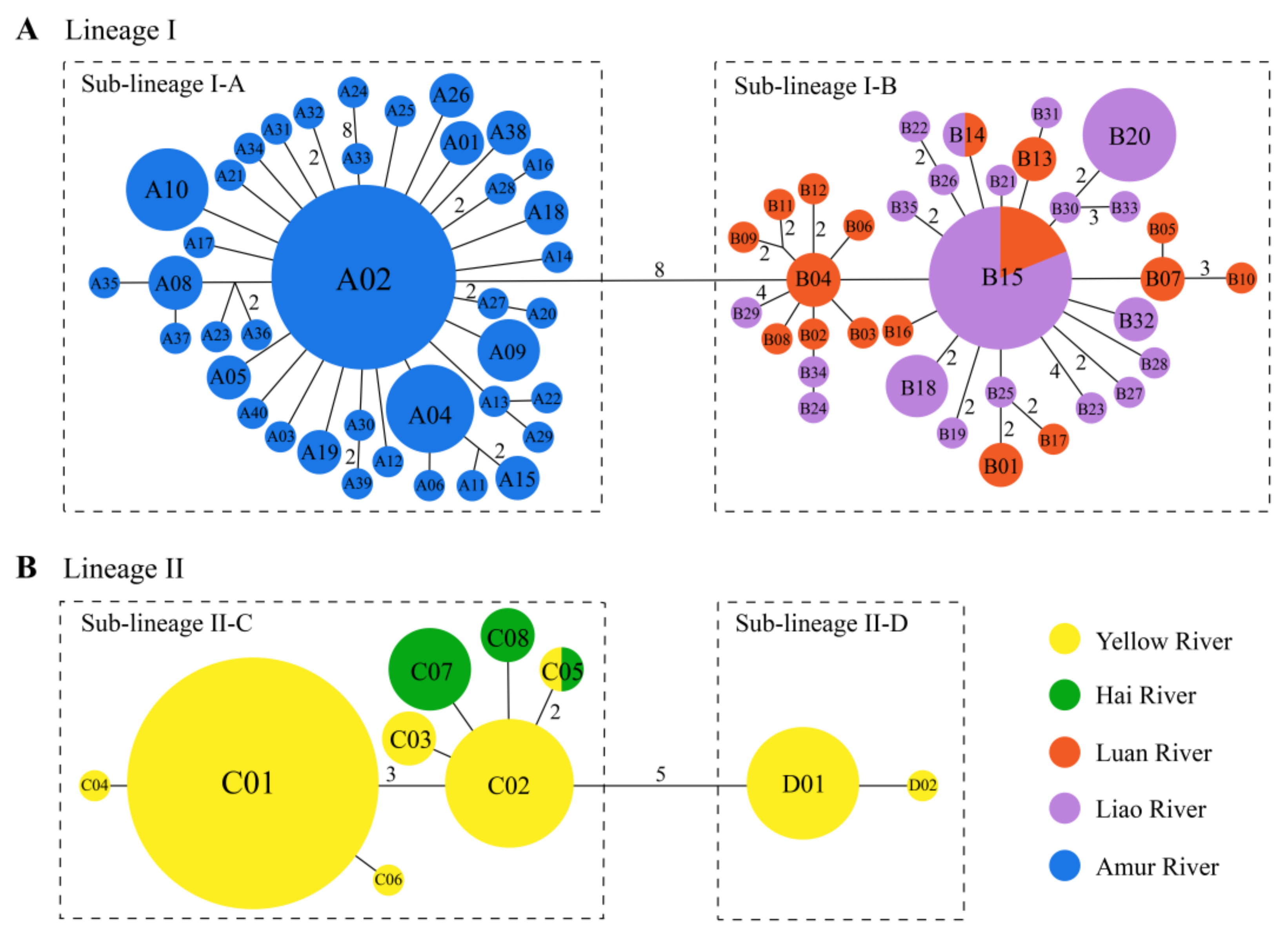
3.2. Genetic Structure of Drainage Populations
3.3. Historical Demography
4. Discussion
4.1. Drivers of Lineage Divergence
4.2. Genetic Structure and Historical Demography
4.3. Implications for Conservation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avise, J.C. Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species; Harvard University Press: London, UK, 2000; pp. 135–147. [Google Scholar]
- Avise, J.C. Phylogeography: Retrospect and prospect. J. Biogeogr. 2009, 36, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin, J.D.; Altermatt, F.; Finn, D.S.; Heino, J.; Olden, J.D.; Pauls, S.U.; Lytle, D.A. The role of dispersal in river network metacommunities: Patterns, processes, and pathways. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 63, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.M.; Schmidt, D.J.; Finn, D.S. Genes in streams: Using DNA to understand the movement of freshwater fauna and their riverine habitat. Bioscience 2009, 59, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val, P.; Lyons, N.J.; Gasparini, N.; Willenbring, J.K.; Albert, J.S. Landscape evolution as a diversification driver in freshwater fishes. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 9, 788328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatchez, L.; Wilson, C.C. Comparative phylogeography of nearctic and palearctic fishes. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unmack, P.J.; Hammer, M.P.; Adams, M.; Johnson, J.B.; Dowling, T.E. The role of continental shelf width in determining freshwater phylogeographic patterns in south-eastern Australian pygmy perches (Teleostei: Percichthyidae). Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 1683–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.S.; Oberdorff, T.; Hugueny, B.; Leprieur, F.; Jezequel, C.; Cornu, J.F.; Brosse, S.; Grenouillet, G.; Tedesco, P.A. Global imprint of historical connectivity on freshwater fish biodiversity. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craw, D.; Upton, P.; Burridge, C.P.; Wallis, G.P.; Waters, J.M. Rapid biological speciation driven by tectonic evolution in New Zealand. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.X.; Liu, M.D.; He, D.K. Phylogeography of Triplophysa stenura (Nemacheilidae): Responded to the Mid-Pleistocene climate transition in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Zool. Stud. 2020, 59, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H.; Sun, Y.X.; Wu, H.H.; Li, S.N.; Shen, Z.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Wen, M.; Chen, P.; Gu, Q.H. Pleistocene climate and geomorphology drive the evolution and phylogeographic pattern of Triplophysa robusta (Kessler, 1876). Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 955382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, M.F.; Kim, D.; Gallen, S.F.; Benavides, E.; Keck, B.P.; Wood, J.; Goldberg, S.L.; Larsen, I.J.; Mollish, J.M.; Simmons, J.W.; et al. Erosion of heterogeneous rock drives diversification of Appalachian fishes. Science 2023, 380, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, P. Drainage rearrangement by river capture, beheading and diversion. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1995, 19, 449–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, A.T.; Knowles, L.L. Flowing into the unknown: Inferred paleodrainages for studying the ichthyofauna of Brazilian coastal rivers. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2018, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto-Santos, I.C.A.; Jennings, W.B.; Buckup, P.A. Testing palaeodrainage hypotheses in south-eastern Brazil: Phylogeography of the sinistral livebearer fish of the genus Phalloceros (Cyprinodontiformes: Poeciliidae). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2023, 197, 514–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burridge, C.P.; Craw, D.; Waters, J.M. An empirical test of freshwater vicariance via river capture. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1883–9185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, B.D.; Adams, M.; Mather, P.B.; Hughes, J.M. Statistical phylogeographic tests of competing ‘Lake Carpentaria hypotheses’ in the mouth-brooding freshwater fish, Glossamia aprion (Apogonidae). Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 63, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yin, W.; Chen, A.H.; Li, J.; Lei, G.C.; Fu, C.Z. Phylogeographical analysis of a cold-temperate freshwater fish, the Amur sleeper (Perccottus glenii) in the Amur and Liaohe River Basins of Northeast Asia. Zool. Sci. 2014, 31, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.M.Q.; Berbel, W.M.; Araujo, T.F.P.; Lazzarotto, H.; Tatarenkov, A.; Avise, J.C. Headwater capture evidenced by paleo-rivers reconstruction and population genetic structure of the armored catfish (Pareiorhaphis garbei) in the Serra do Mar Mountains of Southeastern Brazil. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.S.; Thomaz, A.T.; Fagundes, N.J.R. River capture or ancestral polymorphism: An empirical genetic test in a freshwater fish using approximate Bayesian computation. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 131, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S.; Ni, X.M.; Fu, C.Z. Phylogeographical analysis of the freshwater gudgeon Huigobio chenhsienensis (Cypriniformes: Gobionidae) in Southern China. Life 2022, 12, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Machado, C.B.; Affonso, P.; Galetti, P.M. Speciation in coastal basins driven by staggered headwater captures: Dispersal of a species complex, Leporinus bahiensis, as revealed by genome-wide SNP data. Syst. Biol. 2023, 72, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Wu, J.X.; Yang, J.Q.; Chen, J.B.; Yang, J.M.; Li, C.; Lin, H.D.; Zhao, J. Phylogeography and demographic history of the cyprinid fish Barbodes semifasciolatus: Implications for the history of landform changes in south mainland China, Hainan and Taiwan. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1193619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.S.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Chen, L.R.; Zhao, S.L. Geology of Bohai Sea; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.F.; Qiu, J.D.; Saito, Y.; Lu, J.F.; Zhou, L.Y.; Xu, G.; Du, X.L.; Chen, Q. Sedimentary evolution during the last similar to 1.9 Ma near the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea. Paleogeogr. Paleoclimatol. Paleoecol. 2016, 451, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wan, S.M.; Clift, P.D.; Huang, J.; Yu, Z.J.; Zhang, K.D.; Mei, X.; Liu, J.; Han, Z.Y.; Nan, Q.Y.; et al. History of Yellow River and Yangtze River delivering sediment to the Yellow Sea since 3.5 Ma: Tectonic or climate forcing? Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 216, 74–88. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Guo, F.; Wu, H.C.; Yang, H.L.; Qiang, X.K.; Chu, H.X.; He, L.; Mei, X.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; et al. The sedimentary succession of the last 2.25 Myr in the Bohai Strait: Implications for the Quaternary paleoenvironmental evolution of the Bohai Sea. Paleogeogr. Paleoclimatol. Paleoecol. 2022, 585, 110704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tsukamoto, S.; Shang, Z.W.; Tamura, T.; Wang, H.; Frechen, M. Constraining the transgression history in the Bohai Coast China since the Middle Pleistocene by luminescence dating. Mar. Geol. 2019, 416, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.P.; Yang, H.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Tan, H.M.; Chen, Y.X. Phylogeography of Lefua costata in China. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2021, 45, 405–413. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Chen, M.; Tang, Q.Y.; Li, X.J.; Liu, H.Z. Geological events and Pliocene climate fluctuations explain the phylogeographical pattern of the cold water fish Rhynchocypris oxycephalus (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae) in China. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogutskaya, N.G.; Naseka, A.M.; Shedko, S.V.; Vasil’eva, E.D.; Chereshnev, I.A. The fishes of the Amur River: Updated check-list and zoogeography. Ichthyol. Explor. Freshw. 2008, 19, 301–366. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Chi, Y.P.; Wu, P.; Wei, Z.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Sun, L. Reversal of the middle-upper Songhua River in the late Early Pleistocene, Northeast China. Geomorphology 2020, 369, 107373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Chi, Y.P.; Wu, P.; Wei, Z.Y.; Li, S.Q.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, S. Provenance evidence for the early-to-middle Pleistocene drainage reorganization of the Songhua River, NE China. Catena 2023, 224, 107004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang-Liaw, N.H.; Tominaga, K.; Zhang, C.G.; Zhao, Y.H.; Nakajima, J.; Onikura, N.; Watanabe, K. Phylogeography of the Chinese false gudgeon, Abbottina rivularis, in East Asia, with special reference to the origin and artificial disturbance of Japanese populations. Ichthyol. Res. 2019, 66, 460–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.H.; Kravchenko, A.Y.; Merila, J.; Guo, B.C. Phylogenomics of Northeast Asian Pungitius sticklebacks. Divers. Distrib. 2022, 28, 2610–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Jia, J.; Zheng, Y. Time constraints for the Yellow River traversing the Sanmen Gorge. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, G.; Saito, Y.; Ni, G.Z.; Hu, H.; Yu, Z.Y.; Chen, J.P.; Wang, M.; Yuan, X.P.; Wang, L.; et al. Did the modern Yellow River form at the Mid-Pleistocene transition? Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 1603–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Sun, D.H.; Xu, W.H.; Wang, F.; Liang, B.Q.; Ma, Z.W.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.J.; Chen, F.H. Paleomagnetic chrofnology and paleoenvironmental records from drill cores from the Hetao Basin and their implications for the formation of the Hobq Desert and the Yellow River. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 156, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Feng, Q.; Li, Y.F.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Guo, X.Y. Stable oxygen and carbon isotope record from a drill core from the Hetao Basin in the upper reaches of the Yellow River in northern China and its implications for paleolake evolution. Chem. Geol. 2020, 557, 119798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Fan, H.Y.; An, P.; Wen, H.; Yu, L.P. Mega-lake formation in the eastern Hetao Basin, China, during marine isotope stages 7 and 5: A comparison of quartz and feldspar luminescence dating. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1177629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.B.; Ran, Y.K.; Guo, W.S. Division of Quaternary beds and environment evolution in Hubao Basin in China. Quat. Sci. 2007, 27, 632–644. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Fu, J.; Wang, S.; Li, C. Discussion on the epoch of lacustrine strata in Togtoh, Inner Mongolia. J. Geomech. 2013, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, P.Q. Gobioninae. In Fauna Sinica, Osteichthyes: Cypriniformes (II); Chen, Y.Y., Ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 262–389. [Google Scholar]
- Du, T.K.; Zhang, D.Z.; Ding, H. Preliminary studies on the biology of Gobio rivuloides Nichols. J. Ningxia Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2002, 23, 364–366. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.Q.; Hsu, K.C.; Liu, Z.Z.; Su, L.W.; Kuo, P.H.; Tang, W.Q.; Zhou, Z.C.; Liu, D.; Bao, B.L.; Lin, H.D. The population history of Garra orientalis (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) using mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite data with approximate Bayesian computation. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhong, Z.; Dai, W.; Fan, Q.; He, S. Phylogeographic structure, cryptic speciation and demographic history of the sharpbelly (Hemiculter leucisculus), a freshwater habitat generalist from southern China. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.X.; Hsu, K.C.; Kang, B.; Kuo, P.H.; Tsai, W.H.; Liang, C.M.; Lin, H.D.; Wang, W.K. Population structure of Aphyocypris normalis: Phylogeography and systematics. Zookeys 2019, 872, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.X.; Yu, D.; Liu, H.Z. Phylogeographic analysis revealed allopatric distribution pattern and biogeographic processes of the widespread pale chub Opsariichthys acutipinnis-evolans complex (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) in southeastern China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1142810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Yang, X.S.; Ni, X.M.; Fu, C.Z. The role of landscape evolution in the genetic diversification of a stream fish Sarcocheilichthys parvus from Southern China. Front. Genet. 2023, 13, 1075617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 35892-2018; Laboratory Animal—Guideline for Ethical Review of Animal Welfare. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Miller, S.A.; Dykes, D.D.; Polesky, H.F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.H. DAMBE6: New tools for microbial genomics, phylogenetics, and molecular evolution. J. Hered. 2017, 108, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sanchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sanchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchene, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kuhnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006650. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.J.; Mayden, R.L. Molecular systematics of the Cyprinoidea (Teleostei: Cypriniformes), the world’s largest clade of freshwater fishes: Further evidence from six nuclear genes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 52, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, W.J.; Mayden, R.L.; He, S.P. Remarkable phylogenetic resolution of the most complex clade of Cyprinidae (Teleostei: Cypriniformes): A proof of concept of homology assessment and partitioning sequence data integrated with mixed model Bayesian analyses. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 66, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, K.; Sado, T.; Doosey, M.H.; Bart, H.L.; Inoue, J.G.; Nishida, M.; Mayden, R.L.; Miya, M. Evidence from mitochondrial genomics supports the lower Mesozoic of South Asia as the time and place of basal divergence of cypriniform fishes (Actinopterygii: Ostariophysi). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2011, 161, 633–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.R.; Drummond, A.J. bModelTest: Bayesian phylogenetic site model averaging and model comparison. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xie, Z. DAMBE: Software package for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. J. Hered. 2001, 92, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Rohl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, M.J.; Matzke, N.J.; Moore, B.R.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. Bayesian analysis of biogeography when the number of areas is large. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzke, N.J. BioGeoBEARS: Biogeography with Bayesian (and Likelihood) Evolutionary Analysis in R Scripts. R Package; Version 021; University of California Berkeley: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupanloup, I.; Schneider, S.; Excoffier, L. A simulated annealing approach to define the genetic structure of populations. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2571–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.X. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 1997, 147, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornuet, J.M.; Pudlo, P.; Veyssier, J.; Dehne-Garcia, A.; Gautier, M.; Leblois, R.; Marin, J.M.; Estoup, A. DIYABC v2.0: A software to make approximate Bayesian computation inferences about population history using single nucleotide polymorphism, DNA sequence and microsatellite data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1187–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera, A.A.; Palsboll, P.J. Inferring past demographic changes from contemporary genetic data: A simulation-based evaluation of the ABC methods implemented in DIYABC. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, e94–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.; Jeon, H.B.; Suk, H.Y. Evidence of an ancient connectivity and biogeodispersal of a bitterling species, Rhodeus notatus, across the Korean Peninsula. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Huang, X.X.; Wu, Y.F. Palaeolake isolation and biogeographical process of freshwater fishes in the Yellow River. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Luo, J.; Murphy, R.W.; Du, R.; Wu, S.F.; Zhu, C.L.; Li, Y.; Poyarkov, A.D.; Nguyen, S.N.; et al. Quaternary palaeoenvironmental oscillations drove the evolution of the Eurasian Carassius auratus complex (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae). J. Biogeogr. 2012, 39, 2264–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Shan, X.J.; Gorfine, H.; Dai, F.Q.; Wu, Q.; Yang, T.; Shi, Y.Q.; Jin, X.S. Ensemble projections of fish distribution in response to climate changes in the Yellow and Bohai Seas, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, K.M.; Rohling, E.J.; Ramsey, C.B.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Florindo, F.; Heslop, D.; Marra, F.; Roberts, A.P.; Tamisiea, M.E.; et al. Sea-level variability over five glacial cycles. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, W.S.; Bowen, B.W. Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: Insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation. J. Hered. 1998, 89, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.B.; Kutzbach, J.; An, Z.S.; Clemens, S.; Liu, Z.Y.; Liu, W.G.; Liu, X.D.; Shi, Z.G.; Zheng, W.P.; Liang, L.J.; et al. Astronomical and glacial forcing of East Asian summer monsoon variability. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 115, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.J.; Kong, X.H.; Paterson, G.A.; Sun, Y.B.; Wu, Y.B.; Ao, H.; Xian, F.; Du, Y.J.; Tang, L.; Zhou, J.; et al. Eccentricity-paced geomagnetic field and monsoon rainfall variations over the last 870 kyr. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2211495120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Ludwig, A.; Peng, Z.G. Geographical differentiation of the Euchiloglanis fish complex (Teleostei: Siluriformes) in the Hengduan Mountain Region, China: Phylogeographic evidence of altered drainage patterns. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; He, D.K.; Jia, Y.T.; Sun, H.Y.; Chen, Y.F. Phylogeographic studies of schizothoracine fishes on the central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau reveal the highest known glacial microrefugia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J.C. Phylogenetic units and currencies above and below the species level. In Phylogeny and Conservation; Purvis, A., Gittleman, J.L., Brooks, T., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 76–100. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, D.J.; Byrne, M.; Moritz, C. Genetic diversity and conservation units: Dealing with the species-population continuum in the age of genomics. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laikre, L.; Hoban, S.; Bruford, M.W.; Segelbacher, G.; Allendorf, F.W.; Gajardo, G.; Rodríguez, A.G.; Hedrick, P.W.; Heuertz, M.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; et al. Post-2020 goals overlook genetic diversity. Science 2020, 367, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kort, H.; Prunier, J.G.; Ducatez, S.; Honnay, O.; Baguette, M.; Stevens, V.M.; Blanchet, S. Life history, climate and biogeography interactively affect worldwide genetic diversity of plant and animal populations. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, C. Defining ‘Evolutionarily Significant Units’ for conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1994, 9, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.; Deng, J.M.; Wu, Y.F.; Chen, L.Q.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, H.Y.; Lu, Y.; He, D.M. Mapping China’s freshwater fishes: Diversity and biogeography. Fish Fish. 2014, 15, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrello, M.; D’Aloia, C.; Dalongeville, A.; Escalante, M.A.; Guerrero, J.; Perrier, C.; Torres-Florez, J.P.; Xuereb, A.; Manel, S. Evolving spatial conservation prioritization with intraspecific genetic data. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2022, 37, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Fu, C.Z. Three mitochondrial genomes of freshwater fishes in the genus Squalidus (Cypriniformes: Gobionidae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 3779–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, T.Y.; Fu, C.Z. Two mitochondrial genomes of freshwater gudgeons in the genus Gobio (Cypriniformes: Gobionidae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 3072–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, K.; Sado, T.; Mayden, R.L.; Hanzawa, N.; Nakamura, K.; Nishida, M.; Miya, M. Mitogenomic evolution and interrelationships of the Cypriniformes (Actinopterygii: Ostariophysi): The first evidence toward resolution of higher-level relationships of the world’s largest freshwater fish clade based on 59 whole mitogenome sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 2006, 63, 826–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.S.; Cheng, Q.Q.; Yan, Y.B.; Duan, X.C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.P.; Lou, Z.Y.; Du, Y.Y. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence and phylogenetic position of Gobio coriparoides. Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 808–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Cao, K.; Fu, C.Z. Ten fish mitogenomes of the tribe Gobionini (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae: Gobioninae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2018, 3, 802–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Ni, X.M.; Fu, C.Z. The complete mitochondrial genome of Mesogobio lachneri (Cypriniformes: Gobionidae) from Northeast Asia. Mitochondrial DNA B 2022, 7, 1810–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.R.; Bang, I.C. Complete mitochondrial genome of the endangered freshwater fish Microphysogobio rapidus (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae) from Korea. Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.E.; Park, G.S.; Kim, M.C.; Kim, K.H.; Park, H.C.; Lee, I.J.; Shin, J.H. Complete mitochondrial genome of the Korean endemic species Microphysogobio yaluensis (Teleostei, Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae). Mitochondrial DNA A 2016, 27, 3557–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, M.; Nakajima, J.; Mukai, T. Distribution of indigenous and non-indigenous mtDNA haplotypes of Biwia zezera (Cyprinidae) in northern Kyushu, Japan. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 2007, 54, 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.W.; Fu, C.Z. Three mitochondrial genomes of Pseudogobio fishes (Cypriniformes: Gobionidae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 3064–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, C.Z. Three complete mitochondrial genomes of freshwater fishes in the genus Abbottina (Cypriniformes: Gobionidae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2019, 4, 2179–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Fu, C.Z. Four complete mitochondrial genomes of Saurogobio fishes (Cypriniformes: Gobionidae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2019, 4, 2175–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.Y.; Nam, Y.K.; Bang, I.C. Phylogeny and divergence time estimation of Coreoleuciscus splendidus populations (Teleostei: Cypriniformes) endemic to Korea based on complete mitogenome sequences. Genes Genom. 2012, 34, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.J.; Zhao, H.P. The complete mitogenome of Gnathopogon polytaenia (Cypriniformes; Cyprinidae). Mitochondrial DNA A 2016, 27, 1307–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.S.; Lee, W.O.; Lee, J.S. Complete mitochondrial genome of the freshwater gudgeon, Pseudopungtungia nigra (Cypriniformes, Gobioninae). Mitochondrial DNA 2014, 25, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.N.; Kim, S.; Kwak, M. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence of a Korean Pungtungia herzi (Cypriniformes, Gobioninae). Mitochondrial DNA 2014, 25, 414–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.H.; Xia, R.; Lei, G.C.; Fu, C.Z. Complete mitochondrial genome of Pseudorasbora elongata (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae). Mitochondrial DNA 2015, 26, 250–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.R.; Lin, H.D.; Su, L.W.; Tang, W.Q.; Wu, C.Y.; Yang, J.Q. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Sarcocheilichthys nigripinnis (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae). Mitochondrial DNA 2013, 24, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.M.; Chen, Z.J.; Ai, W.M. Complete mitochondrial genome of Sarcocheilichthys parvus (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae). Mitochondrial DNA 2013, 24, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.K.; Xu, G.C.; Nie, Z.J.; Xu, P.; Gu, R.B. Complete mitochondrial genome of Paracanthobrama guichenoti. Mitochondrial DNA A 2016, 27, 727–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.D.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.G.; Peng, Z.G. Comparative study of the complete mitochondrial genomes of the bronze gudgeon (Coreius heterodon) and largemouth bronze gudgeon (Coreius guichenoti). Mitochondrial DNA 2013, 24, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Q.; Fu, C.Z. Complete mitochondrial genome of Ladislavia taczanowskii (Cypriniformes: Gobionidae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2021, 6, 2227–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Lim, Y.H.; Bang, I.C.; Nam, Y.K. Phylogenetic relationships among three new Hemibarbus mitogenome sequences belonging to the subfamily Gobioninae (Teleostei, Cypriniformes, and Cyprinidae). Mitochondrial DNA 2009, 20, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.Y.; Jean, C.T.; Chen, Y.J.; Lin, K.Y.; Liu, M.Y. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Belligobio nummifer (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae). Mitochondrial DNA A 2016, 27, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoto, J.M.; Saitoh, K.; Sasaki, T.; Yonezawa, T.; Adachi, J.; Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Miya, M.; Nishida, M.; Hanzawa, N. Phylogeny and biogeography of highly diverged freshwater fish species (Leuciscinae, Cyprinidae, Teleostei) inferred from mitochondrial genome analysis. Gene 2013, 514, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.E.; Yu, J.N.; Kim, S.; Kwak, M. The complete mitochondrial genome of Kumgang fat minnow Rhynchocypris kumgangensis (Cypriniformes, Leuciscinae) in Korea. Mitochondrial DNA 2012, 23, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ji, P.; Xu, J.; Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Xu, P.; Sun, X. Complete mitochondrial genome of Leuciscus waleckii (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae: Leuciscus). Mitochondrial DNA 2013, 24, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y.; Bang, I.C. Coreoleuciscus aeruginos (Teleostei: Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae), a new species from the Seomjin and Nakdong rivers, Korea. Zootaxa 2015, 3931, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J. The Cyprinidae fossils from middle Miocene of Shanwang Basin. Vert. Palasiat. 1990, 28, 95–127. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.Y.; He, L.J.; Chen, L.C. Tectono-thermal modeling of Cenozoic multiple rift episodes in the Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China and its geodynamic implications. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 107, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Hou, S.K.; Wang, S.Q. Neogene integrative stratigraphy and timescale of China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Drainage | No. of Individuals | No. of Haplotypes | No. of Private Haplotypes | Haplotype Diversity | Nucleotide Diversity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow River | 102 | 8 | 7 | 0.5541 ± 0.0495 | 0.0024 ± 0.0015 |
| Hai River | 11 | 3 | 2 | 0.5636 ± 0.1340 | 0.0011 ± 0.0009 |
| Luan River | 25 | 17 | 15 | 0.9600 ± 0.0233 | 0.0025 ± 0.0015 |
| Liao River | 49 | 20 | 18 | 0.8469 ± 0.0412 | 0.0025 ± 0.0015 |
| Amur River | 99 | 40 | 40 | 0.8667 ± 0.0311 | 0.0018 ± 0.0011 |
| Total | 286 | 85 | 82 | 0.9204 ± 0.0103 | 0.0074 ± 0.0038 |
| Yellow River | Hai River | Luan River | Liao River | Amur River | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow River | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| Hai River | 0.4017 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| Luan River | 0.7459 | 0.7658 | 0.0005 | 0.0000 | |
| Liao River | 0.7539 | 0.7588 | 0.0834 | 0.0000 | |
| Amur River | 0.8145 | 0.8358 | 0.7991 | 0.7987 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, G.; Fu, C. Pleistocene Landscape Dynamics Drives Lineage Divergence of a Temperate Freshwater Fish Gobio rivuloides in Coastal Drainages of Northern China. Genes 2023, 14, 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122146
Ni X, Chen Y, Deng G, Fu C. Pleistocene Landscape Dynamics Drives Lineage Divergence of a Temperate Freshwater Fish Gobio rivuloides in Coastal Drainages of Northern China. Genes. 2023; 14(12):2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122146
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Xiaomin, Yun Chen, Guangmin Deng, and Cuizhang Fu. 2023. "Pleistocene Landscape Dynamics Drives Lineage Divergence of a Temperate Freshwater Fish Gobio rivuloides in Coastal Drainages of Northern China" Genes 14, no. 12: 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122146
APA StyleNi, X., Chen, Y., Deng, G., & Fu, C. (2023). Pleistocene Landscape Dynamics Drives Lineage Divergence of a Temperate Freshwater Fish Gobio rivuloides in Coastal Drainages of Northern China. Genes, 14(12), 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122146





