Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of WRKY Transcription Factors in Akebiatrifoliata: A Bioinformatics Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Used in This Study
2.2. Identification of Akebia trifoliata AkWRKY
2.3. Protein Properties of AkWRKY
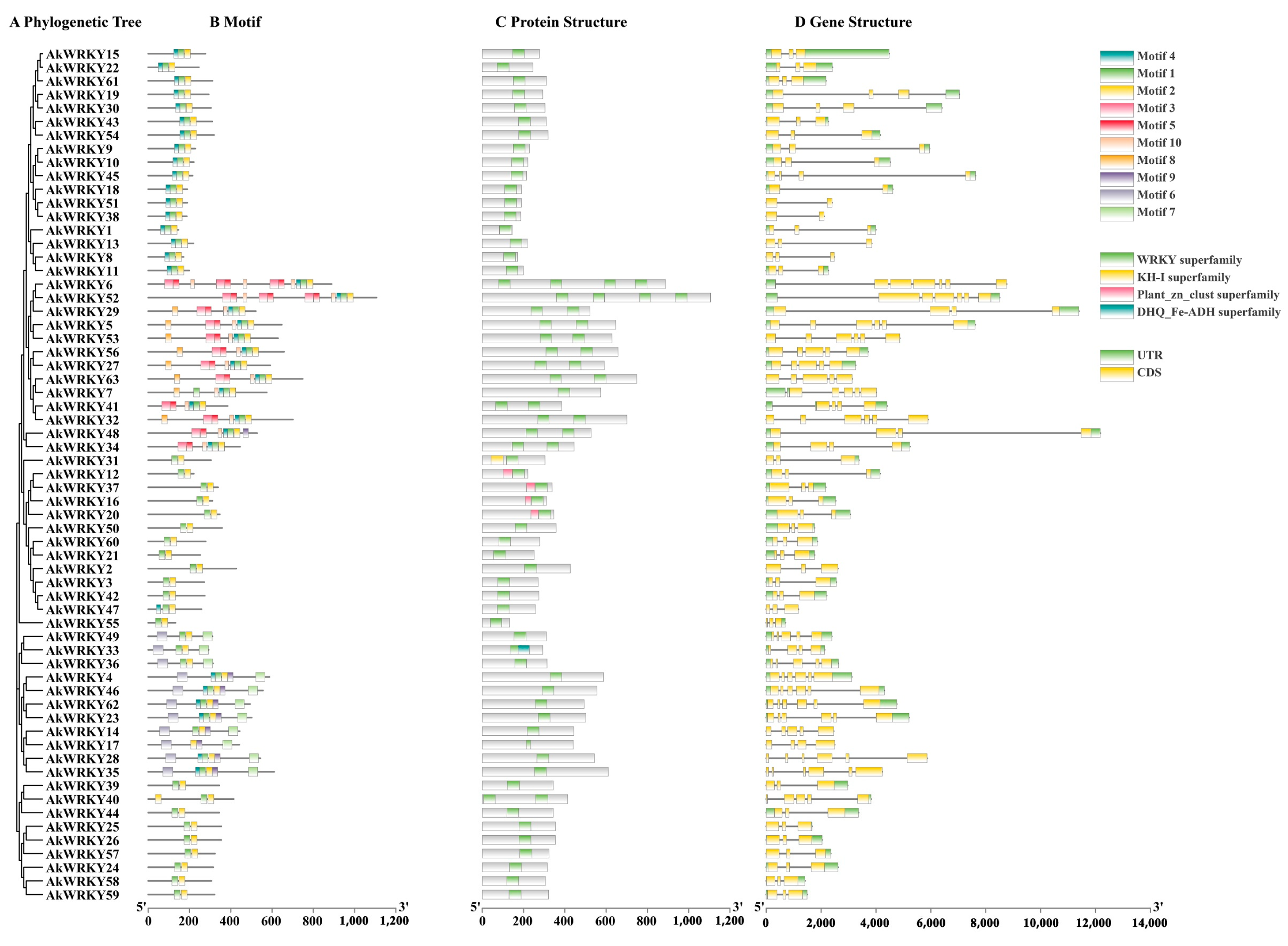
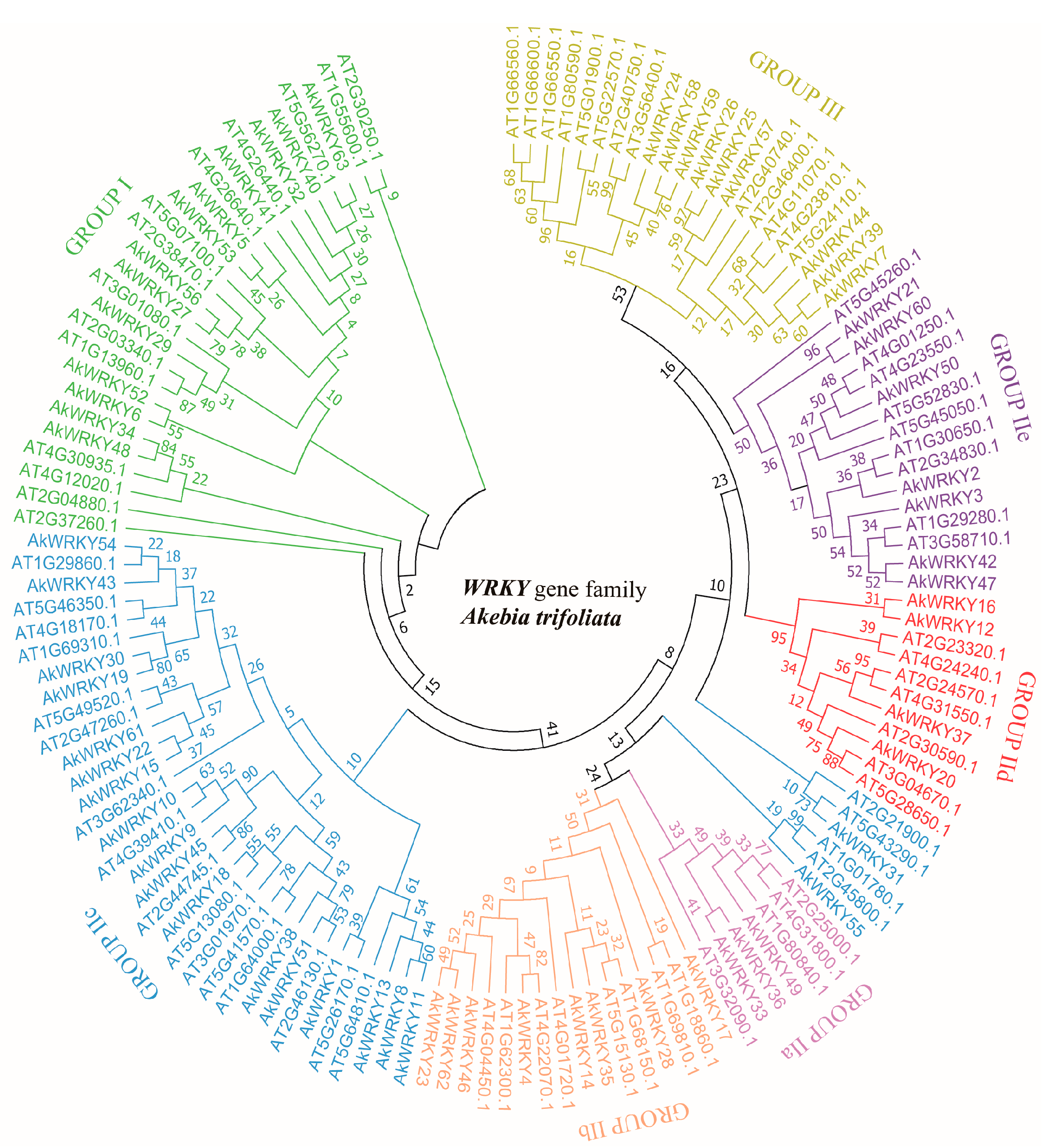
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Exon–Intron Structure Analysis
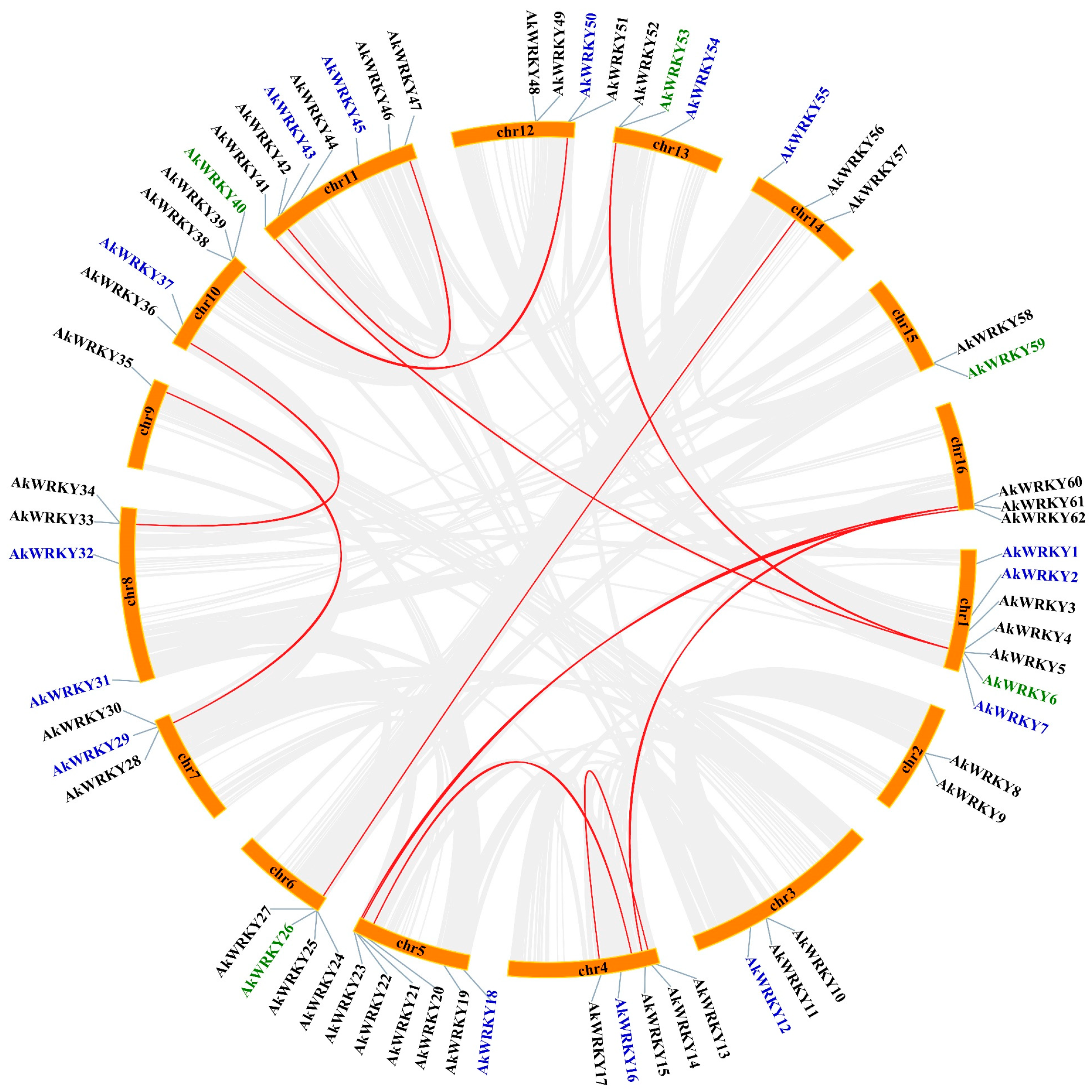
2.6. Chromosomal Location, Gene Replication, and Ka/Ks Analysis
2.7. AkWRKY Gene GO Annotation and KEGG Annotation
2.8. Expression Pattern of AkWRKY Genes in A. trifoliata Fruit Tissues
2.9. Putative Promoter Region Analysis
2.10. Correlation Analysis between AkWRKY Genes and AkNBS Genes
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Classification of the AkWRKY Genes of A. trifoliata
3.2. Basic Information and Motif Composition of the AkWRKY Protein
3.3. Duplication and Natural Selection Type of AkWRKY Genes
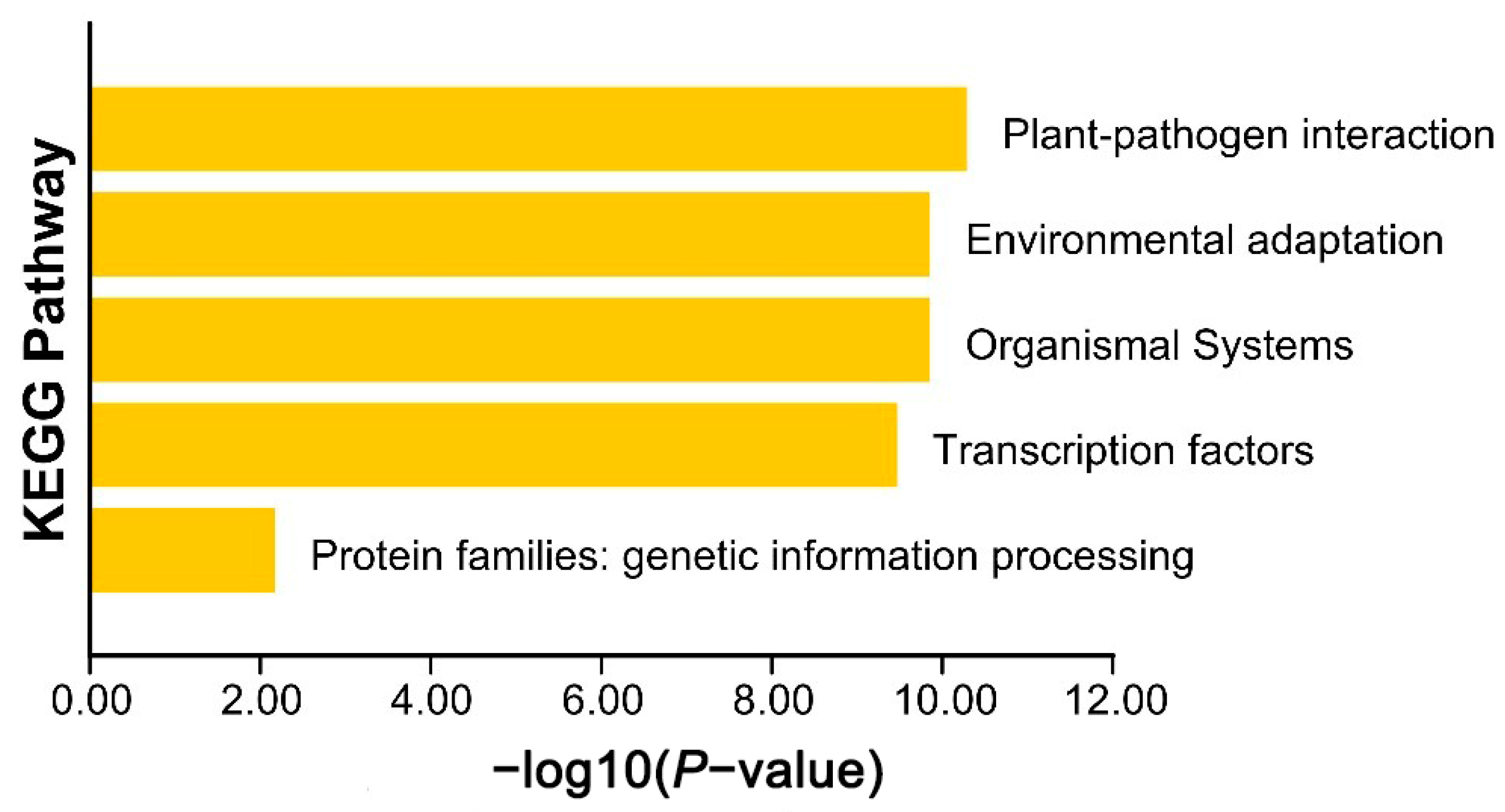
3.4. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis of AkWRKY Genes
3.5. Transcriptome Analysis of AtWRKY Genes in Different Tissues of A. trifoliata Fruit
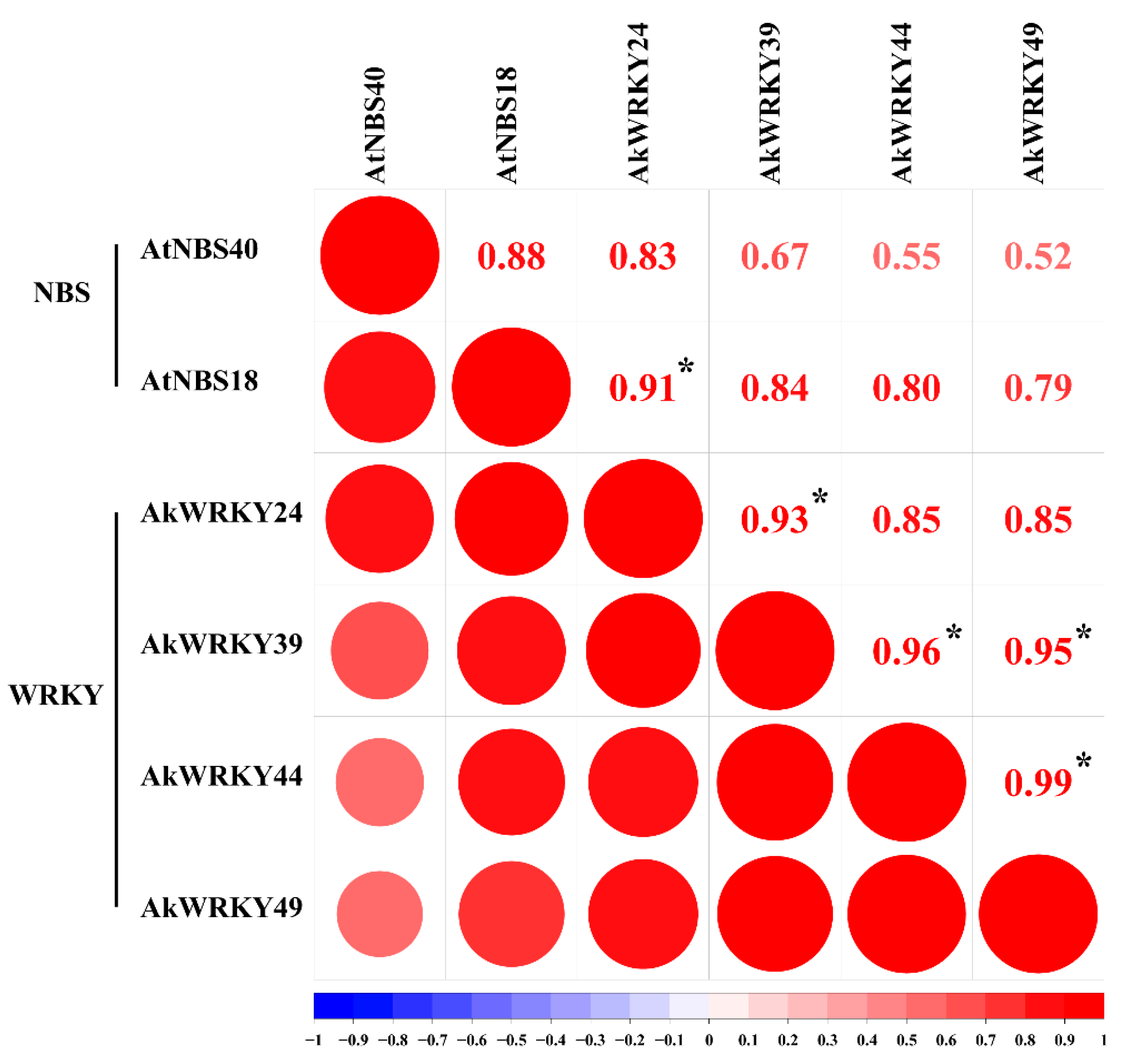
3.6. Putative Downstream Target WRKY and NBS Genes Regulated by WRKY Genes
4. Discussion
4.1. The WRKY Gene Family of A. trifoliata Follows a Conservative Classification System
4.2. The Variation in the Number and Components of Heptapeptides in WRKY Genes
4.3. WRKY Genes Evolutionarily Experienced Genome Duplication and Natural Selection Events
4.4. Prediction of the Potential Downstream Target Genes of WRKY Genes in the Disease Resistance Process
4.5. AkWRKY24 Could Be Involved in the Disease Resistance Process Possibly by Regulating AkNBS18
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.; White, M.J.; MacRae, T.H. Transcription factors and their genes in higher plants. Functional domains, evolution and regulation. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 262, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broun, P. Transcription factors as tools for metabolic engineering in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K.; Kigawa, T.; Inoue, M.; Watanabe, S.; Tateno, M.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yokoyama, S. Structures and evolutionary origins of plant-specific transcription factor DNA-binding domains. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.; Martin, G.; Reuber, L.; Jiang, C.Z.; Keddie, J.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Samaha, R.R.; et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ülker, B.; Somssich, I.E. WRKY transcription factors: From DNA binding towards biological function. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eulgem, T.; Rushton, P.J.; Robatzek, S.; Somssich, I.E. The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Hu, Y.; Vannozzi, A.; Wu, K.; Cai, H.; Qin, Y.; Mullis, A.; Lin, Z.G.; Zhang, L.S. The WRKY transcription factor family in model plants and crops. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2017, 36, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somssich, I.E.; Hahlbrock, K. Pathogen defence in plants—a paradigm of biological complexity. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Z.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yokosho, K.; Ding, B.; Fan, W.; Gong, Q.Q.; Li, G.X.; Wu, R.Y.; Yang, J.L.; Ma, J.F.; et al. Transcription factor WRKY22 promotes aluminum tolerance via activation of OsFRDL4 expression and enhancement of citrate secretion in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol. 2018, 219, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, Y.B.; Yan, X.X.; Huang, Y.; Han, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.B.; Fan, T.T.; Xiao, F.M.; Liu, Y.S.; Cao, S.Q. The WRKY transcription factor, WRKY13, activates PDR8 expression to positively regulate cadmium tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.B.; Yu, D.Q. Arabidopsis WRKY2 transcription factor mediates seed germination and postgermination arrest of development by abscisic acid. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.J.; Yan, J.Y.; Li, G.X.; Wu, Z.C.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zheng, S.J. WRKY41 controls Arabidopsis seed dormancy via direct regulation of ABI3 transcript levels not downstream of ABA. Plant J. 2014, 79, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.Q.; Tan, X.L.; Shan, W.; Kuang, J.F.; Lu, W.J.; Chen, J.Y. Characterization of a transcriptional regulator, BrWRKY6, associated with gibberellin-suppressed leaf senescence of Chinese flowering cabbage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Cui, M.Y.; Hu, Y.; Gao, K.; Xie, Y.G.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, J.Y. Ectopic expression of FvWRKY42, a WRKY transcription factor from the diploid woodland strawberry (Fragaria vesca), enhances resistance to powdery mildew, improves osmotic stress resistance, and increases abscisic acid sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2018, 275, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, Y.; Shinshi, H. Characterization of a novel cis-acting element that is responsive to a fungal elicitor in the promoter of a tobacco class I chitinase gene. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 24, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushton, P.J.; Torres, J.T.; Parniske, M.; Wernert, P.; Hahlbrock, K.; Somssich, I.E. Interaction of elicitor-induced DNA-binding proteins with elicitor response elements in the promoters of parsley PR1 genes. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 5690–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, P.J.; Somssich, I.E. Transcriptional control of plant genes responsive to pathogens. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 1998, 1, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, W.; Fu, P.; Zhong, S.F.; Guan, J.; Luo, P. Developmental stages of Akebia trifoliata fruit based on volume. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2021, 39, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaoka, F.; Kakiuchi, N.; Long, C.; Itoga, M.; Mitsue, A.; Mouri, C.; Mikage, M. Molecular characterization of Akebia plants and the derived traditional herbal medicine. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Yao, X.; Zhong, C.; Chen, X.; Huang, H. Akebia: A potential new fruit crop in China. HortScience 2010, 45, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Wang, H.M.; Zeng, X.H. Research progress of active compounds and pharmacological effects in Akebia trifoliata (Thunb) koidz stems. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 185, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Z.; Ye, H.M.; Zeng, H.Z.; Li, L.H.; Wu, G.Y.; Liu, G.Y. Study on extraction process of active ingredients from Akebia stem and analysis of their anti-gastric cancer activity. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 10, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.L.; Ren, H.Y.; Liang, C.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xu, J.; Pan, Z.Q.; Liu, X.M.; Wu, Z.H.; Fang, Z.Q. Akebia trifoliate (Thunb.) koidz seed extract inhibits the proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines via inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 192749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Tian, A. Study on the extraction and content determination of total flavonoids from the pericarp of Akebia trifoliata. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2010, 4, 250–253. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, L. Research progress on the characteristics of Akebia trifoliata. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2011, 23, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangelsen, E.; Kilian, J.; Berendzen, K.W.; Kolukisaoglu, Ü.H.; Harter, K.; Jansson, C.; Wanke, D. Phylogenetic and comparative gene expression analysis of barley (Hordeum vulgare) WRKY transcription factor family reveals putatively retained functions between monocots and dicots. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, D. Overexpression of OsWRKY72 gene interferes in the abscisic acid signal and auxin transport pathway of Arabidopsis. J. Biosci. 2010, 35, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.L.; Guo, R.R.; Xu, X.Z.; Gao, M.; Li, X.Q.; Song, J.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.P. Evolution and expression analysis of the grape (Vitis vinifera L.) WRKY gene family. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1513–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chi, Y.; Fan, B.; Chen, Z. Characterization of soybean WRKY gene family and identification of soybean WRKY genes that promote resistance to soybean cyst nematode. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Zhong, S.F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Li, Z.; Ren, T.H.; Tan, F.Q.; Shen, J.L.; Li, Q.; et al. Differential expression profile of microsatellites in various tissues of Akebia trifoliata fruit and development of a set of highly effective EST-SSR markers. Genes 2022, 13, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liang, J.; Tan, Q.; Ou, L.F.; Li, X.L.; Zhong, C.H.; Huang, H.L.; Møller, L.M.; Wu, X.J.; Song, S.Q. Insights into triterpene synthesis and unsaturated fatty-acid accumulation provided by chromosomal-level genome analysis of Akebia trifoliata subsp. australis. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.J.; Yu, D.; Jeon, J.S.; Piffanelli, P.; Yamazaki, Y. Nomenclature report on rice WRKY’s—conflict regarding gene names and its solution. Rice 2012, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.Y.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, İ.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Tang, H.B.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.P.; Wang, X.Y.; Lee, T.; Jin, H.Z.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J. KaKs_calculator 2.0: A toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2010, 8, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotz, S.; Garcia-Gomez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Williams, T.D.; Nagaraj, S.H.; Nueda, M.J.; Robles, M.; Talón, M.; Dopazo, J.; Conesa, A. High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3420–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.J.; Zhong, S.F.; Yang, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Guan, J.; Fu, P.; Tan, F.Q.; Ren, T.H.; et al. Identification and characterization of NBS resistance genes in Akebia trifoliata. Front. Plant. Sci. 2021, 12, 758559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, N.; Shan, H.Y.; Su, K.M.; Zhang, J.S.; Meng, Z.; Kong, H.Z.; Chen, Z.D. Interactions among proteins of floral MADS-box genes in basal eudicots: Implications for evolution of the regulatory network for flower development. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 1598–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushton, P.J.; Somssich, I.E.; Ringler, P.; Shen, Q.J. WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinerson, C.I.; Rabara, R.C.; Tripathi, P.; Shen, Q.J.; Rushton, P.J. The evolution of WRKY transcription factors. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Xu, Z.S.; Tian, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.S. Genomic identification of WRKY transcription factors in carrot (Daucus carota) and analysis of evolution and homologous groups for plants. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Ekramoddoullah, A.K.M. Identification and characterization of the WRKY transcription factor family in Pinus monticola. Genome 2009, 52, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, M.; Cheng, L. Genome-wide identification and characterization of WRKY transcriptional factor family in apple and analysis of their responses to waterlogging and drought stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. The WRKY transcription factor superfamily: Its origin in eukaryotes and expansion in plants. BMC Evol. Biol. 2005, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, M.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, J.; da Silva, J.A.T.; Ma, G. Genome-wide characterization, expression profile analysis of WRKY family genes in Santalum album and functional identification of their role in abiotic stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.H.; Anand, S.; Singh, B.; Bohra, A.; Joshi, R. WRKY transcription factors and plant defense responses: Latest discoveries and future prospects. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juretic, N.; Hoen, D.R.; Huynh, M.L.; Harrison, P.M.; Bureau, T.E. The evolutionary fate of MULE-mediated duplications of host gene fragments in rice. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciolkowski, I.; Wanke, D.; Birkenbihl, R.P.; Somssich, I.E. Studies on DNA-binding selectivity of WRKY transcription factors lend structural clues into WRKY-domain function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 68, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Palmqvist, S.; Olsson, H.; Boreén, M.; Ahlandsberg, S.; Jansson, C. A novel WRKY transcription factor, SUSIBA2, participates in sugar signaling in barley by binding to the sugar-responsive elements of the iso1 promoter. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2076–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Verk, M.C.; Pappaioannou, D.; Neeleman, L.; Bol, J.F.; Linthorst, H.J.M. A novel WRKY transcription factor is required for induction of PR-1a gene expression by salicylic acid and bacterial elicitors. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 1983–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Fu, P.; Wang, X.S.; Yu, X.J.; Zhong, S.F.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, C.; Yang, H.; Luo, P.G. Assessment of the breeding potential of a set of genotypes selected from a natural population of Akebia trifoliata (three–leaf Akebia). Horticulturae 2022, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, E.; Ali, S.; Byamukama, E.; Yen, Y.; Nepal, M. Disease resistance mechanisms in plants. Genes 2018, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, T.G.; Chen, W.Q.; Zhong, S.F.; Zhang, H.Y.; Tang, Z.X.; Chang, Z.J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.Q.; et al. Wheat WCBP1 encodes a putative copper-binding protein involved in stripe rust resistance and inhibition of leaf senescence. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.X.; Zhong, S.F.; Liu, N.; Chen, W.Q.; Liu, T.G.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Z.L.; Yang, J.Z.; Luo, P.G. Gene expression profile and physiological and biochemical characterization of hexaploid wheat inoculated with Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 90, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, R.J.; Thon, M.R.; Hacquard, S.; Amyotte, S.G.; Kleemann, J.; Torres, M.F.; Damm, U.; Buiate, E.A.; Epstein, L.; Alkan, N.; et al. Lifestyle transitions in plant pathogenic Colletotrichum fungi deciphered by genome and transcriptome analyses. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Fang, H.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, K.Q. Genome-wide identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs conferring resistance to Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in walnut (Juglans regia). BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonardi, V.; Tang, S.; Stallmann, A.; Roberts, M.; Cherkis, K.; Dangl, J.L. Expanded functions for a family of plant intracellular immune receptors beyond specific recognition of pathogen effectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16463–16468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalde, M.; Barth, M.; Somssich, I.E.; Lippok, B. Members of the Arabidopsis WRKY group III transcription factors are part of different plant defense signaling pathways. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eulgem, T.; Somssich, I.E. Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Besseau, S.; Törönen, P.; Sipari, N.; Kollist, H.; Holm, L.; Palva, E.T. Defense-related transcription factors WRKY70 and WRKY54 modulate osmotic stress tolerance by regulating stomatal aperture in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
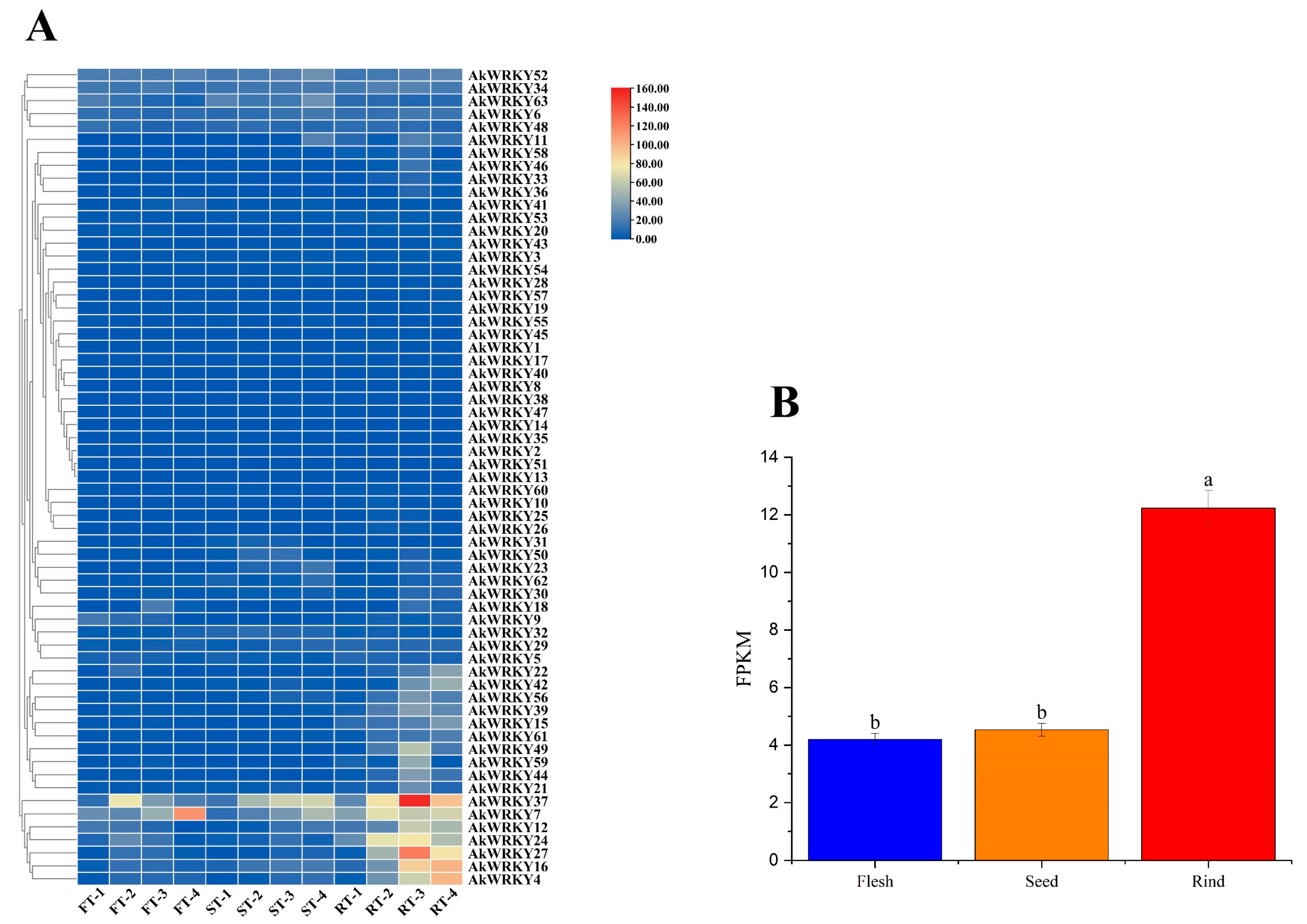
| Type | Num. | Gene Length (Exon Number) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Maen | ||
| Group I | 13 | 3129 (AkWRKY63) | 12,174 (AkWRKY48) | 6365.69 a (5.31) a |
| Group II | 41 | 698 (AkWRKY55) | 7626 (AkWRKY45) | 3368.76 b (3.63) b |
| Subgroup IIa | 3 | |||
| Subgroup IIb | 8 | |||
| Subgroup IIc | 19 | |||
| Subgroup IId | 4 | |||
| Subgroup IIe | 7 | |||
| Group III | 9 | 1411 (AkWRKY58) | 4013 (AkWRKY7) | 2435.00 b (3.33) b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Zhong, S.; Guan, J.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, C.; Tan, F.; Ren, T.; Li, Z.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of WRKY Transcription Factors in Akebiatrifoliata: A Bioinformatics Study. Genes 2022, 13, 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091540
Zhu J, Zhong S, Guan J, Chen W, Yang H, Yang H, Chen C, Tan F, Ren T, Li Z, et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of WRKY Transcription Factors in Akebiatrifoliata: A Bioinformatics Study. Genes. 2022; 13(9):1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091540
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jun, Shengfu Zhong, Ju Guan, Wei Chen, Hao Yang, Huai Yang, Chen Chen, Feiquan Tan, Tianheng Ren, Zhi Li, and et al. 2022. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of WRKY Transcription Factors in Akebiatrifoliata: A Bioinformatics Study" Genes 13, no. 9: 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091540
APA StyleZhu, J., Zhong, S., Guan, J., Chen, W., Yang, H., Yang, H., Chen, C., Tan, F., Ren, T., Li, Z., Li, Q., & Luo, P. (2022). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of WRKY Transcription Factors in Akebiatrifoliata: A Bioinformatics Study. Genes, 13(9), 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091540





