Commonly Assessed Markers in Childhood BCP-ALL Diagnostic Panels and Their Association with Genetic Aberrations and Outcome Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Philadelphia chromosome (Ph)-like ALL or BCR::ABL1-like ALL (Ph-positive ALL without BCR::ABL1 fusion protein) is a subgroup of patients that do not have the BCR::ABL1 fusion protein expressed from the Philadelphia chromosome but have a gene-expression profile similar to that of patients with BCR::ABL1 ALL [19,23,24].
2. Materials and Methods
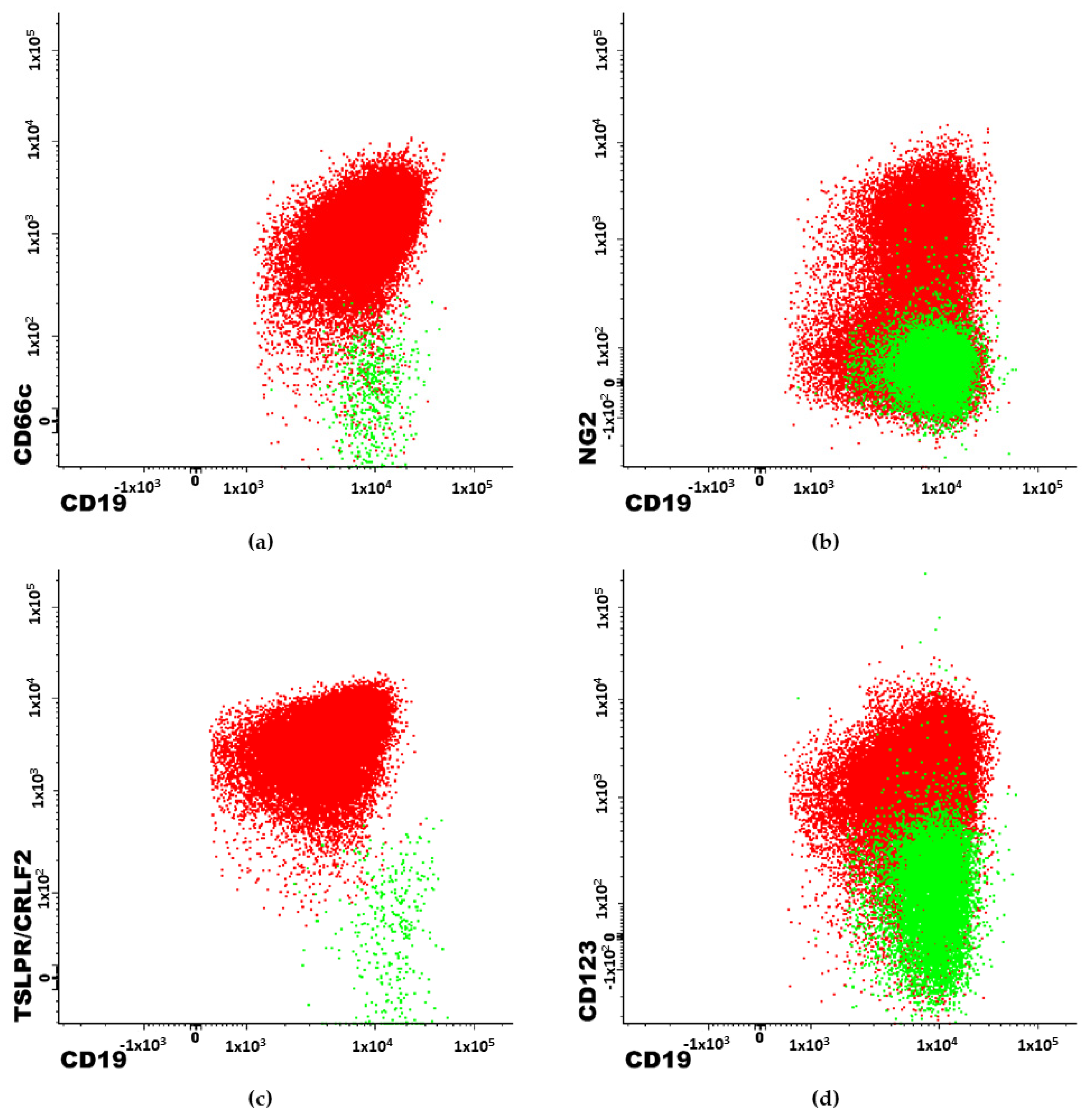
3. Results
- CD19
- CD10
- CD66c
- NG2
- TSLPR/CRLF2
- CD123
- CD9
- CD38
- CD45
- CD20
- CD24
- CD22
- CD13
- Cytoplasmic IgM (cIgM)
- CD15
- CD33
- TdT
- CD81
- CD34
| Antigen | ETV6::RUNX1 | BCR::ABL1 | KMT2A | TCF3::PBX1 | Hyper-Diploidy | Prognosis if + | EGIL Subtype if + |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD10 | + [32,33,35,47,62] | + [6,22,32,34] | − [10,13,32,33,59] | +/− [13,32] | + [11,32] | Good [26] | B-II [13,31] |
| CD66c | − [13,32,38,73] | + [13,21,32,37,38,39] | − [6,32,38] | − [32,38] | + [11,32,33] | Inconclusive | Irrelevant |
| NG2 | − [32] | − [32] | + [10,25,26,32,33] | − [32] | [32] | Poor [3,25,26] | B-I [10,26,32] |
| TSLPR | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | Poor [24,42,43] | Irrelevant |
| CD123 | Low + [45] | + [44] | + [6] | − [6] | + [1,33,44,45,46,74] | Good [3,45] | B-II [45] |
| CD9 | − [6,13,14,32,47] | + [6] | + [6,32] | + [6,32] | ND | Poor [14,47] | Irrelevant |
| CD38 | + [1,33] | − [6,34] | + [6] | + [6] | − [1] | Inconclusive [1,50] | Irrelevant |
| CD45 | Low+ [16,32,33,62] | −/Low+ [32] | Low+ [32] | Low + [32] | − [11,32,53] | Poor [4,51,52] | Irrelevant |
| CD20 | − [13,16,32,62] | + [32] | − [6,13,32,59] | Low + [13,32] | Low+ [32] | Inconclusive [39,54] | Irrelevant |
| CD24 | + [13,32] | + [13,32] | − [13,26,32,33] | + [32] | + [32] | Inconclusive | B-IV [56,57] |
| CD22 | Low+ [32] | Low+ [32] | − [32,59] | + [32] | + [32] | Inconclusive | All [13,31] |
| CD13 | + [13,22,32] | + [16,32,34,39,62] | − [32] | − [32] | − [32] | Inconclusive | Irrelevant |
| cIgM | − [32] | − [32] | − [6,32] | + [6,10,15,32] | − [32] | Poor | B-III [13,31,63,64] |
| CD15 | − [32,62] | − [6,32,39] | + [6,10,13,26,32,59] | − [32] | − [32] | Poor | B-I [13] |
| CD33 | + [13,32] | + [13,22,39] | − [32] | − [32] | − [32] | Poor [1] | Irrelevant |
| TdT | + [13,32] | + [13,32] | Low+ [33]/ + [13,32] | +[32] | +[32] | Inconclusive | B-I, II, III [13,31] |
| CD81 | Low+/−[33] | ND | − [33] | ND | − [33] | Good | Irrelevant |
| CD34 | Low+ [33]/ + [6,13,32,62] | + [6,13,34] | − [6,32,33] | − [6,13,32] | + [32,33] | Inconclusive | Irrelevant |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chulián, S.; Martínez-Rubio, Á.; Pérez-García, V.M.; Rosa, M.; Blázquez Goñi, C.; Rodríguez Gutiérrez, J.F.; Hermosín-Ramos, L.; Molinos Quintana, Á.; Caballero-Velázquez, T.; Ramírez-Orellana, M.; et al. High-Dimensional Analysis of Single-Cell Flow Cytometry Data Predicts Relapse in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Cancers 2020, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, M.S.; Esfandiari, N.; Refoua, S.; Shamaei, M. Characterization of Immunophenotypic Aberrancies in Adult and Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Lessons from Regional Variation. Iran. J. Pathol. 2020, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zheng, J.; Gerasimcik, N.; Lagerstedt, K.; Sjögren, H.; Abrahamsson, J.; Fogelstrand, L.; Mårtensson, I.-L. The Expression Pattern of the Pre-B Cell Receptor Components Correlates with Cellular Stage and Clinical Outcome in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0162638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Singh, J.; Verma, D.; Kumar, R.; Bakhshi, S.; Tanwar, P.; Singh, A.R.; Chopra, A. Prognostic Significance of CD45 Antigen Expression in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2021, 89, 102562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Gao, C.; Wang, C.-J.; Zhao, X.-X.; Li, W.-J.; Li, Z.-G.; Zheng, H.-Y.; Wang, T.-Y.; Zhang, R.-D. Combined Analysis of IKZF1 Deletions and CRLF2 Expression on Prognostic Impact in Pediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 62, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagarakis, N.J.; Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Pavlidis, D.; Marinakis, T.; Kostopoulos, I.V.; Stiakaki, E.; Polychronopoulou, S.; Paterakis, G. Flow Cytometric Predictive Scoring Systems for Common Fusions ETV6/RUNX1, BCR/ABL1, TCF3/PBX1 and Rearrangements of the KMT2A Gene, Proposed for the Initial Cytogenetic Approach in Cases of B-acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2019, 41, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demina, I. Heterogeneity of Childhood Acute Leukemia with Mature B-Cell Immunophenotype. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.C.; Auat, M.; Santos-Pirath, I.M.; Rudolf-Oliveira, R.C.M.; da Silva, J.P.; Lange, B.G.; Siegel, D.; de Moraes, A.C.R.; Del Moral, J.A.G.; Santos-Silva, M.C. The Importance of CD39, CD43, CD81, and CD95 Expression for Differentiating B Cell Lymphoma by Flow Cytometry: CD39, CD43, CD81, AND CD95 FOR LYMPHOMA DIAGNOSIS. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shieban, S.; Byrne, E.; Trivedi, P.; Morilla, R.; Naresh, K.N. Immunohistochemical Distinction of Haematogones from B Lymphoblastic Leukaemia/Lymphoma or B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (B-ALL) on Bone Marrow Trephine Biopsies: A Study on 62 Patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 154, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongen, J.J.M.; Lhermitte, L.; Böttcher, S.; Almeida, J.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Flores-Montero, J.; Rawstron, A.; Asnafi, V.; Lécrevisse, Q.; Lucio, P.; et al. Antibody Panels for Standardized N-Dimensional Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping of Normal, Reactive and Malignant Leukocytes. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1908–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepański, T.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; van Dongen, J.J.M. Flow-Cytometric Immunophenotyping of Normal and Malignant Lymphocytes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. CCLM 2006, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bene, M.; Castoldi, G.; Knapp, W.; Ludwig, W.; Matutes, E.; Orfao, A.; van’t Veer, M. Proposals for the Immunological Classification of Acute Leukemias. Leukemia 1995, 9, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar]
- Szczepański, T.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; van Dongen, J.J.M. Classification Systems for Acute and Chronic Leukaemias. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2003, 16, 561–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunck, C.B.; Terra-Granado, E.; Noronha, E.P.; Wajnberg, G.; Passetti, F.; Pombo-de-Oliveira, M.S.; Emerenciano, M. CD9 Predicts ETV6-RUNX1 in Childhood B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2019, 41, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandri, A.J.; Reid, G.S.D.; Bader, S.A.; Massing, B.G.; Sorensen, P.H.B.; Schultz, K.R. ETV6 (TEL)-AML1 Pre-B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Cells Are Associated with a Distinct Antigen-Presenting Phenotype: Antigen-Presentation Molecules in ETV6-AML1 Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 116, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitz, M.; Rubnitz, J.; Nash, M.; Pullen, D.; Camitta, B. Surface Antigen Phenotype Can Predict TEL-AML1 Rearrangement in Childhood B-Precursor ALL: A Pediatric Oncology Group Study. Leukemia 1998, 12, 1764–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van der Weyden, L.; Giotopoulos, G.; Rust, A.G.; Matheson, L.S.; van Delft, F.W.; Kong, J.; Corcoran, A.E.; Greaves, M.F.; Mullighan, C.G.; Huntly, B.J.; et al. Modeling the Evolution of ETV6-RUNX1–Induced B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Mice. Blood 2011, 118, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubnitz, J.E.; Downing, J.R.; Pui, C.H.; Shurtleff, S.A.; Raimondi, S.C.; Evans, W.E.; Head, D.R.; Crist, W.M.; Rivera, G.K.; Hancock, M.L.; et al. TEL Gene Rearrangement in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A New Genetic Marker with Prognostic Significance. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 15, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, A.; Shiekh, A.A.; Bhat, G.M.; Lone, A.R. Prognostification of ALL by Cytogenetics. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2015, 31, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmeister, T.; Gokbuget, N.; Schwartz, S.; Fischer, L.; Hubert, D.; Sindram, A.; Hoelzer, D.; Thiel, E. Clinical Features and Prognostic Implications of TCF3-PBX1 and ETV6-RUNX1 in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2010, 95, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owaidah, T.M.; Rawas, F.I.; Al khayatt, M.F.; Elkum, N.B. Expression of CD66c and CD25 in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia as a Predictor of the Presence of BCR/ABL Rearrangement. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2008, 1, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrente, F.; Bellesi, S.; Metafuni, E.; Puggioni, P.L.; Marietti, S.; Ciminello, A.M.; Za, T.; Sorà, F.; Fianchi, L.; Sica, S.; et al. Role of Flow-Cytometric Immunophenotyping in Prediction of BCR/ABL1 Gene Rearrangement in Adult B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: FLOW-CYTOMETRY IN BCR/ABL1 ADULT B-ALL. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.G.; Li, Y.; Payne-Turner, D.; Harvey, R.C.; Yang, Y.-L.; Pei, D.; McCastlain, K.; Ding, L.; Lu, C.; Song, G.; et al. Targetable Kinase-Activating Lesions in Ph-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 Revision to the World Health Organization Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.; Renaud, G.; Sant’Ana, M.; Barbieri, C.; Passetti, F.; Pombo-de-Oliveira, M.S. Challenges in the Use of NG2 Antigen as a Marker to Predict MLL Rearrangements in Multi-Center Studies. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schwartz, S.; Rieder, H.; Schläger, B.; Burmeister, T.; Fischer, L.; Thiel, E. Expression of the Human Homologue of Rat NG2 in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Close Association with MLL Rearrangement and a CD10−/CD24−/CD65s+/CD15+ B-Cell Phenotype. Leukemia 2003, 17, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosova, M.; Volejnikova, J.; Porizkova, I.; Holzerova, M.; Pospisilova, D.; Novak, Z.; Vrbkova, J.; Mihal, V. Chromosomal Aberrations in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: 15-Year Single Center Experience. Cancer Genet. 2016, 209, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, J.; Elder, A.; Forster, V.; Heidenreich, O.; Koschmieder, S.; Vormoor, J. CD19: A Multifunctional Immunological Target Molecule and Its Implications for Blineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: CD19 in Blineage ALL. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theunissen, P.M.J.; Sedek, L.; De Haas, V.; Szczepanski, T.; Van Der Sluijs, A.; Mejstrikova, E.; Nováková, M.; Kalina, T.; Lecrevisse, Q.; Orfao, A.; et al. The EuroFlow Consortium. Detailed Immunophenotyping of B-Cell Precursors in Regenerating Bone Marrow of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Patients: Implications for Minimal Residual Disease Detection. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 178, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruse, J.M.; Lewis, R.E.; Sanders, C.M.; Webb, R.N.; Beason, K.L.; Lam, J.; Koehler, J. Diminished CD10, CD13, and CD15 Expression in a Differentiated Granulocyte Population in CML. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2007, 83, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaretti, S.; Zini, G.; Bassan, R. DIAGNOSIS AND SUBCLASSIFICATION OF ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 6, e2014073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrušák, O.; Porwit-MacDonald, A. Antigen Expression Patterns Reflecting Genotype of Acute Leukemias. Leukemia 2002, 16, 1233–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulis, J.; Wawrowski, Ł.; Sędek, Ł.; Wróbel, Ł.; Słota, Ł. Machine Learning Based Analysis of Relations between Antigen Expression and Genetic Aberrations in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, M.; Bortoluci, A.; Alaejos, I.; López-Berges, M.; Rasillo, A.; García-Sanz, R.; García, M.; Sayagués, J.; González, M.; Mateo, G.; et al. Adult Precursor B-ALL with BCR/ABL Gene Rearrangements Displays a Unique Immunophenotype Based on the Pattern of CD10, CD34, CD13 and CD38 Expression. Leukemia 2001, 15, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Horibe, K.; Kiyoi, H.; Miyashita, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Mori, H.; Nozaki, C.; Hasegawa, S.; Kawabe, T.; Kato, K.; et al. Prognostic Significance of TEL/AML1 Fusion Transcript in Childhood B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 1998, 20, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.C.; Waldmann, T.A. Antibody-Based Therapy of Leukaemia. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2009, 11, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, N.; Penther, D.; Vaida, I.; Gruson, B.; Harrivel, V.; Claisse, J.F.; Capiod, J.C.; Lefrere, J.J.; Damaj, G. CD66c Expression in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Strength and Weakness: CD66C IN B-ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2011, 33, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyokawa, N.; Iijima, K.; Tomita, O.; Miharu, M.; Hasegawa, D.; Kobayashi, K.; Okita, H.; Kajiwara, M.; Shimada, H.; Inukai, T.; et al. Significance of CD66c Expression in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2014, 38, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaso, J.; Thomas, D.A.; Cunningham, K.; Jorgensen, J.L.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Medeiros, L.J.; Wang, S.A. Prognostic Significance of Immunophenotypic and Karyotypic Features of Philadelphia Positive B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the Era of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cancer 2011, 117, 4009–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, C.; Montes, R.; Martín, L.; Prat, I.; Hernandez, M.C.; Orfao, A.; Menendez, P. NG2 Antigen Is Expressed in CD34+ HPCs and Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Precursors: Is NG2 Expression in Leukemia Dependent on the Target Cell Where Leukemogenesis Is Triggered? Leukemia 2008, 22, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vetter, T.; Borowski, A.; Wohlmann, A.; Ranjan, N.; Kuepper, M.; Badura, S.; Ottmann, O.G.; Friedrich, K. Blockade of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP) Receptor Inhibits TSLP-Driven Proliferation and Signalling in Lymphoblasts from a Subset of B-Precursor ALL Patients. Leuk. Res. 2016, 40, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorczak, A.; Sedek, L.; Braun, M.; Madzio, J.; Sonsala, A.; Twardoch, M.; Fendler, W.; Nebral, K.; Taha, J.; Bielska, M.; et al. Surface Expression of Cytokine Receptor-Like Factor 2 Increases Risk of Relapse in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Harboring IKZF1 Deletions. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 25971–25982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarno, J.; Savino, A.M.; Buracchi, C.; Palmi, C.; Pinto, S.; Bugarin, C.; Jager, A.; Bresolin, S.; Barber, R.C.; Silvestri, D.; et al. SRC/ABL Inhibition Disrupts CRLF2-Driven Signaling to Induce Cell Death in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 22872–22885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bras, A.E.; Haas, V.; Stigt, A.; Jongen-Lavrencic, M.; Beverloo, H.B.; Marvelde, J.G.; Zwaan, C.M.; Dongen, J.J.M.; Leusen, J.H.W.; Velden, V.H.J. CD123 Expression Levels in 846 Acute Leukemia Patients Based on Standardized Immunophenotyping. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2019, 96, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokic, M.; Bjorklund, E.; Blennow, E.; Mazur, J.; Soderhall, S.; Porwit, A. Overexpression of CD123 Correlates with the Hyperdiploid Genotype in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1016–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan Awad, S.; Kamel, M.M.; Ayoub, M.A.; Kamel, A.M.; Elnoshokaty, E.H.; El Hifnawi, N. Immunophenotypic Characterization of Cytogenetic Subgroups in Egyptian Pediatric Patients With B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2016, 16, S19–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandemer, V.; Aubry, M.; Roussel, M.; Rio, A.-G.; de Tayrac, M.; Vallee, A.; Mosser, J.; Ly-Sunnaram, B.; Galibert, M.-D. CD9 Expression Can Be Used to Predict Childhood TEL/AML1-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Proposal for an Accelerated Diagnostic Flowchart. Leuk. Res. 2010, 34, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakab, K.; Gopcsa, L.; Adam, E.; Domjan, G.; Sarkadi, B.; Paloczi, K. Application of Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping and Multidrug Resistance Assay in B-Cell Acute Lymphoid Leukemia and Multiple Myeloma. Neoplasma 2005, 52, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tsitsikov, E.; Harris, M.H.; Silverman, L.B.; Sallan, S.E.; Weinberg, O.K. Role of CD81 and CD58 in Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Pediatric B Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2018, 40, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Zhang, L.-P.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Lu, A.-D.; Chang, Y.; Zhu, H.-H.; Qin, Y.-Z.; Lai, Y.-Y.; Kong, Y.; Huang, X.-J.; et al. CD38+ CD58− Is an Independent Adverse Prognostic Factor in Paediatric Philadelphia Chromosome Negative B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Patients. Leuk. Res. 2016, 43, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratei, R.; Sperling, C.; Karawajew, L.; Schott, G.; Schrappe, M.; Harbott, J.; Riehm, H.; Ludwig, W.-D. Immunophenotype and Clinical Characteristics of CD45-Negative and CD45-Positive Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 1998, 77, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behm, F.G.; Raimondi, S.C.; Schell, M.J.; Look, A.T.; Rivera, G.K.; Pui, C.-H. Lack of CD45 Antigen on Blast Cells in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Is Associated With Chromosomal Hyperdiploidy and Other Favorable Prognostic Features. Blood 1992, 79, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckenna, R.W.; Asplund, S.L.; Kroft, S.H. Immunophenotypic Analysis of Hematogones (B-Lymphocyte Precursors) and Neoplastic Lymphoblasts by 4-Color Flow Cytometry. Leuk. Lymphoma 2004, 45, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, D.-Y.; Luo, J.-M.; Ou, D.-L. CD20 and Outcome of Childhood Precursor B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Meta-Analysis. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 37, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghetany, M.T.; Patel, J. Assessment of CD24 Expression on Bone Marrow Neutrophilic Granulocytes: CD24 Is a Marker for the Myelocytic Stage of Development. Am. J. Hematol. 2002, 71, 348–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raife, T.J.; Lager, D.J.; Kemp, J.D.; Dick, F.R. Expression of CD24 (BA-1) Predicts Monocytic Lineage in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1994, 101, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, G.F.; Knapp, W. Signal transduction in lymphocytic and myeloid cells via cd24, a newmember of phosphoinositol-anchored membrane-molecules. J. Immunol. 1990, 144, 638–641. [Google Scholar]
- Kinjyo, I.; Matlawska-Wasowska, K.; Chen, X.; Monks, N.R.; Burke, P.; Winter, S.S.; Wilson, B.S. Characterization of the Anti-CD22 Targeted Therapy, Moxetumomab Pasudotox, for B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkhardt, A.; Wuchter, C.; Viehmann, S.; Pils, S.; Teigler-Schlegel, A.; Stanulla, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Ludwig, W.-D.; Janka-Schaub, G.; Schrappe, M.; et al. Infant Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia – Combined Cytogenetic, Immunophenotypical and Molecular Analysis of 77 Cases. Leukemia 2002, 16, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarraz, S.; Hernandez-Campo, P.; Rivas, J.H.; Salvador, C.; Fernandez-Mosteirın, N.; Giralt, M.; Perdiguer, L.; Orfao, A. The Immunophenotype of Different Immature, Myeloid and B-Cell Lineage-Committed CD34 þ Hematopoietic Cells Allows Discrimination between Normal/Reactive and Myelodysplastic Syndrome Precursors. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucio, P.; Gaipa, G.; van Lochem, E.; van Wering, E.; Porwit-MacDonald, A.; Faria, T.; Bjorklund, E.; Biondi, A. BIOMED-I Concerted Action Report: FLow Cytometric Immunophenotyping of Precursor B-ALL with Standardized Triple-Stainings. Leukemia 2001, 15, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Zen, L.; Orfao, A.; Cazzaniga, G.; Masiero, L.; Cocito, M.; Spinelli, M.; Rivolta, A.; Biondi, A.; Zanesco, L.; Basso, G. Quantitative Multiparametric Immunophenotyping in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Correlation with Specific Genotype. I. ETV6/AML1 ALLs Identification. Leukemia 2000, 14, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- ten Hacken, E.; Sivina, M.; Kim, E.; O’Brien, S.; Wierda, W.G.; Ferrajoli, A.; Estrov, Z.; Keating, M.J.; Oellerich, T.; Scielzo, C.; et al. Functional Differences between IgM and IgD Signaling in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 2522–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ten Hacken, E.; Gounari, M.; Ghia, P.; Burger, J.A. The Importance of B Cell Receptor Isotypes and Stereotypes in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy, C.H.; Polski, J.M.; Evans, H.L.; Gardner, L.J. Evaluation of Bone Marrow Specimens With Acute Myelogenous Leukemia for CD34, CD15, CD117, and Myeloperoxidase. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2001, 125, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, E.D.; Schwarz, L.M.; Bloomfield, C.D. Expression of the CD15 Antigen on Normal and Leukemic Myeloid Cells: Effects of Neuraminidase and Variable Detection with a Panel of Monoclonal Antibodies. Mol. Immunol. 1991, 28, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willier, S.; Rothamel, P.; Hastreiter, M.; Wilhelm, J.; Stenger, D.; Blaeschke, F.; Rohlfs, M.; Kaeuferle, T.; Schmid, I.; Albert, M.H.; et al. CLEC12A and CD33 Co-Expression as Preferential Target on Pediatric AML for Combinatorial Immunotherapy. Blood 2021, 138, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, D.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Janossy, G. The Immunologic Detection of Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Leukemia. Blood 1990, 76, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, S.; Rajkumar, A.; Grossman, H.; Szallasi, A. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT)-Negative Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Pediatric Patients: Incidence and Clinical Significance. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2017, 20, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Yun, J.W.; Jung, C.W.; Ju, H.Y.; Koo, H.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, H. Molecular Characteristics of Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase Negative Precursor B-cell Phenotype Burkitt Leukemia with IGH -MYC Rearrangement. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2020, 59, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelák, O.; Kužílková, D.; Thürner, D.; Kiene, M.-L.; Stanar, K.; Stuchlý, J.; Vášková, M.; Starý, J.; Hrušák, O.; Stadler, H.; et al. Lymphocyte Enrichment Using CD81-Targeted Immunoaffinity Matrix: Lymphocyte Enrichment via CD81 Selection. Cytom. A 2017, 91, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uckun, F.; Song, C. Lack of CD24 Antigen Expression in B-Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Is Associated with Intrinsic Radiation Resistance of Primary Clonogenic Blasts. Blood 1993, 81, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrušák, O.; Trka, J.; Zuna, J.; Housková, J.; Bartůňková, J.; Starý, J. Aberrant Expression of KOR-SA3544 Antigen in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Predicts TEL-AML1 Negativity. Leukemia 1998, 12, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Coustan-Smith, E.; Song, G.; Clark, C.; Key, L.; Liu, P.; Mehrpooya, M.; Stow, P.; Su, X.; Shurtleff, S.; Pui, C.-H.; et al. New Markers for Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 6267–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| BCP-ALL Subtype | CD10 | cyIgM | sIgM and/or cyIgK or cyIgL |
|---|---|---|---|
| B-I (pro-B) ALL | − | − | − |
| B-II (common) ALL | + | − | − |
| B-III (pre-B) | + | + | − |
| B-IV (mature) | −/+ | + | + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kulis, J.; Sędek, Ł.; Słota, Ł.; Perkowski, B.; Szczepański, T. Commonly Assessed Markers in Childhood BCP-ALL Diagnostic Panels and Their Association with Genetic Aberrations and Outcome Prediction. Genes 2022, 13, 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081374
Kulis J, Sędek Ł, Słota Ł, Perkowski B, Szczepański T. Commonly Assessed Markers in Childhood BCP-ALL Diagnostic Panels and Their Association with Genetic Aberrations and Outcome Prediction. Genes. 2022; 13(8):1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081374
Chicago/Turabian StyleKulis, Jan, Łukasz Sędek, Łukasz Słota, Bartosz Perkowski, and Tomasz Szczepański. 2022. "Commonly Assessed Markers in Childhood BCP-ALL Diagnostic Panels and Their Association with Genetic Aberrations and Outcome Prediction" Genes 13, no. 8: 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081374
APA StyleKulis, J., Sędek, Ł., Słota, Ł., Perkowski, B., & Szczepański, T. (2022). Commonly Assessed Markers in Childhood BCP-ALL Diagnostic Panels and Their Association with Genetic Aberrations and Outcome Prediction. Genes, 13(8), 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081374






