Transcriptome Analysis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Reveals Fructose Addition Effects on Fengycin Synthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. B. amyloliquefaciens Strain and Culture Medium
2.2. RNA Extraction and RNA Sequencing
2.3. Transcriptome Data and Differential Gene Expression Analysis
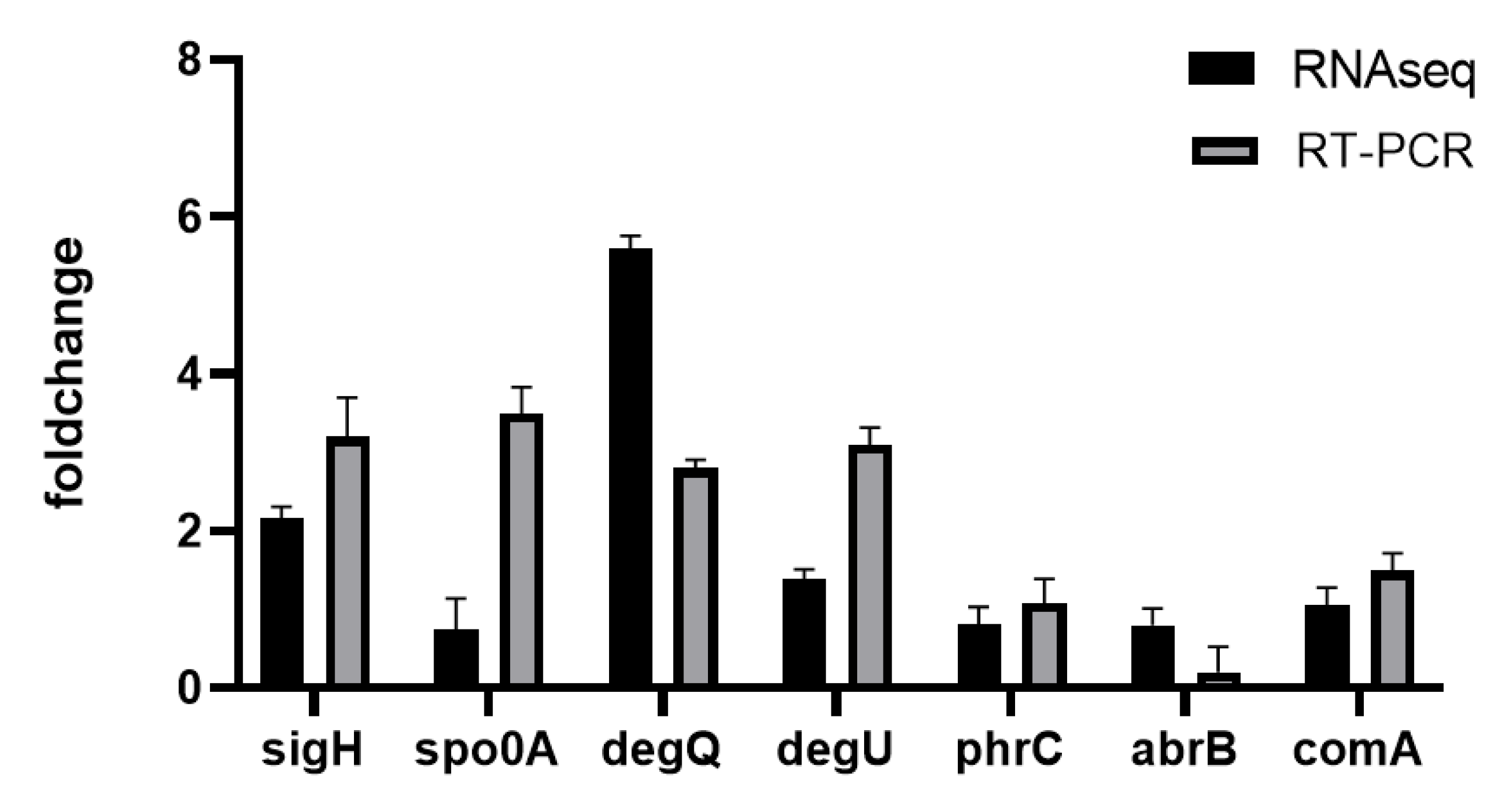
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
3. Results
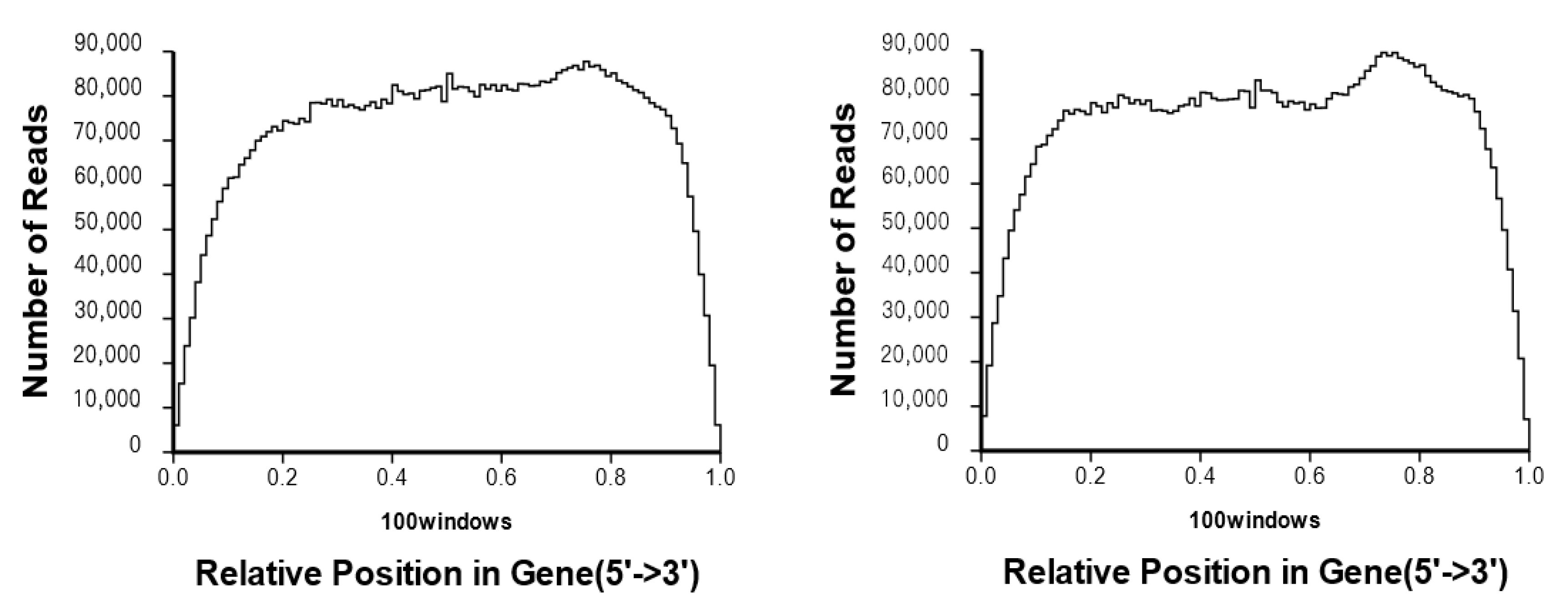
3.1. RNA-Seq Data Analysis
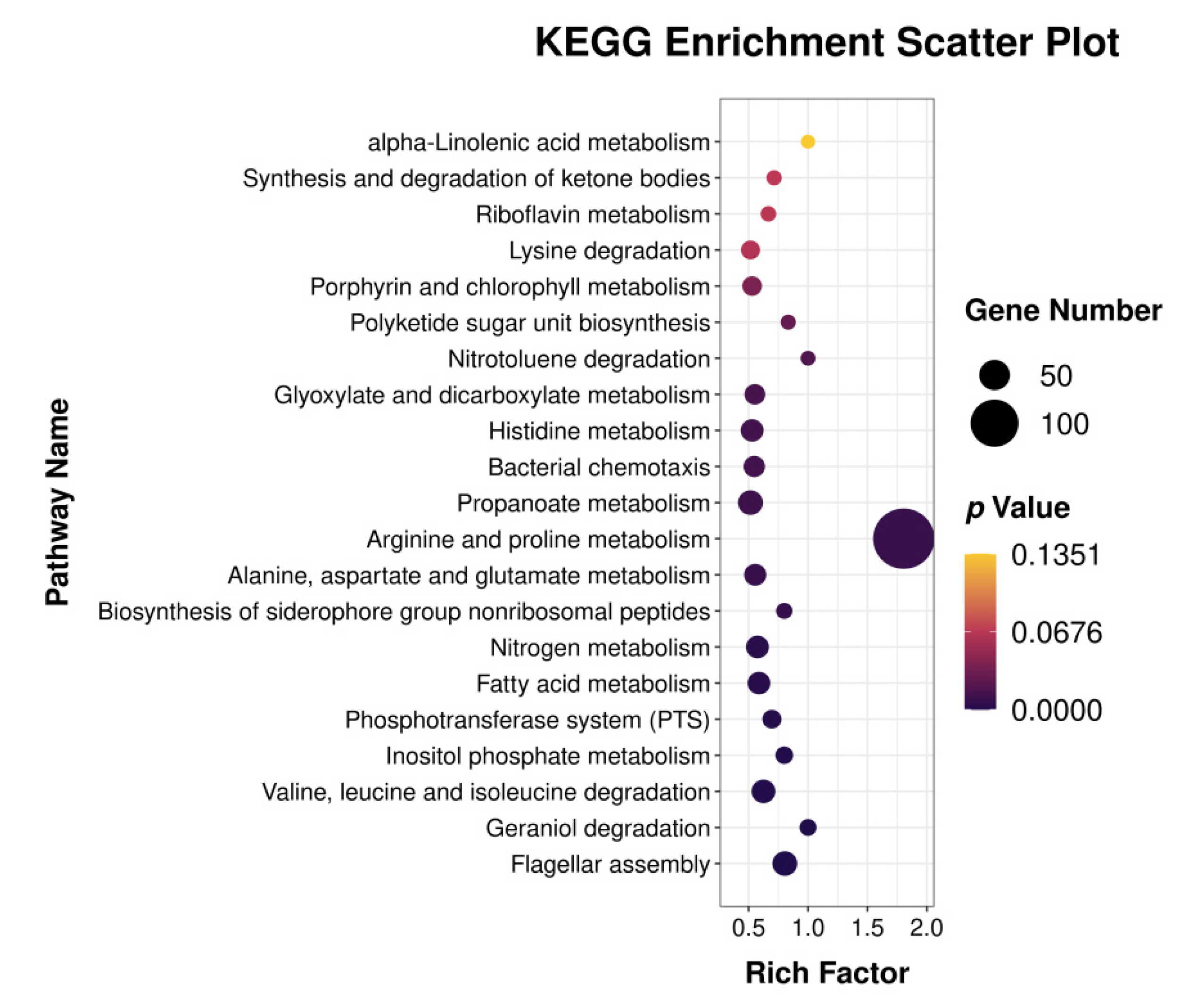
3.2. Differentially Expressed Genes GO Classification and KEGG Pathway
3.3. Differentially Expressed Genes Analysis
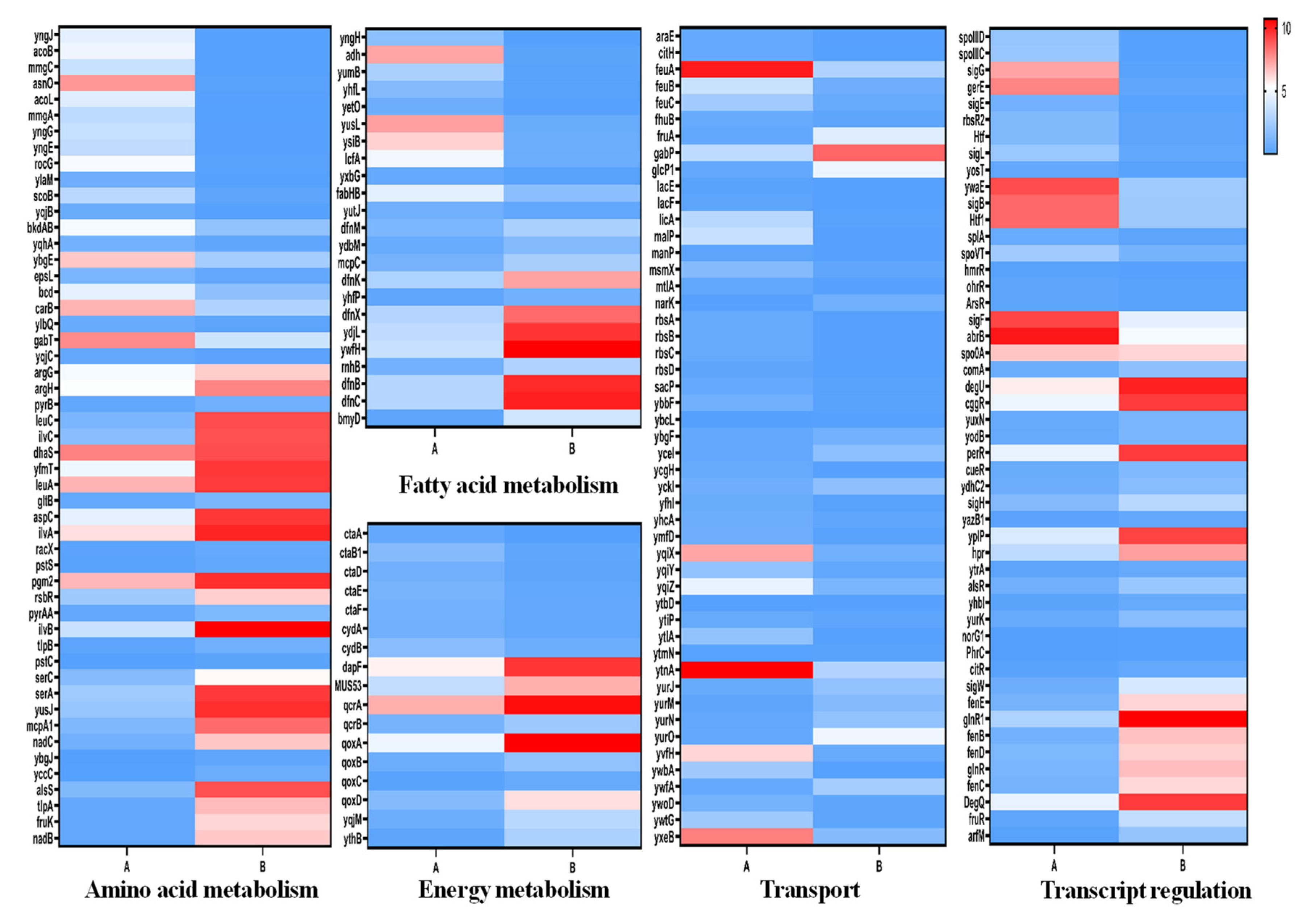
3.3.1. Amino Acid Metabolism
3.3.2. Fatty Acid Metabolism
3.3.3. Energy Metabolism
3.3.4. Transport System
3.3.5. Gene Transcription and Regulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Ngueagni, P.T. A review on new aspects of lipopeptide biosurfactant: Types, production, properties and its application in the bioremediation process. J. Hazard Mater. 2021, 407, 124827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazle Rabbee, M.; Baek, K.-H. Antimicrobial activities of lipopeptides and polyketides of bacillus velezensis for agricultural applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, K.; Dhiman, R.; Sharma, A.; Kanwar, S. Applications of lipopeptide (s) from a Bacillus sp: An overview. Res. J. Recent Sci. 2016, 5, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar, F.; Neubauer, P.; Gimpel, M. Bioactive secondary metabolites from Bacillus subtilis: A comprehensive review. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2038–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, S.A.; Vederas, J.C. Lipopeptides from Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp. a gold mine of antibiotic candidates. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 4–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissler, M.; Heravi, K.M.; Henkel, M.; Hausmann, R. Lipopeptide biosurfactants from Bacillus species. In Biobased Surfactants; Academic Press and AOCS Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 2019; pp. 205–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Zheng, M.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, R.; Zheng, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y. Effect of metal ions on lipopeptide secretion from Bacillus subtilis strain FJAT-4, Negative regulation by Ca2+. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 132, 2167–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, G.; Yu, S.-M.; Lee, Y.H. Influence of light qualities on antifungal lipopeptide synthesis in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens JBC36. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 137, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, Y.; Gancel, F.; Béchet, M.; Drider, D.; Jacques, P. Study of the correlation between fengycin promoter expression and its production by Bacillus subtilis under different culture conditions and the impact on surfactin production. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, Y.; Gancel, F.; Drider, D.; Béchet, M.; Jacques, P. Influence of promoters on the production of fengycin in Bacillus spp. Res. Microbiol. 2016, 167, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wen, J.; Yin, Y.; Wang, P. Metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis based on genome-scale metabolic model to promote fengycin production. 3 Biotech. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Dong, L.; Wang, P.; Li, S.; Zhao, W.; Lu, X.; Zang, X.; Ping, M. The PhoR/PhoP two-component system regulates fengycin production in Bacillus subtilis NCD-2 under low-phosphate conditions. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wushensky, J.A.; Youngster, T.; Mendonca, C.M.; Aristilde, L. Flux connections between gluconate pathway, glycolysis, and pentose–phosphate pathway during carbohydrate metabolism in bacillus megaterium QM B1551. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Cong, J.; Yu, C.; Liu, N.; Liu, J.; Sand, W. Fructose as an additional co-metabolite promotes refractory dye degradation performance and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-R.; Park, Y.-L.; Song, H.-S.; Lee, S.M.; Park, S.L.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.-J.; Bhatia, S.K.; Gurav, R.; Choi, K.-Y.; et al. Fructose-based production of short-chain-length and medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer by arctic pseudomonas sp. B14–6. Polymers 2021, 13, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Qian, S.; Muhammad, U.; Jiang, X.; Han, J.; Lu, Z. Effect of fructose on promoting fengycin biosynthesis in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens fmb-60. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biniarz, P.; Łukaszewicz, M.; Janek, T. Screening concepts, characterization and structural analysis of microbial-derived bioactive lipopeptides: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.; Li, R.; Yang, P.; Luo, W.; Chen, S.; Bilal, M.; Xu, H.; Gu, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; et al. iTRAQ-BASED proteomic analysis of the mechanism of fructose on improving fengycin biosynthesis in Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens. Molecules 2021, 26, 6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peypoux, F.; Michel, G. Controlled biosynthesis of Val 7-and Leu 7-surfactins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 36, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Yin, Y.; Wen, J. Increasing fengycin production by strengthening the fatty acid synthesis pathway and optimizing fermentation conditions. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 177, 108235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Guo, W.; Chen, X. Exogenous addition of alkanoic acids enhanced production of antifungal lipopeptides in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Pc3. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 5367–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inès, M.; Dhouha, G. Lipopeptide surfactants: Production, recovery and pore forming capacity. Peptides 2015, 71, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, S.; Dimitrov, K.; Gancel, F.; Vauchel, P.; Jacques, P. Nikov I Impact of energy supply and oxygen transfer on selective lipopeptide production by Bacillus subtilis BBG21. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 126, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Sarma, S.J. The impact of carbon and nitrogen catabolite repression in microorganisms. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 251, 126831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, H.; Helmann, J.D. Sequential induction of Fur-regulated genes in response to iron limitation in Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114, 12785–12790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, R.; Lei, S.; Xu, X.; Jin, H.; Sun, H.; Zhao, X.; Pang, B.; Shi, J. Key elements and regulation strategies of NRPSs for biosynthesis of lipopeptides by Bacillus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8077–8087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karata, A.Y.; Çetin, S.; Özcengiz, G. The effects of insertional mutations in comQ, comP, srfA, spo0H, spo0A and abrB genes on bacilysin biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gene Struct. Expr. 2003, 1626, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausmann, P.; Lilge, L.; Aschern, M.; Hennemann, K.; Henkel, M.; Hausmann, R.; Morabbi Heravi, K. Influence of B. subtilis 3NA mutations in spo0A and abrB on surfactin production in B. subtilis 168. Microb. Cell Factories 2021, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilge, L.; Vahidinasab, M.; Adiek, I.; Becker, P.; Kuppusamy Nesamani, C.; Treinen, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Morabbi Heravi, K.; Henkel, M.; Hausmann, R. Expression of degQ gene and its effect on lipopeptide production as well as formation of secretory proteases in Bacillus subtilis strains. MicrobiologyOpen 2021, 10, e1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Guo, Q.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, P. DegQ regulates the production of fengycins and biofilm formation of the biocontrol agent Bacillus subtilis NCD-2. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 178, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Sumimoto, S. Bacillus quorum sensing pheromones: ComX and phr. In Quorum Sensing: Microbial Rules of Life; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 201–217. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.; Yu, K.O.; Ramzi, A.B.; Choe, S.H.; Kim, S.W.; Han, S.O. Improvement of surfactin production in Bacillus subtilis using synthetic wastewater by overexpression of specific extracellular signaling peptides, comX and phrC. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Primer Name | Sequence5′-3′ |
|---|---|---|
| 16s rRNA | 16s rRNA-FP | ACGGTCGCAAGACTGAAACT |
| 16s rRNA-RP | TAAGGTTCTTCGCGTTGCTT | |
| Sigma H | Sigma H-FP | TTCAGGAAGGCATGATAGGC |
| Sigma H-RP | GTGTTTCTGGCGAGTAGCTGT | |
| ComA | ComA-FP | GCTCCATCCCATTGACCTC |
| ComA-RP | TTGTCTGTTGATTGTCTCAGTCC | |
| degU | degU-FP | GCAGAAACTCCGCTTGTTG |
| degU-RP | GCTGAAAGAGATGGATGCTGAT | |
| AbrB | AbrB-FP | TGGCAAGTCATGTTTGGTTT |
| AbrB-RP | CGAACTGCGTCGTACTCTTG | |
| PhrC | PhrC-FP | CAGCCGCGATTTTTACAGC |
| PhrC-RP | CGTCATTCCTCTTTCTGTCACAT | |
| Spo0A | Spo0A-FP | CAACGAGGAAATGGAATCAA |
| Spo0A-RP | GCGAAGCAATCTCAATGGTAT | |
| degQ | degQ-FP | ATGGTGAACGAGTCCTAGGT |
| degQ-RP | TAGTCCTGTTCGCCAAATGC |
| Map to Genome | ML Reads Number | MLF Reads Number | ML Percentage | MLF Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Reads | 13303694 | 13586004 | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Total BasePairs | 1197332460 | 1222740360 | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Total Mapped Reads | 11681094 | 11907481 | 87.80% | 87.65% |
| perfect match | 3893131 | 4298706 | 29.26% | 31.64% |
| ≤5 bp mismatch | 7787963 | 7608775 | 58.54% | 56.00% |
| unique match | 10813177 | 10378024 | 81.28% | 76.39% |
| multi-position match | 867917 | 1529457 | 6.52% | 11.26% |
| Total Unmapped Reads | 1622600 | 1678523 | 12.20% | 12.35% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, H.; Xu, H.; Yang, P.; Bilal, M.; Zhu, S.; Zhong, M.; Zhao, L.; Gu, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Reveals Fructose Addition Effects on Fengycin Synthesis. Genes 2022, 13, 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13060984
Lu H, Xu H, Yang P, Bilal M, Zhu S, Zhong M, Zhao L, Gu C, Liu S, Zhao Y, et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Reveals Fructose Addition Effects on Fengycin Synthesis. Genes. 2022; 13(6):984. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13060984
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Hedong, Hai Xu, Panping Yang, Muhammad Bilal, Shaohui Zhu, Mengyuan Zhong, Li Zhao, Chengyuan Gu, Shuai Liu, Yuping Zhao, and et al. 2022. "Transcriptome Analysis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Reveals Fructose Addition Effects on Fengycin Synthesis" Genes 13, no. 6: 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13060984
APA StyleLu, H., Xu, H., Yang, P., Bilal, M., Zhu, S., Zhong, M., Zhao, L., Gu, C., Liu, S., Zhao, Y., & Geng, C. (2022). Transcriptome Analysis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Reveals Fructose Addition Effects on Fengycin Synthesis. Genes, 13(6), 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13060984






