Transcription Regulation of Cell Cycle Regulatory Genes Mediated by NtrX to Affect Sinorhizobium meliloti Cell Division
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Medium
2.2. Recombinant Plasmid Construction
2.3. Bacterial Cell Synchronization
2.4. RNA Extraction, Purification and qRT-PCR
2.5. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. EMSA (Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay)
2.8. NtrX Phosphorylation Assay and Western Blotting
2.9. Microscopy
2.10. DNA Sequencing and Analysis
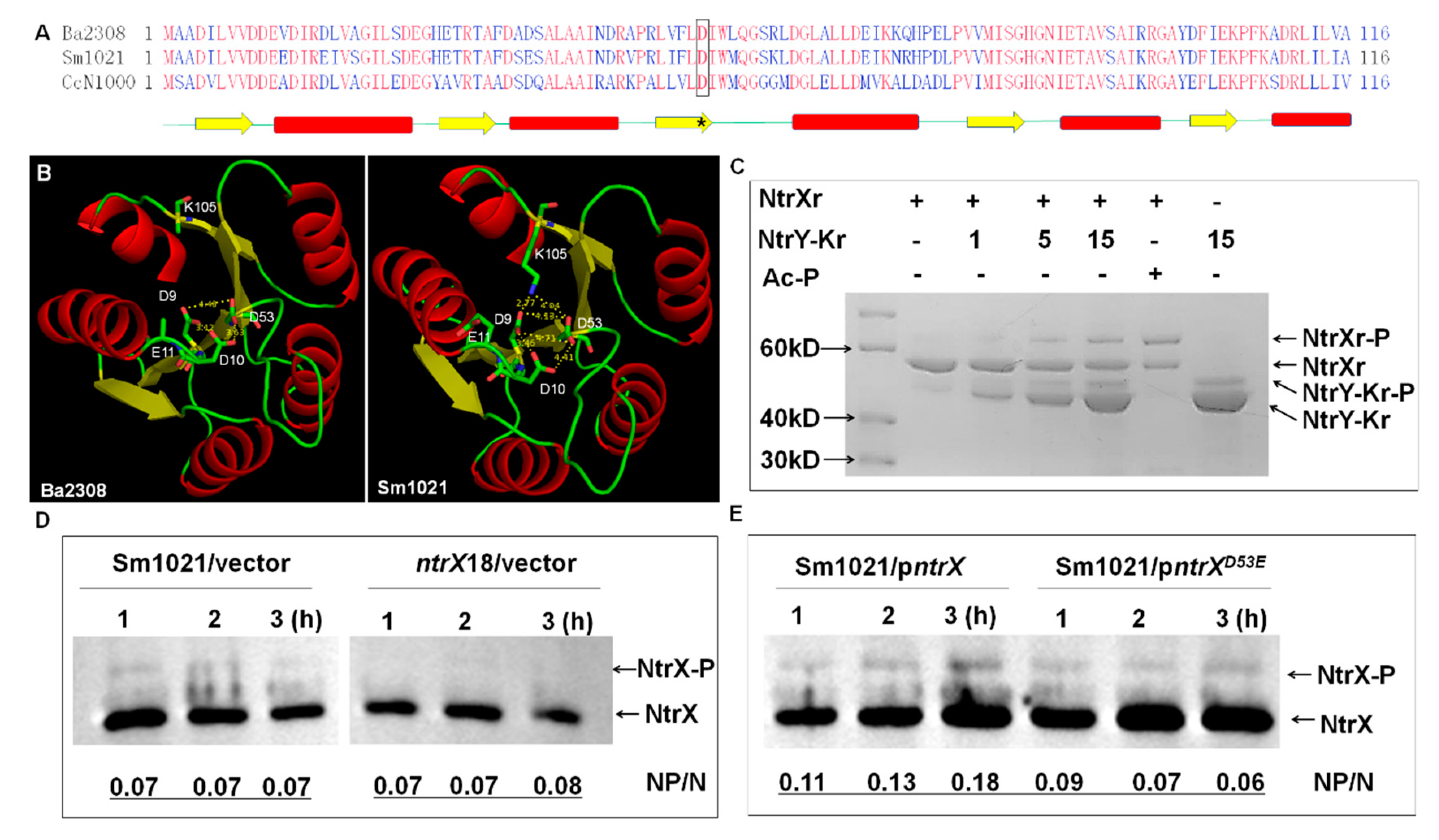
2.11. Analysis of NtrX 3D Structure
3. Results
3.1. Defects of Cell Division Resulting from ntrX Mutation in S. meliloti
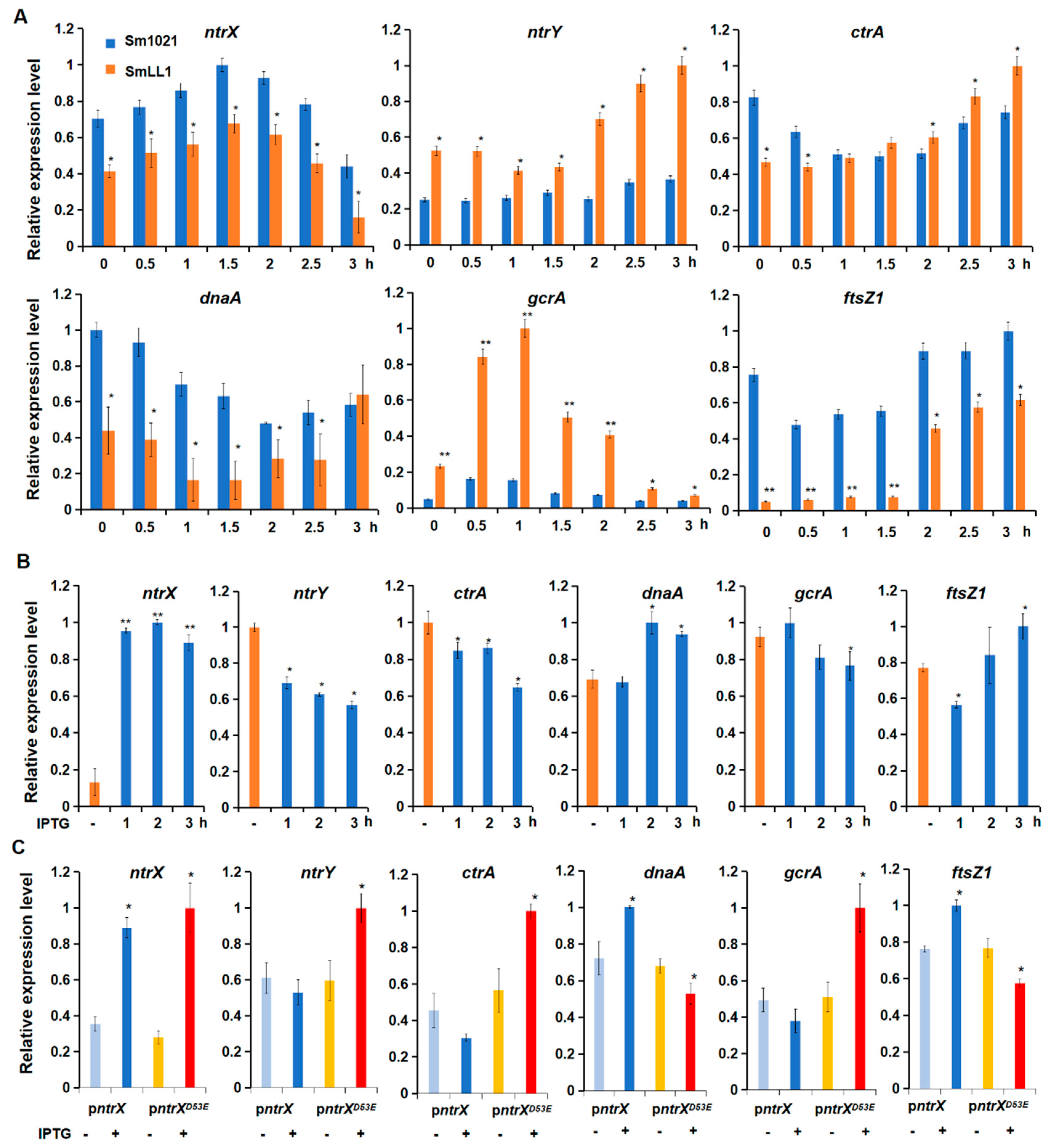
3.2. Transcription of Cell Cycle Regulated Genes under the Regulation of NtrX in S. meliloti
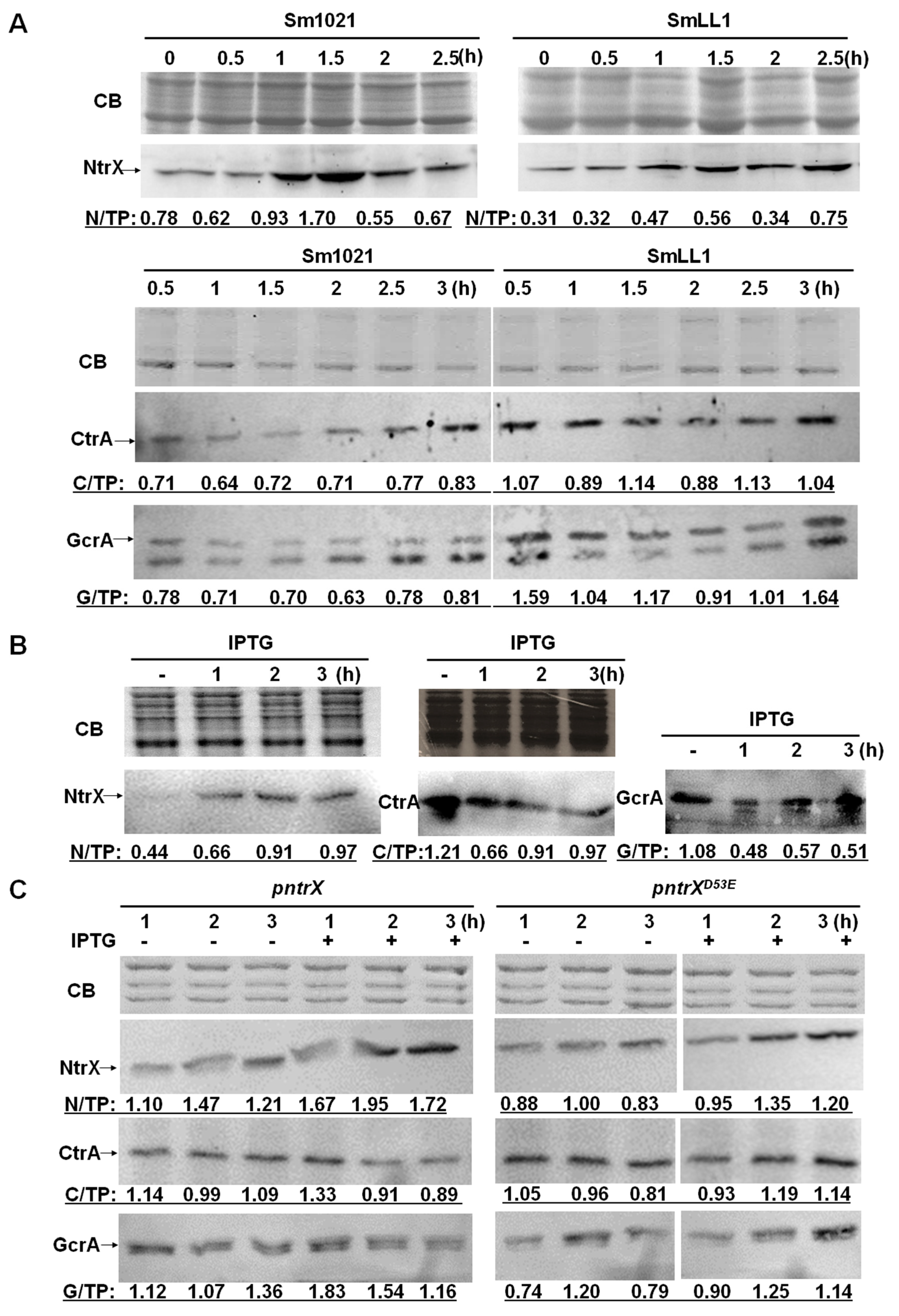
3.3. Levels of CtrA and GcrA Were Affected by NtrX in S. meliloti
3.4. The 53rd Aspartate Residue as a Phosphorylation Site of S. meliloti NtrX
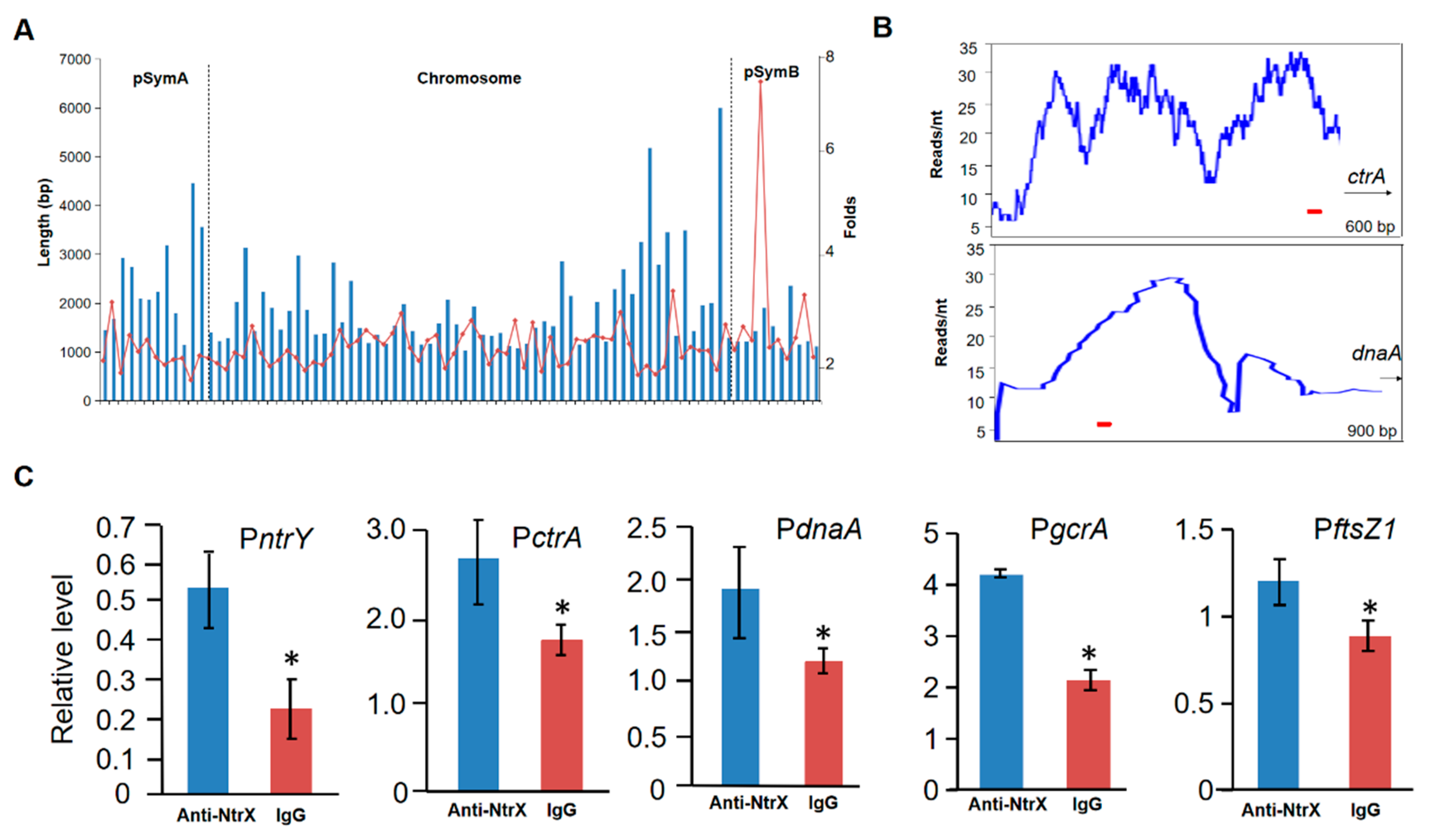
3.5. Direct Binding of the NtrX Protein to the Promoter DNA of Some Cell Cycle Regulatory Genes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laub, M.T.; Shapiro, L.; McAdams, H.H. Systems biology of Caulobacter. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2007, 41, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Laub, M.T.; McAdams, H.H.; Feldblyum, T.; Fraser, C.M.; Shapiro, L. Global analysis of the genetic network controlling a bacterial cell cycle. Science 2020, 290, 2144–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skerker, J.M.; Laub, M.T. Cell-cycle progression and the generation of asymmetry in Caulobacter crescentus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panis, G.; Murray, S.R.; Viollier, P.H. Versatility of global transcriptional regulators in α-Proteobacteria: From essential cell cycle control to ancillary functions. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, C.; Ausmees, N.; Cordwell, S.J.; Shapiro, L.; Laub, M.T. Functions of the CckA histidine kinase in Caulobacter cell cycle control. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, E.G.; Reisinger, S.J.; Skerker, J.M.; Arif, M.; Perchuk, B.S.; Ryan, K.R.; Laub, M.T. Regulation of the bacterial cell cycle by an integrated genetic circuit. Nature 2006, 444, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.M.; Kobayashi, H.; Davies, B.W.; Taga, M.E.; Walker, G.C. How rhizobial symbionts invade plants: The Sinorhizobium-Medicago model. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, W.; Zehirov, G.; Szatmari, A.; Debreczeny, M.; Ishihara, H.; Kevei, Z.; Farkas, A.; Mikulass, K.; Nagy, A.; Tiricz, H.; et al. Plant peptides govern terminal differentiation of bacteria in symbiosis. Science 2010, 327, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, A.; Maróti, G.; Durgő, H.; Györgypál, Z.; Lima, R.M.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Kereszt, A.; Mergaert, P.; Kondorosi, É. Medicago truncatula symbiotic peptide NCR247 contributes to bacteroid differentiation through multiple mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5183–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penterman, J.; Abo, R.P.; De Nisco, N.J.; Arnold, M.F.; Longhi, R.; Zanda, M.; Walker, G.C. Host plant peptides elicit a transcriptional response to control the Sinorhizobium meliloti cell cycle during symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3561–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, J.; Downie, J.A.; Farkas, A.; Bihari, P.; Herczeg, R.; Bálint, B.; Mergaert, P.; Kereszt, A.; Kondorosi, É. Morphotype of bacteroids in different legumes correlates with the number and type of symbiotic NCR peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5041–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.J.; Hung, D.Y.; Reisenauer, A.; Shapiro, L.; Long, S.R. A homolog of the CtrA cell cycle regulator is present and essential in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 3204–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, F.; De Nisco, N.J.; Ferri, L.; Penterman, J.; Fioravanti, A.; Brilli, M.; Mengoni, A.; Bazzicalupo, M.; Viollier, P.H.; Walker, G.C.; et al. Cell Cycle Control by the Master Regulator CtrA in Sinorhizobium meliloti. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; De Nisco, N.J.; Chien, P.; Simmons, L.A.; Walker, G.C. Sinorhizobium meliloti CpdR1 is critical for co-ordinating cell cycle progression and the symbiotic chronic infection. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 73, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, F.; Frage, B.; Ferri, L.; De Nisco, N.J.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Taddei, L.; Fioravanti, A.; Dewitte, F.; Galardini, M.; Brilli, M.; et al. The DivJ, CbrA and PleC system controls DivK phosphorylation and symbiosis in Sinorhizobium meliloti. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 90, 54–71. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.; Biondi, E.G. Coordination of symbiosis and cell cycle functions in Sinorhizobium meliloti. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallies, K.B.; Sadowski, C.; Meng, J.; Chien, P.; Gibson, K.E. Sinorhizobium meliloti CtrA stability is regulated in a CbrA-dependent manner that is influenced by CpdR1. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 2139–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, K.; Klosse, U.; de Bruijn, F.J. Characterization of a novel Azorhizobium caulinodans ORS571 two-component regulatory system, NtrY/NtrX, involved in nitrogen fixation and metabolism. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1991, 231, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, J.; Campos, R.; BenAbdelkhalek, H.; Olivares, J.; Lluch, C.; Sanjuan, J. Rhizobium tropici genes involved in free-living salt tolerance are required for the establishment of efficient nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with Phaseolus vulgaris. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.L.; Assumpção, M.C.; Machado, H.B.; Benelli, E.M.; Souza, E.M.; Pedrosa, F.O. Identification and characterization of the two-component NtrY/NtrX regulatory system in Azospirillum brasilense. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2002, 35, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bonato, P.; Alves, L.R.; Osaki, J.H.; Rigo, L.U.; Pedrosa, F.O.; Souza, E.M.; Zhang, N.; Schumacher, J.; Buck, M.; Wassem, R.; et al. The NtrY-NtrX two-component system is involved in controlling nitrate assimilation in Herbaspirillum seropedicae strain SmR1. Febs. J. 2016, 283, 3919–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, J.; Zeller, T.; Balzer, A.; Haberzettl, K.; Klug, G. Bacterial regulatory networks include direct contact of response regulator proteins: Interaction of RegA and NtrX in Rhodobacter capsulatus. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 13, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmer, K.C.; Alberge, F.; Myers, K.S.; Dohnalkova, A.C.; Schaub, R.E.; Lenz, J.D.; Imam, S.; Dillard, J.P.; Noguera, D.R.; Donohue, T.J. The NtrYX two-component system regulates the bacterial cell envelope. Mbio 2020, 11, e00957-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrica, M.C.; Fernandez, I.; Martí, M.A.; Paris, G.; Goldbaum, F.A. The NtrY/X two-component system of Brucella spp. acts as a redox sensor and regulates the expression of nitrogen respiration enzymes. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 85, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atack, J.M.; Srikhanta, Y.N.; Djoko, K.Y.; Welch, J.P.; Hasri, N.H.; Steichen, C.T.; Vanden Hoven, R.N.; Grimmond, S.M.; Othman, D.S.; Kappler, U.; et al. Characterization of an ntrX mutant of Neisseria gonorrhoeae reveals a response regulator that controls expression of respiratory enzymes in oxidase-positive proteobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2632–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Lin, M.; Rikihisa, Y. Ehrlichia chaffeensis proliferation begins with NtrY/NtrX and PutA/GlnA upregulation and CtrA degradation induced by proline and glutamine uptake. mBio 2014, 5, e02141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, I.; Sycz, G.; Goldbaum, F.A.; Carrica, M.D. Acidic pH triggers the phosphorylation of the response regulator NtrX in alphaproteobacteria. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; Otero, L.H.; Klinke, S.; Carrica, M.D.C.; Goldbaum, F.A. Snapshots of conformational changes shed light into the NtrX receiver domain signal transduction mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 3258–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; Cornaciu, I.; Carrica, M.D.; Uchikawa, E.; Hoffmann, G.; Sieira, R.; Márquez, J.A.; Goldbaum, F.A. Three-dimensional structure of full-length NtrX, an unusual member of the NtrC family of response regulators. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 1192–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xue, H.; Wang, Y.; Yin, R.; Xie, F.; Luo, L. The Sinorhizobium meliloti ntrX gene is involved in succinoglycan production, motility, and symbiotic nodulation on alfalfa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7150–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatrava-Morales, N.; Nogales, J.; Ameztoy, K.; van Steenbergen, B.; Soto, M.J. The NtrY/NtrX system of Sinorhizobium meliloti GR4 regulates motility, EPS I production, and nitrogen metabolism but is dispensable for symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2017, 30, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nisco, N.J.; Abo, R.P.; Wu, C.M.; Penterman, J.; Walker, G.C. Global analysis of cell cycle gene expression of the legume symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3217–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.R.; Gaines, J.; Roop, R.M., 2nd; Farrand, S.K. Broad-host-range expression vectors with tightly regulated promoters and their use to examine the influence of TraR and TraM expression on Ti plasmid quorum sensing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5053–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Eede, G.; Deblaere, R.; Goethals, K.; Van Montagu, M.; Holsters, M. Broad host range and promoter selection vectors for bacteria that interact with plants. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1992, 5, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Xing, S.; An, F.; Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Yu, L.; Luo, L. Sinorhizobium meliloti NtrX interacts with different regions of the visN promoter. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2020, 52, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Xing, S.; Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Li, X.; Staehelin, C.; Yang, M.; Luo, L. Regulation of cysteine residues in LsrB proteins from Sinorhizobium meliloti under free-living and symbiotic oxidative stress. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 19, 5130–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.P.; Walker, G.C. Succinoglycan is required for initiation and elongation of infection threads during nodulation of alfalfa by Rhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 5183–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.J. ChIP-seq: Advantages and challenges of a maturing technology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, K.; Bordoli, L.; Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, J.P.; Reinkensmeier, J.; Barnett, M.J.; Lang, C.; Krol, E.; Giegerich, R.; Long, S.R.; Becker, A. Global mapping of transcription start sites and promoter motifs in the symbiotic α-proteobacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, B.J.; Fiebig, A.; Crosson, S. The ChvG-ChvI and NtrY-NtrX two-component systems coordinately regulate growth of Caulobacter crescentus. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e0019921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, W.W.; Nixon, B.T.; Ronson, C.W.; Ausubel, F.M. Identification and characterization of the Rhizobium meliloti ntrC gene: R. meliloti has separate regulatory pathways for activation of nitrogen fixation genes in free-living and symbiotic cells. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, S.; Zheng, W.; An, F.; Huang, L.; Yang, X.; Zeng, S.; Li, N.; Ouenzar, K.; Yu, L.; Luo, L. Transcription Regulation of Cell Cycle Regulatory Genes Mediated by NtrX to Affect Sinorhizobium meliloti Cell Division. Genes 2022, 13, 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061066
Xing S, Zheng W, An F, Huang L, Yang X, Zeng S, Li N, Ouenzar K, Yu L, Luo L. Transcription Regulation of Cell Cycle Regulatory Genes Mediated by NtrX to Affect Sinorhizobium meliloti Cell Division. Genes. 2022; 13(6):1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061066
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Shenghui, Wenjia Zheng, Fang An, Leqi Huang, Xinwei Yang, Shuang Zeng, Ningning Li, Khadidja Ouenzar, Liangliang Yu, and Li Luo. 2022. "Transcription Regulation of Cell Cycle Regulatory Genes Mediated by NtrX to Affect Sinorhizobium meliloti Cell Division" Genes 13, no. 6: 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061066
APA StyleXing, S., Zheng, W., An, F., Huang, L., Yang, X., Zeng, S., Li, N., Ouenzar, K., Yu, L., & Luo, L. (2022). Transcription Regulation of Cell Cycle Regulatory Genes Mediated by NtrX to Affect Sinorhizobium meliloti Cell Division. Genes, 13(6), 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061066






