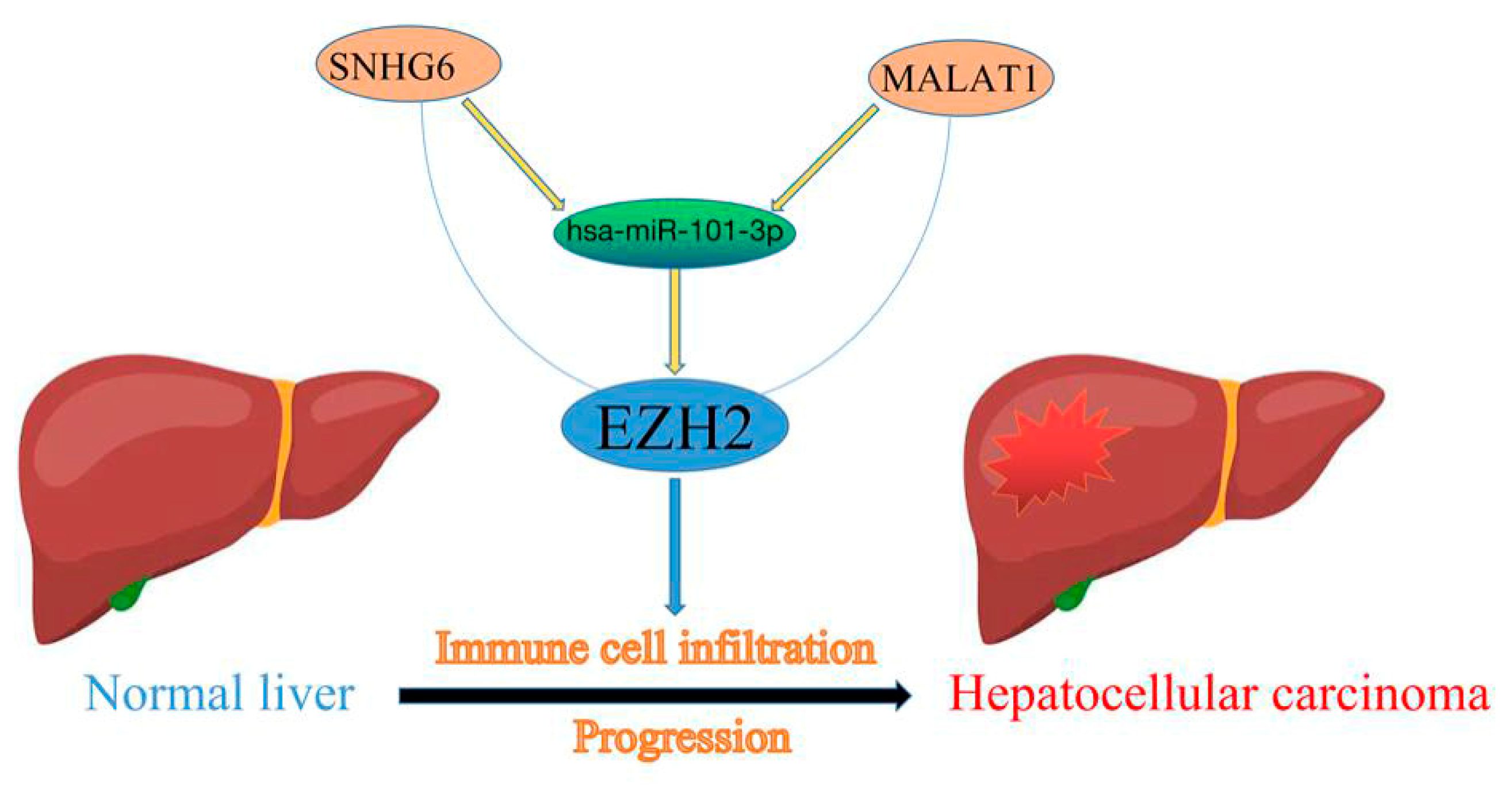
High Expression of EZH2 Mediated by ncRNAs Correlates with Poor Prognosis and Tumor Immune Infiltration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
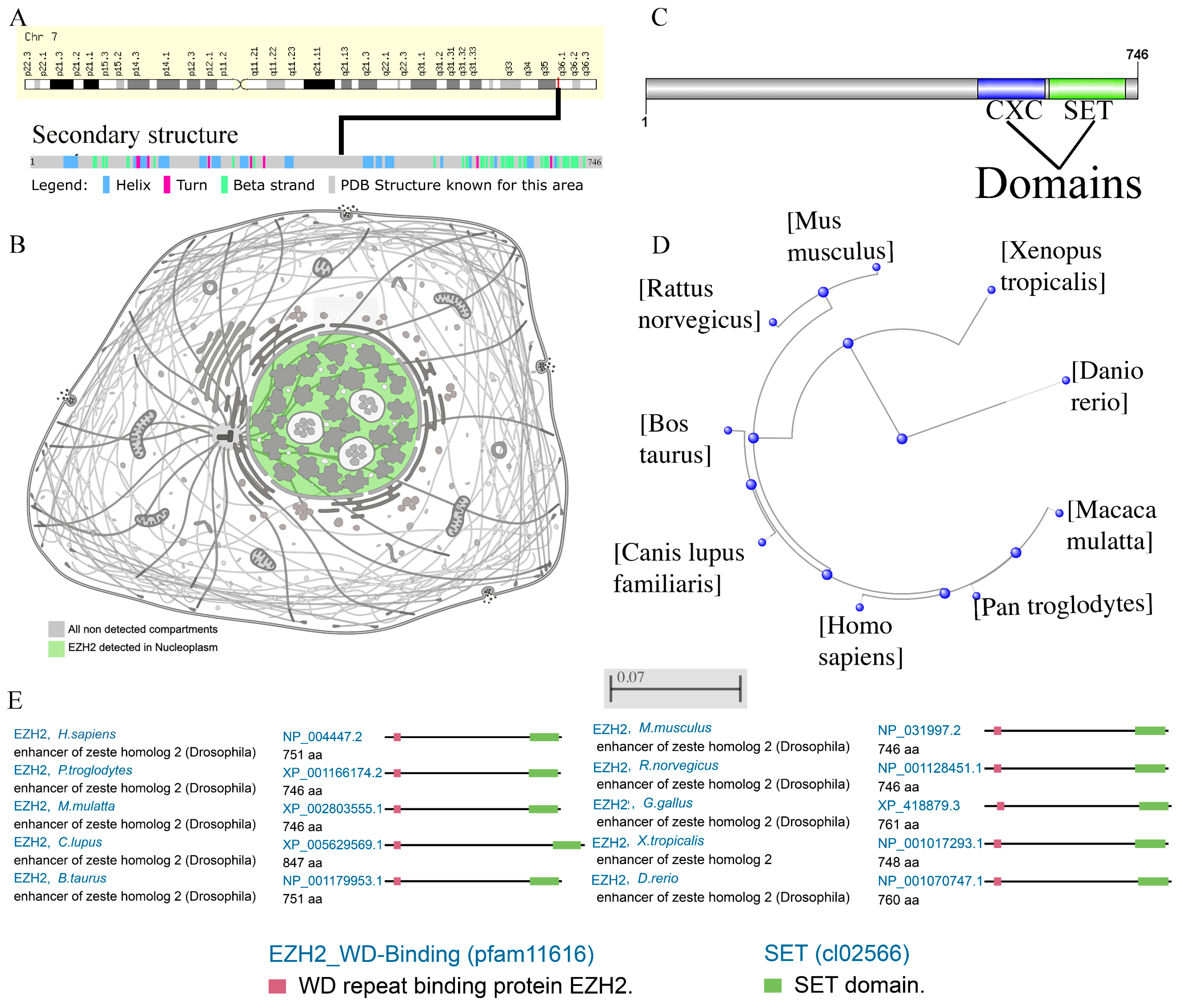
2.1. Omics Analysis of EZH2
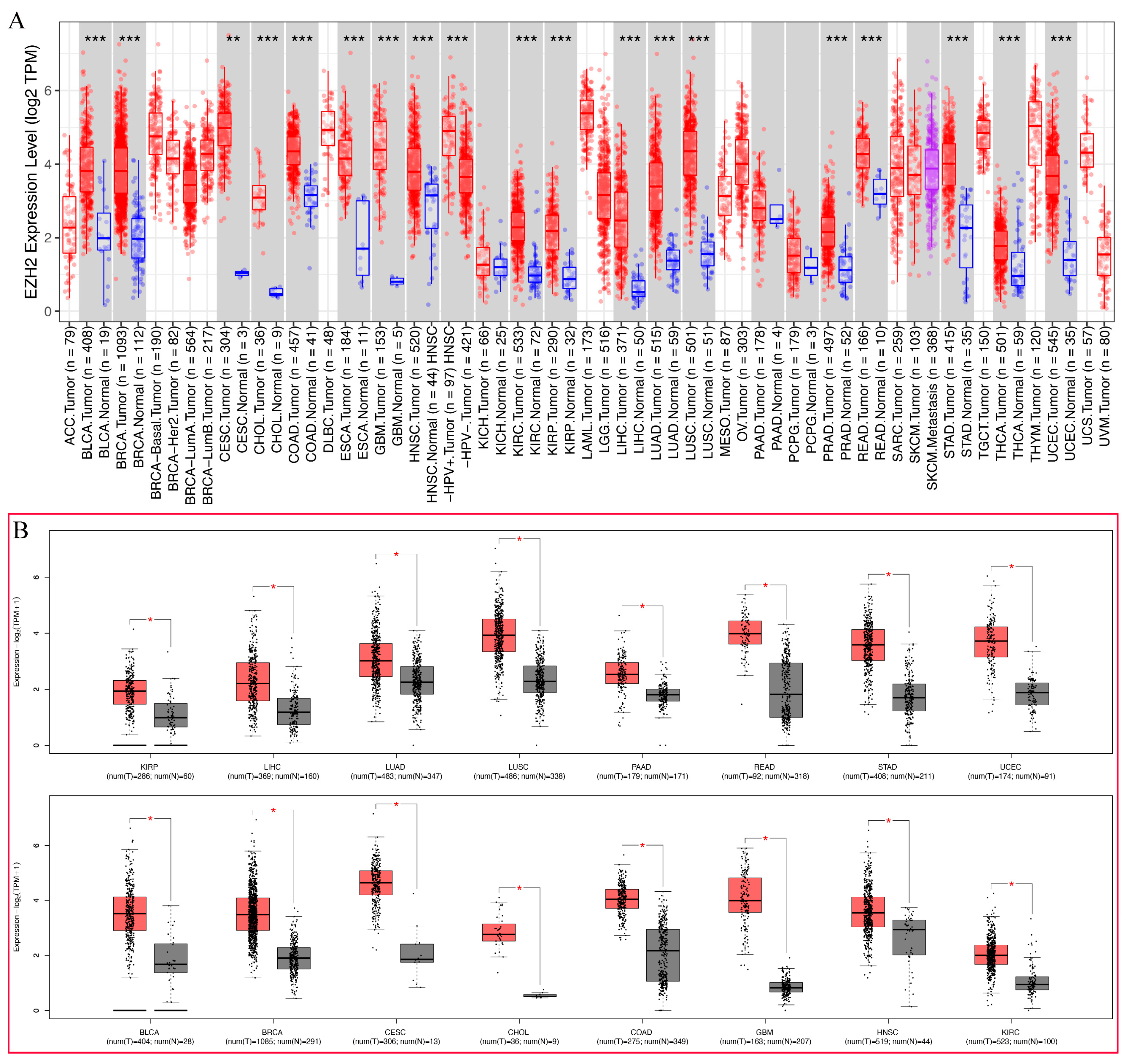
2.2. Expression Analysis of EZH2
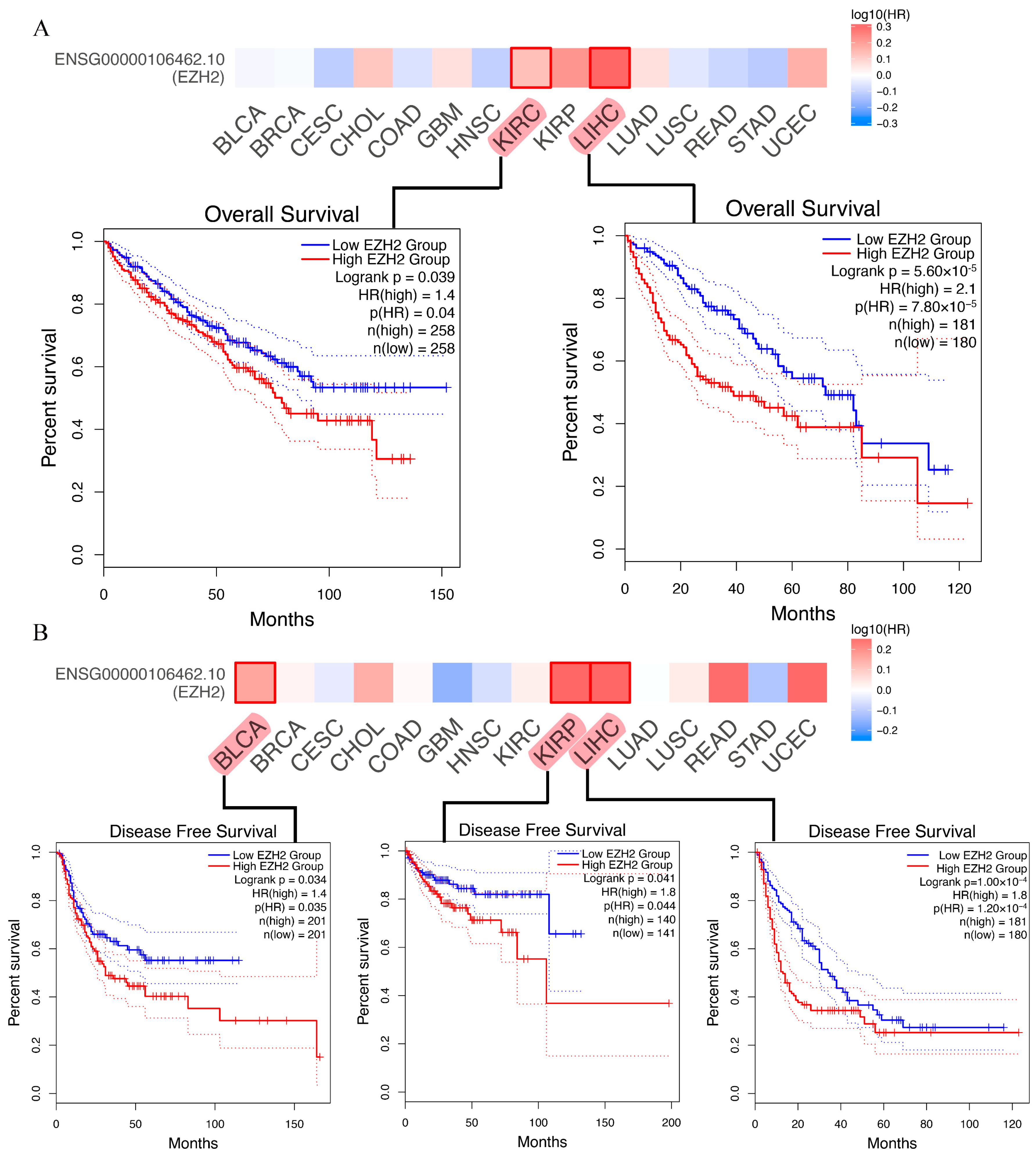
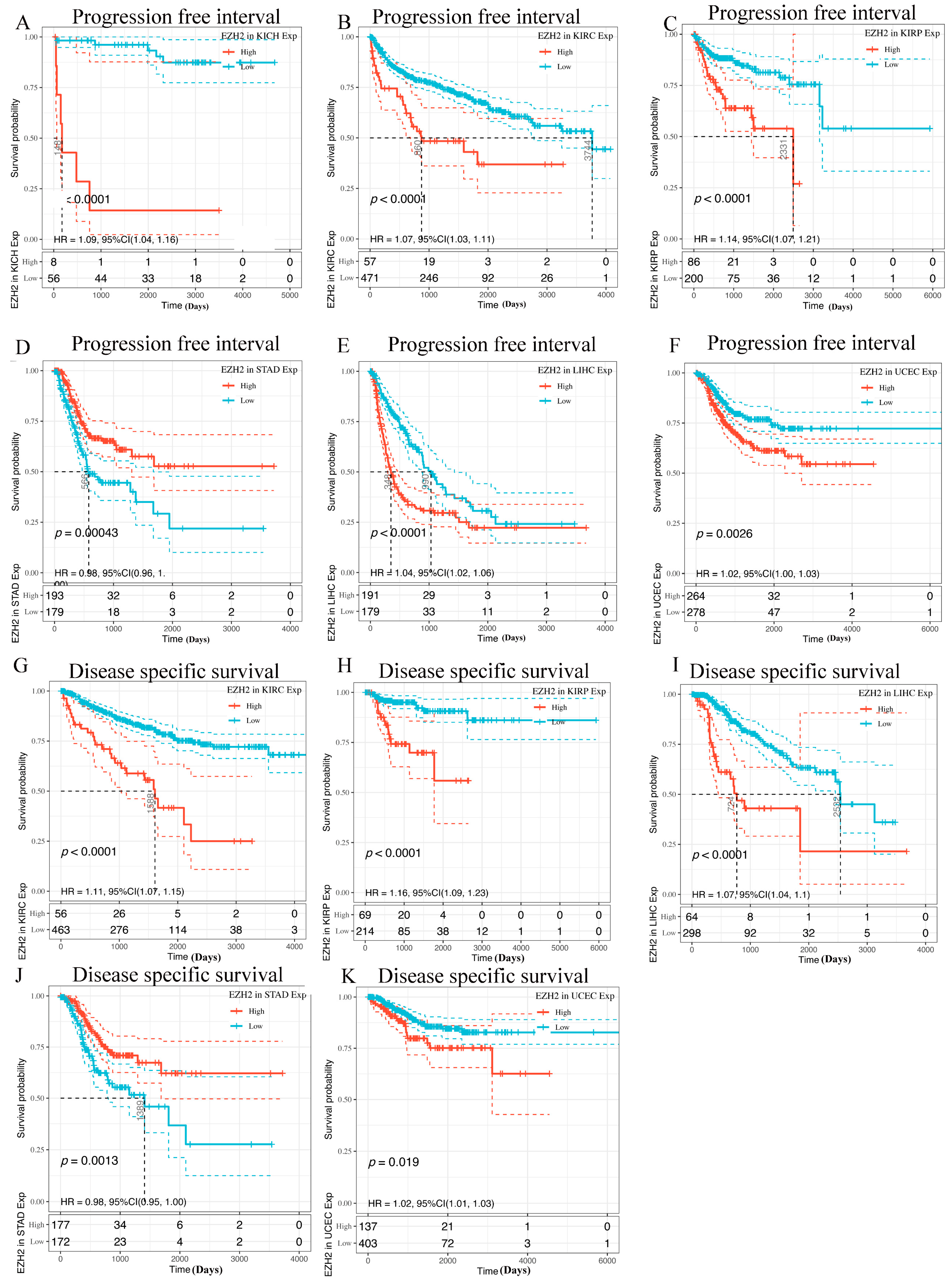
2.3. Prognostic Analysis of EZH2
2.4. Prediction of Upstream miRNAs and lncRNAs of EZH2
2.5. Immune Cell Infiltration, Chemotactic Activities, Immune Cell Biomarkers, and Immune Checkpoint Analysis of EZH2
2.6. Functional Analysis of EZH2
3. Results
3.1. Omics Analysis of EZH2
3.2. Pan-Cancer Analysis of EZH2 Expression
3.3. Prognostic Analysis of EZH2 in Human Cancers
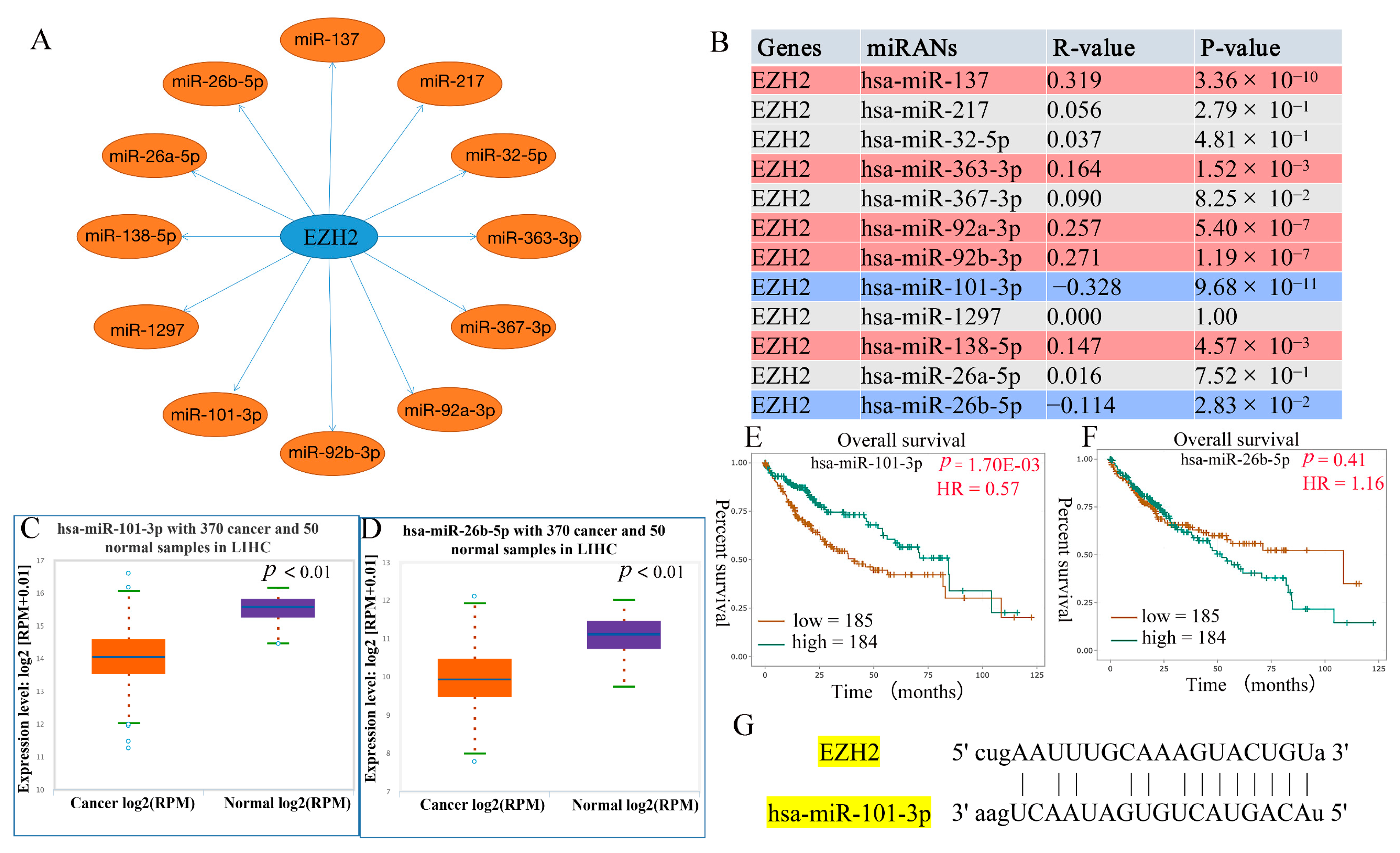
3.4. Prediction of Upstream miRNAs of EZH2
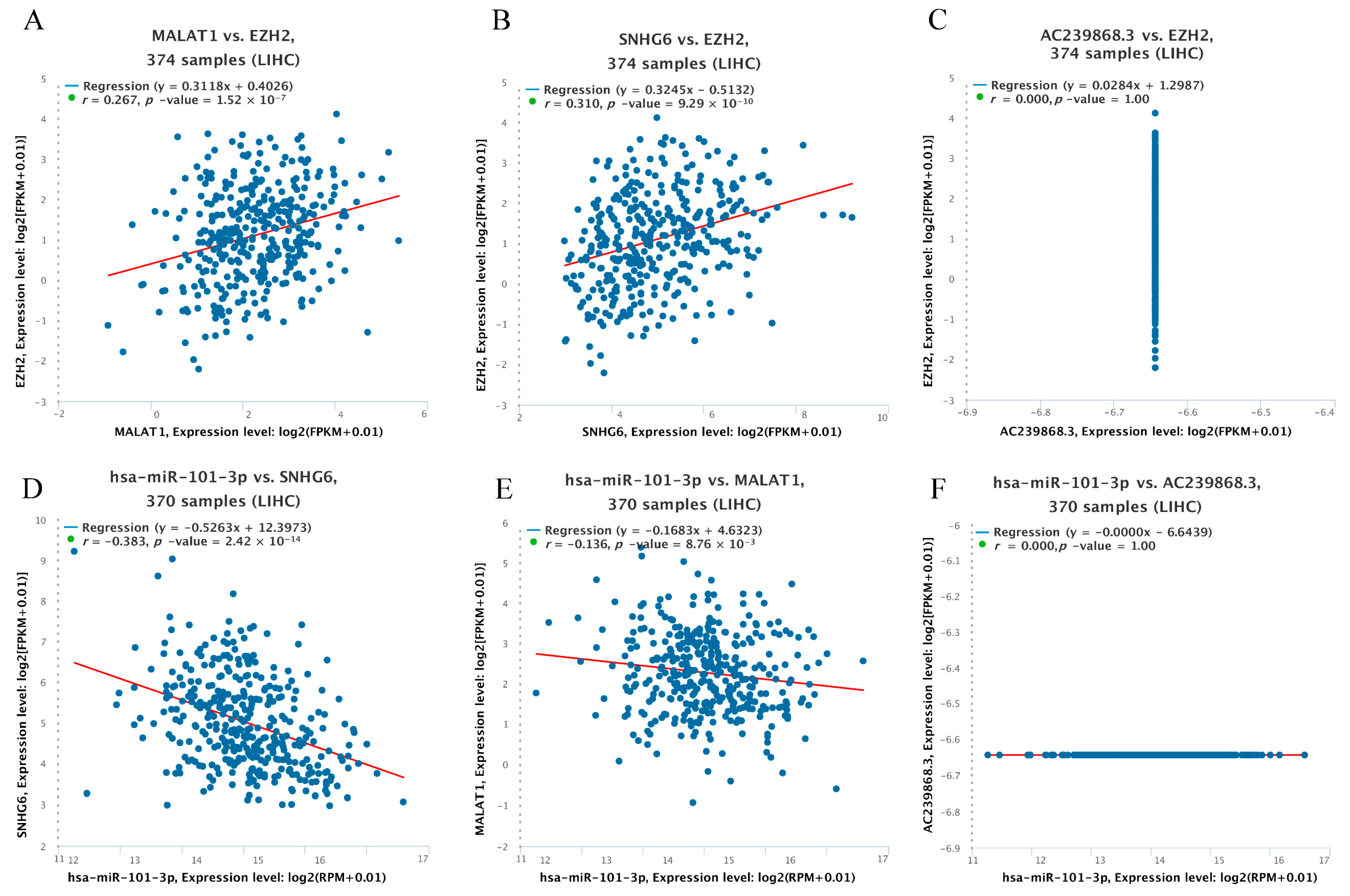
3.5. Prediction of Upstream lncRNAs of hsa-miR-101-3p
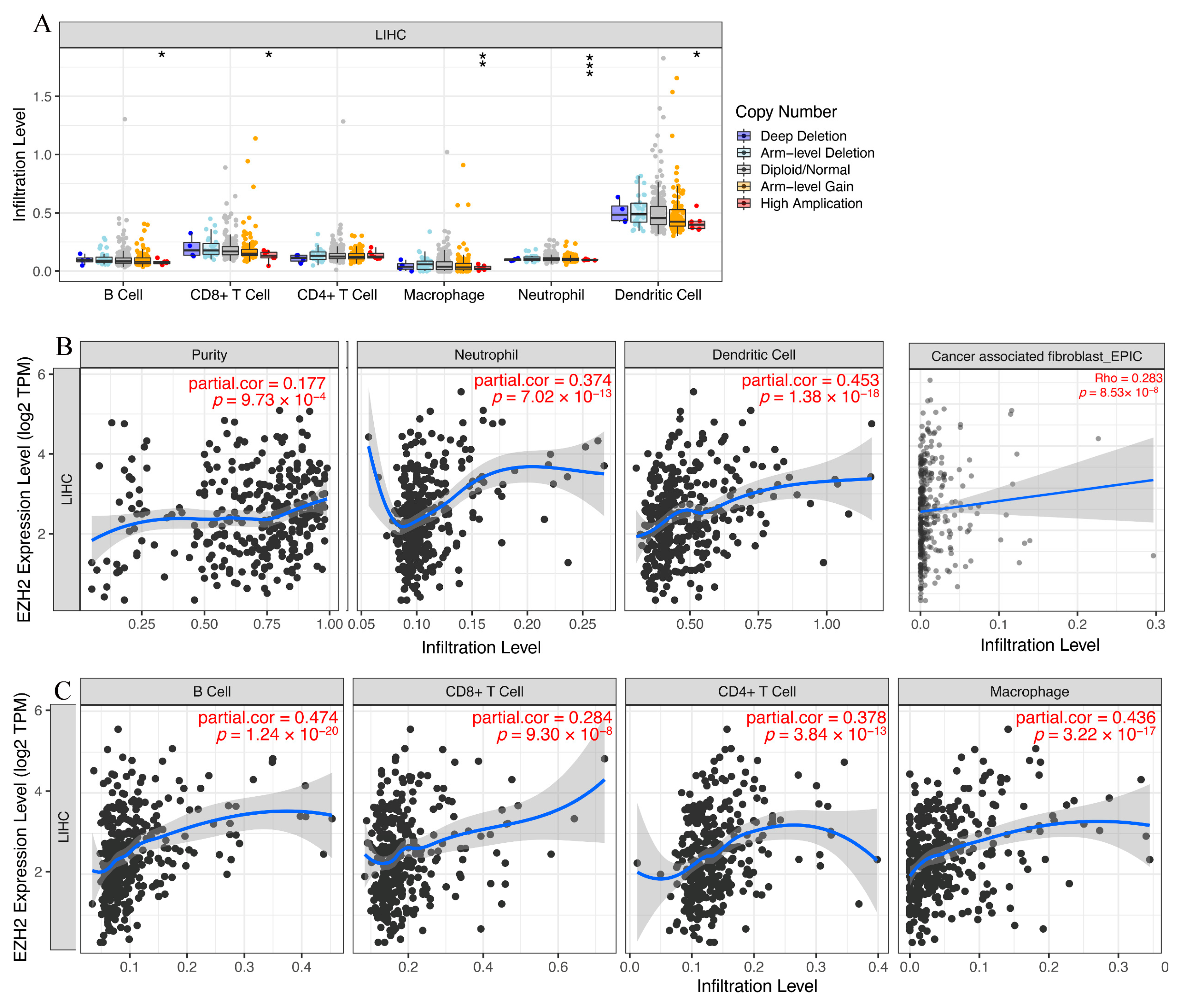
3.6. Immune Cell Infiltration and Chemotactic Activity Analysis of EZH2 in LIHC
3.7. Expression Correlation of EZH2 and Biomarkers of Immune Cells in HCC
3.8. Correlation between EZH2 Expression and Immune Checkpoints in HCC
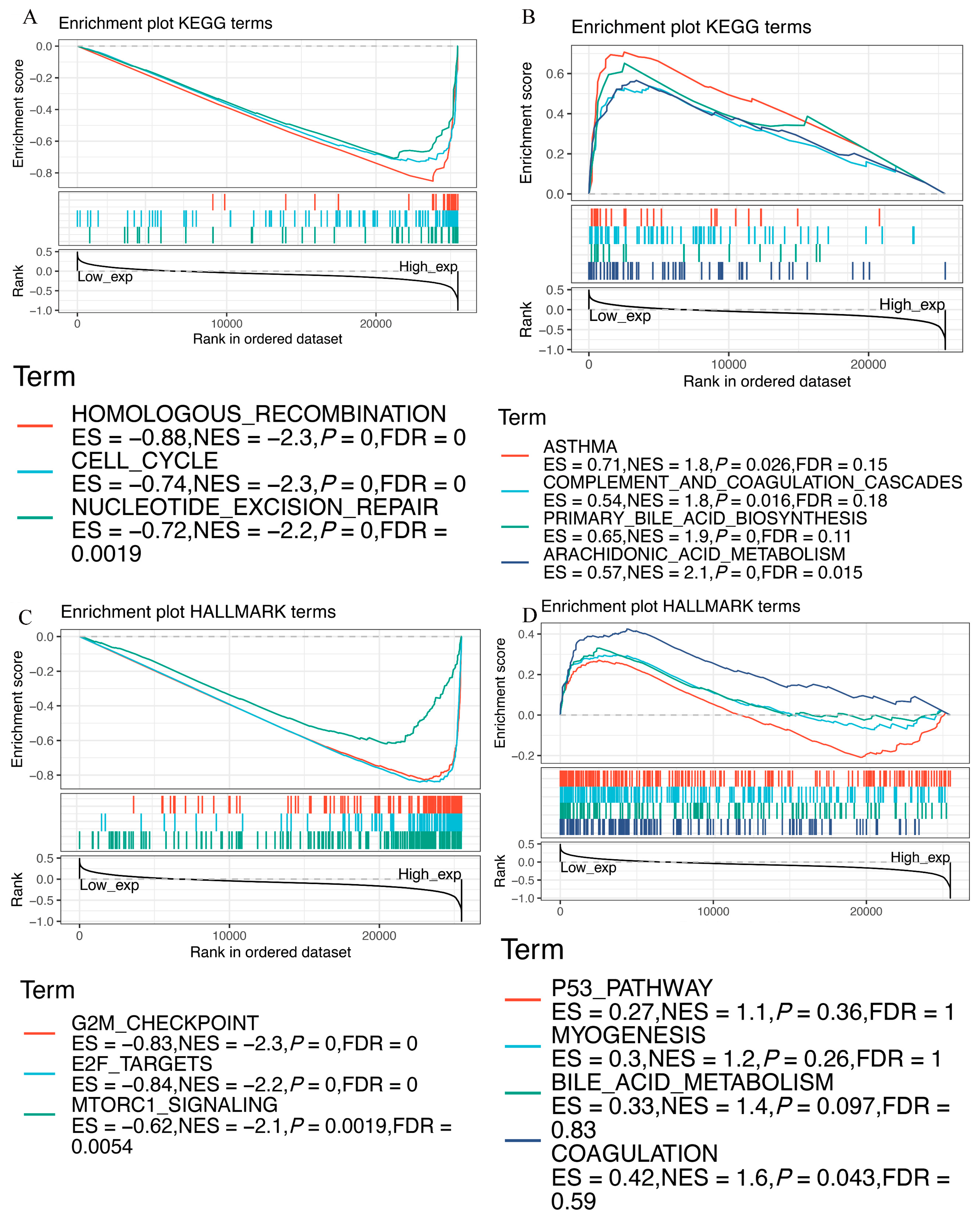
3.9. Functional Analysis of EZH2 by GSEA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| miRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| ncRNAs | Non-coding RNA |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| GTEx | Genotype-Tissue Expression |
| BLCA | Bladder urothelial carcinoma |
| BRCA | Breast invasive carcinoma |
| CESC | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma and Endocervical adenocarcinoma |
| CHOL | Cholangiocarcinoma |
| COAD | Colon adenocarcinoma |
| ESCA | Esophageal carcinoma |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme |
| HNSC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| KICH | Kidney chromophobe |
| KIRC | Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma |
| KIRP | Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma |
| LIHC | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma |
| LUAD | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| LUSC | Lung squamous cell carcinoma |
| PAAD | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma |
| PCPG | Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma |
| PRAD | Prostate adenocarcinoma |
| READ | Rectum adenocarcinoma |
| STAD | Stomach adenocarcinoma |
| THCA | Thyroid carcinoma |
| UCEC | Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 |
| PcG | Polycomb group |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| HPA | Human Protein Atlas |
| FC | Fold change |
| OS | Overall survival |
| DFS | Disease-free survival |
| K-M | Kaplan-Meier |
| DSS | Disease-specific survival |
| PFI | Progression-free interval |
| GSEA | Gene set enrichment analysis |
| CeRNA | Competing endogenous RNA |
| CAFs | Cancer-associated fibroblasts |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| ICB | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
References
- Kocarnik, J.M.; Compton, K.; Dean, F.E.; Fu, W.; Gaw, B.L.; Harvey, J.D.; Henrikson, H.J.; Lu, D.; Pennini, A.; Xu, R. Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived with Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years for 29 Cancer Groups From 2010 to 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 420–444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhu, H.; Dong, L.; Shi, W.; Chen, R.; Song, Z.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Zhou, Y. Integrated Proteogenomic Characterization of HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell 2019, 179, 561–577.e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.-C.; Hsu, H.-C.; Lin, T.-M.; Chang, Y.-S.; Hu, L.-F.; Chen, L.-F.; Lin, S.-H.; Kuo, P.-I.; Chen, W.-S.; Lin, Y.-C.; et al. H1-Antihistamines Reduce the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus, Hepatitis C Virus, or Dual Hepatitis B Virus-Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1206–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Augusto, V.; Singal, A.G.; Eli, P.; Sasan, R.; Riccardo, L.; Kazuhiko, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangro, B.; Sarobe, P.; Hervás-Stubbs, S.; Melero, I. Advances in immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 525–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, J.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Wu, J. Immunotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, where are we? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1874, 188441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvageau, M.; Sauvageau, G. Polycomb Group Proteins: Multi-Faceted Regulators of Somatic Stem Cells and Cancer. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Moral-Morales, A.; González-Orozco, J.C.; Hernández-Vega, A.M.; Hernández-Ortega, K.; Peña-Gutiérrez, K.M.; Camacho-Arroyo, I. EZH2 Mediates Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion Promoted by Estradiol in Human Glioblastoma Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 703733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Lu, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, M.; Fan, D.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Hou, P.; et al. Methylation of EZH2 by PRMT1 regulates its stability and promotes breast cancer metastasis. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 3226–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Mu, P.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, T.; Deng, R.; Feng, G.; Wen, J.; Zhu, X.; Deng, Y. Inhibition of EZH2 and activation of ERRγ synergistically suppresses gastric cancer by inhibiting FOXM1 signaling pathway. Gastric Cancer 2020, 24, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, P.; Hou, P.; Li, M.; Chu, S.; Qiao, S.; Zheng, J.; et al. PRMT1-mediated EZH2 methylation promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Liao, Y.J.; Cai, M.-Y.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liu, T.-H.; Chen, S.-P.; Bian, X.-W.; Guan, X.-Y.; Lin, M.C.; Zeng, Y.-X.; et al. The putative tumour suppressor microRNA-124 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell aggressiveness by repressing ROCK2 and EZH2. Gut 2012, 61, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Du, W.; Guo, W. EZH2: A novel target for cancer treatment. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Roberts, C.W. Targeting EZH2 in cancer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J. EZH2-mediated loss of miR-622 determines CXCR4 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, A.-N.; Jung, S.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, H.; Park, S.G. Clinical Value of EZH2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Potential for Target Therapy. Medicina 2022, 58, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fan, J.; Wang, B.; Traugh, N.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER: A Web Server for Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e108–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Kang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W556–W560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Yang, J.H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, S.; Meng, N.; He, Y.; Lu, R.; Yan, G.R. ncRNA-Encoded Peptides or Proteins and Cancer. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Singer, R.H. Single-molecule imaging of microRNA-mediated gene silencing in cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Guo, Q.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhi, H.; Li, X.; Shang, S.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Y. LnCeCell: A comprehensive database of predicted lncRNA-associated ceRNA networks at single-cell resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D125–D133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yu, F.; Xu, D.; Zheng, H.; Li, M. EZH2, a prominent orchestrator of genetic and epigenetic regulation of solid tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2022, 1877, 188700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Ding, C.; Lin, S.; Wan, D.; Ren, K. Prognostic Biomarkers and Immunotherapeutic Targets among CXC Chemokines in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szeto, G.L.; Finley, S.D. Integrative Approaches to Cancer Immunotherapy. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshida, Y.; Nijman, S.M.B.; Kobayashi, M.; Chan, J.A.; Brunet, J.-P.; Chiang, D.Y.; Villanueva, A.; Newell, P.; Ikeda, K.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Integrative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Common Molecular Subclasses of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7385–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecilla, S.; Sia, D.; Harrington, A.N.; Zhang, Z.; Cabellos, L.; Cornella, H.; Moeini, A.; Campreciós, G.; Leow, W.-Q.; Fiel, M.I.; et al. Trunk mutational events present minimal intra- and inter-tumoral heterogeneity in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuettengruber, B.; Bourbon, H.-M.; Di Croce, L.; Cavalli, G. Genome Regulation by Polycomb and Trithorax: 70 Years and Counting. Cell 2017, 171, 34–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Liu, Q.; Yin, Y.; Wang, H.; Pan, L.; Li, L.; Song, K.; et al. SETD2 Restricts Prostate Cancer Metastasis by Integrating EZH2 and AMPK Signaling Pathways. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 350–365.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Gu, X.; Bao, Z.; Su, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, L. The Mechanism Underlying the ncRNA Dysregulation Pattern in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 847728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinshaw, D.C.; Shevde, L.A. The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaymak, I.; Williams, K.S.; Cantor, J.R.; Jones, R.G. Immunometabolic Interplay in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2020, 39, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Yu, D. Tumor microenvironment as a therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 221, 107753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, L.-J.; Ju, H.-Q.; Liu, G.-P.; Tian, T.; Ma, G.-L.; Lu, Y.-X.; Liu, Z.-X.; Pan, R.-L.; Li, R.-H.; Piao, H.-L. LncRNA CamK-A Regulates Ca2+-Signaling-Mediated Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 71–83.e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Pu, J.; Bai, J.; Yin, Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, J.; Shuai, X.; Gao, J.; Tao, K.; Wang, G. EZH2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through modulating miR-22/galectin-9 axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Xu, M.; Hua, R.-X.; Tan, C.; Zhang, J.; Gong, Y.; Wu, Z.; Weng, W.; Sheng, W.; Guo, W. The polycomb group protein EZH2 induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition and pluripotent phenotype of gastric cancer cells by binding to PTEN promoter. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Steuber, B.; Kopp, W.; Kari, V.; Urbach, L.; Wang, X.; Küffer, S.; Bohnenberger, H.; Spyropoulou, D.; Zhang, Z.; et al. EZH2 Regulates Pancreatic Cancer Subtype Identity and Tumor Progression via Transcriptional Repression of GATA6. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 4620–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Hou, Y.; Yi, X.; Sun, S.; Guo, J.; He, X.; Li, T.; Cai, J.; Wang, Z. EZH2 activates CHK1 signaling to promote ovarian cancer chemoresistance by maintaining the properties of cancer stem cells. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1795–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-Y.; Sun, Q.-C.; Zou, X.-J.; Song, Y.; Li, W.-W.; Guo, Z.-Q.; Liu, S.-S.; Liu, L.; Wu, D.-H. Long noncoding RNA UPK1A-AS1 indicates poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation through interaction with EZH2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Tang, F.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J.; Lei, B.; Li, B.; Wei, Y.; Liang, X.; Tang, B.; He, S. The relationship between the expression of USP22, BMI1, and EZH2 in hepatocellular carcinoma and their impacts on prognosis. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 6987–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Tang, G.; Wei, S.; Chen, G. Knockdown of terminal differentiation induced ncRNA (TINCR) suppresses proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the miR-218-5p/DEAD-box helicase 5 (DDX5) axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 6990–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.; Ding, S.; Chen, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Zou, C.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. Functional analysis of miR-101-3p and Rap1b involved in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, T.; Qi, H.; Xiao, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q. Upregulation of SNHG6 regulates ZEB1 expression by competitively binding miR-101-3p and interacting with UPF1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, N.; He, J.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Huang, W.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, S. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 inhibits the apoptosis and autophagy of hepatocellular carcinoma cell by targeting the microRNA-146a/PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhong, Z.; Tan, H.Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, C.; Wang, N.; Ren, J.; Feng, Y. Suppression of lncRNA MALAT1 by betulinic acid inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting IAPs via miR-22-3p. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Feng, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Shu, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, Z. A Necroptosis-Related lncRNA-Based Signature to Predict Prognosis and Probe Molecular Characteristics of Stomach Adenocarcinoma. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 833928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, J.; Ren, K.; Tian, X.; Gao, H.; Tian, X.; Zhang, X.; Kan, Q. The Heterogeneity of Immune Cell Infiltration Landscape and Its Immunotherapeutic Implications in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, I.; Ramachandran, S.; Zabel, C.; Gaikwad, S.; Srivastava, S.K. The evolutionary legacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servetto, A.; Salomone, F.; Di Costanzo, F.; Iuliano, R.; Marandino, L.; Napolitano, F.; Santaniello, A.; De Placido, P.; De Placido, S.; Di Maio, M.; et al. Inadequate health-related quality of life assessment and reporting in phase III clinical trials of immune checkpoint inhibitors in solid cancers: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2022, 172, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Immune Cells | Chemokine | Cor | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monocytes/macrophages | CCL2 | 0.054 | 2.98 × 10−1 |
| CCL3 | 0.07 | 1.79 × 10−1 | |
| CCL5 | 0.12 | 2.06 × 10−2 | |
| CCL7 | 0.161 | 1.86 × 10−3 | |
| CCL8 | 0.144 | 5.54 × 10−3 | |
| CCL13 | 0.137 | 8.24 × 10−3 | |
| CCL17 | 0.034 | 5.19 × 10−1 | |
| CCL22 | 0.102 | 5.04 × 10−2 | |
| T lymphocytes | CCL2 | 0.054 | 2.98 × 10−1 |
| CCL1 | 0.166 | 1.31 × 10−3 | |
| CCL22 | 0.102 | 5.04 × 10−2 | |
| CCL17 | 0.034 | 5.19 × 10−1 | |
| Mast cells | CCR1 | 0.25 | 1.06 × 10−6 |
| CCR2 | 0.142 | 6.20 × 10−3 | |
| CCR3 | 0.247 | 1.48 × 10−6 | |
| CCR4 | 0.196 | 1.42 × 10−4 | |
| CCR5 | 0.249 | 1.20 × 10−6 | |
| CXCR2 | 0.133 | 1.03 × 10−2 | |
| CXCR4 | 0.297 | 5.58 × 10−9 | |
| Eosinophils | CCL11 | 0.069 | 1.82 × 10−1 |
| CCL24 | −0.006 | 9.07 × 10−1 | |
| CCL26 | 0.283 | 2.85 × 10−8 | |
| CCL5 | 0.12 | 2.06 × 10−2 | |
| CCL7 | 0.161 | 1.86 × 10−3 | |
| CCL13 | 0.137 | 8.24 × 10−3 | |
| CCL3 | 0.07 | 1.79 × 10−1 | |
| Neutrophils | CXCL8 | 0.38 | 6.12 × 10−4 |
| GEPIA | TIMER | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | p | R | p | ||
| B cells | CD19 | 0.110 | 1.10 × 10−1 | 0.244 | 1.92 × 10−6 |
| CD79A | 0.083 | 7.90 × 10−5 | 0.131 | 1.18 × 10−2 | |
| CD8+ T cells | CD8A | 0.200 | 1.40 × 10−5 | 0.180 | 5.05 × 10−4 |
| CD8B | 0.220 | 7.70 × 10−3 | 0.168 | 1.17 × 10−3 | |
| CD4+ T cells | CD4 | 0.140 | 8.20 × 10−1 | 0.217 | 2.44 × 10−5 |
| M1 macrophages | NOS2 | −0.012 | 0.00 × 10−0 | 0.003 | 9.48 × 10−1 |
| IRF5 | 0.440 | 5.00 × 10−1 | 0.482 | 5.97 × 10−23 | |
| PTGS2 | 0.035 | 2.80 × 10−3 | 0.088 | 9.22 × 10−2 | |
| M2 macrophages | CD163 | 0.160 | 2.40 × 10−4 | 0.101 | 5.21 × 10−2 |
| VSIG4 | 0.190 | 2.00 × 10−3 | 0.100 | 5.41 × 10−2 | |
| MS4A4A | 0.160 | 8.30 × 10−1 | 0.102 | 5.07 × 10−2 | |
| Neutrophils | CEACAM8 | 0.011 | 2.40 × 10−11 | 0.094 | 6.95 × 10−2 |
| ITGAM | 0.340 | 2.20 × 10−1 | 0.289 | 1.44 × 10−8 | |
| CCR7 | 0.064 | 2.40 × 10−5 | 0.083 | 1.10 × 10−1 | |
| Dendritic cells | HLA-DPB1 | 0.220 | 9.00 × 10−2 | 0.154 | 2.91 × 10−3 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 0.088 | 1.70 × 10−5 | 0.146 | 4.87 × 10−3 | |
| HLA-DRA | 0.220 | 1.20 × 10−4 | 0.167 | 1.22 × 10−3 | |
| HLA-DPA1 | 0.200 | 7.40 × 10−4 | 0.158 | 2.28 × 10−3 | |
| CD1C | 0.170 | 6.50 × 10−8 | 0.114 | 2.85 × 10−2 | |
| NRP1 | 0.280 | 1.10 × 10−6 | 0.263 | 2.67 × 10−7 | |
| ITGAX | 0.250 | 1.10 × 10−1 | 0.348 | 5.15 × 10−12 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Lin, X.; Wan, Z.; Xiao, M.; Ding, C.; Wan, P.; Li, Q.; Zheng, S. High Expression of EZH2 Mediated by ncRNAs Correlates with Poor Prognosis and Tumor Immune Infiltration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Genes 2022, 13, 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050876
Chen Z, Lin X, Wan Z, Xiao M, Ding C, Wan P, Li Q, Zheng S. High Expression of EZH2 Mediated by ncRNAs Correlates with Poor Prognosis and Tumor Immune Infiltration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Genes. 2022; 13(5):876. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050876
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhitao, Xin Lin, Zhenmiao Wan, Min Xiao, Chenchen Ding, Pengxia Wan, Qiyong Li, and Shusen Zheng. 2022. "High Expression of EZH2 Mediated by ncRNAs Correlates with Poor Prognosis and Tumor Immune Infiltration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Genes 13, no. 5: 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050876
APA StyleChen, Z., Lin, X., Wan, Z., Xiao, M., Ding, C., Wan, P., Li, Q., & Zheng, S. (2022). High Expression of EZH2 Mediated by ncRNAs Correlates with Poor Prognosis and Tumor Immune Infiltration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Genes, 13(5), 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050876






