Preliminary Results of NGS Gene Panel Test Using NSCLC Sputum Cytology and Therapeutic Effect Using Corresponding Molecular-Targeted Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
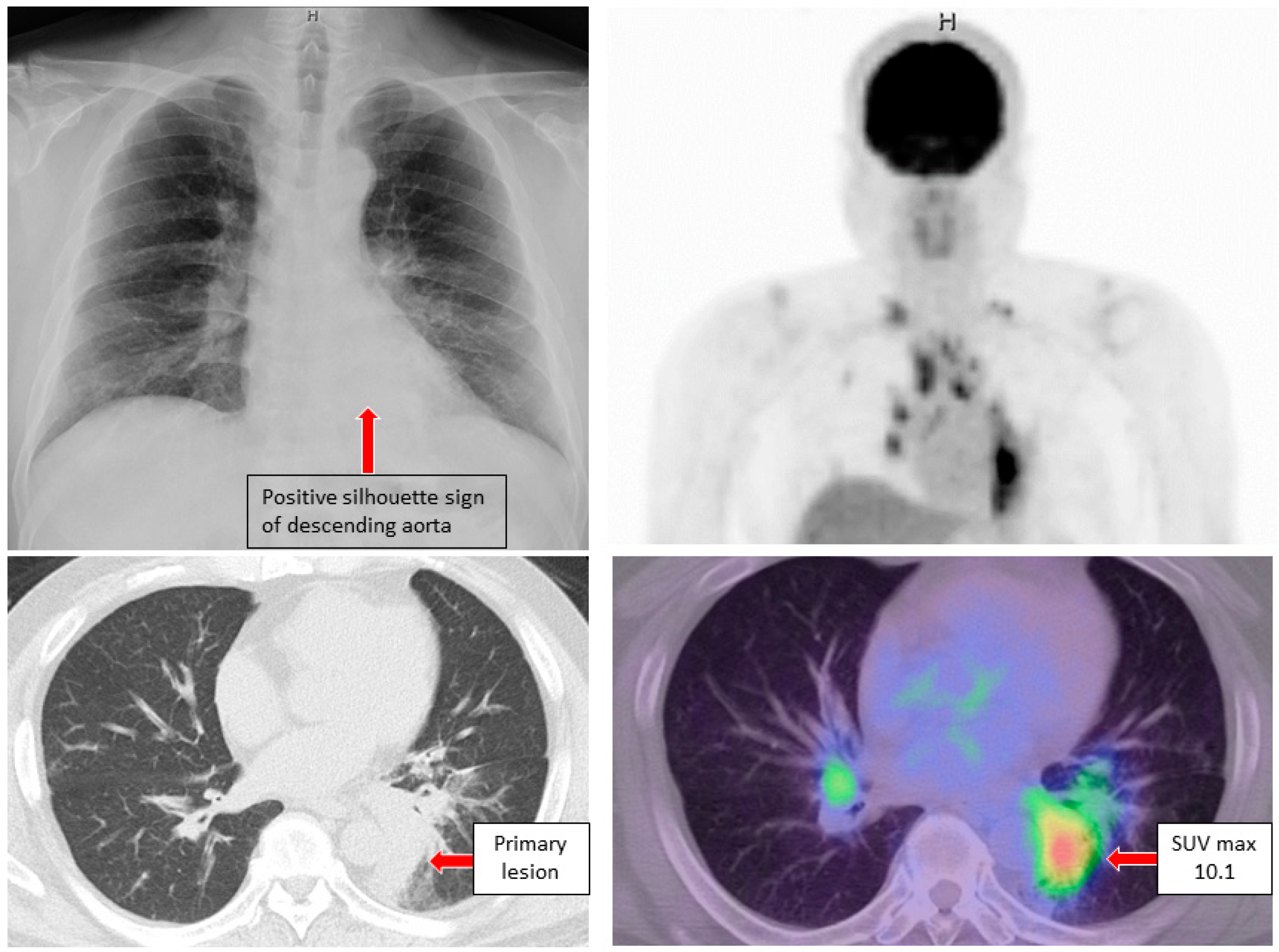
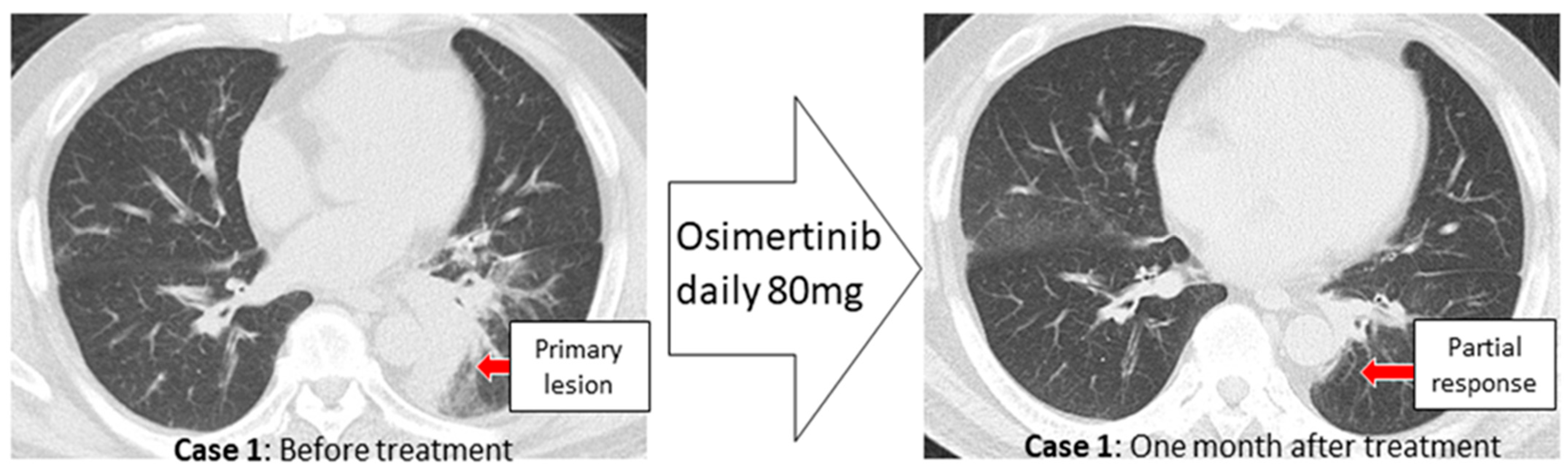
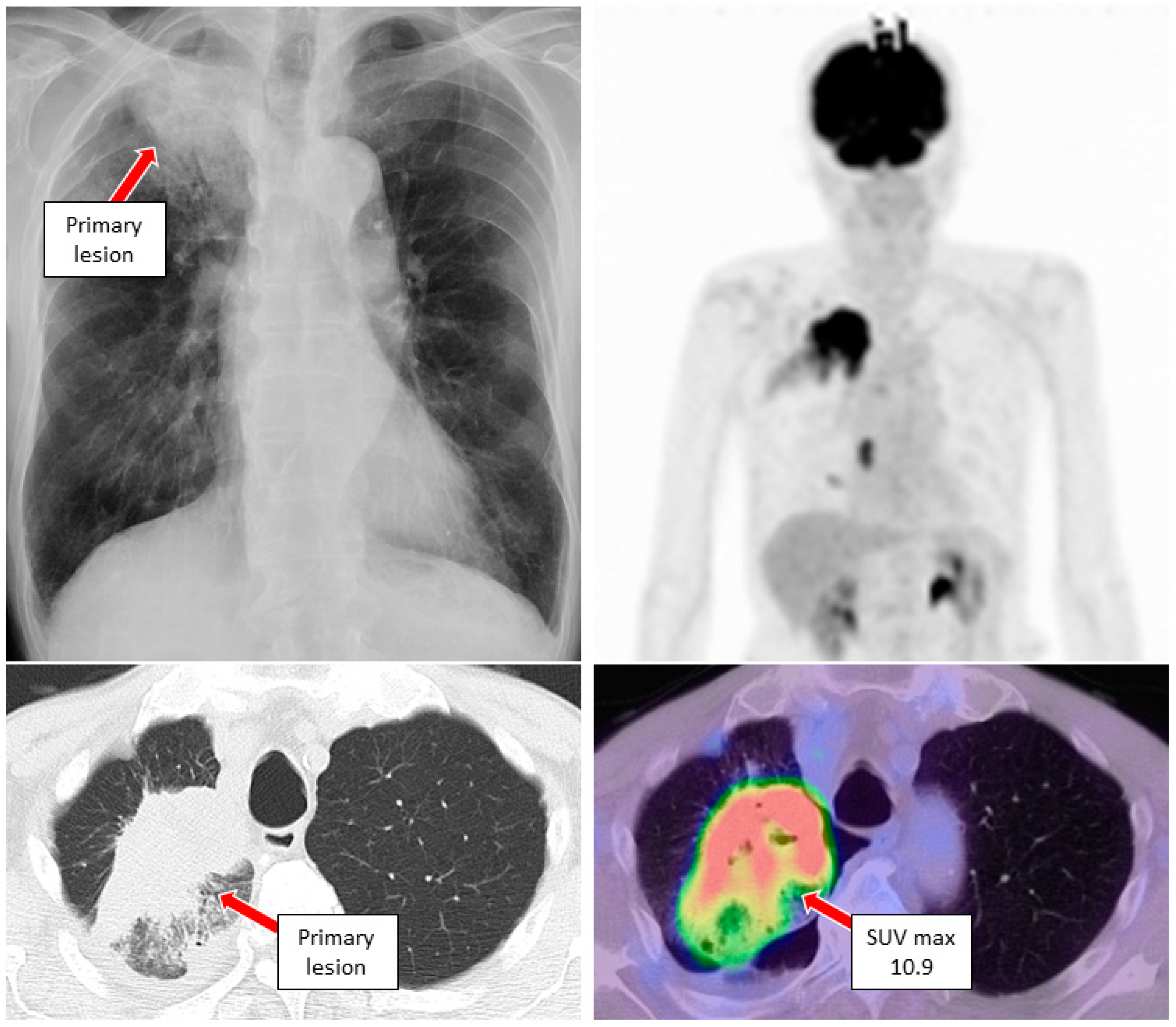
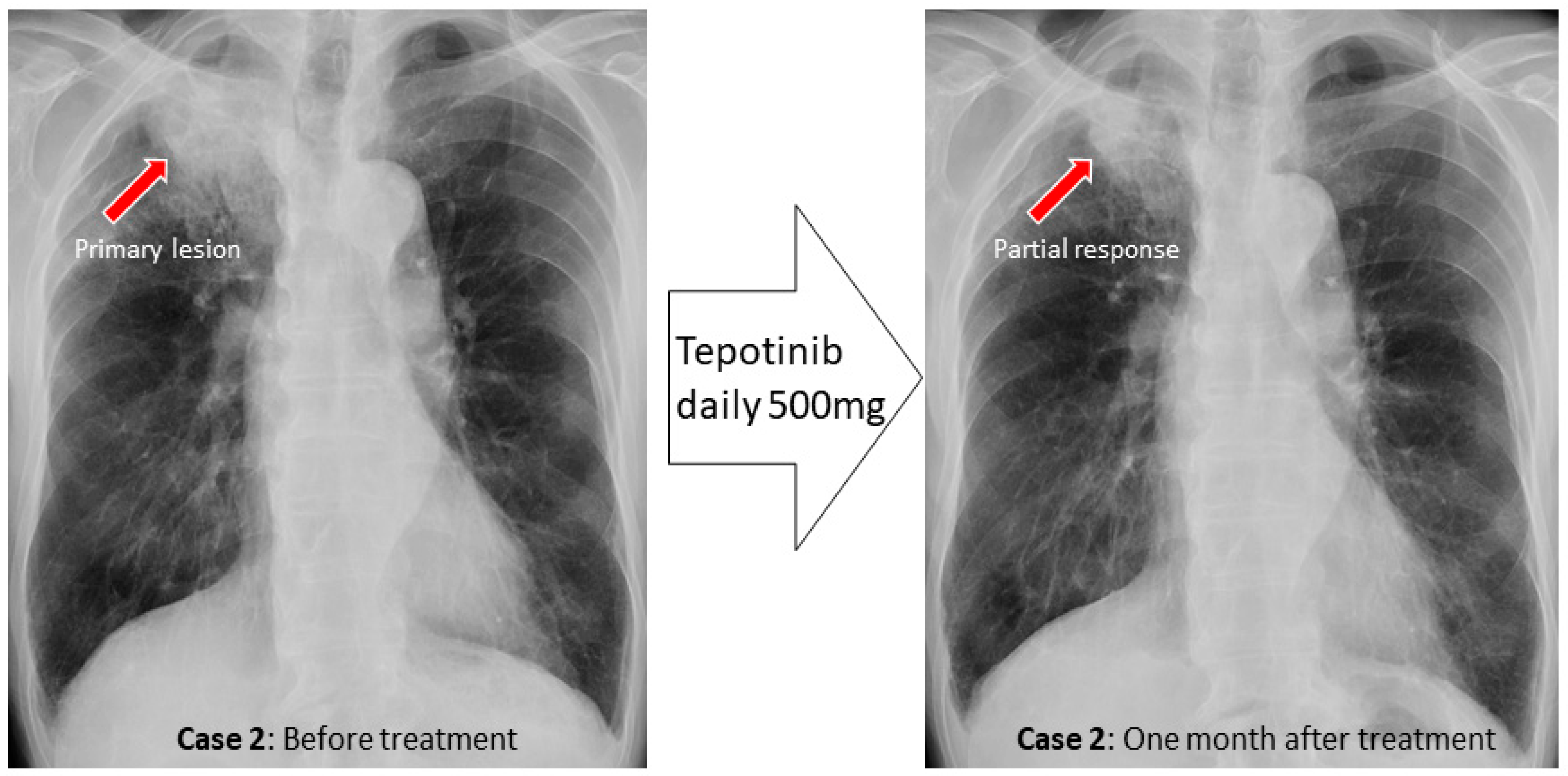
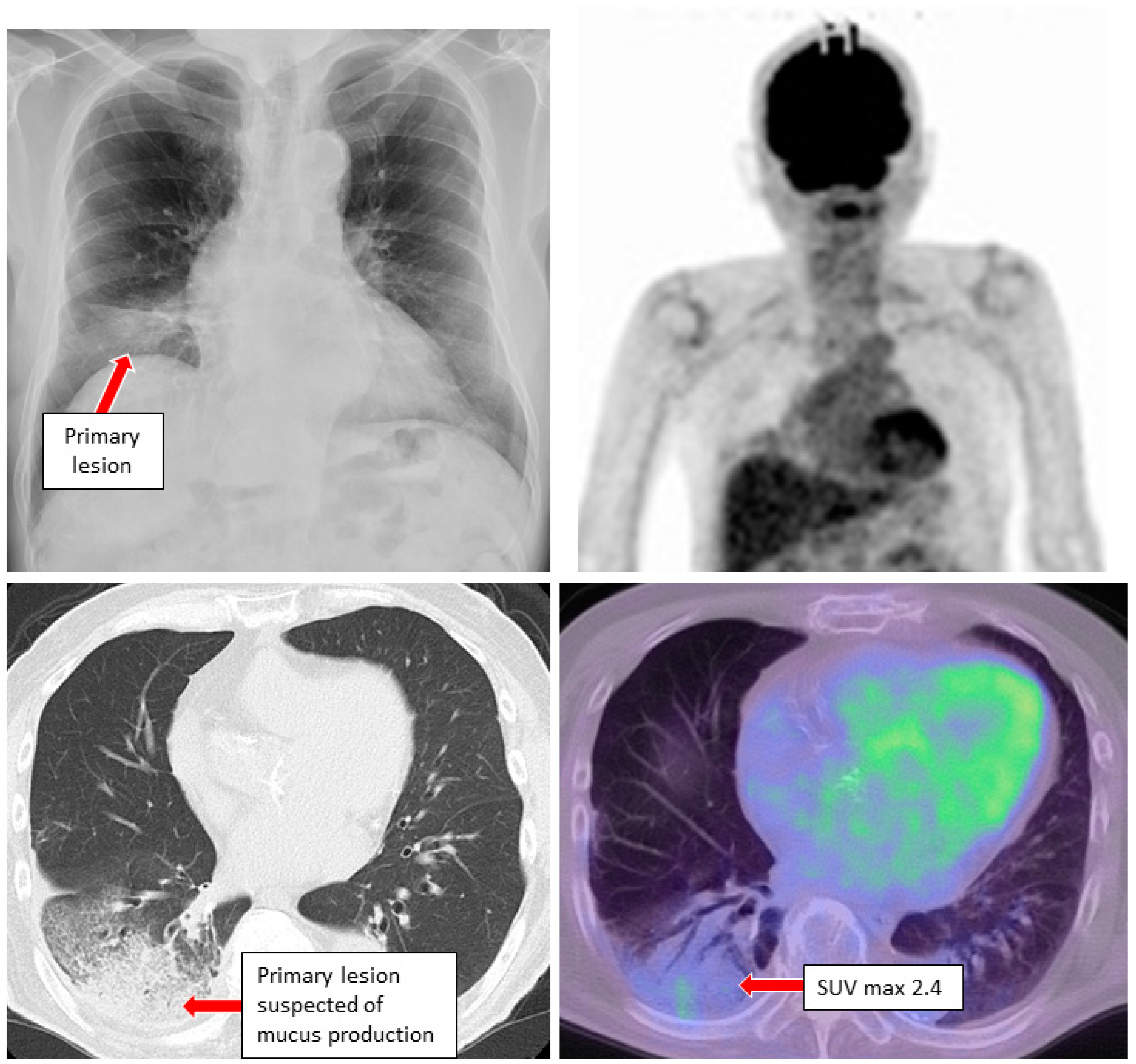
3. Case Reports
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanna, N.; Johnson, D.; Temin, S.; Baker, S.; Brahmer, J.; Ellis, P.M.; Giaccone, G.; Hesketh, P.J.; Jaiyesimi, I.; Leighl, N.B.; et al. Systemic therapy for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3484–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Okami, J.; Nakamura, H.; Honma, K.; Sato, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Kukita, Y.; Nakatsuka, S.; Higashiyama, M. Analytical performance of a highly sensitive system to detect gene variants using next-generation sequencing for lung cancer companion diagnostics. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.P.; Mehta, A.C.; Wahidi, M.M. Establishing the Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. Chest 2013, 143 (Suppl. S5), e142S–e165S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petty, T.L. Sputum cytology for the detection of early lung cancer. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2003, 9, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petty, T.L.; Tockman, M.S.; Palcic, B. Diagnosis of roentgenographically occult lung cancer by sputum cytology. Clin. Chest Med. 2002, 23, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, A.; Freudenberg, N.; Kortsik, C.; Wertzel, H.; Klosa, B.; Hasse, J. Comparison of the sensitivity of sputum and brush cytology in the diagnosis of lung carcinomas. Acta Cytol. 1997, 41, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warth, A. Spread through air spaces (STAS): A comprehensive update. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toyokawa, G.; Yamada, Y.; Tagawa, T.; Kamitani, T.; Yamasaki, Y.; Shimokawa, M.; Oda, Y.; Maehara, Y. Computed tomography features of resected lung adenocarcinomas with spread through air spaces. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 156, 1670–1676.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inage, T.; Nakajima, T.; Yoshino, I.; Yasufuku, K. Early lung cancer detection. Clin. Chest Med. 2018, 39, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Liao, J.; Gao, L.; Shen, J.; Guarnera, M.A.; Zhan, M.; Fang, H.; Stass, S.A.; Jiang, F. Analysis of small nucleolar RNAs in sputum for lung cancer diagnosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 5131–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isaka, T.; Yokose, T.; Ito, H.; Nakayama, H.; Miyagi, Y.; Saito, H.; Masuda, M. Detection of EGFR mutation of pulmonary adenocarcinoma in sputum using droplet digital PCR. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackner, K.; Buder, A.; Hochmair, M.J.; Strieder, M.; Grech, C.; Fabikan, H.; Burghuber, O.C.; Errhalt, P.; Filipits, M. Detection of EGFR Activating and Resistance Mutations by Droplet Digital PCR in Sputum of EGFR-Mutated NSCLC Patients. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, C.S.; Zhao, W.; Liang, Z.X.; Dai, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Miao, K.L.; Cui, D.H.; Chen, L.A. Differences in the genomic profiles of cell-free DNA between plasma, sputum, urine, and tumor tissue in advanced NSCLC. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wei, C.; Wen, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of NGS and ARMS-PCR for detecting EGFR mutations based on 4467 cases of NSCLC patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 148, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunnissen, F.B. Sputum examination for early detection of lung cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 56, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endo, C.; Nakashima, R.; Taguchi, A.; Yahata, K.; Kawahara, E.; Shimagaki, N.; Kamio, J.; Saito, Y.; Ikeda, N.; Sato, M. Inter-rater agreement of sputum cytology for lung cancer screening in Japan. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2015, 43, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morikawa, K.; Kinoshita, K.; Kida, H.; Inoue, T.; Mineshita, M. Preliminary Results of NGS Gene Panel Test Using NSCLC Sputum Cytology and Therapeutic Effect Using Corresponding Molecular-Targeted Drugs. Genes 2022, 13, 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050812
Morikawa K, Kinoshita K, Kida H, Inoue T, Mineshita M. Preliminary Results of NGS Gene Panel Test Using NSCLC Sputum Cytology and Therapeutic Effect Using Corresponding Molecular-Targeted Drugs. Genes. 2022; 13(5):812. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050812
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorikawa, Kei, Kohei Kinoshita, Hirotaka Kida, Takeo Inoue, and Masamichi Mineshita. 2022. "Preliminary Results of NGS Gene Panel Test Using NSCLC Sputum Cytology and Therapeutic Effect Using Corresponding Molecular-Targeted Drugs" Genes 13, no. 5: 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050812
APA StyleMorikawa, K., Kinoshita, K., Kida, H., Inoue, T., & Mineshita, M. (2022). Preliminary Results of NGS Gene Panel Test Using NSCLC Sputum Cytology and Therapeutic Effect Using Corresponding Molecular-Targeted Drugs. Genes, 13(5), 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050812





