Transcriptomic Analysis of the Spleen of Different Chicken Breeds Revealed the Differential Resistance of Salmonella Typhimurium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Diets
2.2. RNA Extraction, cDNA Library Preparation, and RNA-seq
2.3. Differentially Expressed Genes and Function Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
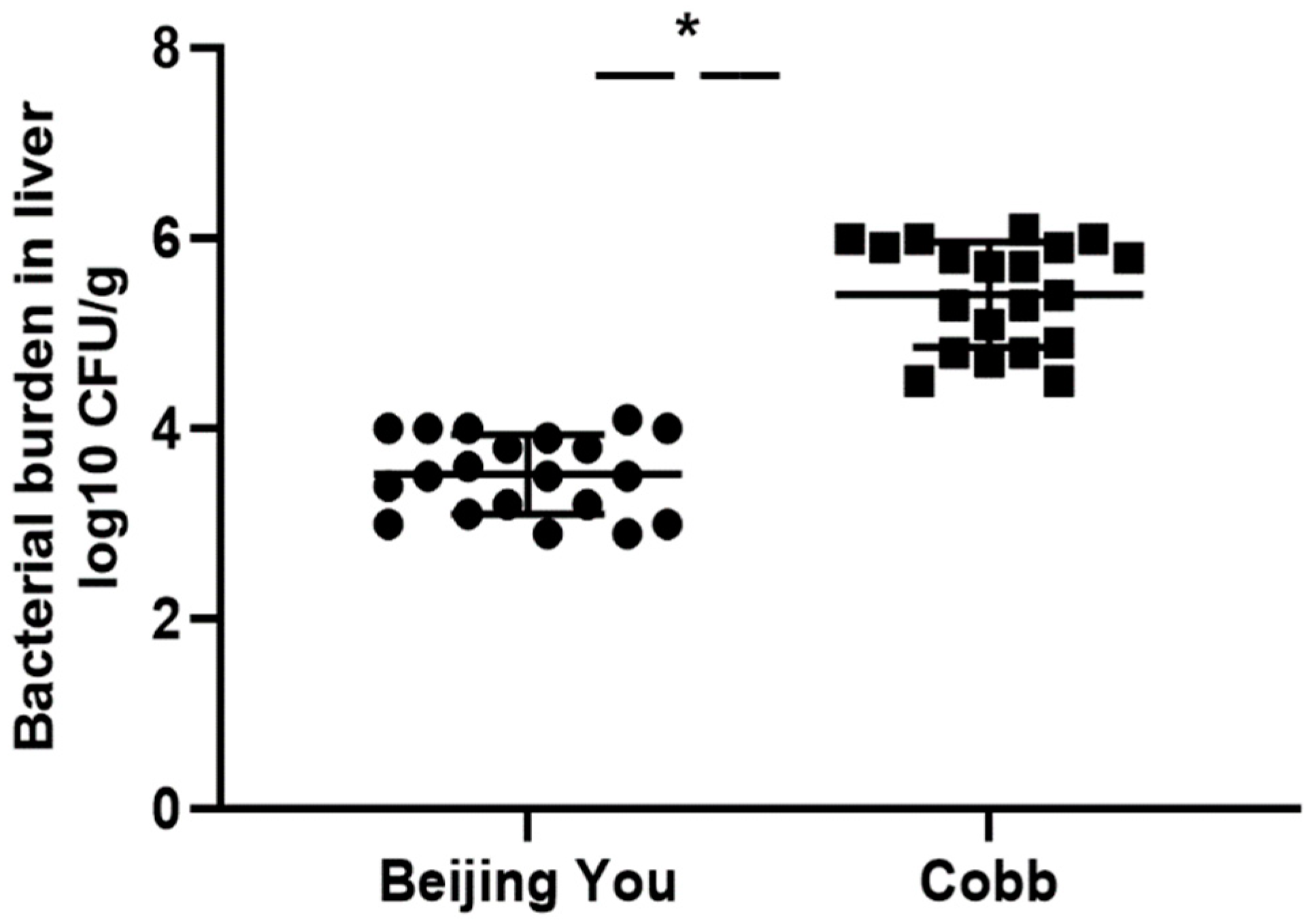
3.1. Overview of the Bacterial Load between BY and Cobb Chicks
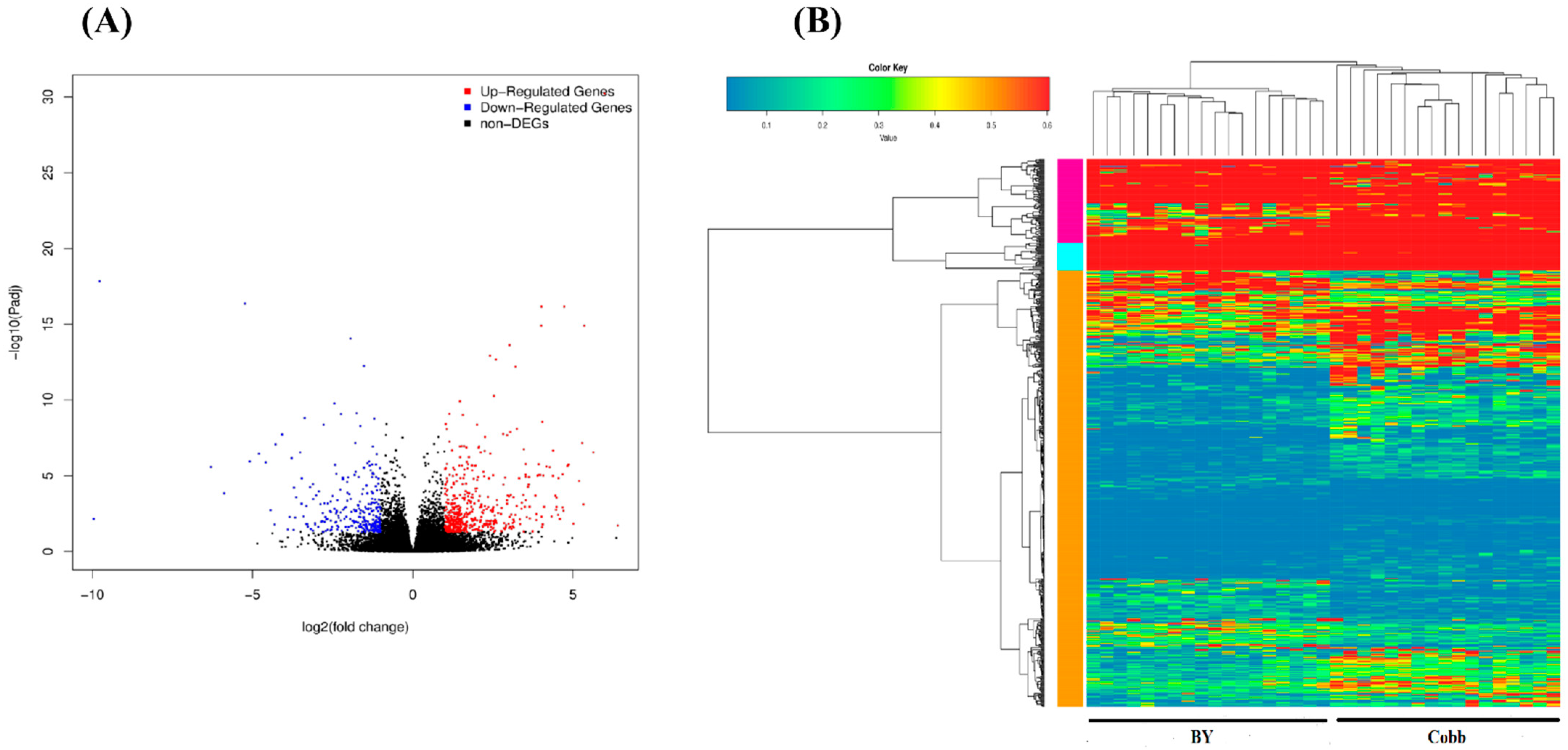
3.2. Sequencing of Spleen Transcriptomes
3.3. DEGs in Response to ST Infection
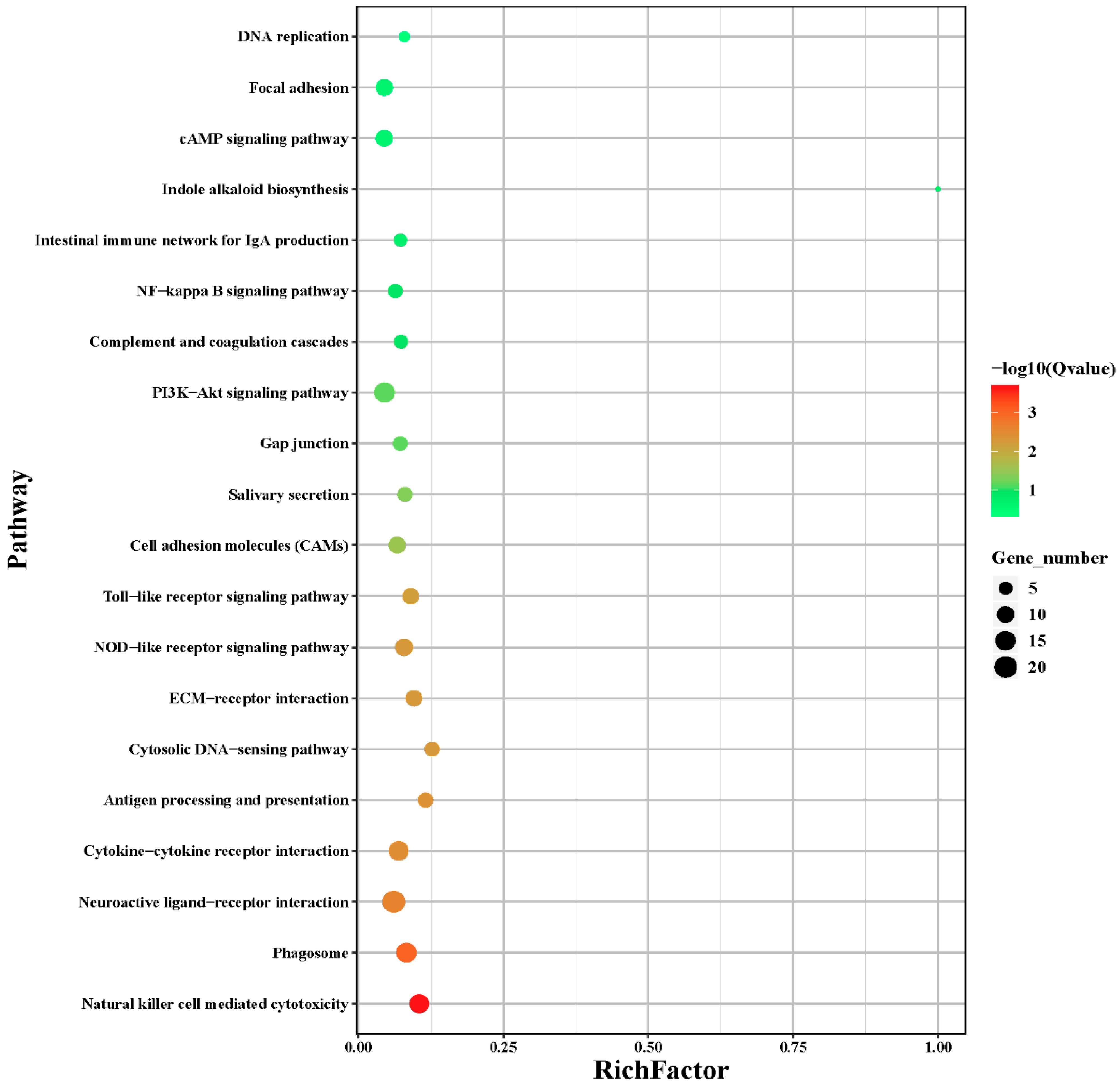
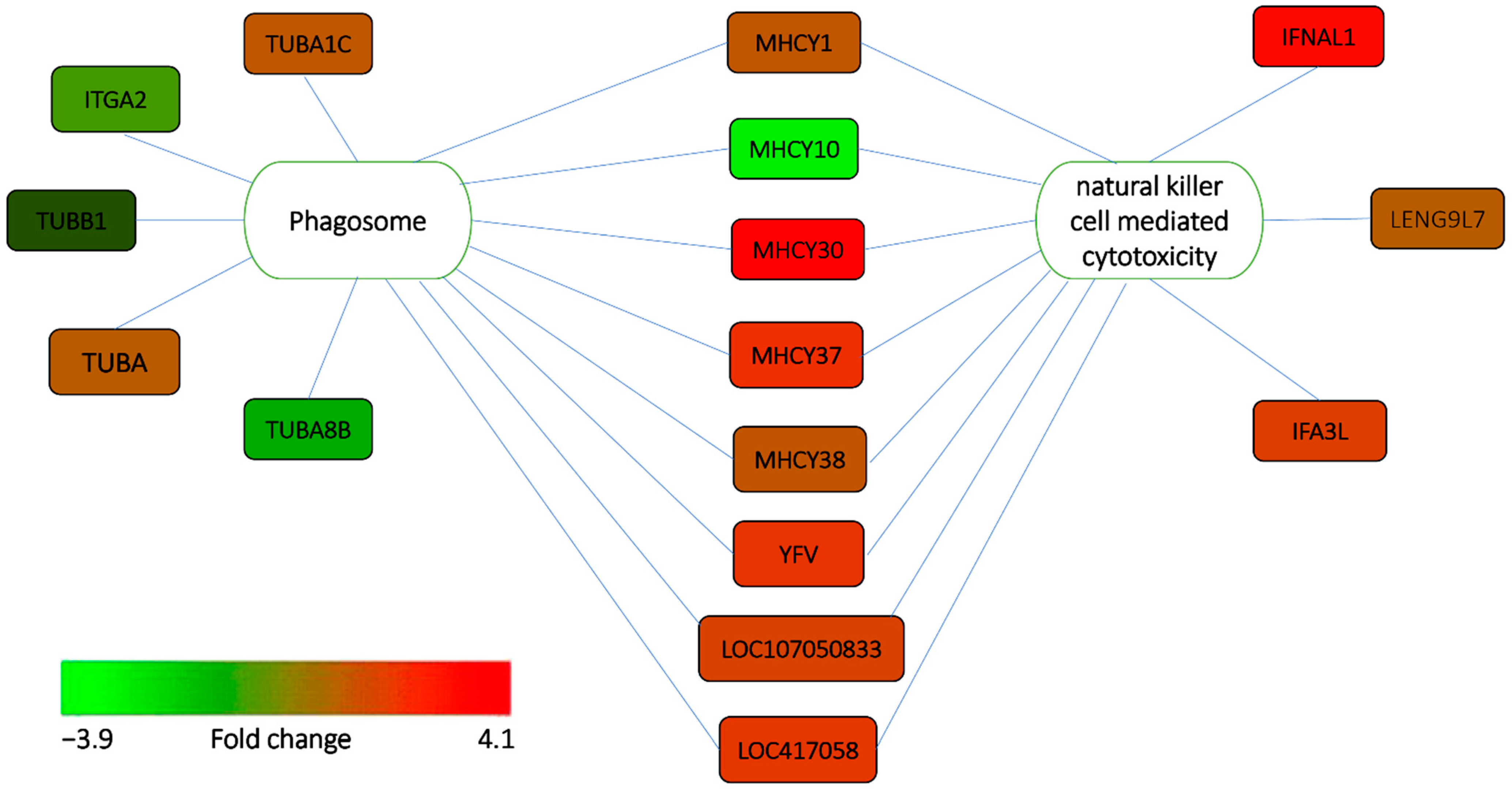
3.4. Functional Enrichment Analysis of the DEGs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calenge, F.; Beaumont, C. Toward integrative genomics study of genetic resistance to Salmonella and Campylobacter intestinal colonization in fowl. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calenge, F.; Kaiser, P.; Vignal, A.; Beaumont, C. Genetic control of resistance to salmonellosis and to Salmonella carrier-state in fowl: A review. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2010, 42, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrow, P.A.; Jones, M.A.; Smith, A.L.; Wigley, P. The long view: Salmonella–the last forty years. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Cao, C.; Cui, S.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, B.J.P.s. Prevalence and characteristics of Salmonella isolates recovered from retail raw chickens in Shaanxi Province, China. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6031–6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Sheng, H.; Shi, C.; Shi, X.; Niu, Q.; Yang, B.J.F.i.M. Prevalence, serotype, antibiotic susceptibility, and genotype of Salmonella in eggs from poultry farms and marketplaces in Yangling, Shaanxi province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, L.; Wu, S.; Zeng, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Wu, H.; et al. Prevalence, bacterial load, and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella serovars isolated from retail meat and meat products China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuPont, H.L.; Steele, J.H. The human health implication of the use of antimicrobial agents in animal feeds. Vet. Q. 1987, 9, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, E. Antibiotic abuse in animal agriculture: Exacerbating drug resistance in human pathogens. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2004, 10, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.Z. Serotypes and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella spp. isolated from farm animals in China. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bar-Shira, E.; Sklan, D.; Friedman, A. Establishment of immune competence in the avian GALT during the immediate post-hatch period. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljumaah, M.R.; Suliman, G.M.; Abdullatif, A.A.; Abudabos, A.M. Effects of phytobiotic feed additives on growth traits, blood biochemistry, and meat characteristics of broiler chickens exposed to Salmonella typhimurium. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5744–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abudabos, A.M.; Aljumaah, M.R.; Aabdullatif, A.; Suliman, G.M. Feed supplementation with some natural products on Salmonella infected broilers’ performance and intestinal injury during the starter period. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 19, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.; Zhao, G.P.; Wen, J.; Chen, J.L.; Zheng, M.Q.; Chen, G.H. Diversity of immune traits between Chinese Beijing-You chicken and White Leghorn. Acta Vet. Et Zootech. 2007, 38, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Liu, R.; Zheng, M.; Sun, Y.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Wen, J.; Zhao, G. The identification of loci for immune traits in chickens using a genome-wide association study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Nie, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Shao, P.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Jiao, W. Evaluation of genetic resistance to Salmonella Pullorum in three chicken lines. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.B.; Wu, C.M.; Wen, J.; Chen, J.L.; Zheng, M.Q.; Zhao, G.P. Association of SNPs in exon 2 of the MHC BF gene with immune traits in two distinct chicken populations: Chinese Beijing-You and White Leghorn. Acta Agric. Scand Sect. A 2009, 59, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.G.; Hunt, J.L. On the use of spleen mass as a measure of avian immune system strength. Oecologia 2004, 138, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiron, A.; Vasilescu, C. Spleen and immunity. Immune implications of splenectomy. Chirurgia 2008, 103, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, M.; Wen, J.; Li, Q.; Zhao, G. Transcriptome analysis of the cecal tonsil of Jingxing yellow chickens revealed the mechanism of differential resistance to Salmonella. Genes 2019, 10, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Xia, P.; Wen, J.; Zheng, M.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, R.; Liu, R.; Zhao, G. Up-regulation of the MyD88-dependent pathway of TLR signaling in spleen and caecum of young chickens infected with Salmonella serovar Pullorum. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ginestet, C. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ijaz, A.; Veldhuizen, E.J.; Broere, F.; Rutten, V.P.; Jansen, C.A.J.P. The interplay between salmonella and intestinal innate immune cells in chickens. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, S.; Tötemeyer, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Akira, S.; Hughes, K.; Gray, D.; Barr, T.; Mastroeni, P.; Maskell, D.J.; Bryant, C.E. Toll-like receptor 4 signalling through MyD88 is essential to control Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection, but not for the initiation of bacterial clearance. Immunology 2009, 128, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Fan, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Everaert, N.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Cui, H. Splenic microRNA expression profiles and integration analyses involved in host responses to Salmonella enteritidis infection in chickens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, H.-I.; Swaggerty, C.L.; Kogut, M.H.; Dowd, S.E.; Li, X.; Pevzner, I.Y.; Zhou, H. Gene expression profiling in chicken heterophils with Salmonella enteritidis stimulation using a chicken 44 K Agilent microarray. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matulova, M.; Rajova, J.; Vlasatikova, L.; Volf, J.; Stepanova, H.; Havlickova, H.; Sisak, F.; Rychlik, I. Characterization of chicken spleen transcriptome after infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature 2002, 420, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Balkwill, F.; Chonchol, M.; Cominelli, F.; Donath, M.Y.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Golenbock, D.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Heneka, M.T.; Hoffman, H.M. A guiding map for inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clark, I.A.; Vissel, B. The meteorology of cytokine storms, and the clinical usefulness of this knowledge. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Tivendale, K.A.; Liu, P.; Feng, Y.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Cai, W.; Mangiamele, P.; Johnson, T.J.; Constantinidou, C.; Penn, C.W. Transcriptome analysis of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O1 in chicken serum reveals adaptive responses to systemic infection. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sandford, E.E.; Orr, M.; Shelby, M.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Johnson, T.J.; Kariyawasam, S.; Liu, P.; Nolan, L.K.; Lamont, S.J. Leukocyte transcriptome from chickens infected with avian pathogenic Escherichia coli identifies pathways associated with resistance. Results Immunol. 2012, 2, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Liu, P.; Nolan, L.K.; Lamont, S.J. Novel pathways revealed in bursa of fabricius transcriptome in response to extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Liu, P.; Nolan, L.K.; Lamont, S.J. Thymus transcriptome reveals novel pathways in response to avian pathogenic Escherichia coli infection. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2803–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, S.; Kaiser, M.; Liu, W.J. Candidate genes for resistance to Salmonella enteritidis colonization in chickens as detected in a novel genetic Salmonella. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2002, 87, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Miller, M.M.; Lamont, S.J.J.I. Association of MHC class I and class II gene polymorphisms with vaccine or challenge response to Salmonella enteritidis in young chicks. Immunogenetics 2002, 54, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morvan, M.G.; Lanier, L.L. NK cells and cancer: You can teach innate cells new tricks. Nat. Cancer 2016, 16, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodoen, M.B.; Lanier, L.L. Natural killer cells as an initial defense against pathogens. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijerink, N.; van den Biggelaar, R.H.; van Haarlem, D.A.; Stegeman, J.A.; Rutten, V.P.; Jansen, C.A. A detailed analysis of innate and adaptive immune responsiveness upon infection with Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis in young broiler chickens. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orange, J.S. Formation and function of the lytic NK-cell immunological synapse. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solana, R.; Tarazona, R.; Gayoso, I.; Lesur, O.; Dupuis, G.; Fulop, T. Innate immunosenescence: Effect of aging on cells and receptors of the innate immune system in humans. Semin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, B.G.; Methner, U.; Pieper, J.; Berndt, A.J.V. Effects of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis on cellular recruitment and cytokine gene expression in caecum of vaccinated chickens. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5423–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, K.J.; He, H.; Swaggerty, C.L.; Kogut, M.H. The avian heterophil. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, O. New concepts in the generation and functions of IgA. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, E.; Balmer, M.L.; Fritz, J.H.; Hapfelmeier, S. Functional flexibility of intestinal IgA–broadening the fine line. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mkaddem, S.B.; Christou, I.; Rossato, E.; Berthelot, L.; Lehuen, A.; Monteiro, R.C. IgA, IgA receptors, and their anti-inflammatory properties. Fc Recept. 2014, 382, 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Palm, N.W.; De Zoete, M.R.; Cullen, T.W.; Barry, N.A.; Stefanowski, J.; Hao, L.; Degnan, P.H.; Hu, J.; Peter, I.; Zhang, W. Immunoglobulin A coating identifies colitogenic bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell 2014, 158, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forbes, S.J.; Eschmann, M.; Mantis, N.J. Inhibition of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium motility and entry into epithelial cells by a protective antilipopolysaccharide monoclonal immunoglobulin A antibody. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forbes, S.J.; Bumpus, T.; McCarthy, E.A.; Corthésy, B.; Mantis, N.J. Transient suppression of Shigella flexneri type 3 secretion by a protective O-antigen-specific monoclonal IgA. MBio 2011, 2, e00042-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freemerman, A.J.; Johnson, A.R.; Sacks, G.N.; Milner, J.J.; Kirk, E.L.; Troester, M.A.; Macintyre, A.N.; Goraksha-Hicks, P.; Rathmell, J.C.; Makowski, L. Metabolic reprogramming of macrophages: Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1)-mediated glucose metabolism drives a proinflammatory phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 7884–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van den Bossche, J.; O’Neill, L.A.; Menon, D. Macrophage immunometabolism: Where are we (going)? Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Table | Description | Count | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0006955 | immune response | 23 | 0.0001 |
| GO:0009617 | response to bacterium | 10 | 0.001 |
| GO:0098542 | defense response to other organism | 11 | 0.0013 |
| GO:0002285 | lymphocyte activation involved in immune response | 6 | 0.0016 |
| GO:0002376 | immune system process | 30 | 0.0058 |
| GO:0006952 | defense response | 18 | 0.0067 |
| GO:0051707 | response to other organism | 13 | 0.0073 |
| GO:0002520 | immune system development | 14 | 0.0129 |
| GO:0050896 | response to stimulus | 94 | 0.013 |
| GO:0009607 | response to biotic stimulus | 13 | 0.0132 |
| GO:0001775 | cell activation | 12 | 0.0205 |
| GO:0032501 | multicellular organismal process | 73 | 0.026 |
| GO:0009605 | response to external stimulus | 24 | 0.031 |
| GO:0007275 | multicellular organism development | 56 | 0.0324 |
| GO:0030154 | cell differentiation | 43 | 0.0396 |
| GO:0045087 | innate immune response | 8 | 0.0462 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elsharkawy, M.S.; Wang, H.; Ding, J.; Madkour, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Li, Q.; Zhao, G.; Wen, J. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Spleen of Different Chicken Breeds Revealed the Differential Resistance of Salmonella Typhimurium. Genes 2022, 13, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050811
Elsharkawy MS, Wang H, Ding J, Madkour M, Wang Q, Zhang Q, Zhang N, Li Q, Zhao G, Wen J. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Spleen of Different Chicken Breeds Revealed the Differential Resistance of Salmonella Typhimurium. Genes. 2022; 13(5):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050811
Chicago/Turabian StyleElsharkawy, Mohamed Shafey, Hailong Wang, Jiqiang Ding, Mahmoud Madkour, Qiao Wang, Qi Zhang, Na Zhang, Qinghe Li, Guiping Zhao, and Jie Wen. 2022. "Transcriptomic Analysis of the Spleen of Different Chicken Breeds Revealed the Differential Resistance of Salmonella Typhimurium" Genes 13, no. 5: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050811
APA StyleElsharkawy, M. S., Wang, H., Ding, J., Madkour, M., Wang, Q., Zhang, Q., Zhang, N., Li, Q., Zhao, G., & Wen, J. (2022). Transcriptomic Analysis of the Spleen of Different Chicken Breeds Revealed the Differential Resistance of Salmonella Typhimurium. Genes, 13(5), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050811








