Glucose-Related Traits and Risk of Migraine—A Potential Mechanism and Treatment Consideration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
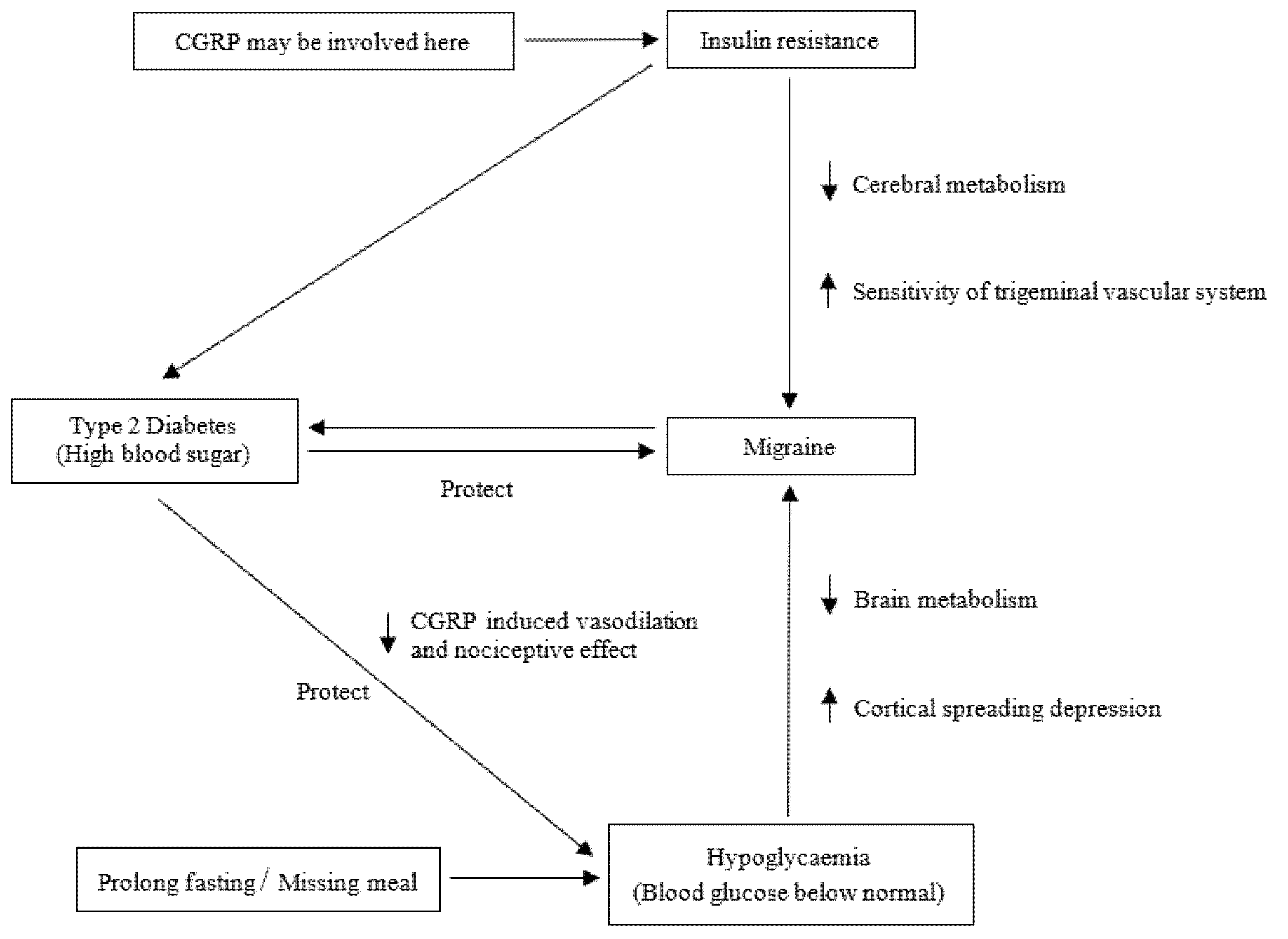
3.1. Migraine and Hypoglycaemia
3.2. Migraine and Insulin Resistance
3.3. Migraine and Diabetes Mellitus
3.4. Migraine and Glucose-Related Traits: Lifestyle Changes and Treatment
3.5. Shared Genetic Basis
3.6. Candidate Gene Association Studies
3.6.1. Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase
3.6.2. Insulin Receptor
3.6.3. Tumour Necrosis Factor
3.6.4. Oestrogen Receptor 1
3.6.5. Nitric Oxide Synthase 3
3.6.6. Paraoxonase 1
3.7. Genome-Wide Association Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerring, Z.F.; Powell, J.E.; Montgomery, G.W.; Nyholt, D.R. Genome-wide analysis of blood gene expression in migraine implicates immune-inflammatory pathways. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, T.; Allen, C.; Arora, M.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brown, A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1545–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdulle, A.M.; Abera, S.F.; Abyu, G.Y.; Ahmed, M.B.; Aichour, A.N.; Aichour, I.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders during 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 877–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Barber, R.M.; Bell, B.; Bertozzi-Villa, A.; Biryukov, S.; Bolliger, I.; Charlson, F.; Davis, A.; Degenhardt, L.; Dicker, D.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 743–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2163–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.W. Migraine. Lancet 2018, 391, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, M.; Prendecki, M.; Kozubski, W.; Lianeri, M.; Dorszewska, J. Molecular factors in migraine. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 50708–50718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloudek, L.M.; Stokes, M.; Buse, D.C.; Wilcox, T.K.; Lipton, R.B.; Goadsby, P.J.; Varon, S.F.; Blumenfeld, A.M.; Katsarava, Z.; Pascual, J.; et al. Cost of healthcare for patients with migraine in five European countries: Results from the International Burden of Migraine Study (IBMS). J. Headache Pain 2012, 13, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, M.; Gustavsson, A.; Stovner, L.J.; Steiner, T.J.; Barré, J.; Katsarava, Z.; Lainez, J.M.; Lampl, C.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; Rastenyte, D.; et al. The cost of headache disorders in Europe: The Eurolight project. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyholt, D.R.; Borsook, D.; Griffiths, L.R. Migrainomics—Identifying brain and genetic markers of migraine. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launer, L.J.; Terwindt, G.M.; Ferrari, M.D. The prevalence and characteristics of migraine in a population-based cohort: The GEM study. Neurology 1999, 53, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [CrossRef]
- Kelman, L. The triggers or precipitants of the acute migraine attack. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Schulz, U.G.; Kuker, W.; Rothwell, P.M. Age-specific association of migraine with cryptogenic TIA and stroke: Population-based study. Neurology 2015, 85, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurth, T.; Winter, A.C.; Eliassen, A.H.; Dushkes, R.; Mukamal, K.J.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C.; Manson, J.E.; Rexrode, K.M. Migraine and risk of cardiovascular disease in women: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2016, 353, i2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, P.A.; Burtness, H.I. Hypoglycemic headache. Endocrinology 1935, 19, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, E.C.; Lisicki, M.; Fischer, D.; Sándor, P.S.; Schoenen, J. The metabolic face of migraine—From pathophysiology to treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, J.N.; Cumings, C.J. Method of precipitating and preventing some migraine attacks. Br. Med. J. 1966, 2, 1242–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pearce, J. Insulin induced hypoglycaemia in migraine. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1971, 34, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacome, D.E. Hypoglycemia rebound migraine. Headache 2001, 41, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Holland, P.R.; Martins-Oliveira, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Schankin, C.; Akerman, S. Pathophysiology of Migraine: A Disorder of Sensory Processing. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 553–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, A.; Pirritano, D.; Consoli, D.; Plastino, M.; Casalinuovo, F.; Cristofaro, S.; Colica, C.; Ermio, C.; De Bartolo, M.; Opipari, C.; et al. Chronic migraine in women is associated with insulin resistance: A cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, J.D.; Roberts, J.; Byer, J.A. The five hour glucose tolerance test and effect of low sucrose diet in migraine. Headache 1978, 18, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavestro, C.; Rosatello, A.; Micca, G.; Ravotto, M.; Marino, M.P.; Asteggiano, G.; Beghi, E. Insulin metabolism is altered in migraineurs: A new pathogenic mechanism for migraine? Headache 2007, 47, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casucci, G.; Villani, V.; Cologno, D.; D’Onofrio, F. Migraine and metabolism. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 33, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainero, I.; Limone, P.; Ferrero, M.; Valfre, W.; Pelissetto, C.; Rubino, E.; Gentile, S.; Lo Giudice, R.; Pinessi, L. Insulin sensitivity is impaired in patients with migraine. Cephalalgia 2005, 25, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigal, M.E.; Kurth, T.; Hu, H.; Santanello, N.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine and cardiovascular disease: Possible mechanisms of interaction. Neurology 2009, 72, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Manack, A.; Serrano, D.; Turkel, C.; Lipton, R.B. Sociodemographic and comorbidity profiles of chronic migraine and episodic migraine sufferers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.C.; Rist, P.M.; Winter, A.C.; Buring, J.E.; Pradhan, A.D.; Loder, E.W.; Kurth, T. Migraine and risk of incident diabetes in women: A prospective study. Cephalalgia 2012, 32, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, S.A.; Hamed, E.A.; Ezz Eldin, A.M.; Mahmoud, N.M. Vascular Risk Factors, Endothelial Function, and Carotid Thickness in Patients with Migraine: Relationship to Atherosclerosis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2010, 19, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, A.I.; Terwindt, G.M.; Picavet, H.S.J.; Verschuren, W.M.M.; Ferrari, M.D.; Launer, L.J. Cardiovascular risk factors and migraine. Neurology 2005, 64, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etminan, M.; Takkouche, B.; Isorna, F.C.; Samii, A. Risk of ischaemic stroke in people with migraine: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ 2005, 330, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merikangas, K.R.; Fenton, B.T.; Cheng, S.H.; Stolar, M.J.; Risch, N. Association between migraine and stroke in a large-scale epidemiological study of the United States. Arch. Neurol. 1997, 54, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, S.; Pistoia, F.; Degan, D.; Carolei, A. Conventional vascular risk factors: Their role in the association between migraine and cardiovascular diseases. Cephalalgia 2015, 35, 146–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torelli, P.; Evangelista, A.; Bini, A.; Castellini, P.; Lambru, G.; Manzoni, G.C. Fasting Headache: A Review of the Literature and New Hypotheses. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2009, 49, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufnagl, K.N.; Peroutka, S.J. Glucose regulation in headache: Implications for dietary management. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2014, 2, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, C. Migraine. Lancet 1933, 1, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Finocchi, C.; Sivori, G. Food as trigger and aggravating factor of migraine. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 33, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierings, E.L.; Ranke, A.H.; Honkoop, P.C. Precipitating and aggravating factors of migraine versus tension-type headache. Headache 2001, 41, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, F.C. Trigger factors and natural history of migraine. Funct. Neurol. 1986, 1, 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Dalkara, T.; Kiliç, K. How does fasting trigger migraine? A hypothesis. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2013, 17, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, L. Precipitating factors in migraine: A retrospective review of 494 patients. Headache 1994, 34, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.C.; Molgaard, C.A.; Gardner, C.H.; Rothrock, J.F.; Stang, P.E. Migraine trigger factors in non-clinical Mexican-American population in San Diego county: Implications for etiology. Cephalalgia 1995, 15, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharff, L.; Turk, D.C.; Marcus, D.A. Triggers of headache episodes and coping responses of headache diagnostic groups. Headache 1995, 35, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroutka, S.J. What Turns on a Migraine? A Systematic Review of Migraine Precipitating Factors. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2014, 18, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Salameh, I.; Plakht, Y.; Ifergane, G. Migraine exacerbation during Ramadan fasting. J. Headache Pain 2010, 11, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, M.J.; Elstein, Y. Prophylactic COX2 inhibitor: An end to the Yom Kippur headache. Headache 2006, 46, 1487–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroutka, S.J. Serum glucose regulation and headache. Headache 2002, 42, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, J.N.; Pyke, D.A. Effect of diabetes on migraine. Lancet 1970, 2, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, E.C.; Putananickal, N.; Orsini, A.-L.; Vogt, D.R.; Sandor, P.S.; Schoenen, J.; Fischer, D. Mitochondrial function and oxidative stress markers in higher-frequency episodic migraine. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.S.; Coman, D.; Calvert, S. Glucose transporter 1 deficiency syndrome and hemiplegic migraines as a dominant presenting clinical feature. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2014, 50, 1025–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, U.; Sukhotinsky, I.; Eikermann-Haerter, K.; Ayata, C. Glucose modulation of spreading depression susceptibility. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Oliveira, M.; Akerman, S.; Holland, P.R.; Hoffmann, J.R.; Tavares, I.; Goadsby, P.J. Neuroendocrine signaling modulates specific neural networks relevant to migraine. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 101, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, H.J.; Peters, M.J.; Esko, T.; Yaghootkar, H.; Schurmann, C.; Kettunen, J.; Christiansen, M.W.; Fairfax, B.P.; Schramm, K.; Powell, J.E.; et al. Systematic identification of trans eQTLs as putative drivers of known disease associations. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Chai, H.S.; Younkin, C.S.; Allen, M.; Crook, J.; Pankratz, V.S.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Rowley, C.N.; Nair, A.A.; Middha, S.; et al. Brain expression genome-wide association study (eGWAS) identifies human disease-associated variants. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensaad, K.; Tsuruta, A.; Selak, M.A.; Vidal, M.N.; Nakano, K.; Bartrons, R.; Gottlieb, E.; Vousden, K.H. TIGAR, a p53-inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis. Cell 2006, 126, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldiken, B.; Guldiken, S.; Taskiran, B.; Koc, G.; Turgut, N.; Kabayel, L.; Tugrul, A. Migraine in metabolic syndrome. Neurologist 2009, 15, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bic, Z.; Blix, G.; Hopp, H.; Leslie, F. In search of the ideal treatment for migraine headache. Med. Hypotheses 1998, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamura, C.; Corbelli, I.; de Tommaso, M.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Di Renzo, A.; Filippi, M.; Jannini, T.B.; Messina, R.; Parisi, P.; et al. Pathophysiological Bases of Comorbidity in Migraine. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 640574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Moro, L.; Rota, E.; Pirovano, E.; Rainero, I. Migraine, Brain Glucose Metabolism and the “Neuroenergetic” Hypothesis: A Scoping Review. J. Pain 2022, 102, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.E.; Arvanitakis, Z.; Macauley-Rambach, S.L.; Koenig, A.M.; Wang, H.-Y.; Ahima, R.S.; Craft, S.; Gandy, S.; Buettner, C.; Stoeckel, L.E.; et al. Brain insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease: Concepts and conundrums. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, J.A.; Testani, D.; Mansur, R.B.; Lee, Y.; Subramaniapillai, M.; McIntyre, R.S. Brain insulin resistance: A treatment target for cognitive impairment and anhedonia in depression. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 315, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, H.J.; Bernecker, C.; Pailer, S.; Fauler, G.; Horejsi, R.; Möller, R.; Lechner, A.; Fazekas, F.; Truschnig-Wilders, M. Hyperinsulinaemia in migraineurs is associated with nitric oxide stress. Cephalalgia 2009, 30, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Diao, Y.; Meng, S.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yang, D.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y. Are Glucose and Insulin Metabolism and Diabetes Associated with Migraine? A Community-Based, Case-Control Study. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2017, 31, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernecker, C.; Pailer, S.; Kieslinger, P.; Horejsi, R.; Möller, R.; Lechner, A.; Wallner-Blazek, M.; Weiss, S.; Fazekas, F.; Truschnig-Wilders, M.; et al. GLP-2 and leptin are associated with hyperinsulinemia in non-obese female migraineurs. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, A.; Marmura, M.J. Metabolic syndrome and migraine. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoi, S.K.; Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in migraine. J. Headache Pain 2012, 13, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, S.; Altobelli, E.; Ornello, R.; Ripa, P.; Pistoia, F.; Carolei, A. Insulin resistance in migraineurs: Results from a case-control study. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porte, D., Jr.; Baskin, D.G.; Schwartz, M.W. Insulin signaling in the central nervous system: A critical role in metabolic homeostasis and disease from C. elegans to humans. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1264–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.W.; Figlewicz, D.P.; Baskin, D.G.; Woods, S.C.; Porte, D., Jr. Insulin in the brain: A hormonal regulator of energy balance. Endocr. Rev. 1992, 13, 387–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinkalp, S.; Simsir, I.Y.; Ertek, S. Insulin resistance in brain and possible therapeutic approaches. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 12, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, L.C.; Hosford, D.A.; Riley, J.H.; Bird, M.I.; White, N.J.; Hewett, D.R.; Peroutka, S.J.; Griffiths, L.R.; Boyd, P.R.; Lea, R.A.; et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphism alleles in the insulin receptor gene are associated with typical migraine. Genomics 2001, 78, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netzer, C.; Freudenberg, J.; Heinze, A.; Heinze-Kuhn, K.; Goebel, I.; McCarthy, L.C.; Roses, A.D.; Gobel, H.; Todt, U.; Kubisch, C. Replication study of the insulin receptor gene in migraine with aura. Genomics 2008, 91, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Pilch, P.F. The insulin receptor: Structure, function, and signaling. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, C319–C334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adashi, E.Y.; Hsueh, A.J.; Bambino, T.H.; Yen, S.S. Disparate effect of clomiphene and tamoxifen on pituitary gonadotropin release in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. 1981, 240, E125–E130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortelli, P.; Pierangeli, G. Hypothalamus and headaches. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 28, S198–S202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.; Goadsby, P.J. The hypothalamic orexinergic system: Pain and primary headaches. Headache 2007, 47, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alstadhaug, K.B. Migraine and the hypothalamus. Cephalalgia 2009, 29, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, L.H.; Allers, A.; May, A. Hypothalamus as a mediator of chronic migraine. Neurology 2017, 88, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denuelle, M.; Fabre, N.; Payoux, P.; Chollet, F.; Geraud, G. Hypothalamic activation in spontaneous migraine attacks. Headache 2007, 47, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Siscovick, D.S.; Sidney, S.; Lewis, C.E.; Kiefe, C.I.; Koepsell, T.D. Oral contraceptive use and association with glucose, insulin, and diabetes in young adult women: The CARDIA Study. Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favoni, V.; Giani, L.; Al-Hassany, L.; Asioli, G.M.; Butera, C.; de Boer, I.; Guglielmetti, M.; Koniari, C.; Mavridis, T.; Vaikjärv, M.; et al. CGRP and migraine from a cardiovascular point of view: What do we expect from blocking CGRP? J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvinsson, L. The Trigeminovascular Pathway: Role of CGRP and CGRP Receptors in Migraine. Headache 2017, 57, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, L.H.; Haderslev, P.A.; Jacobsen, V.B.; Iversen, H.K.; Sperling, B.; Olesen, J. CGRP may play a causative role in migraine. Cephalalgia 2002, 22, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, S.; Johnson, K.W.; Ossipov, M.H.; Aurora, S.K. CGRP and the Trigeminal System in Migraine. Headache 2019, 59, 659–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, D.X.; Ahrén, B.; Nagy, I.; Olsen, U.B.; Brand, C.L.; Sundler, F.; Tabanera, R.; Svendsen, O.; Carr, R.D.; Santha, P.; et al. Capsaicin-sensitive sensory fibers in the islets of Langerhans contribute to defective insulin secretion in Zucker diabetic rat, an animal model for some aspects of human type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.S.; Li, X.; Whiting, L.; Glyn-Jones, S.; Zhang, S.; Hickey, A.J.; Sewell, M.A.; Ruggiero, K.; Phillips, A.R.; Kraegen, E.W.; et al. Mice lacking the neuropeptide alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide are protected against diet-induced obesity. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4257–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, M.; Maleki, F.; Khoramdad, M.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Kolahi, A.-A.; Safiri, S. A systematic literature review of observational studies of the bilateral association between diabetes and migraine. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2021, 15, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.W.; Goadsby, P.J.; Spierings, E.L.; Scherer, J.C.; Sweeney, S.P.; Grayzel, D.S. Safety and efficacy of LY2951742, a monoclonal antibody to calcitonin gene-related peptide, for the prevention of migraine: A phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, A.; Himms-Hagen, J. Resistance to aging-associated obesity in capsaicin-desensitized rats one year after treatment. Obes. Res. 1995, 3, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, M.; Ahrén, B.; Böttcher, G.; Sundler, F. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: Occurrence in pancreatic islets in the mouse and the rat and inhibition of insulin secretion in the mouse. Endocrinology 1986, 119, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, D.X.; Hansen, A.J.; Wilken, M.; Elm, T.; Svendsen, O.; Carr, R.D.; Ahrén, B.; Brand, C.L. Plasma calcitonin gene-related peptide is increased prior to obesity, and sensory nerve desensitization by capsaicin improves oral glucose tolerance in obese Zucker rats. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 153, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighi, F.S.; Rahmanian, M.; Namiranian, N.; Arzaghi, S.M.; Dehghan, F.; Chavoshzade, F.; Sepehri, F. Migraine and type 2 diabetes; is there any association? J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2015, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Split, W.; Szydlowska, M. Headaches in non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Funct. Neurol. 1997, 12, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aamodt, A.H.; Stovner, L.J.; Midthjell, K.; Hagen, K.; Zwart, J.A. Headache prevalence related to diabetes mellitus. The Head-HUNT study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2007, 14, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berge, L.I.; Riise, T.; Fasmer, O.B.; Hundal, O.; Oedegaard, K.J.; Midthjell, K.; Lund, A. Does diabetes have a protective effect on migraine? Epidemiology 2013, 24, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burn, W.K.; Machin, D.; Waters, W.E. Prevalence of migraine in patients with diabetes. Br. Med. J. 1984, 289, 1579–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, K.; Åsvold, B.O.; Midthjell, K.; Stovner, L.J.; Zwart, J.A.; Linde, M. Inverse relationship between type 1 diabetes mellitus and migraine. Data from the Nord-Trøndelag Health Surveys 1995–1997 and 2006–2008. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonazzo, I.C.; Riise, T.; Cortese, M.; Berge, L.I.; Engeland, A.; Bernt Fasmer, O.; Lund, A.; Joachim Ødegaard, K.; Poluzzi, E.; Bjornevik, K. Diabetes is associated with decreased migraine risk: A nationwide cohort study. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagherazzi, G.; El Fatouhi, D.; Fournier, A.; Gusto, G.; Mancini, F.R.; Balkau, B.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Kurth, T.; Bonnet, F. Associations Between Migraine and Type 2 Diabetes in Women: Findings From the E3N Cohort Study. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli Farsani, S.; Souverein, P.C.; van der Vorst, M.M.; Knibbe, C.A.; de Boer, A.; Mantel-Teeuwisse, A.K. Chronic comorbidities in children with type 1 diabetes: A population-based cohort study. Arch. Dis. Child. 2015, 100, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-de-Andrés, A.; Del Barrio, J.L.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; de Miguel-Díez, J.; Jimenez-Trujillo, I.; Martinez-Huedo, M.A.; Jimenez-García, R. Migraine in adults with diabetes; is there an association? Results of a population-based study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets 2018, 11, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantucci, C.; Bottini, P.; Fiorani, C.; Dottorini, M.L.; Santeusanio, F.; Provinciali, L.; Sorbini, C.A.; Casucci, G. Cerebrovascular reactivity and hypercapnic respiratory drive in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 90, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnhoud, A.D.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Dippel, D.W. Relationships of transcranial blood flow Doppler parameters with major vascular risk factors: TCD study in patients with a recent TIA or nondisabling ischemic stroke. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2006, 34, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D. Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy: Update 2006. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1084, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Mancilla, E.; Al-Hassany, L.; Villalón, C.M.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A. Metabolic Aspects of Migraine: Association With Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 686398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F.M.; Aristeidou, S.; Baraldi, C.; Czapinska-Ciepiela, E.K.; Ariadni, D.D.; Di Lenola, D.; Fenech, C.; Kampouris, K.; Karagiorgis, G.; Braschinsky, M.; et al. The association between migraine and physical exercise. J. Headache 2018, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evcili, G.; Utku, U.; Öğün, M.N.; Özdemir, G. Early and long period follow-up results of low glycemic index diet for migraine prophylaxis. J. Turk. Soc. Algol. 2018, 30, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeghi Jahromi, S.; Ghorbani, Z.; Martelletti, P.; Lampl, C.; Togha, M.; On behalf of the School of Advanced Studies of the European Headache Federation (EHF-SAS). Association of diet and headache. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazerani, P. Migraine and Diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervenka, M.C.; Wood, S.; Bagary, M.; Balabanov, A.; Bercovici, E.; Brown, M.G.; Devinsky, O.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Doherty, C.P.; Felton, E.; et al. International Recommendations for the Management of Adults Treated with Ketogenic Diet Therapies. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, C.; Ballerini, G.; Barbanti, P.; Bernardini, A.; D’Arrigo, G.; Egeo, G.; Frediani, F.; Garbo, R.; Pierangeli, G.; Prudenzano, M.P.; et al. Applications of Ketogenic Diets in Patients with Headache: Clinical Recommendations. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, C.; Pinto, A.; Ienca, R.; Coppola, G.; Sirianni, G.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Parisi, V.; Serrao, M.; Spagnoli, A.; Vestri, A.; et al. A Randomized Double-Blind, Cross-Over Trial of very Low-Calorie Diet in Overweight Migraine Patients: A Possible Role for Ketones? Nutrients 2019, 11, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamura, C.; Cecchi, G.; Bravo, M.; Brunelli, N.; Laudisio, A.; Caprio, P.D.; Botti, G.; Paolucci, M.; Khazrai, Y.M.; Vernieri, F. The Healthy Eating Plate Advice for Migraine Prevention: An Interventional Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Xu, C.; Duan, H.; Tian, X.; Zhang, D. Heritability and genome-wide association analyses of fasting plasma glucose in Chinese adult twins. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, K.R.; Johnson, Y.L.; Smitherman, T.A. Migraine. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 138, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, V.; Gervil, M.; Kyvik, K.O.; Olesen, J.; Russell, M.B. The inheritance of migraine with aura estimated by means of structural equation modelling. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 36, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merikangas, K.; Tierney, C.; Martin, N.; Heath, A.; Risch, N. Genetics of migraine in the Australian Twin Registry. New Adv. Headache Res. 1994, 4, 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, B.; Bille, B.; Pedersen, N.L. Genetic influence in headaches: A Swedish twin study. Headache J. Head Face Pain 1995, 35, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honkasalo, M.L.; Kaprio, J.; Winter, T.; Heikkilä, K.; Sillanpää, M.; Koskenvuo, M. Migraine and concomitant symptoms among 8167 adult twin pairs. Headache J. Head Face Pain 1995, 35, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervil, M.; Ulrich, V.; Kaprio, J.; Olesen, J.; Russell, M. The relative role of genetic and environmental factors in migraine without aura. Neurology 1999, 53, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessman, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; Kallela, M.; Palotie, A. The molecular genetics of migraine. Ann. Med. 2004, 36, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, E.J.; Van Baal, C.; Gaist, D.; Kallela, M.; Kaprio, J.; Svensson, D.A.; Nyholt, D.R.; Martin, N.G.; MacGregor, A.J.; Cherkas, L.F. Genetic and environmental influences on migraine: A twin study across six countries. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2003, 6, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyholt, D.R.; Gillespie, N.G.; Heath, A.C.; Merikangas, K.R.; Duffy, D.L.; Martin, N.G. Latent class and genetic analysis does not support migraine with aura and migraine without aura as separate entities. Genet. Epidemiol. 2004, 26, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.K.; Hur, Y.M.; Bouchard, T.J., Jr.; Hassanein, R.S.; Barter, R. Migraine in twins raised together and apart. Headache J. Head Face Pain 1998, 38, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, D.A.; Larsson, B.; Waldenlind, E.; Pedersen, N.L. Shared rearing environment in migraine: Results from twins reared apart and twins reared together. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2003, 43, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, K.L. Genetics of migraine: An update. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2006, 46, S19–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Report on Diabetes; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen, J.; Willemsen, G.; Chen, W.-M.; de Geus, E.J.C.; Boomsma, D.I. Heritability of metabolic syndrome traits in a large population-based sample. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2914–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.B.; Groop, L. Genetics of type 2 diabetes-pitfalls and possibilities. Genes 2015, 6, 87–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øie, L.R.; Kurth, T.; Gulati, S.; Dodick, D.W. Migraine and risk of stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Heath, A.C.; Madden, P.A.F.; Martin, N.G.; Nyholt, D.R. Shared Genetic Factors Underlie Migraine and Depression. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2016, 19, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewuyi, E.O.; Sapkota, Y.; Auta, A.; Yoshihara, K.; Nyegaard, M.; Griffiths, L.R.; Montgomery, G.W.; International Endogene Consortium IEC; andMe Research Team; International Headache Genetics Consortium IHGH; et al. Shared Molecular Genetic Mechanisms Underlie Endometriosis and Migraine Comorbidity. Genes 2020, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewert, K.M.; Klarin, D.; Damrauer, S.M.; Chang, K.-M.; Tsao, P.S.; Assimes, T.L.; Davey Smith, G.; Voight, B.F.; The International Headache Genetics, C. Cross-trait analyses with migraine reveal widespread pleiotropy and suggest a vascular component to migraine headache. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Finucane, H.K.; Anttila, V.; Gusev, A.; Day, F.R.; Loh, P.R.; Duncan, L.; Perry, J.R.; Patterson, N.; Robinson, E.B.; et al. An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainero, I.; Roveta, F.; Vacca, A.; Noviello, C.; Rubino, E. Migraine pathways and the identification of novel therapeutic targets. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.J.; Cai, C.Y.; Yu, P.; Lv, J.; Ling, C.; Shi, W.T.; Jiao, H.X.; Chang, B.C.; Yang, F.H.; Tian, Y.; et al. Quantitative candidate gene association studies of metabolic traits in Han Chinese type 2 diabetes patients. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 15471–15481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, I.; Luan, J.a.; Middelberg, R.P.S.; Harding, A.-H.; Franks, P.W.; Jakes, R.W.; Clayton, D.; Schafer, A.J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Wareham, N.J. Candidate gene association study in type 2 diabetes indicates a role for genes involved in β-cell function as well as insulin action. PLoS Biol. 2003, 1, e20. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.E.; Walker, M. Genetics of Insulin Resistance and the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2016, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, I. Genetics of Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2005, 22, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubino, E.; Ferrero, M.; Rainero, I.; Binello, E.; Vaula, G.; Pinessi, L. Association of the C677T polymorphism in the MTHFR gene with migraine: A meta-analysis. Cephalalgia 2009, 29, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürks, M.; Rist, P.M.; Kurth, T. MTHFR 677C>T and ACE D/I polymorphisms in migraine: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Headache 2010, 50, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaan, Z.; Gaysina, D.; Cohen-Woods, S.; Craddock, N.; Jones, L.; Korszun, A.; Owen, M.; Mente, A.; McGuffin, P.; Farmer, A. Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene Variant (MTHFR C677T) and Migraine: A Case Control Study and Meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2011, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todt, U.; Freudenberg, J.; Goebel, I.; Netzer, C.; Heinze, A.; Heinze-Kuhn, K.; Göbel, H.; Kubisch, C. MTHFR C677T polymorphism and migraine with aura. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 60, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaunisto, M.A.; Kallela, M.; Hämäläinen, E.; Kilpikari, R.; Havanka, H.; Harno, H.; Nissilä, M.; Säkö, E.; Ilmavirta, M.; Liukkonen, J.; et al. Testing of variants of the MTHFR and ESR1 genes in 1798 Finnish individuals fails to confirm the association with migraine with aura. Cephalalgia 2006, 26, 1462–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wu, X.; Zhi, X.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, G. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese population: A meta-analysis of 29 case-control studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, C.; Xiao, S.H.; Wan, B. Association of tagging SNPs in the MTHFR gene with risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus and serum homocysteine levels in a Chinese population. Dis. Markers 2014, 2014, 725731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rubeaan, K.; Siddiqui, K.; Saeb, A.T.M.; Nazir, N.; Al-Naqeb, D.; Al-Qasim, S. ACE I/D and MTHFR C677T polymorphisms are significantly associated with type 2 diabetes in Arab ethnicity: A meta-analysis. Gene 2013, 520, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errera, F.I.; Silva, M.E.; Yeh, E.; Maranduba, C.M.; Folco, B.; Takahashi, W.; Pereira, A.C.; Krieger, J.E.; Passos-Bueno, M.R. Effect of polymorphisms of the MTHFR and APOE genes on susceptibility to diabetes and severity of diabetic retinopathy in Brazilian patients. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2006, 39, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirozzi, F.F.; Belini Junior, E.; Okumura, J.V.; Salvarani, M.; Bonini-Domingos, C.R.; Ruiz, M.A. The relationship between of ACE I/D and the MTHFR C677T polymorphisms in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a population of Brazilian obese patients. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 62, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtain, R.; Tajouri, L.; Lea, R.; MacMillan, J.; Griffiths, L. No mutations detected in the INSR gene in a chromosome 19p13 linked migraine pedigree. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 49, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaunisto, M.A.; Tikka, P.J.; Kallela, M.; Leal, S.M.; Papp, J.C.; Korhonen, A.; Hämäläinen, E.; Harno, H.; Havanka, H.; Nissilä, M.; et al. Chromosome 19p13 loci in Finnish migraine with aura families. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2005, 132B, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ’t Hart, L.M.; Stolk, R.P.; Dekker, J.M.; Nijpels, G.; Grobbee, D.E.; Heine, R.J.; Maassen, J.A. Prevalence of variants in candidate genes for type 2 diabetes mellitus in The Netherlands: The Rotterdam study and the Hoorn study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, L.T.; Stolk, R.; Heine, R.; Grobbee, D.; Van Der Does, F.; Maassen, J. Association of the insulin-receptor variant Met-985 with hyperglycemia and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in the Netherlands: A population-based study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996, 59, 1119. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, L.; Hansen, T.; Clausen, J.O.; Echwald, S.M.; Urhammer, S.A.; Rasmussen, S.K.; Pedersen, O. The Val985Met insulin-receptor variant in the Danish Caucasian population: Lack of associations with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus or insulin resistance. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1997, 60, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaheri, S.; Hajilooi, M.; Rafiei, A. The G-308A promoter variant of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene is associated with migraine without aura. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Fu, P. The TNF-alpha-308 G/A polymorphism is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus: An updated meta-analysis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golshani, H.; Haghani, K.; Dousti, M.; Bakhtiyari, S. Association of TNF-α 308 G/A Polymorphism With Type 2 Diabetes: A Case–Control Study in the Iranian Kurdish Ethnic Group. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2015, 6, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.H.; Ding, Y.L.; Xiu, L.C.; Pan, H.Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhong, S.Q.; Liu, W.W.; Rao, S.Q.; Kong, D.L. A meta-analysis of the association between TNF-α-308 G>A polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Han Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.-N.; Zhao, C.; Sun, C.-H.; Li, Y. Meta-Analysis of TNF 308 G/A Polymorphism and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.P.; Grove, J.; Daly, A.K.; Stewart, M.W.; Avery, P.J.; Walker, M. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha gene promoter polymorphism and decreased insulin resistance. Diabetologia 1998, 41, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, C.; Niu, Y.; Sun, C. Lack of association between TNF 238 G/A polymorphism and type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol. 2009, 46, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Qu, Y. Association of tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter polymorphism (TNF-α 238 G/A and TNF-α 308 G/A) with diabetic mellitus, diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy: A meta-analysis. Curr. Eye Res. 2014, 39, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Han, R.; Chen, M.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, X.; Ma, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Jiang, S. Associations of estrogen receptor alpha gene polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2018, 50, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, T.-H.; Lu, W.-H.; Mu, P.-W.; Yang, Y.-F.; Liang, W.-W.; Li, C.-X.; Lin, G.-P. Estrogen receptor alpha gene polymorphism associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and the serum lipid concentration in Chinese women in Guangzhou. Chin. Med. J. 2006, 119, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, M.M.; Freedman, B.I.; Langefeld, C.D.; Williams, A.H.; Hicks, P.J.; Colicigno, C.J.; Beck, S.R.; Brown, W.M.; Rich, S.S.; Bowden, D.W. A genome-wide scan for type 2 diabetes in African-American families reveals evidence for a locus on chromosome 6q. Diabetes 2004, 53, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, N.J.; Lea, R.A.; Quinlan, S.; MacMillan, J.; Griffiths, L.R. The estrogen receptor 1 G594A polymorphism is associated with migraine susceptibility in two independent case/control groups. Neurogenetics 2004, 5, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Colson, N.J.; Lea, R.A.; Quinlan, S.; MacMillan, J.; Griffiths, L.R. Investigation of hormone receptor genes in migraine. Neurogenetics 2005, 6, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürks, M.; Rist, P.M.; Kurth, T. Sex hormone receptor gene polymorphisms and migraine: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 1306–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oterino, A.; Pascual, J.; de Alegría, C.R.; Valle, N.; Castillo, J.; Bravo, Y.; González, F.; Sánchez-Velasco, P.; Cayón, A.; Leyva-Cobián, F. Association of migraine and ESR1 G325C polymorphism. Neuroreport 2006, 17, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.M.; Martins-Oliveira, A.; Speciali, J.G.; Luizon, M.R.; Izidoro-Toledo, T.C.; Silva, P.S.; Dach, F.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase haplotypes associated with aura in patients with migraine. DNA Cell Biol. 2011, 30, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.M.; Luizon, M.R.; Speciali, J.G.; Martins-Oliveira, A.; Dach, F.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Interaction among nitric oxide (NO)-related genes in migraine susceptibility. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 370, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriello, M.; Oterino, A.; Pascual, J.; Castillo, J.; Colás, R.; Alonso-Arranz, A.; Ruiz-Alegría, C.; Quintela, E.; Montón, F.; Ruiz-Lavilla, N. Lack of association of endothelial nitric oxide synthase polymorphisms and migraine. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2008, 48, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, E.; Kofteridis, D.; Stratigi, K.; Petraki, E.; Vazgiourakis, V.; Fragouli, E.; Mamoulakis, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Goulielmos, G.N. Intron 4 a/b polymorphism of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene is associated with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes in a genetically homogeneous population. Hum. Immunol. 2008, 69, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhang, X.; Kang, S.; Wu, Y. Association of endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Endocr. J. 2013, 60, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrab-Mohseni, M.; Tabatabaei-Malazy, O.; Hasani-Ranjbar, S.; Amiri, P.; Kouroshnia, A.; Bazzaz, J.T.; Farahani-Shrhabi, M.; Larijani, B.; Amoli, M.M. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase VNTR (intron 4 a/b) polymorphism association with type 2 diabetes and its chronic complications. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 91, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eröz, R.; Bahadir, A.; Dikici, S.; Tasdemir, S. Association of endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms (894G/T,−786T/C, G10T) and clinical findings in patients with migraine. Neuromol. Med. 2014, 16, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroni, B.; Rao, R.; Liberini, P.; Venturelli, E.; Cossandi, M.; Archetti, S.; Caimi, L.; Padovani, A. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (Glu298Asp) polymorphism is an independent risk factor for migraine with aura. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2006, 46, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, L.D.; Barlassina, C.; Citterio, L.; Galluccio, E.; Berzuini, C.; Setola, E.; Valsecchi, G.; Lucotti, P.; Pozza, G.; Bernardinelli, L.; et al. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase polymorphisms are associated with type 2 diabetes and the insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressler, J.; Pankow, J.S.; Coresh, J.; Boerwinkle, E. Interaction between the NOS3 gene and obesity as a determinant of risk of type 2 diabetes: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Martín, E.; Martínez, C.; Serrador, M.; Alonso-Navarro, H.; Navacerrada, F.; Agúndez, J.A.G.; Jiménez-Jiménez, F.J. Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) polymorphisms and risk for migraine. J. Neurol. 2010, 257, 1482–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldırım, S.; Akar, S.; Kuyucu, M.; Yıldırım, A.; Dane, S.; Aygül, R. Paraoxonase 1 gene polymorphisms, paraoxonase/arylesterase activities and oxidized low-density lipoprotein levels in patients with migraine. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2011, 29, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, G.; Negro, A.; D’Alonzo, L.; Aimati, L.; Simmaco, M.; Martelletti, P.; Borro, M. Lack of association between oxidative stress-related gene polymorphisms and chronic migraine in an Italian population. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flekač, M.; Škrha, J.; Zidkova, K.; Lacinova, Z.; Hilgertova, J. Paraoxonase 1 gene polymorphisms and enzyme activities in diabetes mellitus. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agachan, B.; Yilmaz, H.; Karaali, Z.; İsbir, T. Paraoxonase 55 and 192 polymorphism and its relationship to serum paraoxonase activity and serum lipids in Turkish patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Cell Biochem. Funct. Cell. Biochem. Modul. Act. Agents Dis. 2004, 22, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabina, S.-A.P.; Lehner, A.N.; Frank, E.; Parthasarathy, S.; Santanam, N. Oxidative inactivation of paraoxonase—Implications in diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2005, 1725, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, S.; Jansen, E.; Kruijshoop, M.; Beekhof, P.; Blaak, E.; Van Der Kallen, C.; Van Greevenbroek, M.; Feskens, E. Paraoxonase 1 phenotype distribution and activity differs in subjects with newly diagnosed Type 2 diabetes (the CODAM Study). Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shao, A.; Jiang, Z.; Tsai, H.; Liu, W. The exploration of mechanisms of comorbidity between migraine and depression. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4505–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, S.; Cox, H.C.; Lea, R.A.; Griffiths, L.R. The role of the MTHFR gene in migraine. Headache 2012, 52, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Geng, P.; Ma, M.; Yu, S.; Yang, M.; He, M.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, W. MTHFR C677T polymorphism and migraine risk: A meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 336, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Pradhan, S.; Mittal, B. Role of the ACE ID and MTHFR C677T polymorphisms in genetic susceptibility of migraine in a north Indian population. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 277, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürks, M.; Zee, R.Y.; Buring, J.E.; Kurth, T. MTHFR 677C->T and ACE D/I polymorphisms and migraine attack frequency in women. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodhini, D.; Sandhiya, M.; Ghosh, S.; Majumder, P.P.; Rao, M.R.; Mohan, V.; Radha, V. Association of His1085His INSR gene polymorphism with type 2 diabetes in South Indians. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2012, 14, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masternak, M.M.; Al-Regaiey, K.A.; Lim, M.M.D.R.; Jimenez-Ortega, V.; Panici, J.A.; Bonkowski, M.S.; Bartke, A. Effects of caloric restriction on insulin pathway gene expression in the skeletal muscle and liver of normal and long-lived GHR-KO mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2005, 40, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villegas, R.; Delahanty, R.; Williams, S.; Li, H.; O’Brian, R.; Shi, J.; Cai, Q.; Xiang, Y.B.; Shu, X.O. Genetic Variation and Insulin Resistance in Middle-Aged Chinese Men. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2015, 79, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, T.M.; Haider, N.; Kahn, C.R. Defining the underlying defect in insulin action in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rahilly, S.; Krook, A.; Morgan, R.; Reese, A.; Flier, J.; Moller, D. Insulin receptor and insulin-responsive glucose transporter (GLUT 4) mutations and polymorphisms in a Welsh type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic population. Diabetologia 1992, 35, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainero, I.; Grimaldi, L.; Salani, G.; Valfre, W.; Rivoiro, C.; Savi, L.; Pinessi, L. Association between the tumor necrosis factor-α−308 G/A gene polymorphism and migraine. Neurology 2004, 62, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, E.; Bakhtadze, E.; Cilio, C.; Agardh, E.; Groop, L.; Agardh, C.-D. Association between LTA, TNF and AGER polymorphisms and late diabetic complications. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, L.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Dongiovanni, P.; Santorelli, G.; Branchi, A.; Taioli, E.; Fiorelli, G.; Fargion, S. Tumor necrosis factor α promoter polymorphisms and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.G.; Li, Y.; Ryan, M.F.; Gibney, E.R.; Brennan, L.; Roche, H.M.; Williams, C.M.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Vimaleswaran, K.S. Association of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter polymorphism with change in triacylglycerol response to sequential meals. Nutr. J. 2015, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, N.J.; Lea, R.A.; Quinlan, S.; Griffiths, L.R. No role for estrogen receptor 1 gene intron 1 Pvu II and exon 4 C325G polymorphisms in migraine susceptibility. BMC Med. Genet. 2006, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lipton, R.B.; Diamond, S.; Reed, M.; Diamond, M.L.; Stewart, W.F. Migraine diagnosis and treatment: Results from the American Migraine Study II. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2001, 41, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, F.; Alessi, C.; Maggino, T.; Zanchin, G. Headache during pregnancy. Cephalalgia 1997, 17, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, E.A. Headache and hormone replacement therapy in the postmenopausal woman. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2009, 11, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, E.A. Oestrogen and attacks of migraine with and without aura. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Mehrotra, S.; Villalón, C.M.; Perusquía, M.; Saxena, P.R.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A. Potential role of female sex hormones in the pathophysiology of migraine. Pharmacology 2007, 113, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oterino, A.; Toriello, M.; Cayón, A.; Castillo, J.; Colas, R.; Alonson-Arranz, A.; Ruiz-Alegria, C.; Quintela, E.; Monton, F.; Ruiz-Lavilla, N.; et al. Multilocus analyses reveal involvement of the ESR1, ESR2, and FSHR genes in migraine. Headache 2008, 48, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ereqat, S.; Cauchi, S.; Eweidat, K.; Elqadi, M.; Nasereddin, A. Estrogen receptor 1 gene polymorphisms (PvuII and XbaI) are associated with type 2 diabetes in Palestinian women. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, G.; Cseh, K.; Winkler, G.; Vargha, P.; Braun, E.; Takács, I.; Lakatos, P. Vitamin D and estrogen receptor gene polymorphisms in type 2 diabetes mellitus and in android type obesity. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 144, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motawi, T.M.; El-Rehany, M.A.; Rizk, S.M.; Ramzy, M.M.; El-Roby, D.M. Genetic polymorphism of estrogen receptor alpha gene in Egyptian women with type II diabetes mellitus. Meta Gene 2015, 6, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnér, C.; Svartberg, J.; Giwercman, A.; Giwercman, Y.L. Estrogen receptor alpha single nucleotide polymorphism as predictor of diabetes type 2 risk in hypogonadal men. Aging Male 2013, 16, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oliveira-Paula, G.H.; Lacchini, R.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: From biochemistry and gene structure to clinical implications of NOS3 polymorphisms. Gene 2016, 575, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, G. Enhanced, unaltered and impaired nitric oxide-mediated endothelium-dependent relaxation in experimental diabetes mellitus: Importance of disease duration. Diabetologia 1999, 42, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukry, A.; Shalaby, S.M.; Abdelazim, S.; Abdelazim, M.; Ramadan, A.; Ismail, M.I.; Fouad, M. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms and the risk of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2012, 16, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J. Nitric oxide-related drag targets in headache. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolisso, G.; Tagliamonte, M.; Rizzo, M.; Giugliano, D. Advancing age and insulin resistance: New facts about an ancient history. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 29, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Bonafé, M.; Marfella, R.; Ragno, E.; Giugliano, D.; Franceschi, C.; Paolisso, G. LL-paraoxonase genotype is associated with a more severe degree of homeostasis model assessment IR in healthy subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Abbott, C.A.; Mackness, M.I.; Kumar, S.; Boulton, A.J.; Durrington, P.N. Serum paraoxonase activity, concentration, and phenotype distribution in diabetes mellitus and its relationship to serum lipids and lipoproteins. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 1812–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Suehiro, T.; Inoue, M.; Nakauchi, Y.; Morita, T.; Arii, K.; Ito, H.; Kumon, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Serum paraoxonase activity and its relationship to diabetic complications in patients with non—Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 1998, 47, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Rotter, J.I. Genome-wide association studies. JAMA 2019, 322, 1705–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gormley, P.; Anttila, V.; Winsvold, B.S.; Palta, P.; Esko, T.; Pers, T.H.; Farh, K.-H.; Cuenca-Leon, E.; Muona, M.; Furlotte, N.A. Meta-analysis of 375,000 individuals identifies 38 susceptibility loci for migraine. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, V.; Winsvold, B.S.; Gormley, P.; Kurth, T.; Bettella, F.; McMahon, G.; Kallela, M.; Malik, R.; de Vries, B.; Terwindt, G.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies new susceptibility loci for migraine. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautakangas, H.; Winsvold, B.S.; Ruotsalainen, S.E.; Bjornsdottir, G.; Harder, A.V.E.; Kogelman, L.J.A.; Thomas, L.F.; Noordam, R.; Benner, C.; Gormley, P.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of 102,084 migraine cases identifies 123 risk loci and subtype-specific risk alleles. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Taliun, D.; Thurner, M.; Robertson, N.R.; Torres, J.M.; Rayner, N.W.; Payne, A.J.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Scott, R.A.; Grarup, N.; et al. Fine-mapping type 2 diabetes loci to single-variant resolution using high-density imputation and islet-specific epigenome maps. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagou, V.; Mägi, R.; Hottenga, J.-J.; Grallert, H.; Perry, J.R.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Marullo, L.; Rybin, D.; Jansen, R.; Min, J.L. Sex-dimorphic genetic effects and novel loci for fasting glucose and insulin variability. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Spracklen, C.N.; Zhang, W.; Ng, M.C.Y.; Petty, L.E.; Kitajima, H.; Yu, G.Z.; Rüeger, S.; Speidel, L.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Trans-ancestry genetic study of type 2 diabetes highlights the power of diverse populations for discovery and translation. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujkovic, M.; Keaton, J.M.; Lynch, J.A.; Miller, D.R.; Zhou, J.; Tcheandjieu, C.; Huffman, J.E.; Assimes, T.L.; Lorenz, K.; Zhu, X.; et al. Discovery of 318 new risk loci for type 2 diabetes and related vascular outcomes among 1.4 million participants in a multi-ancestry meta-analysis. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.; Voight, B.F.; Lyssenko, V.; Burtt, N.P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Chen, H.; Roix, J.J.; Kathiresan, S.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Daly, M.J. Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride levels. Science 2007, 316, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J.; Mohlke, K.L.; Bonnycastle, L.L.; Willer, C.J.; Li, Y.; Duren, W.L.; Erdos, M.R.; Stringham, H.M.; Chines, P.S.; Jackson, A.U. A genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in Finns detects multiple susceptibility variants. Science 2007, 316, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.P.; Voight, B.F.; Teslovich, T.M.; Ferreira, T.; Segrè, A.V.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Khan, H.; Grallert, H.; Mahajan, A.; et al. Large-scale association analysis provides insights into the genetic architecture and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, A.; Wessel, J.; Willems, S.M.; Zhao, W.; Robertson, N.R.; Chu, A.Y.; Gan, W.; Kitajima, H.; Taliun, D.; Rayner, N.W.; et al. Refining the accuracy of validated target identification through coding variant fine-mapping in type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voight, B.F.; Scott, L.J.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Morris, A.P.; Dina, C.; Welch, R.P.; Zeggini, E.; Huth, C.; Aulchenko, Y.S.; Thorleifsson, G.; et al. Twelve type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci identified through large-scale association analysis. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anttila, V.; Stefansson, H.; Kallela, M.; Todt, U.; Terwindt, G.M.; Calafato, M.S.; Nyholt, D.R.; Dimas, A.S.; Freilinger, T.; Müller-Myhsok, B.; et al. Genome-wide association study of migraine implicates a common susceptibility variant on 8q22.1. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasman, D.I.; Schürks, M.; Anttila, V.; de Vries, B.; Schminke, U.; Launer, L.J.; Terwindt, G.M.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; Fendrich, K.; Völzke, H. Genome-wide association study reveals three susceptibility loci for common migraine in the general population. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.L.H.; Antevska, A.; Link, B.A.; Bogin, B.; Burke, S.J.; Dupuy, S.D.; Collier, J.J.; Levine, Z.A.; Karlstad, M.D.; Do, T.D. α-CGRP disrupts amylin fibrillization and regulates insulin secretion: Implications on diabetes and migraine. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 5853–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, Z.O.; Uluduz, D.; Keskin, F.E.; Erenler, F.; Balcı, H.; Uygunoğlu, U.; Saip, S.; Göksan, B.; Siva, A. Determinants of glucose metabolism and the role of NPY in the progression of insulin resistance in chronic migraine. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward-Caviness, C.K.; Neas, L.M.; Blach, C.; Haynes, C.S.; LaRocque-Abramson, K.; Grass, E.; Dowdy, E.; Devlin, R.B.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Cascio, W.E. Genetic variants in the bone morphogenic protein gene family modify the association between residential exposure to traffic and peripheral arterial disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152670. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Vazquez, I.; Fernández-Veledo, S.; Krämer, D.K.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Garcia-Guerra, L.; Lorenzo, M. Insulin resistance associated to obesity: The link TNF-alpha. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syreeni, A.; Sandholm, N.; Sidore, C.; Cucca, F.; Haukka, J.; Harjutsalo, V.; Groop, P.H. Genome-wide search for genes affecting the age at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. Intern. Med. 2021, 289, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-K.; Liang, C.-S.; Lin, G.-Y.; Tsai, C.-L.; Lee, J.-T.; Sung, Y.-F.; Lin, Y.-K.; Hung, K.-S.; Chen, W.-L.; Yang, F.-C. Identifying genetic variants for age of migraine onset in a Han Chinese population in Taiwan. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hassany, L.; Haas, J.; Piccininni, M.; Kurth, T.; Maassen Van Den Brink, A.; Rohmann, J.L. Giving Researchers a Headache—Sex and Gender Differences in Migraine. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 549038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, B.; Anttila, V.; Freilinger, T.; Wessman, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; Kallela, M.; Artto, V.; Vijfhuizen, L.S.; Göbel, H.; Dichgans, M.; et al. Systematic re-evaluation of genes from candidate gene association studies in migraine using a large genome-wide association data set. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Gamez, E.; Trynka, G. From GWAS to Function: Using Functional Genomics to Identify the Mechanisms Underlying Complex Diseases. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Candidate Genes | Function of Relative Protein | Polymorphisms | Migraine | Glucose-Related Traits | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supporting Association (Reference) | Not Supporting Association (Reference) | Supporting Association (Reference) | Not Supporting Association (Reference) | |||
| Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) | MTHFR enzyme transforms 5, 10-methylene tetrahydrofolate to 5-methyl tetrahydrofolate, an essential part of folate and homocysteine metabolism | C677T | [142,143,144] | [145,146] | [147,148,149] | [150,151] |
| Insulin receptor (INSR) | INSR mediates insulin’s activity on target cells and plays an important function in the regulation of glucose homeostasis | Val985Met, other polymorphisms | [72,73] | [152,153] | [154,155] | [156] |
| Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) | TNF initiates and regulates the chain of events that leads to an inflammatory response | −308 (G/A) | [142,157] | [158,159,160] | [161] | |
| −238 (A/G) | [162] | [163,164] | ||||
| Estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1) | ESR1 has expressed variety of different tissues and organs, including vascular endothelial cells and trigeminal neurones with the linked with hormone system | Pvull (−397 T>C, rs2234693) and Xbal (−351 A>G, rs9340799) | [165] | [166,167] | ||
| G594A | [168,169,170] | [171] | ||||
| Nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3) | NOS3 synthesise nitric oxide from L-arginine, a crucial endogenous endothelial-derived relaxing factor | VNTR (27 bp) in intron 4 | [172,173] | [174] | [175,176,177] | |
| Glu298Asp | [178,179] | [172] | [180,181] | |||
| Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) | Enzyme involved in preventing LDL oxidation and endothelial dysfunction | Gln192Arg | [182] | [183,184] | [185,186,187,188] | |
| 2022 IHGC Migraine | 2018 DIAGRAM T2D | 2021 MAGIC FG | 2021 MAGIC FI | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genes | SNP | CHR | BP | EA | NEA | OR | p-Value | OR | p-Value | OR | p-Value | OR | p-Value |
| PRDM16 | rs10218452 | 1 | 3,075,597 | G | A | 1.12 | 7.26 × 10−71 | 0.99 | 0.27 | 1.00 | 0.450 | 1.00 | 0.985 |
| CAMTA1 | rs10128028 | 1 | 7,055,843 | T | C | 1.03 | 7.66 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.047 | 1.00 | 0.118 | 1.00 | 0.625 |
| TMEM51 | rs12057629 | 1 | 15,538,493 | C | T | 1.04 | 9.38 × 10−14 | 0.99 | 0.4 | 1.00 | 0.666 | 1.00 | 0.999 |
| INPP5B | rs28739509 | 1 | 38,366,907 | C | T | 1.04 | 2.64 × 10−10 | 1.00 | 0.6 | 1.00 | 0.381 | 1.00 | 0.446 |
| C1orf87 | rs11578492 | 1 | 60,529,980 | C | A | 1.03 | 6.25 × 10−9 | - | - | 1.00 | 0.920 | 1.00 | 0.814 |
| near LEPR | rs7511672 | 1 | 66,178,918 | G | A | 1.03 | 1.43 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.17 | 1.00 | 0.681 | 1.00 | 0.388 |
| near RP4-598G3.1 | rs56019088 | 1 | 73,891,226 | I | D | 1.05 | 7.32 × 10−13 | - | - | 1.00 | 0.765 | 1.00 | 0.708 |
| TGFBR3 | rs11165300 | 1 | 92,177,663 | G | T | 1.03 | 4.72 × 10−8 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 0.344 | 0.99 | 0.035 |
| near TSPAN2 | rs2078371 | 1 | 115,677,183 | C | T | 1.11 | 5.87 × 10−42 | 0.97 | 0.0025 | 1.01 | 0.130 | 0.99 | 0.230 |
| MEF2D | rs2274319 | 1 | 156,450,873 | T | C | 1.08 | 2.74 × 10−41 | 1.01 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 0.562 | 0.99 | 0.052 |
| RABGAP1L | rs11487328 | 1 | 174,601,659 | G | C | 1.05 | 1.70 × 10−8 | - | - | 1.00 | 0.633 | 1.00 | 0.689 |
| PLA2G4A | rs6668908 | 1 | 186,913,055 | G | T | 1.03 | 2.22 × 10−8 | 1.01 | 0.22 | 1.00 | 0.629 | 1.01 | 0.045 |
| near MAPKAPK2 | rs56140113 | 1 | 206,843,108 | C | T | 1.04 | 7.76 × 10−9 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.195 | 1.00 | 0.638 |
| KIF26B | rs72764846 | 1 | 245,847,455 | G | A | 1.04 | 5.41 × 10−9 | 1.01 | 0.14 | - | - | - | - |
| MACF1 | rs1472662 | 1 | 39,590,409 | T | G | 1.04 | 1.75 × 10−8 | 1.08 | 1.60 × 10−22 | 1.01 | 0.011 | 1.01 | 0.075 |
| near ADAMTSL4 | rs6693567 | 1 | 150,510,660 | C | T | 1.04 | 1.25 × 10−13 | 0.98 | 0.011 | 1.01 | 0.032 | 1.00 | 0.510 |
| THADA | rs12712881 | 2 | 43,649,780 | A | C | 1.03 | 3.50 × 10−10 | 1.03 | 1.50 × 10−7 | 1.01 | 0.131 | 1.00 | 0.865 |
| ANKRD36C | rs4907224 | 2 | 96,576,609 | A | T | 1.04 | 1.63 × 10−9 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 0.877 | 1.00 | 0.410 |
| ZEB2 | rs7564469 | 2 | 145,258,445 | C | T | 1.04 | 5.06 × 10−9 | 1.03 | 0.00064 | 1.00 | 0.360 | 1.00 | 0.247 |
| near AC064865.1 | rs895219 | 2 | 146,037,564 | C | T | 1.04 | 3.74 × 10−11 | 0.99 | 0.065 | 1.00 | 0.260 | 0.99 | 0.097 |
| MYO3B | rs4668251 | 2 | 171,234,235 | G | C | 1.03 | 7.58 × 10−9 | 1.01 | 0.26 | 1.00 | 0.901 | 1.00 | 0.505 |
| near HOXD10 | rs72923449 | 2 | 176,978,383 | C | A | 1.08 | 4.66 × 10−8 | 1.02 | 0.23 | - | - | - | - |
| CARF | rs138556413 | 2 | 203,832,867 | C | T | 1.14 | 4.15 × 10−16 | 1.03 | 0.12 | - | - | - | - |
| near TRPM8 | rs10166942 | 2 | 234,825,093 | T | C | 1.10 | 9.35 × 10−51 | 0.99 | 0.26 | 1.00 | 0.273 | 1.00 | 0.754 |
| near RNU6-546P | rs843215 | 2 | 156,416,638 | G | A | 1.03 | 2.61 × 10−8 | 1.01 | 0.058 | 1.01 | 0.042 | 1.00 | 0.719 |
| ATRIP | rs7618883 | 3 | 48,498,456 | T | A | 1.03 | 4.16 × 10−8 | 0.99 | 0.13 | 0.99 | 0.010 | 0.99 | 0.074 |
| near TGFBR2 | rs7371912 | 3 | 30,472,786 | A | G | 1.04 | 1.06 × 10−14 | - | - | 1.00 | 0.800 | 1.00 | 0.746 |
| near HNRNPA3P8 | rs950570 | 3 | 80,302,512 | T | C | 1.06 | 1.30 × 10−8 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 1.00 | 0.704 | 1.00 | 0.984 |
| near CADM2 | rs73138150 | 3 | 86,149,109 | T | A | 1.03 | 1.95 × 10−8 | 0.99 | 0.041 | 1.00 | 0.349 | 1.00 | 0.609 |
| near C3orf38 | rs6795209 | 3 | 88,210,464 | A | G | 1.04 | 1.23 × 10−8 | - | - | 1.00 | 0.458 | 0.99 | 0.123 |
| ITGB5 | rs1499963 | 3 | 124,607,055 | C | T | 1.03 | 7.48 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.059 | 1.00 | 0.293 | 1.00 | 0.770 |
| near GPR149 | rs13078967 | 3 | 154,289,946 | A | C | 1.16 | 2.16 × 10−16 | 1.00 | 0.95 | - | - | - | - |
| near SEC63P2 | rs73805934 | 4 | 35,469,918 | G | C | 1.04 | 1.11 × 10−9 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.708 | 1.00 | 0.975 |
| near SPINK2 | rs7684253 | 4 | 57,727,311 | T | C | 1.04 | 4.21 × 10−14 | 1.00 | 0.79 | 1.00 | 0.404 | 1.01 | 0.318 |
| ANKDD1B | rs42854 | 5 | 74,963,277 | G | C | 1.04 | 9.40 × 10−13 | 0.95 | 3.80 × 10−13 | 1.01 | 0.221 | 0.99 | 0.057 |
| near SSBP2 | rs12653216 | 5 | 81,129,663 | T | C | 1.04 | 8.08 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.12 | 1.00 | 0.760 | 1.00 | 0.672 |
| near ZNF474 | rs11957829 | 5 | 121,515,195 | G | A | 1.04 | 1.58 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.41 | 1.00 | 0.839 | 1.00 | 0.885 |
| SNX24 | rs246326 | 5 | 122,306,398 | T | C | 1.05 | 6.80 × 10−10 | 1.01 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.807 | 1.00 | 0.617 |
| near POU4F3 | rs10038882 | 5 | 145,752,008 | T | C | 1.04 | 1.33 × 10−12 | 0.99 | 0.084 | 1.00 | 0.618 | 1.01 | 0.284 |
| TIGD6|HMGXB3 | rs4705403 | 5 | 149,380,493 | A | G | 1.05 | 1.18 × 10−8 | 1.00 | 0.68 | 1.00 | 0.354 | 1.00 | 0.877 |
| near NKX2-5 | rs6556059 | 5 | 172,645,766 | T | C | 1.03 | 8.16 × 10−10 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.99 | 0.158 | 1.01 | 0.286 |
| NSD1 | rs10866704 | 5 | 176,676,461 | A | T | 1.04 | 2.10 × 10−8 | - | - | 1.01 | 0.039 | 1.00 | 0.800 |
| PHACTR1 | rs9349379 | 6 | 12,903,957 | A | G | 1.08 | 1.41 × 10−47 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 1.00 | 0.415 | 1.00 | 0.132 |
| near PRL | rs9295536 | 6 | 22,131,929 | C | A | 1.04 | 7.75 × 10−12 | 1.01 | 0.34 | 1.00 | 0.812 | 1.00 | 0.126 |
| near IER3 | rs9468830 | 6 | 30,749,712 | T | G | 1.04 | 2.38 × 10−8 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.909 | 1.00 | 0.227 |
| EHMT2 | rs74434374 | 6 | 31,850,308 | C | A | 1.08 | 4.52 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.55 | - | - | - | - |
| KCNK5 | rs10456100 | 6 | 39,183,470 | T | C | 1.05 | 9.16 × 10−19 | 0.97 | 8.90 × 10−5 | 1.00 | 0.970 | 1.00 | 0.427 |
| near KRT19P1 | rs34273564 | 6 | 72,321,017 | T | C | 1.03 | 1.00 × 10−10 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.99 | 0.178 | 1.00 | 0.658 |
| FHL5 | rs11153082 | 6 | 97,059,666 | G | A | 1.09 | 7.26 × 10−54 | 1.00 | 0.68 | 1.00 | 0.689 | 1.00 | 0.974 |
| REV3L | rs6568677 | 6 | 111,713,302 | A | G | 1.04 | 2.09 × 10−8 | 1.02 | 0.0047 | 1.00 | 0.559 | 1.00 | 0.783 |
| near GJA1 | rs28455731 | 6 | 121,846,038 | T | G | 1.07 | 8.82 × 10−23 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 0.614 | 0.98 | 0.027 |
| near PCMT1 | rs9383843 | 6 | 150,133,954 | C | A | 1.03 | 1.35 × 10−9 | 1.01 | 0.047 | 1.00 | 0.355 | 1.00 | 0.983 |
| SUGCT | rs10234636 | 7 | 40,427,617 | T | C | 1.09 | 4.43 × 10−28 | 0.99 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 0.743 | 1.00 | 0.413 |
| MLXIPL | rs13235543 | 7 | 73,013,901 | C | T | 1.06 | 3.06 × 10−13 | 0.97 | 0.00038 | 1.00 | 0.419 | 0.98 | 0.003 |
| TSPAN12 | rs56067931 | 7 | 120,481,569 | C | T | 1.04 | 4.83 × 10−8 | 1.00 | 0.67 | 1.00 | 0.479 | 1.00 | 0.858 |
| PTK2B | rs11782789 | 8 | 27,266,287 | A | T | 1.04 | 3.03 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.18 | 1.00 | 0.139 | 1.00 | 0.510 |
| near RP11-573J24.1 | rs4739105 | 8 | 64,496,159 | T | C | 1.04 | 2.85 × 10−8 | 1.01 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.542 | 0.99 | 0.023 |
| NFIB | rs580845 | 9 | 14,103,618 | A | C | 1.03 | 4.30 × 10−8 | 0.99 | 0.31 | 1.00 | 0.778 | 1.00 | 0.226 |
| near RP11-373A6.1 | rs10156578 | 9 | 29,372,501 | C | G | 1.04 | 3.34 × 10−12 | 1.01 | 0.026 | 1.00 | 0.430 | 1.00 | 0.822 |
| TJP2 | rs7034179 | 9 | 71,746,838 | T | C | 1.04 | 1.60 × 10−16 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.99 | 0.496 | 1.01 | 0.684 |
| ZNF462 | rs17723637 | 9 | 109,687,403 | G | A | 1.04 | 8.63 × 10−9 | 1.00 | 0.63 | 1.00 | 0.427 | 1.00 | 0.226 |
| ASTN2 | rs3891689 | 9 | 119,258,583 | C | T | 1.06 | 2.28 × 10−21 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 1.01 | 0.087 | 1.00 | 0.887 |
| near EHMT1 | rs4278223 | 9 | 140,743,200 | T | A | 1.05 | 6.24 × 10−10 | 1.02 | 0.036 | - | - | - | - |
| near R-5SP299 | rs7916911 | 10 | 8,722,944 | T | G | 1.04 | 3.18 × 10−12 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.99 | 0.035 | 1.00 | 0.472 |
| near MLLT10 | rs10828247 | 10 | 21,822,856 | G | A | 1.03 | 7.51 × 10−9 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 1.00 | 0.834 | 1.00 | 0.561 |
| PLCE1 | rs2274224 | 10 | 96039597 | G | C | 1.06 | 3.28 × 10−26 | 1.00 | 0.76 | 1.00 | 0.648 | 1.00 | 0.113 |
| HPSE2 | rs12260159 | 10 | 100,702,737 | G | A | 1.09 | 7.33 × 10−16 | - | - | 1.00 | 0.459 | 1.00 | 0.846 |
| CNNM2 | rs12260436 | 10 | 104,741,114 | C | A | 1.04 | 7.29 × 10−10 | 0.99 | 0.12 | 1.00 | 0.786 | 1.00 | 0.581 |
| RBM20 | rs869432 | 10 | 112,502,662 | A | C | 1.03 | 3.54 × 10−8 | 1.02 | 0.0059 | - | - | - | - |
| HTRA1 | rs2672592 | 10 | 124,230,750 | T | G | 1.04 | 1.22 × 10−12 | 1.00 | 0.9 | 1.00 | 0.567 | 0.99 | 0.272 |
| near GPR26 | rs11248546 | 10 | 125,242,283 | C | T | 1.04 | 1.59 × 10−12 | 1.01 | 0.19 | 1.00 | 0.338 | 1.00 | 0.435 |
| INPP5A | rs200314499 | 10 | 134,479,675 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| near SPATA19 | rs10894756 | 11 | 133,745,852 | G | A | 1.03 | 2.83 × 10−8 | 1.00 | 0.51 | 1.01 | 0.018 | 1.00 | 0.890 |
| MRGPRE | rs12295710 | 11 | 3,249,984 | T | C | 1.05 | 2.86 × 10−16 | 1.00 | 0.89 | - | - | - | - |
| MRVI1 | rs4910165 | 11 | 10,674,044 | G | C | 1.06 | 1.09 × 10−24 | 1.02 | 0.00094 | 1.00 | 0.363 | 1.00 | 0.370 |
| near INSC | rs1003194 | 11 | 15,126,085 | A | G | 1.03 | 2.43 × 10−10 | 0.99 | 0.13 | 1.00 | 0.792 | 1.00 | 0.393 |
| MPPED2 | rs11031122 | 11 | 30,547,438 | C | T | 1.04 | 6.91 × 10−10 | 1.02 | 0.0031 | 1.00 | 0.122 | 1.00 | 0.669 |
| AMBRA1 | rs7932866 | 11 | 46,548,094 | A | G | 1.04 | 2.38 × 10−9 | 1.00 | 0.58 | 0.99 | 0.151 | 1.00 | 0.435 |
| near RAB3IL1 | rs12787928 | 11 | 61,697,078 | A | T | 1.03 | 6.85 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.615 | 0.99 | 0.084 |
| RBM14-RBM4|RBM4 | rs566673 | 11 | 66,401,373 | G | T | 1.03 | 9.07 × 10−9 | 1.01 | 0.1 | 1.00 | 0.955 | 1.00 | 0.713 |
| YAP1 | rs12226331 | 11 | 102,070,976 | T | A | 1.04 | 1.92 × 10−13 | 1.01 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 0.090 | 1.00 | 0.472 |
| near FGF6 | rs2160875 | 12 | 4,527,322 | C | T | 1.07 | 2.72 × 10−36 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.316 | 1.00 | 0.413 |
| PDZRN4 | rs1458170 | 12 | 41,901,277 | C | T | 1.04 | 5.75 × 10−9 | 0.98 | 0.016 | 1.00 | 0.187 | 1.00 | 0.929 |
| LRP1 | rs11172113 | 12 | 57,527,283 | T | C | 1.11 | 1.38 × 10−90 | 0.99 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.219 | 1.00 | 0.469 |
| ATP2B1 | rs4842676 | 12 | 90,091,782 | C | G | 1.04 | 2.26 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.34 | 1.00 | 0.391 | 1.00 | 0.380 |
| near RP11-690J15.1 | rs10777902 | 12 | 98,498,223 | A | C | 1.03 | 1.25 × 10−10 | 0.99 | 0.12 | 1.00 | 0.914 | 1.00 | 0.483 |
| NCOR2 | rs1271309 | 12 | 124,820,705 | G | A | 1.04 | 3.74 × 10−8 | 1.03 | 0.0035 | 0.99 | 0.246 | 1.00 | 0.851 |
| LRCH1 | rs7335684 | 13 | 47,193,696 | G | A | 1.03 | 1.05 × 10−8 | 0.99 | 0.035 | 1.00 | 0.845 | 1.00 | 0.810 |
| RNF219-AS1 | rs7996252 | 13 | 78,876,537 | T | C | 1.03 | 4.11 × 10−8 | 1.01 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.984 | 1.00 | 0.834 |
| near COL4A1 | rs2000660 | 13 | 110,788,441 | A | G | 1.05 | 4.95 × 10−8 | 1.00 | 0.77 | - | - | - | - |
| near RP11-384J4.2 | rs1245463 | 14 | 27,661,650 | A | G | 1.04 | 5.72 × 10−14 | 1.02 | 0.02 | 1.00 | 0.261 | 1.00 | 0.321 |
| near LRFN5 | rs1542668 | 14 | 42,548,912 | G | A | 1.03 | 2.53 × 10−8 | 1.01 | 0.46 | 1.00 | 0.450 | 1.01 | 0.095 |
| near ARID4A | rs28756401 | 14 | 58,761,912 | G | A | 1.03 | 6.40 × 10−9 | 0.97 | 9.70 × 10−7 | 1.00 | 0.699 | 1.00 | 0.551 |
| DLST | rs55707505 | 14 | 75,362,552 | T | C | 1.03 | 2.48 × 10−8 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.558 | 1.00 | 0.321 |
| IFT43 | rs75002882 | 14 | 76,496,477 | G | T | 1.17 | 9.22 × 10−9 | 0.97 | 0.25 | - | - | - | - |
| near ITPK1 | rs11624776 | 14 | 93,595,591 | A | C | 1.05 | 9.75 × 10−19 | 1.00 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 0.898 | 1.00 | 0.674 |
| SERPI-1 | rs28929474 | 14 | 94,844,947 | T | C | 1.12 | 2.54 × 10−9 | 0.90 | 5.90 × 10−6 | - | - | - | - |
| ABHD17C | rs12708529 | 15 | 81,022,364 | A | G | 1.04 | 8.11 × 10−10 | 1.02 | 0.022 | 0.99 | 0.185 | 1.01 | 0.162 |
| HMOX2 | rs12598836 | 16 | 4,534,482 | G | A | 1.04 | 2.21 × 10−10 | - | - | 1.01 | 0.008 | 1.00 | 0.787 |
| CFDP1 | rs8046696 | 16 | 75,442,143 | T | G | 1.04 | 4.76 × 10−14 | 1.00 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 0.398 | 1.00 | 0.919 |
| near ZCCHC14 | rs8052831 | 16 | 87,578,039 | G | A | 1.04 | 8.25 × 10−15 | 1.01 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 0.792 | 1.01 | 0.123 |
| SMG6 | rs9894634 | 17 | 1,967,501 | C | T | 1.03 | 9.64 × 10−11 | 1.02 | 0.0041 | 1.00 | 0.921 | 1.00 | 0.454 |
| ZBTB4 | rs34914463 | 17 | 7,366,619 | T | C | 1.05 | 2.41 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.14 | - | - | - | - |
| HOXB3 | rs11652860 | 17 | 46,632,679 | G | C | 1.03 | 1.07 × 10−8 | 1.01 | 0.15 | - | - | - | - |
| RP11-81K2.1 | rs2119930 | 17 | 47,514,039 | G | T | 1.04 | 6.69 × 10−15 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 1.00 | 0.910 | 1.00 | 0.782 |
| MRC2 | rs12452590 | 17 | 60,720,058 | G | T | 1.04 | 2.03 × 10−10 | 0.97 | 2.50 × 10−6 | - | - | - | - |
| TBC1D16 | rs1285294 | 17 | 77,925,681 | C | T | 1.03 | 4.32 × 10−8 | 1.02 | 0.0064 | 1.01 | 0.075 | 1.00 | 0.289 |
| RNF213 | rs8077768 | 17 | 78,256,432 | C | T | 1.04 | 9.32 × 10−13 | 1.00 | 0.52 | - | - | - | - |
| near RBBP8 | rs7506921 | 18 | 20,201,527 | A | T | 1.04 | 1.17 × 10−11 | - | - | 1.00 | 0.546 | 1.00 | 0.748 |
| near SKOR2 | rs1019990 | 18 | 44,866,736 | C | T | 1.04 | 1.00 × 10−11 | 1.00 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 0.181 | 1.00 | 0.716 |
| near FECH | rs8087942 | 18 | 55,192,245 | A | G | 1.04 | 9.71 × 10−13 | 1.00 | 0.8 | 1.00 | 0.906 | 1.00 | 0.946 |
| CAC-1A | rs10405121 | 19 | 13,339,128 | G | A | 1.03 | 4.74 × 10−10 | 1.00 | 0.58 | 1.00 | 0.865 | 1.00 | 0.758 |
| SUGP1 | rs74182632 | 19 | 19,406,126 | A | G | 1.07 | 1.43 × 10−8 | 1.01 | 0.36 | 1.01 | 0.410 | 0.98 | 0.054 |
| B9D2/TMEM91 | rs1982072 | 19 | 41,864,509 | A | T | 1.04 | 4.22 × 10−11 | 1.01 | 0.22 | 1.00 | 0.773 | 1.00 | 0.279 |
| near JAG1 | rs111404218 | 20 | 10,684,159 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SLC24A3 | rs4814864 | 20 | 19,469,817 | C | G | 1.07 | 1.44 × 10−28 | 0.99 | 0.47 | 1.00 | 0.638 | 1.01 | 0.031 |
| C20orf112 | rs6057599 | 20 | 31,168,439 | T | C | 1.04 | 8.73 × 10−14 | 1.01 | 0.4 | 1.01 | 0.178 | 1.01 | 0.149 |
| ZMYND8 | rs910187 | 20 | 45,841,052 | G | A | 1.04 | 1.14 × 10−10 | 0.98 | 0.001 | 1.00 | 0.211 | 1.00 | 0.574 |
| near MRPS6 | rs28451064 | 21 | 35,593,827 | G | A | 1.07 | 3.52 × 10−15 | 1.02 | 0.031 | - | - | - | - |
| RUNX1 | rs764508 | 21 | 36,935,896 | C | T | 1.03 | 3.28 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.16 | 1.00 | 0.632 | 1.00 | 0.139 |
| near AC006547.14 | rs625686 | 22 | 20,142,932 | C | T | 1.03 | 8.26 × 10−9 | 0.99 | 0.042 | 1.00 | 0.430 | 1.00 | 0.720 |
| near FAM47A | rs1507220 | X | 34,102,712 | A | C | 1.03 | 2.67 × 10−8 | - | - | 0.99 | 0.665 | 1.02 | 0.262 |
| near MED14 | rs4403550 | X | 40,746,484 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.R.; Nyholt, D.R. Glucose-Related Traits and Risk of Migraine—A Potential Mechanism and Treatment Consideration. Genes 2022, 13, 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050730
Islam MR, Nyholt DR. Glucose-Related Traits and Risk of Migraine—A Potential Mechanism and Treatment Consideration. Genes. 2022; 13(5):730. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050730
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Md Rafiqul, and Dale R. Nyholt. 2022. "Glucose-Related Traits and Risk of Migraine—A Potential Mechanism and Treatment Consideration" Genes 13, no. 5: 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050730
APA StyleIslam, M. R., & Nyholt, D. R. (2022). Glucose-Related Traits and Risk of Migraine—A Potential Mechanism and Treatment Consideration. Genes, 13(5), 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050730







