Genome-Wide Detection of Copy Number Variants in Chinese Indigenous Horse Breeds and Verification of CNV-Overlapped Genes Related to Heat Adaptation of the Jinjiang Horse
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preprocessing the Source Data
2.2. Genome-Wide Detection of CNVs and CNVRs
2.3. Gene Annotation and Enrichment Analysis
2.4. Validation of Genes Overlapping with the CNVRs in Jinjiang Horses
2.4.1. Cell Culture and Heat Shock Treatment
2.4.2. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription
2.4.3. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Detection of CNVs in Ten Chinese Indigenous Horse Breeds
3.2. Diversity of CNVRs in Breed Clusters
3.3. Comparison with Other Studies on CNVRs in Horse
3.4. Functional Annotation of the CNVRs in Jinjiang Horses
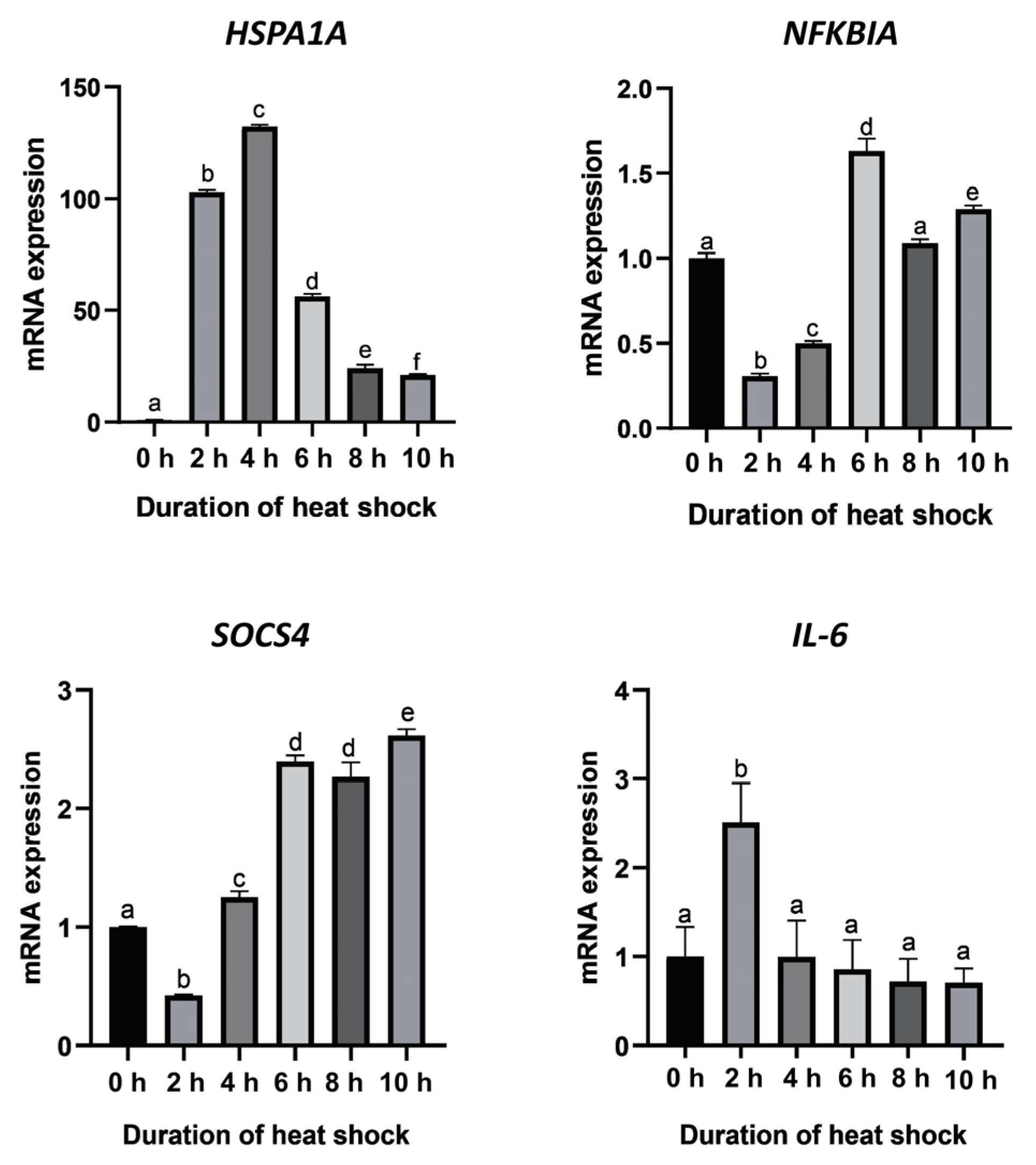
3.5. Validation of Candidate Genes by qPCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feuk, L.; Carson, A.R.; Scherer, S.W. Structural variation in the human genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clop, A.; Vidal, O.; Amills, M. Copy number variation in the genomes of domestic animals. Anim. Genet. 2012, 43, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Hou, Y.; Bickhart, D.M.; Zhou, Y.; Hay, E.H.A.; Song, J.; Sonstegard, T.S.; Van Tassell, C.P.; Liu, G.E. Population-genetic properties of differentiated copy number variations in cattle. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, Y.; Madsen, O.; Megens, H.J.; Frantz, L.A.; Bosse, M.; Crooijmans, R.P.; Groenen, M.A. Copy number variation in the speciation of pigs: A possible prominent role for olfactory receptors. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, M.; da Silva, V.H.; Megens, H.J.; Visker, M.; Ajmone-Marsan, P.; Balteanu, V.A.; Dunner, S.; Garcia, J.F.; Ginja, C.; Kantanen, J.; et al. Distribution and Functionality of Copy Number Variation across European Cattle Populations. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, M.C.; Zhang, Z.; Durkin, K.; Charlier, C.; Lekeux, P.; Georges, M. Detection of copy number variants in the horse genome and examination of their association with recurrent laryngeal neuropathy. Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Hou, C.; Xing, Y.; Cao, J.; Wu, K.; Liu, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Genome-wide detection of copy number variations among diverse horse breeds by array CGH. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, J.; Philipp, U.; Lopes, M.S.; da Camara Machado, A.; Felicetti, M.; Silvestrelli, M.; Distl, O. Analysis of copy number variants by three detection algorithms and their association with body size in horses. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosengren Pielberg, G.; Golovko, A.; Sundstrom, E.; Curik, I.; Lennartsson, J.; Seltenhammer, M.H.; Druml, T.; Binns, M.; Fitzsimmons, C.; Lindgren, G.; et al. A cis-acting regulatory mutation causes premature hair graying and susceptibility to melanoma in the horse. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, J.N.; Hall, G.N. Further studies on the metabolic effects of long distance riding: Golden Horseshoe Ride 1979. Equine Vet. J. 1980, 12, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, C.L.; Magdesian, K.G.; Rhodes, D.M.; Meier, C.A.; Higgins, J.C. Clinical and biochemical abnormalities in endurance horses eliminated from competition for medical complications and requiring emergency medical treatment: 30 cases (2005–2006). J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2009, 19, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlow, M.A.; Dart, A.J.; Jeffcott, L.B. Exertional heat illness: A review of the syndrome affecting racing Thoroughbreds in hot and humid climates. Aust. Vet. J. 2016, 94, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Takahashi, T. Risk factors for exertional heat illness in Thoroughbred racehorses in flat races in Japan (2005–2016). Equine Vet. J. 2020, 52, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, C.; Matthews, T.; Horton, R.M. The emergence of heat and humidity too severe for human tolerance. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaw1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdegaal, E.; Howarth, G.S.; McWhorter, T.J.; Boshuizen, B.; Franklin, S.H.; Vidal Moreno de Vega, C.; Jonas, S.E.; Folwell, L.E.; Delesalle, C.J.G. Continuous Monitoring of the Thermoregulatory Response in Endurance Horses and Trotter Horses During Field Exercise: Baselining for Future Hot Weather Studies. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 708737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Wang, S.; Zeng, G.; Guo, J.; Guo, M.; Dong, X.; Hua, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Ling, Y.; et al. The Origin of a Coastal Indigenous Horse Breed in China Revealed by Genome-Wide SNP Data. Genes 2019, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hadley, D.; Liu, R.; Glessner, J.; Grant, S.F.; Hakonarson, H.; Bucan, M. PennCNV: An integrated hidden Markov model designed for high-resolution copy number variation detection in whole-genome SNP genotyping data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sole, M.; Ablondi, M.; Binzer-Panchal, A.; Velie, B.D.; Hollfelder, N.; Buys, N.; Ducro, B.J.; Francois, L.; Janssens, S.; Schurink, A.; et al. Inter- and intra-breed genome-wide copy number diversity in a large cohort of European equine breeds. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbi-Botto, C.M.; Morales-Durand, H.; Zappa, M.E.; Sadaba, S.A.; Peral-Garcia, P.; Giovambattista, G.; Diaz, S. Genomic structural diversity in Criollo Argentino horses: Analysis of copy number variations. Gene 2019, 695, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurink, A.; da Silva, V.H.; Velie, B.D.; Dibbits, B.W.; Crooijmans, R.; Franois, L.; Janssens, S.; Stinckens, A.; Blott, S.; Buys, N.; et al. Copy number variations in Friesian horses and genetic risk factors for insect bite hypersensitivity. BMC Genet. 2018, 19, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, A.; Liu, X.; Dong, K.; Song, S.; Pan, J.; Yang, M.; Chen, X.; He, X.; Jiang, L.; Ma, Y. Identification of copy number variations in three Chinese horse breeds using 70K single nucleotide polymorphism BeadChip array. Anim. Genet. 2016, 47, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Das, P.J.; McQueen, C.M.; Gerber, V.; Swiderski, C.E.; Lavoie, J.P.; Chowdhary, B.P.; Raudsepp, T. Analysis of genomic copy number variation in equine recurrent airway obstruction (heaves). Anim. Genet. 2016, 47, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Qu, Z.; Das, P.J.; Fang, E.; Juras, R.; Cothran, E.G.; McDonell, S.; Kenney, D.G.; Lear, T.L.; Adelson, D.L.; et al. Copy number variation in the horse genome. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, R.; Cohen, N.; Harrington, J.; Veazey, K.; Juras, R.; Cothran, G.; McCue, M.E.; Skow, L.; Dindot, S.V. Identification of copy number variants in horses. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.L.; Achuthan, P.; Allen, J.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Azov, A.G.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D884–D891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, S.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Li, C.Y.; Wei, L. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W316–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, Y.H.; Wang, P.; Jia, R.M.; Gooneratne, R.; Robert Wang, H.C.; Liao, M.; Ju, X.H. SOCS3 control the activity of NF-kappaB induced by HSP70 via degradation of MyD88-adapter-like protein (Mal) in IPEC-J2 cells. Int. J. Hyperth. 2019, 36, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Interleukin (IL-6) Immunotherapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanesi, L.; Martelli, P.L.; Beretti, F.; Riggio, V.; Dall’Olio, S.; Colombo, M.; Casadio, R.; Russo, V.; Portolano, B. An initial comparative map of copy number variations in the goat (Capra hircus) genome. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicconardi, F.; Chillemi, G.; Tramontano, A.; Marchitelli, C.; Valentini, A.; Ajmone-Marsan, P.; Nardone, A. Massive screening of copy number population-scale variation in Bos taurus genome. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupski, J.R.; Stankiewicz, P. Genomic disorders: Molecular mechanisms for rearrangements and conveyed phenotypes. PLoS Genet. 2005, 1, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuffra, E.; Tornsten, A.; Marklund, S.; Bongcam-Rudloff, E.; Chardon, P.; Kijas, J.M.; Anderson, S.I.; Archibald, A.L.; Andersson, L. A large duplication associated with dominant white color in pigs originated by homologous recombination between LINE elements flanking KIT. Mamm. Genome 2002, 13, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, B.J.; Whan, V.A. A gene duplication affecting expression of the ovine ASIP gene is responsible for white and black sheep. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Shen, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Qi, A.; Yang, S.; Qu, K.; Lan, X.; Huang, B.; Chen, H. Two Different Copy Number Variations of the CLCN2 Gene in Chinese Cattle and Their Association with Growth Traits. Animals 2021, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovo, S.; Ribani, A.; Munoz, M.; Alves, E.; Araujo, J.P.; Bozzi, R.; Charneca, R.; Di Palma, F.; Etherington, G.; Fernandez, A.I.; et al. Genome-wide detection of copy number variants in European autochthonous and commercial pig breeds by whole-genome sequencing of DNA pools identified breed-characterising copy number states. Anim. Genet. 2020, 51, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocchieri, L.; Conway de Macario, E.; Macario, A.J. hsp70 genes in the human genome: Conservation and differentiation patterns predict a wide array of overlapping and specialized functions. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.S., Jr. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 649–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J.; Karin, M. Nuclear factor-kappaB: A pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; May, M.J.; Kopp, E.B. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 225–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszek, A.; Kardynska, M.; Bagnall, J.; Smieja, J.; Spiller, D.G.; Widlak, P.; Kimmel, M.; Widlak, W.; Paszek, P. Heat shock response regulates stimulus-specificity and sensitivity of the pro-inflammatory NF-kappaB signalling. Cell Commun. Signal 2020, 18, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, M.T.; Spitzer, A.L.; Johnson, J.A.; Lee, D.; Harris, H.W. Heat shock inhibits NF-kB activation in a dose- and time-dependent manner. J. Surg. Res. 2005, 129, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, W. Heat shock-mediated regulation of IkappaB-alpha at the post-transcriptional level by HuR. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Duan, P.; Yu, R.; Gu, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Su, L. NFkappaB regulates HSF1 and cJun activation in heat stressinduced intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 3388–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zininga, T.; Ramatsui, L.; Shonhai, A. Heat Shock Proteins as Immunomodulants. Molecules 2018, 23, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Huang, J.; Zhong, H.; Shen, N.; Faggioni, R.; Fung, M.; Yao, Y. Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 141, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepieux, P.; Kwon, H.; Leclerc, N.; Spencer, W.; Richard, S.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. I kappaB alpha physically interacts with a cytoskeleton-associated protein through its signal response domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 7375–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, D.L.; Hilton, D.J. SOCS proteins: Negative regulators of cytokine signaling. Stem. Cells 2001, 19, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Chen, D.; Du, B.; Pan, J. Heat shock response inhibits NF-kappaB activation and cytokine production in murine Kupffer cells. J. Surg. Res. 2005, 129, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.R.; Ryan, M.; Wispe, J.R. Stress response decreases NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and increases I-kappaBalpha expression in A549 cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2423–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Breed Name | Number of Original Samples | Number of Samples after Quality Control | Region | Group | Climate Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kazakh | 17 | 15 | Xinjiang | Kazakh Horse Type | Temperate continental climate |
| Inner Mongolian | 23 | 20 | Inner Mongolia | Mongolian Horse Type | Temperate continental climate |
| Daan | 26 | 25 | Jilin Province | Mongolian Horse Type | Temperate monsoon climate |
| Chakouyi | 34 | 30 | Gansu Province | Hequ Horse Type | Alpine climate |
| Naqu | 29 | 27 | Tibet | Tibetan Horse Type | Alpine climate |
| Jinjiang | 57 | 55 | Fujian Province | Southwest Horse Type | Subtropical maritime monsoon climate |
| Zhaotong | 26 | 25 | Yunnan Province | Southwest Horse Type | Subtropical monsoon climate |
| Tengchong | 22 | 22 | Yunnan Province | Southwest Horse Type | Subtropical monsoon climate |
| Lijiang | 31 | 28 | Yunnan Province | Southwest Horse Type | Subtropical monsoon climate |
| Baise | 36 | 35 | Guangxi Province | Southwest Horse Type | Subtropical monsoon climate |
| Total | 301 | 282 | - | - | - |
| Breed Name | Sample Size | Number of CNVs | Average Number of Individual CNVs | Average Length of CNVs (Kb) | Length Range of CNVs (Kb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baise | 35 | 64 (24) | 1.83 (0.69) | 270.21 | 3.95~1166.66 |
| Chakouyi | 30 | 54 (23) | 1.80 (0.77) | 209.09 | 2.69~1166.66 |
| Daan | 25 | 34 (10) | 1.36 (0.40) | 307.60 | 23.50~2023.07 |
| Inner_Mongolian | 20 | 37 (8) | 1.85 (0.40) | 253.25 | 2.69~1269.78 |
| Jinjiang | 55 | 134 (72) | 2.44 (1.31) | 204.90 | 2.69~1993.59 |
| Kazakh | 15 | 20 (4) | 1.33 (0.27) | 263.03 | 13.92~1432.70 |
| Lijiang | 28 | 74 (36) | 2.64 (1.29) | 305.76 | 2.69~1886.77 |
| Naqu | 27 | 48 (11) | 1.78 (0.41) | 303.24 | 19.78~1607.80 |
| Tengchong | 22 | 45 (16) | 2.05 (0.73) | 275.73 | 19.30~1993.59 |
| Zhaotong | 25 | 67 (24) | 2.68 (0.96) | 226.83 | 1.06~1578.11 |
| Total | 282 | 577 (228) | 2.05 (0.81) | 261.96 | 1.06~2023.07 |
| Breed Name | Sample Size | CNVRs | Gain | Loss | Mixed | Average Number of Individual CNVRs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baise | 35 | 52 (21) | 36 (11) | 14 (9) | 2 (1) | 1.49 (0.60) |
| Chakouyi | 30 | 50 (24) | 32 (10) | 17 (13) | 1 (1) | 1.67 (0.80) |
| Daan | 25 | 29 (9) | 19 (3) | 10 (6) | 0 (0) | 1.16 (0.36) |
| Inner_Mongolian | 20 | 33 (8) | 22 (1) | 11 (7) | 0 (0) | 1.65 (0.40) |
| Jinjiang | 55 | 113 (64) | 79 (38) | 33 (25) | 1 (1) | 2.05 (1.15) |
| Kazakh | 15 | 19 (6) | 15 (5) | 4 (1) | 0 (0) | 1.27 (0.40) |
| Lijiang | 28 | 63 (31) | 38 (12) | 23 (18) | 2 (1) | 2.25 (1.11) |
| Naqu | 27 | 42 (11) | 26 (3) | 15 (8) | 1 (0) | 1.56 (0.41) |
| Tengchong | 22 | 38 (15) | 30 (9) | 7 (5) | 1 (1) | 1.73 (0.68) |
| Zhaotong | 25 | 56 (22) | 38 (13) | 17 (9) | 1 (0) | 2.24 (0.88) |
| Total | 282 | 495 (211) | 335 (105) | 151 (101) | 9 (5) | 1.76 (0.75) |
| Chr | Length of Chromosomes (Mb) | Number of CNVRs | Length of CNVRs (bp) | Percentage (%) | Average Length of CNVRs (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 188.26 | 34 | 6,227,042 | 3.31% | 183,148.29 |
| 2 | 121.35 | 16 | 1,984,086 | 1.64% | 124,005.38 |
| 3 | 121.35 | 17 | 2,359,505 | 1.94% | 138,794.41 |
| 4 | 109.46 | 24 | 2,907,700 | 2.66% | 121,154.17 |
| 5 | 96.76 | 7 | 458,305 | 0.47% | 65,472.14 |
| 6 | 87.23 | 8 | 556,343 | 0.64% | 69,542.88 |
| 7 | 100.79 | 9 | 1,237,197 | 1.23% | 137,466.33 |
| 8 | 97.56 | 9 | 1,463,869 | 1.50% | 162,652.11 |
| 9 | 85.79 | 4 | 753,364 | 0.88% | 188,341.00 |
| 10 | 85.16 | 8 | 1,117,790 | 1.31% | 139,723.75 |
| 11 | 61.68 | 3 | 348,307 | 0.56% | 116,102.33 |
| 12 | 36.99 | 11 | 5,799,518 | 15.68% | 527,228.91 |
| 13 | 43.78 | 2 | 434,027 | 0.99% | 217,013.5 |
| 14 | 94.6 | 4 | 653,789 | 0.69% | 163,447.25 |
| 15 | 92.85 | 7 | 979,123 | 1.05% | 139,874.71 |
| 16 | 88.96 | 2 | 701,010 | 0.79% | 350,505.00 |
| 17 | 80.72 | 7 | 832,567 | 1.03% | 118,938.14 |
| 18 | 82.64 | 14 | 2,861,413 | 3.46% | 204,386.64 |
| 19 | 62.68 | 1 | 1,128,766 | 1.80% | 1,128,766.00 |
| 20 | 65.34 | 6 | 698,764 | 1.07% | 116,460.67 |
| 21 | 58.98 | 4 | 658,611 | 1.12% | 164,652.75 |
| 22 | 50.93 | 2 | 973,451 | 1.91% | 486,725.5 |
| 23 | 55.56 | 3 | 504,860 | 0.91% | 168,286.67 |
| 24 | 48.29 | 3 | 520,059 | 1.08% | 173,353.00 |
| 25 | 40.28 | 4 | 1,067,167 | 2.65% | 266,791.75 |
| 26 | 43.15 | 13 | 2,429,584 | 5.63% | 186,891.08 |
| 27 | 40.25 | 4 | 602,367 | 1.50% | 150,591.75 |
| 28 | 47.35 | 2 | 310,645 | 0.66% | 155,322.5 |
| 29 | 34.78 | 4 | 222,270 | 0.64% | 55,567.5 |
| 30 | 31.4 | 2 | 198,567 | 0.63% | 99,283.5 |
| 31 | 26 | 5 | 750,488 | 2.89% | 150,097.6 |
| Total | 2280.92 | 239 | 41,740,554 | 1.83% | 174,646.67 |
| Study | Platform | Breed | Sample | CNVR Count | CNVR Range (kb–Mb) | Genome Enrichment % | Reference Genome | Overlapped CNVR Count with the Present Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doan et al. (2012) | Array CGH | 15 | 16 | 775 | 0.2–3.5 | 3.7 | EquCab 2.0 | 22 |
| Metzger et al. (2013) | Illumina Equine 70 K SNP BeadChip | 17 | 717 | 50 | 0.5–0.9 | 1.7–22.0 | EquCab 2.0 | 28 |
| Dupuis et al. (2013) | Illumina Equine 70 K SNP BeadChip | 4 | 447 | 478 | 0.1–2.7 | 2.3 | EquCab 2.0 | 24 |
| Ghosh et al. (2014) | Array CGH | 16 | 38 | 258 | 1–2.5 | 1.15 | EquCab 2.0 | 19 |
| Wang et al. (2014) | Array CGH | 6 | 6 | 353 | 6.1–0.5 | 0.61 | EquCab 2.0 | 11 |
| Kader et al. (2016) | Illumina Equine 70 K SNP BeadChip | 3 | 96 | 122 | 0.2–2.2 | 0.8 | EquCab 2.0 | 14 |
| Ghosh et al. (2016) | Array CGH | NA | 63 | 245 | NA | NA | EquCab 2.0 | 20 |
| Schurink et al. (2018) | Axiom Equine Genotyping Array (670,796 SNPs) | 1 | 222 | 5350 | 0.12–1.03 | 11.2 | EquCab 2.0 | 22 |
| Solé et al. (2019) | Axiom Equine Genotyping Array (670,796 SNPs) | 8 | 1755 | 939 | 1–21.3 | NA | EquCab 2.0 | 80 |
| Corbi-Botto et al. (2019) | Illumina GGP Equine 70 K | 1 | 24 | 87 | 0.5–2 | 0.6 | EquCab 2.0 | 10 |
| Present study | Illumina Equine 70 K SNP BeadChip | 10 | 300 | 239 | 1.06–2.44 | 1.83 | EquCab 3.0 | - |
| Category | ID | Term | Counts | p-Value | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG | ecb05134 | Legionellosis | 4 | 3.33 × 10−3 | HSPA1A, TNF, NFKBIA |
| KEGG | ecb03040 | Spliceosome | 5 | 5.81 × 10−3 | HSPA1A, HNRNPC, LSM2 |
| KEGG | ecb04064 | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | 4 | 1.02 × 10−2 | LTB, TNF, NFKBIA |
| KEGG | ecb05145 | Toxoplasmosis | 4 | 1.45 × 10−2 | HSPA1A, TNF, NFKBIA |
| KEGG | ecb05166 | Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection | 5 | 1.86 × 10−2 | APC2, LTA, NFKBIA |
| GO_BP | GO:0051092 | Positive regulation of NF-kappa B transcription factor activity | 6 | 1.82 × 10−3 | NFKBIA, TRAPPC9, TNF, HSPA1A |
| GO_BP | GO:0032757 | Positive regulation of interleukin-8 production | 3 | 1.25 × 10−2 | TNF, HSPA1A |
| GO_BP | GO:0007274 | Neuromuscular synaptic transmission | 3 | 1.25 × 10−2 | FCHSD2, CHRNB3, CHRNA6 |
| GO_BP | GO:0002876 | Positive regulation of chronic inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | 2 | 1.31 × 10−2 | LTA, TNF |
| GO_MF | GO:0003676 | Nucleic acid binding | 14 | 1.35 × 10−2 | DAZAP1, CIRBP, RNASE6, ZNF219 |
| GO_MF | GO:0004872 | Receptor activity | 6 | 1.48 × 10−2 | NCR3, LRP1, SLC20A2, CADM2 |
| GO_MF | GO:0005102 | Receptor binding | 7 | 3.02 × 10−2 | NCR3, CADM2, HSPA1A |
| GO_MF | GO:0031072 | Heat shock protein binding | 3 | 3.16 × 10−2 | NFKBIA, HSPA1A |
| GO_CC | GO:0048471 | Perinuclear region of cytoplasm | 11 | 9.40 × 10−3 | APC2, PDE2A, M6PR, HSPA1A |
| GO_CC | GO:0005887 | Integral component of plasma membrane | 18 | 1.42 × 10−2 | LRP1, KCNK9, CADM2 |
| GO_CC | GO:0005913 | Cell–cell adherens junction | 7 | 2.24 × 10−2 | NCR3, BAIAP2L1, HSPA1A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Bi, X.; Ma, H.; Zeng, G.; Guo, J.; Guo, M.; Ling, Y.; Zhao, C. Genome-Wide Detection of Copy Number Variants in Chinese Indigenous Horse Breeds and Verification of CNV-Overlapped Genes Related to Heat Adaptation of the Jinjiang Horse. Genes 2022, 13, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040603
Wang M, Liu Y, Bi X, Ma H, Zeng G, Guo J, Guo M, Ling Y, Zhao C. Genome-Wide Detection of Copy Number Variants in Chinese Indigenous Horse Breeds and Verification of CNV-Overlapped Genes Related to Heat Adaptation of the Jinjiang Horse. Genes. 2022; 13(4):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040603
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Min, Yu Liu, Xiaokun Bi, Hongying Ma, Guorong Zeng, Jintu Guo, Minghao Guo, Yao Ling, and Chunjiang Zhao. 2022. "Genome-Wide Detection of Copy Number Variants in Chinese Indigenous Horse Breeds and Verification of CNV-Overlapped Genes Related to Heat Adaptation of the Jinjiang Horse" Genes 13, no. 4: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040603
APA StyleWang, M., Liu, Y., Bi, X., Ma, H., Zeng, G., Guo, J., Guo, M., Ling, Y., & Zhao, C. (2022). Genome-Wide Detection of Copy Number Variants in Chinese Indigenous Horse Breeds and Verification of CNV-Overlapped Genes Related to Heat Adaptation of the Jinjiang Horse. Genes, 13(4), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040603






