Mechanisms of EGFR-TKI-Induced Apoptosis and Strategies Targeting Apoptosis in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Effectiveness and Limitations of EGFR-TKI Therapy in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC
2.1. Efficacy and Limitations of Single EGFR-TKI Therapy
2.2. Combined EGFR-TKI Therapy and Development of Novel Therapeutic Approaches
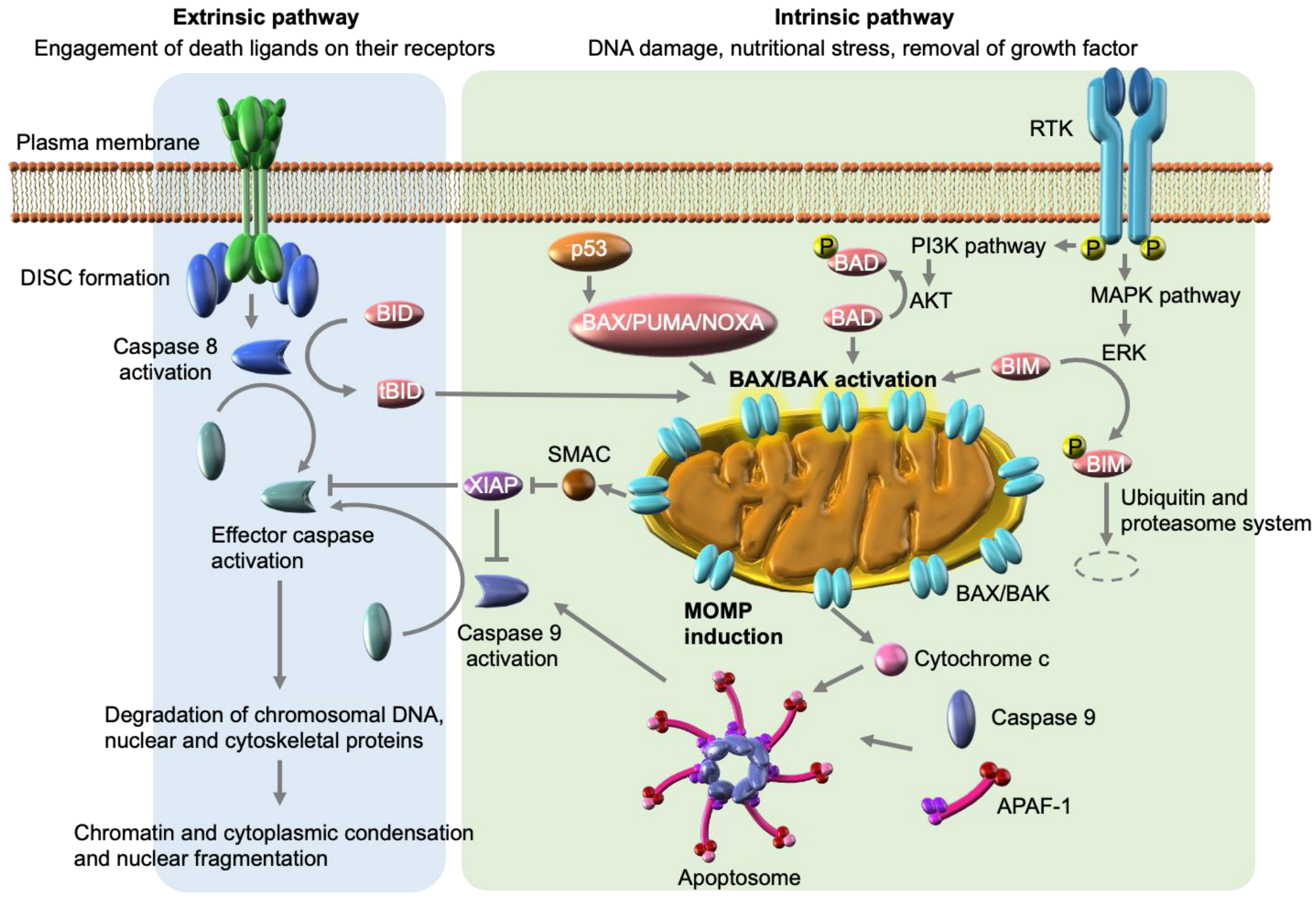
3. Signaling Pathways of Apoptosis
3.1. Intrinsic Apoptosis Pathway
3.2. Extrinsic Apoptosis Pathway
4. Mechanistic Insights into EGFR-TKI-Induced or -Enhanced Apoptosis from Preclinical Models
4.1. Pro-Apoptotic Protein: BIM
4.2. Anti-Apoptotic Proteins: BCL-2, BCL-X, and MCL1
4.3. Extrinsic Pathway in EGFR-TKI-Induced Apoptosis
4.4. Other Mechanisms by which EGFR-TKIs Induce or Enhance Apoptosis
5. Clinical Translation Potential of the Interaction of EGFR-TKIs with Apoptosis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janmaat, M.L.; Kruyt, F.A.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Giaccone, G. Response to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer cells: Limited antiproliferative effects and absence of apoptosis associated with persistent activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase or Akt kinase pathways. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2316–2326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cragg, M.S.; Kuroda, J.; Puthalakath, H.; Huang, D.C.; Strasser, A. Gefitinib-induced killing of NSCLC cell lines expressing mutant EGFR requires BIM and can be enhanced by BH3 mimetics. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 1681–1689; discussion 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Somwar, R.; Politi, K.; Balak, M.; Chmielecki, J.; Jiang, X.; Pao, W. Induction of BIM is essential for apoptosis triggered by EGFR kinase inhibitors in mutant EGFR-dependent lung adenocarcinomas. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.B.; Halmos, B.; Kumar, A.; Schumer, S.T.; Huberman, M.S.; Boggon, T.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Kobayashi, S. BIM mediates EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung cancers with oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 1669–1679; discussion 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.P.; Hillmer, A.M.; Chuah, C.T.; Juan, W.C.; Ko, T.K.; Teo, A.S.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Takahashi, N.; Sawada, K.; Fei, Y.; et al. A common BIM deletion polymorphism mediates intrinsic resistance and inferior responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, L.; Qian, G.; Ren, H.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Chen, M.; Sun, S.Y. The Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitor, Osimertinib, Promotes c-FLIP Degradation, Enhancing Apoptosis Including TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in NSCLC Cells with Activating EGFR Mutations. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Ishikawa, F.; Ohmori, T.; Ando, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Kishino, Y.; Manabe, R.; Hasebe, Y.; Sagara, H.; et al. Diverse Mechanisms of Resistance against Osimertinib, a Third-Generation EGFR-TKI, in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells with an EGFR-Activating Mutation. Cells 2022, 11, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Morita, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Negoro, S.; Okamoto, I.; Tsurutani, J.; Seto, T.; Satouchi, M.; Tada, H.; Hirashima, T.; et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.; Yamamoto, N.; O’Byrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zejnullahu, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Song, Y.; Hyland, C.; Park, J.O.; Lindeman, N.; Gale, C.M.; Zhao, X.; Christensen, J.; et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007, 316, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, D.A.; Ashton, S.E.; Ghiorghiu, S.; Eberlein, C.; Nebhan, C.A.; Spitzler, P.J.; Orme, J.P.; Finlay, M.R.; Ward, R.A.; Mellor, M.J.; et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss, G.; Tsai, C.-M.; Shepherd, F.A.; Bazhenova, L.; Lee, J.S.; Chang, G.-C.; Crino, L.; Satouchi, M.; Chu, Q.; Hida, T.; et al. Osimertinib for pretreated EGFR Thr790Met-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (AURA2): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Ahn, M.J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.; et al. Osimertinib or Platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.G.; Wu, R. Erlotinib-cisplatin combination inhibits growth and angiogenesis through c-MYC and HIF-1alpha in EGFR-mutated lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Pan, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y. Combined gefitinib and pemetrexed overcome the acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosomi, Y.; Morita, S.; Sugawara, S.; Kato, T.; Fukuhara, T.; Gemma, A.; Takahashi, K.; Fujita, Y.; Harada, T.; Minato, K.; et al. Gefitinib Alone Versus Gefitinib Plus Chemotherapy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Mutated Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor: NEJ009 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, R.S.; Chen, D.S.; Ferrara, N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell 2019, 176, 1248–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumov, G.N.; Nilsson, M.B.; Cascone, T.; Briggs, A.; Straume, O.; Akslen, L.A.; Lifshits, E.; Byers, L.A.; Xu, L.; Wu, H.K.; et al. Combined vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) blockade inhibits tumor growth in xenograft models of EGFR inhibitor resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3484–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furugaki, K.; Fukumura, J.; Iwai, T.; Yorozu, K.; Kurasawa, M.; Yanagisawa, M.; Moriya, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Suda, K.; Mizuuchi, H.; et al. Impact of bevacizumab in combination with erlotinib on EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer xenograft models with T790M mutation or MET amplification. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Fukuhara, T.; Furuya, N.; Watanabe, K.; Sugawara, S.; Iwasawa, S.; Tsunezuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, O.; Okada, M.; Yoshimori, K.; et al. Erlotinib plus bevacizumab versus erlotinib alone in patients with EGFR-positive advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NEJ026): Interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Garon, E.B.; Seto, T.; Nishio, M.; Ponce Aix, S.; Paz-Ares, L.; Chiu, C.H.; Park, K.; Novello, S.; Nadal, E.; et al. Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederst, M.J.; Hu, H.; Mulvey, H.E.; Lockerman, E.L.; Garcia, A.R.; Piotrowska, Z.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. The Allelic Context of the C797S Mutation Acquired upon Treatment with Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors Impacts Sensitivity to Subsequent Treatment Strategies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulananda, S.; Do, H.; Musafer, A.; Mitchell, P.; Dobrovic, A.; John, T. Combination Osimertinib and Gefitinib in C797S and T790M EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.J.; Huang, J.; Ye, J.Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Tu, H.Y.; Han-Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.L. Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring EGFR T790M and In Trans C797S Responds to Combination Therapy of First- and Third-Generation EGFR TKIs and Shifts Allelic Configuration at Resistance. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Berghe, T.V.; Vandenabeele, P.; Kroemer, G. The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesavardhana, S.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Kanneganti, T.D. Caspases in Cell Death, Inflammation, and Pyroptosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 567–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enari, M.; Sakahira, H.; Yokoyama, H.; Okawa, K.; Iwamatsu, A.; Nagata, S. A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA during apoptosis, and its inhibitor ICAD. Nature 1998, 391, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deveraux, Q.L.; Reed, J.C. IAP family proteins--suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkavan, H.; Green, D.R. MOMP, cell suicide as a BCL-2 family business. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, C.; Galluzzi, L.; Brunet, M.; Puig, P.E.; Didelot, C.; Kroemer, G. Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danial, N.N. BCL-2 family proteins: Critical checkpoints of apoptotic cell death. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 7254–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.C.; Zong, W.X.; Cheng, E.H.; Lindsten, T.; Panoutsakopoulou, V.; Ross, A.J.; Roth, K.A.; MacGregor, G.R.; Thompson, C.B.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: A requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 2001, 292, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.H.; Wei, M.C.; Weiler, S.; Flavell, R.A.; Mak, T.W.; Lindsten, T.; Korsmeyer, S.J. BCL-2, BCL-X(L) sequester BH3 domain-only molecules preventing BAX- and BAK-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, T.; Reed, J.C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell 1995, 80, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villunger, A.; Michalak, E.M.; Coultas, L.; Mullauer, F.; Bock, G.; Ausserlechner, M.J.; Adams, J.M.; Strasser, A. p53- and drug-induced apoptotic responses mediated by BH3-only proteins puma and noxa. Science 2003, 302, 1036–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sax, J.K.; Fei, P.; Murphy, M.E.; Bernhard, E.; Korsmeyer, S.J.; El-Deiry, W.S. BID regulation by p53 contributes to chemosensitivity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.R.; Dudek, H.; Tao, X.; Masters, S.; Fu, H.; Gotoh, Y.; Greenberg, M.E. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 1997, 91, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.R.; Katsov, A.; Hu, L.; Petros, A.; Fesik, S.W.; Yaffe, M.B.; Greenberg, M.E. 14-3-3 proteins and survival kinases cooperate to inactivate BAD by BH3 domain phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewings, K.E.; Hadfield-Moorhouse, K.; Wiggins, C.M.; Wickenden, J.A.; Balmanno, K.; Gilley, R.; Degenhardt, K.; White, E.; Cook, S.J. ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation of BimEL promotes its rapid dissociation from Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 2856–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Bouillet, P.; Miyazaki, T.; Kadono, Y.; Chikuda, H.; Chung, U.I.; Fukuda, A.; Hikita, A.; Seto, H.; Okada, T.; et al. Regulation of osteoclast apoptosis by ubiquitylation of proapoptotic BH3-only Bcl-2 family member Bim. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 6653–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, T.; Strasser, A.; Jost, P.J. Fas death receptor signalling: Roles of Bid and XIAP. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso Alves, L.; Corazza, N.; Micheau, O.; Krebs, P. The multifaceted role of TRAIL signaling in cancer and immunity. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 5530–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheau, O.; Tschopp, J. Induction of TNF Receptor I-Mediated Apoptosis via Two Sequential Signaling Complexes. Cell 2003, 114, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guicciardi, M.E.; Gores, G.J. Life and death by death receptors. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2009, 23, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantari, C.; Walczak, H. Caspase-8 and bid: Caught in the act between death receptors and mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuida, K.; Haydar, T.F.; Kuan, C.Y.; Gu, Y.; Taya, C.; Karasuyama, H.; Su, M.S.; Rakic, P.; Flavell, R.A. Reduced apoptosis and cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9. Cell 1998, 94, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.M.; Wang, K.; Gross, A.; Zhao, Y.; Zinkel, S.; Klocke, B.; Roth, K.A.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bid-deficient mice are resistant to Fas-induced hepatocellular apoptosis. Nature 1999, 400, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, M.D.; Carrington, E.M.; Kaufmann, T.; Strasser, A.; Huang, D.C.; Kay, T.W.; Allison, J.; Thomas, H.E. Proapoptotic BH3-only protein Bid is essential for death receptor-induced apoptosis of pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, P.J.; Grabow, S.; Gray, D.; McKenzie, M.D.; Nachbur, U.; Huang, D.C.; Bouillet, P.; Thomas, H.E.; Borner, C.; Silke, J.; et al. XIAP discriminates between type I and type II FAS-induced apoptosis. Nature 2009, 460, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.Z.; Crawford, N.; Longley, D.B. The role of Ubiquitination in Apoptosis and Necroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamas-Din, A.; Kale, J.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Mechanisms of action of Bcl-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillet, P.; Metcalf, D.; Huang, D.C.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Kay, T.W.; Kontgen, F.; Adams, J.M.; Strasser, A. Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science 1999, 286, 1735–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, J.; Puthalakath, H.; Cragg, M.S.; Kelly, P.N.; Bouillet, P.; Huang, D.C.; Kimura, S.; Ottmann, O.G.; Druker, B.J.; Villunger, A.; et al. Bim and Bad mediate imatinib-induced killing of Bcr/Abl+ leukemic cells, and resistance due to their loss is overcome by a BH3 mimetic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14907–14912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Shimamura, T.; Perera, S.; Carlson, N.E.; Cai, D.; Shapiro, G.I.; Wong, K.K.; Letai, A. Proapoptotic BH3-only BCL-2 family protein BIM connects death signaling from epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition to the mitochondrion. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11867–11875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Delft, M.F.; Wei, A.H.; Mason, K.D.; Vandenberg, C.J.; Chen, L.; Czabotar, P.E.; Willis, S.N.; Scott, C.L.; Day, C.L.; Cory, S.; et al. The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.; Balmanno, K.; Hadfield, K.; Weston, C.; Cook, S.J. Activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway promotes phosphorylation and proteasome-dependent degradation of the BH3-only protein, Bim. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 18811–18816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukazawa, H.; Noguchi, K.; Masumi, A.; Murakami, Y.; Uehara, Y. BimEL is an important determinant for induction of anoikis sensitivity by mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickenden, J.A.; Jin, H.; Johnson, M.; Gillings, A.S.; Newson, C.; Austin, M.; Chell, S.D.; Balmanno, K.; Pritchard, C.A.; Cook, S.J. Colorectal cancer cells with the BRAF(V600E) mutation are addicted to the ERK1/2 pathway for growth factor-independent survival and repression of BIM. Oncogene 2008, 27, 7150–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, M.S.; Jansen, E.S.; Cook, M.; Harris, C.; Strasser, A.; Scott, C.L. Treatment of B-RAF mutant human tumor cells with a MEK inhibitor requires Bim and is enhanced by a BH3 mimetic. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3651–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuribara, R.; Honda, H.; Matsui, H.; Shinjyo, T.; Inukai, T.; Sugita, K.; Nakazawa, S.; Hirai, H.; Ozawa, K.; Inaba, T. Roles of Bim in apoptosis of normal and Bcr-Abl-expressing hematopoietic progenitors. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 6172–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezawa, K.; Okamoto, I.; Nishio, K.; Janne, P.A.; Nakagawa, K. Role of ERK-BIM and STAT3-survivin signaling pathways in ALK inhibitor-induced apoptosis in EML4-ALK-positive lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2140–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, A.C.; Corcoran, R.B.; Ebi, H.; Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Chung, E.; Incio, J.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Pollack, S.F.; Song, Y.; et al. BIM expression in treatment-naive cancers predicts responsiveness to kinase inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Molina, M.A.; Drozdowskyj, A.; Gimenez-Capitan, A.; Bertran-Alamillo, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Gervais, R.; Massuti, B.; Wei, J.; Moran, T.; et al. The impact of EGFR T790M mutations and BIM mRNA expression on outcome in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC treated with erlotinib or chemotherapy in the randomized phase III EURTAC trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Bai, H.; Yan, B.; Li, R.; Shao, M.; Xiong, L.; Han, B. Mimicking the BIM BH3 domain overcomes resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 108522–108533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cardona, A.F.; Rojas, L.; Wills, B.; Arrieta, O.; Carranza, H.; Vargas, C.; Otero, J.; Corrales-Rodriguez, L.; Martin, C.; Reguart, N.; et al. BIM deletion polymorphisms in Hispanic patients with non-small cell lung cancer carriers of EGFR mutations. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68933–68942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Ku, B.M.; Lim, S.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.M.; Ahn, J.S.; et al. The BIM Deletion Polymorphism and its Clinical Implication in Patients with EGFR-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated with EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Cheng, N.; Ren, R.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Ren, S.; et al. The Bim deletion polymorphism clinical profile and its relation with tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2014, 120, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.F.; Wu, L.X.; Chen, H.F.; Zhu, Y.C.; Wang, W.X.; Xu, C.W.; Lin, X.P.; Xie, D.F.; Du, K.Q. Association between BIM polymorphism and lung cancer outcomes: A meta-analysis. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 64, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Yamada, T.; Ebi, H.; Sano, T.; Nanjo, S.; Ishikawa, D.; Sato, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Sekido, Y.; et al. EGFR-TKI resistance due to BIM polymorphism can be circumvented in combination with HDAC inhibition. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2428–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, A.F.; Ordonez-Reyes, C.; Ruiz-Patino, A.; Garcia-Robledo, J.E.; Barron, L.Z.; Recondo, G.; Rojas, L.; Corrales, L.; Martin, C.; Barron, F.; et al. EGFR Inhibitors Plus Bevacizumab are Superior than EGFR Inhibitors Alone as First-Line Setting in Advanced NSCLC with EGFR Mutations and BIM Deletion Polymorphisms (BIM-CLICaP). JCO Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; He, Y.; Jiang, T.; Ren, S.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Su, C.; Chen, X.; et al. EGFR-TKIs plus chemotherapy demonstrated superior efficacy than EGFR-TKIs alone as first-line setting in advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation and BIM deletion polymorphism. Lung Cancer 2018, 120, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Oh, Y.T.; Deng, L.; Zhang, G.; Qian, G.; Zhang, S.; Ren, H.; Wu, G.; Legendre, B., Jr.; Anderson, E.; et al. Overcoming Acquired Resistance to AZD9291, A Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitor, through Modulation of MEK/ERK-Dependent Bim and Mcl-1 Degradation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6567–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Q.; Shih, W.; Ling, C.H.; Tsao, M.S. Immunohistochemical markers of prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer: A review and proposal for a multiphase approach to marker evaluation. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 59, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.; Malek, M.; Zha, J.; Yue, P.; Kassees, R.; Berry, L.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Sampath, D.; Belmont, L.D. Navitoclax enhances the efficacy of taxanes in non-small cell lung cancer models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Bebb, G.; Tan, S.; Ng, R.; Yan, H.; Sartor, J.R.; Mayer, L.D.; Bally, M.B. Antitumor efficacy of oblimersen Bcl-2 antisense oligonucleotide alone and in combination with vinorelbine in xenograft models of human non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7662–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sartorius, U.A.; Krammer, P.H. Upregulation of Bcl-2 is involved in the mediation of chemotherapy resistance in human small cell lung cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 97, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuta, K.; Takemura, K.; Kihara, M.; Naito, S.; Lee, E.; Shimizu, E.; Yamauchi, A. Defects in apoptotic signal transduction in cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 13, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjo, S.; Wu, W.; Karachaliou, N.; Blakely, C.M.; Suzuki, J.; Chou, Y.T.; Ali, S.M.; Kerr, D.L.; Olivas, V.R.; Shue, J.; et al. Deficiency of the splicing factor RBM10 limits EGFR inhibitor response in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Yamamoto, N.; Kimura, M.; Nishio, K.; Yamane, H.; Nakajima, K. RBM10 regulates alternative splicing. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroukhim, R.; Mermel, C.H.; Porter, D.; Wei, G.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Donovan, J.; Barretina, J.; Boehm, J.S.; Dobson, J.; Urashima, M.; et al. The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature 2010, 463, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senichkin, V.V.; Streletskaia, A.Y.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Kopeina, G.S. Molecular Comprehension of Mcl-1: From Gene Structure to Cancer Therapy. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booy, E.P.; Henson, E.S.; Gibson, S.B. Epidermal growth factor regulates Mcl-1 expression through the MAPK-Elk-1 signalling pathway contributing to cell survival in breast cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2367–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.A.; Hosono, Y.; Turner, C.; Jacob, S.; Lochmann, T.L.; Murakami, Y.; Patel, N.U.; Ham, J.; Hu, B.; Powell, K.M.; et al. Increased Synthesis of MCL-1 Protein Underlies Initial Survival of EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer to EGFR Inhibitors and Provides a Novel Drug Target. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5658–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, A.C.; Li, D.; Song, Y.; Liang, M.C.; Yeap, B.Y.; Bronson, R.T.; Lifshits, E.; Chen, Z.; Maira, S.M.; Garcia-Echeverria, C.; et al. Differential induction of apoptosis in HER2 and EGFR addicted cancers following PI3K inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19503–19508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Deng, Y.; Qian, L.; Vallega, K.A.; Zhang, G.; Deng, X.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Fang, D.D.; Zhai, Y.; et al. Overcoming acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitors by targeting activation of intrinsic apoptotic pathway through Mcl-1 inhibition, Bax activation, or both. Oncogene 2022, 41, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bivona, T.G.; Hieronymus, H.; Parker, J.; Chang, K.; Taron, M.; Rosell, R.; Moonsamy, P.; Dahlman, K.; Miller, V.A.; Costa, C.; et al. FAS and NF-kappaB signalling modulate dependence of lung cancers on mutant EGFR. Nature 2011, 471, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Nakabayashi, O.; Nakano, H. FLIP the Switch: Regulation of Apoptosis and Necroptosis by cFLIP. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 30321–30341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Wilson, N.S.; Ashkenazi, A. Proapoptotic DR4 and DR5 signaling in cancer cells: Toward clinical translation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.; Shi, P.; Fan, S.; He, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Sun, S.Y. Downregulation of death receptor 4 is tightly associated with positive response of EGFR mutant lung cancer to EGFR-targeted therapy and improved prognosis. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3964–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Ohmori, T.; Inoue, F.; Kadofuku, T.; Hosaka, T.; Ishida, H.; Shirai, T.; Okuda, K.; Hirose, T.; Horichi, N.; et al. Enhancement of sensitivity to tumor necrosis factor alpha in non-small cell lung cancer cells with acquired resistance to gefitinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8872–8879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmori, T.; Yamaoka, T.; Ando, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Kishino, Y.; Manabe, R.; Sagara, H. Molecular and Clinical Features of EGFR-TKI-Associated Lung Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, T.; Arata, S.; Homma, M.; Homma, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Ando, K.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Ohba, M.; Tsurutani, J.; et al. Blockade of EGFR Activation Promotes TNF-Induced Lung Epithelial Cell Apoptosis and Pulmonary Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Guo, G.; Gerber, D.E.; Gao, B.; Peyton, M.; Huang, C.; Minna, J.D.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Kernstine, K.; Cai, L.; et al. TNF-driven adaptive response mediates resistance to EGFR inhibition in lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2500–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.; Larisch, S. Targeting XIAP for Promoting Cancer Cell Death-The Story of ARTS and SMAC. Cells 2020, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Smith, D.C.; Wang, S. Small-molecule SMAC mimetics as new cancer therapeutics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S. Promises and Challenges of Smac Mimetics as Cancer Therapeutics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 5030–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonan, A.M.; Bunch, K.P.; Chen, J.Q.; Herrmann, M.A.; Lee, J.M.; Kohn, E.C.; O’Sullivan, C.C.; Jordan, E.; Houston, N.; Takebe, N.; et al. Pharmacodynamic markers and clinical results from the phase 2 study of the SMAC mimetic birinapant in women with relapsed platinum-resistant or -refractory epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer 2016, 122, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaravadi, R.K.; Schilder, R.J.; Martin, L.P.; Levin, M.; Graham, M.A.; Weng, D.E.; Adjei, A.A. A Phase I Study of the SMAC-Mimetic Birinapant in Adults with Refractory Solid Tumors or Lymphoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pemmaraju, N.; Carter, B.Z.; Bose, P.; Jain, N.; Kadia, T.M.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; DiNardo, C.D.; Bledsoe, S.; Daver, N.G.; et al. Final results of a phase 2 clinical trial of LCL161, an oral SMAC mimetic for patients with myelofibrosis. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3163–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregni, M.; Ciribilli, Y.; Zawacka-Pankau, J.E. The Therapeutic Potential of the Restoration of the p53 Protein Family Members in the EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadepalli, V.S.; Deb, S.P.; Deb, S.; Rao, R.R. Lung cancer stem cells, p53 mutations and MDM2. Subcell Biochem. 2014, 85, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, D.L.; Byers, L.A.; Kurie, J.M. Smoking, p53 mutation, and lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zou, Z.; Becker, N.; Anderson, M.; Sumpter, R.; Xiao, G.; Kinch, L.; Koduru, P.; Christudass, C.S.; Veltri, R.W.; et al. EGFR-mediated Beclin 1 phosphorylation in autophagy suppression, tumor progression, and tumor chemoresistance. Cell 2013, 154, 1269–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaravadi, R.K.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Yin, X.M.; Weiss, W.A.; Takebe, N.; Timmer, W.; DiPaola, R.S.; Lotze, M.T.; White, E. Principles and current strategies for targeting autophagy for cancer treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Lam, S.K.; Mak, J.C.; Zheng, C.Y.; Ho, J.C. Erlotinib-induced autophagy in epidermal growth factor receptor mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2013, 81, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, M.; Nguyen, A.P.; Le Grand, J.N.; Arbour, N.; Vanderluit, J.L.; Park, D.S.; Opferman, J.T.; Slack, R.S. MCL-1 is a stress sensor that regulates autophagy in a developmentally regulated manner. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, W.T.; Shiau, C.W.; Chen, H.L.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, C.S.; Cheng, A.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, K.F. Mcl-1-dependent activation of Beclin 1 mediates autophagic cell death induced by sorafenib and SC-59 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Bassik, M.C.; Moresi, V.; Sun, K.; Wei, Y.; Zou, Z.; An, Z.; Loh, J.; Fisher, J.; Sun, Q.; et al. Exercise-induced BCL2-regulated autophagy is required for muscle glucose homeostasis. Nature 2012, 481, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattingre, S.; Tassa, A.; Qu, X.; Garuti, R.; Liang, X.H.; Mizushima, N.; Packer, M.; Schneider, M.D.; Levine, B. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 2005, 122, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Huang, F.; Xu, X.; He, H.; Zhang, Y. High expression of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha related with acquired resistant to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okon, I.S.; Coughlan, K.A.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Zou, M.H. Gefitinib-mediated reactive oxygen specie (ROS) instigates mitochondrial dysfunction and drug resistance in lung cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 9101–9110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teppo, H.R.; Soini, Y.; Karihtala, P. Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Mechanisms of Action of Targeted Cancer Therapy. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1485283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Oeck, S.; Zhang, G.J.; Schramm, A.; Glazer, P.M. Hypoxia Induces Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer Cells via Upregulation of FGFR1 and the MAPK Pathway. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 4655–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, F.J.; Sedov, E.; Koren, E.; Koessinger, A.L.; Cloix, C.; Zerbst, D.; Athineos, D.; Anand, J.; Campbell, K.J.; Blyth, K.; et al. Apoptotic stress-induced FGF signalling promotes non-cell autonomous resistance to cell death. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.M.; Song, A.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.; Ahn, Y.O.; Keam, B.; Jeon, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, D.H.; Heo, D.S. Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to AZD9291: A Mutation-Selective, Irreversible EGFR Inhibitor. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Zhang, X.; Cai, X.; Peng, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. BIM deletion polymorphism predicts poor response to EGFR-TKIs in nonsmall cell lung cancer: An updated meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e14568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, F.; Sun, L.; Yang, Q.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Y. Prognostic Value of BIM Deletion in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Patients Treated with EGFR-TKIs: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 3621828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S.; Hase, T.; Shimizu, S.; Ando, M.; Hata, A.; Murakami, H.; Kawakami, T.; Nagase, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Fujiwara, T.; et al. Phase I study of vorinostat with gefitinib in BIM deletion polymorphism/epidermal growth factor receptor mutation double-positive lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S.; Yoshimura, K.; Fujiwara, T.; Ando, M.; Shimizu, S.; Nagase, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Katakami, N.; Inoue, A.; et al. Phase I study of combined therapy with vorinostat and gefitinib to treat BIM deletion polymorphism-associated resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer (VICTROY-J): A study protocol. J. Med. Investig. 2017, 64, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertino, E.M.; Gentzler, R.D.; Clifford, S.; Kolesar, J.; Muzikansky, A.; Haura, E.B.; Piotrowska, Z.; Camidge, D.R.; Stinchcombe, T.E.; Hann, C.; et al. Phase IB Study of Osimertinib in Combination with Navitoclax in EGFR-mutant NSCLC Following Resistance to Initial EGFR Therapy (ETCTN 9903). Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klener, P.; Sovilj, D.; Renesova, N.; Andera, L. BH3 Mimetics in Hematologic Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyauchi, E.; Morita, S.; Nakamura, A.; Hosomi, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Ikeda, S.; Seike, M.; Fujita, Y.; Minato, K.; Ko, R.; et al. Updated Analysis of NEJ009: Gefitinib-Alone Versus Gefitinib Plus Chemotherapy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Mutated EGFR. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3587–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudomi, T. Advances in target therapy for lung cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 40, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Classification | Mechanisms | BCL-2 Family Proteins | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-apoptotic proteins | Sequester of pro-apoptotic proteins | BCL-2, BCL-XL, MCL-1 | |
| Pro-apoptotic proteins | |||
| effectors | Induction of MOMP | BAX, BAK | |
| activators | Direct activation of BAX/BAK Inhibition of anti-apoptotic proteins | BIM, BID, PUMA | |
| sensitizers | Inhibition of anti-apoptotic proteins | BAD, NOXA, BIK, BMF, HRK | |
| Classification | Mechanism | Proteins Associated with EGFR-TKI-Induced Apoptosis |
|---|---|---|
| Intrinsic apoptosis pathway | Pro-apoptotic | BIM, BAX, BID, BCL-XS |
| Anti-apoptotic | BCL-XL, MCL-1 | |
| Extrinsic apoptosis pathway | Pro-apoptotic | FAS |
| Anti-apoptotic | c-FLIP, IKKb, DR4, TNF, IAPs |
| BIM mRNA Expression | Treatment | Patients (n = 42) | ORR | PFS: Month (95% CI) | p | OS: Month (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| high | Erlotinib | 16 | 87.5% | 12.9 (9.7–23.9) | 0.0122 (HR = 0.49) | 24.5 (14-NR) | 0.323 (HR = 0.53) |
| low/intermediate | Erlotinib | 26 | 34.6% | 7.2 (2.6–12.3) | 20.8 (8.9–32.5) |
| Treatment | Patients | DCR (%) (95% CI) | PFS: Month (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Takeuchi et al. [126] | Gefitinib (250 mg) + Vorinostat (400 mg) | 12 1 | 83.3% (0.52–0.98) | 5.2 (1.4–15.7) |
| Bertino et al. [127] | Osimertinib (80 mg) + Navitoclax (150 mg) | 27 2 | 100% | 16.8 (3.5-NR) |
| Treatment | Patients | ORR (%) (95% CI) | p | PFS: Month (95% CI) | p | OS: Month (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu et al. [78] | EGFR-TKIs 1 | 36 | 38.9 | 0.046 | 4.7 | 0.008 | 14.2 | 0.107 |
| EGFR-TKIs 1 + platinum-based chemotherapy 2 | 29 | 65.5 | 7.2 | 18.5 | ||||
| Cardona et al. [77] | EGFR-TKIs | 15 | 40 (15.2–64.7) | <0.001 | 7.87 (7.5–10.5) | 0.001 | 25.4 | 0.06 |
| EGFR-TKIs + Bevacizumab | 18 | 94.4 (83.8–100) | 11.12 (9.83–14.5) | 30.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishihara, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Ishikawa, F.; Higuchi, K.; Hasebe, Y.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Ando, K.; Kuroda, Y.; et al. Mechanisms of EGFR-TKI-Induced Apoptosis and Strategies Targeting Apoptosis in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Genes 2022, 13, 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122183
Nishihara S, Yamaoka T, Ishikawa F, Higuchi K, Hasebe Y, Manabe R, Kishino Y, Kusumoto S, Ando K, Kuroda Y, et al. Mechanisms of EGFR-TKI-Induced Apoptosis and Strategies Targeting Apoptosis in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Genes. 2022; 13(12):2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122183
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishihara, Shigetoshi, Toshimitsu Yamaoka, Fumihiro Ishikawa, Kensuke Higuchi, Yuki Hasebe, Ryo Manabe, Yasunari Kishino, Sojiro Kusumoto, Koichi Ando, Yusuke Kuroda, and et al. 2022. "Mechanisms of EGFR-TKI-Induced Apoptosis and Strategies Targeting Apoptosis in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" Genes 13, no. 12: 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122183
APA StyleNishihara, S., Yamaoka, T., Ishikawa, F., Higuchi, K., Hasebe, Y., Manabe, R., Kishino, Y., Kusumoto, S., Ando, K., Kuroda, Y., Ohmori, T., Sagara, H., Yoshida, H., & Tsurutani, J. (2022). Mechanisms of EGFR-TKI-Induced Apoptosis and Strategies Targeting Apoptosis in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Genes, 13(12), 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122183







