Abstract
Currently, metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is a leading global cause of chronic liver disease, and is expected to become one of the most common indications of liver transplantation. MAFLD is associated with obesity, involving multiple mechanisms such as alterations in lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, hyperinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, cell apoptosis, oxidative stress, and extracellular matrix formation. However, the onset and progression of MAFLD is variable among individuals, being influenced by intrinsic (personal) and external environmental factors. In this context, sequence structural variants across the human genome, epigenetic phenomena (i.e., DNA methylation, histone modifications, and long non-coding RNAs) affecting gene expression, gut microbiota dysbiosis, and metabolomics/lipidomic fingerprints may account for differences in MAFLD outcomes through interactions with nutritional features. This knowledge may contribute to gaining a deeper understanding of the molecular and physiological processes underlying MAFLD pathogenesis and phenotype heterogeneity, as well as facilitating the identification of biomarkers of disease progression and therapeutic targets for the implementation of tailored nutritional strategies. This comprehensive literature review highlights the potential of nutrigenetic, nutriepigenetic, nutrimetagenomic, nutritranscriptomics, and nutrimetabolomic approaches for the prevention and management of MAFLD in humans through the lens of precision nutrition.
1. Introduction
Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) was recently proposed as a more appropriate overarching term rather than nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) to refer to a chronic liver disease typically associated with obesity, with a more focused clinical approach [1]. The MAFLD spectrum ranges from simple steatosis (abnormal accumulation of triglycerides in the hepatocyte) to steatohepatitis (the inflammatory advanced stage of this disease), cirrhosis, and even liver cancer [2]. Currently, MAFLD is a leading global cause of chronic liver disease, and is expected to become one of the most common indications of liver transplantation [3].
MAFLD pathogenesis involves multiple mechanisms such as disruptions in lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, hyperinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, cell apoptosis, oxidative stress, extracellular matrix formation (fibrosis), and intestinal microbiota alterations [4]. However, the onset and progression of MAFLD is variable among individuals, being influenced by genetic, epigenetic, and food environments specific to each population [5].
In this context, a number of DNA sequence structural variants across the human genome have been associated with the susceptibility and severity of MAFLD trough interactions with nutritional factors [6]. In addition, dietary regulation of gene expression affecting MAFLD pathogenesis may involve epigenetic mechanisms including DNA methylation, histone modifications, and long non-coding RNA features [7]. Of note, gut microbiota dysbiosis is a common feature in MAFLD patients, mainly combined with nutritionally unbalanced poor diets [8]. Furthermore, metabolomic and lipidomic fingerprints related to food consumption have been identified as potential biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of MAFLD development and phenotype categorization [9].
This knowledge may contribute to gaining a deeper understanding of the molecular and physiopatological mechanisms underlying MAFLD, as well as facilitating the identification of therapeutic targets for the design of tailored nutritional strategies. This literature review provides examples of emerging nutrigenetic, nutriepigenetic, nutrimetagenomic, nutritranscriptomics, and nutrimetabolomic approaches for the prevention and management of MAFLD in humans through the lens of precision nutrition (Figure 1).
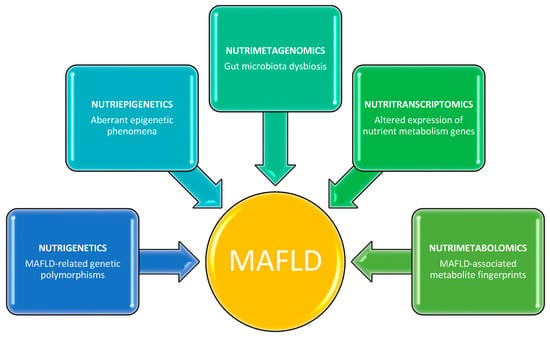
Figure 1.
Multi-omics nutritional approaches for identifying potential targets involved in the pathogenesis of MAFLD.
1.1. Nutrigenetics
The variability in MAFLD phenotypes can be influenced by the genetic background under certain nutritional conditions [10]. For example, after carbohydrate overfeeding (consuming an extra 1000 kcal/d with 98% of energy from carbohydrates over 3 weeks), an increase in liver fat content and serum triglycerides concentrations was observed in PNPLA3*GG homozygous subjects for the rs738409 polymorphism, but not in PNPLA3*CC carriers [11]. In agreement with these findings, carbohydrate/sugar consumption was positively associated with hepatic fat deposition only in overweight Hispanic children carrying the PNPLA3 GG genotype [12]. Accordingly, this genotype was also related to higher degrees of hepatic steatosis in adolescents who reported drinking sweetened drinks at least once weekly [13].
Of note, liver fat accumulation and the serum levels of alanine aminotransferase were influenced by the interaction between the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake and the PNPLA3 GG genotype in children and adolescents [14]. Similarly, the intakes of several dietary types of unsaturated fat (including monounsaturated fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and omega-6 fatty acids) were differentially associated with liver fibrosis by PNPLA3 G risk alleles [15]. Remarkably, it was demonstrated that the PNPLA3 rs738409 variant significantly modulated the relationship between MAFLD-related fibrosis severity and the intakes of carbohydrates, omega-3 fatty acids, total isoflavones, methionine, and choline intakes in non-Hispanic whites [16]. Interestingly, a meta-analysis demonstrated that people with the GG genotype of the PNPLA3 rs738409 variant were 105% more likely to develop MAFLD, followed by the CG heterozygotes (19% higher risk of MAFLD); conversely, those carrying the CC genotype had a 52% lower chance of presenting this outcome [17].
In addition to PNPLA3 variations, it was evidenced that obese adolescents with the TT genotype of the GCKR rs1260326 polymorphism underwent higher rates of liver de novo lipogenesis after an acute carbohydrate (75 g glucose and 25 g fructose) challenge [18]. In addition, participants with the minor haplotype in the 22q13 loci (comprising LARGE rs240072, RBFOX2 rs11089778, TRIOBP rs12628603, PNPLA3 rs738409, and PARVB rs2073080 genetic variants) had a higher MAFLD risk that was exacerbated by high carbohydrate intake (75% of energy from carbohydrates) and noodle/meat-rich dietary patterns (70th percentiles) in Koreans [19]. Furthermore, high fruit intake (>2 portions/d) increased the risk of MAFLD in subjects carrying the risk alleles of at least one of the following metabolic gene polymorphisms involved in oxidative stress: GSTT1*null, GSTM1*null, SULT1A1*2, CYP2E1*6, and CYP1A1*2A [20]. Moreover, an increase in fish intake by one portion/week exerted an additive effect on the risk of developing MAFLD in subjects carrying the risk allele of the TM6SF2 rs58542926 variant [21].
Some studies have also evaluated the influence of genetic polymorphisms in response to nutritional interventions in MAFLD. In this regard, the PNPLA3 GG genotype was associated with greater liver fat reductions compared with CC homozygotes after consuming a hypocaloric (1000 kcal deficit/d) low-carbohydrate diet (20 g/d of carbohydrates) for 6 days [22]. Likewise, PNPLA3 GG genotype carriers displayed a significant change in hepatic fat and plasma triglyceride levels at the end of an intervention with a low-omega 6:omega 3 ratio (4:1) normocaloric diet in obese youth [23]. Furthermore, it was reported that subjects carrying the T allele of the SH2B1 rs7359397 polymorphism showed a greater decrease in liver fat content when prescribed an energy-restricted treatment (−30% of the individual’s requirements) for 6 months [24].
Concerning the use of nutritional supplements for treating MAFLD, it was demonstrated that the PNPLA3 G allele attenuated the beneficial effect of 6 months of supplementation (silymarin 60% plus 30 IU vitamin E/d) on reducing plasma transaminases levels in MAFLD patients [25]. Findings from the WELCOME trial also revealed that the PNPLA3 GG genotype worsened liver fat status and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) tissue enrichment after 4 g DHA + eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) supplementation for 15–18 months in subjects with MAFLD [26]. Comparably, the PNPLA3 G allele led to a decreased response to DHA supplementation (250–500 mg/d) in children with MAFLD [27].
1.2. Nutriepigenetics
Dysregulation of epigenetic phenomena (including DNA methylation, histone modifications, and long non-coding RNA features) can alter cell phenotype and related physiological functions, leading to the onset and progression of diverse chronic diseases, including MAFLD [28].
DNA methylation: Of note, a nutriepigenetic analysis demonstrated that a low carbohydrate diet (37–40% of energy from carbohydrates) alone or combined with aerobic exercise over 6 months can protect against the progression of MAFLD by inducing methylation changes at the GAB2 gene in blood [29]. In addition, a differential DNA methylation pattern at the A2MP1 gene was identified in MAFLD participants adhering to either an isocaloric low-fat (30% of calories from fat) diet or Mediterranean low-carbohydrate (40–70 g/d of carbohydrates) diet plus 28 g walnuts/d over 18 months [30]. Moreover, in vitro analyses using HepG2 human hepatoma cells revealed that resveratrol administration attenuated glucose-induced MAFLD development through DNA methylation modification of the NRF2 gene promoter [31].
Histone modifications: In vitro assays have shown that tannic acid (a hydrolysable tannin polyphenol found in many dietary plant products such as coffee, tea, cocoa, and sorghum grain) ameliorates lipid accumulation via downregulation of lipogenesis-related gene (SREBP-1c, ACLY, FASN, PPARγ) expression and inhibition of histone acetyltransferase activity in HepG2 human cells [32]. Using this same cell line, black mulberry fruit extract markedly reduced the expression of proteins associated with lipogenesis, which was attributed to suppression of total acetylated lysine as well as specific histone acetylation of proteins H3K14 and H3K27 [33]. Likewise, Schisandra chinensis berry extract protected against steatosis development by inhibiting histone H3K9 acetylation in oleic acid-treated HepG2 cells [34].
Long non-coding RNA: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a role in nutrient metabolism (i.e., dietary fatty acids) by modulating gene expression, with potential applications as biomarkers in metabolic diseases including MAFLD [35]. Accordingly, miR-26a potentially contributed to the regulation of fatty acid and sterol homeostasis in an in vitro cell model of MAFLD induced by palmitic acid (PA) and oleic acid (OA), which occur naturally in various animal and vegetable fats and oils [36]. Likewise, PA supply led to decreased miR-139-5p, miR-30b-5p, miR-422a, and miR-146a in human hepatocytes, in parallel with increased lipogenesis and fatty acid transport, but also led to decreased glucose metabolism and diminished fatty acid oxidation [37]. Furthermore, miR-122 [38], miR-34a [39], miR-141 [40], and miR-23b [41] influenced nutrient-induced MAFLD pathogenesis by targeting sirtuin 1 in vitro. Moreover, the long non-coding RNA-H19 promoted hepatic lipogenesis in human liver cells treated with PA/OA by directly altering the miR-130a/PPARγ axis [42]. Several vitamin D-modulated miRNAs (such as miR-27, miR-125, miR-155, miR-192, miR-223, miR-375, and miR-378) have been identified as potentially relevant to MAFLD pathogenesis, emphasizing the importance of measuring serum and hepatic miRNAs in response to vitamin D supplementation in upcoming trials [43].
1.3. Nutrimetagenomics
Advances in sequencing methods have allowed the identification and taxonomic characterization of microbial communities and their effects on health using genomic techniques, such as 16S rRNA amplicon or shotgun metagenomic sequencing [44]. Growing evidence supports the modulatory role of diet in human gut microbiome composition, affecting several metabolic pathways in the host [45]. In particular, it has been reported that dietary cholesterol, fiber, fat, or carbohydrates could modify the microbiome to contribute to the development of MAFLD and its accompanying liver complications [46].
This knowledge emphasizes the search for nutritional strategies improving metabolic and liver-related markers in MAFLD by restoring the homeostasis of the intestinal microbiota [47]. Interestingly, an increase in nutritional fiber (from 19 g/d to 29 g/d) resulted in reduced liver enzymes and improved hepatic steatosis in patients with MAFLD undergoing weight reduction, possibly by altering intestinal permeability [48]. Correspondingly, it has been suggested that the incorporation of prebiotics (non-digestible carbohydrates) into the diet may reduce hepatic lipids and ameliorate risk factors associated with MAFLD [49]. Accordingly, it was reported that supplementation with inulin-type fructans (ITF) prebiotics (16 g/d of inulin/oligofructose for 3 months) in obese women led to higher abundances in Bifidobacterium and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii as well as a decrease in Bacteroides intestinalis, B. vulgatus, and Propionibacterium, with potential implications in the management of obesity-related liver disease [50]. Furthermore, children who were overweight or obese and received oligofructose-enriched inulin (8 g/day for 16 weeks) underwent significant reductions in abdominal body fat deposition and serum levels of triglycerides and IL-6 (involved in MAFLD outcomes); these findings were associated with increases in species of the genus Bifidobacterium and decreases in Bacteroides vulgatus [51]. Indeed, novel therapeutic approaches for the prevention and management of MAFLD targeting the microbiota include the administration of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics [52].
Of note, dietary components provide nutrients for bacteria utilization, which then produce metabolites putatively implicated in the pathophysiology of MAFLD [53]. The mechanisms underlying hepatic responses to the bioactive substances from gut bacteria (short-chain fatty acids, indole and its derivatives, trimethylamine, secondary bile acids, carotenoids, and phenolic compounds) have been related to the regulation of glycolipid metabolism, immune signaling response, and redox homeostasis [54]. In this regard, total fecal concentrations of microbiome-derived short-chain fatty acids (acetate and propionate) positively correlated with BMI, fasting insulinemia, and insulin resistance in obese women, whose concentrations were significantly reduced after 16 g/d of ITF administration for 3 months in these patients [55].
In addition, polyphenols exert important health benefits due to their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-adipogenic properties, being able to modulate the composition of intestinal microbes, which in turn, catabolize polyphenols to release bioactive metabolites [56]. Remarkably, the consumption of grape pomace extract for 4 weeks reduced the serum levels of trimethylamine N-oxide (a metabolite associated with MAFLD severity) in healthy volunteers for reshaping the gut microbiota [57]. Likewise, MAFLD patients treated with litchi-derived polyphenol (oligonol) improved liver steatosis through reducing pathogenic bacteria (Dorea, Romboutsia, Erysipelotrichaceae UCG-003, and Agathobacter) and increasing beneficial bacteria (such as Akkermansia, Lachnospira, Dialister, and Faecalibacterium) [58]. Moreover, it has been reported that the effects of polyphenols on the regulation of intestinal barrier integrity via induction of transcriptional factors, kinases, and enzymes may account for their positive impact on liver health [59]. Interestingly, changes in microbiome composition (β diversity and specific bacteria) were associated with intrahepatic fat losses after consuming a green Mediterranean diet enriched with green plants and polyphenols for 18 months [60].
In addition, unbalanced intakes of omega 3 fatty acids may affect the gut microbiota homeostasis and alter their absorption, bioavailability, and biotransformation, leading to altered nutrient release to the liver [61]. Therefore, balanced intakes of omega-3 fatty acids may exert a therapeutic role in MAFLD by reverting the altered microbiota profile and increasing the production of anti-inflammatory compounds [62]. For this purpose, the intake of fish oil (rich in omega 3 fatty acids) has been recommended for promoting intestinal wall integrity by interacting with host immune cells [63].
1.4. Nutritranscriptomics
The effect of diet on the risk of MAFLD may involve changes in gene expression patterns of critical metabolic genes [64]. For instance, a nutrigenomic study showed that the higher consumption of fructose in patients with MAFLD was accompanied by upregulation of hepatic TLR4 and PAI-1 mRNA expression compared to controls, increasing intestinal translocation of bacterial endotoxin [65]. The excessive intake of fructose in patients with MAFLD was also related to a parallel increase in hepatic mRNA expression of fructokinase (an important enzyme for fructose metabolism) and fatty acid synthase (implicated in lipogenesis) genes [66]. In liver cells, PNPLA3 expression was reversibly suppressed by glucose depletion and increased by glucose refeeding [67]. Of note, dietary polyphenols (resveratrol, quercetin, catechin, and berberine) protected against steatosis in an in vitro model of MAFLD by modulating the expression of mRNA for enzymes participating in lipid metabolism and mitochondrial function [68]. In a similar assay, catechin, quercetin, and resveratrol increased the expression of manganese superoxide dismutase (antioxidant enzyme) and prevented a large increase in the inflammatory TNF-α expression [69].
1.5. Nutrimetabolomics
Nutritional metabolomics (nutrimetabolomics) is a key analytical tool that allows the comprehensive metabolic analysis of physiological measurements and energy balance, expediting our ability to identify metabolic diseases that are influenced by foods and nutrients/bioactive compounds to develop targeted diet-based treatments [70]. Thus, nutrimetabolomics focuses on the analysis of many hundreds of metabolites in complex specimens (biofluids, tissues, or cells) to provide better and more individualized biomarkers related to the dietary effects on health and disease [71].
In this context, a systematic review covering the analysis of circulating biomarkers following MAFLD syndrome revealed significant differences in the metabolism of amino acids, fatty acids, and vitamins in MAFLD patients compared to healthy controls [72]. In addition, urinary metabolome testing contributed to defining a metabolic fingerprint associated with MAFLD in obese children by identifying metabolic pathways and metabolites reflecting typical obesity dietary habits and gut–liver axis perturbations [73]. In line with this finding, a Western non-vegetarian dietary pattern positively correlated with a serum metabolite profile characterized by branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), aromatic amino acids, and short-chain acylcarnitines, which in turn, were adversely associated with metabolic alterations including a liver fat measurement [74]. In contrast, plasma alkylresorcinol metabolite, a biomarker for whole-grain intake, was inversely associated with the risk of MAFLD in Chinese adults [75].
Of note, a significant increase in BCAA isoleucine was also identified as a metabolomic salivary signature of obesity-related liver disease in children [76]. Notably, several nutrient-related metabolites (glycocholic acid, taurocholic acid, phenylalanine, and BCAA) increased according to the severity of MAFLD, while glutathione concentrations decreased [77]. Metabolite profiling or serum samples showed that aminotransferase concentrations are a signature of liver metabolic perturbations in MAFLD patients, particularly at the amino acid metabolism and Krebs cycle level [78]. Moreover, serum metabolomic studies found differences in ether- and ester-containing phospholipids as well as in the amino acids lysine, glycine, and isoleucine between obese healthy and obese MAFLD groups [79]. Furthermore, metabolites significantly associated with steatohepatitis in children included methionine, phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylcholine, sphingolipids, and purine, with relevance in the nutrition field [80].
Regarding micronutrients, the metabolome characterization of human livers showed that vitamin A homeostasis is disrupted in MAFLD and potentially contributes to disease progression, as demonstrated by the hepatic decreased concentrations of retinyl palmitate (RP), all-trans-retinoic acid (atRA), 13-cisRA, and 4-oxo-atRA in these samples [81]. Indeed, altered vitamin A metabolism enhances profibrogenic gene expression, hepatic stellate cell activation, and collagen deposition in the liver, providing insights into cell-specific contributions to vitamin A loss and leading to novel nutritional interventions in liver fibrosis [82]. In a two-stage metabolic tissue screening, hydroquinone and nicotinic acid (NA) were inversely correlated with histological MAFLD severity, whereas only the human nutritional intake of NA equivalent was consistent with a protective effect of this compound against MAFLD progression [83].
2. Conclusions
MAFLD is a complex disease, where several endogenous and exogenous factors are involved. Advances in omics technologies are allowing approaches toward multifactorial diseases from a more comprehensive and integral perspective. In this regard, nutrigenetic studies have identified polymorphisms in genes related to lipid metabolism and oxidative stress as associated with the risk of developing MAFLD depending on the dietary consumption of carbohydrates and fats. Selected changes in the expression of lipogenesis-related genes may involve epigenetic mechanisms such as differentially methylated promoter regions, histone acetylation, and specific miRNA induction. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that some nutritional strategies (i.e., prebiotics) reduce liver fat deposition by modulating the gut microbiota and restoring the integrity of the intestinal barrier. In addition, nutrigenomic research has evidenced the upregulation of steatogenic genes after fructose or glucose overloads, which can be reversed by adequate intakes of plant-derived polyphenols (resveratrol, quercetin, and catechin). Furthermore, the biofluid concentrations of several nutrient-related metabolites (such as brain chain amino acids and phospholipids) have been used as biomarkers for the severity of MAFLD. Although more investigation in humans is still necessary, these scientific insights may contribute to gaining a deeper understanding of the molecular and physiological processes underlying MAFLD pathogenesis and phenotype heterogeneity, as well as enabling the characterization of biomarkers of disease progression and severity. This knowledge may also facilitate the identification of therapeutic targets for the implementation of tailored dietary strategies for the prevention, prognosis, and monitoring of MAFLD outcomes through the lens of precision nutrition.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; International Consensus Panel. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeren, J.; Scheja, L. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and lipoprotein metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, M.G.; Majumdar, A. Metabolic associated fatty liver disease: Addressing a new era in liver transplantation. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 1168–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, W.; Ma, T.; Cai, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; She, Z.; Wan, F.; Li, H. Liver Fibrosis and MAFLD: From Molecular Aspects to Novel Pharmacological Strategies. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 761538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, W.; Schürmann, A. Genetic and epigenetic factors determining NAFLD risk. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; DeForest, N.; Majithia, A.R. Human Genetics to Identify Therapeutic Targets for NAFLD: Challenges and Opportunities. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 777075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Sanabria, J.S.; Escutia-Gutiérrez, R.; Rosas-Campos, R.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J.S.; Sandoval-Rodríguez, A. An Update in Epigenetics in Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 770504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.; Rivera, L.; Furness, J.B.; Angus, P.W. The role of the gut microbiota in NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoodi, M.; Gastaldelli, A.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Arretxe, E.; Alonso, C.; Gaggini, M.; Brosnan, J.; Anstee, Q.M.; Millet, O.; Ortiz, P.; et al. Metabolomics and lipidomics in NAFLD: Biomarkers and non-invasive diagnostic tests. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 835–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, M.; Longo, M.; Rustichelli, A.; Dongiovanni, P. Nutrition and Genetics in NAFLD: The Perfect Binomium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevastianova, K.; Santos, A.; Kotronen, A.; Hakkarainen, A.; Makkonen, J.; Silander, K.; Peltonen, M.; Romeo, S.; Lundbom, J.; Lundbom, N.; et al. Effect of short-term carbohydrate overfeeding and long-term weight loss on liver fat in overweight humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.N.; Lê, K.A.; Walker, R.W.; Vikman, S.; Spruijt-Metz, D.; Weigensberg, M.J.; Allayee, H.; Goran, M.I. Increased hepatic fat in overweight Hispanic youth influenced by interaction between genetic variation in PNPLA3 and high dietary carbohydrate and sugar consumption. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobili, V.; Liccardo, D.; Bedogni, G.; Salvatori, G.; Gnani, D.; Bersani, I.; Alisi, A.; Valenti, L.; Raponi, M. Influence of dietary pattern, physical activity, and I148M PNPLA3 on steatosis severity in at-risk adolescents. Genes Nutr. 2014, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, N.; Savoye, M.; Kim, G.; Marotto, K.; Shaw, M.M.; Pierpont, B.; Caprio, S. Hepatic fat accumulation is modulated by the interaction between the rs738409 variant in the PNPLA3 gene and the dietary omega6/omega3 PUFA intake. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.B.; Arenaza, L.; Rios, C.; Plows, J.F.; Berger, P.K.; Alderete, T.L.; Fogel, J.L.; Nayak, K.; Mohamed, P.; Hwang, D.; et al. PNPLA3 Genotype, Arachidonic Acid Intake, and Unsaturated Fat Intake Influences Liver Fibrosis in Hispanic Youth with Obesity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Pirola, C.J.; Sookoian, S.; Wilson, L.A.; Belt, P.; Liang, T.; Liu, W.; Chalasani, N. Impact of the Association Between PNPLA3 Genetic Variation and Dietary Intake on the Risk of Significant Fibrosis in Patients with NAFLD. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, N.; Darvishi, N.; Mansouri, K.; Ghasemi, H.; Hosseinian-Far, M.; Darvishi, F.; Mohammadi, M. Association between PNPLA3 rs738409 polymorphism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, N.; Caprio, S.; Pierpont, B.; Van Name, M.; Savoye, M.; Parks, E.J. Hepatic De Novo Lipogenesis in Obese Youth Is Modulated by a Common Variant in the GCKR Gene. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1125–E1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kang, S. High carbohydrate and noodle/meat-rich dietary patterns interact with the minor haplotype in the 22q13 loci to increase its association with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease risk in Koreans. Nutr. Res. 2020, 82, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, L.; Dall’armi, V.; Cefalo, C.; Nedovic, B.; Arzani, D.; Amore, R.; Rapaccini, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ricciardi, W.; Grieco, A.; et al. A case-control study on the effect of metabolic gene polymorphisms, nutrition, and their interaction on the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Genes Nutr. 2014, 9, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafati, I.P.; Dimitriou, M.; Borsa, D.; Vlachogiannakos, J.; Revenas, K.; Kokkinos, A.; Ladas, S.D.; Dedoussis, G.V. Fish intake interacts with TM6SF2 gene variant to affect NAFLD risk: Results of a case-control study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevastianova, K.; Kotronen, A.; Gastaldelli, A.; Perttilä, J.; Hakkarainen, A.; Lundbom, J.; Suojanen, L.; Orho-Melander, M.; Lundbom, N.; Ferrannini, E.; et al. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 (adiponutrin) confers sensitivity to weight loss-induced decrease in liver fat in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Name, M.A.; Savoye, M.; Chick, J.M.; Galuppo, B.T.; Feldstein, A.E.; Pierpont, B.; Johnson, C.; Shabanova, V.; Ekong, U.; Valentino, P.L.; et al. A Low ω-6 to ω-3 PUFA Ratio (n-6:n-3 PUFA) Diet to Treat Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Youth. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2314–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Diaz-Del-Campo, N.; Marin-Alejandre, B.A.; Cantero, I.; Monreal, J.I.; Elorz, M.; Herrero, J.I.; Benito-Boillos, A.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Tur, J.A.; et al. Differential response to a 6-month energy-restricted treatment depending on SH2B1 rs7359397 variant in NAFLD subjects: Fatty Liver in Obesity (FLiO) Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 3043–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.; Laserna, C.; Rojo, M.Á.; Mora, N.; García Sánchez, C.; Pina, M.; Sigüenza, R.; Durà, M.; Primo, D.; Izaola, O.; et al. Role of the PNPLA3 polymorphism rs738409 on silymarin + vitamin E response in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2018, 110, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorletti, E.; West, A.L.; Bhatia, L.; Hoile, S.P.; McCormick, K.G.; Burdge, G.C.; Lillycrop, K.A.; Clough, G.F.; Calder, P.C.; Byrne, C.D. Treating liver fat and serum triglyceride levels in NAFLD, effects of PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 genotypes: Results from the WELCOME trial. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, V.; Bedogni, G.; Donati, B.; Alisi, A.; Valenti, L. The I148M variant of PNPLA3 reduces the response to docosahexaenoic acid in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Med. Food 2013, 16, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Milagro, F.I.; Allayee, H.; Chmurzynska, A.; Choi, M.S.; Curi, R.; De Caterina, R.; Ferguson, L.R.; Goni, L.; Kang, J.X.; et al. Guide for Current Nutrigenetic, Nutrigenomic, and Nutriepigenetic Approaches for Precision Nutrition Involving the Prevention and Management of Chronic Diseases Associated with Obesity. J. Nutrigenet. Nutr. 2017, 10, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yuan, F.; Yue, S.; Jiang, F.; Ren, D.; Liu, L.; Bi, Y.; Guo, Z.; Ji, L.; Han, K.; et al. Effect of exercise and diet intervention in NAFLD and NASH via GAB2 methylation. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaskolka Meir, A.; Keller, M.; Müller, L.; Bernhart, S.H.; Tsaban, G.; Zelicha, H.; Rinott, E.; Kaplan, A.; Gepner, Y.; Shelef, I.; et al. Effects of lifestyle interventions on epigenetic signatures of liver fat: Central randomized controlled trial. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.; Teimouri, M.; Shabani, M.; Koushki, M.; Babaei Khorzoughi, R.; Namvarjah, F.; Izadi, P.; Meshkani, R. Resveratrol alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through epigenetic modification of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 119, 105667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.Y.; Song, J.H.; Lee, J.; Shin, E.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, J.T.; Choi, H.K. Tannic acid, a novel histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, prevents non-alcoholic fatty liver disease both in vivo and in vitro model. Mol. Metab. 2019, 19, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, H.K.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, J.T. Black Mulberry Extract Elicits Hepatoprotective Effects in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Models by Inhibition of Histone Acetylation. J. Med. Food 2021, 24, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.Y.; Shin, E.J.; Choi, H.K.; Kim, S.H.; Sung, M.J.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, J.T. Schisandra chinensis berry extract protects against steatosis by inhibiting histone acetylation in oleic acid-treated HepG2 cells and in the livers of diet-induced obese mice. Nutr. Res. 2017, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald-Ramos, K.; Martínez-Ibarra, A.; Monroy, A.; Miranda-Ríos, J.; Cerbón, M. Effect of Dietary Fatty Acids on MicroRNA Expression Related to Metabolic Disorders and Inflammation in Human and Animal Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.; Darwish, H.A.; Eldeib, K.M.; Abdel Azim, S.A. miR-26a Potentially Contributes to the Regulation of Fatty Acid and Sterol Metabolism In Vitro Human HepG2 Cell Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 8515343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, J.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Mercader, J.M.; Sabater, M.; Rovira, Ò.; Gironès, J.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; Ortega, F.J. Decreased lipid metabolism but increased FA biosynthesis are coupled with changes in liver microRNAs in obese subjects with NAFLD. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.K.; Dai, W.; Zheng, Y.W.; Zhao, S.P. miR-122 promotes hepatic lipogenesis via inhibiting the LKB1/AMPK pathway by targeting Sirt1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, M.; Cao, Y.; Ma, L.; Shen, Y.; Velikanova, A.A.; Li, X.; Sun, C.; Zhao, Y. miR-34a regulates lipid metabolism by targeting SIRT1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with iron overload. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 695, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, Z.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Abdolvahabi, Z.; Ghorbanhosseini, S.S.; Hesari, Z.; Yarahmadi, S.; Ezzati-Mobasser, S.; Seiri, P.; Borji, M.; Meshkani, R.; et al. microRNA-141 is associated with hepatic steatosis by downregulating the sirtuin1/AMP-activated protein kinase pathway in hepatocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borji, M.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Shafiee, S.M.; Owji, A.A.; Abdolvahabi, Z.; Hesari, Z.; Ilbeigi, D.; Seiri, P.; Yousefi, Z. Down-Regulation of SIRT1 Expression by mir-23b Contributes to Lipid Accumulation in HepG2 Cells. Biochem. Genet. 2019, 57, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, G.D.; Liu, B. LncRNA-H19 promotes hepatic lipogenesis by directly regulating miR-130a/PPARγ axis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Moon, R.; Thorne, J.L.; Moore, J.B. NAFLD and vitamin D: Evidence for intersection of microRNA-regulated pathways. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2021, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, D.; Bonham, K.S.; Rowland, S.; Pattanayak, C.W.; RESONANCE Consortium; Klepac-Ceraj, V. Comparative Analysis of 16S rRNA Gene and Metagenome Sequencing in Pediatric Gut Microbiomes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 670336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Vázquez, S.; Aragonès, G.; Del Bas, J.M.; Escoté, X. Diet, Gut Microbiota and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Three Parts of the Same Axis. Cells 2020, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, X. Diet and gut microbiome in fatty liver and its associated liver cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moszak, M.; Szulińska, M.; Walczak-Gałęzewska, M.; Bogdański, P. Nutritional Approach Targeting Gut Microbiota in NAFLD-To Date. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, M.; Maciejewska, D.; Ryterska, K.; Czerwińka-Rogowska, M.; Jamioł-Milc, D.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Milkiewicz, P.; Raszeja-Wyszomirska, J.; Stachowska, E. Gut Permeability Might be Improved by Dietary Fiber in Individuals with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Undergoing Weight Reduction. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieze, A.; Holleman, F.; Zoetendal, E.G.; de Vos, W.M.; Hoekstra, J.B.; Nieuwdorp, M. The environment within: How gut microbiota may influence metabolism and body composition. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewulf, E.M.; Cani, P.D.; Claus, S.P.; Fuentes, S.; Puylaert, P.G.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B.; de Vos, W.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Thissen, J.P.; et al. Insight into the prebiotic concept: Lessons from an exploratory, double blind intervention study with inulin-type fructans in obese women. Gut 2013, 62, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolucci, A.C.; Hume, M.P.; Martínez, I.; Mayengbam, S.; Walter, J.; Reimer, R.A. Prebiotics Reduce Body Fat and Alter Intestinal Microbiota in Children Who Are Overweight or with Obesity. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Suk, K.T.; Kim, B.Y. Modulation of gut microbiome in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pro-, pre-, syn-, and antibiotics. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, D.; Stewart, C.J.; Day, C.P.; Trenell, M. Gut Microbiota and Lifestyle Interventions in NAFLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W. Gut Microbiota-Derived Components and Metabolites in the Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, N.; Dewulf, E.M.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B.; Cani, P.D.; Mahillon, J.; de Vos, W.M.; Thissen, J.P.; Gueimonde, M.; de Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; et al. Inulin-type fructans modulate intestinal Bifidobacterium species populations and decrease fecal short-chain fatty acids in obese women. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Zheng, H. Dietary Polyphenol, Gut Microbiota, and Health Benefits. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, G.; Maisto, M.; Schisano, C.; Ciampaglia, R.; Narciso, V.; Tenore, G.C.; Novellino, E. Effects of Grape Pomace Polyphenolic Extract (Taurisolo®) in Reducing TMAO Serum Levels in Humans: Preliminary Results from a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Cross-Over Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinato, T.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Dissayabutra, T.; Chutaputti, A.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Chuaypen, N. Litchi-Derived Polyphenol Alleviates Liver Steatosis and Gut Dysbiosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Bibi, S.; Du, M.; Suzuki, T.; Zhu, M.J. Regulation of the intestinal tight junction by natural polyphenols: A mechanistic perspective. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3830–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaskolka Meir, A.; Rinott, E.; Tsaban, G.; Zelicha, H.; Kaplan, A.; Rosen, P.; Shelef, I.; Youngster, I.; Shalev, A.; Blüher, M.; et al. Effect of green-Mediterranean diet on intrahepatic fat: The DIRECT PLUS randomised controlled trial. Gut 2021, 70, 2085–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shama, S.; Liu, W. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Gut Microbiota: A Reciprocal Interaction in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, L.; Molinari, R.; Farinon, B.; Merendino, N. Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on the Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolini, C. Effects of Fish n-3 PUFAs on Intestinal Microbiota and Immune System. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaiou, M.; Amrani, R.; Rihn, B.; Hajri, T. Dietary Patterns Influence Target Gene Expression through Emerging Epigenetic Mechanisms in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuy, S.; Ladurner, R.; Volynets, V.; Wagner, S.; Strahl, S.; Königsrainer, A.; Maier, K.P.; Bischoff, S.C.; Bergheim, I. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in humans is associated with increased plasma endotoxin and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 concentrations and with fructose intake. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Cirillo, P.; Sautin, Y.; McCall, S.; Bruchette, J.L.; Diehl, A.M.; Johnson, R.J.; Abdelmalek, M.F. Fructose consumption as a risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Ito, K.; Huang, K.H.; Sae-tan, S.; Lambert, J.D.; Ross, A.C. Shifts in dietary carbohydrate-lipid exposure regulate expression of the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated gene PNPLA3/adiponutrin in mouse liver and HepG2 human liver cells. Metabolism 2014, 63, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, H.; Omidian, K.; Bandy, B. Dietary Polyphenols Protect Against Oleic Acid-Induced Steatosis in an In Vitro Model of NAFLD by Modulating Lipid Metabolism and Improving Mitochondrial Function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiei, H.; Omidian, K.; Bandy, B. Comparison of dietary polyphenols for protection against molecular mechanisms underlying nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a cell model of steatosis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeMieux, M.J.; Aljawadi, A.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Nutrimetabolomics. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, A.; Capozzi, F. Foodomics for healthy nutrition. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2014, 17, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, C.; Noto, A.; Ibba, L.; Deidda, M.; Fanos, V.; Muntoni, S.; Leoni, V.P.; Atzori, L. Contribution of Metabolomics to the Understanding of NAFLD and NASH Syndromes: A Systematic Review. Metabolites 2021, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troisi, J.; Pierri, L.; Landolfi, A.; Marciano, F.; Bisogno, A.; Belmonte, F.; Palladino, C.; Guercio Nuzio, S.; Campiglia, P.; Vajro, P. Urinary Metabolomics in Pediatric Obesity and NAFLD Identifies Metabolic Pathways/Metabolites Related to Dietary Habits and Gut-Liver Axis Perturbations. Nutrients 2017, 9, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Gadgil, M.D.; Newgard, C.B.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Ilkayeva, O.R.; Scholtens, D.M.; Hu, F.B.; Kanaya, A.M.; et al. Dietary Patterns among Asian Indians Living in the United States Have Distinct Metabolomic Profiles That Are Associated with Cardiometabolic Risk. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Deng, Y.; Geng, X.; Fang, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Zhan, M.; Li, D.; Zhu, K.; Li, H.; et al. Plasma Alkylresorcinol Metabolite, a Biomarker for Whole-Grain Intake, Is Inversely Associated with Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Case-Control Study of Chinese Adults. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troisi, J.; Belmonte, F.; Bisogno, A.; Pierri, L.; Colucci, A.; Scala, G.; Cavallo, P.; Mandato, C.; Di Nuzzi, A.; Di Michele, L.; et al. Metabolomic Salivary Signature of Pediatric Obesity Related Liver Disease and Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masarone, M.; Troisi, J.; Aglitti, A.; Torre, P.; Colucci, A.; Dallio, M.; Federico, A.; Balsano, C.; Persico, M. Untargeted metabolomics as a diagnostic tool in NAFLD: Discrimination of steatosis, steatohepatitis and cirrhosis. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookoian, S.; Castaño, G.O.; Scian, R.; Fernández Gianotti, T.; Dopazo, H.; Rohr, C.; Gaj, G.; San Martino, J.; Sevic, I.; Flichman, D.; et al. Serum aminotransferases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are a signature of liver metabolic perturbations at the amino acid and Krebs cycle level. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.; Eder, S.K.; Felder, T.K.; Paulweber, B.; Zandanell, S.; Stechemesser, L.; Schranz, M.; Strebinger, G.; Huber-Schönauer, U.; Niederseer, D.; et al. Clinical and metabolic characterization of obese subjects without non-alcoholic fatty liver: A targeted metabolomics approach. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordy, K.; Li, F.; Lee, D.J.; Kinchen, J.M.; Jew, M.H.; La Rocque, M.E.; Zabih, S.; Saavedra, M.; Woodward, C.; Cunningham, N.J.; et al. Metabolomic Predictors of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Advanced Fibrosis in Children. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 713234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Kirkwood, J.; Won, K.J.; Tjota, N.; Jeong, H.; Isoherranen, N. Characterization of Vitamin A Metabolome in Human Livers with and without Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czuba, L.C.; Wu, X.; Huang, W.; Hollingshead, N.; Roberto, J.B.; Kenerson, H.L.; Yeung, R.S.; Crispe, I.N.; Isoherranen, N. Altered vitamin A metabolism in human liver slices corresponds to fibrogenesis. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Schönfels, W.; Patsenker, E.; Fahrner, R.; Itzel, T.; Hinrichsen, H.; Brosch, M.; Erhart, W.; Gruodyte, A.; Vollnberg, B.; Richter, K.; et al. Metabolomic tissue signature in human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease identifies protective candidate metabolites. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).