Abstract
Zinc finger-homeodomain proteins are amongst the most prominent transcription factors (TFs) involved in biological processes, such as growth, development, and morphogenesis, and assist plants in alleviating the adverse effects of abiotic and biotic stresses. In the present study, genome-wide identification and expression analyses of the maize ZHD gene family were conducted. A total of 21 ZHD genes with different physicochemical properties were found distributed on nine chromosomes in maize. Through sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis, we divided ZHD proteins into eight groups that have variations in gene structure, motif distribution, and a conserved ZF domain. Synteny analysis indicated duplication in four pairs of genes and the presence of orthologues of maize in monocots. Ka/Ks ratios suggested that strong pure selection occurred during evolution. Expression profiling revealed that the genes are evenly expressed in different tissues. Most of the genes were found to make a contribution to abiotic stress response, plant growth, and development. Overall, the evolutionary research on exons and introns, motif distributions, and cis-acting regions suggests that these genes play distinct roles in biological processes which may provide a basis for further study of these genes’ functions in other crops.
1. Introduction
The zinc finger-homeodomain (ZF-HD) TFs, containing a conserved zinc finger (ZF) domain in the N-terminal and a homeodomain (HD) in the C-terminal, are members of a plant-specific TF superfamily [1]. The ZF-HD gene family plays an important role in plant developmental processes and stress responses. ZHD genes are plant-specific, nearly all intronless, and are related to MINI ZINC FINGER genes that possess only the zinc finger. Phylogenetic analysis suggested that ZHDs have expanded considerably during angiosperm evolution [1]. Biotic and abiotic stresses, such as drought, salinity, heavy metals, high temperatures, heat stress, chilling stress, insects, pathogens, mechanical injury, etc., cause severe damage in terms of kmo, plant growth, development, yield, and quality [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. A well-specialized gene network encodes numerous proteins that systematically control plant growth. To control plant differential growth, flowering, development, alleviation of the adverse impacts of both abiotic and biotic stresses, signal transduction, and morphogenesis, a special class of proteins called transcription factors (TFs) bind the particular DNA or nucleotide sequences responsible for these functions [11]. TFs help plants endure adverse conditions by regulating the binding of specific promoter cis-elements involved in signalling [12]. TFs are found in a wide range of regulatory proteins that can bind to DNA/RNA sequences and participate actively in protein–protein interactions [2].
A conserved homeodomain, which consists of 60 amino acids and has a characteristic three-helix shape, can interact with a variety of DNA sequences [13]. HD domain proteins are divided into subgroups based on their size, structure, location, and connection with other proteins: WUSCHEL-related HB (WOX), knotted-related HB (KNOX), Bell-type HD, and zinc finger motif-associated HD (ZF-HD), leucine zipper-associated HD (HD-Zip), and HD associated with a finger domain (PHD finger) [14,15]. ZF-HD is engaged in signal transduction in plants under various abiotic and biotic conditions and has aroused the curiosity of researchers interested in learning more about this TF’s role in plants. ZF-HD proteins were first identified as potential regulators of the C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (PEP-Case) in C4 Flaveriatrinervia species [16]. An N’-end conserved zinc finger domain with zinc ions, rich in cystine or histidine residues, and a cysteine-rich N′-end conserved zinc-finger domain (ZF) with zinc ions and cysteine or histidine residues are two structural properties of these proteins [17], along with a C′ -end conserved homeodomain (HD) [1]. ZF motifs are surrounded by cysteine or histidine residues, either singly or in pairs, and are stabilized by a zinc ion in the form of a finger-shaped loop [1]. The N-terminal part or ZF domain has two types of domains, CH2C and C3H2, separated by a variable-length spacer. The primary function of the HD domain of the ZF-HD transcription factor is to bind DNA sequences to activate or repress the targeted genes [18]. Protein–DNA interactions mediated by HD are enhanced by ZF domains.
There is clear evidence underscoring that ZF-HD/ZHD proteins play a pivotal role in alleviating the adverse effects of environmental stresses [1,19,20,21]. For instance, Arabidopsis ZHD4 protein expression is upregulated in case of drought, salinity, and cold stress [22]. Additionally, AtZHD1 and AtZHD10 improve drought tolerance [23] and simultaneously modulate hormone signalling [24]. In another model crop, rice, among 14 ZHDs proteins, four respond to cold and drought stress and can bind with the promoter region of the DREB1 gene family [25]. Other crops, such as Chinese cabbage, have 31 ZF-HD/ZHD genes [1]. Recent studies have reported the upregulation of ZHD genes under various abiotic stress conditions. For instance, four ZHDs in cucumber [26], ten ZHDs in wheat [27], NtZHD21 in tobacco [19], LlZHD4 in Lilium lancifolium [20], and barley’s HvZHD1 were upregulated under abiotic stresses, such as cold, drought, salt, water deficiency, etc.
Furthermore, ZF-HD/ZHD genes can modulate biological processes in plants [14]. For instance, in Arabidopsis, AtZHD5 is responsible for leaf size enlargement, AtZHD10 is involved in hypocotyl elongation, and AtZHD8 [24], tomato SlZF-HD7, and tartary buckwheat FtZF-HD11 (Fagopyrum tataricum) [28,29] play vital parts in the flowering of these plants. Furthermore, earlier research has revealed that the majority of Chinese cabbage BraZF-HD genes and wheat TaZF-HDs are involved in biological activities [1,29].
Z. mays L. is the most extensively grown cereal crop in Africa and South America. Nowadays, it is becoming popular in developing countries, such as Bangladesh, and in developed countries [30] for use in human and animal consumable products, such as corn syrup, corn starch, baby corn, and feed. The world’s maize production climbed from 313 million tons in 1971 to 1162 million tons in 2020, with an average yearly growth rate of 3.07 percent (https://knoema.com/atlas/World/topics/Agriculture/Crops-Production-Quantity-tonnes/Maize-production) (accessed on 1 September 2020). Abiotic stresses, such as intense water logging, extreme temperature, and drought, affect maize production significantly [31]. Drought, high salinity conditions, and extreme temperatures all cause transcription factors (TFs), such as ZHDTF, to interact with cis-elements or other TF proteins to respond to various stresses in signal transduction pathways of stress response which control plant growth and development by protecting plants [32,33]. Since maize crop yield is highly damaged by abiotic stresses, it is essential to identify the ZF-HD gene family roles in this crop.
To date, no study has been carried out on the ZF-HD/ZHD gene family in maize (Z. mays). So far, functional analysis of ZmZHD9 has been performed to identify the role of the gene in the case of drought stress [34]. We proceeded to adopt a bioinformatics approach for a genome-wide characterization and evolutionary analysis of ZHD genes and their encoded proteins in the maize genome [35]. We intended to analyze chromosomal locations, gene structures, promoter elements, evolutionary relationships, distinct tissue expressions, duplication patterns, and miRNA patterns. Our results lay the groundwork for exploring the mechanisms of ZHD genes in response to various abiotic stresses in maize.
2. Results
2.1. Identification of ZHD Family Genes and Sequence Analysis of Their Proteins
In Z. mays, twenty-one ZF-HD genes were found. The names of the genes identified were chosen from those given by GrassTFDB [36] (Table 1). Out of 10 chromosomes, chromosome number 9 of maize did not possess any one of the 21 ZF-HD domains. The lengths of the protein sequences varied from 89 aa to 655 aa, whereas their molecular weights ranged from 9.8 kDa to 71.6 kDa (Table 1). In both cases, ZmZHD13 and ZmZHD18 showed the minimum and maximum amino acid lengths and molecular weights (Table 1). The genes ZmZHD10, ZmZHD12, ZmZHD15, ZmZHD16, and ZmZHD17 are associated with theoretical pI values less than 7, while the rest of them showed values higher than 7 (Table 1), which shows the values where the amino acids can be neutral. The GRAVY values of ZmZHDs ranged from −0.985 to −0.138, demonstrating that the proteins are hydrophilic in nature (Table 1). Although all the ZmZHD proteins are in the nucleus, some of them are also located in the cell wall and chloroplasts (Table 1). From all the parameters, we can predict that ZmZHD proteins have diverse physicochemical properties.

Table 1.
Detailed information about the ZmZHD genes and corresponding proteins in Z. mays L.
2.2. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Construction
To conclude the evolutionary analysis, we performed a multiple sequence alignment and built a phylogenetic tree for maize ZmZHD proteins and ZHD proteins of other species using protein sequences of 21 maize ZHDs, 14 rice ZHDs, 15 Arabidopsis ZHDs, 16 foxtail millet ZHDs, 14 sorghum ZHDs, 11 barley ZHDs, 21 purple false brome (Brachypodiumdistachyon) ZHDs, and 13 Heller’s rosette grass (Dichantheliumoligosanthes) ZHDs. In two multiple sequence alignments (MSAs), MSA1 contains only ZmZHD proteins (Figure 1). Motif 1 and Motif 4 are presented, which represent the ZF (zinc finger) domains (Supplementary Materials, Table S1). ZHD proteins are classified into eight groups, I to VIII, according to the popularized tobacco and wheat ZHD family classifications [19,37]. Clade 1 is the smallest class, containing about 7.2% of the total 125 ZHD proteins, and Clade VIII is the largest class, containing 22.4% of the total 125 ZHD proteins. (Figure 2). In the largest group, around 21% of maize and barley proteins, about 14% of rice and foxtail millet proteins are present (Figure 2). Clade VII is next to the largest one and contains about 17% of the ZHD proteins found in all the mentioned species. Among these, approximately 19% are found in maize, 15% in rice, millet, and sorghum, and 10% in Arabidopsis and barley (Figure 2). In Clades III and VIII, all plant proteins are present asymmetrically.

Figure 1.
Multiple sequence alignment of the conserved domains of the members of the ZmZHD gene family in maize. Motifs 1 and 4 represent ZF domains.
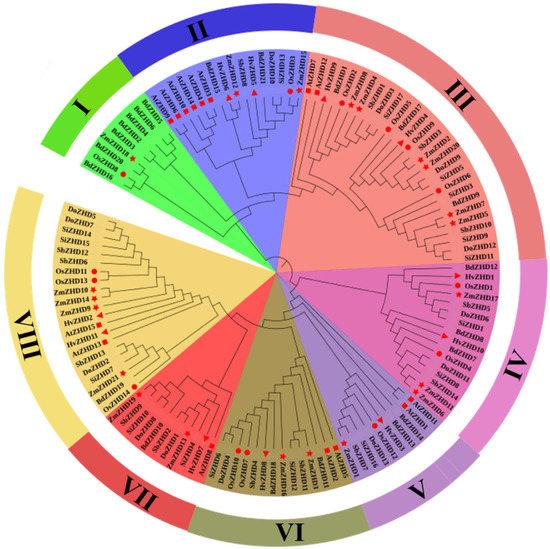
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of full-length ZHD protein sequences from Z. mays (Zm, maize), Arabidopsis thaliana (At, Arabidopsis), Oryzasativa (Os, rice), Sorghum bicholor (Sb, sorghum), Brachypodiumdistachyon (Bd, purple false brome), and Dichantheliumoligosanthes (Do, Heller’s rosette grass). Red circles, red checkmarks, and red triangle, red rectangular, and red stars indicate Arabidopsis, and rice sequences, maize respectively.
2.3. Chromosomal Location, Gene Structure, and Motif Composition Analysis
Twenty-one ZmZHDs were mapped onto 10 Z. mays chromosomes, according to their locations (Supplementary File S1, Figure S1). ZmZHD genes are not symmetrically distributed across all of the 10 chromosomes. None of the 21 genes is located on chromosome number 9 (Chr9). Chr4 contains four genes, while Chr1 and Chr2 contain 3 genes, and Chr3, Chr5, and Chr10 contain 2 genes each (Supplementary File S1, Figure S1). By inputting the entire lengths of the ZmZHD protein sequences, a phylogenetic tree was created to examine the evolutionary connections among the 21 ZmZHD genes. This tree was split into two classes, Class I and Class II, which were further divided into four and three subclasses, respectively (Figure 3A). We identified at least two motifs and a maximum of seven motifs in ZHD proteins using MEME (Figure 3C). All contain Motif 1 and Motif 4 in their sequences, and these constituted the most highly conserved parts of the ZF domain. Class I genes contain a greater number of motifs than Class II genes. Interestingly, Motif 2 and Motif 3 are present in all the members of class I, while they are only present in Subclass IIb. Motif 9 was detected in the specific subfamily subclass Ic. Almost all the ZmZHD genes have no introns in their sequences (Figure 3B). Only about 24% of the genes have introns ranging from 1 to 4, while only two of the genes have UTR regions in their sequences (Figure 3B).
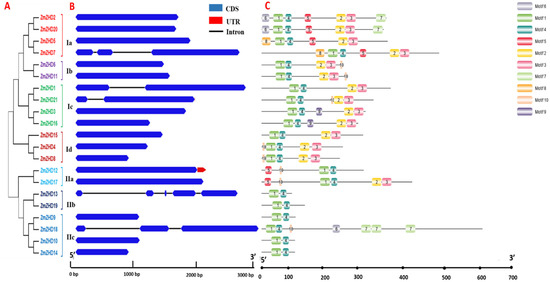
Figure 3.
The phylogenetic relationships, conserved motifs, and gene structures of ZmZHD proteins and ZmZHD genes. (A) A maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree of the maize proteins was constructed from full-length sequences in MEGA 11.0 with 1000 bootstrap replicates. (B) The gene structures of the ZmZHD genes include introns (black lines), exons (blue rectangles), and untranslated regions (UTRs, red rectangles). The scale bar indicates 0.5 kb. (C) Distribution of conserved motifs in the ZmZHD proteins. The colored boxes represent Motifs 1–10. The scale bar indicates 100 aa.
2.4. Analysis of Cis-Elements in ZmZHD Promoters
Even though cis-acting elements are non-coding DNA sequences, they influence transcriptomic processes in gene promoter regions. Plant CARE software was used to identify around 25 cis-acting regions from the 2000 bp upstream regions of the genomic sequences of the ZmZHD genes (Figure 4). ZmZHD genes contain plant-growth- and development-related promoters, such as circadian, the O2- site, as-1, the AAGAA- motif, the CCAAT- motif, the GCN4- motif, and the RY- element (Figure 4). Abscisic acid-responsive ABRE, the MeJA-responsive CGTCA- motif, the gibberellic acid-responsive GARE motif, salicylic acid-responsive TCA-element, TGA-element, and auxin-responsive AUxRR-core are hormone-responsive cis-elements found in the ZmZHD promoters (Figure 4). Stress-related components were found in several promoters, including TC-rich repeats implicated in defense and stress response, as well as low-temperature-response (LTR)-related motifs, and MYB and MYB binding sites were found in all ZmZHD promoters, these being implicated in the induction of drought, high-salt, and low-temperature responses (Figure 4). These results indicated that ZHD genes in maize are mainly responsible for hormonal and biotic and abiotic stress tolerance.
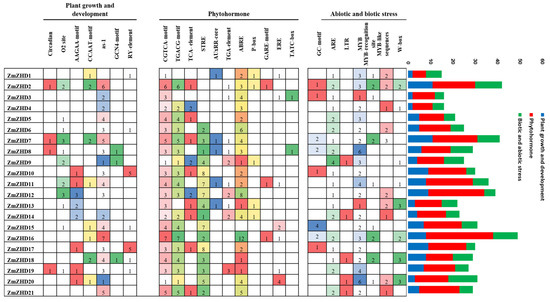
Figure 4.
Cis-acting elements identified in the promoter regions of ZmZHD genes.
2.5. Synteny and Evolutionary Analysis of ZmZHDGenes
Gene duplication is a common occurrence in all organisms that results in the creation of new functional genes from previously existing ones, which drives evolution. As a result, we used Advanced Circos in TBtools to perform a microsynteny analysis to evaluate duplications among the ZmZHD genes. In four gene pairs, segmental duplications were discovered (Figure 5). To further investigate the gene duplications in the ZHD gene family, a duel synteny analysis was performed including maize and four other plants: sorghum, foxtail millet, the Oryza indica group, and Arabidopsis (Figure 6). The results showed that all the monocots, i.e., sorghum, foxtail millet, and the Oryza indica group, have 21 syntenic relations with maize while Arabidopsis has only one (Figure 6). As a result, there was more genetic overlap found between maize and monocot genomes than between Z. mays and dicot genomes. In addition, all monocot genes had orthologues in maize, implying that maize has undergone additional whole-genome duplication (WGD) events during its evolution. We computed Ka, Ks, and Ka/Ks values for four homologous ZmZHD gene pairs to examine evolutionary limitations and selection pressures on the ZmZHD genes (Supplementary File S2, Table S2). Ks values can be used to retrodict the time of whole-genome duplication (WGD) occurrences, since they indicate the background base substitution rate [38,39]. The Ks values for the ZmZHD gene pairs varied from 0.04 to 91.87, implying that a large-scale ZmZHD gene duplication event occurred between 7066.56 and 2.88 million years ago (MYA) (Supplementary File S2, Table S2). The gene pairs’ Ka/Ks ratios were all less than 1.0, suggesting that these genes were subjected to strong purifying selection during evolution.
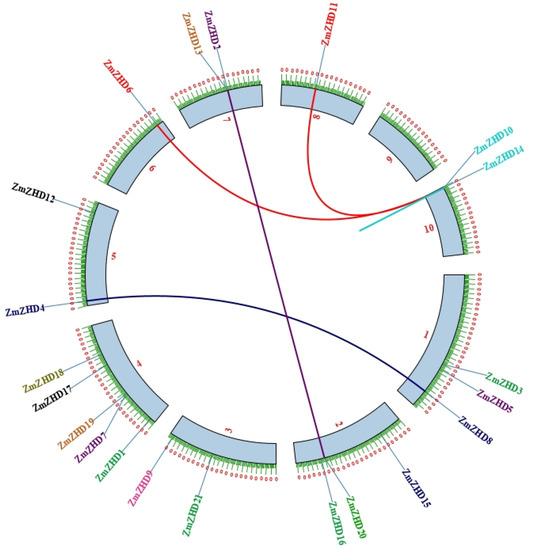
Figure 5.
Chromosomal distribution and inter-chromosomal relationships of ZmZHD genes. Red lines connect duplication gene pairs between ZmZHD10 and ZmZHD11 and between ZmZHD6 and ZmZHD10; blue lines connect duplication gene pairs between ZmZHD4 and ZmZHD8, and violet lines connect duplication gene pairs between ZmZHD2 and ZmZHD20.
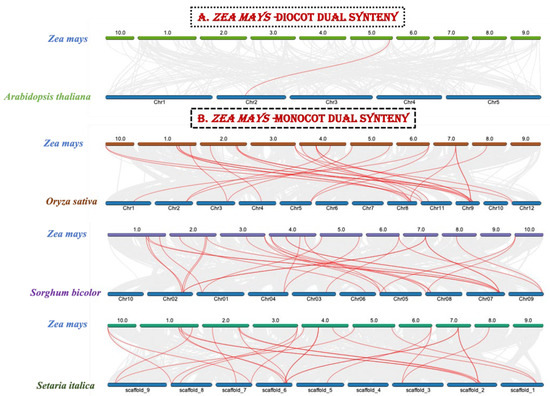
Figure 6.
Synteny analysis of the maize genome with one monocot (A) and three dicot (B) plant genomes. The gray lines represent aligned blocks between the paired genomes, and the red lines indicate syntenic ZHD gene pairs. We performed both dual synteny and specific gene family synteny analyses for the maize genome, this being one of the most important fields in comparative genomic analysis, as it is the basis of evolutionary studies at both the gene and genome levels. We used the species-specific gene family protein sequences, but not in the synteny analysis, as most of the causes have not been properly studied, for instance, the chromosomal gene positions are quite enigmatic. Insofar as we could find well-researched sequences online, we retrieved and dual-synteny-analyzed them. In addition, a specific gene family from the maize genome synteny analysis was studied to comprehend duplication occurrences and internal evolutionary processes.
2.6. Construction of a PPI Network and Expression Profiling of ZmZHD Genes in Various Tissues
To predict potential interactions among the proteins, we used the STRING database (https://string-db.org/) accessed on 1 September 2022. Only 8 proteins, ZmZHD2, ZmZHD3, ZmZHD3, ZmZHD3, ZmZHD3, ZmZHD3, ZmZHD3, ZmZHD3, ZmZHD5, ZmZHD6, ZmZHD7, ZmZHD11, ZmZHD16, and ZmZHD20, out of the 21 were correlated at the medium level (0.400) and at the highest level (0.900) of confidence (Figure 7). Each of the eight proteins is interconnected with the other four. ZmZHD6, for example, is closely linked to ZmZHD2, ZmZHZD5, ZmZHD7, and ZmZHD20. The core nodes of ZmZHD6 and ZmZHD11 only have high confidence levels for their associated proteins (highest confidence level, 0.900) (Figure 7 and Supplementary File S2, Table S3).
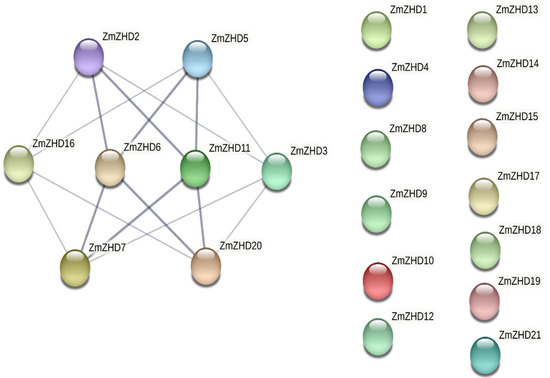
Figure 7.
Interaction network of the ZHD proteins in Z. mays L. Deep ash-colored lines indicate the highest level of confidence (0.900), and faded ash-colored lines indicate a medium level of confidence (0.400). Lineless proteins do not have any relationship with other proteins. Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) play a crucial role in cellular functions and biological processes, including cell–cell interactions and metabolic and developmental control in all organisms. We performed in silico protein–protein interaction analyses within the family for phylogenetic profiling and to identify structural patterns and homologous pairs, intracellular localizations, and post-translational modifications among the proteins. Furthermore, we considered the interaction and involvement of major signalling or stress pathways, though we avoid discussion of these subjects due to their complexity.
Specific gene expression patterns in certain developmental activities in plants can usually be predicted with tissue-specific transcriptome data. Among ZmZHD genes, ZmZHD11 is expressed in almost all of the 16 tissues in maize plants. The expression levels of the Group A proteins, ZmZHD2, ZmZHD4, ZmZHD11, and ZmZHD21, for the sixteen tissues were high in comparison to those of the others (Figure 8 and Supplementary File S2, Table S4). The protein expression levels were even for all the tissues, for example, maize unpollinated silk (US), vegetative meristem (VM), pericarp and aleurone (PA), embryo after pollination (EmAP), endosperm after pollination (EnAP), internode (IN), mature leaf (ML), mature female spikelet (MFS), primary root (PR), secondary root (SR), root differentiation zone (RDZ), root elongation zone (REZ), stomatal divisional zone of the leaf (SDZL), tip of ear primordium (TEP), germinated embryo (GEM), and growth zone of leaf (GZL) tissues. We can predict that the expression profiles of the Group A genes are much higher than those of the others.
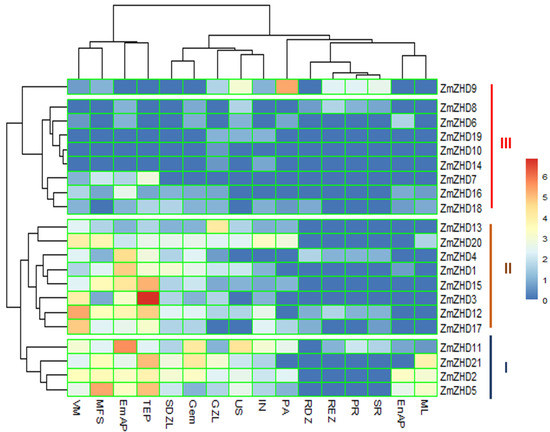
Figure 8.
Heatmap showing the expression levels of ZmZHD genes in different tissues. Normalized Log2 (FPKM + 1) values are plotted against respective tissues. Tissue name abbreviations are as follows: unpollinated silk (US), vegetative meristem (VM), pericarp and aleurone (PA), embryo after pollination (EmAP), endosperm after pollination (EnAP), internode (IN), mature leaf (ML), mature female spikelet (MFS), primary root (PR), secondary root (SR), root differentiation zone (RDZ), root elongation zone (REZ), stomatal divisional zone of the leaf (SDZL), tip of the primordium (TEP), germinated embryo (Gem), growth zone of the leaf (GZL).
2.7. MiRNA Target Site Prediction and Validation
miRNAs cleave mRNA or inhibit translation to produce proteins and regulate target gene expressions. About 29 miRNA families were found in the maize genome, with 188 members, and 26 of 29 families exhibited perfect and sometimes nearly perfect target sequences. All the mature miRNA sequences were predicted against the CDSs of ZmZHD genes and 77 miRNAs were shown to be present (Supplementary File S2, Table S5). miRNA167 has ten target sites in ZmZHD5, miRNA4109 has seven target sites in ZmZHD1, and miRN4099 and miRN4186 have four target sites in ZmZHD10 and ZmZHD21, respectively (Figure 9). One miRNA, miR2275, has target sites in different genes, such as ZmZHD1, ZmZHD15, ZmZHD1, ZmZHD4, ZmZHD15, ZmZHD20, and ZmZHD1, and most of the rest of the miRNAs have one or two target sites (Supplementary File S2, Table S5). These results reveal the correlations of Zma-miRNA167 and miRNA4109 with other miRNA families.
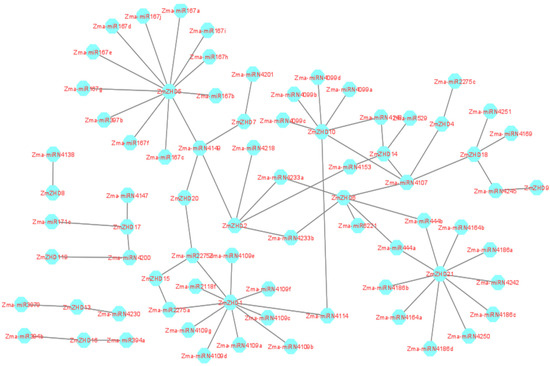
Figure 9.
Picture of the regulatory network relationships between the putative miRNAs and their targeted maize ZHD genes.
3. Discussion
A conserved zinc finger (ZF) domain on the N-terminal and a homeodomain on the C-terminal is present in the zinc finger-homeodomain (ZF-HD). The homeodomain possesses a highly conserved structure containing approximately 60 amino acids. The homeodomain is folded into a recognition helix, which has a characteristic three-helix structure that is attached to the main sulcus of DNA, forming a special link with DNA [40]. ZF-HD transcription factors are only present in plants and play an important role in plant growth and development, as well as biotic and abiotic stress alleviation [41]. About 21 ZmZHD genes were found in maize in TFDB and BLASTp searches.
ZHD genes are exhibited only in terrestrial plants and expanded during angiosperm evolution [1,42]. Various evolutionary and structural analyses have been performed for the structural analysis of ZmZHD domains. These involved various methods, such as sequence alignment, phylogenetic tree, gene structure, motif organization, synteny, and gene duplication analyses. The function of a gene family is determined by the extent and the types of conserved regions basically present in an appropriate sequence alignment. Multiple sequence alignments showed that Motif 1 and Motif 4, which is popularly known as the ZF dimer (Figure 1), are consistent with those of other plant species [1,42], indicating that ZHD proteins have similar structures. ZmZHD genes were categorized into eight groups (I-VIII) in our tree analysis (Figure 2), which is consistent with earlier phylogenetic research on the crops [37,43,44,45,46,47]. Except for Groups I, IV, and VII, ZF-HD/ZHD proteins from Arabidopsis, rice, and maize were found to be in the majority of the groupings (Figure 2). Maize and rice were found in Groups I and IV, but only Arabidopsis and maize were found in Group VII (Figure 2), indicating a protein divergence from both monocots and dicots. Evolutionary insights can be extracted from the gene structures of the gene families [26]. In our gene structure study, most of the genes in the ZF-HD/ZHD gene family do not contain introns or UTRs (Figure 3B), and this phenomenon can be observed in many species [21,42,48]; the loss of introns might lead to an immediate response to abiotic stress.
On the contrary, five genes have one to four introns (Figure 3B), indicating the structural divergence of the maize ZF-HD/ZHD gene family. Except for tomatoes, our findings imply that ZF-HD/ZHD family genes have been largely conserved in evolution, along with their functions. In previous studies of ZF-HD/ZHD genes in other plants, researchers have concluded that these genes have undergone severe purifying selection, and their functions cannot be differentiated [42,48,49,50,51,52]. Motif analysis showed various conserved motifs of ZmZHD proteins in Classes I and II, revealing similar motifs present in the same subclass in the phylogenetic tree that are functionally similar (Figure 3A,C). Gene duplication mechanisms, such as segmental duplication, tandem repeats, and retro- and/or replicate transposition, contributed to biological evolution [53]. Many gene families have been documented to have expanded as a result of segmental duplication [54]. The gene pairs’ Ka/Ks ratios indicate that they have undergone purifying selection during genome-wide evolution, and the ZmZHD gene family’s duplication times vary from 2.88 to 7066.56 MYA (Supplementary File S2, Table S2).
Abiotic stresses adversely affect the growth and development of maize and ultimately affect economic production. ZF-HD/ZHD TFs play pivotal roles in the biological processes of plants [28]. For instance, in Arabidopsis, overexpressed ZF-HD1 upregulated several stress-inducible genes, eventually leading to significant increases in drought resistance [23]. So far, in maize crops, the expression patterns of ZmZHDs under abiotic stress have not yet been properly investigated. TF mechanisms depend on the cis-elements present in the related genes, which actually regulate the stress signalling and expression of the responsible genes. Numerous cis-elements were identified in a promoter region analysis of plant hormones and abiotic stresses (Figure 4), reflecting the ZmZHD gene expression roles in the external environment. Abscisic acid-responsive ABRE, MeJA-responsive CGTCA-motif, gibberellic acid responsive GARE-motif, salicylic acid-responsive TCA-element, TGA-element, and auxin-responsive AUxRR-core are hormone responsive cis-elements found in the ZmZHD promoters (Figure 4). Stress-related components were found in several promoters, including TC-rich repeats implicated in defense and stress response, as well as low-temperature response (LTR)-related motifs, and MYB and MYB binding sites were found in all ZmZHD promoters, these being implicated in the induction of drought, high-salt, and low-temperature responses. This shows that ZF-ZHD genes are stimulated by stress and that they are involved in stress-mediated pathways. Several studies have shown ZF-HD/ZHD gene participation in the case of abiotic/biotic stress. For example, the ZF-HD/ZHD gene family in Arabidopsis, tomato, cotton, grape, and Chinese cabbage was found to be involved in fighting various stress conditions, such as salt, drought, heat, and cold, by regulating stress-related hormones, such as ABA [1,27,42]. MYB and ARE help plants endure abiotic stress and are found in all the maize ZHD genes, especially ZmZHD8 and ZmZHD20, in the case of MYB, and ZmZHD9, in the case of ARE (Figure 5). These findings suggest that these genes are responsible for maize tolerance to abiotic stress. ZF-HD is involved in a variety of biological activities in plants, including growth, development, and stress reduction [55]. Specific biological activities are determined by tissue-specific expression patterns [56]. The majority of Arabidopsis ZF-HD/ZHD genes are located in floral tissues, indicating that they play a role in floral development regulation [42]. ZmZHD2, ZmZHD5, and ZmZHD21 exhibited greater expression patterns in floral tissues in this investigation (Figure 8), indicating that they may be involved in maize pollination [56,57]. The greater expression patterns of Cluster I and II genes in the heatmap for floral (unpollinated silk, endosperm after pollination, female spikelet, tip of ear primordium) and vegetative tissues (Figure 8) may have implications for their growth and development. ZmZHD6 and ZmZHD11 are the key genes in our study. They interact with other genes (Figure 7) and the ZF-HD protein dimerization region, including proteins, ZF-HD homeobox protein, and zinc finger-homeodomain protein (Supplementary File S2, Table S3).
MicroRNA was found to regulate the cellular responses of plants under stress conditions, such as salinity, cold, and dehydration [57,58,59,60]. Stress-responsive transcription factors (TFs) or functional genes are mainly targeted by several miRNAs [61]. Thus, miRNA may be involved in responses to stress conditions. Ten miR167 genes found in the maize ZHD genes (Supplementary File S2, Table S5) represent auxin response factor protein annotations found in maize [62]. This microRNA involved in maize shoot and leaf development enhances auxin response [62]. Another microRNA that regulates five ZmZHD genes (Supplementary File S2, Table S5) has not had its function elucidated yet. All of these results provide a valuable foundation for further future molecular investigations of ZmZHD genes and pave the way for the development of new varieties of maize.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Gene Retrieval and Sequence Analysis of the ZHD Gene Family in Maize
A BLASTp database search for Z. mays ZF dimers (PF04770) (sequence: vrYreClrNhaaslGghavDGCgeFmasgeegtaeaLkCaaCgCHrnFHrree) against Arabidopsis, sorghum, and rice was run to identify ZF-HD genes. For greater accuracy, ZF dimer domains (PF04770) were extracted from the Pfam database (http://pfam.xfam.org) accessed on 1 September 2022, and used to ensure the presence of this domain in the selected ZF-HD/ZHD genes, with an E-value < 1 × 10−5. Genome sequences, coding sequences (CDSs), and proteins sequences of Z. mays were retrieved from the Maize Genome Database (MaizeGDB; https://www.maizegdb.org/) accessed on 1 September 2022. Twenty-one ZmZHD gene domains were predicted using the Pfam database [63] and the SMART conserved domain search tool [64,65]. To estimate physiochemical properties, such as molecular weight (MW), isoelectric point (PI), and grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY), the ExPASyProtParam tool (http://www.expasy.org/protparam/) accessed on 1 September 2022, subcellular localization of the retrieved genes, and Cell-Ploc 2.0 were used (Chou and Shen, 2010), respectively. Arabidopsis (15), the rice indica group (14), foxtail millet (16), sorghum (14), barley (11), purple false brome (Brachypodium distachyon) (21), and Heller’s rosette grass (Dichanthelium oligosanthes) ZF-HD protein sequences (Supplementary File S2, Table S6) were retrieved from different databases, such as the TIAR database (https://www.Arabidopsis.org/) accessed on 1 September 2022, the iTAK database [66], and the Plant TFDB database [67]. The HMMER web server and the InterPro online tool (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/) accessed on 1 September 2022 were used for the confirmation of the ZF domains of these protein sequences [63].
4.2. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Construction
The amino acid sequences extracted from maize (21), Arabidopsis (15), the rice indica group (14), foxtail millet (16), sorghum (14), barley (11), purple false brome (B. distachyon) (21), and Heller’s rosette grass (D. oligosanthes) were aligned using the ClustalX v2.1 multiple sequence alignment tool [68] and then exported to Genedoc for further elaboration of these protein sequences (https://www.nrbcs.org/gfx/genedoc/ebinet.htm) accessed on 1 September 2022 [69]. In the MEGA11.0 program, a phylogenetic tree was built using the neighbor-joining (NJ) technique with 1000 bootstrap replicates, and the tree was updated using iTOL (https://itol.embl.de/) accessed on 1 September 2022 [65,70].
For the following reasons, we favored the neighbor-joining method above others. The basic objective was to reconstruct phylogenetic trees using evolutionary distance information. The idea behind this approach is to identify the out pairs at each level of clustering, starting with a star-shaped tree, that have the shortest overall branch length. Using this technique, the branch lengths and topology of a parsimonious tree can be easily determined. This method’s primary goal is to establish relationships between sequences based on their genetic distances; however, the evolutionary model does not account for this. We checked and rechecked the ZF dimer (PF04770) domain in both the HMMER and Conserved Domains Database (CDD) and the Resources-NCBI database for confirmation. Both are good materials for bioinformatics, with advantages and disadvantages. We used BLASTp and HMMER for different purposes. To discover our chosen gene family sequences and to check the published data, we performed a BLASTp search of our domain sequences against the genome databases or annotation projects for the chosen plant species.
4.3. Chromosomal Locations, Motif Compositions, and Exon and Intron Distributions
The chromosomal locations of the 21 genes identified on the 10 maize chromosomes were mapped using the MapGene2Chrom web v2 web tool [71], and information was gleaned from Maize GDB (https://www.maizegdb.org/) accessed on 1 September 2022. The positions of the conserved motifs of these 21 ZHD protein sequences were analyzed by setting a maximum width of 50, a minimum width ≥6, and a motif number of 10; other parameters were set to default in the online MEME tool (http://meme-suite.org/) accessed on 1 September 2022 [72]. For exon and intron distributions, the gene structure display server (GSDS) web tool [43] was used to align genomic sequences with the CDSs of the 21 maize ZHD genes.
4.4. Cis-Acting Elements and Functional Prediction
Putative cis-elements in maize ZHD genes of about 5 to 10 bp were retrieved using the Plant CARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) accessed on 1 September 2022 [73] web-based tool. The 2000 bp upstream sequence for each gene from the start codon was extracted from Phytozome 13 (https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/) accessed on 1 September 2022 for cis-regulatory element extraction, as the upstream region contained cis-elements that bound the transcription factors that regulate target genes [74].
4.5. Synteny Analysis of ZHD Proteins and ks/ka Ratios
Protein sequences of Z. mays were compared with protein sequences from the rice indica group, sorghum, and foxtail millet using TBtools software. Synteny relationships and duplication events among the ZHD proteins were predicted using MCScan [75], and the findings about gene duplications with gene pairs were used to identify duplications in the ZmZHD genes of maize along with those of several monocots and dicots, the results being visualized in TBtools [76]. An NCBI BLAST search was run considering 80% sequence similarity against each of the maize ZHD proteins to determine gene duplications [77]. The protein sequences of duplicated gene pairs were first aligned in Clustal Omega [78]. Then, the sequence alignments of proteins and their associated cDNA sequences were used, by means of the PAL2NAL online tool, to determine the relevant codon alignments [79]. Finally, Ks and Ks values were estimated using PAML’s CODEML software and the generated codon alignments [36]. The synonymous substitution rate (Ks), nonsynonymous substitution rate (Ka), and Ka/Ks ratio were calculated for homologous gene pairs using Ka/Ks Calculator2.0 [46]. The equation T = Ks/2λ (where λ = 6.5 × 10−9) was used to compute evolutionary divergence periods within the ZHD gene family.
4.6. Protein–Protein Interaction and Z. mays L. RNA-Sequencing Data Analysis
Protein–protein interactions were assessed with the aid of the STRING database, with a medium (0.400) confidence level, to determine the interrelationships among the 21 ZmZHD proteins. The Expression Atlas database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gxa/home) accessed on 1 September 2022 was used to obtain ZmZHD RNA-sequencing data [80], which were previously collected and analyzed by Walley et al. [81]. We collected data for a total of 16 tissues of Z. mays L.: unpollinated silk (US), vegetative meristem (VM), pericarp and aleurone (PA), embryo after pollination (EAM), endosperm after pollination (EAP), internode (IN), mature leaf (ML), female spikelet (FL), primary root (PR), secondary root (SR), root differentiation zone (RDZ), root elongation zone (REZ), stomatal divisional zone of the leaf (SDZF), tip of ear primordium (TED), germinated embryo (GE), and growth zone of the leaf (GZL) tissues. In the acquisition of expression data, the fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped reads (FPKM) unit was utilized. The FPKM values were transferred to log2 (FPKM + 1) form and then a heatmap was built using the pheatmap package in Rstudio [82].
4.7. MiRNA Target Site Prediction
To determine the target sites of the 21 genes in the ZmZHD gene family in maize, first, mature miRNA was retrieved from the PmiREM server (https://www.pmiren.com/) accessed on 1 September 2022. Then, the CDSs of the 21 genes were searched against mature miRNAs using the online server tool PsRNA (https://www.zhaolab.org/psRNATarget/) accessed on 1 September 2022, with the default parameters [83]. The linkages between the predicted miRNAs were constructed using Cytoscape software (https://www.omicshare.com/tools/) accessed on 1 September 2022 [84].
5. Conclusions
In this study, we divided the 21 ZHD genes in maize (Z. mays) into two groups through phylogenetic analysis. Based on evolutionary research, these proteins were classified into seven subgroups. Exon–intron arrangements, motifs, and cis-acting regions were all comparable for the genes grouped. These Z. mays ZHD genes may play a role in biological processes and environmental stress control, according to the promoter and expression profiles of tissue-specific RNA sequencing studies. This study provides a foundation for exploring the roles of these genes in stressful environments and investigating their molecular mechanisms.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/genes13112112/s1: Supplementary File S1, Figure S1: Chromosomal location of the ZmZHD genes in the 10 chromosomes of Z. mays. Figure S2: Synteny analysis of the maize genome with A. thaliana and Oryza sativa. And Figure S3: Synteny analysis of the maize genome with S. bicolor and S. italic. Supplementary File S2, Table S1: List of 10 motifs along with description. Table S2: Ks, Ka and Ks/Ka calculation and divergent time of the duplication maize ZHD pairs. Table S3a: Interaction among proteins with confidence level. Table S3b: List of node annotations. Table S4: Tissue specific transcriptome data in FPKM unit. Table S5: List of miRNA found in ZmZHD genes along with target alignments. Table S6: Sequences of the protein sequences of the selected species.
Author Contributions
M.A.U.I., M.H.B.K. and A.M.U.D.: Experimental work, Methodology, Data analysis, Writing—original draft. M.S.H., J.A.N., Z.K. and Q.A. (Qurban Ali 1): Methodology, Formal analyses, Software. M.A.U.I., M.S., M.M., R.M.A. and Q.A. (Qurban Ali 2): Software, Validations, Writing—review and editing. M.A.S.: Conceptualization, Writing—review and editing. H.M.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Correspondence, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Lushan Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences (no. 2021ZWZX28, to Hakim Manghwar).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, W.; Wu, P.; Li, Y.; Hou, X. Genome-wide analysis and expression patterns of ZF-HD transcription factors under different developmental tissues and abiotic stresses in Chinese cabbage. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoso, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Ritonga, F.N.; Ali, Q. WRKY transcription factors (TFs): Molecular switches to regulate drought, temperature, and salinity stresses in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1039329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Q.; Ahsan, M.; Ali, F.; Aslam, M.; Khan, N.H.; Munzoor, M.; Mustafa, H.S.B.; Muhammad, S. Heritability, heterosis and heterobeltiosis studies for morphological traits of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings. Adv. Life Sci. 2013, 1, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, Q.; Ahsan, M.; Kanwal, N.; Ali, F.; Ali, A.; Ahmed, W.; Ishfaq, M.; Saleem, M. Screening for drought tolerance: Comparison of maize hybrids under water deficit condition. Adv. Life Sci. 2016, 3, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, Q.; Ali, A.; Ahsan, M.; Nasir, I.A.; Abbas, H.G.; Ashraf, M.A. Line× Tester analysis for morpho-physiological traits of Zea mays L seedlings. Adv. Life Sci. 2014, 1, 242–253. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Ali, Q.; Manghwar, H.; Zhu, D. Identification, Phylogeny, Divergence, Structure, and Expression Analysis of A20/AN1 Zinc Finger Domain Containing Stress-Associated Proteins (SAPs) Genes in Jatropha curcas L. Genes 2022, 13, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Q.; Ayaz, M.; Mu, G.; Hussain, A.; Yuanyuan, Q.; Yu, C.; Xu, Y.; Manghwar, H.; Gu, Q.; Wu, H.; et al. Revealing Plant Growth-Promoting Mechanisms of Bacillus strains in Elevating Rice Growth and Its Interaction with Salt Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Q.; Ayaz, M.; Yu, C.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Wu, H.; Gao, X. Cadmium Tolerant Microbial Strains Possess Different Mechanisms for Cadmium Biosorption and Immobilization in Rice Seedlings. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajer, F.U.; Samma, M.K.; Ali, Q.; Rajar, W.A.; Gao, X. Bacillus spp.-Mediated Growth Promotion of Rice Seedlings and Suppression of Bacterial Blight Disease under Greenhouse Conditions. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Q.; Yu, C.; Hussain, A.; Ali, M.; Ahmar, S.; Sohail, M.A. Genome engineering technology for durable disease resistance: Recent progress and future outlooks for sustainable agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 860281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuda, N.; Ohme-Takagi, M. Functional analysis of transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 1232–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, L.L.; da Fonseca Dos Santos, R.; Neto, J.P.B.; Guida-Santos, M.; Crovella, S.; Benko-Iseppon, A.M. Transcription factors involved in plant resistance to pathogens. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariel, F.D.; Manavella, P.A.; Dezar, C.A.; Chan, R.L. The true story of the HD-Zip family. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englbrecht, C.C.; Schoof, H.; Böhm, S. Conservation, diversification and expansion of C2H2 zinc finger proteins in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. BMC Genom. 2004, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbach, T.; Scheer, N.; Werr, W. Transcriptional activation by the PHD finger is inhibited through an adjacent leucine zipper that binds 14–3-3 proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 3542–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windhövel, A.; Hein, I.; Dabrowa, R.; Stockhaus, J. Characterization of a novel class of plant homeodomain proteins that bind to the C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene of Flaveria trinervia. Plant Mol. Biol. 2001, 45, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.S.; Majumdar, I.; Grishin, N.V. Structural classification of zinc fingers: Survey and summary. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, M.; Ali, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, R. Salt Tolerant Bacillus Strains Improve Plant Growth Traits and Regulation of Phytohormones in Wheat under Salinity Stress. Plants 2022, 11, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xie, M.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ding, A.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y. Systematic investigations of the ZF-HD gene family in tobacco reveal their multiple roles in abiotic stresses. Agronomy 2021, 11, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lyu, Y. Functional characterization of Lilium lancifolium cold-responsive Zinc Finger Homeodomain (ZFHD) gene in abscisic acid and osmotic stress tolerance. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalmani, A.; Muhammad, I.; Sharif, R.; Zhao, C.; Ullah, U.; Zhang, D.; Jing, X.-Q.; Amin, B.; Jia, P.; Mobeen Tahir, M. Zinc finger-homeodomain genes: Evolution, functional differentiation, and expression profiling under flowering-related treatments and abiotic stresses in plants. Evol. Bioinform. 2019, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, O.; Vogt, S.; Uhlemann, R.; Zschiesche, W.; Humbeck, K. Stress induced and nuclear localized HIPP26 from Arabidopsis thaliana interacts via its heavy metal associated domain with the drought stress related zinc finger transcription factor ATHB29. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 69, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.S.P.; Nakashima, K.; Sakuma, Y.; Osakabe, Y.; Qin, F.; Simpson, S.D.; Maruyama, K.; Fujita, Y.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Co-expression of the stress-inducible zinc finger homeodomain ZFHD1 and NAC transcription factors enhances expression of the ERD1 gene in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 49, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrella, G.; Davidson, M.L.; O’Donnell, L.; Nastase, A.-M.; Herzyk, P.; Breton, G.; Pruneda-Paz, J.L.; Kay, S.A.; Chory, J.; Kaiserli, E. ZINC-FINGER interactions mediate transcriptional regulation of hypocotyl growth in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4503–E4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, D.D.; Barros, P.M.; Cordeiro, A.M.; Serra, T.S.; Lourenço, T.; Chander, S.; Oliveira, M.M.; Saibo, N.J. Seven zinc-finger transcription factors are novel regulators of the stress responsive gene OsDREB1B. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3643–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Zhu, C.; Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Y. Identification and transcriptional analysis of zinc finger-homeodomain (ZF-HD) family genes in cucumber. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 884–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L. Zinc finger-homeodomain transcriptional factors (ZF-HDs) in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): Identification, evolution, expression analysis and response to abiotic stresses. Plants 2021, 10, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, K.; Nath, U.K.; Robin, A.H.K.; Park, J.-I.; Lee, D.-J.; Kim, M.-B.; Kim, C.K.; Lim, K.-B.; Nou, I.S.; Chung, M.-Y. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of zinc finger homeodomain (ZHD) family genes reveal likely roles in organ development and stress responses in tomato. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sun, W.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, T.; Huang, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, G.; Tang, Z.; Bu, T.; Li, C. Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in tartary buckwheat (Fagopyum Tataricum). BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shi, X.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Ammiraju, J.S.; Kudrna, D.A.; Xiong, W.; Wang, H.; Dai, Z.; Zheng, Y. Genomic resources for gene discovery, functional genome annotation, and evolutionary studies of maize and its close relatives. Genetics 2013, 195, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, I.; de Vos, R.C.; Bones, A.M.; Hall, R.D. Plant molecular stress responses face climate change. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujjar, R.S.; Akhtar, M.; Singh, M. Transcription factors in abiotic stress tolerance. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 19, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udvardi, M.K.; Kakar, K.; Wandrey, M.; Montanari, O.; Murray, J.; Andriankaja, A.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Benedito, V.; Hofer, J.M.; Chueng, F. Legume transcription factors: Global regulators of plant development and response to the environment. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wei, L.; Cao, L.; Qiu, X.; Fu, J.; Wang, G.; Ku, L.; Wang, T. Function analysis of ZmZHD9, a positive regulator in drought stress response in transgenic maize. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnable, P.S.; Ware, D.; Fulton, R.S.; Stein, J.C.; Wei, F.; Pasternak, S.; Liang, C.; Zhang, J.; Fulton, L.; Graves, T.A. The B73 maize genome: Complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science 2009, 326, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Nishiyama, M.Y.; Fuentes, B.G.; Souza, G.M.; Janies, D.; Gray, J.; Grotewold, E. GRASSIUS: A platform for comparative regulatory genomics across the grasses. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nai, G.; Mao, J.; Lu, S.; Li, Y.; Ma, Z.; Chen, B. Genome-wide analysis and expression characterization of zinc finger homeodomain (ZHD) family genes responsed to different abiotic stresses and hormonal treatments in grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Wang, H.; Guo, C.; Zhang, N.; Zeng, L.; Chen, Y.; Ma, H.; Qi, J. Widespread whole genome duplications contribute to genome complexity and species diversity in angiosperms. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.H.B.; Raza, M.A.; Yu, H.Q.; Khan, I.; Sun, F.A.; Feng, L.Y.; Qu, J.T.; Fu, F.L.; Li, W.C. Expression, subcellular localization, and interactions of CPK family genes in maize. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhu, C.; Xie, S.; Weng, J.; Lin, Y.; Lai, Z.; Guo, Y. Genome-wide analysis of zinc finger motif-associated homeodomain (ZF-HD) family genes and their expression profiles under abiotic stresses and phytohormones stimuli in tea plants (Camellia sinensis). Sci. Hortic. 2021, 281, 109976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, B.; Wen, F.; Zhao, M.; Xia, Q.; Yang, D.-H.; Wang, G. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of HD-ZIP I gene subfamily in Nicotiana tabacum. Genes 2019, 10, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, T.; Li, J.; Yao, M.; Xu, X. Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of zinc-finger homeodomain transcription factors in tomato under abiotic stress. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2018, 143, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, H.; Xia, P.; Hu, Y.; Zhan, C.; Li, Y.; Gong, S.; Li, Y.; Ma, D. Genome-wide identification of ZF-HD gene family in Triticum aestivum: Molecular evolution mechanism and function analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yin, X.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Genome-wide identification, evolution and expression analysis of the grape (Vitis vinifera L.) zinc finger-homeodomain gene family. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5730–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-P.; Wan, H.-L.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J. γ-MYN: A new algorithm for estimating Ka and Ks with consideration of variable substitution rates. Biol. Direct 2009, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ayaz, A.; Zheng, M.; Yang, X.; Zaman, W.; Zhao, H.; Lü, S. Arabidopsis KCS5 and KCS6 Play Redundant Roles in Wax Synthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Cheng, X.; Cao, Y.; Su, X.; Manzoor, M.A.; Gao, J.; Cai, Y.; Lin, Y. Zinc finger-homeodomain transcriptional factors (ZHDs) in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum): Genome-wide identification and expression analysis in fiber development. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, A.; Huang, H.; Zheng, M.; Zaman, W.; Li, D.; Saqib, S.; Zhao, H.; Lü, S. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of GmLACS2–3 reveals its involvement in cutin and suberin biosynthesis along with abiotic stress tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Pan, C.; Lu, J.; Zaman, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Lü, S. Lupeol Accumulation Correlates with Auxin in the Epidermis of Castor. Molecules 2021, 26, 2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Ali, S.; Manghwar, H.; Saqib, S.; Ullah, F.; Ayaz, A.; Zaman, W. Melatonin function and crosstalk with other phytohormones under normal and stressful conditions. Genes 2022, 13, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaquat, F.; Munis, M.F.H.; Arif, S.; Haroon, U.; Shi, J.; Saqib, S.; Zaman, W.; Che, S.; Liu, Q. PacBio single-molecule long-read sequencing reveals genes tolerating manganese stress in Schima superba saplings. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 635043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Landherr, L.L.; Frohlich, M.W.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Ma, H.; DePamphilis, C.W. Patterns of gene duplication in the plant SKP1 gene family in angiosperms: Evidence for multiple mechanisms of rapid gene birth. Plant J. 2007, 50, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.K.-G.; Irish, V.F. The Arabidopsis zinc finger-homeodomain genes encode proteins with unique biochemical properties that are coordinately expressed during floral development. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Bruex, A.; Kainkaryam, R.M.; Zheng, X.; Huang, L.; Woolf, P.J.; Schiefelbein, J. Tissue-specific profiling reveals transcriptome alterations in Arabidopsis mutants lacking morphological phenotypes. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3175–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; DePamphilis, C.W.; Ma, H. Phylogenetic analysis of the plant-specific zinc finger-homeobox and mini zinc finger gene families. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2008, 50, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Liang, R.; Ge, L.; Li, W.; Xiao, H.; Lin, H.; Ruan, K.; Jin, Y. Identification of drought-induced microRNAs in rice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 354, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, G.; Sutoh, K.; Zhu, J.-K.; Zhang, W. Identification of cold-inducible microRNAs in plants by transcriptome analysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gene Regul. Mech. 2008, 1779, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkar, R.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, J.-K. Identification of novel and candidate miRNAs in rice by high throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Long, M. A cytosolic NADP-malic enzyme gene from rice (Oryza sativa L.) confers salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y. Differential expression of miRNAs in response to salt stress in maize roots. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER web server: Interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL): An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Fei, Z. iTAK-Identification and Classification of Plant Transcription Factors and Protein Kinases. In Proceedings of the Plant and Animal Genome XXII Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–15 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Tian, F.; Yang, D.-C.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Kong, L.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. PlantTFDB 4.0: Toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1040–D1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, K.B. GeneDoc: Analysis and visualization of genetic variation. Embnew. News 1997, 4, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangtao, C.; Yingzhen, K.; Qian, W.; Yuhe, S.; Daping, G.; Jing, L.; Guanshan, L. MapGene2Chrom, a tool to draw gene physical map based on Perl and SVG languages. Yi Chuan Hered. 2015, 37, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; You, J.; Xie, K.; Xie, W.; Xiong, L. Systematic sequence analysis and identification of tissue-specific or stress-responsive genes of NAC transcription factor family in rice. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2008, 280, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.-H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Peng, X. Genome-wide identification and phylogenetic analysis of zinc finger Homeodomain family genes in Brassica napus. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2019, 54, 699. [Google Scholar]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences. In Multiple Sequence Alignment Methods; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Suyama, M.; Torrents, D.; Bork, P. PAL2NAL: Robust conversion of protein sequence alignments into the corresponding codon alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W609–W612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryszak, R.; Keays, M.; Tang, Y.A.; Fonseca, N.A.; Barrera, E.; Burdett, T.; Füllgrabe, A.; Fuentes, A.M.-P.; Jupp, S.; Koskinen, S. Expression Atlas update–An integrated database of gene and protein expression in humans, animals and plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D746–D752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walley, J.W.; Sartor, R.C.; Shen, Z.; Schmitz, R.J.; Wu, K.J.; Urich, M.A.; Nery, J.R.; Smith, L.G.; Schnable, J.C.; Ecker, J.R. Integration of omic networks in a developmental atlas of maize. Science 2016, 353, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolde, R.; Vilo, J. GOsummaries: An R package for visual functional annotation of experimental data. F1000Research 2015, 4, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhao, P.X. psRNATarget: A plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W155–W159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otasek, D.; Morris, J.H.; Bouças, J.; Pico, A.R.; Demchak, B. Cytoscape automation: Empowering workflow-based network analysis. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).