Abstract
Ticks rank second in the world as vectors of disease. Tick infestation is one of the factors threatening the health and survival of giant pandas. Here, we describe the mitogenomes of Ixodes acutitarsus and Ixodes ovatus parasitizing giant pandas, and perform comparative and phylogenetic genomic analyses on the newly sequenced and other available mitogenomes of hard ticks. All six newly determined mitogenomes contain a typical gene component and share an ancient Arthropoda gene arrangement pattern. Our study suggests that I. ovatus is a species complex with high genetic divergence, indicating that different clades of I. ovatus represent distinct species. Comparative mitogenomic analyses show that the average A + T content of Ixodidae mitogenomes is 78.08%, their GC-skews are strongly negative, while AT-skews fluctuate around 0. A large number of microsatellites are detected in Ixodidae mitogenomes, and the main microsatellite motifs are mononucleotide A and trinucleotide AAT. We summarize five gene arrangement types, and identify the trnY-COX1-trnS1-COX2-trnK-ATP8-ATP6-COX3-trnG fragment is the most conserved region, whereas the region near the control region is the rearrangement hotspot in Ixodidae mitogenomes. The phylogenetic trees based on 15 genes provide a very convincing relationship (Ixodes + (Robertsicus + ((Bothriocroton + Haemaphysalis) + (Amblyomma + (Dermacentor + (Rhipicentor + (Hyalomma + Rhipicephalus))))))) with very strong supports. Remarkably, Archaeocroton sphenodonti is embedded in the Haemaphysalis clade with strong supports, resulting in paraphyly of the Haemaphysalis genus, so in-depth morphological and molecular studies are essential to determine the taxonomic status of A. sphenodonti and its closely related species. Our results provide new insights into the molecular phylogeny and evolution of hard ticks, as well as basic data for population genetics assessment and efficient surveillance and control for the giant panda-infesting ticks.
1. Introduction
Ticks, which are common hematophagous ectoparasites, are capable of parasitizing almost all groups of terrestrial vertebrates, including mammals, birds, lizards, snakes, and toads [1,2,3]. Ticks rank second in the world as vectors of disease, and they can harbor and transmit a great variety of pathogens, including virus, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and nematode, to humans, livestock, and wildlife [2,4,5,6]. More than 28 species of ticks are known to cause a variety of human diseases [5,7]. Tick-borne diseases cause severe illness and even death in animals and humans, resulting in significant loss of life and property [5,8,9]. Ticks and tick-borne diseases are a serious public health concern and have drawn heightened attention from clinicians and researchers.
The giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) is one of the most recognized flagship and umbrella species for biodiversity conservation in the world, and its conservation work is a showcase program for the Chinese government and its collaborators and has attracted worldwide attention [10,11,12]. Currently, there is a large population of giant pandas, including 1864 wild individuals living in 2.58 million hectares of habitat and 673 captive individuals. However, the development of giant panda population is still hampered by many factors such as infectious diseases [13,14,15,16]. There is still a lot of work to do to further consolidate the achievements of giant panda conservation.
The diseases caused by parasites have major impacts on the health and survival of giant pandas [15]. Up to now, 35 parasites species have been identified from giant pandas, and 13 of them are hard ticks (Ixodidae, including nine Haemaphysalis species, three Ixodes species, and one Dermacentor species) [17]. The infection rate of ticks in giant pandas is very high, even up to 100%, both in the wild and in captivity [17]. Ticks can cause even more damage by spreading pathogens, such as protozoans and viruses. The Babesia sp., one of the most widespread tick-borne protozoan parasites that can cause Babesiosis, is detected in the blood of giant panda [18]. Thirty-two viral species are detected in the giant panda-infesting ticks, half of which show homology to viruses carried by giant pandas and their associated host species [19]. More seriously, the mixed parasitism of a variety of ticks is common on giant pandas [17,20].
Correct identification of tick species is essential for the study of ticks and tick-borne pathogens [21]. The conventional method for identifying ticks is based on microscopic observation of morphological features, which is suitable for adult ticks [3]. Many tick species share great morphological similarities and therefore group into species complexes until differentiating characters can be described [22]. The mitochondrial genome (mitogenome) is a reliable marker for cryptic species identification, phylogenetic studies, and population genetics analysis, and has been widely used in animals [23,24,25,26,27,28], including in ticks [7,21,29]. In recent years, the number of sequenced mitogenomes of Ixodidae species has increased significantly, but the mitogenome studies on parasitic ticks of giant pandas have only been performed for three Haemaphysalis species [30,31,32]. The mitogenomes of another ten Ixodidae species infesting giant pandas have not been reported. Our knowledge of the genetic diversity of these ticks is lacking. Recently, we found that our wild-training giant panda individuals living in Yingjing County of Sichuan Province were also infected with ticks, which were identified as I. acutitarsus (Karsch, 1880) and I. ovatus Neumann, 1899 by morphological and preliminary molecular identification. Cases of giant pandas infected with these two ticks have been reported in Tianquan, Baoxing, and Wenchuan of Sichuan, and Wenxian of Gansu [17].
Comparative mitogenomic analyses are of great significance for understanding the biodiversity and evolution, and mitogenomic data can provide efficient phylogenetic signals for a wide variety of animal groups [3,24,33,34]. The phylogenetic relationships of hard ticks have been studied in depth [3,4,35,36,37,38,39], but comprehensive comparative mitogenome analyses of them are rarely performed. Herein, we sequenced the mitogenomes of the giant panda-infecting ticks I. acutitarsus and I. ovatus through high-throughput sequencing technology, and performed comparative and phylogenetic genomic analyses for the newly sequenced and publicly available mitogenomes of hard ticks.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection and DNA Extraction
Our team is developing a program to release captive-bred giant pandas into the wild by adopting the Human-Assisted Soft Release Method. Through this method, our investigators can examine the trained giant pandas and collect more data in the wild without undergoing anesthesia [19,40]. A total of eight adult ticks were collected from the body surface of our wild-training giant pandas living in Yingjing Area of Giant Panda National Park (102°19′30″ E–102°57′0″ E, 29°28′30″ N–29°57′0″ N) from March to April 2022, and stored in 95% ethanol. These ticks were identified as I. acutitarsus (specimen numbers PB2022006–PB2022009) and I. ovatus (specimen numbers PB2022017–PB2022020) according to morphological characters and nucleotide BLAST results of ITS2 and COX1 genes. Two of them (specimen numbers PB2022009 and PB2022020) were kept as voucher specimens and deposited at Chengdu Research Base of Giant Panda Breeding, and the genomic DNA of the remaining six ticks were extracted using the DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany).
2.2. Library Preparation and Mitogenome Sequencing
Genomic DNA samples were sent to Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) for High-throughput sequencing. For each sample, approximately 300 ng genomic DNA were sheared into fragments of 400–500 bp using Covaris S220 system (Covaris, Woburn, MA, USA), and used for Illumina sequencing libraries preparation using Hieff NGS MaxUp II DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (YEASEN, Shanghai, China). Sequencing was performed on Illumina Novaseq 6000 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) with a paired-end read length of 150 bp according to the standard protocols, and sequencing reads (raw data) were exported to the FASTQ format.
2.3. Mitogenome Assembly and Annotation
The raw data were processed for quality control and preprocessing using fastp v0.36 [41]. The high-quality clean data were assembled into contiguous sequences using SPAdes v3.15 with different K-mer parameters [42]. On the basis of NCBI BLAST searches, the contigs mapped to tick mitochondrial genome sequence were used for generating the circular mitogenomes of the two examined Ixodes species.
Mitogenome annotation was performed as previously described [33]. MITOS WebServer (http://mitos2.bioinf.uni-leipzig.de/index.py, accessed on 25 July 2022) [43] was used to predetermine protein-coding genes (PCGs), ribosomal RNA genes (rRNAs), and transfer RNA genes (tRNAs) and define their respective gene boundaries based on invertebrate mitochondrial genetic code. PCGs were reconfirmed using NCBI ORFfinder (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html, accessed on 25 July 2022) [44], and tRNAs were rechecked using tRNAscan-SE web server (http://lowelab.ucsc.edu/tRNAscan-SE/, accessed on 25 July 2022) [45] and ARWEN online services (http://130.235.244.92/ARWEN/, accessed on 25 July 2022) [46] based on their proposed cloverleaf secondary structures and anticodon sequences. As a further step toward improving the mitogenome annotations, all fragments were aligned with other Ixodes species’ homologs (e.g., I. granulatus OM368258, OM368272; I. ovatus OM317739). Finally, OGDRAW v1.3.1 (https://chlorobox.mpimp-golm.mpg.de/OGDraw.html, accessed on 25 July 2022) [47] was used to visualize the mitogenome organization.
2.4. Available Mitogenome Retrieval
We searched Ixodidae sequences on GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, accessed on 28 July 2022) based on keyword ‘Ixodidae’, and obtained 479 initial results by setting sequence length to ‘10,000–30,000 bp’ and selecting the ‘mitochondrion’ sequence. Among them, 128 results were filtered out due to incomplete sequencing or lacking annotation information, and 351 mitogenome sequences were finally selected for subsequent analysis (Table S1). We retrieved these 351 Ixodidae mitogenomes from GenBank using PhyloSuite v1.2.2 [48].
2.5. Comparative Mitogenomic Analyses
All 351 retrieved mitogenomes belonging to 107 species and 10 genera were used for comparative mitogenomic analyses (Table S1), in combination with our six newly determined mitogenomes. The sequences were aligned with MAFFT online service (https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/, accessed on 28 July 2022) using ‘--auto’ strategy [49]. The nucleotide composition, variable sites statistics, and Kimura 2-parameters (K2P) genetic distance of the mitogenomes were calculated using MEGA v11 [50]. The following formulas were used to measure nucleotide composition bias: AT-skew = (A − T)/(A + T) and GC-skew = (G − C)/(G + C) [51]. Krait v1.3.3 [52] and MISA-web (https://webblast.ipk-gatersleben.de/misa/, accessed on 29 July 2022) [53] were used to screen the mitogenomes for microsatellite sequences. The minimum repeat numbers for each perfect microsatellite type were set to 10 for mono-, 5 for di-, 4 for tri-, 3 for tetra-, 3 for penta-, and 3 for hexa-nucleotides, respectively [54,55]. The microsatellite count per kilobase pair sequence was defined as the relative abundance (RA) of microsatellite and was measured by the following formula: RA = (total number of microsatellite loci)/(whole mitogenome size) × 1000 [52,54]. DnaSP v6.12.03 [56] was used to calculate the nucleotide diversity of rRNAs and PCGs, and conduct sliding window analysis of whole mitogenomes implementing window size of 200 bp and a step size of 20 bp. The qMGR web server (https://qmgr.hnnu.edu.cn/, accessed on 30 July 2022) [57] was used to conduct the gene arrangement analysis by calculating the rearrangement frequency (RF) of single gene and the total rearrangement score (RS) of every gene arrangement type in Ixodidae group, and the ancient Arthropoda gene arrangement type was chosen as the benchmark arrangement [24,58,59].
These data were visualized as graphs generated by ImageGP v1.0 (http://www.ehbio.com/Cloud_Platform/front/#/, accessed on 31 July 2022) [60] and OmicStudio tool (https://www.omicstudio.cn/tool, accessed on 31 July 2022).
2.6. Mitogenomic Phylogenetic Analyses
Many of the 351 retrieved Ixodidae mitogenomes belong to the same species (e.g., multiple representatives for Amblyomma testudinarium, Haemaphysalis longicornis, Hyalomma marginatum, and I. ricinus), so we only selected 226 representative mitogenomes belonging to 107 tick species and 10 genera to reconstruct phylogenetic relationships (Table S1), in combination with the six newly determined mitogenomes in this study. To root the trees, we used Argas africolumbae (Argasidae) and Nuttalliella namaqua (Nuttalliellidae) as outgroups according to the evolutionary relationships of the Ixodida [3,61,62].
Two rRNAs and 13 PCGs sequences from 234 mitogenomes were aligned in batches with MAFFT v7.313 [63] using ‘Normal’ or ‘Codon’ alignment mode and ‘--auto’ strategy, then trimmed gap sites with trimAl v1.2 [64] using ‘automated1′ command, and eventually concatenated into one multi-gene dataset consisting of 12,892 bp sequence, which was used for phylogenetic tree inference. The Bayesian Inference (BI) phylogenetic tree was constructed using MrBayes v3.2.6 [65] under a partition model (two parallel runs, ten million generations), in which the initial 25% of sampled data was discarded as burn-in. Maximum Likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree was constructed using IQ-TREE v1.6.8 [66] under Edge-linked partition model for ten thousand replicates of ultrafast bootstraps [67], as well as the SH–aLRT branch test [68]. The best-fit Edge-linked partition substitution model was chosen by ModelFinder [69] using BIC criterion (Table S2). All of the above analyses were implemented in PhyloSuite v1.2.2 [48].
The phylogenetic trees were visualized by iTOL v6 (https://itol.embl.de/, accessed on 31 July 2022) [70].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Newly Sequenced Mitogenomes
3.1.1. General Characteristics
We successfully sequenced and characterized six mitochondrial genomes of two hard tick species, I. ovatus and I. acutitarsus. The newly determined mitogenomes of I. ovatus were circular genomes with 14,539 bp, 14,543 bp, and 14,543 bp in size (Figure 1), which were larger than previously published mitogenomes of the same species (14,507–14,520 bp). The newly determined mitogenomes of I. acutitarsus were 14,472 bp, 14,473 bp, and 14,473 bp in size (Figure 1), which were the smallest complete mitogenomes of hard ticks so far.

Figure 1.
Structural representation of the mitogenomes of I. ovatus and I. acutitarsus. The arrows represent the transcription direction of genes on heavy (outside) and light (inside) chain of the mitogenomes. The tRNAs are abbreviated by the one-letter code for the corresponding amino acid, and the anticodons are indicated in parentheses. The inner circle is the G + C content graph of mitogenome OP244856.
These six mitogenomes shared the same gene content and arrangement, which was consistent with previous studies [59,62,71]. They had a typical gene content, including 22 tRNAs, 13 PCGs, two rRNAs, and one control region (CR, also named A + T rich region), of which 15 genes (trnC, trnF, trnH, trnL1, trnL2, trnP, trnQ, trnV, trnY, ND1, ND4, ND4L, ND5, rrnL, and rrnS) were transcribed from the light chain (Figure 1, Table S3). The gene arrangements of the six mitogenomes were the same as the ancient Arthropoda gene arrangement type [58]. In these mitogenomes, all 13 PCGs were started with the typical initiation codon ATA/ATT/ATC/ATG. ATP6, ATP8, COX1, ND3, ND4, ND4L, and ND6 genes were terminated by the canonical termination codon TAA/TAG, while the other six genes (COX2, COX3, CYTB, ND1, ND2, and ND5) were ended with the truncated termination codon T (Table S3). The usage of incomplete stop codon T was a common feature in many metazoans [35,38,72,73,74], and it may be converted into complete termination codon TAA by polyadenylation after transcription [75].
The CR of I. ovatus and I. acutitarsus was located between rrnS and trnI (Figure 1). The I. ovatus CR was 333–334 bp in size, and its A + T content reached 71.77–71.86%, which was lower than the overall A + T content of the whole mitogenome (75.20–75.29%). The I. acutitarsus CR was only 343–344 bp in size, but it contained higher A + T content than the whole mitogenome (82.22–82.27% vs. 78.28–78.30%).
3.1.2. Tick-Box Motif
Montagna et al. identified a 17 bp degenerate consensus sequence (5′-TTGyrTChwwwTwwGdA-3′) named Tick-Box motif in all tick mitogenomes, and found this motif was always present in only two or three fixed genomic positions: downstream of ND1 (mainly in noncoding regions), near the 3′-end of rrnL (occasionally within trnL1), and/or inside small noncoding region located between trnQ and trnF in some Metastriata ticks [76]. In our newly determined and other publicly available mitogenomes of I. ovatus and I. acutitarsus, we found the identical motifs were located within trnL1 (5′-TTGTATCAAATTTAGAA-3′) and downstream of ND1 (5′-TTGTrTCCTTTTwAGAA-3′). Other research teams also detected the Tick-Box motifs in Amblyomma americanum, Dendrobates auratus, D. silvarum, Ha. kitaokai, Ha. longicornis, Hy. marginatum, Hy. rufipes, Rhipicephalus microplus, and many soft tick mitogenomes [37,38,62,77,78,79,80,81]. Although Lu et al. reported that no sequence identical to the Tick-Box consensus motif was present in I. vespertilionis mitogenome [82], we successfully found the motif within trnL1 (5′-TTGTATCAAATTTAGAA-3′) and downstream of ND1 (5′-TTGTATCCTTTTGAGAA-3′) on the light chain.
3.1.3. Genetic Divergence, Nucleotide Variation, and Diversity
The K2P genetic distances were listed in Table 1 and Table 2. The genetic divergence between some individuals was very high. The recommended species boundaries for ticks were 0.0525 for rrnL and 0.0613 for COX1 [83,84]. Based on this criterion, we considered I. ovatus and I. acutitarsus as two species complexes and divided seven I. ovatus individuals into four groups and five I. acutitarsus individuals into two groups. Recently, one study also found that I. ovatus was species complex with high genetic diversity [22], and a potential cryptic species was revealed in the I. ovatus group [7]. Therefore, all results suggested that different groups of I. ovatus might represent distinct species. Unfortunately, no between-group morphological comparisons were performed in our study. In-depth morphological comparisons and molecular studies need to be performed to resolve the taxonomic status of the I. ovatus and I. acutitarsus species complexes.

Table 1.
The pairwise K2P genetic distances for I. ovatus species complex based on the rrnL (upper right matrix) and COX1 (lower left matrix) genes.

Table 2.
The pairwise K2P genetic distances for I. acutitarsus species complex based on the rrnL (upper right matrix) and COX1 (lower left matrix) genes.
Our six newly determined mitogenomes were grouped into the I. ovatus group 4 and I. acutitarsus group 2 (Table 1 and Table 2), respectively. For these two species groups, we calculated the nucleotide variable site percentage and the nucleotide diversity level. At the mitochondrial genome-wide level, the nucleotide variable site percentage and the nucleotide diversity level of I. ovatus group 4 were 0.41% and 0.0027, respectively, which were slightly lower than the corresponding values of I. acutitarsus group 2 (0.53% and 0.0029) (Figure 2A). Sliding window analysis of the mitogenomes showed a similar nucleotide diversity result between these two groups (Figure 2B). As shown in Figure 2A, at the mitochondrial single-gene level of these two species groups, ND3 had the highest and rrnS had the lowest nucleotide variable site proportion, and the same situation also appeared at the nucleotide diversity level. Very low nucleotide diversity in rrnS was also found among nine Ixodes species [71].
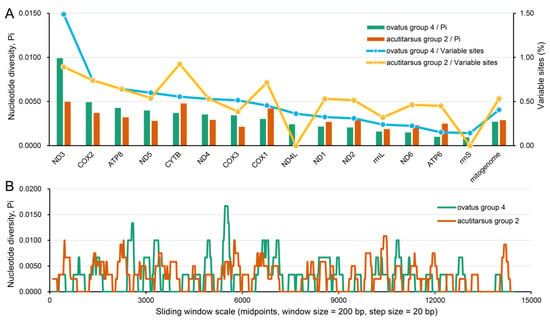
Figure 2.
Nucleotide variation and diversity of I. ovatus group 4 and I. acutitarsus group 2 mitogenomes. (A) Variable nucleotide sites statistics and nucleotide diversity estimates of I. ovatus group 4 and I. acutitarsus group 2 mitochondrial genes. (B) Sliding window analysis of the complete mitogenome alignments between I. ovatus group 4 and I. acutitarsus group 2. I. ovatus group 4 include three mitogenomes with GenBank IDs OP244856–OP244858. I. acutitarsus group 2 include four mitogenomes with GenBank IDs OL800704, OP244859–OP244861.
3.2. Comparative Mitogenomic Analyses of Ixodidae Species
3.2.1. Nucleotide Composition and Skewness
We calculated the nucleotide composition of 357 Ixodidae mitogenomes representing 107 species of 10 genera. The Ixodidae mitogenomes size averaged 14,752 bp, the longest reached 15,307 bp (Dermacentor sp. OM368308), and the smallest was only 14,472 bp (I. acutitarsus OP244861).
At the mitochondrial genome-wide level, most Ixodidae species had the characteristics of T% > A% > C% > G% except Ha. montgomeryi MW751681 and a few Ixodes species with the characteristics of A% > T% > C% > G% (Figure S1). In metazoan mitogenomes, A + T content is generally higher than G + C content [33,61,85,86,87,88]. Previous statistics indicated the A + T content of Ixodidae mitogenomes was over 70% [71]. Wang et al. also found the ticks (including Ixodidae, Argasidae and Nuttalliellidae) had high A + T content with a mean of 75.51%, and the A + T content in Ixodidae family was higher than in the Argasidae family [61]. In this study, we further accurately calculated that the average A + T content of Ixodidae mitogenomes was 78.08%, ranging from 72.28% (Ixodes sp. MW021452) to 81.06% (Ha. danieli OM368292). Such a high proportion of A + T content was also present in other arthropod groups, such as Araneae [34] and Lepidoptera [89]. Among 10 genera of the Ixodidae family, Ixodes genus had the largest A + T content variation range from 72.28% to 79.98%, and its average was 77.56%, which was smaller than 79.51% (75.53–80.76%) of the Amblyomma genus, 79.15% (77.20–79.80%) of the Hyalomma genus, 78.24% (76.75–79.30%) of the Dermacentor genus, 78.21% (74.57–80.37%) of the Rhipicephalus genus, and larger than 77.40% (76.40–81.06%) of the Haemaphysalis genus (Figure 3A).

Figure 3.
Nucleotide content and skewness of Ixodidae mitogenomes. (A) Intergenus comparison of A+T content of Ixodidae mitogenomes. (B) Intergenus comparison of AT-skew and GC skew of Ixodidae mitogenomes.
Strand asymmetry of nucleotide composition is usually described as skewness and measured by AT-skew and GC-skew values [90,91]. As shown in Figure 3B, the AT-skews of Ixodidae mitogenomes fluctuated around 0 (−0.038–0.033) and averaged −0.017, revealing that the A content and T content were relatively close; the GC-skews were strongly negative (−0.366–−0.097), with the mean of −0.172, indicating a higher occurrence of C than G; the GC-skews of Ixodes species were smaller than those of non-Ixodes species. Generally, GC-skew of heavy chain of metazoan mitogenome was negative, while AT-skew was positive [74,91,92,93]. Apparently, the AT-skew of Ixodidae mitogenomes deviated from the general characteristics of metazoan mitogenomes. Negative AT-skews had also been found in the mitogenomes of other taxonomic groups, such as Lepidoptera [86,89] and Araneae [34]. Such skews towards a particular nucleotide can be related to asymmetric mutational constraints [92].
We also counted the nucleotide composition of individual genes in these 357 Ixodidae mitogenomes. At the mitochondrial single-gene level (including 13 PCGs and two rRNAs), A + T content of Ixodidae species ranged from 70.31% (COX1) to 86.47% (ATP8), which was much larger than the G + C content (Figure 4A); AT-skews ranged from −0.209 (ND3) to 0.034 (rrnS) (Figure 4B); GC-skews ranged from −0.562 (ATP8) to 0.375 (ND4L) (Figure 4C); ND1, ND4, ND4L, ND5, rrnL, and rrnS genes transcribed by the light chain had higher GC-skew values than those genes transcribed by the heavy chain, while only rrnL and rrnS had higher AT-skews than other genes (Figure S2).
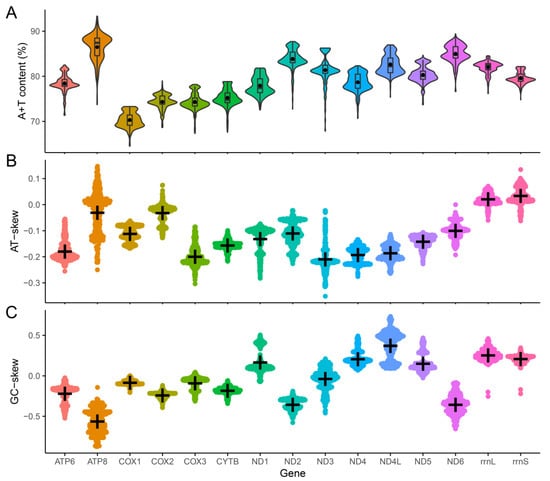
Figure 4.
Nucleotide content and skewness of Ixodidae mitochondrial PCGs and rRNAs. (A) A+T content of Ixodidae mitochondrial genes. (B) AT-skew of Ixodidae mitochondrial genes. (C) GC-skew of Ixodidae mitochondrial genes.
3.2.2. Microsatellite Characteristics
Microsatellites, also known as Short Tandem Repeats (STRs) and Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs), are tandem repeats of simple sequence motifs widely found in eukaryotic genomes [94]. They exhibit extensive polymorphism due to copy number variations of each specific repeat unit, and are considered an important type of repeated sequences that are popular as molecular markers for genetic diversity analysis [95]. Copy number variations of microsatellites in protein-coding genes can lead to frameshift mutations in proteins that can cause deleterious effects [96]. Microsatellites of nuclear genomes have been extensively studied, whereas surveys of microsatellites in organelle genomes are rare [54,55,86,96]. In this study, we successfully detected 11–17 perfect microsatellite loci in the I. acutitarsus species complex mitogenomes and 4–6 perfect microsatellite loci in the I. ovatus species complex mitogenomes, and found five microsatellite types, including mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, and penta-nucleotides (Figure 5A). The relative abundances of mitochondrial microsatellite loci were 0.760–1.175 for the I. acutitarsus species complex, 0.276–0.414 for the I. ovatus species complex, respectively (Figure 5B). Recently, Chen et al. also found a large number of microsatellites in the D. silvarum mitogenome [96].

Figure 5.
Statistics of microsatellite identified in Ixodidae mitogenomes. (A) The microsatellite loci counts and (B) their relative abundances of I. acutitarsus and I. ovatus species complex mitogenomes. Ia1–5 represent I. acutitarsus species complex mitogenomes with GenBank IDs OL800704, OM368264, and OP244859–OP244861; Io1–7 represent I. ovatus species complex mitogenomes with GenBank IDs OM317739, OM368266, OM368268, OM366269, and OP244856–OP244858. (C) The counts statistics of different microsatellite motif in Ixodidae and Ixodes mitogenomes.
We also performed microsatellite sequence analysis for the Ixodidae family for the first time. A total of 917 and 4367 microsatellite loci, belonging to mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, and hexa-nucleotides six microsatellite types, were detected from 83 Ixodes and 357 Ixodidae mitogenomes, respectively (Figure 5C). The counts of different microsatellite types varied greatly, with mononucleotides microsatellites accounting for the highest proportion, reaching 50.82% (466/917 for the Ixodes genus) and 44.08% (1925/4367 for the Ixodidae family), respectively, followed by trinucleotide microsatellites, reaching 16.03% (147/917 for the Ixodes genus) and 26.54% (1159/4367 for the Ixodidae family), respectively (Figure 5C). From the analysis of the microsatellite motif, there were 19 motifs in Ixodes mitogenomes and 28 motifs in Ixodidae mitogenomes; the main microsatellite motifs in both Ixodes and Ixodidae mitogenomes were mononucleotides A, followed by trinucleotides AAT (Figure 5C).
3.2.3. Gene Rearrangement
Gene arrangement comparison is an important tool for resolving deep-level phylogenetic relationships [97,98]. Genome rearrangement analysis is a routine analysis in comparative mitochondrial genomics [33,72,73,99,100,101]. Regarding the Ixodidae mitogenomes, Black and Roehrdanz first reported two gene arrangement types [102], and Shao et al. further summed up three types [59], which were confirmed by another study [76]. Later, one unique gene arrangement model for the metastriate Ixodidae was described in Amblyomma transversale (now named Africaniella transversale) mitogenome [62]. Just recently, another novel arrangement trnA-trnR-trnN-trnE-trnS1-trnF was discovered in I. fecialis mitogenomes [103]. Additionally, Duan et al. reported that Hy. asiaticum had a novel genome arrangement trnA-trnR-trnN-trnS1-ND1-trnE-trnL2-rrnL that differs from the typical metastriate Ixodidae arrangement trnA-trnR-trnN-trnS1-trnE-ND1-trnL2-rrnL [71]; however, our analysis found that this novel arrangement type was caused by an annotation error of the ND1 gene.
In this study, we summarized five different gene arrangement types based on the comparison of all available Ixodidae complete mitogenomes to date (Figure 6A). The gene arrangement types T1, T2, and T3 were discovered in Prostriata ticks, while T4 and T5 were found in Metastriata ticks (Figure 7). Type T1 was identical to the ancient Arthropoda gene arrangement type found in Limulus polyphemus [58], which was assumed to be the ancestral type of arthropods and also found in Liphistiidae spiders [24,34], Nuttalliellidae ticks [104,105], and Argasidae ticks [59,104]. The non-Australasian Prostriata ticks had type T1, and almost all Australasian Prostriata ticks had type T2, except that I. fecialis owned type T3; Type T4 was the most common type, occurring in almost all Metastriata ticks, whereas type T5 only occurred in Am. transversale (now named Af. transversale). Among the five gene arrangement types, there were three types of gene position changes: duplication of CR, inversion of trnC and trnP, shuffling of many genes, and translocation of many genes. Compared to the ancient Arthropoda gene arrangement type, type T5 had the highest RS value (Figure 6B), indicating that it undergone the most complex changes. Furthermore, the RF value of 14 mitochondrial genes was only 0 (Figure 6C), indicating that their adjacent genes were not rearranged. The highest RF value was assigned to CR, followed by trnL1 and trnC. We identified that the segment trnY-COX1-trnS1-COX2-trnK-ATP8-ATP6-COX3-trnG was the most conservative region, while the region near CR was the rearrangement hot spot in Ixodidae mitogenomes.
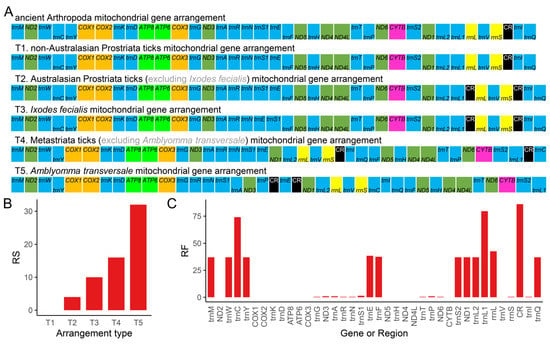
Figure 6.
Mitochondrial gene arrangements of Ixodidae species. (A) The five mitochondrial gene arrangement types in Ixodidae group. (B) The rearrangement score (RS) of every gene arrangement type in Ixodidae group. (C) The rearrangement frequency (RF) of different mitochondrial genes or region in Ixodidae group. The tRNAs are abbreviated by the one-letter code for the corresponding amino acid, trnL1 = tRNA-Leu(CUN), trnL2 = tRNA-Leu(UUR), trnS1 = tRNA-Ser(AGN), and trnS2 = tRNA-Ser(UCN).
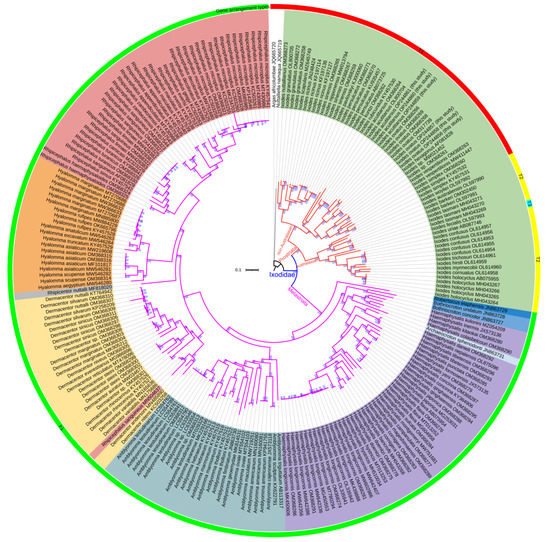
Figure 7.
ML tree of Ixodidae species inferred from the concatenated DNA sequences of 15 mitochondrial genes. A. africolumbae and N. namaqua act as the outgroup. Ultrafast bootstrap percentage (UBP) is given at each node. The different colors of the outer ring represent different gene arrangement types in Figure 6.
3.3. Mitogenomic Phylogenetic Analyses of Ixodidae Species
Unstable and uncertain phylogenetic relationships may affect our understanding of diversity and evolutionary history [25]. Molecular identification of existing and new species can be assisted by gene fragments (e.g., rrnL and COX1) [20,106], but complete mitogenomes may provide more accurate signals than gene fragments for phylogenetic reconstruction [23,33,61,73]. In this study, the phylogenetic analyses were conducted based on 13 PCGs and 2 rRNAs, which were concatenated into a sequence matrix of 12,892 bp representing 87% of the entire mitogenome alignments.
The ML and BI phylogenetic analyses yielded two highly similar topologies using the same sequence matrix (Figure 7 and Figure S3). Compared to previous studies [3,39], at the genus level, our study inferred more forceful phylogenetic relationships with stronger support (100% UBP, 1.00 BPP). Both ML and BI tree topologies delimited two lineages: Prostriata and Metastriata. The Prostriata lineage consisted of the single genus Ixodes; the Australasian Ixodes clade and the non-Australasian Ixodes clade were clustered with strong support (100% UBP, 1.00 BPP). The Ixodes genus was located at the basal position of the Ixodidae family, as in previous studies based on PCGs dataset [3,4,38,81,107], not clustered with the Argasidae ticks [36]. The tick I. ovatus parasitizing giant pandas clustered with the conspecific individuals infesting other animals, as I. acutitarsus did. The subclade ((I. simplex + I. vespertilionis) + Ixodes sp.) formed the sister-group relationship with I. ovatus, and I. rubicundus was the sister taxon of I. acutitarsus. The Metastriata lineage was further divided into eight clades with the relationship (Robertsicus + ((Bothriocroton + Haemaphysalis) + (Amblyomma + (Dermacentor + (Rhipicentor + (Hyalomma + Rhipicephalus)))))), as in previous mitochondrial PCGs phylogeny [3,7]. Most genera were fully supported as monophyletic groups, while Haemaphysalis genus was the paraphyletic group. Ar. sphenodonti was embedded in the Haemaphysalis clade with very strong support (100% UBP, 1.00 BPP), which was consistent with previous studies based on 13 mitochondrial PCGs [3,38]. It implied that the taxonomy of Ar. sphenodonti was debatable. At one time, Ar. sphenodonti was classified as Amblyomma sphenodonti [35]. Burger et al. found the polyphyly of the genus Amblyomma according to ML tree inferred from combined mitochondrial and nuclear DNA datasets, and thought that Am. sphenodonti and Amblyomma elaphense did not belong in the genus Amblyomma [108]. Later, they established two new monotypic genera, Archaeocroton and Robertsicus, for these two species [109]. Based on our phylogenetic inferences, we suggest that, in the future, an in-depth morphological comparison among Ar. sphenodonti, Ha. colasbelcouri, Ha. kitaokai, Ha. kolonini, Ha. inermis, and other Haemaphysalis species is necessary to determine whether Ha. colasbelcouri, Ha. kitaokai, Ha. Kolonini, and Ha. inermis could be assigned to the Archaeocroton genus or whether a new genus could be established for them.
4. Conclusions
In the present study, we obtained six complete mitogenomes of two Ixodes species parasitized on giant pandas, discussed the comparative mitogenomic characteristics with other available Ixodidae mitogenomes, and carried out the phylogenetic reconstruction of Ixodidae family. The newly determined mitogenomes of I. ovatus and I. acutitarsus were 14,539–14,543 bp and 14,472–14,473 bp, respectively. These six mitogenomes had the typical gene set comprising 22 tRNAs, 13 PCGs, two rRNAs, and one control region, and their gene arrangement type was the same as that of non-Australasian Prostriata ticks. In I. ovatus and I. acutitarsus mitogenomes, two Tick-Box motifs were found. We found that I. ovatus was a species complex with high genetic divergence, and thought that different groups of I. ovatus might represent distinct species. Comparative mitogenomic analyses revealed that the Ixodidae species had relatively high overall A + T content with a mean of 78.08%; their GC-skews of whole mitogenome were strongly negative, and the GC-skews of the light-chain-transcribed genes were higher than that of the heavy-chain-transcribed genes; their AT-skews of whole mitogenome fluctuated around 0, which deviated from the general characteristics of the metazoan mitogenomes. A large number of microsatellites such as (A)n and (AAT)n existed in Ixodidae mitogenomes. Five different mitochondrial gene arrangement types (T1–T5) were found, involving duplication of CR, inversion of trnC, and translocation of many genes. Type T4 was the most common type and was shared by almost all Metastriata ticks. The trnY-COX1-trnS1-COX2-trnK-ATP8-ATP6-COX3-trnG segment was the most conserved region, while the region near CR was the hotspot of mitochondrial genome rearrangements in Ixodidae. ML and BI phylogenetic analyses based on 13 PCGs and two rRNAs sequences showed great consistency in genus level relationships (Ixodes + (Robertsicus + ((Bothriocroton + Haemaphysalis) + (Amblyomma + (Dermacentor + (Rhipicentor + (Hyalomma + Rhipicephalus))))))) with strong support. Most genera were fully supported as monophyletic groups, while the Haemaphysalis genus was the paraphyletic group. Ar. sphenodonti was embedded in Haemaphysalis clade with very strong support. These results expand our knowledge of the diversity and evolution of Ixodidae mitogenomes, and provide more genetic information for control and prevention of tick diseases.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/genes13112049/s1, Table S1. The tick species and their corresponding mitogenomes used in this study; Table S2. The appropriate partition-specific substitution model used in both ML and BI analyses; Table S3. Annotations of the mitogenomes of I. ovatus and I. acutitarsus; Figure S1. Nucleotide composition of Ixodidae mitogenomes; Figure S2. AT-skew and GC-skew of Ixodidae mitochondrial PCGs and rRNAs; Figure S3. BI tree of Ixodidae species inferred from the concatenated DNA sequences of 15 mitochondrial genes. Bayesian posterior probability (BPP) is given at each node.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.Q.; Data curation, J.Y.; Formal analysis, J.L.; Funding acquisition, W.B., F.X. and J.Z.; Investigation, J.L., X.Y., W.B., F.X., R.M., Y.Z., G.L., J.G. and Z.L.; Methodology, J.L., J.Y. and G.Q.; Project administration, W.W. and G.Q.; Resources, X.Y., W.B., H.Y., and Z.L.; Supervision, G.Q.; Visualization, J.L., J.Y. and X.Y.; Writing—original draft, J.L. and J.Y.; Writing—review and editing, J.L., J.Y., X.Y., W.B., H.Y., F.X., G.Z., J.Z., D.Y., R.M., Y.Z., G.L., J.G., W.W., Z.L. and G.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U21A20193), the Chengdu Research Base of Giant Panda Breeding (Grant Nos. CPB2022P14 and CPB2022Y15), the Chengdu Giant Panda Breeding Research Foundation (Grant No. CPF2017-20), and the Human-Assisted Soft Release Project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The complete mitogenome sequences obtained in this study are openly available in the GenBank database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/) under the accession IDs OP244856-OP244861.
Acknowledgments
We thank HOME for Researchers (http://www.home-for-researchers.com/, accessed on 30 September 2022) for the linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript. We truly thank Jacob R. Owens for polishing the language of the final manuscript. We also acknowledge the reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- de Oliveira, G.M.B.; Araújo, A.d.C.; Santos, J.R.; da Silva, I.W.G.; Labruna, M.B.; Horta, M.C. Lack of seasonality of Amblyomma rotundatum (Acari: Ixodidade) on Rhinella jimi (Anura: Bufonidae) in a semi-arid region of northeastern Brazil. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, W.M.A.; Moustafa, M.A.M.; Thu, M.J.; Kakisaka, K.; Chatanga, E.; Ogata, S.; Hayashi, N.; Taya, Y.; Ohari, Y.; Naguib, D.; et al. Comparative mitogenomics elucidates the population genetic structure of Amblyomma testudinarium in Japan and a closely related Amblyomma species in Myanmar. Evol. Appl. 2022, 15, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, D.; Du, C.; Xu, R.; Guo, X.; Yang, X. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Ixodes granulatus (Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 2347–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnard, D.; Shao, R. Mitochondrial genome analysis reveals intraspecific variation within Australian hard tick species. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wang, J.; Shi, W.; Du, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhan, W.; Jiang, J.-F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Ji, P.; et al. Large-scale comparative analyses of tick genomes elucidate their genetic diversity and vector capacities. Cell 2020, 182, 1328–1340.e1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.-P.; Wang, Y.-X.; Fan, Z.-W.; Ji, Y.; Liu, M.-j.; Zhang, W.-H.; Li, X.-L.; Zhou, S.-X.; Li, H.; Liang, S.; et al. Mapping ticks and tick-borne pathogens in China. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Hou, X.; Ge, M.; Xu, H.; Yu, B.; Liu, J.; Shao, R.; Holmes, E.C.; Lei, C.; Shi, M. The diversity and evolutionary relationships of ticks and tick-borne bacteria collected in China. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonenshine, D.E. Range expansion of tick disease vectors in North America: Implications for spread of tick-borne disease. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Agwanda, B.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J.; Kuria, S.; Yang, J.; Masika, M.; Tang, S.; Lichoti, J.; et al. Viromes and surveys of RNA viruses in camel-derived ticks revealing transmission patterns of novel tick-borne viral pathogens in Kenya. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Costanza, R.; Dai, Q.; Stoeckl, N.; Gu, X.; Farber, S.; Nie, Y.; Kubiszewski, I.; Hu, Y.; Swaisgood, R.; et al. The value of ecosystem services from giant panda reserves. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2174–2180.e2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; McShea, W.J.; Wang, D.; Gu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Shen, X. Retreat of large carnivores across the giant panda distribution range. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.V.; Pimm, S.L. China’s endemic vertebrates sheltering under the protective umbrella of the giant panda. Conserv. Biol. 2016, 30, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvistendahl, M. Captive pandas succumb to killer virus. Science 2015, 347, 700–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, S.; Shan, T.; Hou, R.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Virome comparisons in wild-diseased and healthy captive giant pandas. Microbiome 2017, 5, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Koehler, A.V.; Gasser, R.B. Parasites of the giant panda: A risk factor in the conservation of a species. In Adv Parasitol; Rollinson, D., Stothard, J.R., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; Volume 99, pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Yue, C.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Shen, Q.; Su, X.; Qi, D.; et al. Viral metagenomics unveiled extensive communications of viruses within giant pandas and their associated organisms in the same ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Karim, M.R.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. Review on parasites of wild and captive giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca): Diversity, disease and conservation impact. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 13, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Deng, Z.; Qi, D.; Li, Y.; Bi, W.; Ma, R.; Yang, G.; Luo, X.; Hou, R.; Liu, S. First detection and molecular identification of Babesia sp. from the giant panda, Ailuropoda melanoleuca, in China. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Zhao, M.; Wang, H.; Hou, R.; Qin, K.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, W.; Gu, J.; et al. Virome of giant panda-infesting ticks reveals novel bunyaviruses and other viruses that are genetically close to those from giant pandas. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02034-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-y.; Zhao, G.-h.; Jia, Y.-q.; Bian, Q.-q.; Du, S.-z.; Fang, Y.-q.; Qi, M.-z.; Yu, S.-k. Characterization of Haemaphysalis flava (Acari: Ixodidae) from Qingling subspecies of giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca qinlingensis) in Qinling Mountains (central China) by morphology and molecular markers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, W.M.A.; Moustafa, M.A.M.; Kelava, S.; Barker, D.; Matsuno, K.; Nonaka, N.; Shao, R.; Mans, B.J.; Barker, S.C.; Nakao, R. Reconstruction of mitochondrial genomes from raw sequencing data provides insights on the phylogeny of Ixodes ticks and cautions for species misidentification. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.-Z.; Li, X.-S.; Yin, S.-Q.; Zhu, D.; Xue, J.-B.; Li, S.-G. High genetic diversity in hard ticks from a China-Myanmar border county. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Qiu, Y.-B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.-Z.; Woodman, N.; Maldonado, J.E.; Pan, X. Mitogenome and phylogenetic analyses support rapid diversification among species groups of small-eared shrews genus Cryptotis (Mammalia: Eulipotyphla: Soricidae). Zool. Res. 2021, 42, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, W.-T.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Liu, M.; Xing, C.-W.; Cao, Y.; Luo, F.-Z.; Yuan, M.-L. Mitochondrial phylogenomics provides insights into the phylogeny and evolution of spiders (Arthropoda: Araneae). Zool. Res. 2022, 43, 566–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Yan, S.-S.; Xiao, N.; Zhou, J.-J.; Wang, X.-L.; Chen, W.-C.; Deng, H.-Q.; Zhang, B.-W.; Zhou, J. Phylogenetic analysis of combined mitochondrial genome and 32 nuclear genes provides key insights into molecular systematics and historical biogeography of Asian warty newts of the genus Paramesotriton (Caudata: Salamandridae). Zool. Res. 2022, 43, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Guo, X. Complete mitochondrial genomes of five racerunners (Lacertidae: Eremias) and comparison with other lacertids: Insights into the structure and evolution of the control region. Genes 2022, 13, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Shen, C.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Wu, L.; Storey, K.B.; Yu, D.-N.; Zhang, J.-Y. The genetic diversity and the divergence time in extant primitive mayfly, Siphluriscus chinensis Ulmer, 1920 using the mitochondrial genome. Genes 2022, 13, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Thapa, A.; Fan, H.; Ma, T.; Wu, Q.; Ma, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, B.; Li, M.; Yan, L.; et al. Genomic evidence for two phylogenetic species and long-term population bottlenecks in red pandas. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.; Kelava, S.; Seeman, O.D.; Shao, R.; Seaniger, J.R.; Jones, M.K.; Apanaskevich, M.A.; Nakao, R.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Barker, S.C. Rediscovery of Ixodes confusus in Australia with the first description of the male from Australia, a redescription of the female and the mitochondrial (mt) genomes of five species of Ixode. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Deng, L.; Wei, M.; Wu, K.; Huang, S.; Li, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Characterization of the complete mitogenome sequence of the giant panda tick Haemaphysalis hystricis. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 1191–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Deng, L.; Wei, M.; Wu, K.; Huang, S.; Li, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. The mitochondrial genome of the giant panda tick Haemaphysalis flava (Acari, Ixodidae) from Southwest China. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Deng, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Complete mitogenome of the giant panda tick Haemaphysalis longicornis (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 3203–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Wu, W.; Feng, F.; Wang, Q.; Ying, X.; Qi, D.; Qi, G. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Otus lettia: Exploring the mitochondrial evolution and phylogeny of owls (Strigiformes). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6, 3443–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, M.; Hu, S.-Y.; Luo, F.-Z.; Yuan, M.-L. Comparative mitogenomic analyses provide evolutionary insights into the retrolateral tibial apophysis clade (Araneae: Entelegynae). Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 974084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, T.D.; Shao, R.; Beati, L.; Miller, H.; Barker, S.C. Phylogenetic analysis of ticks (Acari: Ixodida) using mitochondrial genomes and nuclear rRNA genes indicates that the genus Amblyomma is polyphyletic. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2012, 64, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Zheng, A.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, X. The complete mitochondrial genome and phylogenetic analysis of Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann (Acari: Ixodidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2017, 2, 856–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavatte, J.-M.; Octavia, S. The complete mitochondrial genome of Dermacentor (Indocentor) auratus (Acari, Ixodidae). Parasite 2021, 28, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciloglu, A.; Ibis, O.; Yildirim, A.; Aktas, M.; Duzlu, O.; Onder, Z.; Simsek, E.; Yetismis, G.; Ellis, V.A.; Inci, A. Complete mitochondrial genome characterization and phylogenetic analyses of the main vector of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus: Hyalomma marginatum Koch, 1844. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, D.; Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Du, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Haemaphysalis (Alloceraea) kolonini (Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Hou, R.; Owens, J.R.; Spotila, J.R.; Valitutto, M.; Yin, G.; Paladino, F.V.; Wu, F.; Qi, D.; Zhang, Z. Field metabolic rates of giant pandas reveal energetic adaptations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Al-Arab, M.; Bernhart, S.H.; Reinhardt, F.; Stadler, P.F.; Middendorf, M.; Bernt, M. Improved annotation of protein-coding genes boundaries in metazoan mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10543–10552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombel, I.T.; Sykes, K.F.; Rayner, S.; Johnston, S.A. ORF-FINDER: A vector for high-throughput gene identification. Gene 2002, 282, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canbäck, B.; Laslett, D. ARWEN: A program to detect tRNA genes in metazoan mitochondrial nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yue, B. Krait: An ultrafast tool for genome-wide survey of microsatellites and primer design. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.-X.; Zhu, R.-L.; Liu, Y. Simple sequence repeats in bryophyte mitochondrial genomes. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, F.; Chen, S. The complete chloroplast genomes of two Lancea species with comparative analysis. Molecules 2018, 23, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kan, X.; Miao, G.; Hu, S.; Sun, Q.; Tian, W. qMGR: A new approach for quantifying mitochondrial genome rearrangement. Mitochondrion 2020, 52, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrov, D.V.; Boore, J.L.; Brown, W.M. The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the horseshoe crab Limulus polyphemu. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.; Barker, S.C.; Mitani, H.; Aoki, Y.; Fukunaga, M. Evolution of duplicate control regions in the mitochondrial genomes of metazoa: A case study with australasian Ixodes ticks. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, Y.-X.; Huang, L. ImageGP: An easy-to-use data visualization web server for scientific researchers. iMeta 2022, 1, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, S.; Pei, T.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J. Tick mitochondrial genomes: Structural characteristics and phylogenetic implications. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelava, S.; Mans, B.J.; Shao, R.; Moustafa, M.A.M.; Matsuno, K.; Takano, A.; Kawabata, H.; Sato, K.; Fujita, H.; Ze, C.; et al. Phylogenies from mitochondrial genomes of 120 species of ticks: Insights into the evolution of the families of ticks and of the genus Amblyomm. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate Maximum-Likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: Recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W256–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.Y.; Chen, Z.; Fu, Y.T.; Liu, G.H.; Suleman; Cheng, T.Y. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genomes of two Ixodes ticks, I. nipponensis and Ixodes (Pholeoixodes) sp. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2021, 35, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Li, B.; Ouyang, B. Three new Ranidae mitogenomes and the evolution of mitochondrial gene rearrangements among Ranidae species. Asian Herpetol. Res. 2018, 9, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhou, M.; Yang, J. Complete mitochondrial genome of Japalura flaviceps: Deep insights into the phylogeny and gene rearrangements of Agamidae species. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Sun, H.-Q.; Li, C.-J.; Zhao, W.-X.; Yao, Y.-X. The complete mitochondrial genome of Platygaster robiniae (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae): A novel tRNA secondary structure, gene rearrangements and phylogenetic implications. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 18, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagna, M.; Sassera, D.; Griggio, F.; Epis, S.; Bandi, C.; Gissi, C. Tick-Box for 3′-end formation of mitochondrial transcripts in Ixodida, basal Chelicerates and Drosophila. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Newkirk, A.J.; Burroughs, M.; Changayil, S.S.; Dasch, G.A. The mitochondrial genome of the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum). Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2015, 6, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.-T.; Qiu, J.-H.; Chang, Q.-C.; Wang, C.-R. Complete mitochondrial genomes of Dermacentor silvarum and comparative analyses with another hard tick Dermacentor nitens. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 169, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.K.; Muthiyan, R.; Ponraj, P.; Muniswamy, K.; Sunder, J.; Kundu, A.; Karunakaran, D.; George, Z.; Kundu, M.S.; Ahmed, S.K.Z.; et al. Mitogenome analysis of Indian isolate of Rhipicephalus microplus clade A sensu (Burger et al., 2014): A first report from Maritime South-East Asia. Mitochondrion 2019, 49, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, S.; Pei, T.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J. The complete mitochondrial genome and expression profile of mitochondrial protein-coding genes in the bisexual and parthenogenetic Haemaphysalis longicornis. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, F. The complete mitochondrial genome of Hyalomma rufipes (Acari: Ixodidae) from China and comparative analysis of mitogenomes in genus Hyalomma. Int. J. Acarol. 2022, 48, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zuo, X.; Jiang, D.; Yang, X. The complete mitochondrial genome of Ixodes vespertilionis (Acari: Ixodidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6, 3001–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C.; Yuan, X.; Jia, G.; Deng, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; et al. Assessment of four DNA fragments (COI, 16S rDNA, ITS2, 12S rDNA) for species identification of the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Feng, C.; Jia, G.; Lin, X. Development of a DNA barcoding system for the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Mitochondrial DNA 2014, 25, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Cai, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Comparative mitochondrial genomic analyses of three chemosynthetic vesicomyid clams from deep-sea habitats. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 7261–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wahlberg, N.; Liao, C.-Q.; Wang, C.-B.; Ma, F.-Z.; Huang, G.-H. Fourteen complete mitochondrial genomes of butterflies from the genus Lethe (Lepidoptera, Nymphalidae, Satyrinae) with mitogenome-based phylogenetic analysis. Genomics 2020, 112, 4435–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Dai, R.; Yang, M. Comparative mitogenomes of six species in the subfamily Iassinae (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) and phylogenetic analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, H.; Zhao, W.-T.; Kibet, J.C.; Sitko, J.; Nie, P. Morphological and complete mitogenomic characterisation of the acanthocephalan Polymorphus minutus infecting the duck Anas platyrhynchos. Folia Parasitol. 2021, 68, 015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, L.; Liao, C.-Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Huang, G.-H. Comparative mitochondrial genome analysis and phylogenetic relationship among lepidopteran species. Gene 2022, 830, 146516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-J.; Shi, M.; Chen, X.-X.; Sharkey, M.J.; van Achterberg, C.; Ye, G.-Y.; He, J.-H. New views on strand asymmetry in insect mitochondrial genomes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Qu, M.; Zhang, X.; Ding, S. A comprehensive description and evolutionary analysis of 22 grouper (Perciformes, Epinephelidae) mitochondrial genomes with emphasis on two novel genome organizations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanin, A.; Léger, N.; Deutsch, J. Evidence for multiple reversals of asymmetric mutational constraints during the evolution of the mitochondrial genome of Metazoa, and consequences for phylogenetic inferences. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-J.; Bai, Y.; Dong, Y. A rearrangement of the mitochondrial genes of centipedes (Arthropoda, Myriapoda) with a phylogenetic analysis. Genes 2022, 13, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Hu, J.; Li, X. The evolution and application of microsatellites. Hereditas 2003, 25, 615–619. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Wang, Y. The application of microsatellite DNA markers in conservation genetics of endangered animals. Biodivers. Sci. 2004, 12, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xuan, Y.; Liang, G.; Yang, X.; Yu, Z.; Barker, S.C.; Kelava, S.; Bu, W.; Liu, J.; Gao, S. Precise annotation of tick mitochondrial genomes reveals multiple copy number variation of short tandem repeats and one transposon-like element. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, J.L.; Collins, T.M.; Stanton, D.; Daehler, L.L.; Brown, W.M. Deducing the pattern of arthropod phytogeny from mitochondrial DNA rearrangements. Nature 1995, 376, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, J.L.; Lavrov, D.V.; Brown, W.M. Gene translocation links insects and crustaceans. Nature 1998, 392, 667–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaña-Lozano, P.; Moreno-Carmona, M.; Ochoa-Capera, M.; Medina, N.S.; Boore, J.L.; Prada, C.F. Comparative genomic analysis of vertebrate mitochondrial reveals a differential of rearrangements rate between taxonomic class. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, X. Comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes in two subspecies of the sunwatcher toad-headed agama (Phrynocephalus helioscopus): Prevalent intraspecific gene rearrangements in Phrynocephalus. Genes 2022, 13, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayivi, S.P.; Tong, Y.; Storey, K.B.; Yu, D.-N.; Zhang, J.-Y. The mitochondrial genomes of 18 new Pleurosticti (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) exhibit a novel trnQ-NCR-trnI-trnM gene rearrangement and clarify phylogenetic relationships of subfamilies within Scarabaeidae. Insects 2021, 12, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, W.C.I.; Roehrdanz, R.L. Mitochondrial gene order is not conserved in arthropods: Prostriate and metastriate tick mitochondrial genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 1772–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.; Kelava, S.; Shao, R.; Seeman, O.D.; Jones, M.K.; Nakao, R.; Barker, S.C.; Apanaskevich, D.A. Description of the female, nymph and larva and mitochondrial genome, and redescription of the male of Ixodes barkeri Barker, 2019 (Acari: Ixodidae), from the short-beaked echidna, Tachyglossus aculeatus, with a consideration of the most suitable subgenus for this tick. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, T.D.; Shao, R.; Labruna, M.B.; Barker, S.C. Molecular phylogeny of soft ticks (Ixodida: Argasidae) inferred from mitochondrial genome and nuclear rRNA sequences. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mans, B.J.; Featherston, J.; Kvas, M.; Pillay, K.-A.; de Klerk, D.G.; Pienaar, R.; de Castro, M.H.; Schwan, T.G.; Lopez, J.E.; Teel, P.; et al. Argasid and ixodid systematics: Implications for soft tick evolution and systematics, with a new argasid species list. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Ren, J.-L.; Lyu, Z.-T.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Lv, K.; Wu, J.-W.; Li, J.-T. Taxonomic revision of Amolops chunganensis (Pope, 1929) (Amphibia: Anura) and description of a new species from southwestern China, with discussion on Amolops monticola group and assignment of species groups of the genus Amolops. Zool. Res. 2021, 42, 574–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Jiang, D.; Du, C.; Rao, C.; Yin, J.; Fang, Y.; Yang, X. Complete mitochondrial genome and phylogenetic analysis of Ixodes acutitarsus (Acari: Ixodidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2022, 7, 1134–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, T.D.; Shao, R.; Barker, S.C. Phylogenetic analysis of the mitochondrial genomes and nuclear rRNA genes of ticks reveals a deep phylogenetic structure within the genus Haemaphysalis and further elucidates the polyphyly of the genus Amblyomma with respect to Amblyomma sphenodonti and Amblyomma elaphense. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S.C.; Burger, T.D. Two new genera of hard ticks, Robertsicus n. gen. and Archaeocroton n. gen., and the solution to the mystery of Hoogstraal’s and Kaufman’s “primitive” tick from the Carpathian Mountains. Zootaxa 2018, 4500, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).