Transcriptional Pausing and Activation at Exons-1 and -2, Respectively, Mediate the MGMT Gene Expression in Human Glioblastoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomic Databases
2.2. Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBSs) and CpG Islands
2.3. Glioblastoma Cell Culture
2.4. Western Blotting (WB)
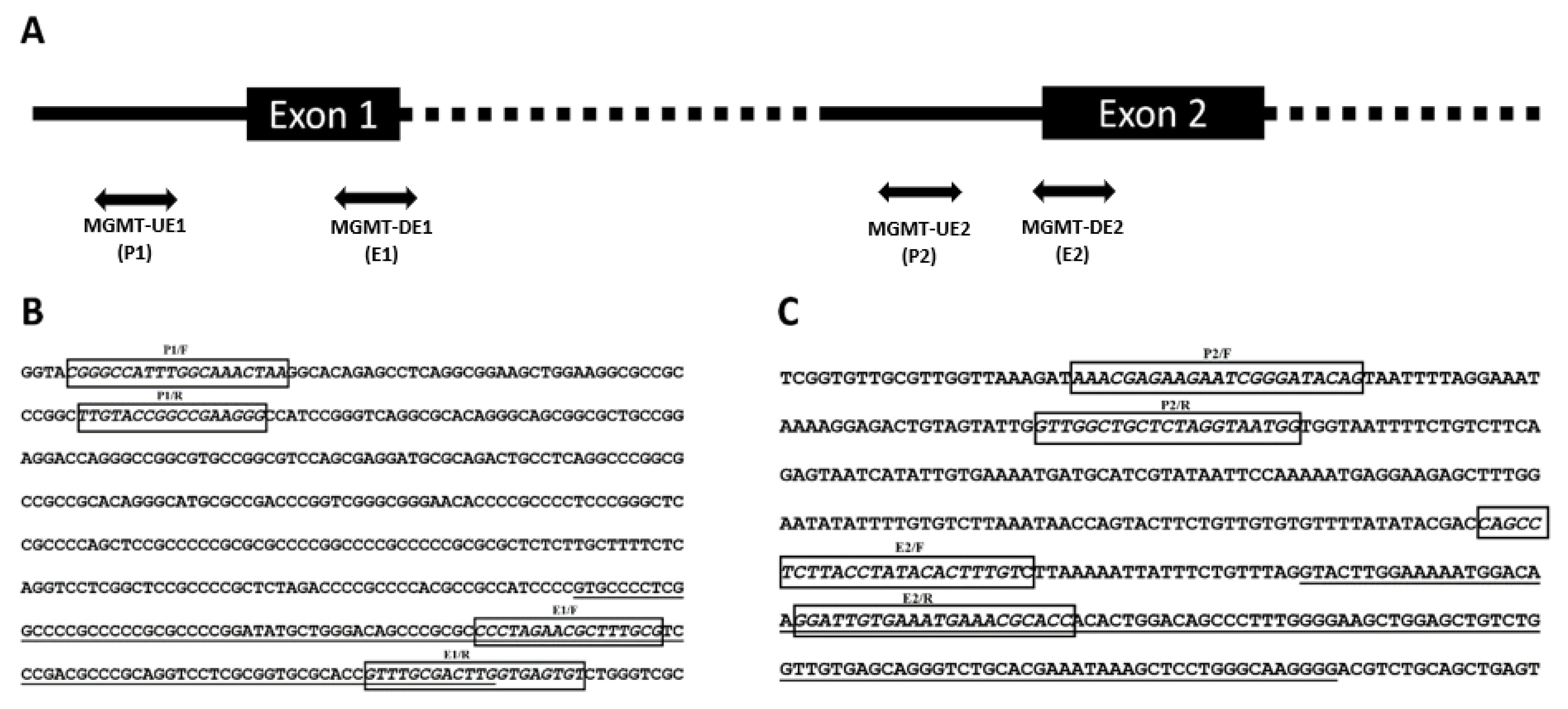
2.5. RNA Extraction, Conventional RT-PCR, and RT-qPCR
2.6. Nuclear Run-On (NRO) Transcription Assays
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Context of MGMT Locus, MGMT Promoters, and Enhancer Sequences in the Vicinity
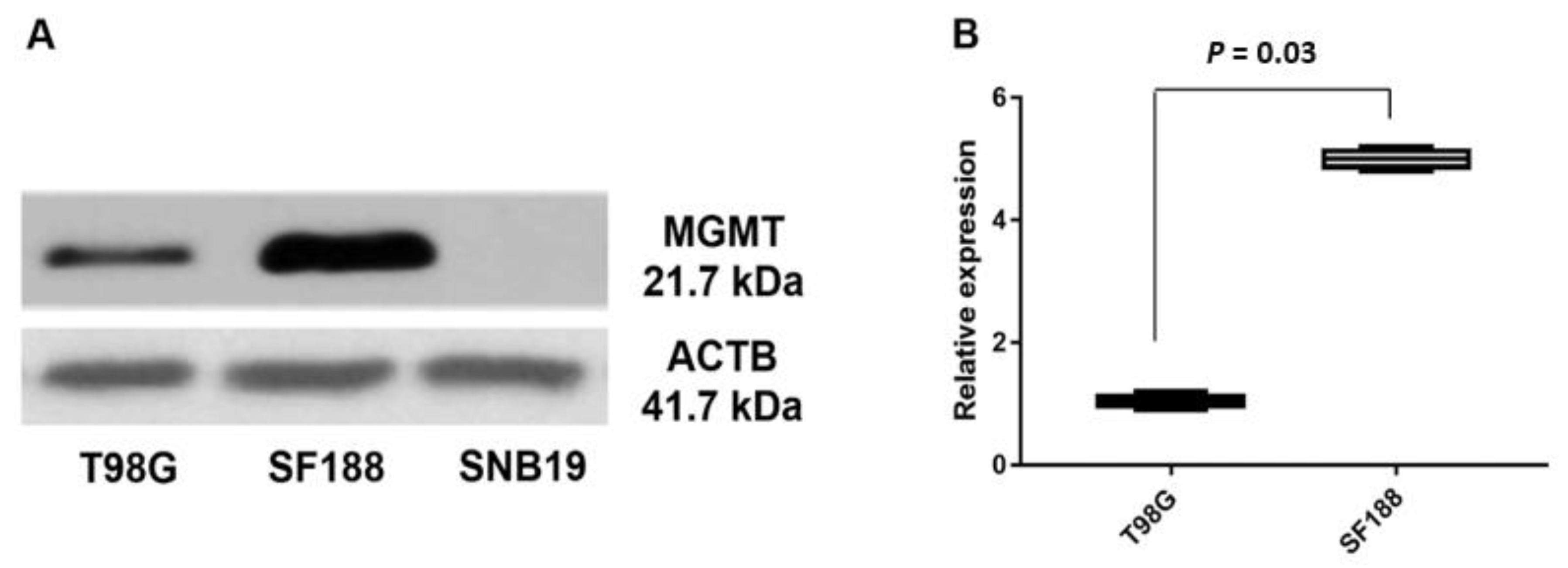
3.2. Expression of MGMT Promoters Proximal to Exon 1 and Exon 2 in MGMT-Proficient and -Deficient GBM Cell Lines
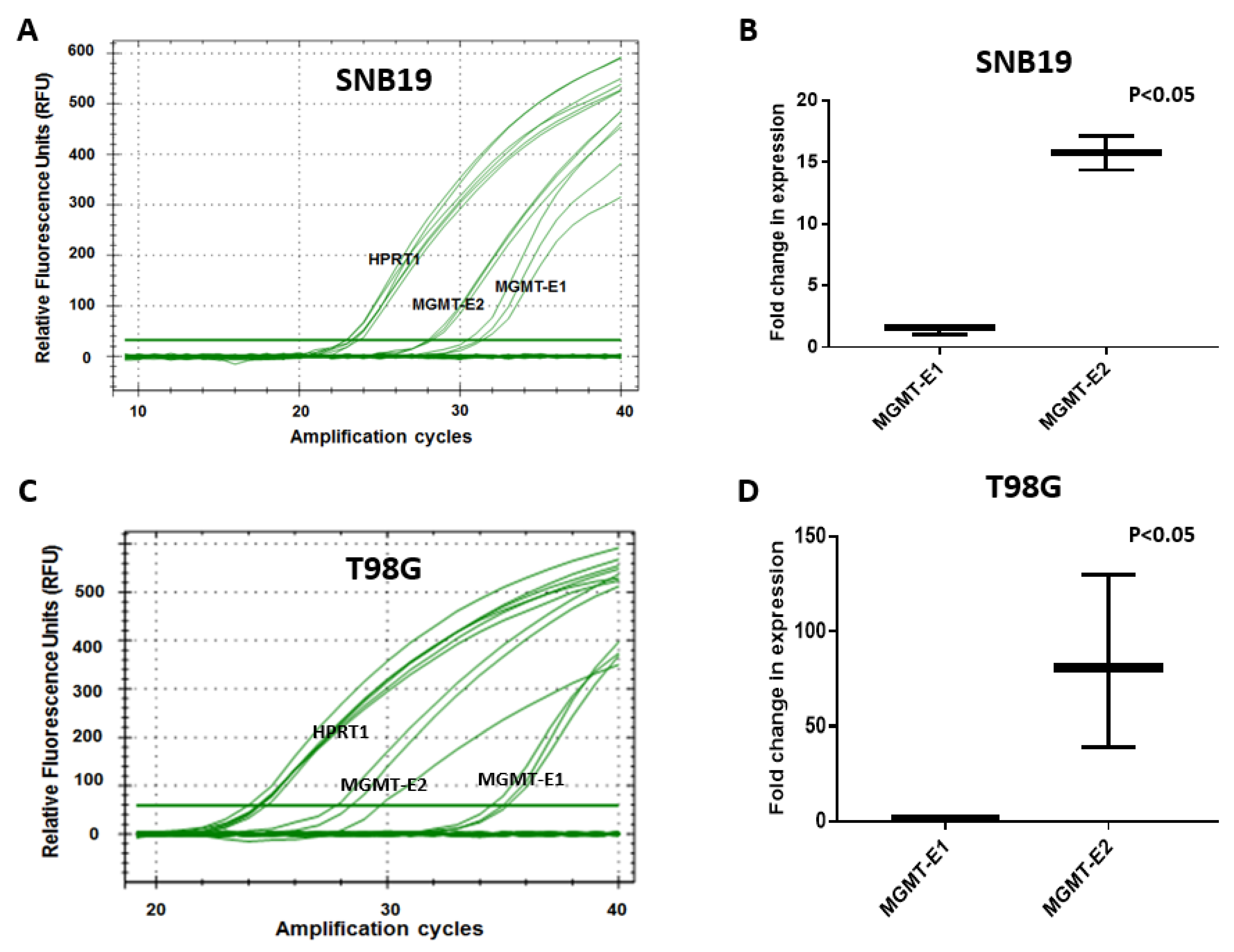
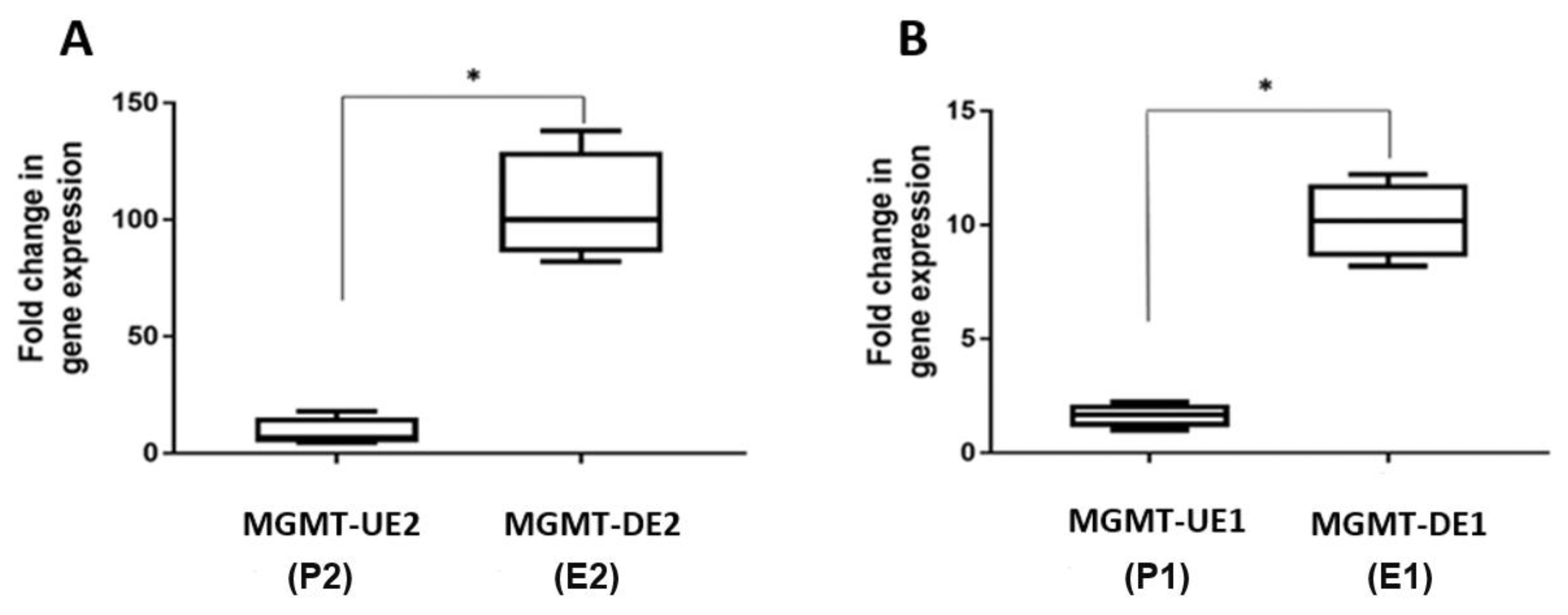
3.3. RT q-PCR Analysis of MGMT-E1, MGMT-E2, and MGMT-E5 Expression
3.4. Quantitation of MGMT-E1 and MGMT-E2 Transcription Rates by Nuclear Run-On (NRO) Transcription Assays
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pegg, A.E. Repair of O6-alkylguanine by alkyltransferases. Mutat. Res. Mutat. Res. 2000, 462, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaina, B.; Christmann, M. DNA repair in personalized brain cancer therapy with temozolomide and nitrosoureas. DNA Repair 2019, 78, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishina, Y.; Duguid, E.M.; He, C. Direct Reversal of DNA Alkylation Damage. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, S.L. Clinical Relevance of MGMT in the Treatment of Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2388–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaina, B.; Margison, G.P.; Christmann, M. Targeting O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase with specific inhibitors as a strategy in cancer therapy. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 3663–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkaria, J.N.; Kitange, G.J.; James, C.D.; Plummer, R.; Calvert, H.; Weller, M.; Wick, W. Mechanisms of chemoresistance to alkylating agents in malignant glioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2900–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubbs, J.L.; Pegg, A.E.; Tainer, J.A. DNA binding, nucleotide flipping, and the helix-turn-helix motif in base repair by O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase and its implications for cancer chemotherapy. DNA Repair 2007, 6, 1100–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim Al-Obaide, M.A.; Arutla, V.; Bacolod, M.D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Srivenugopal, K.S. Genomic Space of MGMT in Human Glioma Revisited: Novel Motifs, Regulatory RNAs, NRF1, 2, and CTCF Involvement in Gene Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.C.; Potter, P.M.; Tano, K.; Shiota, S.; Mitra, S.; Brent, T.P. Characterization of the promoter region of the human O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 6163–6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrini, G.; Fabbri, E.; Lo Nigro, C.; Dechecchi, M.C.; Gambari, R. Regulation of expression of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase and the treatment of glioblastoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binabaj, M.M.; Bahrami, A.; ShahidSales, S.; Joodi, M.; Joudi Mashhad, M.; Hassanian, S.M.; Anvari, K.; Avan, A. The prognostic value of MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma: A meta-analysis of clinical trials. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacolod, M.D.; Barany, F. MGMT Epigenetics: The Influence of Gene Body Methylation and other Insights Derived from Integrated Methylomic, Transcriptomic, and Chromatin Analyses for Various Cancer Types. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Stupp, R.; Reifenberger, G.; Brandes, A.A.; van den Bent, M.J.; Wick, W.; Hegi, M.E. MGMT promoter methylation in malignant gliomas: Ready for personalized medicine? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, J.F.; Futscher, B.W.; Tano, K.; Graunke, D.M.; Pieper, R.O. Graded methylation in the promoter and body of the O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) gene correlates with MGMT expression in human glioma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 17228–17237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandith, A.A.; Qasim, I.; Zahoor, W.; Shah, P.; Bhat, A.R.; Sanadhya, D.; Shah, Z.A.; Naikoo, N.A. Concordant association validates MGMT methylation and protein expression as favorable prognostic factors in glioma patients on alkylating chemotherapy (Temozolomide). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everhard, S.; Tost, J.; El Abdalaoui, H.; Crinière, E.; Busato, F.; Marie, Y.; Gut, I.G.; Sanson, M.; Mokhtari, K.; Laigle-Donadey, F.; et al. Identification of regions correlating MGMT promoter methylation and gene expression in glioblastomas. Neuro Oncol. 2009, 11, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, M.; Oba-Shinjo, S.M.; Camargo, A.A.; Moura, R.P.; Aguiar, P.H.; Cabrera, H.N.; Begnami, M.; Rosemberg, S.; Teixeira, M.J.; Marie, S.K. Correlation of MGMT promoter methylation status with gene and protein expression levels in glioblastoma. Clinics 2011, 66, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobola, M.S.; Alnoor, M.; Chen, J.Y.; Kolstoe, D.D.; Silbergeld, D.L.; Rostomily, R.C.; Blank, A.; Chamberlain, M.C.; Silber, J.R. O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase activity is associated with response to alkylating agent therapy and with MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma and anaplastic glioma. BBA Clin. 2015, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, E.L.; Stark, A.L.; Zhang, W.; Dolan, M.E.; Godley, L.A. The role of gene body cytosine modifications in MGMT expression and sensitivity to temozolomide. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Malta, T.M.; De Souza, C.F.; Sabedot, T.S.; Silva, T.C.; Mosella, M.S.; Kalkanis, S.N.; Snyder, J.; Castro, A.V.B.; Noushmehr, H. Glioma CpG island methylator phenotype (G-CIMP): Biological and clinical implications. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, M.; Garcia-Foncillas, J.; Andion, E.; Goodman, S.N.; Hidalgo, O.F.; Vanaclocha, V.; Baylin, S.B.; Herman, J.G. Inactivation of the DNA-Repair Gene MGMT and the Clinical Response of Gliomas to Alkylating Agents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krex, D.; Klink, B.; Hartmann, C.; von Deimling, A.; Pietsch, T.; Simon, M.; Sabel, M.; Steinbach, J.P.; Heese, O.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. German Glioma Network. Long-term survival with glioblastoma multiforme. Brain 2007, 130, 2596–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.F.; de Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; et al. MGMT Gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Xuan, Z.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, M.Q. TRED: A transcriptional regulatory element database, new entries, and other development. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D137–D140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivenugopal, K.S.; Mullapudi, S.R.; Shou, J.; Hazra, T.K.; Ali-Osman, F. Protein phosphorylation is a regulatory mechanism for O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase in human brain tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 282–287. [Google Scholar]
- Valente, V.; Teixeira, S.A.; Neder, L.; Okamoto, O.K.; Oba-Shinjo, S.M.; Marie, S.K.; Scrideli, C.A.; Paçó-Larson, M.L.; Carlotti, C.G., Jr. Selection of suitable housekeeping genes for expression analysis in glioblastoma using quantitative RT-PCR. BMC Mol. Biol. 2009, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smale, S.T. Nuclear Run-on Assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Hart, J.R.; Kaikkonen, M.U.; Weinberg, M.S.; Vogt, P.K.; Morris, K.V. Quantification of nascent transcription by bromouridine immunocapture nuclear run-on RT-qPCR. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-Y.; Shiekhattar, R. Architectural and functional commonalities between enhancers and promoters. Cell 2015, 162, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlyueva, D.; Stampfel, G.; Stark, A. Transcriptional enhancers: From properties to genome-wide predictions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Gan, H.; Wang, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Fang, D.; Kitange, G.J.; He, L.; Hu, Z.; Parney, I.F.; et al. A novel enhancer regulates MGMT expression and promotes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auger, N.; Thillet, J.L.; Wanherdrick, K.; Idbaih, A.; Legrier, M.-E.; Dutrillaux, B.; Sanson, M.; Poupon, M.F. Genetic alterations associated with acquired temozolomide resistance in SNB-19, a human glioma cell line. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y. Temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme. Genes Dis. 2016, 3, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risueno, A.; Roson-Burgo, B.; Dolnik, A.; Hernandez-Rivas, J.M.; Bullinger, L.; Rivas, J.D.L. A robust estimation of exon expression to identify alternatively spliced genes applied to human tissues and cancer samples. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzluff, W.F.; Huang, R.C.C. Transcription of RNA in isolated nuclei. In Transcription and Translation, a Practical Approach; Hames, B.D., Higgins, S.J., Eds.; IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1986; pp. 89–128. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, L.C.; Remack, J.S.; Brent, T.P. In vitro methylation of the O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter reduces transcription. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1217, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Paranjpe, A.; Bailey, N.I.; Konduri, S.; Bobustuc, G.C.; Ali-Osman, F.; Yusuf, M.A.; Punganuru, S.R.; Madala, H.R.; Basak, D.; Mostofa, A.; et al. New insights into estrogenic regulation of O6-methylguanine DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) in human breast cancer cells: Co-degradation of ER- and MGMT proteins by fulvestrant or O6-benzylguanine indicates fresh avenues for therapy. J. Biomed. Res. 2016, 30, 393–410. [Google Scholar]
- Fornace, A.J., Jr.; Papathanasiou, M.A.; Hollander, M.C.; Yarosh, D.B. Expression of the O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase gene MGMT in MER+ and MER- human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 7908–7911. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, J.E.F.; Kadonaga, J.T. The RNA polymerase II core promoter: A key component in the regulation of gene expression. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.; Landry, H.M.; Churchman, L.S. Pause & Go: From the discovery of RNA polymerase pausing to its functional implications. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2017, 46, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Strobl, L.J.; Eick, D. Hold back of RNA polymerase II at the transcription start site mediates down-regulation of c-myc in vivo. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3307–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumm, A.; Meulia, T.; Brunvand, M.; Groudine, M. The block to transcriptional elongation within the human c-myc gene is determined in the promoter-proximal region. Genes Dev. 1992, 6, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, D.L.; Groudine, M. Novel promoter upstream of the human c-myc gene and regulation of c-myc expression in B-cell lymphomas. Mol. Cell Biol. 1986, 6, 3481–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, L.J.; Engel, J.D. DNA-binding specificities of the GATA transcription factor family. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 4011–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granok, H.; Leibovitch, B.A.; Shaffer, C.D.; Elgin, S.C. Chromatin. Gaga over GAGA factor. Curr. Biol. 1995, 5, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.-Y.; Chang, Y.-L.; Swamy, K.B.S.; Chiang, R.-L.; Huang, D.-H. GAGA factor, a positive regulator of global gene expression, modulates transcriptional pausing and organization of upstream nucleosomes. Epigenetics Chromatin 2016, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino-Torchia, M.L.; Ashwell, J.D. Getting MAD at MYC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9821–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakilas, G.K.; Perdikopanis, N.; Hatzigeorgiou, A. Solving the transcription start site identification problem with ADAPT-CAGE: A machine learning algorithm for the analysis of CAGE data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
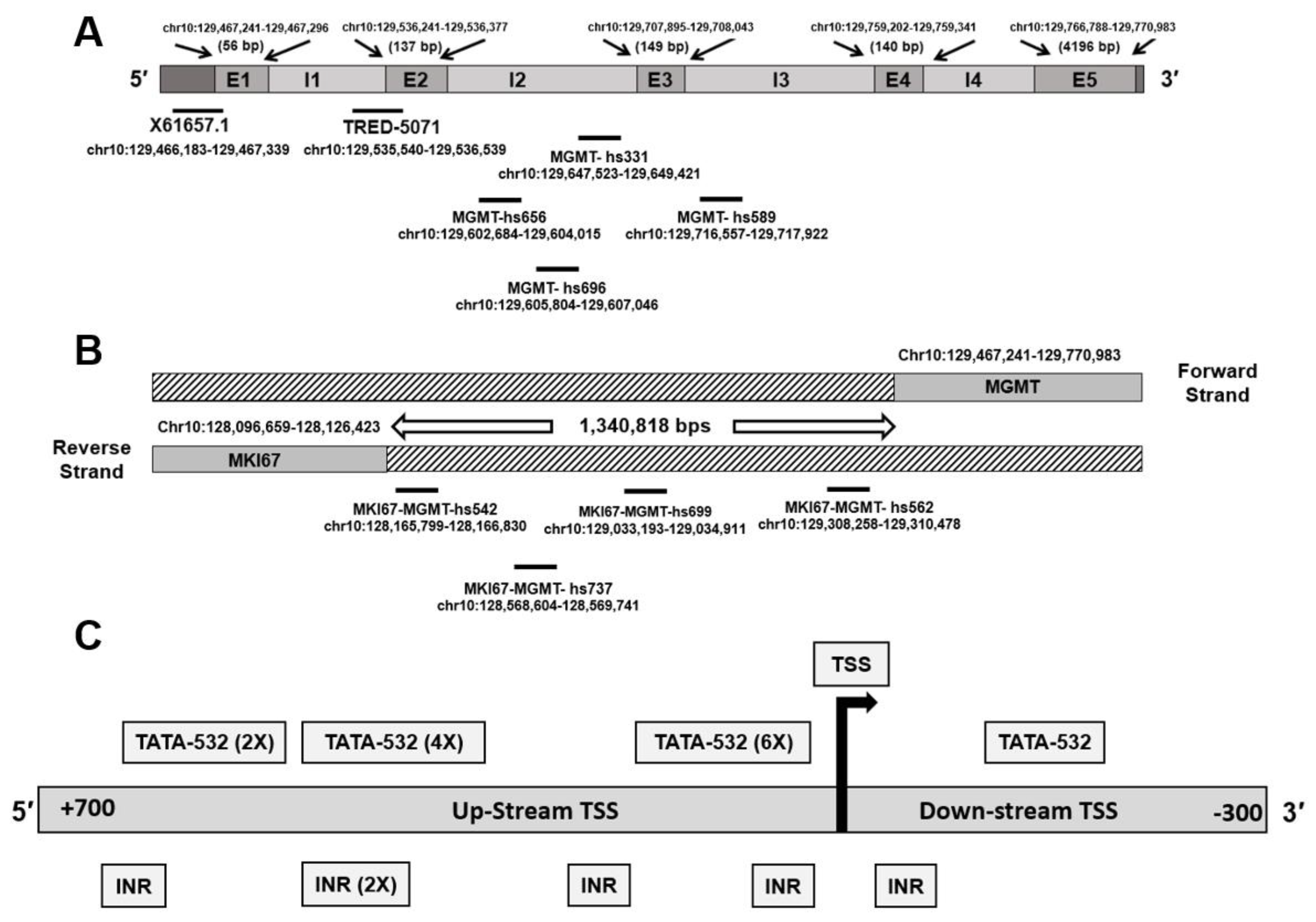



| Type | ID | Bracketing Genes | Coordinates (hg38) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Promoter | MGMT-E1 promoter (X61657.1) | MGMT (5′ UTR) | chr10:129,466,183–129,467,339 | Harris et al. 1991 [9] |
| promoter | MGMT-E2 promoter (TRED-5071) | MGMT | chr10:129,535,540–129,536,539 | TRED-5071, [8] and this study |
| Enhancer | MGMT-hs331 | MGMT (intragenic) | chr10:129,647,523–129,649,421 | VISTA Enhancer Browser https://enhancer.lbl.gov, accessed on 14 May 2021. |
| Enhancer | MKI67-MGMT-hs542 | MKI67-MGMT | chr10:128,165,799–128,166,830 | |
| Enhancer | MKI67-MGMT- hs562 | MKI67-MGMT | chr10:129,308,258–129,310,478 | |
| Enhancer | MGMT- hs589 | MGMT (intragenic) | chr10:129,716,557–129,717,922 | |
| Enhancer | MGMT-hs656 | MGMT (intragenic) | chr10:129,602,684–129,604,015 | |
| Enhancer | MGMT-hs696 | MGMT (intragenic) | chr10:129,605,804–129,607,046 | |
| Enhancer | MKI67-MGMT-hs699 | MKI67-MGMT | chr10:129,033,193–129,034,911 | |
| Enhancer | MKI67-MGMT- hs737 | MKI67-MGMT | chr10:128,568,604–128,569,741 | |
| Enhancer | MKI67-MGMT | MKI167- MGMT | Chr10:130,704,894– 130,708,206 | Chen et al. 2018 [32] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Obaide, M.A.I.; Srivenugopal, K.S. Transcriptional Pausing and Activation at Exons-1 and -2, Respectively, Mediate the MGMT Gene Expression in Human Glioblastoma Cells. Genes 2021, 12, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12060888
Al-Obaide MAI, Srivenugopal KS. Transcriptional Pausing and Activation at Exons-1 and -2, Respectively, Mediate the MGMT Gene Expression in Human Glioblastoma Cells. Genes. 2021; 12(6):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12060888
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Obaide, Mohammed A. Ibrahim, and Kalkunte S. Srivenugopal. 2021. "Transcriptional Pausing and Activation at Exons-1 and -2, Respectively, Mediate the MGMT Gene Expression in Human Glioblastoma Cells" Genes 12, no. 6: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12060888
APA StyleAl-Obaide, M. A. I., & Srivenugopal, K. S. (2021). Transcriptional Pausing and Activation at Exons-1 and -2, Respectively, Mediate the MGMT Gene Expression in Human Glioblastoma Cells. Genes, 12(6), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12060888






