Muscat Flavor in Grapevine: A Digital PCR Assay to Track Allelic Variation in VvDXS Gene
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Muscat Flavor
1.2. VvDXS Gene
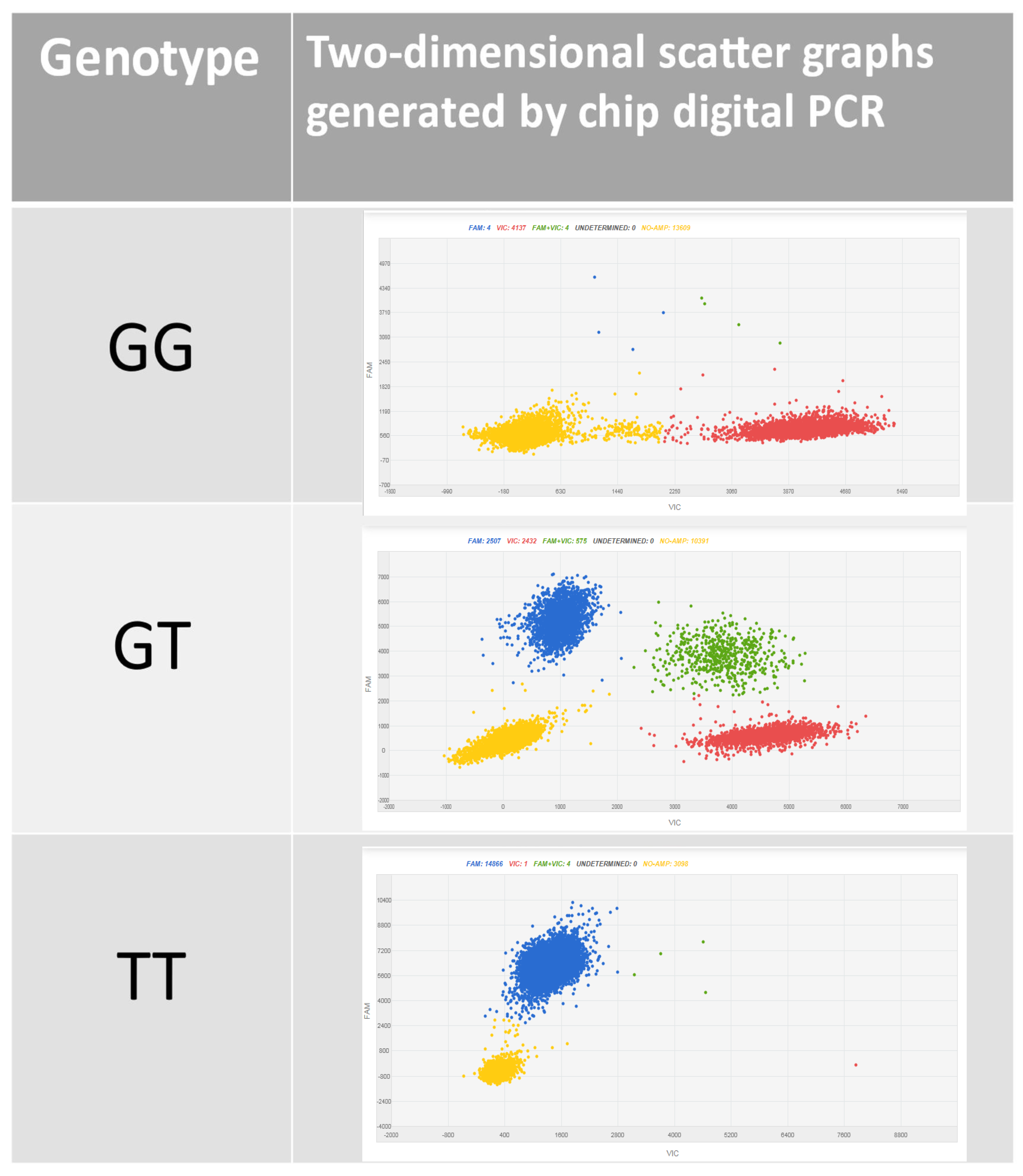
1.3. Digital PCR
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Grapevine Varieties
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Amplification and Sequencing
| DXS8fw | CAACAACGTCATTGCTGTCATAG (5′-3′) |
| DXS8rw | GCTAGACAGAACAGGTAAGATTTC (5′-3′) |
2.4. Chip Digital PCR
- 96 °C for 10 min;
- 55 °C for 2 min and 98 °C denaturation for 30 s, repeated for 45 cycles;
- 60 °C for 2 min.
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.; Massonnet, M.; Cantu, D. The Genetic Basis of Grape and Wine Aroma. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespan, M.; Milani, N. The Muscats: A Molecular Analysis of Synonyms, Homonyms and Genetic Relationships within a Large Family of Grapevine Cultivars. Vitis 2001, 40, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ruffa, P.; Raimondi, S.; Boccacci, P.; Abbà, S.; Schneider, A. The Key Role of “Moscato Bianco” and “Malvasia Aromatica di Parma” in the Parentage of Traditional Aromatic Grape Varieties. Tree Gen. Genomes 2016, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, C.; Tumino, G.; Gardiman, M.; Crespan, M.; Bignami, C.; de Palma, L.; Barbagallo, M.G.; Muganu, M.; Morcia, C.; Novello, V.; et al. Parentage Atlas of Italian Grapevine Varieties as Inferred from SNP Genotyping. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 605934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doligez, A.; Audiot, E.; Baumes, R.; This, P. QTLs for Muscat Flavour and Monoterpenic Odorant Content in Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Mol. Breed. 2006, 18, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchêne, E.; Butterlin, G.; Claudel, P.; Dumas, V.; Jaegli, N.; Merdinoglu, D. A Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) Deoxy-D-xylulose Synthase Gene Co-locates with a Major Quantitative Trait Loci for Terpenol Content. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battilana, J.; Costantini, L.; Emanuelli, F.; Sevini, F.; Segala, C.; Moser, S.; Velasco, R.; Versini, G.; Grando, M.S. The 1-deoxy-D: -xylulose 5-phosphate Synthase Gene Co-localizes with a Major QTL Affecting Monoterpene Content in Grapevine. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalla Costa, L.; Emanuelli, F.; Trenti, M.; Moreno-Sanz, P.; Lorenzi, S.; Coller, E.; Moser, S.; Slaghenaufi, D.; Cestaro, A.; Larcher, R.; et al. Induction of Terpene Biosynthesis in Berries of Microvine Transformed with VvDXS1 Alleles. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 8, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuelli, F.; Battilana, J.; Costantini, L.; Le Cunff, L.; Boursiquot, J.-M.; This, P.; Grando, M.S. A Candidate Gene Association Study on Muscat Flavor in Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuelli, F.; Sordo, M.; Lorenzi, S.; Battilana, J.; Grando, M.S. Development of User-friendly Functional Molecular Markers for VvDXS Gene Conferring Muscat Flavor in Grapevine. Mol. Breed. 2014, 33, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkouropoulos, G.; Ganopoulos, I.; Doulis, A.; Nikolaou, N.; Mylona, P. High Resolution Melting (HRM) Analysis on VviDXS to Reveal Muscats or Non-muscats among Autochthonous Greek Wine Producing Grape Varieties. OENO One 2016, 50, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcia, C.; Ghizzoni, R.; Delogu, C.; Andreani, L.; Carnevali, P.; Terzi, V. Digital PCR: What Relevance to Plant Studies? Biology 2020, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morcia, C.; Terzi, V.; Ghizzoni, R.; Vaiuso, C.; Delogu, C.; Andreani, L.; Venturini, A.; Carnevali, P.; Pompa, P.P.; Tumino, G. Digital PCR for Genotype Quantification: A Case Study in a Pasta Production Chain. Biology 2021, 10, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanato, P.; Biscarini, F. Digital PCR as New Approach to SNP Genotyping in Sugar Beet. Sugar Tech. 2016, 18, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Serrano-Heras, G.; Castaño, M.J.; Solera, J. Real-time PCR Detection Chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 439, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Meng, Y.; Sui, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Fu, B. Comparison of Four Digital PCR Platforms for Accurate Quantification of DNA Copy Number of a Certified Plasmid DNA Reference Material. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whale, A.S.; Huggett, J.F.; Tzonev, S. Fundamentals of Multiplexing with Digital PCR. Biomol. Det. Quant. 2016, 10, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demeke, T.; Dobnik, D. Critical Assessment of Digital PCR for the Detection and Quantification of Genetically Modified Organisms. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4039–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobnik, D.; Štebih, D.; Blejec, A.; Morisset, D.; Žel, J. Multiplex Quantification of Four DNA Targets in One Reaction with Bio-Rad Droplet Digital PCR System for GMO Detection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rački, N.; Dreo, T.; Gutierrez-Aguirre, I.; Blejec, A.; Ravnikar, M. Reverse Transcriptase Droplet Digital PCR Shows High Resilience to PCR Inhibitors from Plant, Soil and Water Samples. Plant Methods 2014, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuelli, F.; Battilana, J.; Costantini, L.; Grando, M.S. Molecular Breeding of Grapevine for Aromatic Quality and Other Traits Relevant to Viticulture. In Breeding for Fruit Quality; Jenks, M.A., Bebeli, P.J., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2011; pp. 247–260. [Google Scholar]
- Di Gaspero, G.; Foria, S. Molecular Grapevine Breeding Techniques. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition, Grapevine Breeding Programs for the Wine Industry; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 23–37. ISBN 9781782420750. [Google Scholar]
| Variety | Muscat Flavor | Sequence at 1822 SNP | FAM Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chardonnay Muscat clone | + | G/G | 0 |
| Chardonnay non-Muscat clone | − | G/G | 0 |
| Aleatico | + | G/T | 49.8 |
| Chasselas Musqué | + | G/G | 0 |
| Early Muscat | + | G/T | 50 |
| Moscato bianco | + | G/T | 52.9 |
| Moscato di Scanzo | + | G/T | 49.6 |
| Muscat reine des vignes | + | G/T | 50 |
| Muscat Susanna | + | G/T | 49.3 |
| Malvasia nera | + | T/T | 99.9 |
| Muskat Vostochnyi | + | T/T | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morcia, C.; Tumino, G.; Raimondi, S.; Schneider, A.; Terzi, V. Muscat Flavor in Grapevine: A Digital PCR Assay to Track Allelic Variation in VvDXS Gene. Genes 2021, 12, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12050747
Morcia C, Tumino G, Raimondi S, Schneider A, Terzi V. Muscat Flavor in Grapevine: A Digital PCR Assay to Track Allelic Variation in VvDXS Gene. Genes. 2021; 12(5):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12050747
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorcia, Caterina, Giorgio Tumino, Stefano Raimondi, Anna Schneider, and Valeria Terzi. 2021. "Muscat Flavor in Grapevine: A Digital PCR Assay to Track Allelic Variation in VvDXS Gene" Genes 12, no. 5: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12050747
APA StyleMorcia, C., Tumino, G., Raimondi, S., Schneider, A., & Terzi, V. (2021). Muscat Flavor in Grapevine: A Digital PCR Assay to Track Allelic Variation in VvDXS Gene. Genes, 12(5), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12050747








