New Mutations in HFE2 and TFR2 Genes Causing Non HFE-Related Hereditary Hemochromatosis
Abstract
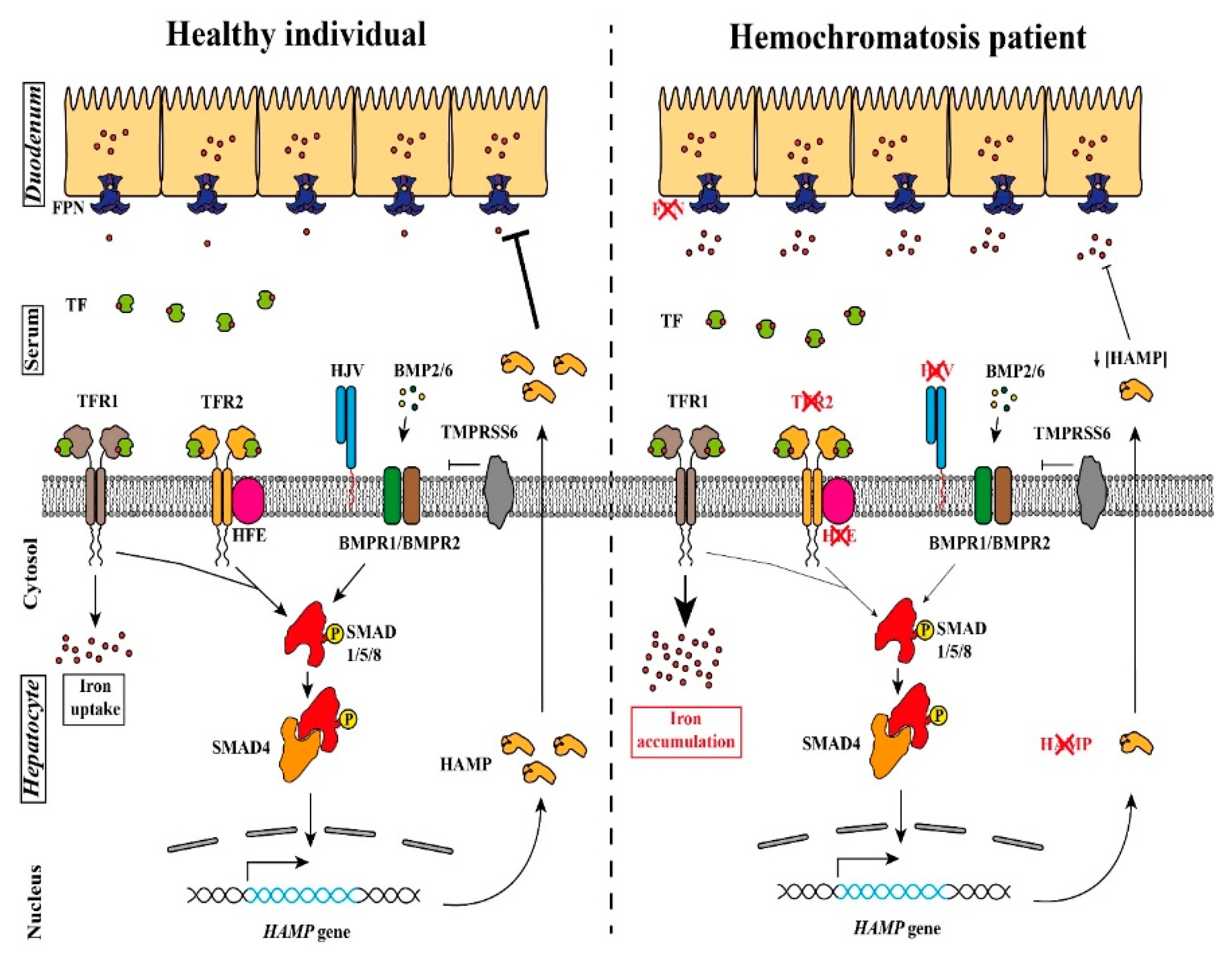
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.1.1. Non-HFE HH Related Due to Mutations in the HFE2 Gene: Family 1
2.1.2. Non-HFE HH Related Due to Mutations in the HFE2 Gene: Family 2
2.1.3. Non-HFE HH Related Due to Mutations in the TFR2 Gene: Family A
2.1.4. Non-HFE HH Related Due to Mutations in the TFR2 Gene: Family B
2.1.5. Non-HFE HH Related Due to Mutations in the TFR2 Gene: Family C
2.2. DNA Sequencing and Analysis
2.3. Hepcidin Determination
2.4. Computational Studies
2.4.1. Computational Model of TFR2 and TFR2/TF Based on Comparative Modeling with TFR1 Crystal Structure
2.4.2. Sequence Similarity Network of TFR1 and TFR2 Orthologs
3. Results
3.1. Novel Cases of Non-HFE Related HH
3.2. Identification of New Mutations Associated with Non-HFE Related HH
3.2.1. Mutations in the HFE2 Gene
3.2.2. Mutations in the TFR2 Gene
3.3. Computational Studies on the TFR2 p.Asp680Tyr Mutation
3.3.1. Modeling the Effect of the Asp680Tyr Mutation over TFR2 Activity
3.3.2. Conservation of TFR2 Position 680 in TFR2 and TFR1 Orthologues
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Appendix A
| Patient Number | N° Families | Ancestry | Molecular Defects. HJV Protein: NP_998818.1. HFE2 Gene: NM_213653.4 | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutation 1 | Domain Mutation 1 | Mutation 2 | Domain Mutation 2 | ||||
| 1 | 1 | Greece | Ile281Thr | Mature Protein | Ile281Thr | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 2 | 2 | Japan | Ile281Thr | Mature Protein | Ile281Thr | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 3 | 2 | Japan | Ile281Thr | Mature Protein | Ile281Thr | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 4 | 3 | China | Ile281Thr | Mature Protein | Cys321Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 5 | 4 | China | Ile281Thr | Mature Protein | Cys321Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 6 | 4 | China | Ile281Thr | Mature Protein | Cys321Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 7 | 5 | China | Ile281Thr | Mature Protein | Cys208Ter/Arg6Ser | Mature Protein/Signal peptide | [22] |
| 8 | 6 | Canada | Ile222Asn | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 9 | 7 | Greece | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 10 | 8 | Greece | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 11 | 9 | Greece | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 12 | 10 | Greece | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 13 | 11 | Greece | Cys361fsTer366 | Mature Protein | Cys361fsTer366 | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 14 | 12 | Greece | Gly99Val | Mature Protein | Gly99Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 15 | 13 | Greece | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 16 | 14 | Greece | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Arg326Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 17 | 15 | Greece | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 18 | 16 | France | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 19 | 17 | China | Cys321Ter | Mature Protein | His104Arg | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 20 | 18 | China | Cys321Ter | Mature Protein | Val274Met | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 21 | 19 | China | Gln312Ter | Mature Protein | Gln312Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 22 | 20 | China | Phe103Leu | Mature Protein | Phe103Leu | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 23 | 21 | France | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 24 | 22 | France | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 25 | 23 | France (North African) | Arg385Ter | Mature Protein | Arg385Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 26 | 24 | France | His180Arg | Mature Protein | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 27 | 25 | France | Ala384Val | Mature Protein | Arg288Trp | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 28 | 26 | France | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 29 | 27 | African American | Arg54Ter | Mature Protein | Arg54Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 30 | 28 | Romania | Gly66Ter | Mature Protein | Gly66Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 31 | 29 | Japan | Tyr150Cys | Mature Protein | Val274Met | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 32 | 30 | United States | Cys80Arg | Mature Protein | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 33 | 31 | United States | Cys80Arg | Mature Protein | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 34 | 31 | United States | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 35 | 31 | United States | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 36 | 31 | United States | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 37 | 31 | United States | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 38 | 32 | United States | Ile222Asn | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 39 | 33 | Bangladesh | Cys80Tyr | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 40 | 34 | Pakistan | Gly99Arg | Mature Protein | Gly99Arg | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 41 | 35 | Pakistan | Gly99Arg | Mature Protein | Gly99Arg | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 42 | 36 | Pakistan | Pro192Leu | Mature Protein | Pro192Leu | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 43 | 37 | Pakistan | Leu194Pro | Mature Protein | Leu194Pro | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 44 | 38 | Sri Lanka | Ala343ProfsTer23 | Mature Protein | Ala343ProfsTer23 | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 45 | 39 | Australia | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 46 | 40 | Australia | Cys80Arg | Mature Protein | Arg326Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 47 | 41 | Australia | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 48 | 42 | Italy | Arg385Ter | Mature Protein | Arg385Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 49 | 43 | Italy | Phe170Ser | Mature Protein | Phe170Ser | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 50 | 44 | Italy | Trp191Cys | Mature Protein | Trp191Cys | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 51 | 45 | Italy | Arg385Ter | Mature Protein | Arg385Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 52 | 46 | Italy | Asp149fsTer245 | Mature Protein | Asp149fsTer245 | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 53 | 47 | Italy | Ser205Arg | Mature Protein | Gly250Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 54 | 48 | Italy | Phe170Ser | Mature Protein | Phe170Ser | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 55 | 49 | Italy | Val74fsTer113 | Mature Protein | Asn269fsTer311 | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 56 | 49 | Italy | Asp149fsTer245 | Mature Protein | Asp149fsTer245 | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 57 | 50 | Italy | Arg131fsTer245 | Mature Protein | Arg131fsTer245 | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 58 | 51 | Canada/Italy | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 59 | 52 | Italy | Ser85Pro | Mature Protein | Ser85Pro | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 60 | 53 | France | Arg288Trp | Mature Protein | Arg288Trp | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 61 | 54 | Italy | Asp172E | Mature Protein | Gly319fsTer341 | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 62 | 55 | Australia/English | Ala168Asp | Mature Protein | Ala168Asp | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 63 | 56 | Albania | Leu101Pro | Mature Protein | Gly99Arg | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 64 | 57 | Italy | Asp149fsTer245 | Mature Protein | Asp149fsTer245 | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 65 | 58 | Canada/Italy | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 66 | 59 | Iran | Cys89Arg | Mature Protein | Cys89Arg | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 67 | 59 | Iran | Cys89Arg | Mature Protein | Cys89Arg | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 68 | 60 | English/Ireland | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gln116Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 69 | 61 | Croatia | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 70 | 62 | Germany | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 71 | 63 | Germany | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 72 | 64 | Slovakia | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Ser328fsTer337 | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 73 | 64 | Slovakia | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Ser328fsTer337 | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 74 | 65 | Germany | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 75 | 66 | Germany | Cys119Phe | Mature Protein | Cys119Phe | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 76 | 67 | Netherland | Leu165Ter | Mature Protein | Leu165Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 77 | 68 | France | Arg176Cys | Mature Protein | Arg176Cys | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 78 | 69 | France | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Arg176Cys | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 79 | 70 | Japan | Asp249His | Mature Protein | Asp249His | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 80 | 71 | Japan | Gln312Ter | Mature Protein | Gln312Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 81 | 72 | Japan | Gln312Ter | Mature Protein | Gln312Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 82 | 73 | Caucasian | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Cys321Trp | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 83 | 74 | India | Asp355Tyr | Mature Protein | Asp355Tyr | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 84 | 74 | India | Asp355Tyr | Mature Protein | Asp355Tyr | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 85 | 75 | Romania | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 86 | 76 | Caucasian | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | Gly320Val | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 87 | 77 | Italy | Cys317Ser | Mature Protein | Cys317Ser | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 88 | 78 | India | Gly336Ter | Mature Protein | Gly336Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 89 | 79 | India | Gly336Ter | Mature Protein | Gly336Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 90 | 80 | India | Gly336Ter | Mature Protein | Gly336Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 91 | 81 | India | Gly336Ter | Mature Protein | Gly336Ter | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 92 | 82 | India | 5′UTR −358 (G > A) | - | 5′UTR −358 (G > A) | - | [22] |
| 93 | 83 | India | 5′UTR −358 (G > A) | - | 5′UTR −358 (G > A) | - | [22] |
| 94 | 84 | China | Cys321Ter | Mature Protein | Gln6His | Signal Peptide | [22] |
| 95 | 85 | English/Ireland | Leu28SerfsTer24 | Signal Peptide | Leu28SerfsTer24 | Signal Peptide | [22] |
| 96 | 86 | Brazil | Gln233fsTer245 | Mature Protein | Gln233fsTer245 | Mature Protein | [22] |
| 97 | 87 | Saudi Arabia | His166Arg | Mature Protein | His166Arg | Mature Protein | [23] |
| 98 | 87 | Saudi Arabia | His166Arg | Mature Protein | His166Arg | Mature Protein | [23] |
| 99 | 88 | Spain | Asp149ThrfsTer97 | Mature Protein | Asp149ThrfsTer97 | Mature Protein | This work |
| 100 | 89 | Spain | Arg63Ter | Mature Protein | Arg63Ter | Mature Protein | This work |
| Ancestry | N° Families | N° Affected Patients | Molecular Defects. TFR2 Protein: NP_003218.2. TFR2 Gene: NM_003227.3 | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutation 1 | Domain Mutation 1 | Mutation 2 | Domain Mutation 2 | ||||
| Iranian | 1 | 1 | AVAQ 621_624del (reported as AVAQ 594_597del) | Extracellular | AVAQ 621_624del (reported as AVAQ 594_597del) | Extracellular | [24] |
| Spanish | 1 | 1 | p.Gly373Asp | Extracellular | Not found | - | [24] |
| Spanish | 1 | 1 | p.Arg420His | Extracellular | Not found | - | [24] |
| Italian | 1 | 1 | c.614 + 4A > G | Intronic | c.614 + 4A > G | Intronic | [24] |
| 1 | 1 | p.Phe280Leu | PA | Not found | - | [24] | |
| Italian | 1 | 1 | p.Arg396Ter | Extracellular | c.1538 − 2A > G | Intronic | [24] |
| Italian | 1 | 1 | p.Asn411del | Extracellular | p.Ala444Thr | Peptidase M28 | [24] |
| Italian | 1 | 2 | c.2137 − 1G > A (reported as IVS17 + 5636G > A) | Intronic | c.2137 − 1G > A (reported as IVS17 + 5636G > A) | Intronic | [24] |
| Native American/white | 1 | 1 | p.Asp189N | Extracellular | Not found in TFR2, HAMP promoter mutation −443C > T in heterozygosity | - | [24] |
| Taiwanese | 1 | 1 | p.Arg468His (reported as p.Arg481His) | Peptidase M28 | Not found | - | [24] |
| Italian | 1 | 2 | p.Met172Lys | Extracellular | p.Met172Lys | Extracellular | [24] |
| Scoth-Irish American | 1 | 1 | p.Arg396Ter | Arg396Ter | p.Arg455Gln | Peptidase M28 | [24] |
| Italian | 1 | 3 | p.Gln317Ter | Extracellular | p.Gln317Ter | Extracellular | [24] |
| Japanese | 1 | 1 | p.Ser556AlafsTer6 (reported as p.Val561Ter | Peptidase M28 | p.Ser556AlafsTer6 (reported as p.Val561Ter | Peptidase M28 | [24] |
| Japanese | 1 | 1 | p.Leu490Arg | Peptidase M28 | p.Leu490Arg | Peptidase M28 | [24] |
| North French | 1 | 2 | p.Arg105Ter | Near TM | p.Arg105Ter | Near TM | [24] |
| Italian | 2 | 2 | p.Tyr250Ter | PA | p.Tyr250Ter | PA | [24] |
| Japanese | 1 | 3 | AVAQ 621_624del (reported as AVAQ 594_597del) | Extracellular | AVAQ 621_624del (reported as AVAQ 594_597del) | Extracellular | [24] |
| Italian | 3 | 3 | p.Val22Ile | Near Endo | Not found in TFR2 (1 patient also homozygous for HFE Cys282Tyr) | - | [24] |
| Italian | 1 | 3 | AVAQ 621_624del (reported as AVAQ 594_597del) | Extracellular | AVAQ 621_624del (reported as AVAQ 594_597del) | Extracellular | [24] |
| Portuguese | 1 | 3 | p.Gln690Pro | TFR Dimeric | p.Gln690Pro | TFR Dimeric | [24] |
| Asiatic | 1 | 1 | p.Arg455Gln | Peptidase M28 | not found in TFR2 (patient also homozygous for HFE Cys282Tyr) | - | [24] |
| Italian | 1 | 6 | p.Arg30ProfsTer31 (reported as p.Glu60Ter) | Cytosolic | p.Arg30ProfsTer31 (reported as p.Glu60Ter) | Cytosolic | [24] |
| Italian | 1 | 1 | p.Met172Lys | Extracellular | p.Met172Lys | Extracellular | [24] |
| Italian | 2 | 6 | p.Tyr250Ter | PA | p.Tyr250Ter | PA | [24] |
| Spanish | 1 | 1 | p.Phe280Leu | PA | not found in TFR2 (patient also heterozygous for HFE His63Asp) | - | [24] |
| African | 1 | 1 | p.Gly430Arg | Peptidase M28 | p.Tyr504Cys | Peptidase M28 | [24] |
| Italian | 1 | 1 | p.Thr740Met | TFR Dimeric | p.Thr740Met | TFR Dimeric | [24] |
| Italian | 1 | 1 | p.Leu615ProfsTer177 | Near Peptidase M28 | Not found | - | [24] |
| Italian | 1 | 1 | p.Ser531GlnfsTer6 | Peptidase M28 | Not found | - | [24] |
| French | 1 | 1 | p.Arg678Pro | TFR Dimeric | p.Arg678Pro | TFR Dimeric | [24] |
| French | 1 | 1 | p.Asn412Ile | Extracellular | p.Asn412Ile | Extracellular | [24] |
| North Africa | 1 | 1 | p.Gly430Arg | Peptidase M28 | p.Gly430Arg | Extracellular | [24] |
| French | 1 | 1 | p.Leu85_Ala96delinsPro | TM | p.Gly735Ser | TFR Dimeric | [24] |
| French | 1 | 1 | p.Ala444Thr | Peptidase M28 | p.Gly792Arg | TFR Dimeric | [24] |
| French | 1 | 1 | p.Arg730Cys | TFR Dimeric | p.Trp781Ter | TFR Dimeric | [24] |
| French | 1 | 1 | p.Met705HisfsTer87 | TFR Dimeric | p.Gly792Arg | TFR Dimeric | [24] |
| Spanish | 1 | 2 | p.Gly792Arg | TFR Dimeric | p.Gly792Arg | TFR Dimeric | [24] |
| Spanish | 1 | 1 | p.Gly792Arg | TFR Dimeric | c.1606 − 8A > G | Intronic | [24] |
| Spanish | 1 | 1 | p.Gln306Ter | PA | p.Gln672Ter | TFR Dimeric | [24] |
| Mexican | 1 | 1 | p.Ser470Ile | Peptidase M28 | p.Ser470Ile | Peptidase M28 | [25] |
| Spanish | 1 | 1 | p.Trp781Ter | TFR Dimeric | p.Trp781Ter | TFR Dimeric | This work |
| Asiatic | 1 | 2 | p.Asp680Tyr | TFR Dimeric | p.Asp680Tyr | TFR Dimeric | This work |
| Spanish | 1 | 1 | p.Gln672Ter | TFR Dimeric | p.Gln672Ter | TFR Dimeric | This work |



References
- Hentze, M.W.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Galy, B.; Camaschella, C. Two to tango: Regulation of Mammalian iron metabolism. Cell 2010, 142, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetto, A.; Papanikolaou, G.; Politou, M.; Alberti, F.; Girelli, D.; Christakis, J.; Loukopoulos, D.; Camaschella, C. Mutant antimicrobial peptide hepcidin is associated with severe juvenile hemochromatosis. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, H.; Yang, R.; Hirama, T.; Vuong, P.T.; Kawano, S.; Gombart, A.F.; Koeffler, H.P. Molecular cloning of transferrin receptor 2. A new member of the transferrin receptor-like family. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 20826–20832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nai, A.; Lidonnici, M.R.; Rausa, M.; Mandelli, G.; Pagani, A.; Silvestri, L.; Ferrari, G.; Camaschella, C. The second transferrin receptor regulates red blood cell production in mice. Blood 2015, 125, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, L.; Nai, A.; Dulja, A.; Pagani, A. Hepcidin and the BMP-SMAD pathway: An unexpected liaison. Vitam. Horm. 2019, 110, 71–99. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, R.E.; Ahmann, J.R.; Migas, M.C.; Waheed, A.; Koeffler, H.P.; Kawabata, H.; Britton, R.S.; Bacon, B.R.; Sly, W.S. Targeted mutagenesis of the murine transferrin receptor-2 gene produces hemochromatosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10653–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.F.; Summerville, L.; Lusby, P.E.; Subramaniam, V.N. First phenotypic description of transferrin receptor 2 knockout mouse, and the role of hepcidin. Gut 2005, 54, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, D.F.; Summerville, L.; Subramaniam, V.N. Targeted disruption of the hepatic transferrin receptor 2 gene in mice leads to iron overload. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartnikas, T.B.; Wildt, S.J.; Wineinger, A.E.; Schmitz-Abe, K.; Markianos, K.; Cooper, D.M.; Fleming, M.D. A novel rat model of hereditary hemochromatosis due to a mutation in transferrin receptor 2. Comp. Med. 2013, 63, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.H.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, C.; Zerfas, P.; Cooperman, S.; Eckhaus, M.; Rouault, T.; Mishra, L.; et al. A role of SMAD4 in iron metabolism through the positive regulation of hepcidin expression. Cell Metab. 2005, 2, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meynard, D.; Kautz, L.; Darnaud, V.; Canonne-Hergaux, F.; Coppin, H.; Roth, M.P. Lack of the bone morphogenetic protein BMP6 induces massive iron overload. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muckenthaler, M.U.; Rivella, S.; Hentze, M.W.; Galy, B. A Red Carpet for Iron Metabolism. Cell 2017, 168, 344–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrangelo, A. Hereditary hemochromatosis—A new look at an old disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2383–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, J.N.; Gnirke, A.; Thomas, W.; Tsuchihashi, Z.; Ruddy, D.A.; Basava, A.; Dormishian, F.; Domingo, R.; Ellis, M.C., Jr.; Fullan, A.; et al. A novel MHC class I-like gene is mutated in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, G.; Samuels, M.E.; Ludwig, E.H.; MacDonald, M.L.; Franchini, P.L.; Dubé, M.P.; Andres, L.; MacFarlane, J.; Sakellaropoulos, N.; Politou, M.; et al. Mutations in HFE2 cause iron overload in chromosome 1q-linked juvenile hemochromatosis. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camaschella, C.; Roetto, A.; Calì, A.; De Gobbi, M.; Garozzo, G.; Carella, M.; Majorano, N.; Totaro, A.; Gasparini, P. The gene TFR2 is mutated in a new type of haemochromatosis mapping to 7q22. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrangelo, A.; Caleffi, A.; Henrion, J.; Ferrara, F.; Corradini, E.; Kulaksiz, H.; Stremmel, W.; Andreone, P.; Garuti, C. Juvenile hemochromatosis associated with pathogenic mutations of adult hemochromatosis genes. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gérolami, V.; Le Gac, G.; Mercier, L.; Nezri, M.; Bergé-Lefranc, J.L.; Férec, C. Early-onset haemochromatosis caused by a novel combination of TFR2 mutations(p.R396X/c.1538-2 A>G) in a woman of Italian descent. Haematologica 2008, 93, e45–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardou-Jacquet, E.; Cunat, S.; Beaumont-Epinette, M.P.; Kannengiesser, C.; Causse, X.; Sauvion, S.; Pouliquen, B.; Deugnier, Y.; David, V.; Loréal, O.; et al. Variable age of onset and clinical severity in transferrin receptor 2 related haemochromatosis: Novel observations. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Détivaud, L.; Island, M.L.; Jouanolle, A.M.; Ropert, M.; Bardou-Jacquet, E.; Le Lan, C.; Mosser, A.; Leroyer, P.; Deugnier, Y.; David, V.; et al. Ferroportin diseases: Functional studies, a link between genetic and clinical phenotype. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girelli, D.; Busti, F.; Brissot, P.; Cabantchik, I.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Porto, G. Hemochromatosis classification: Update and recommendations by the BIOIRON Society. Blood 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, A.; Tatsumi, Y.; Sakai, K.; Toki, Y.; Ikuta, K.; Oohigashi, Y.; Takagi, J.; Kato, K.; Takami, K. Juvenile Hemochromatosis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqanatish, J.; Alsowailmi, B.; Alfarhan, H.; Alhamzah, A.; Alharbi, T. Juvenile Hemochromatosis: Rheumatic Manifestations of 2 Sisters Responding to Deferasirox Treatment. A Case Series and Literature Review. Open Access Rheumatol. Res. Rev. 2021, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, R.; Shvartsman, M.; Morán, E.; Lois, S.; Aranda, J.; Barqué, A.; de la Cruz, X.; Bruguera, M.; Vagace, J.M.; Gervasini, G.; et al. Functional consequences of transferrin receptor-2 mutations causing hereditary hemochromatosis type 3. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2015, 3, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, A.A.; Suchi, M.; Vitola, B. A Rare Case Of a 2-year-old Boy with Alagille Syndrome and Type 3 Hereditary Hemochromatosis with TFR2 Mutation. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, e68–e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, D.F.; Summerville, L.; Crampton, E.M.; Subramaniam, V.N. Defective trafficking and localization of mutated transferrin receptor 2: Implications for type 3 hereditary hemochromatosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 294, C383–C390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, S.; Trombini, P.; Bernasconi, D.P.; Redaelli, I.; Pelucchi, S.; Bovo, G.; Di Gennaro, F.; Zucchini, N.; Paruccini, N.; Piperno, A. Simultaneous liver iron and fat measures by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with hyperferritinemia. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.C.; Enriquez, C.; Ghugre, N.; Otto-Duessel, M.; Aguilar, M.; Nelson, M.D.; Moats, R.; Coates, T.D. Physiology and pathophysiology of iron cardiomyopathy in thalassemia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1054, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.J.; Holden, S.; Davis, B.; Prescott, E.; Charrier, C.C.; Bunce, N.H.; Firmin, D.N.; Wonke, B.; Porter, J.; Walker, J.M.; et al. Cardiovascular T2-star (T2*) magnetic resonance for the early diagnosis of myocardial iron overload. Eur. Heart J. 2001, 22, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, R.; Pelucchi, S.; Perseghin, P.; Corengia, C.; Piperno, A. Erythrocytapheresis plus erythropoietin: An alternative therapy for selected patients with hemochromatosis and severe organ damage. Haematologica 2005, 90, 717–718. [Google Scholar]
- Vila Cuenca, M.; Marchi, G.; Barqué, A.; Esteban-Jurado, C.; Marchetto, A.; Giorgetti, A.; Chelban, V.; Houlden, H.; Wood, N.W.; Piubelli, C.; et al. Genetic and Clinical Heterogeneity in Thirteen New Cases with Aceruloplasminemia. Atypical Anemia as a Clue for an Early Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopanos, C.; Tsiolkas, V.; Kouris, A.; Chapple, C.E.; Albarca Aguilera, M.; Meyer, R.; Massouras, A. VarSome: The human genomic variant search engine. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, B.; Andrej, S. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2016, 86, 5.6.1–5.6.30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaver-Fay, A.; Tyka, M.; Lewis, S.M.; Lange, O.F.; Thompson, J.; Jacak, R.; Kaufman, K.; Renfrew, P.D.; Smith, C.A.; Sheffler, W.; et al. ROSETTA3: An object-oriented software suite for the simulation and design of macromolecules. Methods Enzymol. 2011, 487, 545–574. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sayers, E.W.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; Funk, K.; Kelly, C.; Kim, S.; et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D13–D21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zak, O.; Aisen, P.; Harrison, S.C.; Walz, T. Structure of the human transferrin receptor-transferrin complex. Cell 2004, 116, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alford, R.F.; Leaver-Fay, A.; Jeliazkov, J.R.; O’Meara, M.J.; DiMaio, F.P.; Park, H.; Shapovalov, M.V.; Renfrew, P.D.; Mulligan, V.K.; Kappel, K.; et al. The Rosetta All-Atom Energy Function for Macromolecular Modeling and Design. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 13, 3031–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubljevic, V.; Sali, A.; Goding, J.W. A conserved RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) motif in the transferrin receptor is required for binding to transferrin. Biochem. J. 1999, 341 Pt 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, H.J.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E.; Babbitt, P.C. Using sequence similarity networks for visualization of relationships across diverse protein superfamilies. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Family 1—Patient II.1 | Family 2—Patient II.2 | Normal Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ex | M | M | |
| Age at clinical diagnosis | 37 | 34 | |
| Hemoglobin, Hb (g/L) | 14.6 (a) | 14.9 (c) | M: 13.5–17.5 |
| 14.7 (b) | 16.7 (e) | F: 12.1–15.1 | |
| MCV (fl) | 86.5 (a) | 94.4 (c) | 80–95 |
| 84 (b) | 94.4 (e) | ||
| Serum iron (µg/dL) | 247 (a) | 267 (d) | 59–158 |
| 80 (b) | 109 (e) | ||
| Serum ferritin (µg/L) | 4620 (a) | 650 (c) 3952 (d) 27 (e) | M: 12–300 |
| 29 (b) | F: 12–200 | ||
| Transferrin (mg/dL) | 198 (a) | 218 (d) | 220–400 |
| 406 (b) | 313 (e) | ||
| Transferrin Saturation (%) | 87 (a) | 84 (d) | 20–50 |
| 14 (b) | 25 (e) | ||
| Total Iron Binding Capacity (µg/dL) | n.a. | 301 (d) | 250–400 |
| 432 (e) | |||
| Hepcidin levels (ng/mL) | n.a. | 0.19 | M: 29–254 * |
| F: 17–286 * | |||
| MRI liver | 457 µmol Fe/g (a) | July 2019: 47 µmol Fe/g. | <36 μmol Fe/g |
| 30 µmol Fe/g (b) | |||
| 13 µmol Fe/g (2020) | |||
| MRI heart | 9 ms (a) | No iron overload | |
| 15 ms (b) | |||
| 30 ms (2020) | |||
| Treatments | Phlebotomy (2014) | Phlebotomy Desferoxamine (until March 2020) | |
| Erythroapheresis | |||
| Desferoxamine (2014) | |||
| rHuEPO (2014) | |||
| Genetics | HFE2: NM_213653.3: | HFE2: NM_213653.3: c.187C > T; c.187C > T p.Arg63Ter; p.Arg63Ter | |
| c.445delG; c.445delG | |||
| p.Asp149ThrfsTer97; | |||
| p.Asp149ThrfsTer97 |
| Family A— Patient II.1 | Family A— Patient II.2 | Family B— Patient II.1 | Family C—Patient II.2 | Normal Range | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | M | M | M | M | |
| Age at clinical diagnosis | 35 | 37 | 46 | 25 | |
| Hemoglobin, Hb (g/L) | 12.8 | 14.1 | 15 *** | 13.1 | M: 13.5–17.5 F: 12.1–15.1 |
| MCV (fl) | n.a. | 98.7 | 93.1 *** | n.a. | 80–95 |
| Serum iron (µg/dL) | 244 | 240 | 282 *** | n.a. | 59–158 |
| Serum ferritin (ng/mL) | 2000 244 ** | 2000 6 ** | 66 *** | 2037 16 # | M: 12–300 F: 12–200 |
| Transferrin (mg/dL) | n.a. | 191 | 241 *** | n.a. | 220–400 |
| Transferrin Saturation (%) | 98 80 ** | 100 6 ** | 83.6 *** | 94.8 4.8 # | 20–50 |
| Total Iron Binding Capacity (µg/dL) | n.a. | 242.6 | n.a. | n.a. | 250–400 |
| Hepcidin levels (ng/mL) | 0.23 | 0.01 | n.a. | n.a. | M: 29–254 * F: 17–286 * |
| MRI liver | 282.97 µmol Fe/g (a) 15.9 mg Fe/g (a) | 265 µmol Fe/g (b) 14.9 mg Fe/g (b) 217.56 µmol Fe/g (c) 12.22 mg Fe/g (c) 70.33 µmol Fe/g (d) 3.95 mg Fe/g (d) | 300 µmol Fe/g <36 μmol Fe/g *** | 123.9 µmol Fe/g | <36 μmol Fe/g |
| Treatments | Phlebotomy Desferoxamine | Phlebotomy Desferoxamine | Erythroapheresis Phlebotomy | Phlebotomy | |
| Genetics | TFR2: NM_003227.4: c.2038G > T; c.2038G > T p.Asp680Tyr; p.Asp680Tyr | TFR2: NM_003227.4: c.2038G > T; c.2038G > T p.Asp680Tyr; p.Asp680Tyr | TFR2: NM_003227.3: c.2343G > A; c.2343G > A p.Trp781Ter; p.Trp781Ter HFE: p.Cys282Tyr | TFR2: NM_003227.4: c.2014C > T; c.2014C > T p.Gln672Ter; p.Gln672Ter |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández, G.; Ferrer-Cortès, X.; Venturi, V.; Musri, M.; Pilquil, M.F.; Torres, P.M.M.; Rodríguez, I.H.; Mínguez, M.À.R.; Kelleher, N.J.; Pelucchi, S.; et al. New Mutations in HFE2 and TFR2 Genes Causing Non HFE-Related Hereditary Hemochromatosis. Genes 2021, 12, 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121980
Hernández G, Ferrer-Cortès X, Venturi V, Musri M, Pilquil MF, Torres PMM, Rodríguez IH, Mínguez MÀR, Kelleher NJ, Pelucchi S, et al. New Mutations in HFE2 and TFR2 Genes Causing Non HFE-Related Hereditary Hemochromatosis. Genes. 2021; 12(12):1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121980
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández, Gonzalo, Xenia Ferrer-Cortès, Veronica Venturi, Melina Musri, Martin Floor Pilquil, Pau Marc Muñoz Torres, Ines Hernandez Rodríguez, Maria Àngels Ruiz Mínguez, Nicholas J. Kelleher, Sara Pelucchi, and et al. 2021. "New Mutations in HFE2 and TFR2 Genes Causing Non HFE-Related Hereditary Hemochromatosis" Genes 12, no. 12: 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121980
APA StyleHernández, G., Ferrer-Cortès, X., Venturi, V., Musri, M., Pilquil, M. F., Torres, P. M. M., Rodríguez, I. H., Mínguez, M. À. R., Kelleher, N. J., Pelucchi, S., Piperno, A., Alberca, E. P., Ricós, G. G., Giró, E. C., Pérez-Montero, S., Tornador, C., Villà-Freixa, J., & Sánchez, M. (2021). New Mutations in HFE2 and TFR2 Genes Causing Non HFE-Related Hereditary Hemochromatosis. Genes, 12(12), 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121980






