The Genetic Landscape of Patent Foramen Ovale: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sources
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
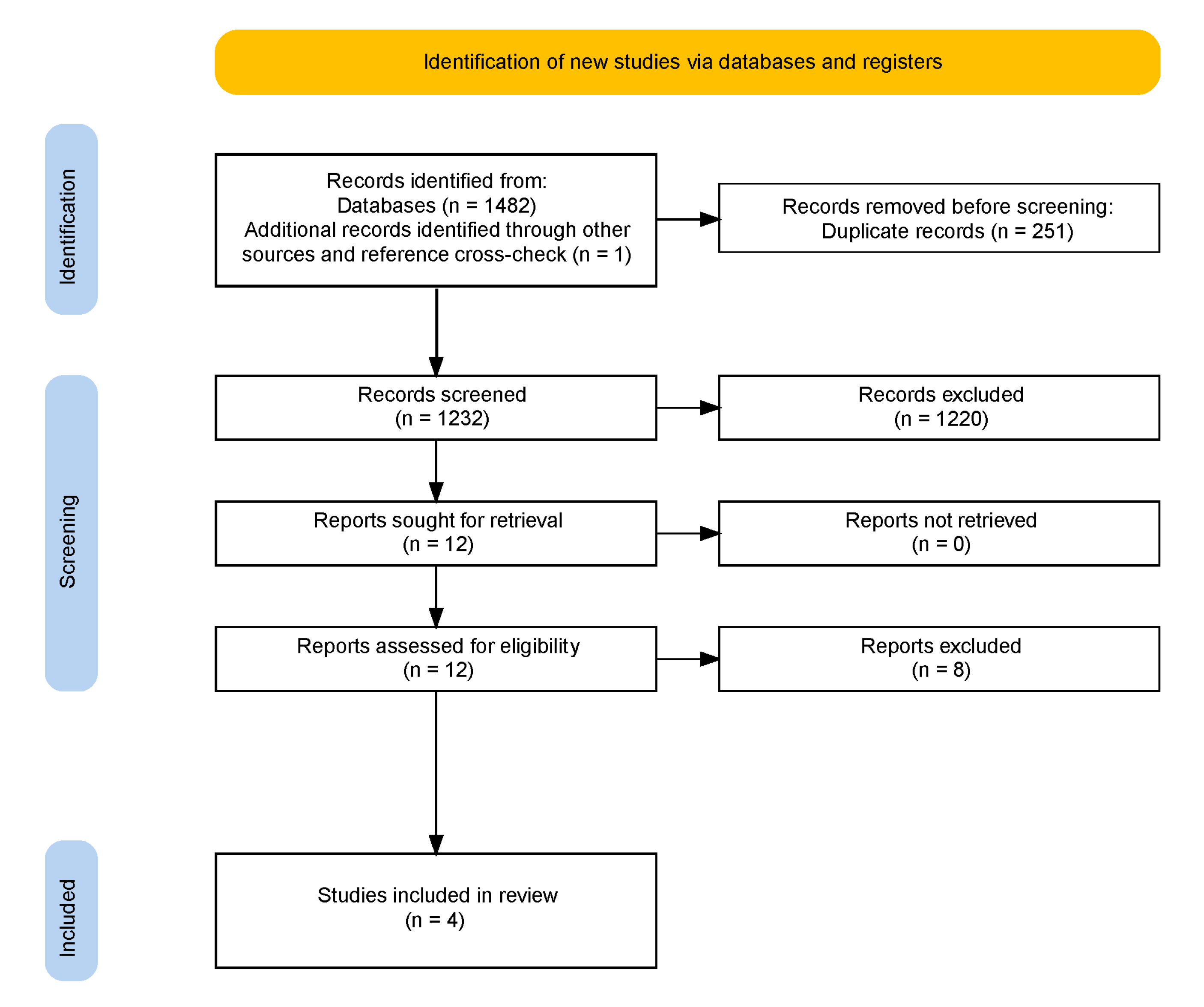
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Homma, S.; Sacco, R.L. Patent Foramen Ovale and Stroke. Circulation 2005, 112, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, A.H.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Frogoudaki, A.; Vrettou, A.; Ikonomidis, I.; Paraskevaidis, I.; Parissis, J.; Bogiatzi, C.; Zompola, C.; et al. Transcranial Doppler versus Transthoracic Echocardiography for the Detection of Patent Foramen Ovale in Patients with Cryptogenic Cerebral Ischemia: A Systematic Review and Diagnostic Test Accuracy Meta-Analysis. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, S.; Messé, S.R.; Rundek, T.; Sun, Y.-P.; Franke, J.; Davidson, K.; Sievert, H.; Sacco, R.L.; Tullio, M.R.D. Patent Foramen Ovale. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 66, 15086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, P.T.; Scholz, D.G.; Edwards, W.D. Incidence and Size of Patent Foramen Ovale during the First 10 Decades of Life: An Autopsy Study of 965 Normal Hearts. Mayo Clin. Proc. Mayo Clin. 1984, 59, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Sette, M.; Angeli, S.; Leandri, M.; Ferriero, G.; Bruzzone, G.L.; Finocchi, C.; Gandolfo, C. Migraine with Aura and Right-to-Left Shunt on Transcranial Doppler: A Case-Control Study. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 1998, 8, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwerzmann, M.; Nedeltchev, K.; Lagger, F.; Mattle, H.P.; Windecker, S.; Meier, B.; Seiler, C. Prevalence and Size of Directly Detected Patent Foramen Ovale in Migraine with Aura. Neurology 2005, 65, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmshurst, P.T.; Pearson, M.J.; Nightingale, S.; Walsh, K.P.; Morrison, W.L. Inheritance of Persistent Foramen Ovale and Atrial Septal Defects and the Relation to Familial Migraine with Aura. Heart 2004, 90, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arquizan, C.; Coste, J.; Touboul, P.-J.; Mas, J.-L. Is Patent Foramen Ovale a Family Trait? Stroke 2001, 32, 1563–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, B.; Wang, T.; Moorman, A.F.M. Evolution and Development of the Atrial Septum. Anat. Rec. 2019, 302, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, G.C.; Gurtu, R.; McCollum, C.; Newman, W.G.; Wang, T. Foramen Ovale Closure Is a Process of Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Leading to Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- High, F.A.; Epstein, J.A. The Multifaceted Role of Notch in Cardiac Development and Disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, M.G.; Gramlich, M.; Sunde, M.; Schmitt, K.R.; Lee, S.H.Y.; Richter, S.; Kersten, A.; Perrot, A.; Panek, A.N.; Khatib, I.H.A.; et al. A Gain-of-Function TBX20 Mutation Causes Congenital Atrial Septal Defects, Patent Foramen Ovale and Cardiac Valve Defects. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 47, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.L.; Yutzey, K.E.; Benson, D.W. Transcription factors and congenital heart defects. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2006, 68, 97–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchlenz, H.W.; Saurer, G.; Weihs, W.; Rehak, P. Persisting Eustachian Valve in Adults: Relation to Patent Foramen Ovale and Cerebrovascular Events. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiog. 2004, 17, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, S.S.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Shishehbor, M.H.; de Oliveira, E.I.; Borek, P.P.; Krasuski, R.A.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Kapadia, S.R. Morphology of the Patent Foramen Ovale in Asymptomatic Versus Symptomatic (Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack) Patients. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 103, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, S.G.; Mitsias, P.D. Patent Foramen Ovale in Cryptogenic Ischemic Stroke: Direct Cause, Risk Factor, or Incidental Finding? Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharobeam, A.; Churilov, L.; Parsons, M.; Donnan, G.A.; Davis, S.M.; Yan, B. Patterns of Infarction on MRI in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke and Cardio-Embolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 606521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessels, T.; Wessels, C.; Ellsiepen, A.; Reuter, I.; Trittmacher, S.; Stolz, E.; Jauss, M. Contribution of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Determination of Stroke Etiology. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Elgendy, A.Y.; Saver, J.L.; Amin, Z.; Boudoulas, K.D.; Carroll, J.D.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Grunwald, I.Q.; Gertz, Z.M.; Hijazi, Z.M.; Horlick, E.M.; et al. Proposal for Updated Nomenclature and Classification of Potential Causative Mechanism in Patent Foramen Ovale–Associated Stroke. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology: A Proposal for Reporting. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the Mean and Variance from the Median, Range, and the Size of a Sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belvís, R.; Tizzano, E.F.; Martí-Fàbregas, J.; Leta, R.G.; Baena, M.; Carreras, F.; Pons-Lladó, G.; Baiget, M.; Martí-Vilalta, J.L. Mutations in the NKX2-5 Gene in Patients with Stroke and Patent Foramen Ovale. Clin. Neurol. Neurosur. 2009, 111, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, D.A.; Kirk, E.P.; Yeoh, T.; Chandar, S.; McKenzie, F.; Taylor, P.; Grossfeld, P.; Fatkin, D.; Jones, O.; Hayes, P.; et al. Cardiac Homeobox Gene NKX2-5 Mutations and Congenital Heart Disease Associations with Atrial Septal Defect and Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 2072–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollmann, A.; Kornej, J.; Adams, V.; Arya, A.; Piorkowski, C.; Hindricks, G.; Husser, D. Patent Foramen Ovale in Atrial Fibrillation: Relation with Chromosome 4q25 Variants and Rhythm Outcome of Catheter Ablation. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 873–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjaneh, M.M.; Kirk, E.P.; Posch, M.G.; Ozcelik, C.; Berger, F.; Hetzer, R.; Otway, R.; Butler, T.L.; Blue, G.M.; Griffiths, L.R.; et al. Investigation of Association between PFO Complicated by Cryptogenic Stroke and a Common Variant of the Cardiac Transcription Factor GATA4. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schernthaner, C.; Danmayr, F.; Daburger, A.; Eichinger, J.; Hammerer, M.; Strohmer, B. High Incidence of Echocardiographic Abnormalities of the Interatrial Septum in Patients Undergoing Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. Echocardiography 2013, 30, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, K.; Lavergne, T.; Cohen, A.; Guize, L.; Bousser, M.-G.; Heuzey, J.-Y.L.; Amarenco, P. Significant Association of Atrial Vulnerability with Atrial Septal Abnormalities in Young Patients with Ischemic Stroke of Unknown Cause. Stroke 2000, 31, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P.E.; Martin, P.J.; Pugh, P.J.; Warburton, E.A.; Cheriyan, J.; Belham, M. Increased Incidence of Interatrial Block in Younger Adults with Cryptogenic Stroke and Patent Foramen Ovale. Cereb. Dis. Extra 2011, 1, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Arnar, D.O.; Helgadottir, A.; Gretarsdottir, S.; Holm, H.; Sigurdsson, A.; Jonasdottir, A.; Baker, A.; Thorleifsson, G.; Kristjansson, K.; et al. Variants Conferring Risk of Atrial Fibrillation on Chromosome 4q25. Nature 2007, 448, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.; Campione, M. The Role of Pitx2 during Cardiac Development Linking Left–Right Signaling and Congenital Heart Diseases. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2003, 13, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessari, A.; Pietrobon, M.; Notte, A.; Cifelli, G.; Gage, P.J.; Schneider, M.D.; Lembo, G.; Campione, M. Myocardial Pitx2 Differentially Regulates the Left Atrial Identity and Ventricular Asymmetric Remodeling Programs. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucourt, M.; Houliston, E.; Besnardeau, L.; Kimelman, D.; Lepage, T. The Pitx2 Homeobox Protein Is Required Early for Endoderm Formation and Nodal Signaling. Dev. Biol. 2001, 229, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mommersteeg, M.T.M.; Hoogaars, W.M.H.; Prall, O.W.J.; Vries, C.d.G.; Wiese, C.; Clout, D.E.W.; Papaioannou, V.E.; Brown, N.A.; Harvey, R.P.; Moorman, A.F.M.; et al. Molecular Pathway for the Localized Formation of the Sinoatrial Node. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjansson, R.P.; Benonisdottir, S.; Oddsson, A.; Galesloot, T.E.; Thorleifsson, G.; Aben, K.K.; Davidsson, O.B.; Jonsson, S.; Arnadottir, G.A.; Jensson, B.O.; et al. Sequence Variant at 4q25 near PITX2 Associates with Appendicitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, A.J.; Pulit, S.L.; van den Berg, L.H.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Veldink, J.H.; Ruigrok, Y.M.; Klijn, C.J.M.; Algra, A.; van Dijk, E.J.; Koudstaal, P.J.; et al. A Replication Study of Genetic Risk Loci for Ischemic Stroke in a Dutch Population: A Case-Control Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, J.L.; Leung, L.Y.; Peterson, R.B.; Sitton, C.W.; Sarraj, A.; Riascos, R.F.; Brinjikji, W. Ischemic Infarction in Young Adults: A Review for Radiologists. Radiographics 2019, 39, 1629–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, H.-C.; Chutinet, A.; Easton, J.D.; Granger, C.B.; Kleine, E.; Marquardt, L.; Meyerhoff, J.; Zini, A.; Sacco, R.L. Dabigatran or Aspirin After Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source in Patients with Patent Foramen Ovale: Results from RE-SPECT ESUS. Stroke 2021, 52, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, E.P.; Sunde, M.; Costa, M.W.; Rankin, S.A.; Wolstein, O.; Castro, M.L.; Butler, T.L.; Hyun, C.; Guo, G.; Otway, R.; et al. Mutations in Cardiac T-Box Factor Gene TBX20 Are Associated with Diverse Cardiac Pathologies, Including Defects of Septation and Valvulogenesis and Cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, J.-J.; Benson, D.W.; Basson, C.T.; Pease, W.; Silberbach, G.M.; Moak, J.P.; Maron, B.J.; Seidman, C.E.; Seidman, J.G. Congenital Heart Disease Caused by Mutations in the Transcription Factor NKX2-5. Science 1998, 281, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biben, C.; Weber, R.; Kesteven, S.; Stanley, E.; McDonald, L.; Elliott, D.A.; Barnett, L.; Köentgen, F.; Robb, L.; Feneley, M.; et al. Cardiac Septal and Valvular Dysmorphogenesis in Mice Heterozygous for Mutations in the Homeobox Gene Nkx2-5. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stennard, F.A.; Costa, M.W.; Lai, D.; Biben, C.; Furtado, M.B.; Solloway, M.J.; McCulley, D.J.; Leimena, C.; Preis, J.I.; Dunwoodie, S.L.; et al. Murine T-Box Transcription Factor Tbx20 Acts as a Repressor during Heart Development, and Is Essential for Adult Heart Integrity, Function and Adaptation. Development 2005, 132, 2451–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, V.; Kathiriya, I.S.; Barnes, R.; Schluterman, M.K.; King, I.N.; Butler, C.A.; Rothrock, C.R.; Eapen, R.S.; Hirayama-Yamada, K.; Joo, K.; et al. GATA4 Mutations Cause Human Congenital Heart Defects and Reveal an Interaction with TBX5. Nature 2003, 424, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, S.; Carrera, P.; Sette, M.D.; Assini, A.; Grandis, M.; Biancolini, D.; Ferrari, M.; Gandolfo, C. Very High Prevalence of Right-to-Left Shunt on Transcranial Doppler in an Italian Family with Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Angiopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy. Eur. Neurol. 2001, 46, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco, S.; Anzola, G.P.; Rizzuto, N. Methodological Issues in Right-to-Left Shunt Detection in CADASIL Patients. Stroke 2009, 40, e509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blue, G.M.; Humphreys, D.; Szot, J.; Major, J.; Chapman, G.; Bosman, A.; Kirk, E.P.; Sholler, G.F.; Harvey, R.P.; Dunwoodie, S.L.; et al. The Promises and Challenges of Exome Sequencing in Familial, Non-Syndromic Congenital Heart Disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 230, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahm, H.; Jia, M.; Dreßen, M.; Wirth, F.F.M.; Puluca, N.; Gilsbach, R.; Keavney, B.; Cleuziou, J.; Beck, N.; Bondareva, O.; et al. Congenital Heart Disease Risk Loci Identified by Genome-Wide Association Study in European Patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 131, e141837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Author, Year, Country of Patients | Study Design | Genotyping Method | Population | Sample Size | Mean Age (Years, SD) | Male (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belvis, 2009, Spain [22] | case–control | gene specific amplification and sequencing | Stroke/TIA patients with or without PFO | 100 | 56.5 (12.4) | 58% |
| Bollmann, 2010, Germany [24] | case–control | commercial real-time PCR for specific SNP + FRET | Atrial fibrillation patients with or without PFO | 508 | 57 (10) | 70% |
| Elliott, 2003, Australia [23] | cohort | gene specific amplification and sequencing | PFO with paradoxical embolism which underwent percutaneous closure | 25 | 48.7 (15.3) | 48% |
| Marjaneh, 2011, Australia & Germany [25] | case–control | gene specific amplification and sequencing commercial genotyping for specific SNP | PFO (with or without stroke/TIA) vs. controls | 752 | 58.7 (12.2) | 54.8% |
| NKX2-5 | Allelic Frequency | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belvis, 2009 [22] | c.172A > G 1 Glu21 = | found in the 36% of healthy controls (30%AG and 6%GG) (G = 4.11e−1 *) | Stroke with PFO: 21/34 (62%) vs. Stroke without PFO: 33/66 (50%) | p = 0.295 |
| c.182C > T 1 Arg25Cys | not found in 100 screened alleles from healthy controls (T = 4.14e−3 *) | Stroke with PFO: 0/34 (0%) vs. Stroke without PFO: 2/66 (3%) | p = 0.547 | |
| c.2357G > A 1 | not found in 100 screened alleles from healthy controls | Stroke with PFO: 1/34 (3%) vs. Stroke without PFO: 0/66 (0%) | p = 0.340 | |
| c.2850C > A 1 | found in the 60% of healthy controls (40%AC and 20%AA) | Stroke with PFO: 19/34 (56%) vs. Stroke without PFO: 35/66 (53%) | p = 0.835 | |
| Elliott, 2003 [23] | - | - | No mutations found in PFO patients | |
| Chromosome 4q25 | ||||
| Bollmann, 2010 [24] | chr4:110789013C > T rs2200733 rs10033464 | T = 0.184 * | AF without PFO vs. AF with PFO: OR 0.610, 95% CI 0.378–0.984 No association with PFO | p = 0.043 |
| GATA4 | ||||
| Marjaneh, 2011 [25] | c.1647A > G Ser377Gly 1 | G = 0.104 * | PFO (with or without stroke/TIA): 46/183 (25%) vs. controls: 73/340 (21%) | p = 0.340 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paolucci, M.; Vincenzi, C.; Romoli, M.; Amico, G.; Ceccherini, I.; Lattanzi, S.; Bersano, A.; Longoni, M.; Sacco, S.; Vernieri, F.; et al. The Genetic Landscape of Patent Foramen Ovale: A Systematic Review. Genes 2021, 12, 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121953
Paolucci M, Vincenzi C, Romoli M, Amico G, Ceccherini I, Lattanzi S, Bersano A, Longoni M, Sacco S, Vernieri F, et al. The Genetic Landscape of Patent Foramen Ovale: A Systematic Review. Genes. 2021; 12(12):1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121953
Chicago/Turabian StylePaolucci, Matteo, Chiara Vincenzi, Michele Romoli, Giulia Amico, Isabella Ceccherini, Simona Lattanzi, Anna Bersano, Marco Longoni, Simona Sacco, Fabrizio Vernieri, and et al. 2021. "The Genetic Landscape of Patent Foramen Ovale: A Systematic Review" Genes 12, no. 12: 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121953
APA StylePaolucci, M., Vincenzi, C., Romoli, M., Amico, G., Ceccherini, I., Lattanzi, S., Bersano, A., Longoni, M., Sacco, S., Vernieri, F., Pascarella, R., Valzania, F., & Zedde, M. (2021). The Genetic Landscape of Patent Foramen Ovale: A Systematic Review. Genes, 12(12), 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121953








