Beyond Sector Retinitis Pigmentosa: Expanding the Phenotype and Natural History of the Rhodopsin Gene Codon 106 Mutation (Gly-to-Arg) in Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartong, D.T.; Berson, E.L.; Dryja, T.P. Retinitis pigmentosa. Lancet 2006, 368, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, A.C. Retinal photoreceptor dystrophies LI. Edward Jackson Memorial Lecture. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1995, 119, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comander, J.; Weigel-DiFranco, C.; Maher, M.; Place, E.; Wan, A.; Harper, S.; Sandberg, M.A.; Navarro-Gomez, D.; Pierce, E.A. The Genetic Basis of Pericentral Retinitis Pigmentosa-A Form of Mild Retinitis Pigmentosa. Genes 2017, 8, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandberg, M.A.; Gaudio, A.R.; Berson, E.L. Disease course of patients with pericentral retinitis pigmentosa. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 140, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, E.L.; Howard, J. Temporal aspects of the electroretinogram in sector retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1971, 86, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bietti, G.B. Su alcune forme atipiche o rare di degenerazione retinica (degenerazione tappetoretiniche e quadri morbosi similari). Boll Oculist 1937, 16, 1159–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Krill, A.E.; Archer, D.; Martin, D. Sector retinitis pigmentosa. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1970, 69, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, G.A.; Alexander, K.R.; Anderson, R.J. Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. A method of classification. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1985, 103, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, E.M.; Kimura, A.E.; Nichols, B.E.; Khadivi, P.; Fishman, G.A.; Sheffield, V.C. Regional distribution of retinal degeneration in patients with the proline to histidine mutation in codon 23 of the rhodopsin gene. Ophthalmology 1991, 98, 1806–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, E.L.; Gouras, P.; Gunkel, R.D.; Myrianthopoulos, N.C. Dominant retinitis pigmentosa with reduced penetrance. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1969, 81, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, E.L.; Simonoff, E.A. Dominant retinitis pigmentosa with reduced penetrance. Further studies of the electroretinogram. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1979, 97, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryja, T.P.; McGee, T.L.; Hahn, L.B.; Cowley, G.S.; Olsson, J.E.; Reichel, E.; Sandberg, M.A.; Berson, E.L. Mutations within the rhodopsin gene in patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryja, T.P.; McGee, T.L.; Reichel, E.; Hahn, L.B.; Cowley, G.S.; Yandell, D.W.; Sandberg, M.A.; Berson, E.L. A point mutation of the rhodopsin gene in one form of retinitis pigmentosa. Nature 1990, 343, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckenlively, J.R.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Daiger, S.P. Autosomal dominant sectoral retinitis pigmentosa. Two families with transversion mutation in codon 23 of rhodopsin. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1991, 109, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, G.A.; Stone, E.M.; Gilbert, L.D.; Kenna, P.; Sheffield, V.C. Ocular findings associated with a rhodopsin gene codon 58 transversion mutation in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1991, 109, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, G.A.; Stone, E.M.; Sheffield, V.C.; Gilbert, L.D.; Kimura, A.E. Ocular findings associated with rhodopsin gene codon 17 and codon 182 transition mutations in dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1992, 110, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, G.A.; Vandenburgh, K.; Stone, E.M.; Gilbert, L.D.; Alexander, K.R.; Sheffield, V.C. Ocular findings associated with rhodopsin gene codon 267 and codon 190 mutations in dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1992, 110, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, G.A.; Stone, E.M.; Gilbert, L.D.; Sheffield, V.C. Ocular findings associated with a rhodopsin gene codon 106 mutation. Glycine-to-arginine change in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1992, 110, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, M.; Grewal, P.S.; Narayan, A.; Alser, M.; Ali, N.; Fujinami, K.; Webster, A.R.; Michaelides, M. Sector Retinitis Pigmentosa: Extending the Molecular Genetics Basis and Elucidating the Natural History. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 221, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.; Fishman, G.A.; Alexander, K.R.; Anderson, R.J.; Derlacki, D.J. Visual acuity impairment in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Ophthalmology 1996, 103, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budu, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Hayasaka, S.; Yamada, T.; Hayasaka, Y. Rhodopsin gene codon 106 mutation (Gly-to-Arg) in a Japanese family with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 44, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandra, M.; Anandula, V.; Authiappan, V.; Sundaramurthy, S.; Raman, R.; Bhattacharya, S.; Govindasamy, K. Retinitis pigmentosa: Mutation analysis of RHO, PRPF31, RP1, and IMPDH1 genes in patients from India. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Consugar, M.B.; Navarro-Gomez, D.; Place, E.M.; Bujakowska, K.M.; Sousa, M.E.; Fonseca-Kelly, Z.D.; Taub, D.G.; Janessian, M.; Wang, D.Y.; Au, E.D.; et al. Panel-based genetic diagnostic testing for inherited eye diseases is highly accurate and reproducible, and more sensitive for variant detection, than exome sequencing. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reichel, E.; Bruce, A.M.; Sandberg, M.A.; Berson, E.L. An electroretinographic and molecular genetic study of X-linked cone degeneration. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1989, 108, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, E.L. Electroretinographic findings in retinitis pigmentosa. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 1987, 31, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marmor, M.F. The electroretinogram in retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1979, 97, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannaccone, A.; Man, D.; Waseem, N.; Jennings, B.J.; Ganapathiraju, M.; Gallaher, K.; Reese, E.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Klein-Seetharaman, J. Retinitis pigmentosa associated with rhodopsin mutations: Correlation between phenotypic variability and molecular effects. Vis. Res. 2006, 46, 4556–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massof, R.W.; Finkelstein, D. Vision threshold profiles in sector retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1979, 97, 1899–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, A.B.; Hansen, R.M. The relation of rhodopsin and scotopic retinal sensitivity in sector retinitis pigmentosa. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1988, 105, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.H.; Davenport, C.M.; Hennessey, J.C.; Maumenee, I.H.; Jacobson, S.G.; Heckenlively, J.R.; Nowakowski, R.; Fishman, G.; Gouras, P.; Nathans, J. Rhodopsin mutations in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 6481–6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berson, E.L.; Rosner, B.; Sandberg, M.A.; Dryja, T.P. Ocular findings in patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa and a rhodopsin gene defect (Pro-23-His). Arch. Ophthalmol. 1991, 109, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasiou, D.; Aguila, M.; Bellingham, J.; Li, W.; McCulley, C.; Reeves, P.J.; Cheetham, M.E. The molecular and cellular basis of rhodopsin retinitis pigmentosa reveals potential strategies for therapy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 62, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naash, M.L.; Peachey, N.S.; Li, Z.Y.; Gryczan, C.C.; Goto, Y.; Blanks, J.; Milam, A.H.; Ripps, H. Light-induced acceleration of photoreceptor degeneration in transgenic mice expressing mutant rhodopsin. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996, 37, 775–782. [Google Scholar]
- Nadal-Nicolas, F.M.; Kunze, V.P.; Ball, J.M.; Peng, B.T.; Krishnan, A.; Zhou, G.; Dong, L.; Li, W. True S-cones are concentrated in the ventral mouse retina and wired for color detection in the upper visual field. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortin-Martinez, A.; Nadal-Nicolas, F.M.; Jimenez-Lopez, M.; Alburquerque-Bejar, J.J.; Nieto-Lopez, L.; Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Villegas-Perez, M.P.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Agudo-Barriuso, M. Number and distribution of mouse retinal cone photoreceptors: Differences between an albino (Swiss) and a pigmented (C57/BL6) strain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.M.; Yin, Z.Q.; Liu, K.; Huo, S.J. Temporal and spatial characteristics of cone degeneration in RCS rats. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 55, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greferath, U.; Huynh, M.; Jobling, A.I.; Vessey, K.A.; Venables, G.; Surrao, D.; O’Neill, H.C.; Limnios, I.J.; Fletcher, E.L. Dorsal-Ventral Differences in Retinal Structure in the Pigmented Royal College of Surgeons Model of Retinal Degeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 553708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.V.; Teng, D.; Konar, G.J.; Agakishiev, D.; Biggs-Garcia, A.; Harris-Bookman, S.; McNally, M.M.; Garzon, C.; Sastry, S.; Singh, M.S. Characterization and allogeneic transplantation of a novel transgenic cone-rich donor mouse line. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 210, 108715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanito, M.; Kaidzu, S.; Ohira, A.; Anderson, R.E. Topography of retinal damage in light-exposed albino rats. Exp. Eye Res. 2008, 87, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, A.; Place, E.; Pierce, E.A.; Comander, J. Characterizing variants of unknown significance in rhodopsin: A functional genomics approach. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 1127–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Case Number | Research ID | Sex | Age of Symptom Onset | At Presentation | At Last Follow-Up | Additional Notable Diagnoses | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Symptoms | Snellen BCVA | V4e Field Description | Age | Snellen BCVA | V4e Field Description | |||||
| 1 * | OGI3683_0052104 | M | N/A | 13 | None | 20/20 OD 20/20 OS | Full OU | N/A | N/A | N/A | None |
| 2 * | OGI3683_0052103 | F | 12 | 15 | Nyctalopia, delayed dark adaptation | 20/20 OD 20/20 OS | Full OU; I4e mid-peripheral relative scotoma OU | N/A | N/A | N/A | None |
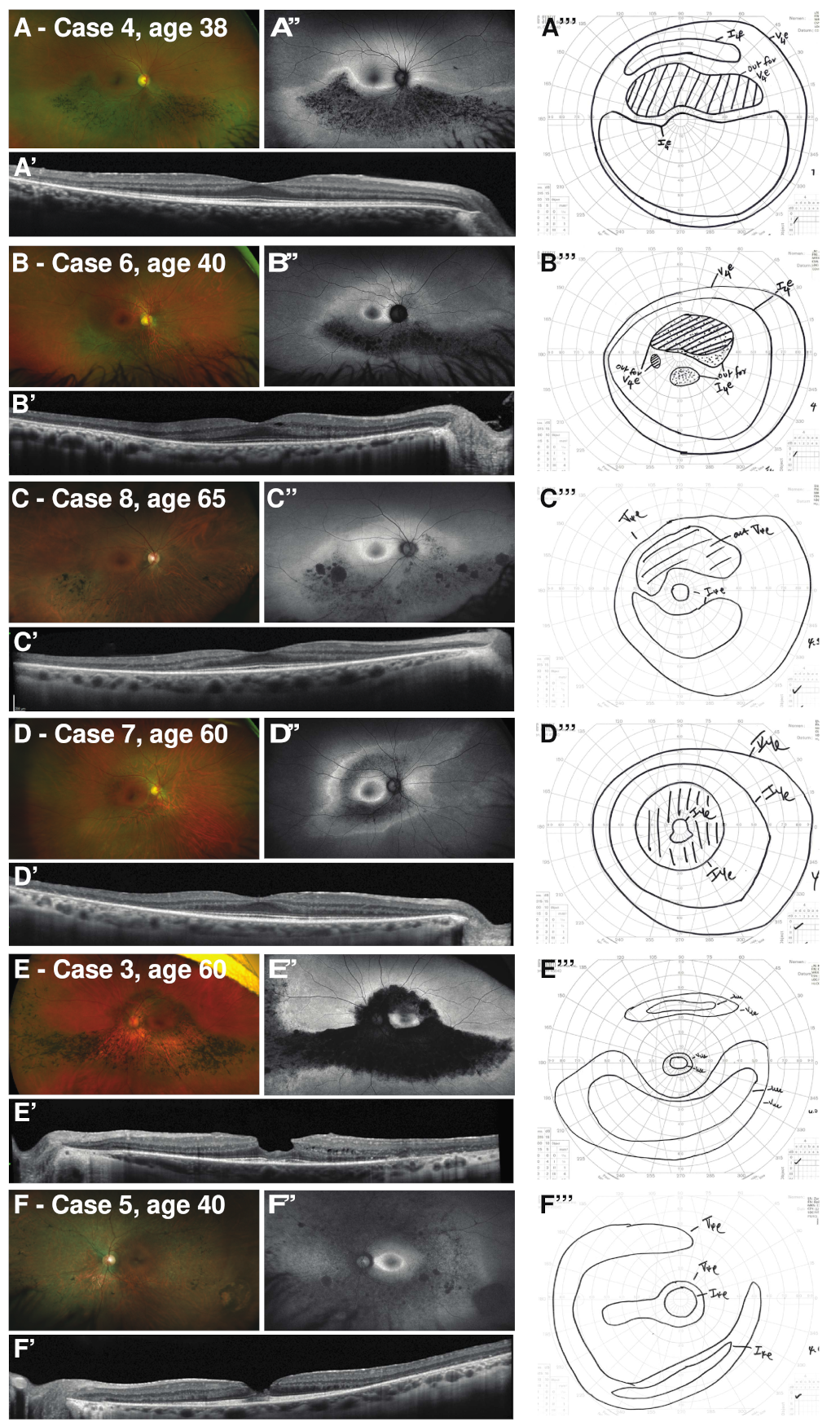
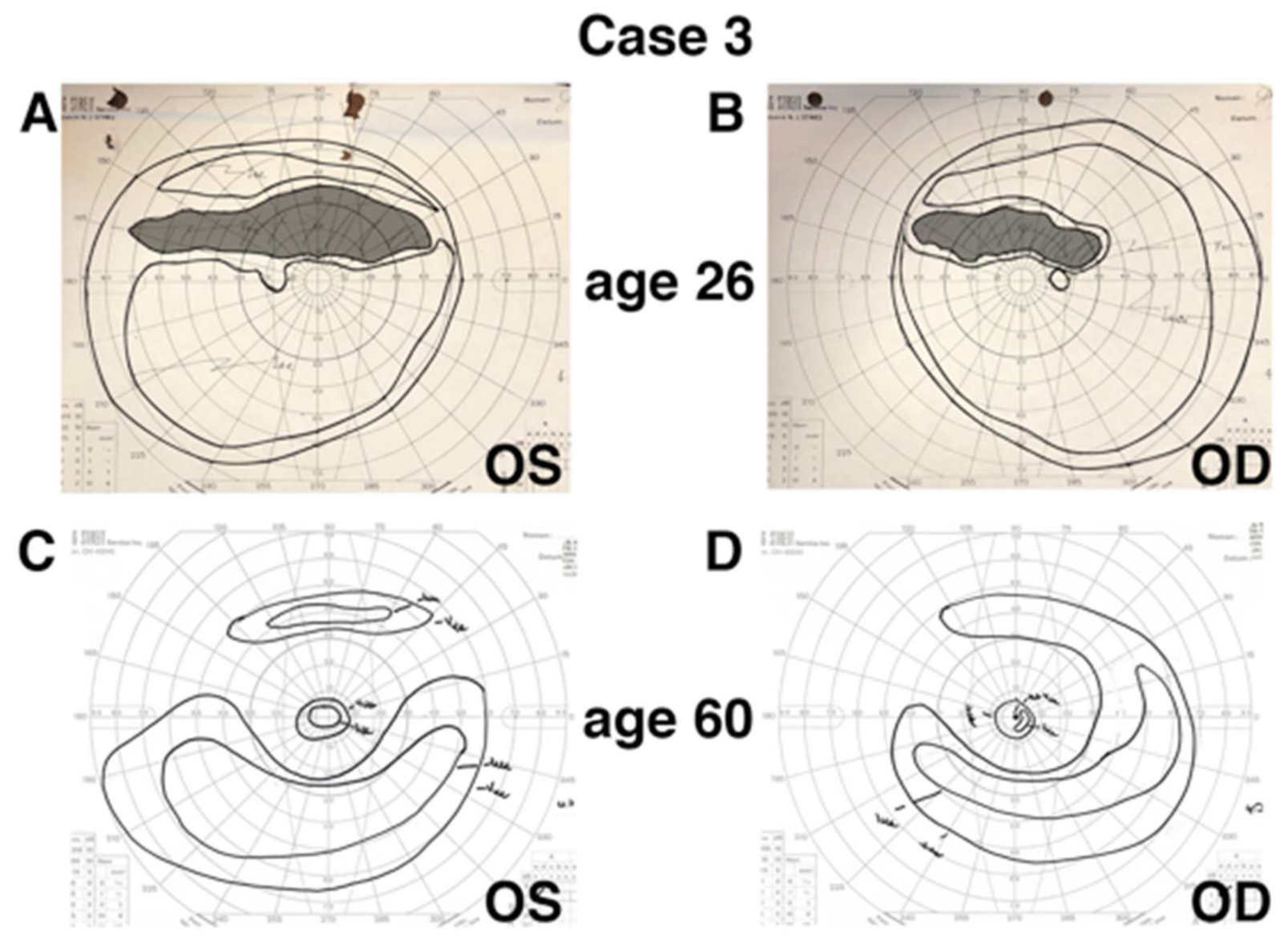
| 3 | OGI992_001975 | F | Early 20 s | 26 | Superior visual field defect | 20/20 OD 20/20 OS | Superior near-peripheral scotoma OU | 60 | 20/100 OD 20/20 OS | Pericentral ring scotoma | Macular hole OD (closed) Macular pseudohole OS |
| 4 | OGI3707_0052135 | F | 38 | 38 | Flashes in superior visual field | 20/20 OD 20/20 OS | Superior near-peripheral scotoma OU | N/A | N/A | N/A | None |
| 5 | OGI3706_0052134 | M | Childhood | 40 | Delayed dark adaptation, blurry vision OD | 20/100 OD 20/20 OS | Pericentral-to-mid-peripheral ring scotoma OU | N/A | N/A | N/A | Macular hole OD (open) Macular pseudohole OS |
| 6 | OGI3708_0052136 | M | 38 | 40 | Blurry vision, near-peripheral field defect | 20/20 OD20/20 OS | Superior near-peripheral scotoma OU, with inferior near-peripheral scotoma OS | N/A | N/A | N/A | X-linked deuteranomalous defect |
| 7 | OGI3705_0052133 | F | Childhood | 47 | Nyctalopia, near-peripheral field defect | 20/20 OD2 20/20 OS | Pericentral ring scotoma OU | 60 | 20/20 OD 20/20 OS | Pericentral ring scotoma OU | None |
| 8 | OGI686_001369 | F | 47 | 59 | Nyctalopia, near-peripheral field defect | 20/20 OD 20/20 OS | Superior mid-peripheral scotoma OU | 65 | 20/25 OD 20/40 OS | Superior mid-peripheral scotoma OU | None |
| 9 † | OGI3683_0052102 | F | Mid-40 s | 45 | Mild delayed dark adaptation | 20/20 OD 20/20 OS | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | None |
| At Presentation | At Last Follow-Up | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case Number | Research ID | Fundoscopy | Fundus AF | SD-OCT | ffERG ** | Fundoscopy | Fundus AF | SD-OCT | ffERG ** |
| 1 * | OGI3683_0052104 | Normal macular and peripheral retinal pigmentation | Faint, diffuse hypoAF along arcades with surrounding hyperAF border in temporal perifovea forming partial ring | Preserved lamination in fovea and peripheral macula; subtle attenuation of ONL in temporal macula | Normal rod and cone responses. IT: 28 ms OD/28 ms OS | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2 * | OGI3683_0052103 | Mid-peripheral depigmentation and rare bone spicule pigmentation; mild vessel attenuation | Parafoveal hyperAF ring; mid-peripheral hypoAF; some far-anterior preserved AF | Preserved lamination in fovea; attenuation of ONL and loss of outer retinal banding in peripheral macula. Mild CME OD and mild-moderate CME OS. | Mildly subnormal, but readily detectable, rod-isolated (40% OD; 49% OS) and cone-isolated (42% OU) responses. IT: 38 ms OD/40 ms OS | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 3 | OGI992_001975 | Sectoral atrophy and bone spicule pigmentation inferior near-periphery and nasally | Unavailable | Unavailable | Normal rod and cone responses. IT: 32 ms OD/32 ms OS | Ring of near-peripheral atrophy overlying arcades with inferior and nasal extension into mid-periphery with bone spicule pigmentation. Foveal hypopigmentation OD. | Ring of pericentral hypoAF overlying arcades with inferior and nasal extension into mid- and far-periphery.Foveal hypoAF OD. | Foveal thinning and outer retinal atrophy with subretinal hyperreflective material OD. Macular pseudohole with epiretinal membrane, and preserved outer retinal banding in fovea, with small inner retinal pseudocysts in temporal parafovea OS. Attenuation of ONL and loss of outer retinal banding in peripheral macula OU. | Subnormal, but readily detectable, rod-isolated (46% OD; 52% OS) and cone-isolated (52% OD; 68% OS) responses. IT: 37 ms OD/34 ms OS |
| 4 | OGI3707_0052135 | Sectoral atrophy and bone spicule pigmentation inferior near-periphery and nasally | Sectoral band of hypoAF in area of spicules in inferior near-periphery and nasally, with hyperAF border in inferior perifovea. | Preserved lamination in fovea; attenuation of ONL and loss of outer retinal banding in inferior macula. | Mildly subnormal, but readily detectable, rod-isolated (36% OD; 39% OS) and cone-isolated (78% OD; 66% OS) responses. IT: 30 ms OD/30 ms OS | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 5 | OGI3706_0052134 | Near- to mid-peripheral atrophy with sparse bone spicule pigmentation and far-peripheral sparing. Macular hole OD; macular pseudohole OS. | Near- to mid-peripheral hypoAF with far-peripheral preserved AF. Perifoveal hyperAF ring OU. | Full-thickness macular hole OD; macular pseudohole OS. Attenuation of ONL and loss of outer retinal banding in peripheral macula. | Subnormal, but detectable, rod-isolated (20% OD; 17% OS) and cone-isolated (58% OD; 52% OS) responses. IT: 37 ms OD/38 ms OS | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 6 | OGI3708_0052136 | Sectoral atrophy and sparse bone spicule pigmentation inferior near-periphery and nasally | Sectoral band of hypoAF in inferior near-periphery and nasally. Ring of AF change overlying arcades with hyperAF ring in perifovea. | Preserved lamination in fovea; attenuation of ONL and loss of outer retinal banding in peripheral macula. | Normal rod and cone responses. IT: 35 ms OD/34 ms OS | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 7 | OGI3705_0052133 | Near- to mid-peripheral atrophy with rare bone spicule pigmentation and far-peripheral sparing. | Unavailable | Unavailable | Subnormal, but readily detectable, rod-isolated (63% OD; 48% OS) responses. Normal cone-isolated responses. IT: 33 ms OD/33 ms OS | Near- to mid-peripheral atrophy with rare bone spicule pigmentation and far-peripheral sparing. | Near- to mid-peripheral hypoAF with far-peripheral preserved AF. Perifoveal hyperAF ring OU. | Preserved lamination in foveal; attenuation of ONL and loss of outer retinal banding in peripheral macula. | Subnormal, but readily detectable, rod-isolated (52% OD; 46% OS) responses. Normal cone-isolated responses. Rod-isolated responses OD slightly diminished compared to presentation.IT: 31 ms OD/33 ms OS |
| 8 | OGI686_001369 | Sectoral atrophy and bone spicule pigmentation inferior near-periphery and nasally | Unavailable | Preserved lamination in fovea; attenuation of ONL and loss of outer retinal banding in peripheral macula. | Subnormal, but readily detectable, rod-isolated (55%) responses OD and normal responses OS. Subnormal but readily detectable cone-isolated (64% OU) responses. IT: 37 ms OD/35 ms OS | Sectoral atrophy and bone spicule pigmentation inferior near-periphery and nasally | Sectoral band of hypoAF in inferior near-periphery and nasally. Ring of AF change overlying arcades with hyperAF ring in perifovea. | Preserved lamination in fovea; attenuation of ONL and loss of outer retinal banding in peripheral macula. | Subnormal, but readily detectable, rod-isolated (36% OD; 34% OS) and cone-isolated (62%; 74%) responses. IT: 34 ms OD/35 ms OS |
| 9 † | OGI3683_0052102 | Sectoral atrophy and sparse bone spicule pigmentation inferior near-periphery and nasally | Sectoral band of hypoAF in inferior near-periphery and nasally. Ring of AF change overlying arcades with hyperAF ring in perifovea. | Preserved lamination in fovea; attenuation of ONL and loss of outer retinal banding in peripheral macula. | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ballios, B.G.; Place, E.M.; Martinez-Velazquez, L.; Pierce, E.A.; Comander, J.I.; Huckfeldt, R.M. Beyond Sector Retinitis Pigmentosa: Expanding the Phenotype and Natural History of the Rhodopsin Gene Codon 106 Mutation (Gly-to-Arg) in Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa. Genes 2021, 12, 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121853
Ballios BG, Place EM, Martinez-Velazquez L, Pierce EA, Comander JI, Huckfeldt RM. Beyond Sector Retinitis Pigmentosa: Expanding the Phenotype and Natural History of the Rhodopsin Gene Codon 106 Mutation (Gly-to-Arg) in Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa. Genes. 2021; 12(12):1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121853
Chicago/Turabian StyleBallios, Brian G., Emily M. Place, Luis Martinez-Velazquez, Eric A. Pierce, Jason I. Comander, and Rachel M. Huckfeldt. 2021. "Beyond Sector Retinitis Pigmentosa: Expanding the Phenotype and Natural History of the Rhodopsin Gene Codon 106 Mutation (Gly-to-Arg) in Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa" Genes 12, no. 12: 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121853
APA StyleBallios, B. G., Place, E. M., Martinez-Velazquez, L., Pierce, E. A., Comander, J. I., & Huckfeldt, R. M. (2021). Beyond Sector Retinitis Pigmentosa: Expanding the Phenotype and Natural History of the Rhodopsin Gene Codon 106 Mutation (Gly-to-Arg) in Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa. Genes, 12(12), 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121853






