Individual Oligogenic Background in p.D91A-SOD1 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
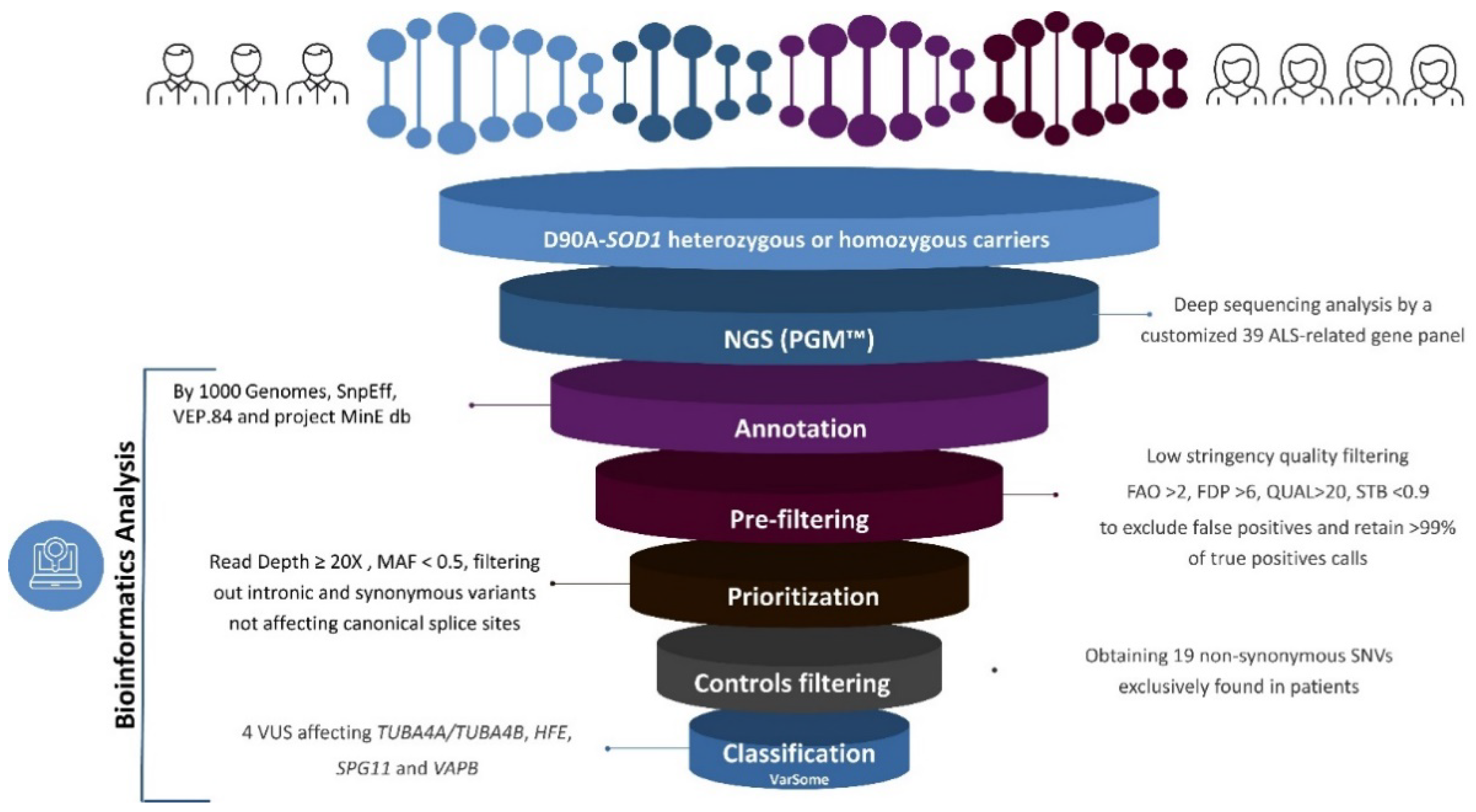
2.2. NGS Analysis
2.3. eQTLs
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renton, A.E.; Chiò, A.; Traynor, B.J. State of play in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis genetics. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, L.P.; Shneider, N.A. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandres-Ciga, S.; Noyce, A.J.; Hemani, G.; Nicolas, A.; Calvo, A.; Mora, G.; Arosio, A.; Barberis, M.; Bartolomei, I.; Battistini, S.; et al. Shared polygenic risk and causal inferences in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felbecker, A.; Camu, W.; Valdmanis, P.N.; Sperfeld, A.D.; Waibel, S.; Steinbach, P.; Rouleau, G.A.; Ludolph, A.C.; Andersen, P.M. Four familial ALS pedigrees discordant for two SOD1 mutations: Are all SOD1 mutations pathogenic? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia Wismayer, M.; Farrugia Wismayer, A.; Pace, A.; Vassallo, N.; Cauchi, R.J. SOD1 D91A variant in the southernmost tip of Europe: A heterozygous ALS patient resident on the island of Gozo. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 27, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, H.L.; Berg, J.S.; Brooks, L.D.; Bustamante, C.D.; Evans, J.P.; Landrum, M.J.; Ledbetter, D.H.; Maglott, D.R.; Martin, C.L.; Nussbaum, R.L.; et al. ClinGen — The Clinical Genome Resource. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, P.M.; Nilsson, P.; Ala-Hurula, V.; Keränen, M.L.; Tarvainen, I.; Haltia, T.; Nilsson, L.; Binzer, M.; Forsgren, L.; Marklund, S.L. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis associated with homozygosity for an Asp90Ala mutation in CuZn-superoxide dismutase. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, P.M.; Forsgren, L.; Binzer, M.; Nilsson, P.; Ala-Hurula, V.; Keränen, M.L.; Bergmark, L.; Saarinen, A.; Haltia, T.; Tarvainen, I.; et al. Autosomal recessive adult-onset amyohophic lateral sclerosis associated with homozygosity for Asp90A1a CuZn-superoxide dismutase mutation A clinical and genealogical study of 36 patients. Brain 1996, 119, 1153–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robberecht, W.; Aguirre, T.; Van Den Bosch, L.; Tilkin, P.; Cassiman, J.J.; Matthijs, G. D90A heterozygosity in the SOD1 gene is associated with familial and apparently sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 1996, 47, 1336–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsova, V.I.; Limborska, S.A.; Slominsky, P.A.; Levitskaya, N.I.; Levitsky, G.N.; Shadrina, M.I.; Kondratyeva, E.A. Sporadic ALS associated with the D90A CU,ZN superoxide dismutase mutation in Russia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2001, 8, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, F.; Battistini, S.; Mancuso, M.; Greco, G.; Ricci, C.; Volpi, N.; Del Corona, A.; Piazza, S.; Siciliano, G. D90A-SOD1 mutation in ALS: The first report of heterozygous Italian patients and unusual findings. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2010, 11, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parton, M.J.; Broom, W.; Andersen, P.M.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Nigel Leigh, P.; Powell, J.F.; Shaw, C.E. D90A-SOD1 mediated amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A single founder for all cases with evidence for a Cis-acting disease modifier in the recessive haplotype. Hum. Mutat. 2002, 20, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisa Conforti, F.; Sprovieri, T.; Mazzei, R.; Patitucci, A.; Ungaro, C.; Zoccolella, S.; Magariello, A.; Bella, V.L.; Tessitore, A.; Tedeschi, G.; et al. Further evidence that D90A-SOD1 mutation is recessively inherited in ALS patients in Italy. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2009, 10, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernard, E.; Pegat, A.; Svahn, J.; Bouhour, F.; Leblanc, P.; Millecamps, S.; Thobois, S.; Guissart, C.; Lumbroso, S.; Mouzat, K. Clinical and Molecular Landscape of ALS Patients with SOD1 Mutations: Novel Pathogenic Variants and Novel Phenotypes. A Single ALS Center Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoris, J.; Moulard, B.; Briolotti, V.; Hayer, M.; Durieux, A.; Clavelou, P.; Malafosse, A.; Rouleau, G.A.; Camu, W. Coexistence of dominant and recessive familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with the D90A Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation within the same country. Eur. J. Neurol. 2000, 7, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, J.L.; Ryan, É.B.; Esengul, Y.T.; Siddique, N.; Siddique, T. Intricacies of aetiology in intrafamilial degenerative disease. Brain Commun. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistini, S.; Giannini, F.; Greco, G.; Bibbò, G.; Ferrera, L.; Marini, V.; Causarano, R.; Casula, M.; Lando, G.; Patrosso, M.C.; et al. SOD1 mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2005, 252, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Blitterswijk, M.; van Es, M.A.; Hennekam, E.A.M.; Dooijes, D.; van Rheenen, W.; Medic, J.; Bourque, P.R.; Schelhaas, H.J.; van der Kooi, A.J.; de Visser, M.; et al. Evidence for an oligogenic basis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 3776–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, P.M. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis associated with mutations in the CuZn superoxide dismutase gene. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2006, 6, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, C.K.; Mayeux-Portas, V.; Khoris, J.; Briolotti, V.; Clavelou, P.; Camu, W.; Rouleau, G.A. Compound heterozygous D90A and D96N SOD1 mutations in a recessive amyotrophic lateral sclerosis family. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 49, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parton, M.J.; Andersen, P.M.; Broom, W.J.; Shaw, C.E. Compound heterozygosity and variable penetrance inSOD1 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pedigrees. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luigetti, M.; Conte, A.; Madia, F.; Marangi, G.; Zollino, M.; Mancuso, I.; Dileone, M.; Del Grande, A.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Tonali, P.A.; et al. Heterozygous SOD1 D90A mutation presenting as slowly progressive predominant upper motor neuron amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 30, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuuluvainen, L.; Kaivola, K.; Mönkäre, S.; Laaksovirta, H.; Jokela, M.; Udd, B.; Valori, M.; Pasanen, P.; Paetau, A.; Traynor, B.J.; et al. Oligogenic basis of sporadic ALS The example of SOD1 p.Ala90Val mutation. Neurol Genet 2019, 5, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feneberg, E.; Turner, M.R.; Ansorge, O.; Talbot, K. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with a heterozygous D91A SOD1 variant and classical ALS-TDP neuropathology. Neurology 2020, 95, 595–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, I.R.A.; Bigio, E.H.; Ince, P.G.; Geser, F.; Neumann, M.; Cairns, N.J.; Kwong, L.K.; Forman, M.S.; Ravits, J.; Stewart, H.; et al. Pathological TDP-43 distinguishes sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with SOD1 mutations. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Ihara, M.; Urushitani, M.; Yamashita, H.; Kondo, T.; Tanigaki, A.; Oono, M.; Kawamata, J.; Ikemoto, A.; Kawamoto, Y.; et al. An autopsy case of SOD1-related ALS with TDP-43 positive inclusions. Neurology 2011, 77, 1993–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattante, S.; Ciura, S.; Rouleau, G.A.; Kabashi, E. Defining the genetic connection linking amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) with frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.P.; Van Broeckhoven, C.; van der Zee, J. ALS Genes in the Genomic Era and their Implications for FTD. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 404–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, S.; Shatunov, A.; Sproviero, W.; Jones, A.R.; Shoai, M.; Hughes, D.; Al Khleifat, A.; Malaspina, A.; Morrison, K.E.; Shaw, P.J.; et al. A comprehensive analysis of rare genetic variation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the UK. Brain 2017, 140, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, W.J.; Johnson, D.V.; Garber, M.; Andersen, P.M.; Lennon, N.; Landers, J.; Nusbaum, C.; Russ, C.; Brown, R.H. DNA sequence analysis of the conserved region around the SOD1 gene locus in recessively inherited ALS. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 463, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Miller, R.G.; Swash, M.; Munsat, T.L. El Escorial revisited: Revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Mot. Neuron Disord. 2000, 1, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungaro, C.; Sprovieri, T.; Morello, G.; Perrone, B.; Spampinato, A.G.; Simone, I.L.; Trojsi, F.; Monsurrò, M.R.; Spataro, R.; La Bella, V.; et al. Genetic investigation of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients in south Italy: A two-decade analysis. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 99, 99.e7–99.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Chalabi, A.; Van Den Berg, L.H.; Veldink, J. Gene discovery in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Implications for clinical management. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ungaro, C.; Citrigno, L.; Trojsi, F.; Sprovieri, T.; Gentile, G.; Muglia, M.; Monsurrò, M.R.; Tedeschi, G.; Cavallaro, S.; Conforti, F.L. ALS and CHARGE syndrome: A clinical and genetic study. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2018, 4, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.; Coldren, C.; Karunamurthy, A.; Kip, N.S.; Klee, E.W.; Lincoln, S.E.; Leon, A.; Pullambhatla, M.; Temple-Smolkin, R.L.; Voelkerding, K.V.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for Validating Next-Generation Sequencing Bioinformatics Pipelines. J. Mol. Diagnostics 2018, 20, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Spek, R.A.A.; van Rheenen, W.; Pulit, S.L.; Kenna, K.P.; van den Berg, L.H.; Veldink, J.H. The project MinE databrowser: Bringing large-scale whole-genome sequencing in ALS to researchers and the public. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2019, 20, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damiati, E.; Borsani, G.; Giacopuzzi, E. Amplicon-based semiconductor sequencing of human exomes: Performance evaluation and optimization strategies. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Summa, S.D.; Malerba, G.; Mori, A.; Mijatovic, V.; Pinto, R.; Tommasi, S. Quality measures to improve variant calling of Ion Torrent data. In Proceedings of the NETTAB & IB, Bari, Italy, 14–16 October 2015; Available online: http://www.igst.it/nettab/2015/files/2017/02/NETTAB2015_DeSumma.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2021).
- Kopanos, C.; Tsiolkas, V.; Kouris, A.; Chapple, C.E.; Albarca Aguilera, M.; Meyer, R.; Massouras, A. VarSome: The human genomic variant search engine. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benson, M.; Brown, G.R.; Chao, C.; Chitipiralla, S.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Jang, W.; et al. ClinVar: Improving access to variant interpretations and supporting evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1062–D1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rentzsch, P.; Witten, D.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD: Predicting the deleteriousness of variants throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D886–D894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguet, F.; Barbeira, A.N.; Bonazzola, R.; Jo, B.; Kasela, S.; Liang, Y.; Parsana, P.; Aguet, F.; Battle, A.; Brown, A.; et al. The GTEx Consortium atlas of genetic regulatory effects across human tissues. Science 2020, 369, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hysi, P.G.; Choquet, H.; Khawaja, A.P.; Wojciechowski, R.; Tedja, M.S.; Yin, J.; Simcoe, M.J.; Patasova, K.; Mahroo, O.A.; Thai, K.K.; et al. Meta-analysis of 542,934 subjects of European ancestry identifies new genes and mechanisms predisposing to refractive error and myopia. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuckovic, D.; Bao, E.L.; Akbari, P.; Lareau, C.A.; Mousas, A.; Jiang, T.; Chen, M.-H.; Raffield, L.M.; Tardaguila, M.; Huffman, J.E.; et al. The Polygenic and Monogenic Basis of Blood Traits and Diseases. Cell 2020, 182, 1214–1231.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, V.; Stricker, S.; Kreuz, F.; Minnerop, M.; Gillessen-Kaesbach, G.; Zühlke, C. Ataxia with oculomotor apraxia type 2: Novel mutations in six patients with juvenile age of onset and elevated serum α-fetoprotein. Neuropediatrics 2008, 39, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arning, L.; Epplen, J.T.; Rahikkala, E.; Hendrich, C.; Ludolph, A.C.; Sperfeld, A.-D. The SETX missense variation spectrum as evaluated in patients with ALS4-like motor neuron diseases. Neurogenetics 2013, 14, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høyer, H.; Braathen, G.J.; Busk, Ø.L.; Holla, Ø.L.; Svendsen, M.; Hilmarsen, H.T.; Strand, L.; Skjelbred, C.F.; Russell, M.B. Genetic Diagnosis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease in a Population by Next-Generation Sequencing. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghani, M.; Lang, A.E.; Zinman, L.; Nacmias, B.; Sorbi, S.; Bessi, V.; Tedde, A.; Tartaglia, M.C.; Surace, E.I.; Sato, C.; et al. Mutation analysis of patients with neurodegenerative disorders using NeuroX array. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 545.e9–545.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crimella, C.; Arnoldi, A.; Crippa, F.; Mostacciuolo, M.L.; Boaretto, F.; Sironi, M.; D’Angelo, M.G.; Manzoni, S.; Piccinini, L.; Turconi, A.C.; et al. Point mutations and a large intragenic deletion in SPG11 in complicated spastic paraplegia without thin corpus callosum. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 46, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensato, V.; Castellotti, B.; Gellera, C.; Pareyson, D.; Ciano, C.; Nanetti, L.; Salsano, E.; Piscosquito, G.; Sarto, E.; Eoli, M.; et al. Overlapping phenotypes in complex spastic paraplegias SPG11, SPG15, SPG35 and SPG48. Brain 2014, 137, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, S.; Shoai, M.; Fratta, P.; Sidle, K.; Orrell, R.; Sweeney, M.G.; Shatunov, A.; Sproviero, W.; Jones, A.; Al-Chalabi, A.; et al. Investigation of next-generation sequencing technologies as a diagnostic tool for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1600.e5–1600.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrestian, N.; Dupré, N.; Gan-Or, Z.; Szuto, A.; Chen, S.; Venkitachalam, A.; Brisson, J.-D.; Warman-Chardon, J.; Ahmed, S.; Ashtiani, S.; et al. Clinical and genetic study of hereditary spastic paraplegia in Canada. Neurol. Genet. 2017, 3, e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krüger, S.; Battke, F.; Sprecher, A.; Munz, M.; Synofzik, M.; Schöls, L.; Gasser, T.; Grehl, T.; Prudlo, J.; Biskup, S. Rare Variants in Neurodegeneration Associated Genes Revealed by Targeted Panel Sequencing in a German ALS Cohort. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verde, F.; Tiloca, C.; Morelli, C.; Doretti, A.; Poletti, B.; Maderna, L.; Messina, S.; Gentilini, D.; Fogh, I.; Ratti, A.; et al. PON1 is a disease modifier gene in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Association of the Q192R polymorphism with bulbar onset and reduced survival. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 1469–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Su, L.; Sheng, J.; Lv, W.; Chen, G.; Xu, Z. Association of progranulin polymorphism rs5848 with neurodegenerative diseases: A meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, B.; Conforti, F.L. Common mutations of interest in the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: How common are common mutations in ALS genes? Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-De-Souza, D.; Guest, P.C.; Mann, D.M.; Roeber, S.; Rahmoune, H.; Bauder, C.; Kretzschmar, H.; Volk, B.; Baborie, A.; Bahn, S. Proteomic analysis identifies dysfunction in cellular transport, energy, and protein metabolism in different brain regions of atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 2533–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademakers, R.; Eriksen, J.L.; Baker, M.; Robinson, T.; Ahmed, Z.; Lincoln, S.J.; Finch, N.; Rutherford, N.J.; Crook, R.J.; Josephs, K.A.; et al. Common variation in the miR-659 binding-site of GRN is a major risk factor for TDP43-positive frontotemporal dementia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 3631–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aronica, E.; Baas, F.; Iyer, A.; ten Asbroek, A.L.M.A.; Morello, G.; Cavallaro, S. Molecular classification of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by unsupervised clustering of gene expression in motor cortex. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 74, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.Y.; Syu, J.S.; Han, T.Y.; Cheng, H.L.; Lu, F.I.; Wang, C.Y. Cell Cycle-Dependent Localization of Dynactin Subunit p150glued at Centrosome. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaMonte, B.H.; Wallace, K.E.; Holloway, B.A.; Shelly, S.S.; Ascaño, J.; Tokito, M.; Van Winkle, T.; Howland, D.S.; Holzbaur, E.L.F. Disruption of dynein/dynactin inhibits axonal transport in motor neurons causing late-onset progressive degeneration. Neuron 2002, 34, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCann, E.P.; Henden, L.; Fifita, J.A.; Zhang, K.Y.; Grima, N.; Bauer, D.C.; Chan Moi Fat, S.; Twine, N.A.; Pamphlett, R.; Kiernan, M.C.; et al. Evidence for polygenic and oligogenic basis of Australian sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 58, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepheard, S.R.; Parker, M.D.; Cooper-Knock, J.; Verber, N.S.; Tuddenham, L.; Heath, P.; Beauchamp, N.; Place, E.; Sollars, E.S.A.; Turner, M.R.; et al. Value of systematic genetic screening of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.P.; Brown, R.H.; Cleveland, D.W. Decoding ALS: From genes to mechanism. Nature 2016, 539, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abati, E.; Bresolin, N.; Comi, G.; Corti, S. Silence superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1): A promising therapeutic target for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, D.A.; Davidson, B.L. Gene therapy for ALS: A review. Mol. Ther. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| p.D91A SOD1 zygosity | Survival Time | Progression Rate | Phenotype | Contributing Risk Factors Proposed | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hom | More than two years | Slow | Spinal ALS * | Contributing variants mitigating the phenotype not yet identified | [1,9,14,15,16] |
| Het | More than two years | Slow | Spinal ALS | Heterozygous compound in SOD1 | [16,17,21,22,23,24] |
| Het | About two years | Fast | Variable forms of ALS ** | Contributing variants or TDP-43 inclusions not yet identified | [4,5,25] |
| FALS or SALS | Sample ID | Mutant Allele | Gender M/F | Site of Onset | Age of Onset (yrs) | Disease Duration (yrs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FALS | P1 | Hom | F | LL | 68 | n/a |
| FALS | P2 | Hom | M | LL | 49 | 8 a |
| FALS | P3 | Hom | F | LL | 46 | 2.2 a |
| SALS | P4 | Hom | F | LL | 55 | 8.4 b |
| SALS | P5 | Hom | M | UL | 33 | 22 b |
| SALS | P6 | Het | M | LL | 52 | 2.5 c |
| ALS | P7 | Het | F | LL | 54 | 2 a |
| Gene | V | rs ID | VA | VF | MAF | VarSome | ClinVar | Proj. MinE | CADD PHRED Score | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCTN1 | c. * 21C>T | rs11555696 | 3′ UTR | 0.14 | 0.022720/ 0.02188 | LB | B | n/a | 8.217 | [44] |
| TUBA4A | c.227-74C>T | rs45488900 | Intron | 0.28 | -/0.12853 | VUS | n/a | n/a | 5.309 | [45] |
| TUBA4B | n.-1456G>T | Upstream | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 5.309 | n/a | ||
| NEK1 | c.2255A>G; p.Glu752Gly | rs34099167 | Missense | 0.4 | 0.14032/ 0.09304 | B | B | n/a | 25.1 | n/a |
| NEK1 | c.1388C>T; p.Ala463Val | rs34540355 | Missense | 0.14 | 0.035127/ 0.03250 | B | B/LB | 0.0593/0.0603 | 16.28 | n/a |
| HFE | c.-48C>G | rs41266793 | 5′ UTR | 0.14 | -/- | VUS | n/a | n/a | 0.233 | n/a |
| FIG4 | c. * 29G>A | rs10659 | 3′ UTR | 0.14 | 0.046277/ 0.07829 | B | B | n/a | 0.408 | n/a |
| SETX | c. * 849G>T | rs74975459 | 3′ UTR | 0.14 | -/0.01150 | B | B | n/a | 3.561 | n/a |
| SETX | c.59G>A; p.Arg20His | rs79740039 | Missense | 0.14 | 0.009062/ 0.00653 | B | B | 0.00882/0.00764 | 0.166 | [46,47,48] |
| SPG11 | c.7069C>T; p.Leu2357 Phe | rs139334167 | Missense | 0.14 | -/0.00083 | VUS | CIoP | 0.00183/0.00164 | 25.8 | [49] |
| SPG11 | c.2083G>A; p.Ala695Thr | rs78183930 | Missense | 0.14 | 0.012527/ 0.01897 | B | B | 0.0121/0.0150 | 26.8 | [49,50,51,52,53] |
| PG11 | c.1108G>A; p.Glu370Lys | rs77697105 | Missense | 0.14 | 0.016740/ 0.02196 | B | B/LB | 0.0182/0.0194 | 21.6 | n/a |
| FUS | c. * 910C>T | rs118018900 | Downstream | 0.14 | 0.04772/ 0.02543 | B | B | n/a | 1.015 | n/a |
| PFN1 | c.-342T>C | rs148770753 | 5′ UTR | 0.14 | -/0.00848 | B | n/a | n/a | 10.19 | n/a |
| VAPB | c. * 753C>G | rs6070466 | 3′ UTR | 0.14 | 0.01155/ 0.00452 | B | B | n/a | 15.82 | n/a |
| VAPB | c. * 1265G>C | rs7400 | 3′ UTR | 0.14 | 0.05550/ 0.09272 | B | B | n/a | 14.85 | n/a |
| VAPB | c. * 2819A>G | rs74568509 | 3′ UTR | 0.14 | 0.04862/ 0.07642 | B | B | n/a | 0.673 | n/a |
| VAPB | c. * 4520T>C | rs763514 | 3′ UTR | 0.14 | 0.05098/ 0.10229 | B | B | n/a | 0.83 | n/a |
| VAPB | c. * 6182C>T | rs76708676 | 3′ UTR | 0.14 | 0.02834/ 0.01132 | VUS | B | n/a | 0.515 | n/a |
| APEX1 | c. * 2A>T | rs17112002 | 3′ UTR | 0.14 | 0.003300/ 0.00373 | LB | n/a | n/a | 5.682 | [54] |
| Patient ID | FALS or SALS | p.D91A SOD1 | Genes | HGVSc/HGVSp | Zygosity | rs ID | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | FALS | Hom | DCTN1 | c. * 21C>T | Het | rs11555696 | |
| NEK1 | c.2255A>G; p.Glu752Gly | Hom | rs34099167 | ||||
| P2 | FALS | Hom | PON1 | c.575A>G; p.Gln192Arg | Het | rs662 | [55] |
| GRN | c. * 78C>T | Het | rs5848 | [56] | |||
| P3 | FALS | Hom | HFE | c.-48C>G | Het | rs41266793 | |
| FIG4 | c. * 29G>A | Het | rs10659 | ||||
| GRN | c. * 78C>T | Het | rs5848 | [56] | |||
| P4 | SALS | Hom | TUBA4A/TUBA4B | c.227-74C>T/ n.-1456G>T | Het | rs45488900 | |
| SPG11 | c.7069C>T; p.Leu2357 Phe | Het | rs139334167 | ||||
| VAPB | c. * 753C>G | Het | rs6070466 | ||||
| PON1 | c.575A>G; p.Gln192Arg | Het | rs662 | [55] | |||
| GRN | c. * 78C>T | Hom | rs5848 | [56] | |||
| P5 | SALS | Hom | TUBA4A/TUBA4B | c.227-74C>T/ n.-1456G>T | Hom | rs45488900 | |
| NEK1 | c.2255A>G; p.Glu752Gly | Het | rs34099167 | ||||
| PFN1 | c.-342T>C | Het | rs148770753 | ||||
| VAPB | c. * 6182C>T | Het | rs76708676 | ||||
| APEX1 | c. * 2A>T | Het | rs17112002 | [54] | |||
| GRN | c. * 78C>T | Het | rs5848 | [56] | |||
| P6 | SALS | Het | NEK1 | c.1388C>T; p.Ala463Val | Het | rs34540355 | |
| SPG11 | c.2083G>A; p.Ala695Thr | Het | rs78183930 | [49,52] | |||
| SPG11 | c.1108G>A; p.Glu370Lys | Het | rs77697105 | ||||
| PON1 | c.575A>G; p.Gln192Arg | Het | rs662 | [55] | |||
| GRN | c. * 78C>T | Het | rs5848 | [56] | |||
| P7 | SALS | Het | NEK1 | c.2255A>G; p.Glu752Gly | Het | rs34099167 | |
| SETX | c. * 849G>T | Het | rs74975459 | ||||
| SETX | c.59G>A; p.Arg20His | Het | rs79740039 | [47] | |||
| FUS | c. * 910C>T | Het | rs118018900 | ||||
| VAPB | c. * 1265G>C | Het | rs7400 | ||||
| VAPB | c. * 2819A>G | Het | rs74568509 | ||||
| VAPB | c. * 4520T>C | Het | rs763514 | ||||
| PON1 | c.575A>G; p.Gln192Arg | Het | rs662 | [55] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gentile, G.; Perrone, B.; Morello, G.; Simone, I.L.; Andò, S.; Cavallaro, S.; Conforti, F.L. Individual Oligogenic Background in p.D91A-SOD1 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Genes 2021, 12, 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121843
Gentile G, Perrone B, Morello G, Simone IL, Andò S, Cavallaro S, Conforti FL. Individual Oligogenic Background in p.D91A-SOD1 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Genes. 2021; 12(12):1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121843
Chicago/Turabian StyleGentile, Giulia, Benedetta Perrone, Giovanna Morello, Isabella Laura Simone, Sebastiano Andò, Sebastiano Cavallaro, and Francesca Luisa Conforti. 2021. "Individual Oligogenic Background in p.D91A-SOD1 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients" Genes 12, no. 12: 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121843
APA StyleGentile, G., Perrone, B., Morello, G., Simone, I. L., Andò, S., Cavallaro, S., & Conforti, F. L. (2021). Individual Oligogenic Background in p.D91A-SOD1 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Genes, 12(12), 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121843








