Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the MADS-Box Gene Family in Theobroma cacao
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of MADS-Box Genes in Theobroma cacao
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Classification of MADS-Box Genes
2.3. Conserved Motif and Gene Structure Analysis
2.4. Chromosomal Localization and Gene Duplication
2.5. Analysis of Cis-Acting Element in MADS-Box Genes’ Promoters
3. Results
3.1. Identification of MADS-Box Genes in Theobroma cacao
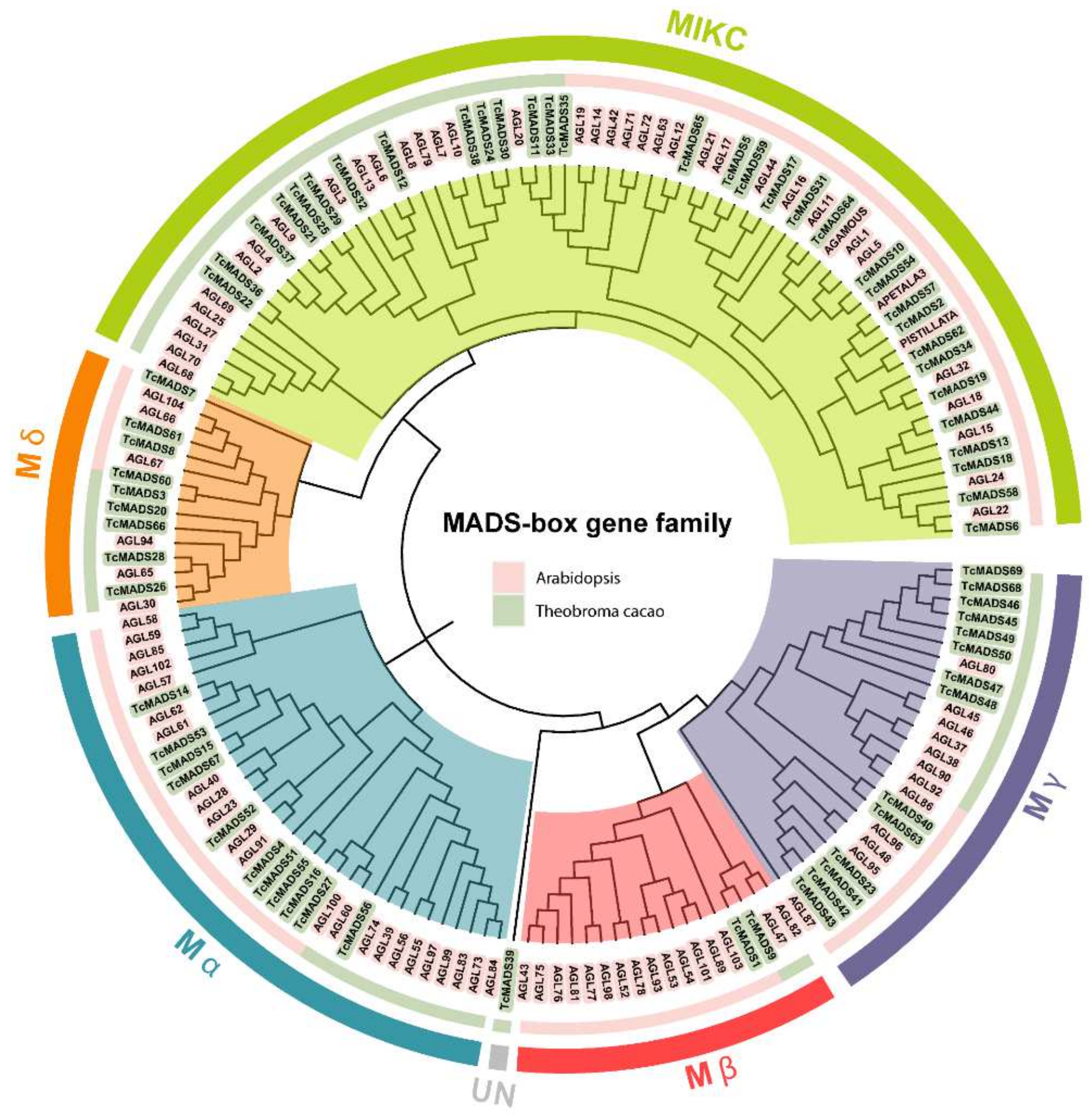
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Classification of the MADS-Box Gene
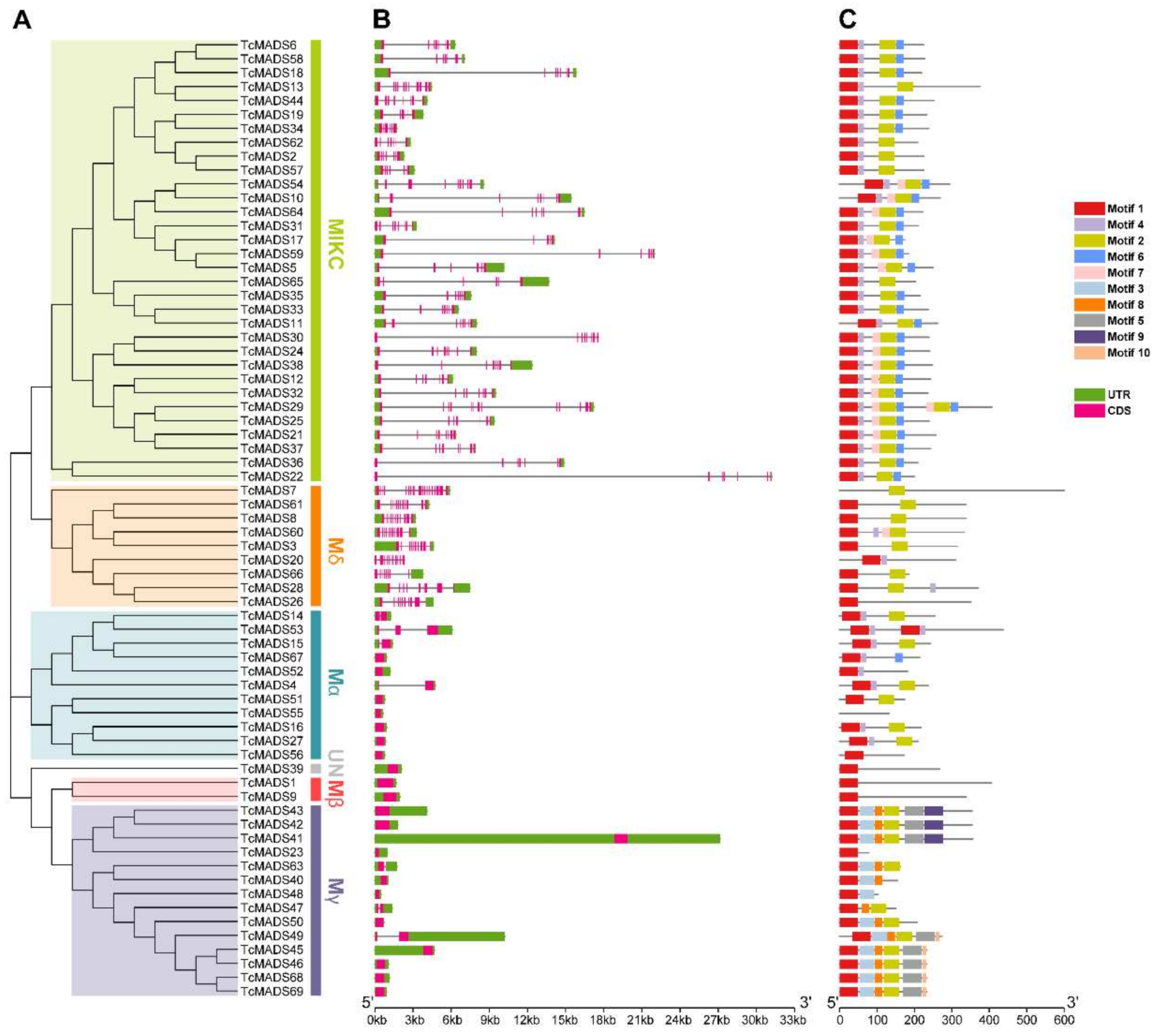
3.3. Conserved Motif and Structure Analysis
3.4. Genome Distribution and Gene Evolution Analysis of TcMADS Genes
3.5. Analysis of Putative Promoter Regions in TcMADS Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Bodt, S.; Raes, J.; Van de Peer, Y.; Theissen, G. And then there were many: MADS goes genomic. Trends Plant Sci. 2003, 8, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passmore, S.; Elble, R.; Tye, B.K. A protein involved in minichromosome maintenance in yeast binds a transcriptional enhancer conserved in eukaryotes. Genes Dev. 1989, 3, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanofsky, M.F.; Ma, H.; Bowman, J.L.; Drews, G.N.; Feldmann, K.A.; Meyerowitz, E.M. The protein encoded by the Arabidopsis homeotic gene agamous resembles transcription factors. Nature 1990, 346, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, H.; Beltrán, J.P.; Huijser, P.; Pape, H.; Lönnig, W.E.; Saedler, H.; Schwarz-Sommer, Z. Deficiens, a homeotic gene involved in the control of flower morphogenesis in Antirrhinum majus: The protein shows homology to transcription factors. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, C.; Runswick, M.; Pollock, R.; Treisman, R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell 1988, 55, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, K.; Melzer, R.; Theissen, G. MIKC-type MADS-domain proteins: Structural modularity, protein interactions and network evolution in land plants. Gene 2005, 347, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henschel, K.; Kofuji, R.; Hasebe, M.; Saedler, H.; Münster, T.; Theissen, G. Two ancient classes of MIKC-type MADS-box genes are present in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.; Shen, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Robertson, M.; Helliwell, C.A.; Ito, T.; Meyerowitz, E.; Yu, H. A repressor complex governs the integration of flowering signals in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, W.; Ying, H.; Helliwell, C.A.; Taylor, J.M.; Peacock, W.J.; Dennis, E.S. FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) regulates development pathways throughout the life cycle of Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6680–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrándiz, C.; Liljegren, S.J.; Yanofsky, M.F. Negative regulation of the SHATTERPROOF genes by FRUITFULL during Arabidopsis fruit development. Science 2000, 289, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrándiz, C.; Gu, Q.; Martienssen, R.; Yanofsky, M.F. Redundant regulation of meristem identity and plant architecture by FRUITFULL, APETALA1 and CAULIFLOWER. Development 2000, 127, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, C.; Hennig, L.; Spillane, C.; Pien, S.; Gruissem, W.; Grossniklaus, U. The Polycomb-group protein MEDEA regulates seed development by controlling expression of the MADS-box gene PHERES1. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1540–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Lin, H.; Chen, A.; Lau, M.; Jernstedt, J.; Dubcovsky, J. Wheat VRN1, FUL2 and FUL3 play critical and redundant roles in spikelet development and spike determinacy. Development 2019, 146, dev175398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michaels, S.D.; Amasino, R.M. FLOWERING LOCUS C encodes a novel MADS domain protein that acts as a repressor of flowering. Plant Cell. 1999, 11, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moser, M.; Asquini, E.; Miolli, G.V.; Weigl, K.; Hanke, M.V.; Flachowsky, H.; Si-Ammour, A. The MADS-box gene MdDAM1 controls growth cessation and bud dormancy in Apple. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Filleur, S.; Rahman, A.; Gotensparre, S.; Forde, B.G. Nutritional regulation of ANR1 and other root-expressed MADS-box genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 2005, 222, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutter, C.; Schöb, H.; Stadler, M.; Meins, F.J.; Si-Ammour, A. MicroRNA-mediated regulation of stomatal development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2007, 19, 2417–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parenicová, L.; de Folter, S.; Kieffer, M.; Horner, D.S.; Favalli, C.; Busscher, J.; Cook, H.E.; Ingram, R.M.; Kater, M.M.; Davies, B.; et al. Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of the complete MADS-box transcription factor family in Arabidopsis: New openings to the MADS world. Plant Cell. 2003, 15, 1538–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leseberg, C.H.; Li, A.; Kang, H.; Duvall, M.; Mao, L. Genome-wide analysis of the MADS-box gene family in Populus trichocarpa. Gene 2006, 378, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fatima, M.; Zhou, P.; Ma, Q.; Ming, R. Analysis of MADS-box genes revealed modified flowering gene network and diurnal expression in pineapple. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fatima, M.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, D.; Ming, R. Expression profiling of MADS-box gene family revealed its role in vegetative development and stem ripening in S. spontaneum. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Tu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Meng, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; He, B. Genome-wide identification and expression profile of the MADS-box gene family in Erigeron breviscapus. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustiga, G.M.; Gezan, S.A.; Phillips-Mora, W.; Arciniegas-Leal, A.; Mata-Quirós, A.; Motamayor, J.C. Phenotypic description of Theobroma cacao L. for yield and vigor traits from 34 hybrid families in Costa Rica based on the genetic basis of the parental population. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, R.; Flammer, A.J.; Hollenberg, N.K.; Lüscher, T.F. Cocoa and cardiovascular health. Circulation 2009, 119, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Argout, X.; Salse, J.; Aury, J.M.; Guiltinan, M.J.; Droc, G.; Gouzy, J.; Allegre, M.; Chaparro, C.; Legavre, T.; Maximova, S.N. The genome of Theobroma cacao. Nat. Genet. 2011, 3, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, S.; Wu, R.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Y. Genome-wide analysis of the NAC Domain transcription factor gene family in Theobroma cacao. Genes 2019, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva Monteiro de Almeida, D.; Oliveira Jordão do Amaral, D.; Del-Bem, L.E.; Bronze Dos Santos, E.; Santana Silva, R.J.; Peres Gramacho, K.; Vincentz, M.; Micheli, F. Genome-wide identification and characterization of cacao WRKY transcription factors and analysis of their expression in response to witches’ broom disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187346. [Google Scholar]
- Martins Alves, A.M.; Pereira Menezes Reis, S.; Peres Gramacho, K.; Micheli, F. The glutathione peroxidase family of Theobroma cacao: Involvement in the oxidative stress during witches’ broom disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3698–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wu, B.; Yan, L.; Qin, X.; Lai, J. Metabolome and transcriptome profiling of Theobroma cacao provides insights into the molecular basis of pod color variation. J. Plant Res. 2021, 134, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, G. Using ggtree to visualize data on tree-like structures. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 69, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yue, J.X.; Tian, D.; Chen, J.Q. Recent duplications dominate NBS-encoding gene expansion in two woody species. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2008, 280, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyama, M.; Torrents, D.; Bork, P. PAL2NAL: Robust conversion of protein sequence alignments into the corresponding codon alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W609–W612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, X.; Liu, C.; Song, L.; Li, M. PaMADS7, a MADS-box transcription factor, regulates sweet cherry fruit ripening and softening. Plant Sci. 2020, 301, 110634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Xu, B.Y.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Z.Q. The interaction of MADS-box transcription factors and manipulating fruit development and ripening. Yi Chuan 2010, 32, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vrebalov, J.; Ruezinsky, D.; Padmanabhan, V.; White, R.; Medrano, D.; Drake, R.; Schuch, W.; Giovannoni, J. A MADS-box gene necessary for fruit ripening at the tomato ripening-inhibitor (rin) locus. Science 2002, 296, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, M.; Nakano, T.; Shima, Y.; Ito, Y. A large-scale identification of direct targets of the tomato MADS box transcription factor RIPENING INHIBITOR reveals the regulation of fruit ripening. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smaczniak, C.; Immink, R.G.; Angenent, G.C.; Kaufmann, K. Developmental and evolutionary diversity of plant MADS-domain factors: Insights from recent studies. Development 2012, 139, 3081–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, Y.; Bi, C.; He, B.; Ye, N.; Yin, T.; Xu, L.A. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the MADS-box gene family in Salix suchowensis. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Airoldi, C.A.; Davies, B. Gene duplication and the evolution of plant MADS-box transcription factors. J. Genet. Genom. 2012, 39, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.Y.; Simons, C.; Firth, A.E.; Brown, C.M.; Hellens, R.P. Effect of 5’UTR introns on gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeffares, D.C.; Penkett, C.J.; Bähler, J. Rapidly regulated genes are intron poor. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Guang, X.; Zhang, Y. Genome-wide analysis of the MADS-box gene family in Watermelon. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 80, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Zhang, R.Z.; Guo, J.J.; Liu, D.M.; Li, A.L.; Fan, R.C.; Mao, L.; Zhang, X.Q. Genome-wide analysis of the MADS-box gene family in Brachypodium distachyon. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84781. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, R.; Agarwal, P.; Ray, S.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, V.P.; Tyagi, A.K.; Kapoor, S. MADS-box gene family in rice: Genome-wide identification, organization and expression profiling during reproductive development and stress. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ning, K.; Han, Y.; Chen, Z.; Luo, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Fan, S.; Wang, Q. Genome-wide analysis of MADS-box family genes during flower development in lettuce. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 1868–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Zahn, L.; Guindon, S.; Wall, P.K.; Kong, H.; Ma, H.; DePamphilis, C.W.; Leebens-Mack, J. Evolution of plant MADS box transcription factors: Evidence for shifts in selection associated with early angiosperm diversification and concerted gene duplications. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 2229–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Garcia, C.M.; Finer, J.J. Identification and validation of promoters and cis-acting regulatory elements. Plant Sci. 2014, 217–218, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, C.L.; Geisler, M. Genome-wide computational identification of biologically significant cis-regulatory elements and associated transcription factors from rice. Plants 2019, 8, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Gene Name | Gene ID | Physicochemical Characteristics | SL | ORF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI | MW (Da) | Length (aa) | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | ||||
| TcMADS1 | TCM_000239 | 9.48 | 46,436.9 | 406 | 39.09 | 77.32 | nucleus | 1221 |
| TcMADS2 | TCM_000266 | 9.59 | 26,095.8 | 224 | 46.52 | 87.1 | chloroplast | 675 |
| TcMADS3 | TCM_000725 | 9.91 | 36,097.68 | 315 | 58.23 | 83.87 | nucleus | 948 |
| TcMADS4 | TCM_000878 | 6.85 | 26,140.89 | 237 | 41.11 | 78.23 | chloroplast | 714 |
| TcMADS5 | TCM_000931 | 9.12 | 29,034.14 | 250 | 45.33 | 84.56 | chloroplast | 753 |
| TcMADS6 | TCM_000992 | 6.55 | 25,353.79 | 224 | 53.32 | 85.76 | nucleus | 675 |
| TcMADS7 | TCM_001181 | 5.86 | 66,752.75 | 600 | 48.76 | 77.52 | nucleus | 1803 |
| TcMADS8 | TCM_001182 | 5.43 | 37,831.38 | 337 | 62.2 | 73.77 | nucleus | 1014 |
| TcMADS9 | TCM_001335 | 9.19 | 38,279.15 | 338 | 38.49 | 68.11 | nucleus | 1017 |
| TcMADS10 | TCM_001841 | 9.85 | 31,109.18 | 269 | 62.98 | 6.17 | chloroplast | 810 |
| TcMADS11 | TCM_005456 | 8.91 | 30,163.08 | 262 | 53.63 | 84.89 | endomembrane system | 789 |
| TcMADS12 | TCM_005458 | 9.08 | 27,810.84 | 243 | 38.49 | 82.3 | nucleus | 732 |
| TcMADS13 | TCM_005818 | 8.51 | 42,280.27 | 375 | 42.75 | 101.09 | nucleus | 1128 |
| TcMADS14 | TCM_006323 | 9.42 | 28,732.02 | 254 | 52.22 | 62.24 | nucleus | 765 |
| TcMADS15 | TCM_006324 | 9.15 | 27,699.77 | 243 | 43.97 | 85.56 | nucleus | 732 |
| TcMADS16 | TCM_006325 | 5.42 | 24,228.12 | 218 | 45.89 | 55.96 | nucleus | 657 |
| TcMADS17 | TCM_007324 | 9.52 | 20,330.45 | 174 | 48.32 | 100.29 | chloroplast | 525 |
| TcMADS18 | TCM_007378 | 8.96 | 24,754.12 | 219 | 51.13 | 85.11 | chloroplast | 660 |
| TcMADS19 | TCM_007713 | 7.74 | 27,574.3 | 233 | 66.54 | 80.73 | chloroplast | 702 |
| TcMADS20 | TCM_007787 | 9.12 | 36,022.57 | 310 | 46.31 | 92.13 | nucleus | 933 |
| TcMADS21 | TCM_008703 | 8.5 | 29,428.29 | 258 | 46.99 | 82.79 | nucleus | 777 |
| TcMADS22 | TCM_008716 | 5.92 | 22,921.21 | 199 | 56.26 | 89.65 | nucleus | 600 |
| TcMADS23 | TCM_008973 | 9.39 | 8995.45 | 78 | 51.89 | 96.15 | chloroplast | 237 |
| TcMADS24 | TCM_011475 | 8.97 | 28,016.08 | 241 | 57.36 | 80.17 | nucleus | 726 |
| TcMADS25 | TCM_011478 | 6.61 | 27,447.96 | 240 | 58.38 | 73.62 | nucleus | 723 |
| TcMADS26 | TCM_011687 | 6.33 | 39,385.48 | 351 | 47.73 | 78.66 | nucleus | 1056 |
| TcMADS27 | TCM_012489 | 6.85 | 23,710.15 | 210 | 40.52 | 71.57 | nucleus | 633 |
| TcMADS28 | TCM_014051 | 6.13 | 41,766.39 | 370 | 51.46 | 77.22 | chloroplast | 1113 |
| TcMADS29 | TCM_014337 | 8.79 | 46,247.61 | 407 | 52.14 | 88.87 | nucleus | 1224 |
| TcMADS30 | TCM_014345 | 9.06 | 27,737.47 | 239 | 50.17 | 76.78 | nucleus | 720 |
| TcMADS31 | TCM_014661 | 9.83 | 24,429.07 | 210 | 55.07 | 86.33 | chloroplast | 633 |
| TcMADS32 | TCM_015044 | 8.82 | 27,249.02 | 236 | 53.76 | 86.78 | nucleus | 711 |
| TcMADS33 | TCM_015049 | 9.88 | 27,106.38 | 237 | 47.23 | 90.13 | chloroplast | 714 |
| TcMADS34 | TCM_015674 | 5.47 | 27,657.45 | 238 | 69.7 | 87.65 | nucleus | 717 |
| TcMADS35 | TCM_016147 | 9.24 | 24,830.39 | 215 | 63.31 | 73.95 | nucleus | 648 |
| TcMADS36 | TCM_017242 | 8.51 | 24,320.82 | 209 | 47.08 | 86.75 | nucleus | 630 |
| TcMADS37 | TCM_018979 | 9.07 | 27,740.63 | 243 | 34.06 | 85.14 | nucleus | 732 |
| TcMADS38 | TCM_018981 | 8.77 | 28,366.14 | 248 | 62.86 | 80.24 | nucleus | 747 |
| TcMADS39 | TCM_019362 | 8.23 | 30,811.58 | 267 | 58.24 | 70.15 | nucleus | 804 |
| TcMADS40 | TCM_021050 | 9.7 | 17,902.07 | 155 | 45.29 | 89.94 | chloroplast | 468 |
| TcMADS41 | TCM_022993 | 9.51 | 40,637.63 | 356 | 53.16 | 76.71 | chloroplast | 1071 |
| TcMADS42 | TCM_023006 | 9.2 | 38,815.19 | 354 | 58.36 | 70.54 | nucleus | 1065 |
| TcMADS43 | TCM_023041 | 8.93 | 38,451.37 | 354 | 59.01 | 69.49 | nucleus | 1065 |
| TcMADS44 | TCM_024579 | 6.04 | 28,901.4 | 252 | 61.39 | 85.48 | nucleus | 759 |
| TcMADS45 | TCM_025670 | 8.86 | 26,594.65 | 233 | 64.66 | 74.12 | chloroplast | 702 |
| TcMADS46 | TCM_025671 | 9.37 | 26,384.43 | 233 | 63.02 | 70.39 | nucleus | 702 |
| TcMADS47 | TCM_025674 | 9.64 | 16,948.73 | 150 | 36.03 | 79.4 | nucleus | 453 |
| TcMADS48 | TCM_025676 | 10.29 | 11,744.9 | 103 | 56.26 | 68.25 | chloroplast | 312 |
| TcMADS49 | TCM_026842 | 9.26 | 30,499 | 273 | 46.06 | 71.87 | nucleus | 822 |
| TcMADS50 | TCM_026845 | 9.47 | 23,787.52 | 207 | 49.15 | 78.74 | chloroplast | 624 |
| TcMADS51 | TCM_029234 | 4.91 | 19,812.05 | 174 | 42.71 | 76.21 | nucleus | 525 |
| TcMADS52 | TCM_029518 | 9.52 | 20,156.2 | 182 | 44.45 | 79.84 | chloroplast | 549 |
| TcMADS53 | TCM_029519 | 9.64 | 49,499.24 | 437 | 50.15 | 68.56 | nucleus | 1314 |
| TcMADS54 | TCM_029596 | 9.68 | 34,012.76 | 294 | 66.03 | 74.05 | nucleus | 885 |
| TcMADS55 | TCM_032402 | 9.25 | 13,764.45 | 132 | 34.38 | 60.68 | nucleus | 399 |
| TcMADS56 | TCM_032403 | 7.74 | 19,620.34 | 172 | 50.98 | 74.24 | chloroplast | 519 |
| TcMADS57 | TCM_034148 | 9.08 | 26,051.7 | 225 | 33.21 | 88.36 | chloroplast | 678 |
| TcMADS58 | TCM_034501 | 7.64 | 25,504.16 | 227 | 55.81 | 91.06 | nucleus | 684 |
| TcMADS59 | TCM_034549 | 9.62 | 21,512.84 | 184 | 50.3 | 88.42 | chloroplast | 555 |
| TcMADS60 | TCM_034757 | 5.45 | 37,593.54 | 333 | 59.52 | 84.83 | nucleus | 1002 |
| TcMADS61 | TCM_034970 | 5.26 | 38,476.16 | 337 | 60.18 | 82.43 | nucleus | 1014 |
| TcMADS62 | TCM_035212 | 8.87 | 24,432.87 | 209 | 61.75 | 78.42 | nucleus | 630 |
| TcMADS63 | TCM_036473 | 9.34 | 18,742.04 | 162 | 41.19 | 99.38 | chloroplast | 489 |
| TcMADS64 | TCM_036541 | 9.43 | 25,550.24 | 222 | 61.61 | 91.4 | chloroplast | 669 |
| TcMADS65 | TCM_036568 | 9.52 | 23,170.78 | 203 | 56.62 | 87 | nucleus | 612 |
| TcMADS66 | TCM_037394 | 9.62 | 21,551.01 | 186 | 42.9 | 92.31 | chloroplast | 561 |
| TcMADS67 | TCM_040735 | 9.76 | 24,088.7 | 214 | 39.18 | 87.01 | chloroplast | 645 |
| TcMADS68 | TCM_042799 | 4.84 | 26,046.39 | 233 | 57.5 | 68.28 | nucleus | 702 |
| TcMADS69 | TCM_042848 | 4.81 | 26,121.69 | 233 | 55.41 | 75.41 | nucleus | 702 |
| Tandem Duplicated Gene Pairs | Chromosome | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TcMADS43&TcMADS42 | ChrV | 0.108301 | 0.103758 | 1.04379 |
| TcMADS43&TcMADS41 | ChrV | 0.213254 | 0.170408 | 1.25143 |
| TcMADS42&TcMADS41 | ChrV | 0.215878 | 0.236528 | 0.912695 |
| TcMADS49&TcMADS50 | ChrV | 0.098915 | 0.237876 | 0.415826 |
| TcMADS45&TcMADS46 | ChrV | 0.078058 | 0.111367 | 0.700902 |
| TcMADS68&TcMADS69 | ChrII | 0.035449 | 0.086453 | 0.410042 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Hou, S.; Sun, Z.; Chen, J.; Meng, J.; Liang, D.; Wu, R.; Guo, Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the MADS-Box Gene Family in Theobroma cacao. Genes 2021, 12, 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111799
Zhang Q, Hou S, Sun Z, Chen J, Meng J, Liang D, Wu R, Guo Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the MADS-Box Gene Family in Theobroma cacao. Genes. 2021; 12(11):1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111799
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qianqian, Sijia Hou, Zhenmei Sun, Jing Chen, Jianqiao Meng, Dan Liang, Rongling Wu, and Yunqian Guo. 2021. "Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the MADS-Box Gene Family in Theobroma cacao" Genes 12, no. 11: 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111799
APA StyleZhang, Q., Hou, S., Sun, Z., Chen, J., Meng, J., Liang, D., Wu, R., & Guo, Y. (2021). Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the MADS-Box Gene Family in Theobroma cacao. Genes, 12(11), 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111799





