The Influences of Bioinformatics Tools and Reference Databases in Analyzing the Human Oral Microbial Community
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatic and Statistical Analysis
2.4. Reference Databases
2.5. Data Availability
3. Results
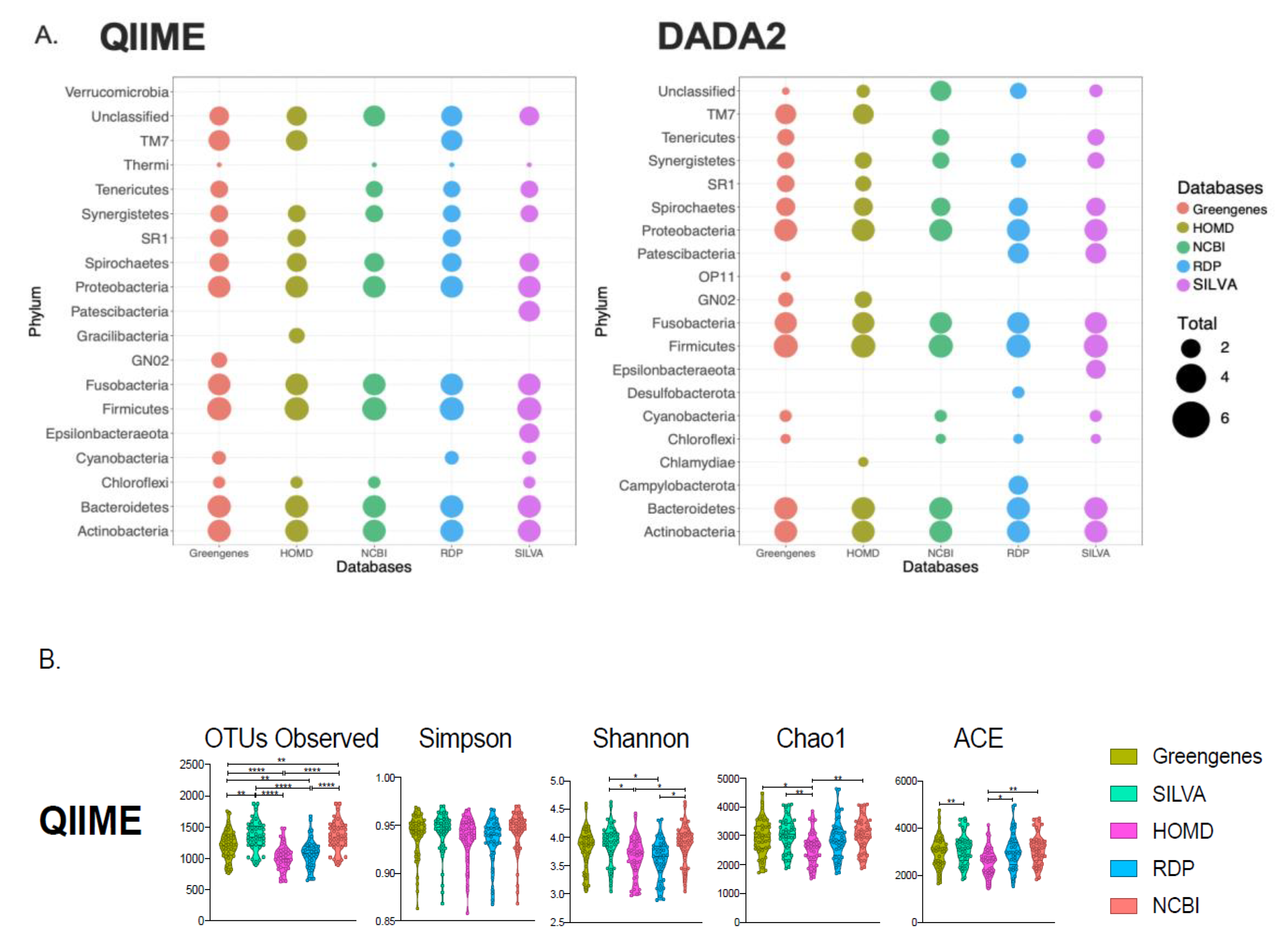
3.1. Comparisons of Taxonomic Composition and Diversity from Different Databases
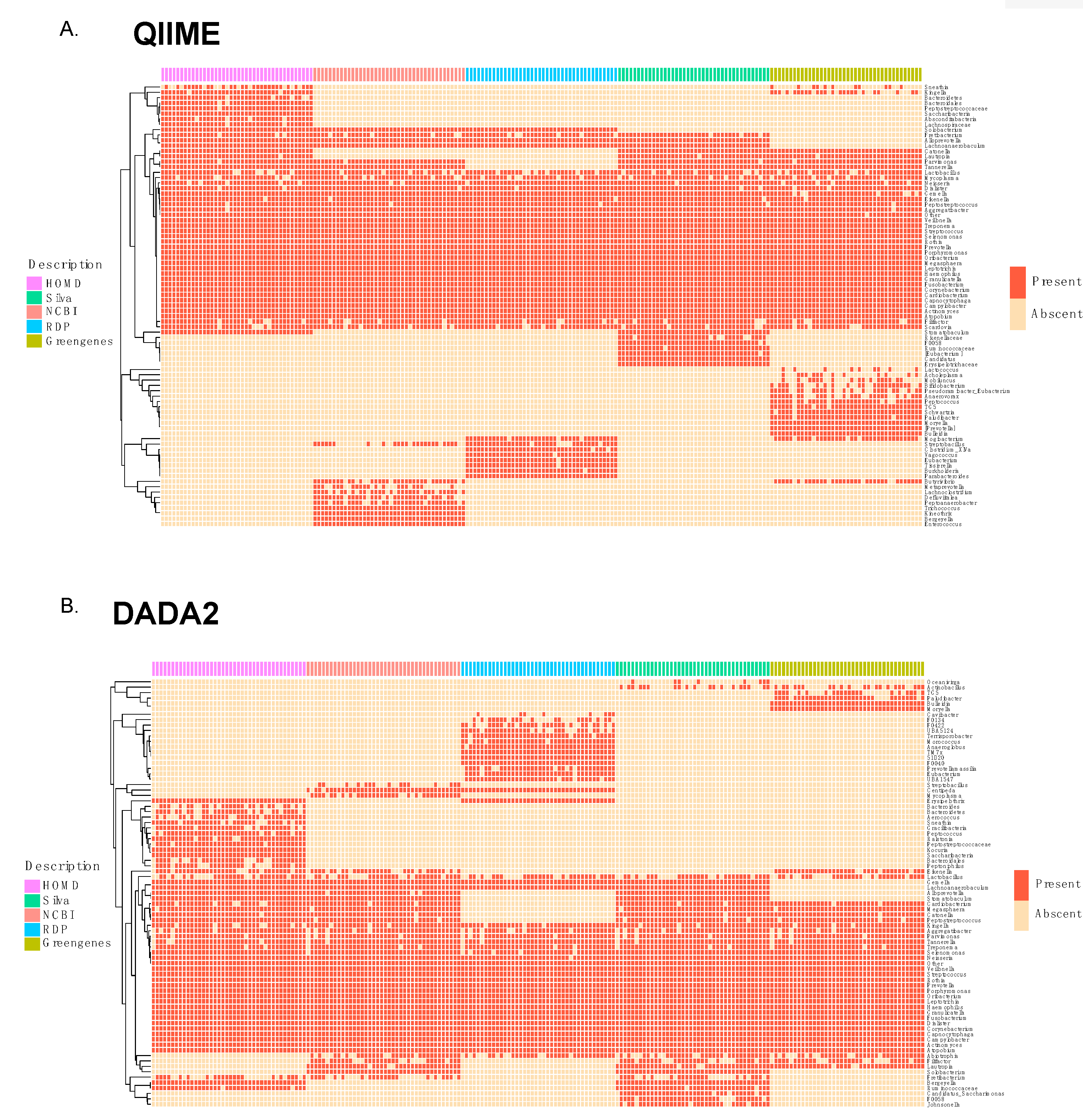
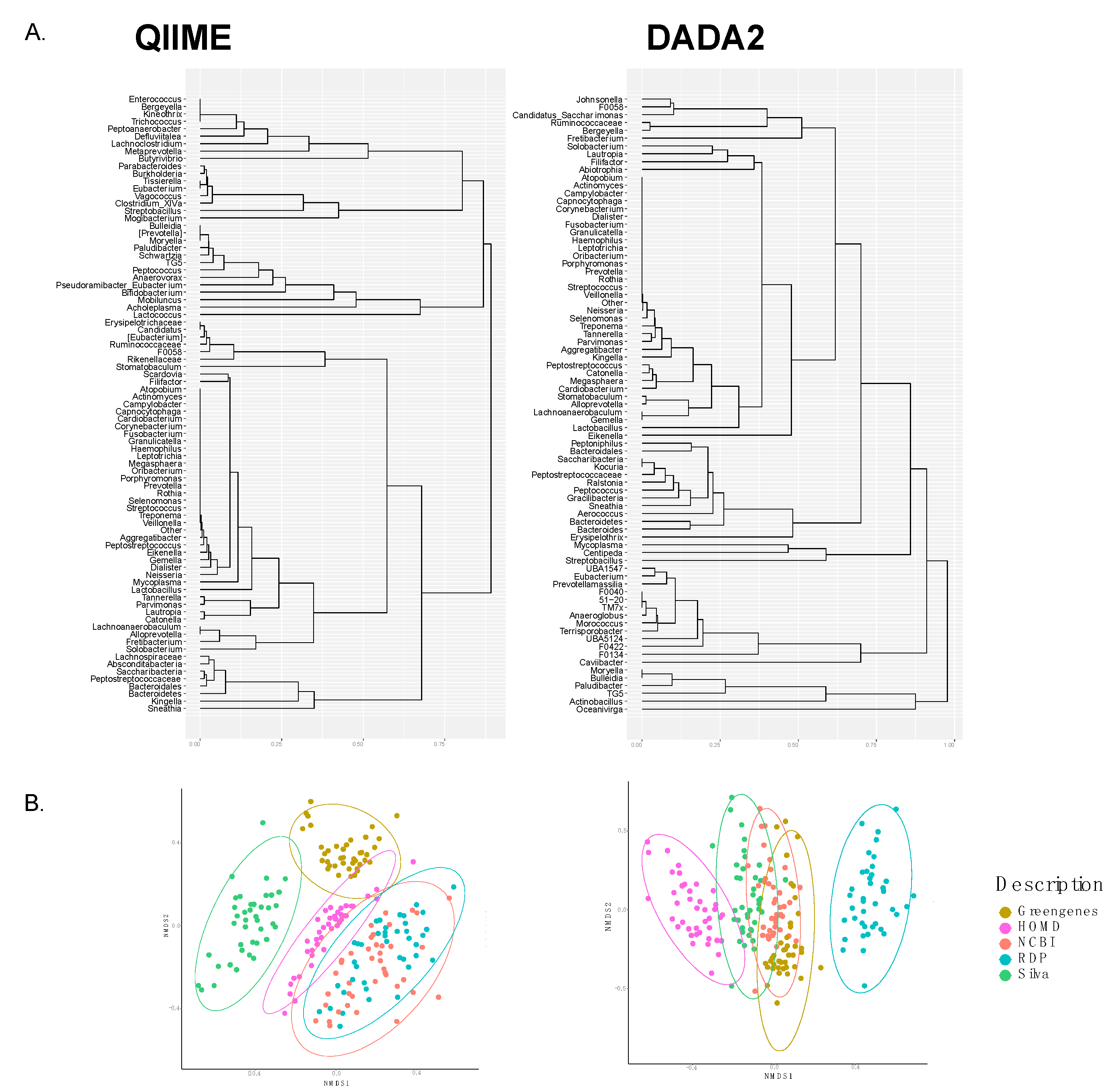
3.2. Comparison of Taxonomic Annotation at Genus Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pollock, J.; Glendinning, L.; Wisedchanwet, T.; Watson, M. The Madness of Microbiome: Attempting To Find Consensus “Best Practice” for 16S Microbiome Studies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The Human Microbiome Project. Nature 2007, 449, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Rani, A.; Metwally, A.; McGee, H.S.; Perkins, D.L. Analysis of the Microbiome: Advantages of Whole Genome Shotgun Versus 16s Amplicon Sequencing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Teng, J.L.; Tse, H.; Yuen, K.Y. Then and Now: Use of 16s Rdna Gene Sequencing for Bacterial Identification and Discovery of Novel Bacteria in Clinical Microbiology Laboratories. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 908–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belizario, J.E.; Napolitano, M. Human Microbiomes and their Roles in Dysbiosis, Common Diseases, and Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, M.A.; Schloss, P.D. The Impact of DNA Polymerase and Number of Rounds of Amplification in PCR on 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Data. mSphere 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amore, R.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Schirmer, M.; Kenny, J.G.; Gregory, R.; Darby, A.C.; Shakya, M.; Podar, M.; Quince, C.; Hall, N. A Comprehensive Benchmarking Study of Protocols and Sequencing Platforms for 16S rRNA Community Profiling. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golob, J.L.; Margolis, E.; Hoffman, N.G.; Fredricks, D.N. Evaluating the Accuracy of Amplicon-Based Microbiome Computational Pipelines on Simulated Human Gut Microbial Communities. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Accuracy of Taxonomy Prediction for 16S rRNA and Fungal ITS Sequences. Peer J. 2018, 6, e4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, E.; Twin, J.; Bulach, D.M.; Garland, S.M.; Tabrizi, S.N. A Comparison of Three Bioinformatics Pipelines for the Analysis of Preterm Gut Microbiota Using 16s rRNA Gene Sequencing Data. J. Proteomics Bioinform. 2015, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; I Gordon, J.; et al. QIIME Allows Analysis of High-Throughput Community Sequencing Data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilakanta, H.; Drews, K.L.; Firrell, S.; Foulkes, M.; Jablonski, K.A. A Review of Software for Analyzing Molecular Sequences. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.J.; Callahan, B.J.; Fisher, D.S.; Holmes, S.P. Denoising PCR-Amplified Metagenome Data. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D. Reintroducing Mothur: 10 Years Later. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysara, M.; Njima, M.; Leys, N.; Raes, J.; Monsieurs, P. From Reads to Operational Taxonomic Units: An Ensemble Processing Pipeline for Miseq Amplicon Sequencing Data. Gigascience 2017, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Carlsen, T.; Mevik, B.-H.; Enger, P.; Blaalid, R.; Shalchian-Tabrizi, K.; Kauserud, H. CLOTU: An Online Pipeline for Processing and Clustering of 454 Amplicon Reads into Otus Followed by Taxonomic Annotation. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, F.; Tadeo, R.; Voigt, A.Y.; Bork, P.; Raes, J. LotuS: An Efficient and User-Friendly OTU Processing Pipeline. Microbiome 2014, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.J.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An Improved Greengenes Taxonomy with Explicit Ranks for Ecological and Evolutionary Analyses of Bacteria and Archaea. ISME J. 2011, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidak, B.L.; Cole, J.R.; Lilburn, T.G.; Parker, C.T.J.; Saxman, P.R.; Stredwick, J.M.; Garrity, G.M.; Li, B.; Olsen, G.J.; Pramanik, S.; et al. The RDP (Ribosomal Database Project) Continues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federhen, S. The NCBI Taxonomy Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D136–D143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balvociute, M.; Huson, D.H. SILVA, RDP, Greengenes, NCBI and OTT—How Do These Taxonomies Compare? BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” Taxonomic Frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Cochrane, G.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I. International Nucleotide Sequence Database C: The International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D21–D24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, A Chimera-Checked 16s rRNA Gene Database and Workbench Compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chen, T.; Izard, J.; Paster, B.J.; Tanner, A.C.R.; Yu, W.-H.; Lakshmanan, A.; Wade, W.G. The Human Oral Microbiome. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5002–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, W.G. The Oral Microbiome in Health and Disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Hayes, R.B. Oral Microbiome and Oral and Gastrointestinal Cancer Risk. Cancer Causes Controle 2012, 23, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, P.; Eslami, H.; Yousefi, M.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Aghazadeh, M.; Kafil, H.S. Role of Oral Microbiome on Oral Cancers, A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Wu, J.; Peters, B.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Purdue, M.P.; Abnet, C.C.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Miller, G.; et al. Human Oral Microbiome and Prospective Risk for Pancreatic Cancer: A Population-Based Nested Case-Control Study. Gut 2018, 67, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escapa, I.F.; Chen, T.; Huang, Y.; Gajare, P.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Lemon, K.P. New Insights into Human Nostril Microbiome from the Expanded Human Oral Microbiome Database (eHOMD): A Resource for the Microbiome of the Human Aerodigestive Tract. mSystems 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, G.F.; Paulpillai, M.; Evans, R.J.; Singleton, E.G.; Heishman, S.J. Breath Carbon Monoxide and Semiquantitative Saliva Cotinine as Biomarkers for Smoking. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2010, 25, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, P.I.; Dye, B.A.; Wei, L.; Slade, G.D.; Thornton-Evans, G.O.; Beck, J.D.; Taylor, G.W.; Borgnakke, W.S.; Page, R.C.; Genco, R.J. Self-Reported Measures for Surveillance of Periodontitis. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Pirrung, M.; McCue, L.A. FQC Dashboard: Integrates FastQC Results into a Web-Based, Interactive, and Extensible Fastq Quality Control Tool. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3137–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didion, J.P.; Martin, M.; Collins, F.S. Atropos: Specific, Sensitive, and Speedy Trimming of Sequencing Reads. Peer J. 2017, 5, e3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, D.; Jude, B.A.; Lamendella, R.; Keesing, F.; Perron, G.G. Exposure to Arsenic Alters the Microbiome of Larval Zebrafish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, A Package of R Functions for Community Ecology. J. Vegetation Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingsdag, S.; Nelson, S.; Coleman, N.V. Bacterial Communities Associated with Apical Periodontitis and Dental Implant Failure. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2016, 27, 31307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SILVA rRNA Database Project. Available online: https://www.arb-silva.de/browser/lsu/CP002345 (accessed on 11 July 2020).
- Trembath-Reichert, E.; Butterfield, D.A.; Huber, J.A. Active Subseafloor Microbial Communities from Mariana Back-Arc Venting Fluids Share Metabolic Strategies Across Different Thermal Niches and Taxa. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2264–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.L.; Bor, B.; Agnello, M.; Shi, W.; He, X. Ecology of the Oral Microbiome: Beyond Bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, T.; Campos, M.D.; Lucic-Mercy, E.; Arnholdt-Schmitt, B. Misannotation Awareness: A Tale of Two Gene-Groups. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritari, J.; Salojärvi, J.; Lahti, L.; de Vos, W.M. Improved Taxonomic Assignment of Human Intestinal 16S rRNA Sequences by a Dedicated Reference Database. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, R.; Myers, G.S.A.; Tettelin, H.; Eisen, J.A.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Dodson, R.J.; Davidsen, T.M.; DeBoy, R.T.; Fouts, D.E.; Haft, D.H.; et al. Comparison of the Genome of the Oral Pathogen Treponema denticola with Other Spirochete Genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5646–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizova, M.V.; Muller, P.; Panikov, N.; Mandalakis, M.; Hohmann, T.; Hazen, A.; Fowle, W.; Prozorov, T.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Epstein, S. Stomatobaculum Longum Gen. Nov., sp. Nov., an Obligately Anaerobic Bacterium from the Human Oral Cavity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1450–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.; Chamberlain, L.M.; Schofield, K.M.; Wells, J.M.; Le Page, R.W. Oral Vaccination of Mice Against Tetanus with Recombinant Lactococcus Lactis. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downes, J.; Olsvik, B.; Hiom, S.J.; Spratt, D.A.; Cheeseman, S.L.; Olsen, I.; Weightman, A.J.; Wade, W. Bulleidia extructa gen. nov., sp. nov., Isolated from the Oral Cavity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Ahmad, A.; Pelz, K.; Schirrmeister, J.F.; Hellwig, E.; Pukall, R. Characterization of the First Oral Vagococcus Isolate from a Root-Filled Tooth with Periradicular Lesions. Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, M.R.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Camerlengo, T.; Joshi, V.M.; Kumar, P.S. Deep Sequencing Identifies Ethnicity-Specific Bacterial Signatures in the Oral Microbiome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, M.A.; Bhattacharya, C.; Ryon, K.; Meierovich, S.; Shaaban, H.; Westfall, D.; Mohammad, R.; Kuchin, K.; Afshinnekoo, E.; Danko, D.C.; et al. The Microbe Directory v2.0: An Expanded Database of Ecological and Phenotypical Features of Microbes. BioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Chuvochina, M.; Waite, D.W.; Rinke, C.; Skarshewski, A.; Chaumeil, P.A.; Hugenholtz, P. A Standardized Bacterial Taxonomy Based on Genome Phylogeny Substantially Revises the Tree of Life. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allali, I.; Arnold, J.W.; Roach, J.; Cadenas, M.B.; Butz, N.; Hassan, H.M.; Koci, M.D.; Ballou, A.; Mendoza, M.; Ali, R.; et al. A Comparison of Sequencing Platforms and Bioinformatics Pipelines for Compositional Analysis of the Gut Microbiome. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas-Molina, J.A.; Peralta-Sánchez, J.M.; González, A.; McMurdie, P.J.; Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ursell, L.K.; Lauber, C.; Zhou, H.; Song, S.J.; et al. Chapter Nineteen—Advancing Our Understanding of the Human Microbiome Using QIIME. In Methods in Enzymology; DeLong, E.F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 531, pp. 371–444. [Google Scholar]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human Gut Microbiome Viewed Across Age and Geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sierra, M.A.; Li, Q.; Pushalkar, S.; Paul, B.; Sandoval, T.A.; Kamer, A.R.; Corby, P.; Guo, Y.; Ruff, R.R.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; et al. The Influences of Bioinformatics Tools and Reference Databases in Analyzing the Human Oral Microbial Community. Genes 2020, 11, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11080878
Sierra MA, Li Q, Pushalkar S, Paul B, Sandoval TA, Kamer AR, Corby P, Guo Y, Ruff RR, Alekseyenko AV, et al. The Influences of Bioinformatics Tools and Reference Databases in Analyzing the Human Oral Microbial Community. Genes. 2020; 11(8):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11080878
Chicago/Turabian StyleSierra, Maria A., Qianhao Li, Smruti Pushalkar, Bidisha Paul, Tito A. Sandoval, Angela R. Kamer, Patricia Corby, Yuqi Guo, Ryan Richard Ruff, Alexander V. Alekseyenko, and et al. 2020. "The Influences of Bioinformatics Tools and Reference Databases in Analyzing the Human Oral Microbial Community" Genes 11, no. 8: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11080878
APA StyleSierra, M. A., Li, Q., Pushalkar, S., Paul, B., Sandoval, T. A., Kamer, A. R., Corby, P., Guo, Y., Ruff, R. R., Alekseyenko, A. V., Li, X., & Saxena, D. (2020). The Influences of Bioinformatics Tools and Reference Databases in Analyzing the Human Oral Microbial Community. Genes, 11(8), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11080878




