A Minimal Genetic Passkey to Unlock Many Legume Doors to Root Nodulation by Rhizobia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids and Growth Conditions
2.2. Assembly of Mini Symbiotic Plasmids
2.3. Plant Assays and Analysis of Root Nodules
2.4. Detection of Plant Immune Responses
2.5. qPCR-Based Determination of pMiniSym2 Copy Number
3. Results
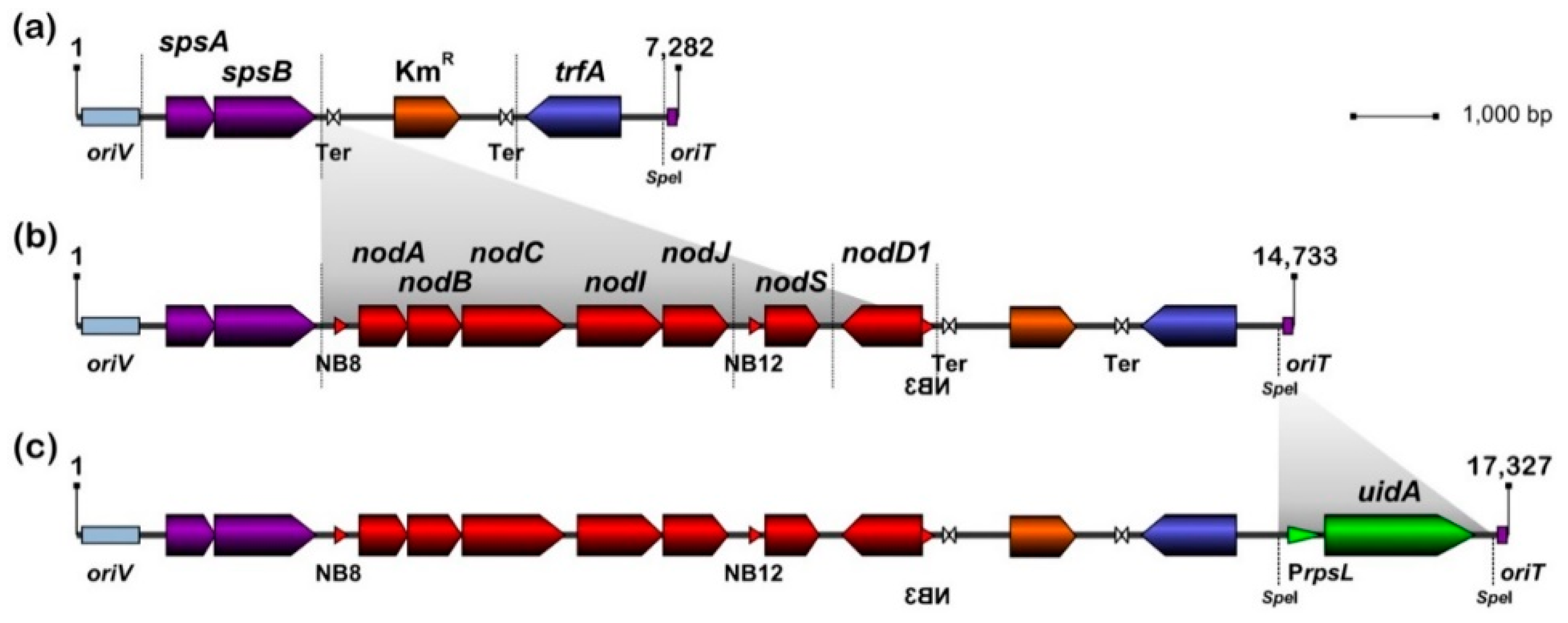
3.1. Design and Assembly of pMiniSym1, pMiniSym2 and pMiniSym2-Gus Replicons
3.2. pMiniSym2 Is Maintained as a Low-Copy Replicon in ANU265
3.3. pMiniSym2 Confers Nodulation to ANU265 Transconjugants
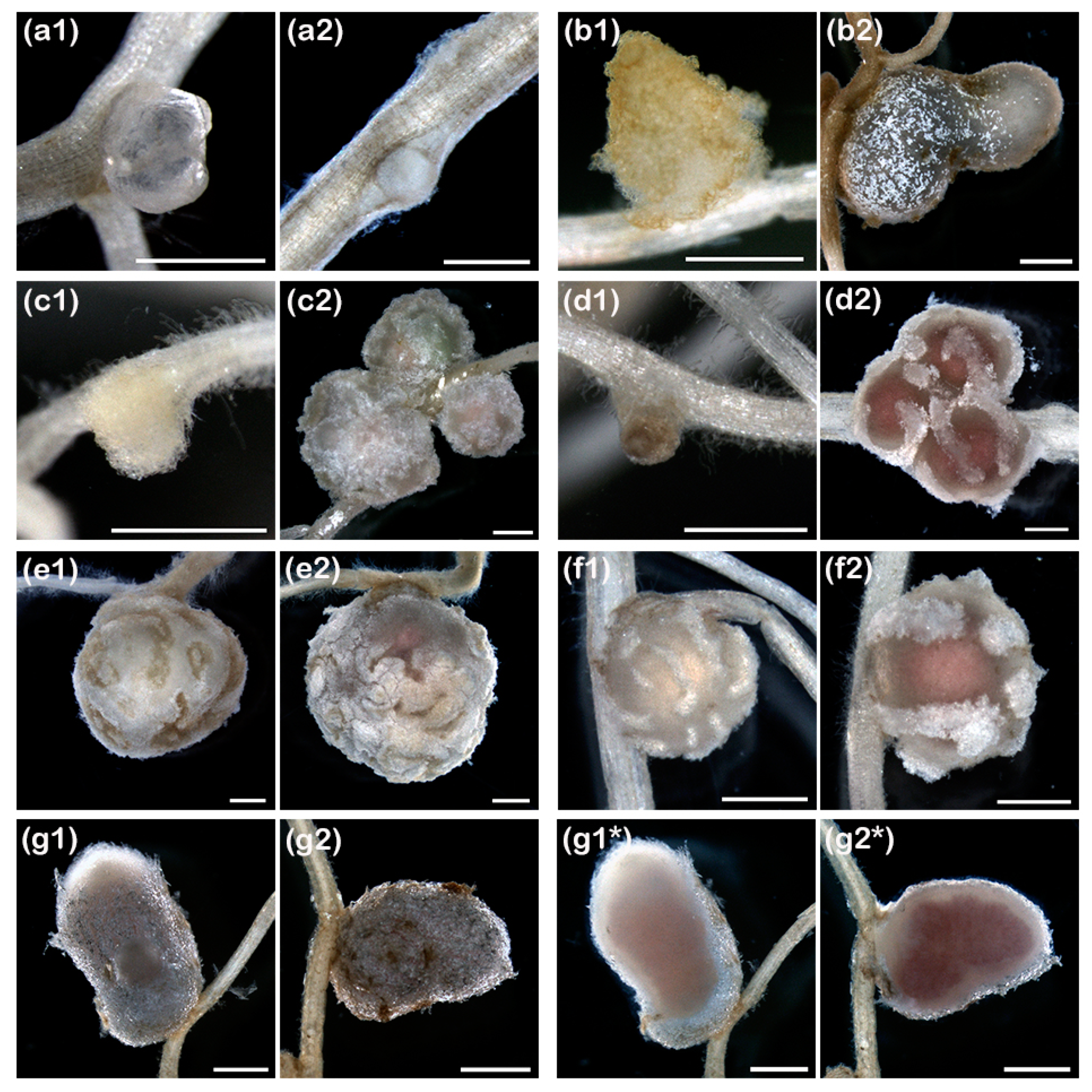
3.4. On Several Legume Hosts, pMiniSym2 Allows ANU265 to Reach Nodule Cells
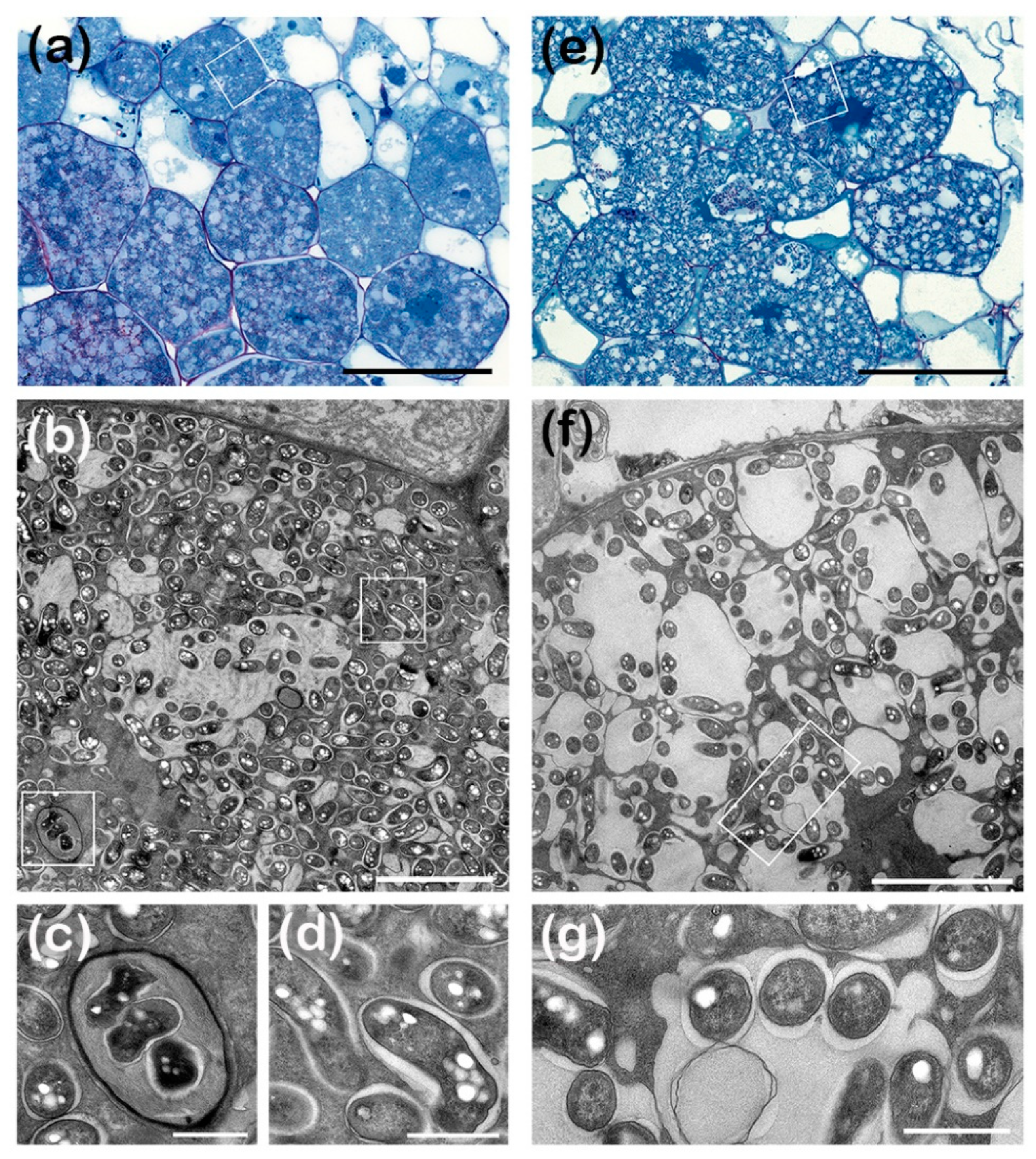
3.5. ANU265::pMiniSym2 Establishes Intracellular Colonies in L. leucocephala Nodule Cells
3.6. Infection of Cowpea and Siratro Nodules by ANU265::pMiniSym2 is Countered by Plant Immune Responses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gresshoff, P.M.; Hayashi, S.; Biswas, B.; Mirzaei, S.; Indrasumunar, A.; Reid, D.; Samuel, S.; Tollenaere, A.; van Hameren, B.; Hastwell, A.; et al. The value of biodiversity in legume symbiotic nitrogen fixation and nodulation for biofuel and food production. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 172, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldroyd, G.E.; Murray, J.D.; Poole, P.S.; Downie, J.A. The rule of engagement in the legume-rhizobial symbiosis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2011, 45, 119–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gage, D.J. Infection and invasion of roots by symbiotic, nitrogen-fixing rhizobia during nodulation of temperate legumes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 280–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downie, J.A. Legume nodulation. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R184–R190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, L.E.; Jeon, K.W.; Stacey, G. Homology in endosymbiotic systems: The term ‘symbiosome’. In Molecular Genetics of Plant-Microbe Interactions; Palacios, R.A.V.D.P.S., Ed.; APS Press: St-Paul, MN, USA, 1988; pp. 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Halane, M.K.; Gassmann, W.; Stacey, G. The role of plant innate immunity in the Legume-Rhizobium symbiosis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2017, 68, 535–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourion, B.; Berrabah, F.; Ratet, P.; Stacey, G. Rhizobium-legume symbioses: The crucial role of plant immunity. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotocka, B.; Kopcińska, J.; Skalniak, M. The meristem in indeterminate root nodules of Faboideae. Symbiosis 2012, 58, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.T.; Schilderink, S.; Moling, S.; Deinum, E.E.; Kondorosi, É.; Franssen, H.; Kulikova, O.; Niebel, A.; Bisseling, T. Fate map of Medicago truncatula root nodules. Development 2014, 141, 3517–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G. The Evolution of Determinate and Indeterminate Nodules Withing the Papilionoideae Subfamily. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gibson, K.E.; Kobayashi, H.; Walker, G.C. Molecular determinants of a symbiotic chronic infection. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 413–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldroyd, G.E.; Downie, J.A. Coordinating nodule morphogenesis with rhizobial infection in legumes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 519–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, W.J.; Jabbouri, S.; Perret, X. Keys to symbiotic harmony. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 5641–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, P.; Ramachandran, V.; Terpolilli, J. Rhizobia: From saprophytes to endosymbionts. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, J.E.; Zhu, H.Y. Genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying symbiotic specificity in legume-Rhizobium interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perret, X.; Staehelin, C.; Broughton, W.J. Molecular basis of symbiotic promiscuity. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 180–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, J.T.; Long, S.R. Induction of Rhizobium meliloti nodC expression by plant exudate requires nodD. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 6609–6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaink, H.P.; Wijffelman, C.A.; Pees, E.; Okker, R.J.H.; Lugtenberg, B.J.J. Rhizobium nodulation gene nodD as a determinant of host specificity. Nature 1987, 328, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerouge, P.; Roche, P.; Faucher, C.; Maillet, F.; Truchet, G.; Promé, J.C.; Dénarié, J. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature 1990, 344, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Haeze, W.; Holsters, M. Nod factor structures, responses, and perception during initiation of nodule development. Glycobiology 2002, 12, 79r–105r. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaink, H.P.; Wijfjes, A.H.M.; Lugtenberg, B.J.J. Rhizobium NodI and NodJ proteins play a role in the efficiency of secretion of lipochitin oligosaccharides. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 6276–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, L.; Dominguez, J.; Santana, O.; Quinto, C. The role of the nodI and nodJ genes in the transport of Nod metabolites in Rhizobium etli. Gene 1996, 173, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lopez, M.; D’Haeze, W.; Mergaert, P.; Verplancke, C.; Promé, J.-C.; van Montagu, M.; Holsters, M. Role of nodI and nodJ in lipochitooligosaccharide secretion in Azorhizobium caulinodans and Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 20, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demont-Caulet, N.; Maillet, F.; Tailler, D.; Jacquinet, J.C.; Promé, J.C.; Nicolaou, K.C.; Truchet, G.; Beau, J.M.; Dénarié, J. Nodule-inducing activity of synthetic Sinorhizobium meliloti nodulation factors and related lipo-chitooligosaccharides on alfalfa. Importance of the acyl chain structure. Plant Physiol. 1999, 120, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relić, B.; Perret, X.; Estrada-Garcia, M.T.; Kopcińska, J.; Golinowski, W.; Krishnan, H.B.; Pueppke, S.G.; Broughton, W.J. Nod factors of Rhizobium are a key to the legume door. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 13, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Haeze, W.; Gao, M.; De Rycke, R.; van Montagu, M.; Engler, G.; Holsters, M. Roles for azorhizobial Nod factors and surface polysaccharides in intercellular invasion and nodule penetration, respectively. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 1998, 11, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Broghammer, A.; Krusell, L.; Blaise, M.; Sauer, J.; Sullivan, J.T.; Maolanon, N.; Vinther, M.; Lorentzen, A.; Madsen, E.B.; Jensen, K.J.; et al. Legume receptors perceive the rhizobial lipochitin oligosaccharide signal molecules by direct binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13859–13864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.; Radutoiu, S.; Stougaard, J. Legume LysM receptors mediate symbiotic and pathogenic signalling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 39, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limpens, E.; van Zeijl, A.; Geurts, R. Lipochitooligosaccharides modulate plant host immunity to enable endosymbioses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemberg, G.V.; Kamst, E.; Harteveld, M.; Vanderdrift, K.M.G.M.; Haverkamp, J.; Thomasoates, J.E.; Lugtenberg, B.J.J.; Spaink, H.P. A central domain of Rhizobium NodE protein mediates host-specificity by determining the hydrophobicity of fatty acyl moieties of nodulation factors. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 16, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmin, J.L.; Wilson, K.E.; Carlson, R.W.; Davies, A.E.; Downie, J.A. Resistance to nodulation of cv. Afghanistan peas is overcome by nodX, which mediates an O-acetylation of the Rhizobium leguminosarum lipo-oligosaccharide nodulation factor. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 10, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, A.; Cervantes, E.; Wong, C.-H.; Broughton, W.J. nodSU, two new nod genes of the broad host range Rhizobium strain NGR234 encode host-specific nodulation of the tropical tree Leucaena leucocephala. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 1990, 3, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radutoiu, S.; Madsen, L.H.; Madsen, E.B.; Jurkiewicz, A.; Fukai, E.; Quistgaard, E.M.; Albrektsen, A.S.; James, E.K.; Thirup, S.; Stougaard, J. LysM domains mediate lipochitin-oligosaccharide recognition and Nfr genes extend the symbiotic host range. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3923–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deakin, W.J.; Broughton, W.J. Symbiotic use of pathogenic strategies: Rhizobial protein secretion systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staehelin, C.; Krishnan, H.B. Nodulation outer proteins: Double-edged swords of symbiotic rhizobia. Biochem. J. 2015, 470, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, S.; Tittabutr, P.; Teulet, A.; Thouin, J.; Fardoux, J.; Chaintreuil, C.; Gully, D.; Arrighi, J.F.; Furuta, N.; Miwa, H.; et al. Rhizobium-legume symbiosis in the absence of Nod factors: Two possible scenarios with or without the T3SS. ISME J. 2016, 10, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teulet, A.; Busset, N.; Fardoux, J.; Gully, D.; Chaintreuil, C.; Cartieaux, F.; Jauneau, A.; Comorge, V.; Okazaki, S.; Kaneko, T.; et al. The rhizobial type III effector ErnA confers the ability to form nodules in legumes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 21758–21768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaharada, Y.; Nielsen, M.W.; Kelly, S.; James, E.K.; Andersen, K.R.; Rasmussen, S.R.; Fuchtbauer, W.; Madsen, L.H.; Heckmann, A.B.; Radutoiu, S.; et al. Differential regulation of the Epr3 receptor coordinates membrane-restricted rhizobial colonization of root nodule primordia. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.J.; Muszynski, A.; Kawaharada, Y.; Hubber, A.M.; Sullivan, J.T.; Sandal, N.; Carlson, R.W.; Stougaard, J.; Ronson, C.W. Conditional requirement for exopolysaccharide in the Mesorhizobium-Lotus symbiosis. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2013, 26, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fred, E.B.; Baldwin, I.L.; McCoy, E. Root Nodule Bacteria and Leguminous Plants; University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Pueppke, S.G.; Broughton, W.J. Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234 and R. fredii USDA257 share exceptionally broad, nested host ranges. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 1999, 12, 293–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, W.J.; Heycke, N.; Meyer, z.A.H.; Pankhurst, C.E. Plasmid linked nif and nod genes in fast-growing rhizobia that nodulate Glycine max, Psophocarpus tetragonolobus, and Vigna unguiculata. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, X.; Broughton, W.J.; Brenner, S. Canonical ordered cosmid library of the symbiotic plasmid of Rhizobium species NGR234. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 1923–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeisser, C.; Liesegang, H.; Krysciak, D.; Bakkou, N.; Le Quéré, A.; Wollherr, A.; Heinemeyer, I.; Morgenstern, B.; Pommerening-Röser, A.; Flores, M.; et al. Rhizobium sp. NGR234 possesses a remarkable number of secretion systems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4035–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiberg, C.; Fellay, R.; Bairoch, A.; Broughton, W.J.; Rosenthal, A.; Perret, X. Molecular basis of symbiosis between Rhizobium and legumes. Nature 1997, 387, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, N.A.; Hau, C.Y.; Trinick, M.J.; Shine, J.; Rolfe, B.G. Heat curing of a Sym plasmid in a fast-growing Rhizobium sp. that is able to nodulate legumes and the nonlegume Parasponia sp. J. Bacteriol. 1983, 153, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Naciri-Graven, Y.; Broughton, W.J.; Perret, X. Flavonoids induce temporal shifts in gene-expression of nod-box controlled loci in Rhizobium sp. NGR234. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, X.; Freiberg, C.; Rosenthal, A.; Broughton, W.J.; Fellay, R. High-resolution transcriptional analysis of the symbiotic plasmid of Rhizobium sp. NGR234. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 32, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassam, B.J.; Djordjevic, M.A.; Redmond, J.W.; Batley, M.; Rolfe, B.G. Identification of a nodD-dependent locus in the Rhizobium strain NGR234 activated by phenolic factors secreted by soybeans and other legumes. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 1988, 1, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, G.L.; Nayudu, M.; Strange, K.K.L.; Rolfe, B.G. The nodD1 gene from Rhizobium strain NGR234 is a key determinant in the extension of host range to the nonlegume Parasponia. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 1988, 1, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, N.P.; Talmont, F.; Wieruszeski, J.M.; Promé, D.; Promé, J.C. Structural determination of symbiotic nodulation factors from the broad host-range Rhizobium species NGR234. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 289, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viprey, V.; Del Greco, A.; Golinowski, W.; Broughton, W.J.; Perret, X. Symbiotic implications of type III protein secretion machinery in Rhizobium. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, W.J.; Hanin, M.; Relić, B.; Kopcińska, J.; Golinowski, W.; Simsek, S.; Ojanen-Reuhs, T.; Reuhs, B.; Marie, C.; Kobayashi, H.; et al. Flavonoid-inducible modifications to rhamnan O antigens are necessary for Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234-legume symbioses. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3654–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbour University Press: Cold Spring Harbour, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Beringer, J.E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1974, 84, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, W.J.; Wong, C.H.; Lewin, A.; Samrey, U.; Myint, H.; Meyer, z.A.H.; Dowling, D.N.; Simon, R. Identification of Rhizobium plasmid sequences involved in recognition of Psophocarpus, Vigna, and other legumes. J. Cell Biol. 1986, 102, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, D.G.; Young, L.; Chuang, R.Y.; Venter, J.C.; Hutchison, C.A., 3rd; Smith, H.O. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figurski, D.H.; Helinski, D.R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 1648–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumeaux, C.; Bakkou, N.; Kopcińska, J.; Golinowski, W.; Westenberg, D.J.; Müller, P.; Perret, X. Functional analysis of the nifQdctA1y4vGHIJ operon of Sinorhizobium fredii strain NGR234 using a transposon with a NifA-dependent read-out promoter. Microbiology 2011, 157, 2745–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, W.J.; Dilworth, M.J. Control of leghaemoglobin synthesis in snake beans. Biochem. J. 1971, 125, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherni, A.E.; Perret, X. Deletion of rRNA operons of Sinorhizobium fredii strain NGR234 and impact on symbiosis with legumes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourcy, M.; Brocard, L.; Pislariu, C.I.; Cosson, V.; Mergaert, P.; Tadege, M.; Mysore, K.S.; Udvardi, M.K.; Gourion, B.; Ratet, P. Medicago truncatula DNF2 is a PI-PLC-XD-containing protein required for bacteroid persistence and prevention of nodule early senescence and defense-like reactions. New Phytologist 2013, 197, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasse, J.; de Billy, F.; Truchet, G. Abortion of infection during the Rhizobium meliloti-alfalfa symbiotic interaction is accompanied by a hypersensitive reaction. Plant J. 1993, 4, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Providenti, M.A.; O’Brien, J.M.; Ewing, R.J.; Paterson, E.S.; Smith, M.L. The copy-number of plasmids and other genetic elements can be determined by SYBR-Green-based quantitative real-time PCR. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 65, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Romero, M.A.; Soberón, N.; Pérez-Oseguera, A.; Téllez-Sosa, J.; Cevallos, M.A. Structural elements required for replication and incompatibility of the Rhizobium etli symbiotic plasmid. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 3117–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.D.; Gutterson, N. An efficient mobilizable cosmid vector, pRK7813, and its use in a rapid method for marker exchange in Pseudomonas fluorescens strain HV37a. Gene 1987, 61, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrecht, B.; Vanderleyden, J.; Michiels, J. Stable RK2-derived cloning vectors for the analysis of gene expression and gene function in Gram-negative bacteria. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2001, 14, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellay, R.; Frey, J.; Krisch, H. Interposon mutagenesis of soil and water bacteria: A family of DNA fragments designed for in vitro insertional mutagenesis of Gram-negative bacteria. Gene 1987, 52, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbouri, S.; Fellay, R.; Talmont, F.; Kamalaprija, P.; Burger, U.; Relić, B.; Promé, J.C.; Broughton, W.J. Involvement of nodS in N-methylation and nodU in 6-O-carbamoylation of Rhizobium sp. NGR234 Nod factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 22968–22973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkou, N. Characterization of the Endosymbiotic forms of Sinorhizobium sp. strain NGR234. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Geneva, Genevam, Switzerland, 2011. n°4286. [Google Scholar]
- Fossou, R.K.; Pothier, J.F.; Zézé, A.; Perret, X. Bradyrhizobium ivorense sp. nov. as a potential local bioinoculant for Cajanus cajan cultures in Côte d’Ivoire. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuberre, C.; Plancot, B.; Driouich, A.; Moore, J.P.; Bardor, M.; Gügi, B.; Vicré, M. Plant immunity is compartmentalized and specialized in roots. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.; Andrews, M.E. Specificity in legume-rhizobia symbioses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.M.; Kobayashi, H.; Davies, B.W.; Taga, M.E.; Walker, G.C. How rhizobial symbionts invade plants: The Sinorhizobium-Medicago model. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relić, B.; Staehelin, C.; Fellay, R.; Jabbouri, S.; Boller, T.; Broughton, W.J. Do Nod-factor levels play a role in host-specificity? In Proceeding of the 1st European Nitrogen Fixation Conference, Szeged, Hungary, 28 August–2 September 1994; pp. 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, W.; Tian, Y.; Xiong, J.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, R.J.; Li, H.M.; Wen, J.; Mysore, K.S.; et al. Role of the Nod factor hydrolase MtNFH1 in regulating Nod factor levels during rhizobial infection and in mature nodules of Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, C.; Deakin, W.J.; Viprey, V.; Kopciñska, J.; Golinowski, W.; Krishnan, H.B.; Perret, X.; Broughton, W.J. Characterisation of Nops, Nodulation outer proteins, secreted via the type III secretion system of NGR234. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, S.; Kaneko, T.; Sato, S.; Saeki, K. Hijacking of leguminous nodulation signaling by the rhizobial type III secretion system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17131–17136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Tang, F.; Gao, M.; Krishnan, H.B.; Zhu, H. R gene-controlled host specificity in the legume-rhizobia symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18735–18740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H. Rj4, a gene controlling nodulation specificity in soybeans, encodes a thaumatin-like protein but not the one previously reported. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadou, C.; Pascal, G.; Mangenot, S.; Glew, M.; Bontemps, C.; Capela, D.; Carrère, S.; Cruveiller, S.; Dossat, C.; Lajus, A.; et al. Genome sequence of the β-rhizobium Cupriavidus taiwanensis and comparative genomics of rhizobia. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, L.H.; Tirichine, L.; Jurkiewicz, A.; Sullivan, J.T.; Heckmann, A.B.; Bek, A.S.; Ronson, C.W.; James, E.K.; Stougaard, J. The molecular network governing nodule organogenesis and infection in the model legume Lotus japonicus. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voroshilova, V.A.; Demchenko, K.N.; Brewin, N.J.; Borisov, A.Y.; Tikhonovich, I.A. Initiation of a legume nodule with an indeterminate meristem involves proliferating host cells that harbour infection threads. New Phytologist 2009, 181, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Stacey, N.; Liu, C.W.; Wen, J.Q.; Mysore, K.S.; Torres-Jerez, I.; Vernié, T.; Tadege, M.; Zhou, C.N.; Wang, Z.Y.; et al. Rhizobial infection is associated with the development of peripheral vasculature in nodules of Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodpothong, P.; Sullivan, J.T.; Songsrirote, K.; Sumpton, D.; Cheung, K.W.J.T.; Thomas-Oates, J.; Radutoiu, S.; Stougaard, J.; Ronson, C.W. Nodulation gene mutants of Mesorhizobium loti R7A-nodZ and nolL mutants have host-specific phenotypes on Lotus spp. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Host Plant | Tribe | Nodule Type | ANU265:: pMiniSym2 | NGR234 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cajanus cajan (Lab 22) | Ph. | DN* | pNod | Nod+ |
| C. cajan cv. “Light Brown” | Ph. | DN* | pNod | Nod+ |
| Cicer arietinum cv. Nayer | Ci. | IDN | Nod− | Nod− |
| Crotalaria juncea | Co. | IDN | Nod− | Nod+ |
| Desmodium intortum | De. | DN | Nod− | Nod+ |
| Flemingia congesta | Ph. | DN | Nod+/− | Nod+ |
| Glycine canescens 007 | Ph. | DN | Nod− | Nod+ |
| Lablab purpureus | Ph. | DN | Nod+/− | Nod+ |
| Leucaena leucocephala | Mim. | IDN | Nod+ | Nod+ |
| Lotus corniculatus cv. Malejovsky | Lo. | DN | Nod− | Nod− |
| Lotus japonicus cv. Gifu | Lo. | DN | Nod− | Nod+ |
| Macroptilium atropurpureum cv. Siratro | Ph. | DN | Nod+ | Nod+ |
| Medicago sativa cv. Gemini | Tr. | IDN | Nod− | Nod− |
| Medicago truncatula cv. Jemalong | Tr. | IDN | Nod− | Nod− |
| Mimosa pudica | Mim. | IDN | Nod− | Nod− |
| Pachyrhizus tuberosus | Ph. | DN | Nod− | Nod+/− |
| Stylosanthes guianensis cv. Schofield | Ae. | ATN | pNod | pNod |
| Tephrosia vogelii | Mil. | DN* | pNod | Nod+ |
| Vigna radiata cv King | Ph. | DN | pNod | Nod+ |
| Vigna unguiculata cv. Blackeye | Ph. | DN | Nod+ | Nod+ |
| V. unguiculata cv. Kacang panjang | Ph. | DN | Nod+ | Nod+ |
| V. unguiculata cv. Red Caloona | Ph. | DN | Nod+ | Nod+ |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Unay, J.; Perret, X. A Minimal Genetic Passkey to Unlock Many Legume Doors to Root Nodulation by Rhizobia. Genes 2020, 11, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050521
Unay J, Perret X. A Minimal Genetic Passkey to Unlock Many Legume Doors to Root Nodulation by Rhizobia. Genes. 2020; 11(5):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050521
Chicago/Turabian StyleUnay, Jovelyn, and Xavier Perret. 2020. "A Minimal Genetic Passkey to Unlock Many Legume Doors to Root Nodulation by Rhizobia" Genes 11, no. 5: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050521
APA StyleUnay, J., & Perret, X. (2020). A Minimal Genetic Passkey to Unlock Many Legume Doors to Root Nodulation by Rhizobia. Genes, 11(5), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050521





