Excitability of Neural Activity is Enhanced, but Neural Discrimination of Odors is Slightly Decreased, in the Olfactory Bulb of Fasted Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
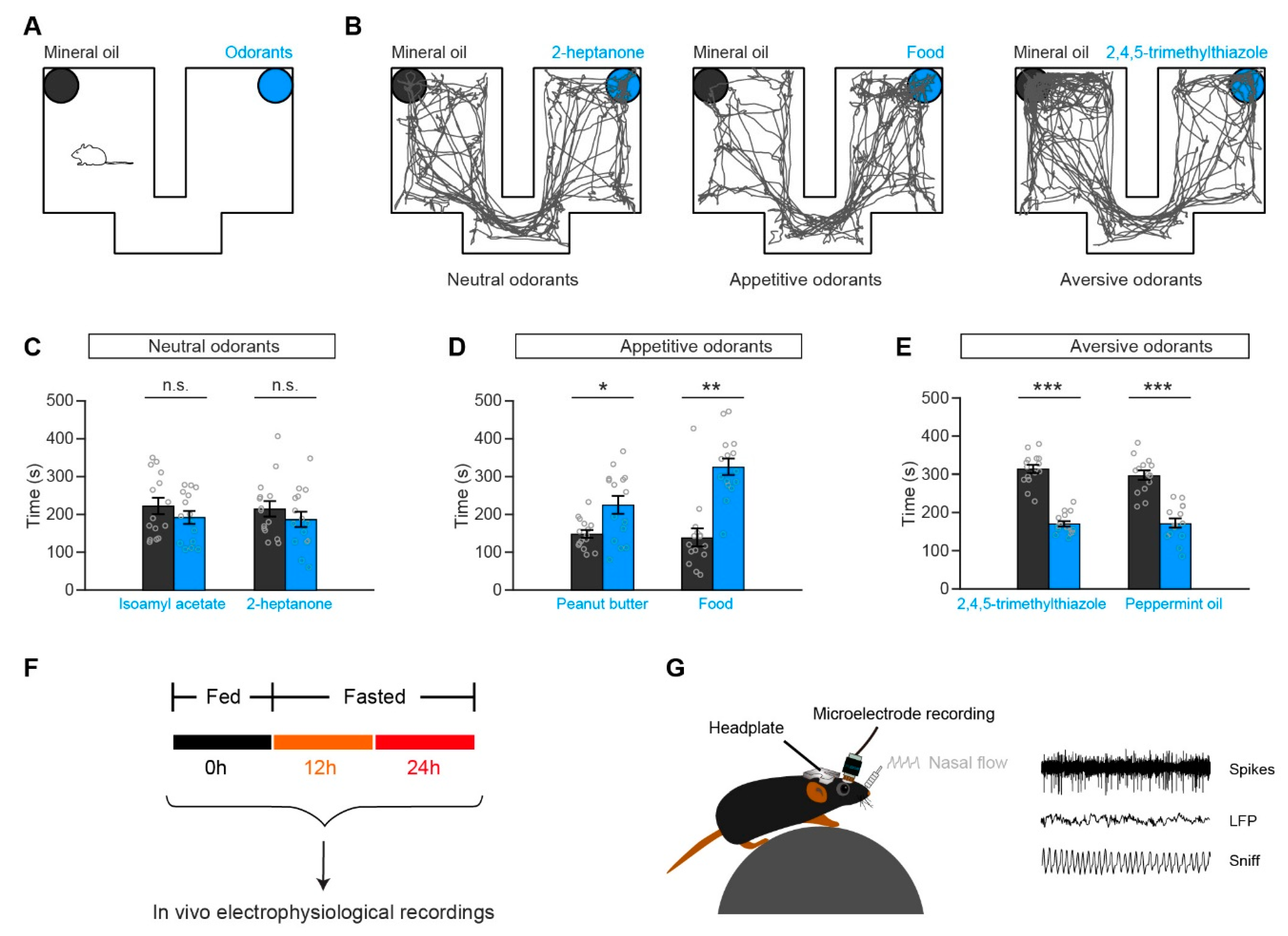
2.2. Odorants and Preference/Avoidance Behavioral Test
2.3. Microelectrode Implantation
2.4. Spike and LFP Recordings
2.5. Odorant Presentation during Electrophysiological Recordings
2.6. Measurement of Sniffing Parameters
2.7. Data Analysis
2.7.1. Olfactory Preference/Avoidance Test
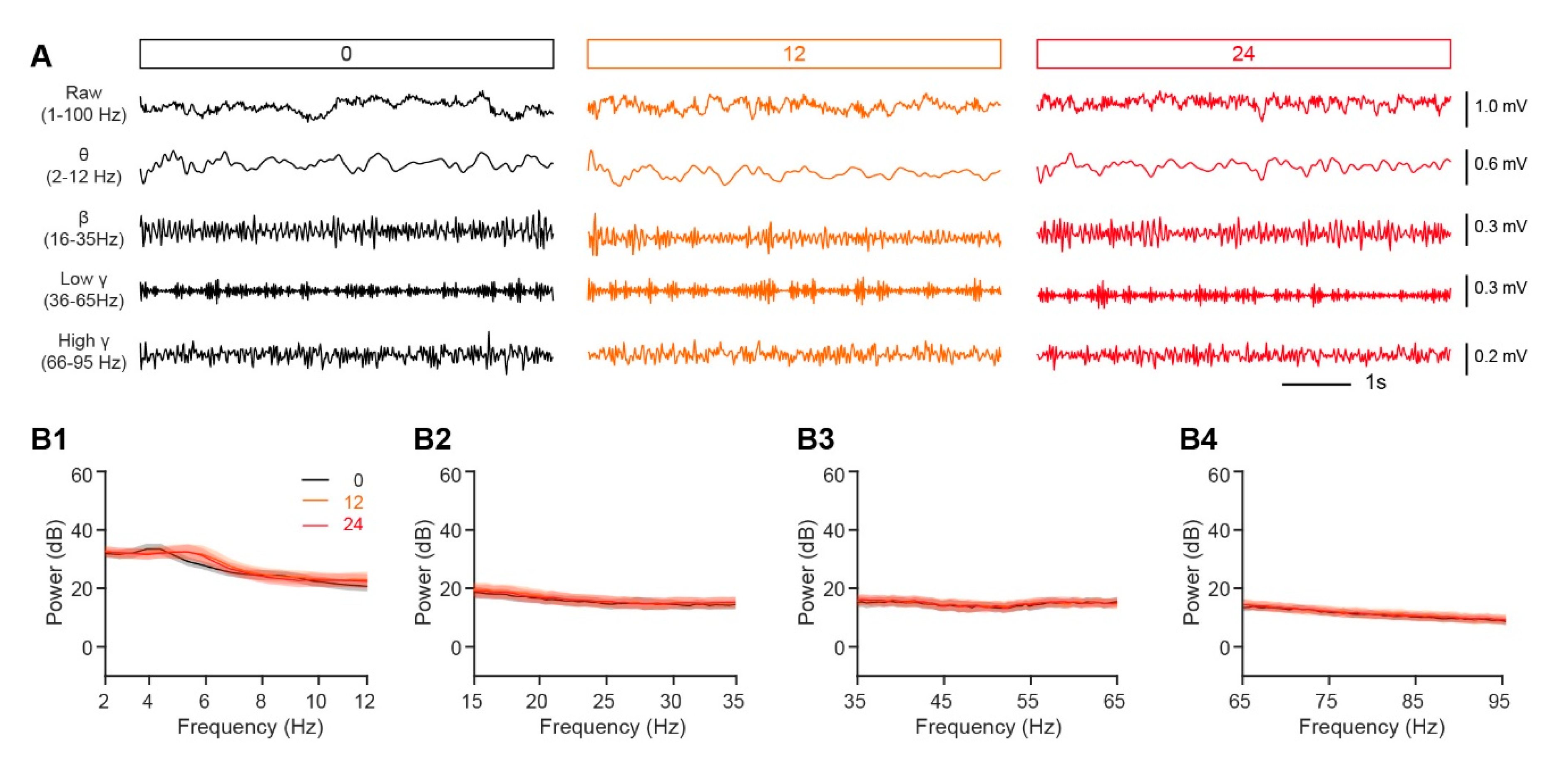
2.7.2. Analysis of LFP Signals
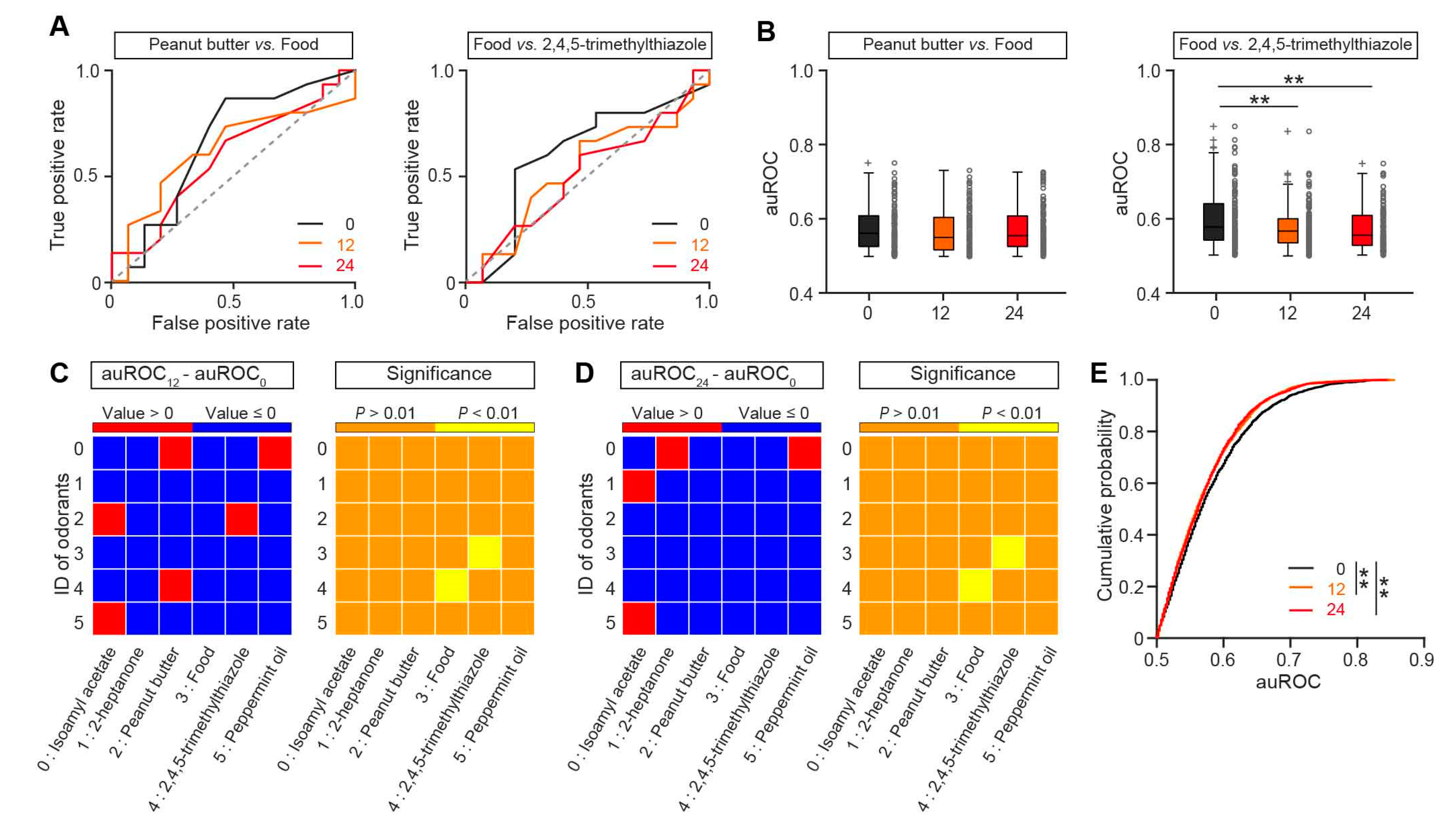
2.7.3. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Analysis
2.7.4. Statistics
3. Results
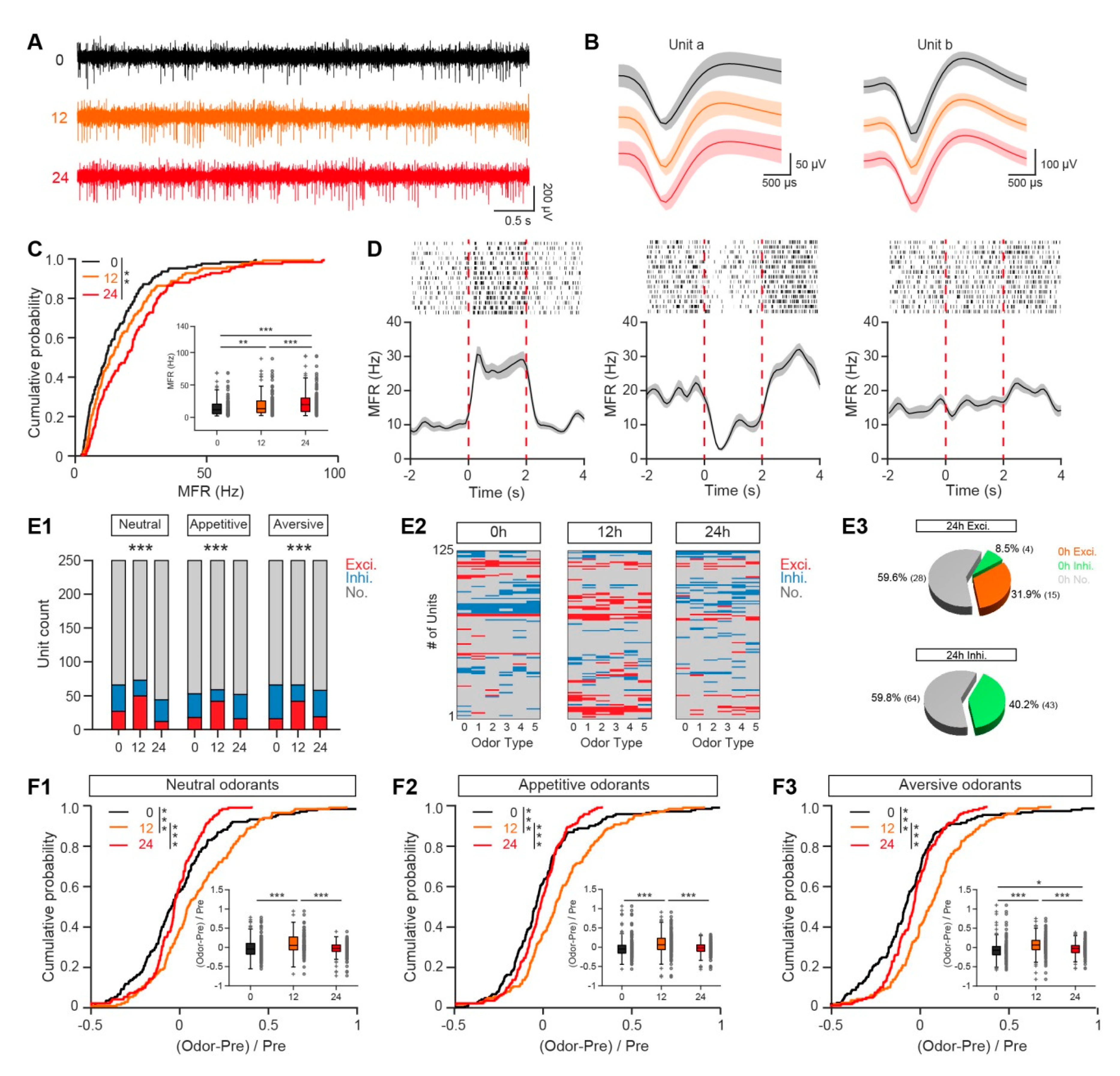
3.1. Baseline Firing Rate and Odor-Evoked Responses are Both Enhanced in a Fasted State
3.2. Neural Discrimination of Odors is Slightly Decreased in the OB of Fasted Mice
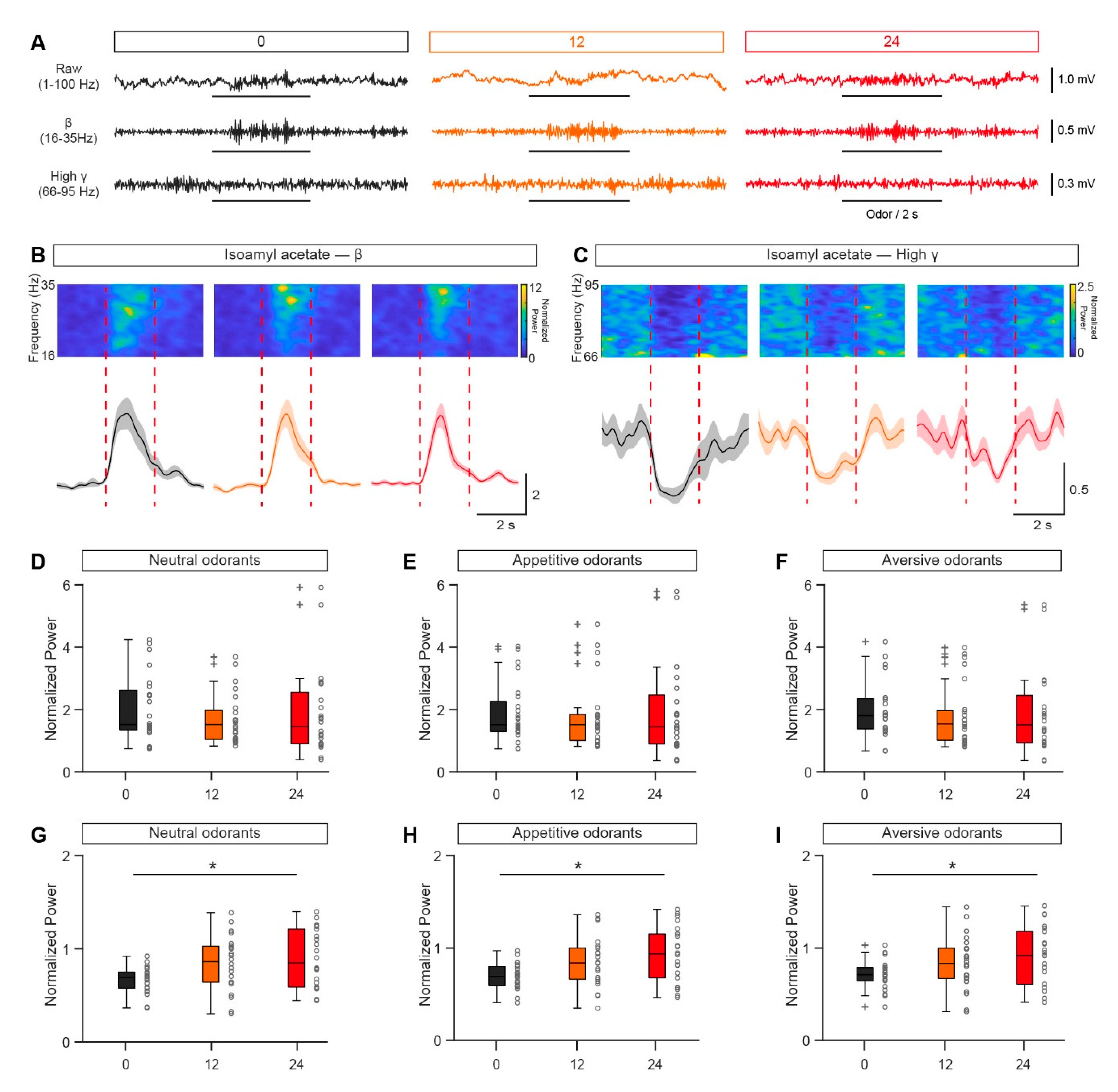
3.3. Odor-Evoked Gamma Responses are Decreased in a Fasted State
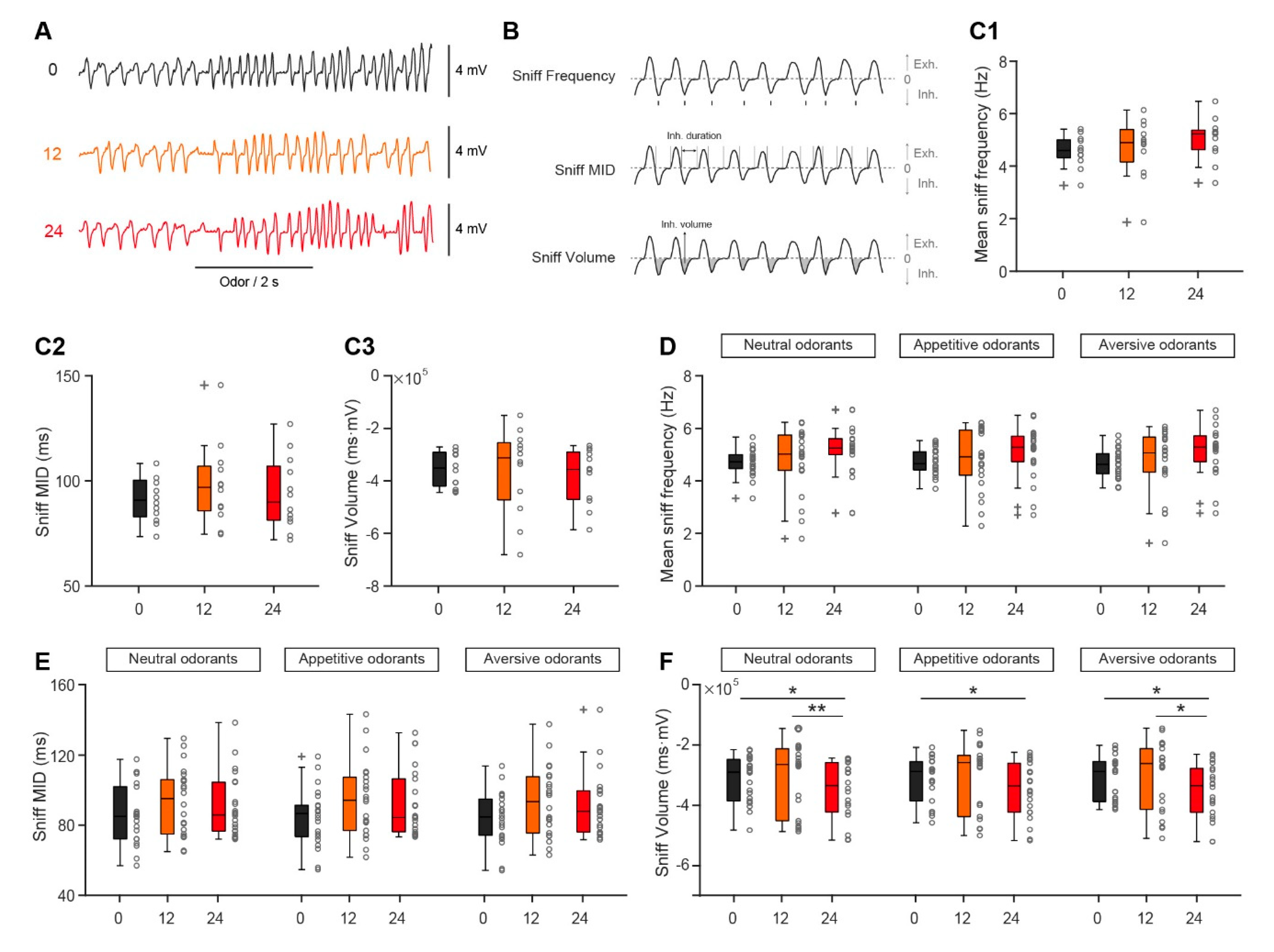
3.4. Slight Decrease in the Sniffing Volume Between Satiated and Fasted States
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soria-Gomez, E.; Bellocchio, L.; Reguero, L.; Lepousez, G.; Martin, C.; Bendahmane, M.; Ruehle, S.; Remmers, F.; Desprez, T.; Matias, I.; et al. The endocannabinoid system controls food intake via olfactory processes. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palouzier-Paulignan, B.; Lacroix, M.C.; Aime, P.; Baly, C.; Caillol, M.; Congar, P.; Julliard, A.K.; Tucker, K.; Fadool, D.A. Olfaction under metabolic influences. Chem. Senses 2012, 37, 769–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, E.T. Taste, olfactory, and food texture processing in the brain, and the control of food intake. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 85, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, M.R. Olfactory influences on appetite and satiety in humans. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 89, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julliard, A.K.; Al Koborssy, D.; Fadool, D.A.; Palouzier-Paulignan, B. Nutrient Sensing: Another Chemosensitivity of the Olfactory System. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julliard, A.K.; Chaput, M.A.; Apelbaum, A.; Aime, P.; Mahfouz, M.; Duchamp-Viret, P. Changes in rat olfactory detection performance induced by orexin and leptin mimicking fasting and satiation. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 183, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, P.; Duchamp-Viret, P.; Chaput, M.A.; Savigner, A.; Mahfouz, M.; Julliard, A.K. Fasting increases and satiation decreases olfactory detection for a neutral odor in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 179, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, J.; Schreder, T.; Kleemann, A.M.; Schopf, V.; Kopietz, R.; Anzinger, A.; Demmel, M.; Linn, J.; Kettenmann, B.; Wiesmann, M. Olfactory detection thresholds and pleasantness of a food-related and a non-food odour in hunger and satiety. Rhinology 2009, 47, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- McClintock, T.S. Achieving singularity in mammalian odorant receptor gene choice. Chem. Senses 2010, 35, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Tachie-Baffour, Y.; Liu, Z.; Baldwin, M.W.; Kruse, A.C.; Liberles, S.D. Non-classical amine recognition evolved in a large clade of olfactory receptors. eLife 2015, 4, e10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, L.; Axel, R. A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: A molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell 1991, 65, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Rao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Restrepo, D. Complex neural representation of odour information in the olfactory bulb. Acta Physiol. 2020, 228, e13333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, N.; Poo, C.; Haddad, R. Coding and transformations in the olfactory system. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 37, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, E.; Rinberg, D. Behavioral readout of spatio-temporal codes in olfaction. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 52, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Geng, C.; Hou, X.Y. Oligomeric amyloid-beta peptide disrupts olfactory information output by impairment of local inhibitory circuits in rat olfactory bulb. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 51, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pager, J.; Giachetti, I.; Holley, A.; Le Magnen, J. A selective control of olfactory bulb electrical activity in relation to food deprivation and satiety in rats. Physiol. Behav. 1972, 9, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apelbaum, A.F.; Chaput, M.A. Rats habituated to chronic feeding restriction show a smaller increase in olfactory bulb reactivity compared to newly fasted rats. Chem. Senses 2003, 28, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Tang, K.; Wu, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, W.; Cao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, A. Leptin modulates olfactory discrimination and neural activity in the olfactory bulb. Acta Physiol. 2019, 227, e13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, P.; Mao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Cao, T.; Xu, J.; Sun, C.; Li, A. Task-Demand-Dependent Neural Representation of Odor Information in the Olfactory Bulb and Posterior Piriform Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 10002–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, C.; Shao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hou, Y.; Li, A. Partial depletion of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra impairs olfaction and alters neural activity in the olfactory bulb. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, D.; Restrepo, D.; Li, A. Insulin Modulates Neural Activity of Pyramidal Neurons in the Anterior Piriform Cortex. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Gire, D.H.; Restrepo, D. Upsilon spike-field coherence in a population of olfactory bulb neurons differentiates between odors irrespective of associated outcome. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 5808–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Guthman, E.M.; Doucette, W.T.; Restrepo, D. Behavioral status influences the dependence of odorant-induced change in firing on pre-stimulus firing rate. J. Neurosci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayakawa, K.; Kobayakawa, R.; Matsumoto, H.; Oka, Y.; Imai, T.; Ikawa, M.; Okabe, M.; Ikeda, T.; Itohara, S.; Kikusui, T.; et al. Innate versus learned odour processing in the mouse olfactory bulb. Nature 2007, 450, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, N.; Zhang, X.; Johnson, C.A.; Yadav, P.N.; Ghashghaei, H.T. Developmentally defined forebrain circuits regulate appetitive and aversive olfactory learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iurilli, G.; Datta, S.R. Population Coding in an Innately Relevant Olfactory Area. Neuron 2017, 93, 1180–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, L.R.; Kondoh, K.; Ye, X.; Yoon, K.H.; Hernandez, M.; Buck, L.B. Combinatorial effects of odorants on mouse behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3300–E3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzsaki, G.; Anastassiou, C.A.; Koch, C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents--EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, C.A.; Kay, L.M. Chemical factors determine olfactory system beta oscillations in waking rats. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 98, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshel, J.; Kopell, N.; Kay, L.M. Olfactory bulb gamma oscillations are enhanced with task demands. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 8358–8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachowiak, M. All in a Sniff: Olfaction as a Model for Active Sensing. Neuron 2011, 71, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, C.; Moreau, K.; Brandolini, M.; Livingstone, B.; Beaufrere, B.; Boirie, Y. Alterations of sensory perceptions in healthy elderly subjects during fasting and refeeding. A pilot study. Gerontology 2002, 48, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabaud, P.; Ravel, N.; Wilson, D.A.; Mouly, A.M.; Vigouroux, M.; Farget, V.; Gervais, R. Exposure to behaviourally relevant odour reveals differential characteristics in rat central olfactory pathways as studied through oscillatory activities. Chem. Senses 2000, 25, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pager, J. Ascending olfactory information and centrifugal influxes contributing to a nutritional modulation of the rat mitral cell responses. Brain Res. 1978, 140, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Koborssy, D.; Palouzier-Paulignan, B.; Canova, V.; Thevenet, M.; Fadool, D.A.; Julliard, A.K. Modulation of olfactory-driven behavior by metabolic signals: Role of the piriform cortex. Brain Struct. Funct. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelminski, Y.; Magnan, C.; Luquet, S.H.; Everard, A.; Meunier, N.; Gurden, H.; Martin, C. Odor-Induced Neuronal Rhythms in the Olfactory Bulb Are Profoundly Modified in ob/ob Obese Mice. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losacco, J.; Ramirez-Gordillo, D.; Gilmer, J.; Restrepo, D. Learning improves decoding of odor identity with phase-referenced oscillations in the olfactory bulb. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, L.M.; Beshel, J.; Brea, J.; Martin, C.; Rojas-Libano, D.; Kopell, N. Olfactory oscillations: The what, how and what for. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, L.M. Olfactory system oscillations across phyla. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2015, 31, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazakoff, B.N.; Lau, B.Y.; Crump, K.L.; Demmer, H.S.; Shea, S.D. Broadly tuned and respiration-independent inhibition in the olfactory bulb of awake mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Ravel, N. Beta and gamma oscillatory activities associated with olfactory memory tasks: Different rhythms for different functional networks? Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, K.R.; Haberly, L.B. Beta and gamma oscillations in the olfactory system of the urethane-anesthetized rat. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 90, 3921–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, N.M.; Guerin, D.; Bhaukaurally, K.; Carleton, A. Similar odor discrimination behavior in head-restrained and freely moving mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, K.M.; Uchida, N. Robust odor coding via inhalation-coupled transient activity in the mammalian olfactory bulb. Neuron 2010, 68, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, K.; Osakada, F.; Tarabrina, A.; Kizer, E.; Callaway, E.M.; Gage, F.H.; Sejnowski, T.J. Diverse Representations of Olfactory Information in Centrifugal Feedback Projections. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7535–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizbinski, K.M.; Dacks, A.M. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Neuromodulation of Olfactory Processing. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, M.L.; Chen, W.R. Neural correlates of olfactory learning: Critical role of centrifugal neuromodulation. Learn. Mem. 2010, 17, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prud’homme, M.J.; Lacroix, M.C.; Badonnel, K.; Gougis, S.; Baly, C.; Salesse, R.; Caillol, M. Nutritional status modulates behavioural and olfactory bulb Fos responses to isoamyl acetate or food odour in rats: Roles of orexins and leptin. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Liu, P.; Chen, F.; Ge, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, A. Excitability of Neural Activity is Enhanced, but Neural Discrimination of Odors is Slightly Decreased, in the Olfactory Bulb of Fasted Mice. Genes 2020, 11, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040433
Wu J, Liu P, Chen F, Ge L, Lu Y, Li A. Excitability of Neural Activity is Enhanced, but Neural Discrimination of Odors is Slightly Decreased, in the Olfactory Bulb of Fasted Mice. Genes. 2020; 11(4):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040433
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jing, Penglai Liu, Fengjiao Chen, Lingying Ge, Yifan Lu, and Anan Li. 2020. "Excitability of Neural Activity is Enhanced, but Neural Discrimination of Odors is Slightly Decreased, in the Olfactory Bulb of Fasted Mice" Genes 11, no. 4: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040433
APA StyleWu, J., Liu, P., Chen, F., Ge, L., Lu, Y., & Li, A. (2020). Excitability of Neural Activity is Enhanced, but Neural Discrimination of Odors is Slightly Decreased, in the Olfactory Bulb of Fasted Mice. Genes, 11(4), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040433




