Insecticide Resistance Profiling of Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles gambiae Populations in the Southern Senegal: Role of Target Sites and Metabolic Resistance Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Samples Collection
2.3. Plasmodium spp. Infection Rate
2.4. WHO Insecticide Susceptibility and Synergist Tests
2.5. Estimation of Resistance Intensity
2.6. Morphological and Molecular Identification of An. gambiae s.l. Species
2.7. Molecular Genotyping of the Vgsc-1014F, Vgsc-1014S, N1575Y and G119S Mutations
2.8. Analysis of the Polymorphism of the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel
2.9. Metabolic Resistance Genes Expression
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Species Composition
3.1.1. Indoor Collection
3.1.2. Larval Collection
3.2. Plasmodium spp. Infection Rate
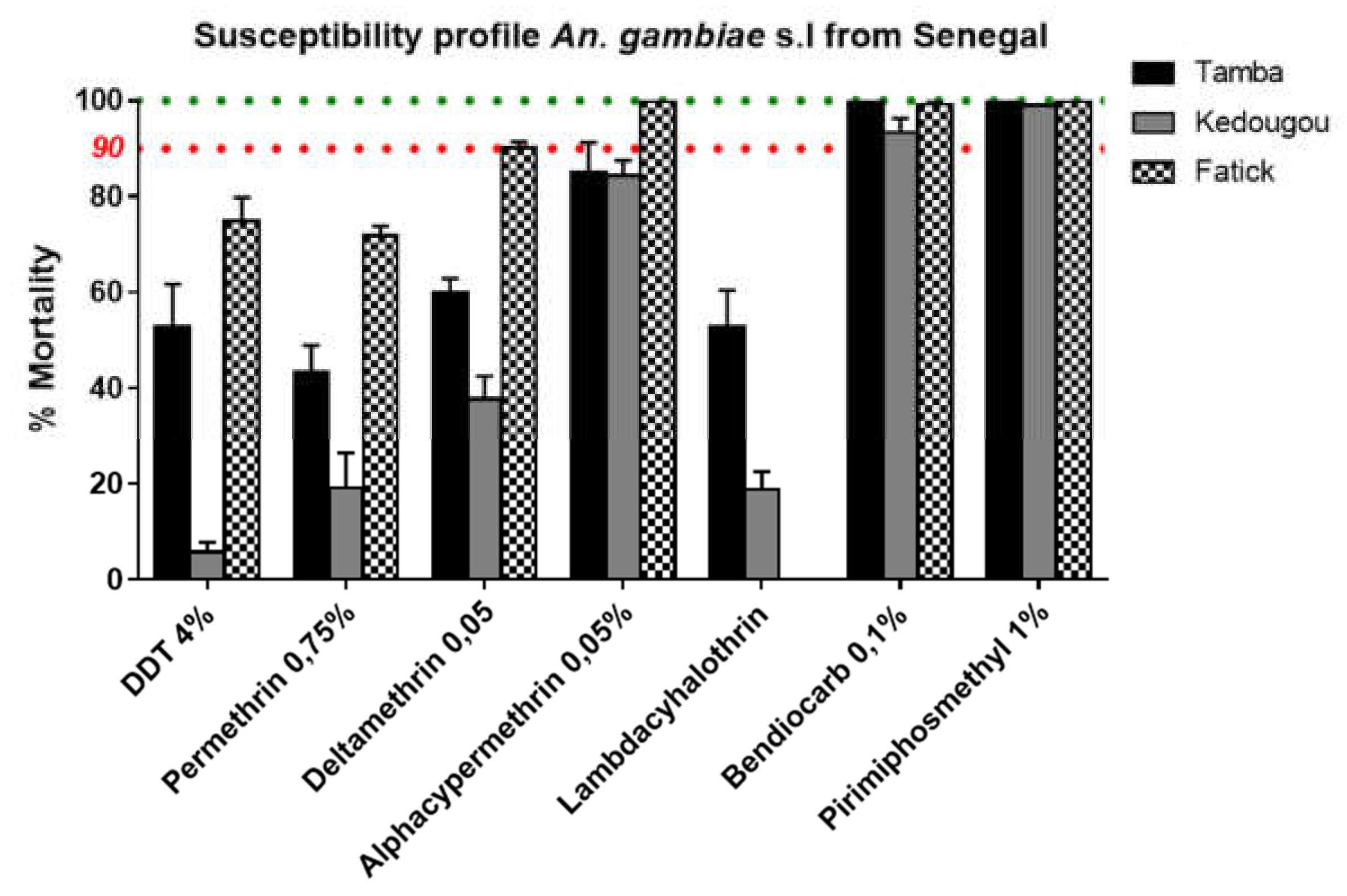
3.3. Insecticide Resistance Profile
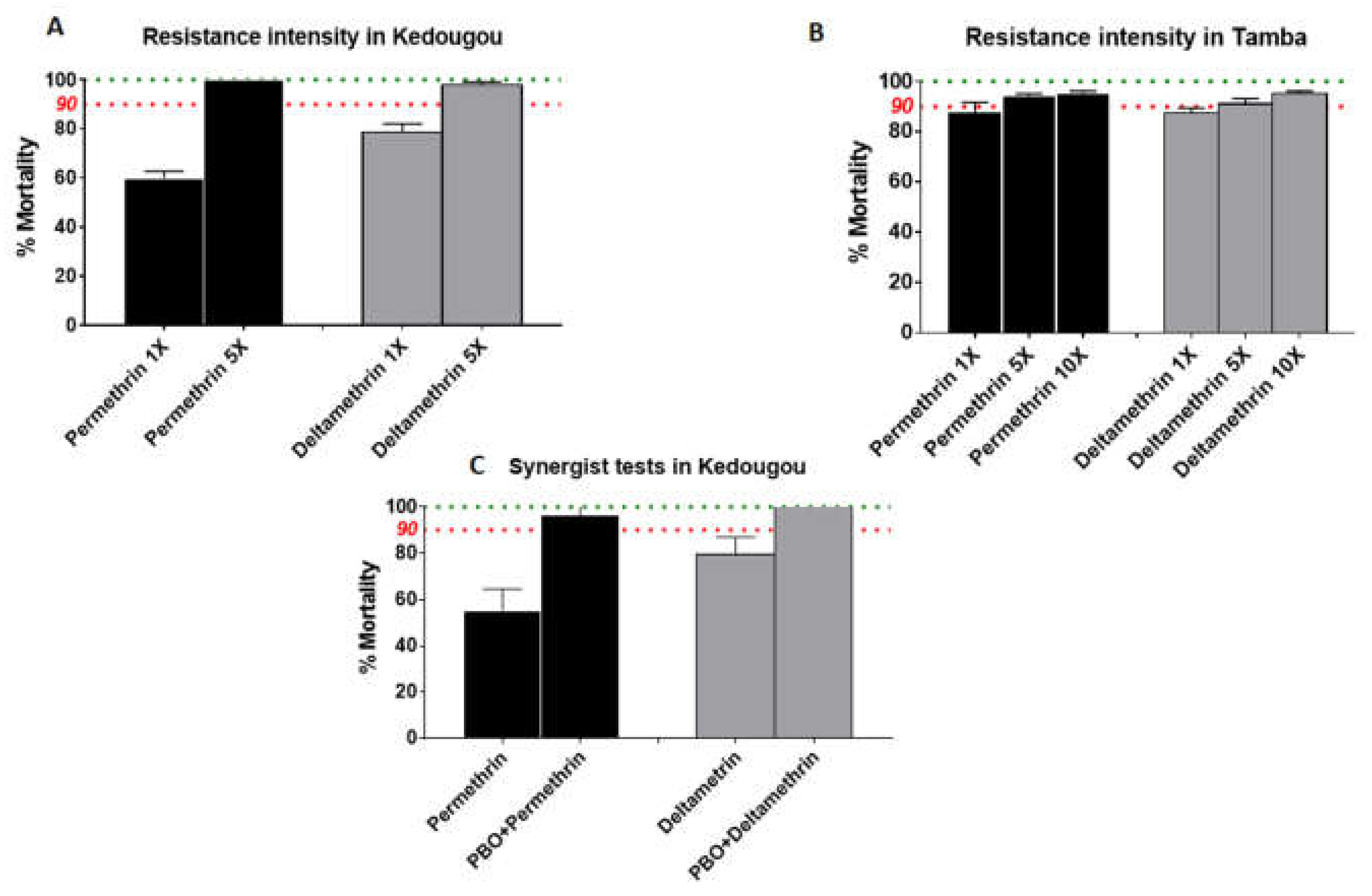
3.4. Estimation of Resistance Intensity
3.5. Synergist Bioassay with PBO
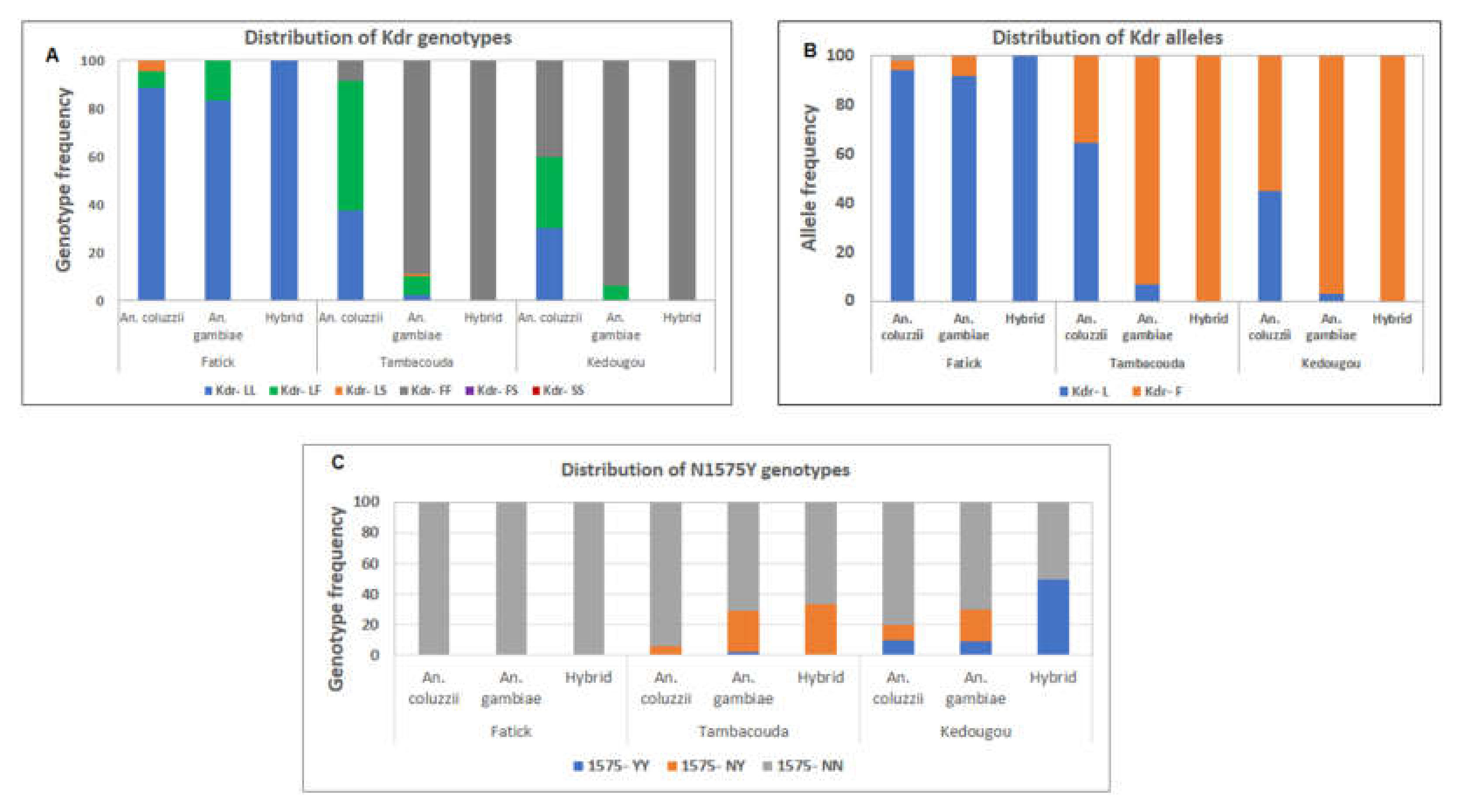
3.6. Distribution of Resistance Markers in the Adult Mosquitoes Collected
3.7. Correlation between the 1014F Mutation and Resistance to Pyrethroid
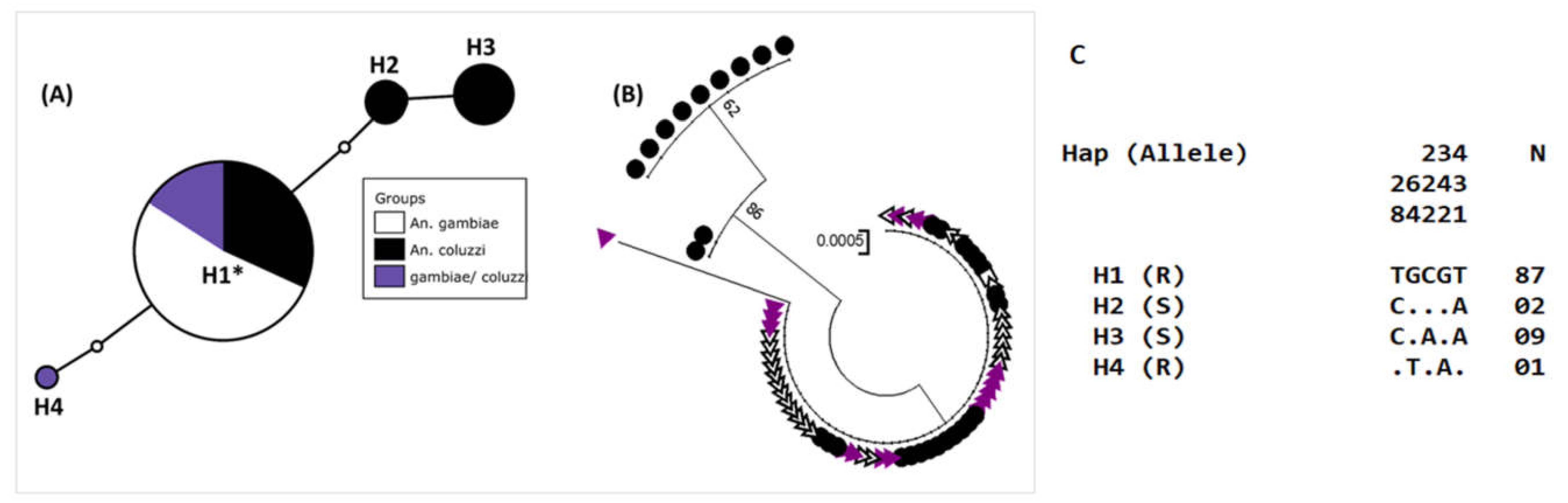
3.8. Genetic Diversity in the kdr Locus of the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel
3.9. Implication of the G119S Mutation in the Observed Bendiocarb Resistance
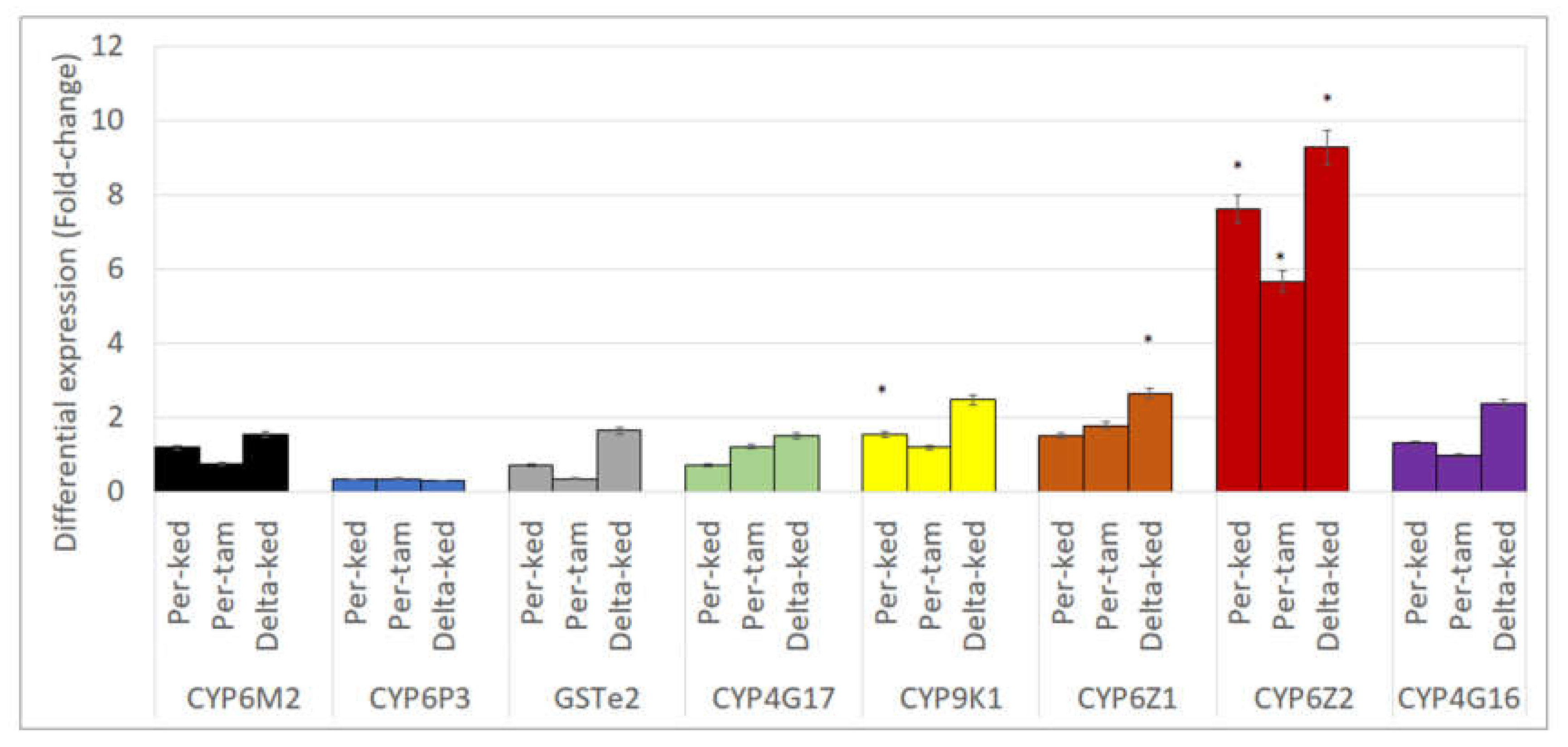
3.10. Expression Profiling of Metabolic Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Availability of Data and Material
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
References
- Okumu, F.O.; Chipwaza, B.; Madumla, E.P.; Mbeyela, E.; Lingamba, G.; Moore, J.; Ntamatungro, A.J.; Kavishe, D.R.; Moore, S.J. Implications of bio-efficacy and persistence of insecticides when indoor residual spraying and long-lasting insecticide nets are combined for malaria prevention. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. World Malaria Report; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; p. 232. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Torres, D.; Chandre, F.; Williamson, M.S.; Darriet, F.; Berge, J.B.; Devonshire, A.L.; Guillet, P.; Pasteur, N.; Pauron, D. Molecular characterization of pyrethroid knockdown resistance (kdr) in the major malaria vector Anopheles gambiae s.s. Insect Mol. Biol. 1998, 7, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranson, H.; Jensen, B.; Vulule, J.M.; Wang, X.; Hemingway, J.; Collins, F.H. Identification BlackwellScience, Ltd of a point mutation in the voltage-gated sodium channel gene of Kenyan Anopheles gambiae associated with resistance to DDT and pyrethroids. Insect Mol. Biol. 2000, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranson, H.; N’Guessan, R.; Lines, J.; Moiroux, N.; Nkuni, Z.; Corbel, V. Pyrethroid resistance in African anopheline mosquitoes: What are the implications for malaria control? Trends Parasitol. 2011, 27, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diabate, A.; Thierry, B.; Chandre, C.; Roch, D.K.; Pierre, K.; Robert, G.T.; Frederic, S.; Pierre, G.; Janet, H.; Marc, H.J. KDR Mutation, a Genetic Marker to Assess Events of Introgression Between the Molecular M and S Forms of Anopheles gambia (Diptera: Culicidae) in the Tropical Savannah Area of West Africa. J. Med. Entomol. 2003, 40, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Della Torre, A.; Fanello, C.; Akogbeto, M.; Dossou-yovo, J.; Favia, G.; Petrarca, V.; Coluzzi, M. Molecular evidence of incipient speciation within Anopheles gambiae s.s. in West Africa. Insect Mol. Biol. 2001, 10, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coetzee, M.; Hunt, R.H.; Wilkerson, R.; Torre, A.D.; Coulibaly, M.B.; Besansky, N.J. Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles amharicus, new members of the Anopheles gambiae complex. Zootaxa 2013, 3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dia, A.K.; Guèye, O.K.; Niang, E.A.; Diédhiou, S.M.; Sy, M.D.; Konaté, A.; Samb, B.; Diop, A.; Konaté, L.; Faye, O. Insecticide resistance in Anopheles arabiensis populations from Dakar and its suburbs: Role of target site and metabolic resistance mechanisms. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djègbè, I.; Boussari, O.; Sidick, A.; Martin, T.; Ranson, H.; Chandre, F.; Akogbéto, M.; Corbel, V. Dynamics of insecticide resistance in malaria vectors in Benin: First evidence of the presence of L1014S kdr mutation in Anopheles gambiae from West Africa. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djogbénou, L.; Pasteur, N.; Akogbéto, M.; Weill, M.; Chandre, F. Insecticide resistance in the Anopheles gambiae complex in Benin: A nationwide survey. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2011, 25, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santolamazza, F.; Calzetta, M.; Etang, J.; Barrese, E.; Dia, I.; Caccone, A.; Donnelly, M.J.; Petrarca, V.; Simard, F.; Pinto, J.; et al. Distribution of knock-down resistance mutations in Anopheles gambiae molecular forms in west and west-central Africa. Malar. J. 2008, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niang, E.A. Université Cheikh Anta Diop de Dakar, Dakar, Senegal, Distribution des Formes Moléculaires d’Anopheles Gambiae s.s. et du Gène de la Résistance au DDT et aux Pyréthrinoides (kdr) chez les Vecteurs du Paludisme au Sénégal. Dakar. Sénégal, UCAD; DEA de Biologie Animale: 97–2009. 2009; Unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Koukpo, C.Z.; Fassinou, A.J.Y.H.; Ossè, R.A.; Agossa, F.R.; Sovi, A.; Sewadé, W.T.; Aboubakar, S.; Assogba, B.S.; Akogbeto, M.C.; Sezonlin, M. The current distribution and characterization of the L1014F resistance allele of the kdr gene in three malaria vectors (Anopheles gambiae, Anopheles coluzzii, Anopheles arabiensis) in Benin (West Africa). Malar. J. 2019, 18, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weill, M.; Chandre, F.; Brengues, C.; Manguin, S.; Akogbeto, M.; Pasteur, N.; Guillet, P.; Raymond, M. The kdr mutation occurs in the Mopti form of Anopheles gambiaes.s. through introgression. Insect Mol. Biol. 2000, 9, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djogbénou, L.; Dabiré, R.; Diabaté, A.; Kengne, P.; Akogbéto, M.; Hougard, J.M.; Chandre, F. Identification and Geographic Distribution of the ACE-1 R Mutation in the Malaria Vector Anopheles gambiae in South-Western Burkina Faso, West Africa. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 78, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djogbénou, L. Vector Control Method against Malaria and Vector Resistance to Insecticides in Africa. Med. Trop. 2009, 69, 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.M.; Liyanapathirana, M.; Agossa, F.R.; Weetman, D.; Ranson, H.; Donnelly, M.J.; Wilding, C.S. Footprints of positive selection associated with a mutation (N1575Y) in the voltage-gated sodium channel of Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6614–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toé, K.H.; N’Falé, S.; Dabiré, R.K.; Ranson, H.; Jones, C.M. The recent escalation in strength of pyrethroid resistance in Anopheles coluzzi in West Africa is linked to increased expression of multiple gene families. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niang, E.H.A.; Konaté, L.; Diallo, M.; Faye, O.; Dia, I. Patterns of insecticide resistance and knock down resistance (kdr) in malaria vectors An. arabiensis, An. coluzzii and An. gambiae from sympatric areas in Senegal. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, C.; Nikou, D.; Blagborough, A.M.; Vontas, J.; Sinden, R.E.; Williamson, M.S.; Field, L.M. PCR-based detection of Plasmodium in Anopheles mosquitoes: A comparison of a new high-throughput assay with existing methods. Malar. J. 2008, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snounou, G.; Viriyakosol, S.; Jarra, W.; Thaithong, S.; Brown, K.N. Identification of the four human malaria parasite species in field samples by the polymerase chain reaction and detection of a high prevalence of mixed infections. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1993, 58, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Test Procedures for Insecticide Resistance Monitoring in Malaria Vector Mosquitoes; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gillies, M.T.; De Meillon, B. The Anophelinae of Africa south of the Sahara (Ethiopian Zoogeographical Region). Publ. S. Afr. Inst. Med. Res. 1968, 54, 1–343. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J. Organization and Mapping of a Sequence on the DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER X and Y Chromosomes That is Transcribed during Spermatogenesis. Genetics 1984, 107, 611–634. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santolamazza, F.; Mancini, E.; Simard, F.; Qi, Y.; Tu, Z.; della Torre, A. Insertion polymorphisms of SINE200 retrotransposons within speciation islands of Anopheles gambiae molecular forms. Malar. J. 2008, 7, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, E.E.; Marcet, P.L.; Sutcliffe, A.C.; Howell, P.I. Authentication scheme for routine verification of genetically similar laboratory colonies: A trial with Anopheles gambiae. BMC Biotechnol. 2009, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, C.; Nikou, D.; Donnelly, M.J.; Williamson, M.S.; Ranson, H.; Ball, A.; Vontas, J.; Field, L.M. Detection of knockdown resistance (kdr) mutations in Anopheles gambiae: A comparison of two new high-throughput assays with existing methods. Malar. J. 2007, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, C.; Nikou, D.; Vontas, J.; Williamson, M.S.; Field, L.M. Development of high-throughput real-time PCR assays for the identification of insensitive acetylcholinesterase (ace-1R) in Anopheles gambiae. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 96, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Lynd, A.; Vicente, J.L.; Santolamazza, F.; Randle, N.P.; Gentile, G.; Moreno, M.; Simard, F.; Charlwood, J.D.; do Rosário, V.E.; et al. Multiple Origins of Knockdown Resistance Mutations in the Afrotropical Mosquito Vector Anopheles gambiae. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.B. A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acid Symp. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimonneau, G.; Pombi, M.; Choisy, M.; Morand, S.; Dabiré, R.K.; Simard, F. Larval habitat segregation between the molecular forms of the mosquito Anopheles gambiae in a rice field area of Burkina Faso, West Africa. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2012, 26, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niang, A.; Epopa, P.S.; Sawadogo, S.P.; Maïga, H.; Konaté, L.; Faye, O.; Dabiré, R.K.; Tripet, F.; Diabaté, A. Does extreme asymmetric dominance promote hybridization between Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles gambiae s.s. in seasonal malaria mosquito communities of West Africa? Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touré, Y.T.; Petrarca, V.; Traoré, S.F.; Coulibaly, A.; Maiga, H.M.; Sankaré, O.; Sow, M.; Di, M.D.; Coluzzi, M. The distribution and inversion polymorphism of chromosomally recognized taxa of the Anopheles gambiae complex in Mali, West Africa. Parassitologia 1998, 40, 477–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diabate, A.; Dabire, R.K.; Kim, E.H.; Dalton, R.; Millogo, N.; Baldet, T.; Simard, F.; Gimnig, J.E.; Hawley, W.A.; Lehmann, T. Larval Development of the Molecular Forms of Anopheles gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae) in Different Habitats: A Transplantation Experiment. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Innocent, D.; Abel, M.A.; Rousseau, D.; Martin, A. Surveillance Entomologique: Dynamique de la population et de la résistance aux insecticides chez Anopheles gambiae s.l en milieu de riziculture irriguée au Sud Bénin. J. Appl. Biosci. 2017, 11, 10943. [Google Scholar]
- Torre, A.D.; Tu, Z.; Petrarca, V. On the distribution and genetic differentiation of Anopheles gambiae s.s. molecular forms. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 35, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdem, C.; Tene Fossog, B.; Simard, F.; Etouna, J.; Ndo, C.; Kengne, P.; Boussès, P.; Etoa, F.-X.; Awono-Ambene, P.; Fontenille, D.; et al. Anthropogenic Habitat Disturbance and Ecological Divergence between Incipient Species of the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles gambiae. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotodjo, A.N.; Richard, V.; Boyer, S.; Doucoure, S.; Diagne, N.; Touré-Baldé, A.; Tall, A.; Faye, N.; Gaudart, J.; Trape, J.-F.; et al. The implication of long-lasting insecticide-treated net use in the resurgence of malaria morbidity in a Senegal malaria endemic village in 2010–2011. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niang, E.H.A.; Touré, A.; Ngom, E.H.M.; Konaté, L.; Faye, O.; Diallo, M.; Dia, I. Malaria Transmission Pattern in an Area Selected for Clinical Trials in the Sudanian Area of Senegal (West Africa). J. Trop. Med. 2013, 2013, 907375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefèvre, T.; Gouagna, L.-C.; Dabire, K.R.; Elguero, E.; Fontenille, D.; Costantini, C.; Thomas, F. Evolutionary lability of odour-mediated host preference by the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2009, 14, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fall Evaluation de la Sensibilité Des Vecteurs du Paludisme Aux Insecticides Dans la Région de Kédougou et Recherche de Mécanismes de Résistance. 2016. Available online: www.memoironline.com (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- Faye, O.; Konate, L.; Diop, A. Profil Entomologique du Sénégal; Senegal National Malaria Control Program: Dakar, Senegal, 2011; p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- Thiaw, O.; Doucouré, S.; Sougoufara, S.; Bouganali, C.; Konaté, L.; Diagne, N.; Faye, O.; Sokhna, C. Investigating insecticide resistance and knock-down resistance (kdr) mutation in Dielmo, Senegal, an area under long lasting insecticidal-treated nets universal coverage for 10 years. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandre, F.; Darrier, F.; Manga, L.; Akogbeto, M.; Faye, O.; Mouchet, J. Situation de la resistance aux pyre thrinoıdes chez Anopheles gambiae sensu lato. Bull. l’Organ. Mond. Santé 1999, 1, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, M.C.; McKenzie, F.E. The contribution of agricultural insecticide use to increasing insecticide resistance in African malaria vectors. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diouf, M.; Diouf, E.; Niang, E.; Diagne, C.; Konaté, L.; Faye, O. Evaluation de l’état physique et de l’efficacité biologique de deux types de moustiquaires imprégnées à longue durée d’action utilisés depuis 5 à 36 mois et collectés dans 11 districts du Sénégal. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2018, 111, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PNLP. Bulletin Epidemiologique Annuel du Paludisme au Senegal 2015. Available online: www.pnlp.sn (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- PNLP. Bulletin Epidemiologique Annuel du Paludisme au Senegal 2017. Available online: www.pnlp.sn (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- Thwing, J.I.; Perry, R.T.; Townes, D.A.; Diouf, M.B.; Ndiaye, S.; Thior, M. Success of Senegal’s first nationwide distribution of long-lasting insecticide-treated nets to children under five-contribution toward universal coverage. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkya, T.E.; Akhouayri, I.; Poupardin, R.; Batengana, B.; Mosha, F.; Magesa, S.; Kisinza, W.; David, J.-P. Insecticide resistance mechanisms associated with different environments in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae: A case study in Tanzania. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbel, V.; N’Guessan, R. Distribution, mechanisms, impact and management of insecticide resistance in Malaria vectors: A pragmatic review. In Anopheles Mosquitoes–New Insights into Malaria Vectors; Manguin, S., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-1188-7. [Google Scholar]
- Awolola, T.S.; Oyewole, I.O.; Amajoh, C.N.; Idowu, E.T.; Ajayi, M.B.; Oduola, A.; Manafa, O.U.; Ibrahim, K.; Koekemoer, L.L.; Coetzee, M. Distribution of the molecular forms of Anopheles gambiae and pyrethroid knock down resistance gene in Nigeria. Acta Trop. 2005, 95, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awolola, T.S.; Oduola, O.A.; Strode, C.; Koekemoer, L.L.; Brooke, B.; Ranson, H. Evidence of multiple pyrethroid resistance mechanisms in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae sensu stricto from Nigeria. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisse, M.B.M.; Keita, C.; Dicko, A.; Dengela, D.; Coleman, J.; Lucas, B.; Mihigo, J.; Sadou, A.; Belemvire, A.; George, K.; et al. Characterizing the insecticide resistance of Anopheles gambiae in Mali. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czeher, C.; Labbo, R.; Arzika, I.; Duchemin, J.-B. Evidence of increasing Leu-Phe knockdown resistance mutation in Anopheles gambiae from Niger following a nationwide long-lasting insecticide-treated nets implementation. Malar. J. 2008, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, G.; Santolamazza, F.; Fanello, C.; Petrarca, V.; Caccone, A.; Della Torre, A. Variation in an intron sequence of the voltage-gated sodium channel gene correlates with genetic differentiation between Anopheles gambiae s.s. molecular forms: Genetic differentiation in A. gambiae molecular forms. Insect Mol. Biol. 2004, 13, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridl, F.C.; Bass, C.; Torrez, M.; Govender, D.; Ramdeen, V.; Yellot, L.; Edu, A.E.; Schwabe, C.; Mohloai, P.; Maharaj, R.; et al. A pre-intervention study of malaria vector abundance in Rio Muni, Equatorial Guinea: Their role in malaria transmission and the incidence of insecticide resistance alleles. Malar. J. 2008, 7, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwane, P.; Etang, J.; Chouaїbou, M.; Toto, J.C.; Koffi, A.; Mimpfoundi, R.; Simard, F. Multiple insecticide resistance mechanisms in Anopheles gambiae s.l. populations from Cameroon, Central Africa. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, L.; Fondjo, E.; Patchoke, S.; Diallo, B.; Lee, Y.; Ng, A.; Ndjemai, H.M.; Atangana, J.; Traore, S.F.; Lanzaro, G.; et al. Relationship Between kdr Mutation and Resistance to Pyrethroid and DDT Insecticides in Natural Populations of Anopheles gambiae. J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edi, A.V.C.; N’Dri, B.P.; Chouaibou, M.; Kouadio, F.B.; Pignatelli, P.; Raso, G.; Weetman, D.; Bonfoh, B. First detection of N1575Y mutation in pyrethroid resistant Anopheles gambiae in Southern Côte d’Ivoire. Wellcome Open. Res. 2017, 2, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, M.J.; Corbel, V.; Weetman, D.; Wilding, C.S.; Williamson, M.S.; Black, W.C. Does kdr genotype predict insecticide-resistance phenotype in mosquitoes? Trends Parasitol. 2009, 25, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okorie, P.N.; Ademowo, O.G.; Irving, H.; Kelly-Hope, L.A.; Wondji, C.S. Insecticide susceptibility of Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes in Ibadan, Southwest Nigeria: Susceptibility to insecticide of Anopheles. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2015, 29, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samb, B.; Konate, L.; Irving, H.; Riveron, J.M.; Dia, I.; Faye, O.; Wondji, C.S. Investigating molecular basis of lambda-cyhalothrin resistance in an Anopheles funestus population from Senegal. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ortelli, F.; Rossiter, L.C.; Hemingway, J.; Ranson, H. The Anopheles gambiae glutathione transferase supergene family: Annotation, phylogeny and expression profiles. BMC Genom. 2003, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolfi, A.; Poulton, B.; Anthousi, A.; Macilwee, S.; Ranson, H.; Lycett, G.J. Functional genetic validation of key genes conferring insecticide resistance in the major African malaria vector, Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25764–25772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djouaka, R.F.; Bakare, A.A.; Coulibaly, O.N.; Akogbeto, M.C.; Ranson, H.; Hemingway, J.; Strode, C. Expression of the cytochrome P450s, CYP6P3 and CYP6M2 are significantly elevated in multiple pyrethroid resistant populations of Anopheles gambiae s.s. from Southern Benin and Nigeria. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, B.J.; Bibby, J.; Pignatelli, P.; Muangnoicharoen, S.; O’Neill, P.M.; Lian, L.-Y.; Müller, P.; Nikou, D.; Steven, A.; Hemingway, J.; et al. Cytochrome P450 6M2 from the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae metabolizes pyrethroids: Sequential metabolism of deltamethrin revealed. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, M.J.; Isaacs, A.T.; Weetman, D. Identification, Validation, and Application of Molecular Diagnostics for Insecticide Resistance in Malaria Vectors. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balabanidou, V.; Kampouraki, A.; MacLean, M.; Blomquist, G.J.; Tittiger, C.; Juárez, M.P.; Mijailovsky, S.J.; Chalepakis, G.; Anthousi, A.; Lynd, A.; et al. Cytochrome P450 associated with insecticide resistance catalyzes cuticular hydrocarbon production in Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9268–9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, V.A.; Jones, C.M.; Pignatelli, P.; Balabanidou, V.; Vontas, J.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Moore, J.D.; Ranson, H. Dissecting the organ specificity of insecticide resistance candidate genes in Anopheles gambiae: Known and novel candidate genes. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vontas, J.; Grigoraki, L.; Morgan, J.; Tsakireli, D.; Fuseini, G.; Segura, L.; Niemczura de Carvalho, J.; Nguema, R.; Weetman, D.; Slotman, M.A.; et al. Rapid selection of a pyrethroid metabolic enzyme CYP9K1 by operational malaria control activities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4619–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Combination of Genotypes at the L1014F-kdr Locus | An. gambiae | |
|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | p-Value | |
| RR vs. RS | 1.3 | 0.2 |
| (0.3–5.1) | ||
| RR vs. SS | 5.3 | 0.1 |
| (0.6–46.5) | ||
| RS vs. SS | 4.0 | 0.3 |
| (0.3–49.6) | ||
| R vs. S | 3.7 | 0.08 |
| (0.7–18.2) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gueye, O.K.; Tchouakui, M.; Dia, A.K.; Faye, M.B.; Ahmed, A.A.; Wondji, M.J.; Nguiffo, D.N.; J. Mugenzi, L.M.; Tripet, F.; Konaté, L.; et al. Insecticide Resistance Profiling of Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles gambiae Populations in the Southern Senegal: Role of Target Sites and Metabolic Resistance Mechanisms. Genes 2020, 11, 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121403
Gueye OK, Tchouakui M, Dia AK, Faye MB, Ahmed AA, Wondji MJ, Nguiffo DN, J. Mugenzi LM, Tripet F, Konaté L, et al. Insecticide Resistance Profiling of Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles gambiae Populations in the Southern Senegal: Role of Target Sites and Metabolic Resistance Mechanisms. Genes. 2020; 11(12):1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121403
Chicago/Turabian StyleGueye, Oumou. K., Magellan Tchouakui, Abdoulaye K. Dia, Mouhamed B. Faye, Amblat A. Ahmed, Murielle J. Wondji, Daniel N. Nguiffo, Leon. M. J. Mugenzi, Frederic Tripet, Lassana Konaté, and et al. 2020. "Insecticide Resistance Profiling of Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles gambiae Populations in the Southern Senegal: Role of Target Sites and Metabolic Resistance Mechanisms" Genes 11, no. 12: 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121403
APA StyleGueye, O. K., Tchouakui, M., Dia, A. K., Faye, M. B., Ahmed, A. A., Wondji, M. J., Nguiffo, D. N., J. Mugenzi, L. M., Tripet, F., Konaté, L., Diabate, A., Dia, I., Gaye, O., Faye, O., Niang, E. H. A., & S. Wondji, C. (2020). Insecticide Resistance Profiling of Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles gambiae Populations in the Southern Senegal: Role of Target Sites and Metabolic Resistance Mechanisms. Genes, 11(12), 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121403








