Transfer-RNA-Derived Fragments Are Potential Prognostic Factors in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Retrieval of tRF Data from MINTbase
2.2. Identification of Survival-Associated tRFs
2.3. Prediction of tRF Binding Proteins
2.4. Relationship between tRF Level and Clinical Features
2.5. Quantification of tRF Levels Using Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
3. Results
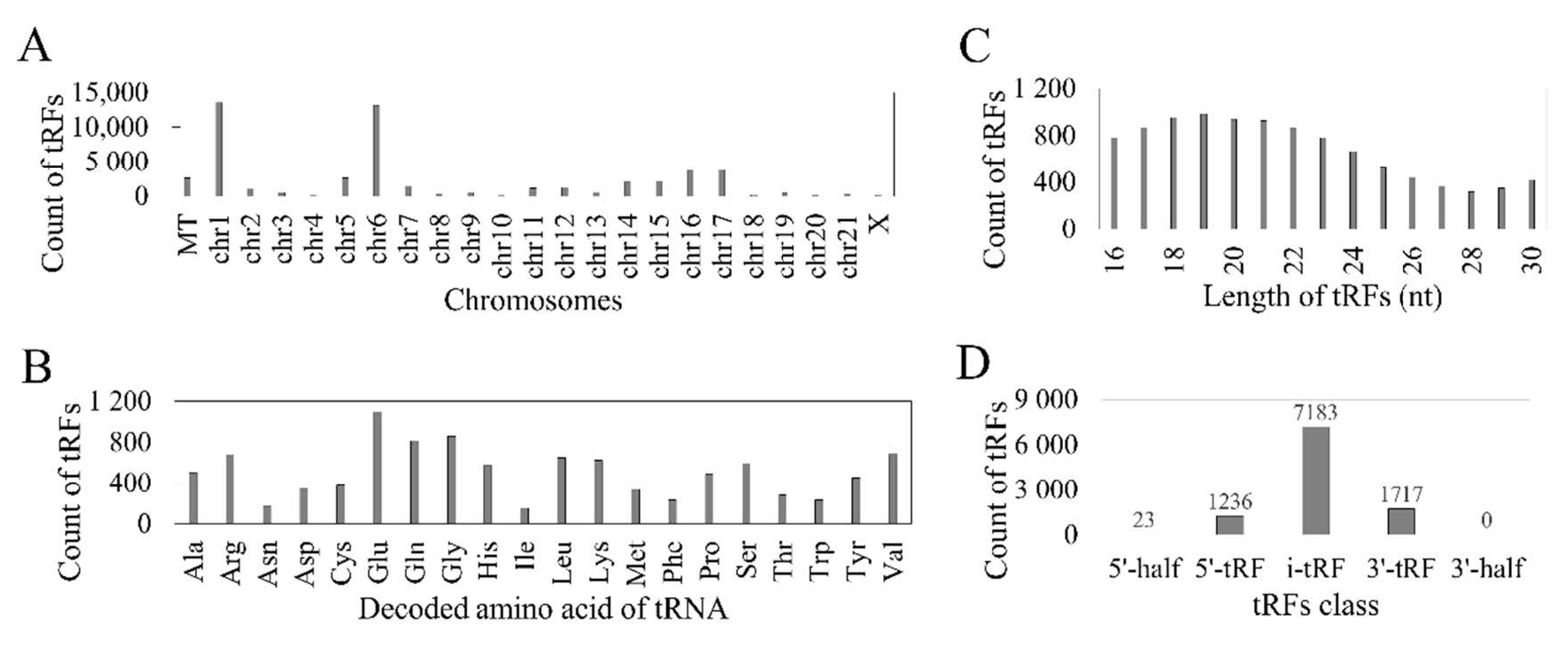
3.1. Reported tRFs in the TCGA HNSC Cohort
3.2. Prognosis-Associated tRFs in SCCHN
3.3. tRF-Interacting Proteins
3.4. The Association between tRF-20-S998LO9D and Clinical Factors
3.5. Investigation of tRF-20 in Our Clinical Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haussecker, D.; Huang, Y.; Lau, A.; Parameswaran, P.; Fire, A.Z.; Kay, M.A. Human tRNA-derived small RNAs in the global regulation of RNA silencing. RNA 2010, 16, 673–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebetsberger, J.V.; Wyss, L.; Mleczko, A.M.; Reuther, J.; Polacek, N. A tRNA-derived fragment competes with mRNA for ribosome binding and regulates translation during stress. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Fuchs, G.; Wang, S.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Park, H.; Roy-Chaudhuri, B.; Cliff, Z.Q.; Xu, J.; Shengchun, W.; et al. A transfer-RNA-derived small RNA regulates ribosome biogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 552, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuscu, C.; Kumar, P.; Kiran, M.; Su, Z.; Malik, A.; Dutta, A. tRNA fragments (tRFs) guide Ago to regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally in a Dicer-independent manner. RNA 2018, 24, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boskovic, A.; Bing, X.Y.; Kaymak, E.; Rando, O.J. Control of noncoding RNA production and histone levels by a 5′ tRNA fragment. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.M.; Parker, R. Stressing Out over tRNA Cleavage. Cell 2009, 138, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telonis, A.G.; Loher, P.; Honda, S.; Jing, Y.; Palazzo, J.; Kirino, Y.; Rigoutsos, I. Dissecting tRNA-derived fragment complexities using personalized transcriptomes reveals novel fragment classes and unexpected dependencies. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24797–24822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzi, N.; Bellodi, C. Novel insights into the emerging roles of tRNA-derived fragments in mammalian development. RNA Biol. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Fu, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F.; Chu, J.; Wu, H.; Huang, X.; et al. Roles of tRNA-derived fragments in human cancers. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ge, J.; Li, T.; Shen, Y.; Guo, J. tRNA-derived fragments and tRNA halves: The new players in cancers. Cancer Lett. 2019, 452, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliatsika, V.; Loher, P.; Telonis, A.G.; Rigoutsos, I. MINTbase: A framework for the interactive exploration of mitochondrial and nuclear tRNA fragments. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pliatsika, V.; Loher, P.; Magee, R.; Telonis, A.G.; Londin, E.; Shigematsu, M.; Kirino, Y.; Rigoutsos, I. MINTbase v2.0: A comprehensive database for tRNA-derived fragments that includes nuclear and mitochondrial fragments from all The Cancer Genome Atlas projects. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D152–D159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borek, E.; Baliga, B.S.; Gehrke, C.W.; Kuo, C.W.; Belman, S.; Troll, W.; Waalkes, T.P. High turnover rate of transfer RNA in tumor tissue. Cancer Res. 1977, 37, 3362–3366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Speer, J.; Gehrke, C.W.; Kuo, K.C.; Waalkes, T.P.; Borek, E. tRNA breakdown products as markers for cancer. Cancer 1979, 44, 2120–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telonis, A.G.; Loher, P.; Magee, R.; Pliatsika, V.; Londin, E.; Kirino, Y.; Rigoutsos, I. tRNA Fragments Show Intertwining with mRNAs of Specific Repeat Content and Have Links to Disparities. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3034–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yao, L.; Yu, X.; Ruan, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, J. Action mechanisms and research methods of tRNA-derived small RNAs. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yan, M.; Cao, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Feng, G.-H.; Peng, H.; Zhang, X.; Qian, J.; et al. Sperm tsRNAs contribute to intergenerational inheritance of an acquired metabolic disorder. Science 2016, 351, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Xu, P.-P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.-B.; Yang, D.-G.; Gao, F.; Yang, M.-L.; Du, L.-J.; Li, J. Pathological significance of tRNA-derived small RNAs in neurological disorders. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekarsky, Y.; Balatti, V.; Palamarchuk, A.; Rizzotto, L.; Veneziano, D.; Nigita, G.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Pass, H.I.; Kipps, T.J.; Liu, C.-G.; et al. Dysregulation of a family of short noncoding RNAs, tsRNAs, in human cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5071–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvedy, M.; Scaravilli, M.; Hoogstrate, Y.; Visakorpi, T.; Jenster, G.; Martens-Uzunova, E.S. A comprehensive repertoire of tRNA-derived fragments in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 24766–24777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balatti, V.; Nigita, G.; Veneziano, D.; Drusco, A.; Stein, G.S.; Messier, T.L.; Farina, N.H.; Lian, J.B.; Tomasello, L.; Liu, C.-G.; et al. tsRNA signatures in cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8071–8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, S.; Loher, P.; Shigematsu, M.; Palazzo, J.P.; Suzuki, R.; Imoto, I.; Rigoutsos, I.; Kirino, Y. Sex hormone-dependent tRNA halves enhance cell proliferation in breast and prostate cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3816–E3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodarzi, H.; Liu, X.; Nguyen, H.C.; Zhang, S.; Fish, L.; Tavazoie, S.F. Endogenous tRNA-Derived Fragments Suppress Breast Cancer Progression via YBX1 Displacement. Cell 2015, 161, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Yang, H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, D.; Fu, S.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xue, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. tRF/miR-1280 Suppresses Stem Cell–like Cells and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3194–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemans, C.R.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The molecular landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature 2015, 517, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgaramella, N.; Gu, X.; Boldrup, L.; Coates, P.J.; Fahraeus, R.; Califano, L.; Tartaro, G.; Colella, G.; Spaak, L.N.; Strom, A.; et al. Searching for New Targets and Treatments in the Battle Against Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck, with Specific Focus on Tumours of the Tongue. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budach, V.; Tinhofer, I. Novel prognostic clinical factors and biomarkers for outcome prediction in head and neck cancer: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e313–e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Yu, J.; Zhou, P. Role of tRNA-derived fragments in cancer: Novel diagnostic and therapeutic targets tRFs in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 393–402. [Google Scholar]
- Dhahbi, J.M.; Lopez, Y.O.N.; Schneider, A.; Victoria, B.; Saccon, T.; Bharat, K.; McClatchey, T.; Atamna, H.; Scierski, W.; Golusinski, P.; et al. Profiling of tRNA Halves and YRNA Fragments in Serum and Tissue From Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients Identify Key Role of 5′ tRNA-Val-CAC-2-1 Half. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, B.V.; Dhahbi, J.M.; Lopez, Y.O.N.; Lamperska, K.; Golusinski, P.; Luczewski, L.; Kolenda, T.; Atamna, H.; Spindler, S.R.; Golusinski, W.; et al. Circulating small non coding RNA signature in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 19246–19263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, E.L.; Meier, P. Nonparametric-Estimation from Incomplete Observations. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1958, 53, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A.; Kosinski, M.; Biecek, P. Survminer: Drawing Survival Curves Using ‘ggplot2’; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, P.; Emara, M.M.; Villen, J.; Gygi, S.P.; Anderson, P. Angiogenin-Induced tRNA Fragments Inhibit Translation Initiation. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.; Yim, D.G.; Lakshmanan, V.; Tirumalai, V.; Koh, J.L.; Park, J.E.; Cheong, J.K.; Low, J.L.; Lim, M.J.; Sze, S.-K.; et al. Dynamic expression of tRNA-derived small RNAs define cellular states. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e47789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.B.; Kazan, H.; Zuberi, K.; Morris, Q.; Hughes, T.R. RBPDB: A database of RNA-binding specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D301–D308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Boldrup, L.; Coates, P.J.; Fahraeus, R.; Wang, L.; Wilms, T.; Norberg-Spaak, L.; Sgaramella, N.; Nylander, K. High immune cytolytic activity in tumor-free tongue tissue confers better prognosis in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2019, 5, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrup, L.; Gu, X.; Coates, P.J.; Norberg-Spaak, L.; Fåhraeus, R.; Laurell, G.; Wilms, T.; Nylander, K. Gene expression changes in tumor free tongue tissue adjacent to tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 19389–19402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, S.; Ivanov, P.; Hu, G.-F.; Anderson, P. Angiogenin cleaves tRNA and promotes stress-induced translational repression. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, P.; O’Day, E.; Emara, M.M.; Wagner, G.; Lieberman, J.; Anderson, P. G-quadruplex structures contribute to the neuroprotective effects of angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18201–18206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.C.-H.; Wang, H.; Wu, M.; Chang, K.; Chang, P.; Liao, C.; Liau, C. Review of emerging biomarkers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in the era of immunotherapy and targeted therapy. Head Neck 2019, 41 (Suppl. 1), 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, K.K.; Harris, J.; Wheeler, R.; Weber, R.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Nguyen-Tân, P.F.; Westra, W.H.; Chung, C.H.; Jordan, R.C.; Lu, C.; et al. Human Papillomavirus and Survival of Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Torabi, S.J.; Yarbrough, W.G.; Mehra, S.; Osborn, H.A.; Judson, B.L. Association of Human Papillomavirus Status at Head and Neck Carcinoma Subsites with Overall Survival. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Begley, M.; Li, Q.; Huang, H.-T.; Lako, A.; Eck, M.J.; Gray, N.S.; Mitchison, T.J.; Cantley, L.C.; Zhao, J.J. Mitotic MELK-eIF4B signaling controls protein synthesis and tumor cell survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9810–9815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazian, D.; Parsyan, A.; Petroulakis, E.; Hershey, J.W.B.; Sonenberg, N. eIF4B controls survival and proliferation and is regulated by proto-oncogenic signaling pathways. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 4106–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobala, A.; Hutvagner, G. Small RNAs derived from the 5′ end of tRNA can inhibit protein translation in human cells. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Liang-Hu, Q.; Luo, Y.-X.; Lin, Q.; Liu, S.-R.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Zhou, H.; Yang, J.; Qu, L. Comprehensive Genomic Characterization of RNA-Binding Proteins across Human Cancers. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, D.G.; McShane, L.M.; Sauerbrei, W.; Taube, S.E. Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic studies (REMARK): Explanation and elaboration. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MINTbase Unique ID (Sequence Derived) | Fragment Sequence | p-Value (Kaplan-Meier log Rank Test) | Number of Tumor | Number of Normal | Average Level in Tumor (RPM) | Average Level in Normal (RPM) | Chr | Type | Amino Acid and Anticodon | Predicted RNA Binding Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tRF-20-S998LO9D | GTCTCTGTGGCGCAATGGAC | 0.0003 | 443 | 16 | 20 | 2 | 1 | 5′-tRF | ArgTCT | eIF4B, SRSF1 |
| tRF-16-I8W47WB | ATTGGTCGTGGTTGTA | 0.0003 | 285 | 37 | 12 | 29 | MT | i-tRF | GluTTC | |
| tRF-16-884U1DD | TCCGGCTCGAAGGACC | 0.0003 | 255 | 37 | 10 | 8 | 14 | 3′-tRF | TyrGTA | SRSF9, eIF4B, SRSF1 |
| tRF-22-8XF6RE98N | TCCTAAGCCAGGGATTGTGGGT | 0.0006 | 466 | 42 | 6 | 11 | 16 | i-tRF | ArgCCT | NONO, RBMX |
| tRF-21-NYDRFU8U0 | CTTTGAATCCAGCGATCCGAG | 0.0011 | 340 | 30 | 3 | 3 | 6 | i-tRF | GlnTTG | YTHDC2, RBMX |
| tRF-21-I8W47W1R0 | ATTGGTCGTGGTTGTAGTCCG | 0.0024 | 507 | 41 | 31 | 49 | MT | i-tRF | GluTTC | |
| tRF-21-LE3JWB61B | CGAATCCGGCTCGAAGGACCA | 0.0030 | 209 | 29 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 3′-tRF | TyrGTA | SRSF9, YTHDC1, eIF4B, SRSF1 |
| tRF-20-6S7P4PWJ | GGCCGGTTAGCTCAGTCGGC | 0.0031 | 303 | 14 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 5′-tRF | IleAAT | |
| tRF-23-Z87HFK8SDZ | TTTGGGTGCGAGAGGTCCCGGGT | 0.0039 | 375 | 30 | 4 | 2 | 14 | i-tRF | ProTGG | FUS, RBMX, SRSF10 |
| tRF-23-H3RXSINH0P | ATAGTGGTTAGTACTCTGCGTTG | 0.0050 | 177 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 1 | i-tRF | HisGTG | YBX1, YTHDC1 |
| tRF-19-Z8SSFKJJ | TTTGGGTCCGAGAGGTCCC | 0.0063 | 155 | 19 | 2 | 2 | 11 | i-tRF | ProTGG | SRSF10 |
| tRF-19-Q99P9PJZ | GCTTCTGTAGTGTAGTGGT | 0.0063 | 260 | 19 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 5′-tRF | ValCAC | |
| tRF-20-MEF91SS2 | CGGATAGCTCAGTCGGTAGA | 0.0069 | 115 | 26 | 2 | 2 | 11 | i-tRF | LysTTT | |
| tRF-30-XSXMSL73VL4Y | TGCCGTGATCGTATAGTGGTTAGTACTCTG | 0.0074 | 388 | 27 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 5′-tRF | HisGTG | YTHDC1 |
| tRF-21-7OFIZ9WUD | GTTAAAGACTTTTTCTCTGAC | 0.0075 | 204 | 8 | 4 | 2 | MT | 3′-tRF | ProTGG | SRSF10, KHDRBS3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, X.; Wang, L.; Coates, P.J.; Boldrup, L.; Fåhraeus, R.; Wilms, T.; Sgaramella, N.; Nylander, K. Transfer-RNA-Derived Fragments Are Potential Prognostic Factors in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Genes 2020, 11, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111344
Gu X, Wang L, Coates PJ, Boldrup L, Fåhraeus R, Wilms T, Sgaramella N, Nylander K. Transfer-RNA-Derived Fragments Are Potential Prognostic Factors in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Genes. 2020; 11(11):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111344
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Xiaolian, Lixiao Wang, Philip J. Coates, Linda Boldrup, Robin Fåhraeus, Torben Wilms, Nicola Sgaramella, and Karin Nylander. 2020. "Transfer-RNA-Derived Fragments Are Potential Prognostic Factors in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck" Genes 11, no. 11: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111344
APA StyleGu, X., Wang, L., Coates, P. J., Boldrup, L., Fåhraeus, R., Wilms, T., Sgaramella, N., & Nylander, K. (2020). Transfer-RNA-Derived Fragments Are Potential Prognostic Factors in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Genes, 11(11), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111344






