Phylogenetic Analysis and Substitution Rate Estimation of Colonial Volvocine Algae Based on Mitochondrial Genomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultures
2.2. Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Substitution Rate Estimation
3. Results
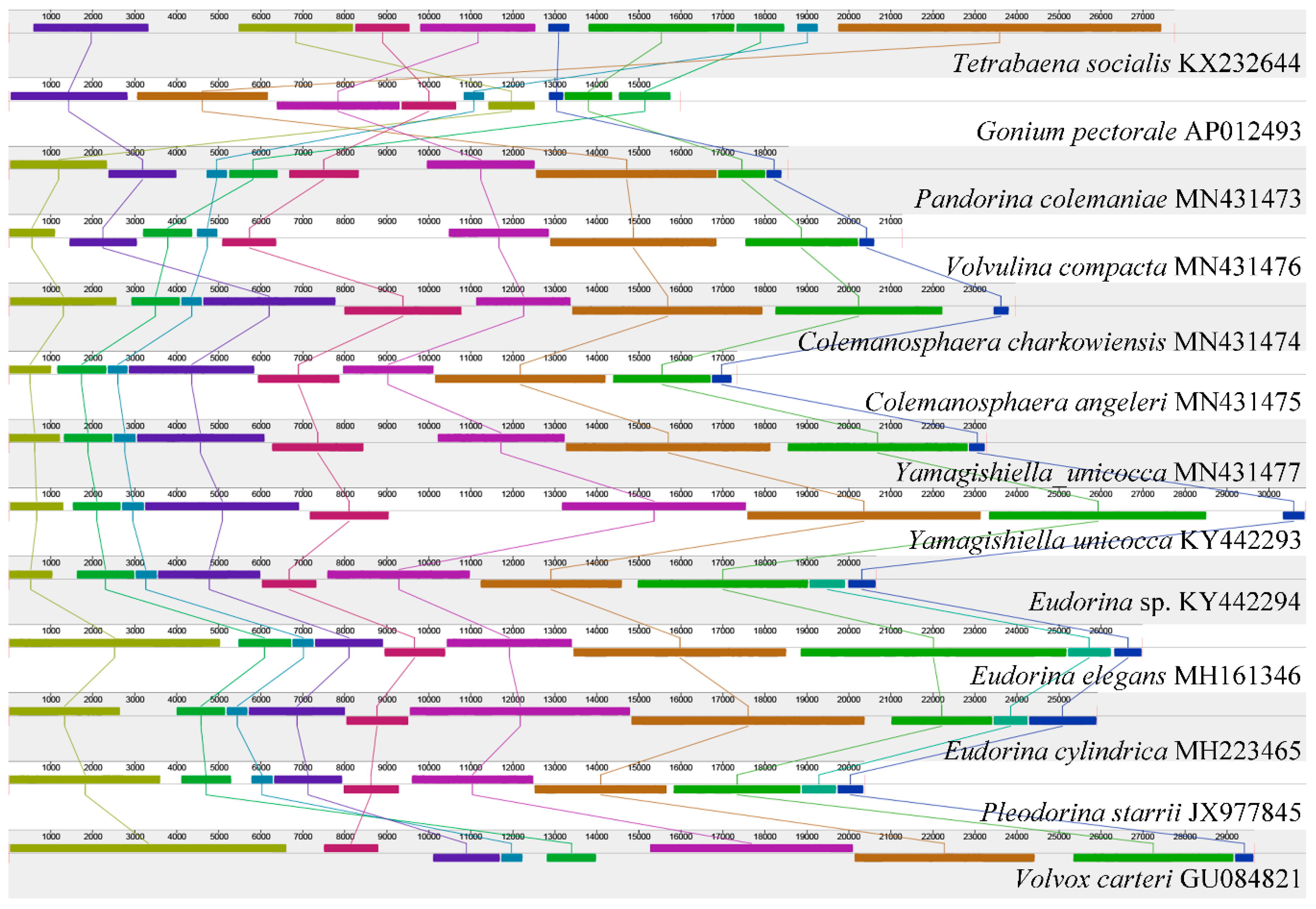
3.1. Mitochondrial Genome of Colonial Volvocine Algae
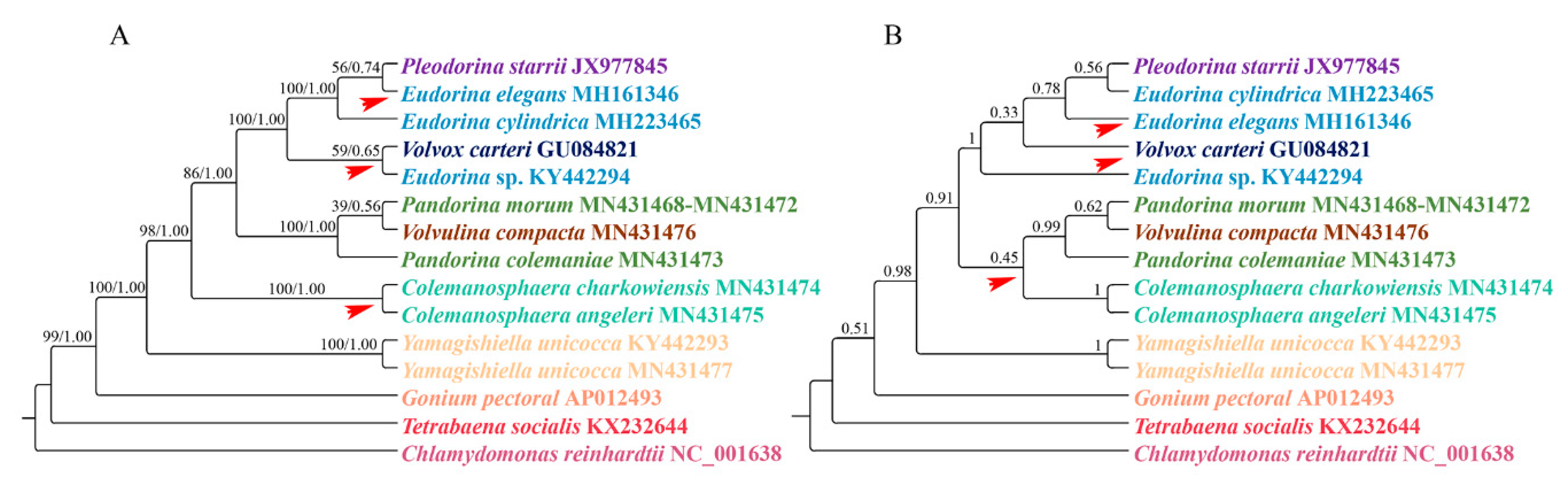
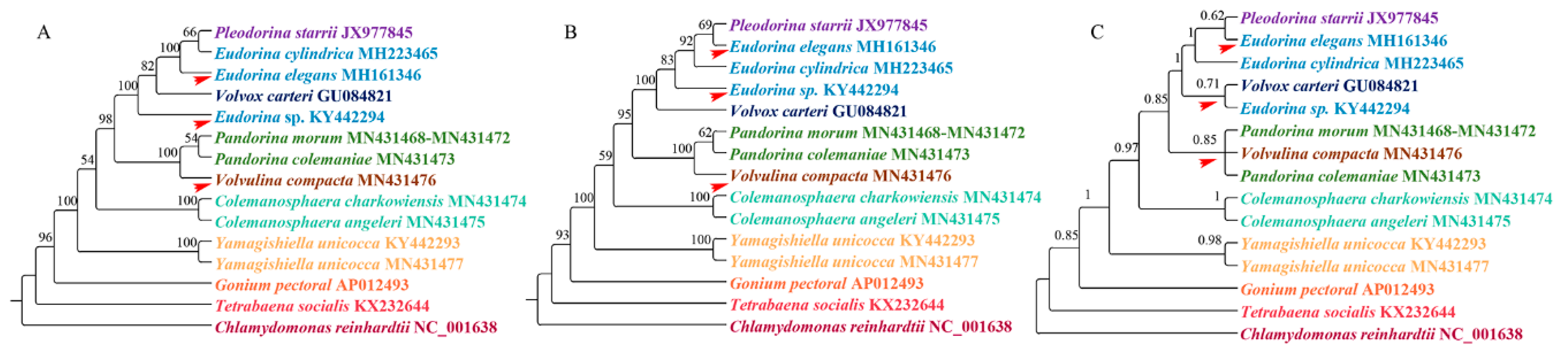
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
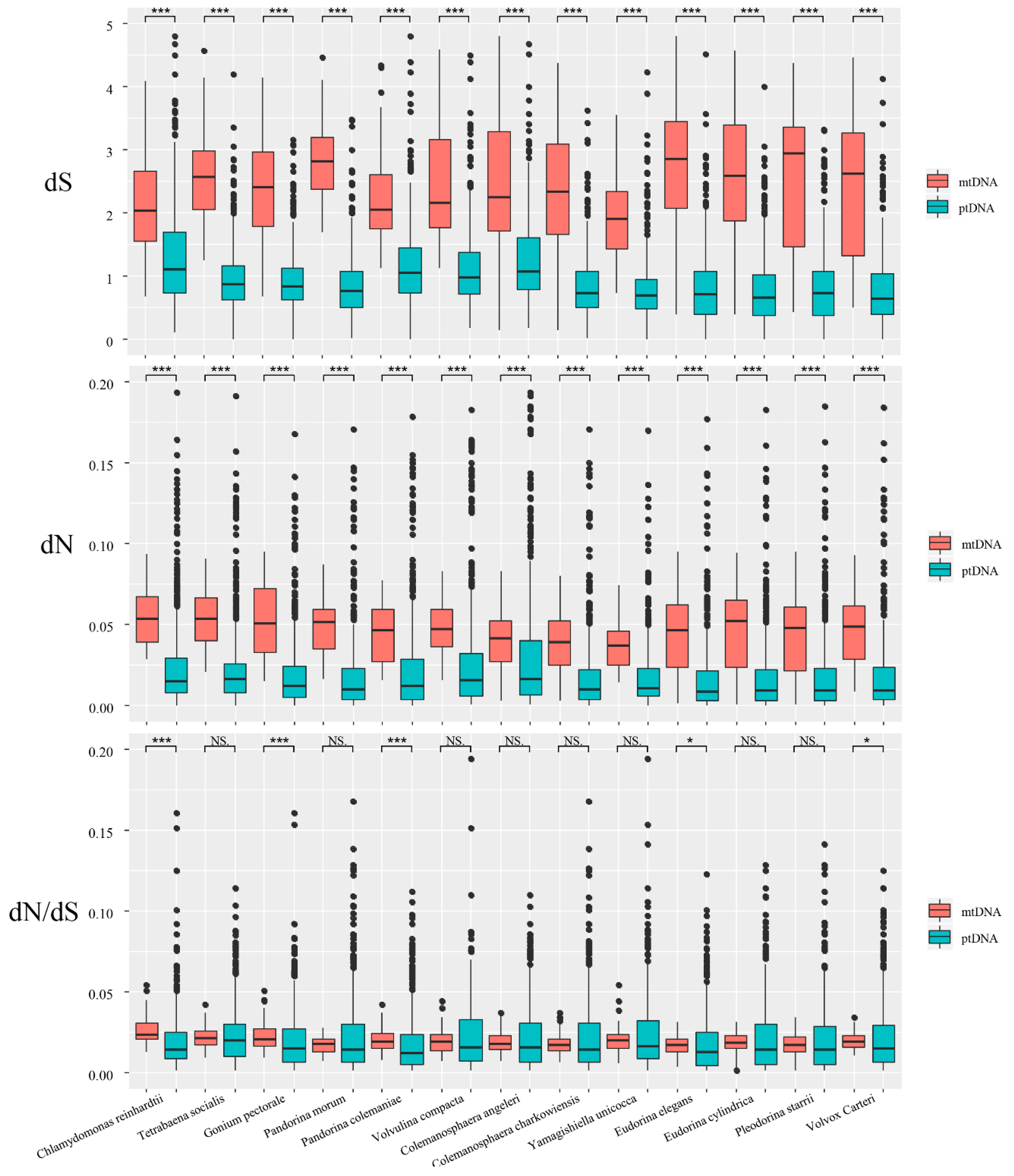
3.3. Substitution Rate Estimation
4. Discussion
4.1. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.2. Substitution Rate Estimation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, L.J.; Coleman, A.W. The linear 20 kb mitochondrial genome of Pandorina morum (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyta). Plant Mol. Biol. 1989, 13, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.R.; Lee, R.W. Low nucleotide diversity for the expanded organelle and nuclear genomes of Volvox carteri supports the mutational-hazard hypothesis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2244–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hamaji, T.; Smith, D.R.; Noguchi, H.; Toyoda, A.; Suzuki, M.; Kawai-Toyooka, H.; Fujiyama, A.; Nishii, I.; Marriage, T.; Olson, O.; et al. Mitochondrial and plastid genomes of the colonial green alga Gonium pectorale give insights into the origins of organelle DNA architecture within the Volvocales. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.R.; Hamaji, T.; Olson, B.J.; Durand, P.M.; Ferris, P.; Michod, R.E.; Featherston, J.; Nozaki, H.; Keeling, P.J. Organelle genome complexity scales positively with organism size in volvocine green algae. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Featherston, J.; Arakaki, Y.; Nozaki, H.; Durand, P.M.; Smith, D.R. Inflated organelle genomes and a circular-mapping mtDNA probably existed at the origin of coloniality in volvocine green algae. Eur. J. Phycol. 2016, 51, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaji, T.; Kawai-Toyooka, H.; Toyoda, A.; Minakuchi, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Fujiyama, A.; Nozaki, H.; Smith, D.R. Multiple independent changes in mitochondrial genome conformation in Chlamydomonadalean algae. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xing, W.; Song, H.; Liu, G.; Hu, Z. Analysis of mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes in two volvocine algae: Eudorina elegans and Eudorina cylindrica (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyta). Eur. J. Phycol. 2019, 54, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.D.; Karol, K.G.; McCourt, R.M.; Delwiche, C.F. Phylogeny of the conjugating green algae based on chloroplast and mitochondrial nucleotide sequence data. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, J.D.; Borsa, P. Mitochondrial phylogeny of grey mullets (Acanthopterygii: Mugilidae) suggests high proportion of cryptic species. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2015, 338, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Song, H.J.; Park, S.I.; Lee, Y.M.; Jeong, S.Y.; Cho, T.O.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, H.; Choi, C.G.; Nelson, W.A.; et al. Mitochondrial and plastid genomes from coralline red algae provide insights into the incongruent evolutionary histories of organelles. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 2961–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhove, M.P.; Briscoe, A.G.; Jorissen, M.W.; Littlewood, D.T.J.; Huyse, T. The first next-generation sequencing approach to the mitochondrial phylogeny of African monogenean parasites (Platyhelminthes: Gyrodactylidae and Dactylogyridae). BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, C.B.; Cox, C.J.; Brito, L.; Pavão, M.M.; Pereira, H.; Ferreira, A.; Ginja, C.; Campino, L.; Bermejo, R.; Parente, M.; et al. Improved phylogeny of brown algae Cystoseira (Fucales) from the Atlantic-Mediterranean region based on mitochondrial sequences. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210143. [Google Scholar]
- Angeler, D.G.; Schagerl, M.; Coleman, A.W. Phylogenetic relationships among isolates of Eudorina species (Volvocales, Chlorophyta) inferred from molecular and biochemical data. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, A.W. Biogeography and speciation in the Pandorina/Volvulina (Chlorophyta) superclade. J. Phycol. 2001, 37, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.K.; Miyaji, K.; Nozaki, H. A taxonomic study of Eudorina unicocca (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyceae) and related species, based on morphology and molecular phylogeny. Eur. J. Phycol. 2008, 43, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hayama, M.; Nakada, T.; Hamaji, T.; Nozaki, H. Morphology, molecular phylogeny and taxonomy of Gonium maiaprilis sp. nov. (Goniaceae, Chlorophyta) from Japan. Phycologia 2010, 49, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, T.; Tomita, M.; Nozaki, H. Volvulina compacta (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyceae), new to Japan, and its phylogenetic position. J. Jpn. Bot. 2010, 85, 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki, H.; Ito, M.; Sano, R.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, M.M.; Takahashi, H.; Kuroiwa, T. Phylogenetic analysis of Yamagishiella and Platydorina (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyta) based on rbcL gene sequences. J. Phycol. 1997, 33, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, H.; Ito, M.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, M.M.; Kuroiwa, T. Phylogenetic analysis of Eudorina species (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyta) based on rbcL gene sequences. J. Phycol. 1997, 33, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, H.; Song, L.; Liu, Y.; Hiroki, M.; Watanabe, M.M. Taxonomic re-examination of a Chinese strain labeled ‘Eudorina sp.’ (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyta) based on morphological and DNA sequence data. Phycol. Res. 1998, 46, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, H.; Misawa, K.; Kajita, T.; Kato, M.; Nohara, S.; Watanabe, M.M. Origin and evolution of the colonial Volvocales (Chlorophyceae) as inferred from multiple, chloroplast gene sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2000, 17, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozaki, H.; Ott, F.D.; Coleman, A.W. Morphology, molecular phylogeny and taxonomy of two new species of Pleodorina (Volvoceae, Chlorophyceae). J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, H.; Yamada, T.K.; Takahashi, F.; Matsuzaki, R.; Nakada, T. New “missing link” genus of the colonial volvocine green algae gives insights into the evolution of oogamy. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozaki, H.; Matsuzaki, R.; Yamamoto, K.; Kawachi, M.; Takahashi, F. Delineating a new heterothallic species of Volvox (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyceae) using new strains of “Volvox africanus”. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Xing, W.; Song, H.; Zhu, H.; Liu, G.; Hu, Z. Evolutionary analysis of unicellular species in Chlamydomonadales through chloroplast genome comparison with the colonial volvocine algae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R. Mutation rates in plastid genomes: They are lower than you might think. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.M.; George, M.; Wilson, A.C. Rapid evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 1967–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, G.; Daoud, H.; Xia, J. Relative rates of synonymous substitutions in the mitochondrial, chloroplast and nuclear genomes of seed plants. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 49, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Arrigo, K.R.; Alderkamp, A.C.; Allen, A.E. Massive difference in synonymous substitution rates among mitochondrial, plastid, and nuclear genes of Phaeocystis algae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 71, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisdale, C.J.; Smith, D.R.; Archibald, J.M. Relative mutation rates in nucleomorph-bearing algae. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, D.B.; Taylor, D.R. Evolutionary rate variation in organelle genomes: The role of mutational processes. In Organelle Genetics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 123–146. [Google Scholar]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; PÜTZ, J.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinf. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Perna, N.T. progressiveMauve: Multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7, Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, F.; Zardoya, R.; Telford, M.J. TranslatorX: Multiple alignment of nucleotide sequences guided by amino acid translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W7–W13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A.; Dunn, C.W. Phyutility: A phyloinformatics tool for trees, alignments and molecular data. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 715–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2, New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8, A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Mark, P.V.D.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2, Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Rabiee, M.; Sayyari, E.; Mirarab, S. ASTRAL-III: Polynomial time species tree reconstruction from partially resolved gene trees. BMC Bioinf. 2018, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.J.; Delsuc, F.; Penny, D. Genome-scale phylogeny and the detection of systematic biases. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4, Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehr, J.D.; Sheath, R.G.; Kociolek, J.P. Freshwater Algae of North America: Ecology and Classification, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bleidorn, C. Sources of error and incongruence in phylogenomic analyses. In Phylogenomics; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 173–193. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffroy, O.; Brinkmann, H.; Delsuc, F.; Philippe, H. Phylogenomics: The beginning of incongruence? Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockhart, P.J.; Steel, M.A.; Hendy, M.D.; Penny, D. Recovering evolutionary trees under a more realistic model of sequence evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1994, 11, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woese, C.R.; Achenbach, L.; Rouviere, P.; Mandelco, L. Archaeal phylogeny: Reexamination of the phylogenetic position of Archaeoglohus fulgidus in light of certain composition-induced artifacts. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1991, 14, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P. Testing a covariotide model of DNA substitution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Nielsen, R. Estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates under realistic evolutionary models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delsuc, F.; Brinkmann, H.; Philippe, H. Phylogenomics and the reconstruction of the tree of life. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xing, W.; Song, H.; Hu, Z.; Liu, G. Comparison of colonial volvocine algae based on phylotranscriptomic analysis of gene family evolution and natural selection. Eur. J. Phycol. 2019, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, T. Utility of low-copy nuclear gene sequences in plant phylogenetics. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 37, 121–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirarab, S.; Bayzid, M.S.; Warnow, T. Evaluating summary methods for multilocus species tree estimation in the presence of incomplete lineage sorting. Syst. Biol. 2014, 65, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayzid, M.S.; Mirarab, S.; Boussau, B.; Warnow, T. Weighted statistical binning: Enabling statistically consistent genome-scale phylogenetic analyses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallo, D.; Posada, D. Multilocus inference of species trees and DNA barcoding. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2016, 371, 20150335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirarab, S.; Reaz, R.; Bayzid, M.S.; Zimmermann, T.; Swenson, M.S.; Warnow, T. ASTRAL: Genome-scale coalescent-based species tree estimation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, i541–i548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.; Vachaspati, P.; Mirarab, S.; Warnow, T. Phylogenomic species tree estimation in the presence of incomplete lineage sorting and horizontal gene transfer. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirarab, S. Species Tree Estimation Using ASTRAL: Practical Considerations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.03826. [Google Scholar]
- Hanschen, E.R.; Herron, M.D.; Wiens, J.J.; Nozaki, H.; Michod, R.E. Repeated evolution and reversibility of self-fertilization in the volvocine green algae. Evolution 2018, 72, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umen, J.; Coelho, S. Algal Sex Determination and the Evolution of Anisogamy. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Cell Number a | Size (kb) | GC Content | Number of Scaffold | Number of Genes | Genbank Accession | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein-Coding Genes b | rRNA Genes | tRNA Genes | ||||||
| Tetrabaena socialis | 4 | 28 | 45% | 1 | 9 | 12 | 3 | KX232644 |
| Gonium pectorale | 8–32 | 16 | 39% | 1 | 8 | 12 | 4 | AP012493 |
| Pandorina morum | 8–16 | 15 | 45% | 5 | 7 | 3 | 1 | MN431468-MN431472 |
| Pandorina colemaniae | 8–16 | 19 | 38% | 1 | 8 | 9 | 3 | MN431473 |
| Volvulina compacta | 8–16 | 22 | 41% | 1 | 8 | 6 | 4 | MN431476 |
| Colemanosphaera angeleri | 16–32 | 18 | 38% | 1 | 10 | 8 | 3 | MN431475 |
| Colemanosphaera charkowiensis | 16–32 | 24 | 38% | 1 | 9 | 8 | 3 | MN431474 |
| Yamagishiella unicocca | 16–32 | 24 | 41% | 1 | 9 | 12 | 3 | MN431477 |
| Yamagishiella unicocca | 16–32 | 31 | 41% | 1 | 12 | 12 | 3 | KY442293 |
| Eudorina elegans | 16–32 | 27 | 33% | 1 | 11 | 12 | 3 | MH161346 |
| Eudorina cylindrica | 16–32 | 26 | 36% | 1 | 9 | 12 | 3 | MH223465 |
| Eudorina sp. | 16–32 | 21 | 38% | 1 | 9 | 12 | 3 | KY442294 |
| Pleodorina starrii | 32–128 | 20 | 38% | 1 | 10 | 12 | 3 | JX977845 |
| Volvox carteri | 500–50,000 | 35 | 34% | 1 | 10 | 13 | 3 | GU084821 |
| Species | Synonymous Substitution (dS) | Nonsynonymous Substitution (dN) | dN/dS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mtDNA | ptDNA | mt:pt | mtDNA | ptDNA | mt:pt | mtDNA | ptDNA | mt:pt | |
| Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | 2.2 ± 0.87 | 1.31 ± 0.83 | 1.8:1 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 2.17:1 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 1.36:1 |
| Tetrabaena socialis | 2.57 ± 0.73 | 0.95 ± 0.52 | 2.74:1 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 2.33:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.88:1 |
| Gonium pectorale | 2.41 ± 0.86 | 0.93 ± 0.51 | 2.84:1 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 2.67:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 1.12:1 |
| Pandorina morum | 2.85 ± 0.66 | 0.82 ± 0.51 | 3.5:1 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 2.65:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.78:1 |
| Pandorina colemaniae | 2.25 ± 0.76 | 1.14 ± 0.65 | 2.07:1 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 1.92:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 1.1:1 |
| Volvulina compacta | 2.54 ± 0.92 | 1.13 ± 0.64 | 2.39:1 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 1.85:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.96:1 |
| Colemanosphaera angeleri | 2.38 ± 1.13 | 1.24 ± 0.69 | 1.95:1 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 1.33:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.87:1 |
| Colemanosphaera charkowiensis | 2.35 ± 1.11 | 0.82 ± 0.54 | 2.96:1 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 2.11:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.81:1 |
| Yamagishiella unicocca | 1.97 ± 0.72 | 0.8 ± 0.52 | 2.55:1 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 2.03:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.81:1 |
| Eudorina elegans | 2.57 ± 1.22 | 0.83 ± 0.61 | 3.1:1 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 2.62:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.93:1 |
| Eudorina cylindrica | 2.49 ± 1.24 | 0.78 ± 0.55 | 3.37:1 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 2.64:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.86:1 |
| Pleodorina starrii | 2.51 ± 1.25 | 0.81 ± 0.57 | 3:1 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 2.44:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.79:1 |
| Volvox carteri | 2.42 ± 1.18 | 0.78 ± 0.56 | 3.21:1 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 2.58:1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.91:1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Xing, W.; Hu, Z.; Liu, G. Phylogenetic Analysis and Substitution Rate Estimation of Colonial Volvocine Algae Based on Mitochondrial Genomes. Genes 2020, 11, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010115
Hu Y, Xing W, Hu Z, Liu G. Phylogenetic Analysis and Substitution Rate Estimation of Colonial Volvocine Algae Based on Mitochondrial Genomes. Genes. 2020; 11(1):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010115
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yuxin, Weiyue Xing, Zhengyu Hu, and Guoxiang Liu. 2020. "Phylogenetic Analysis and Substitution Rate Estimation of Colonial Volvocine Algae Based on Mitochondrial Genomes" Genes 11, no. 1: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010115
APA StyleHu, Y., Xing, W., Hu, Z., & Liu, G. (2020). Phylogenetic Analysis and Substitution Rate Estimation of Colonial Volvocine Algae Based on Mitochondrial Genomes. Genes, 11(1), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010115





