Transferability and Polymorphism of SSR Markers Located in Flavonoid Pathway Genes in Fragaria and Rubus Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Marker and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Primer Development
2.3. DNA Isolation, PCR Amplification and Fragment Analysis
2.4. Genetic Data Analysis
2.5. Chitinase Gene Sequencing and Sequence Alignment
3. Results
3.1. Development and Characterization of SSR Markers
3.2. Cross-Specific Transferability of SSR Markers
3.3. Allelic Polymorphism and Genetic Diversity
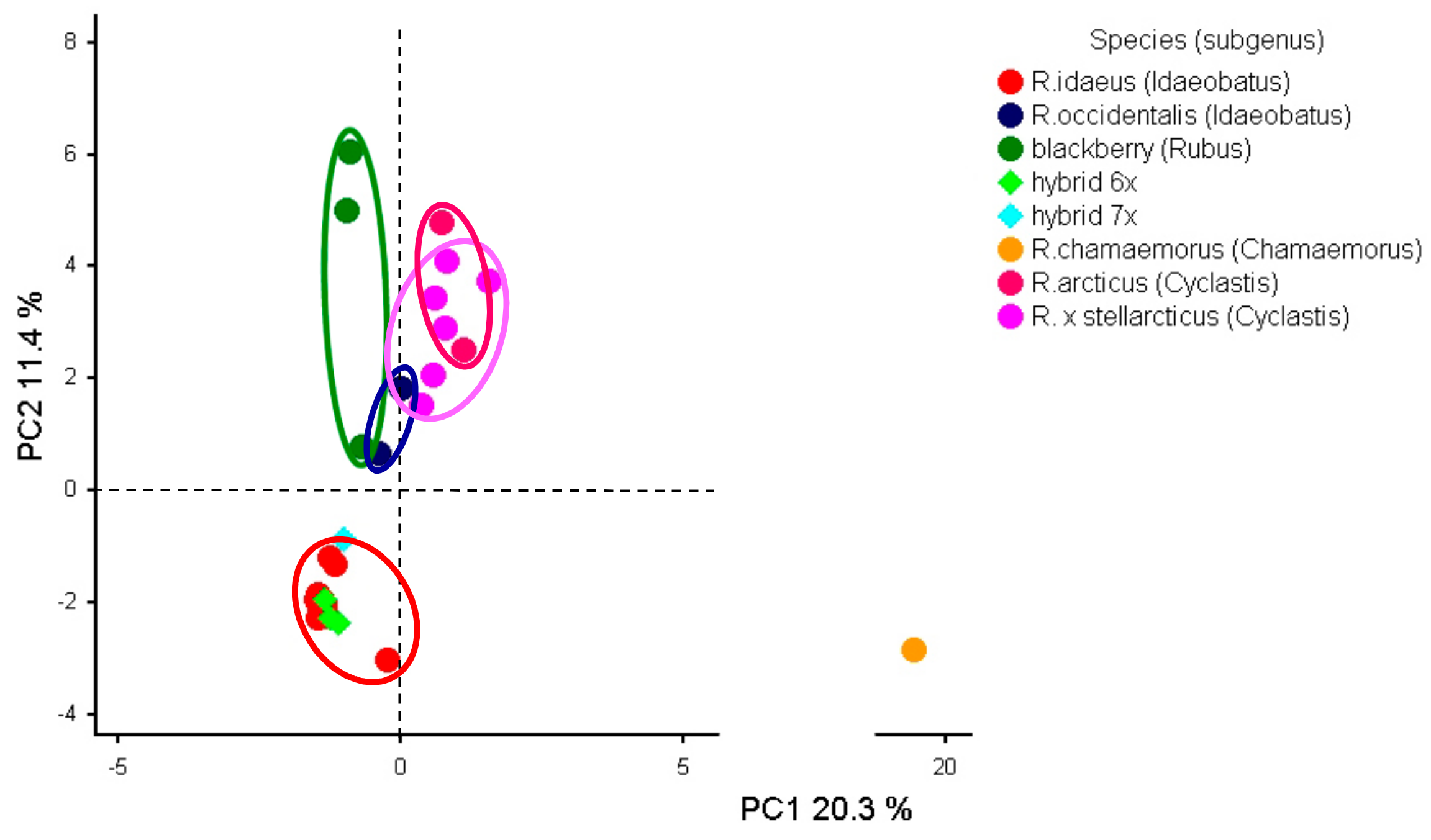
3.4. Genetic Data Analysis
3.5. Sequence Analysis of Chitinase III Genes
4. Discussion
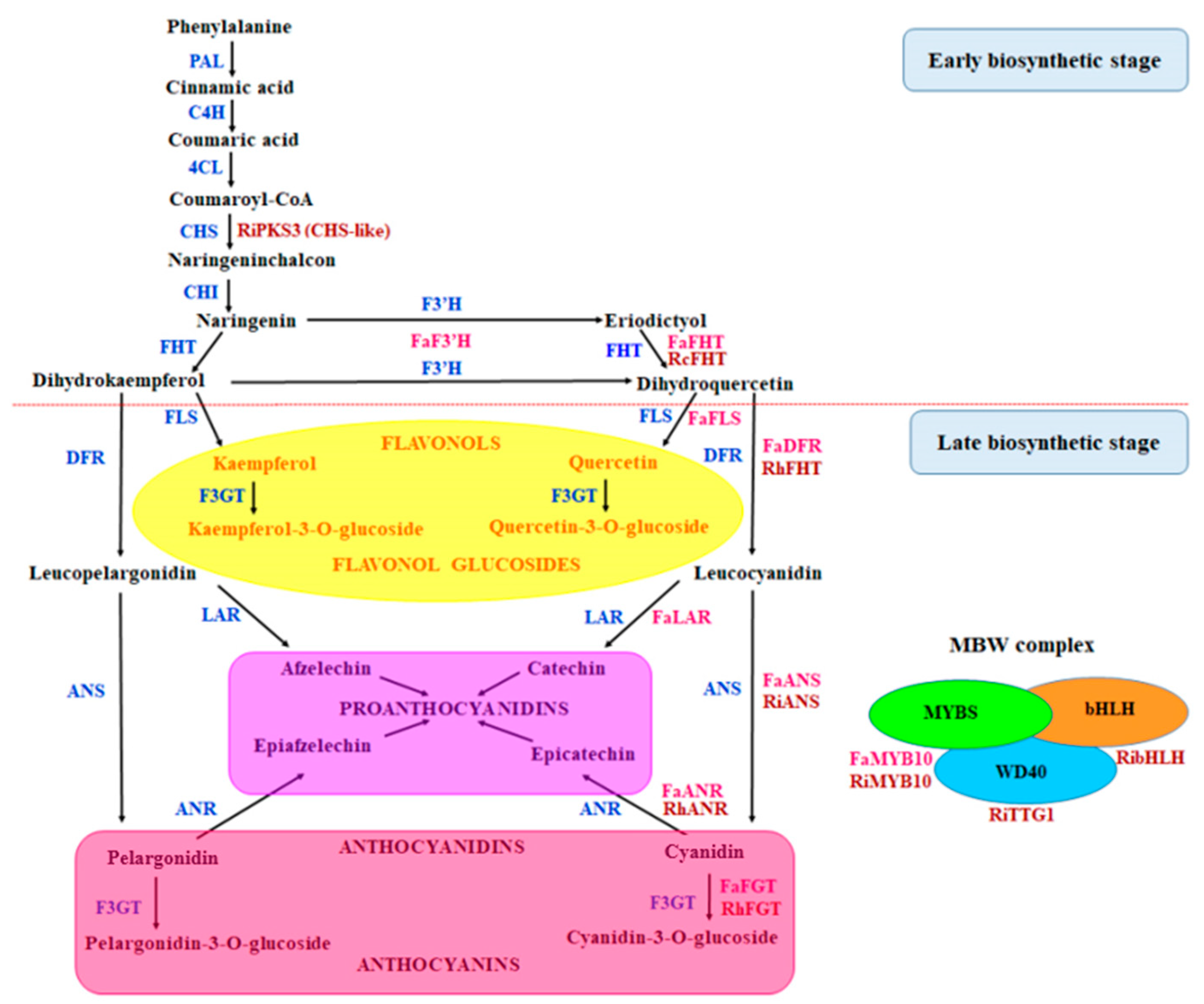
4.1. Choice of Genes and Genic SSR Marker Development
4.2. Choice of Cultivars and Transferability of SSR Markers
4.3. Genetic Diversity of Fragaria and Rubus
4.4. Relationship between Properties of SSR Markers and Their Location
4.5. SSR Markers Representing Transcription Factor (TF) Genes
4.6. Chitinase III as Allergen in Raspberry
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Potter, D.; Eriksson, T.; Evans, R.C.; Oh, S.; Smedmark, J.E.E.; Morgan, D.R.; Kerr, M.; Robertson, K.R.; Arsenault, M.; Dickinson, T.A.; et al. Phylogeny and classification of Rosaceae. Plant System. Evol. 2007, 266, 5–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.M.; Bassil, N.V.; Dossett, M.; Worthington, M.L.; Graham, J. Genetic and genomic resources for Rubus breeding: A roadmap for the future. Hort. Res. 2019, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mezzetti, B.; Giampieri, F.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Zhong, C.-F. Status of strawberry breeding programs and cultivation systems in Europe and the rest of the world. J. Berry Res. 2018, 8, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. 2019. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/ (accessed on 23 October 2019).
- Graham, J.; Jennings, S.N. Raspberry breeding. In Breeding Tree Crops; Jain, S.M., Priyadarshan, M., Eds.; IBH & Science Publication: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 233–248. [Google Scholar]
- Lerceteau-Kohler, E.; Moing, A.; Guerin, G.; Renaud, C.; Petit, A.; Rothan, C.; Denoyes, B. Genetic dissection of fruit quality traits in the octoploid cultivated strawberry highlights the role of homoeo-QTL in their control. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 124, 1059–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swanson, J.-D.; Weber, C.; Finn, C.E.; Fernández-Fernández, F.; Sargent, D.J.; Carlson, J.E.; Graham, J. Raspberries and blackberries. In Genetics, Genomics and Breeding of Berries; Folta, K.M., Kole, C., Eds.; CRC Press, Science Publishers: Manchester, NH, USA, 2011; pp. 64–113. [Google Scholar]
- Liston, A.; Cronn, R.; Ashman, T.-L. Fragaria: A genus with deep historical roots and ripe for evolutionary and ecological insights. Am. J. Bot. 2014, 101, 1686–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edger, P.P.; Poorten, T.J.; Vanburen, R.; Hardigan, M.A.; Colle, M.; Mckain, M.R.; Smith, R.D.; Teresi, S.J.; Nelson, A.D.L.; Wai, C.M.; et al. Origin and evolution of the octoploid strawberry genome. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilmarsson, H.S.; Hytonen, T.; Isobe, S.; Goransson, M.; Toivainen, T.; Hallsson, J.H. Population genetic analysis of a global collection of Fragaria vesca using microsatellite markers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Lv, Y.; Xiong, J.; Ge, C.; Iqbal, S.; Qiao, Y. Identifying genome-wide sequence variations and candidate genes implicated in self-incompatibility by resequencing Fragaria viridis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, T.; Denoyes-Rothan, B.; Lerceteau-Köhler, E. Strawberry. In Fruits and Nuts; Kole, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 189–205. [Google Scholar]
- Bushakra, J.M.; Lewers, K.S.; Staton, M.E.; Zhebentyayeva, T.; Saski, C.A. Developing expressed sequence tag libraries and the discovery of simple sequence repeat markers for two species of raspberry (Rubus L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amsellem, L.; Dutech, C.; Billotte, N. Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellite loci in Rubus alceifolius Poir (Rosaceae), an invasive weed in La Reunion island. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2001, 1, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.M.; Wilson, F.; Hadonou, A.M.; Tobutt, K.R. Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellites in diploid strawberry (Fragaria vesca L.) for mapping, diversity studies and clone identification. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2003, 3, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnejja, M.; Garcia-Mas, J.; Audergon, J.-M.; Arús, P. Prunus microsatellite marker transferability across rosaceous crops. Tree Genet. Genomes 2010, 6, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushakra, J.M.; Stephens, M.J.; Atmadjaja, A.N.; Lewers, K.S.; Symonds, V.V.; Udall, J.A.; Chagne, D.; Buck, E.J.; Gardiner, S.E. Construction of black (Rubus occidentalis) and red (R.idaeus) raspberry linkage maps and their comparison to the genomes of strawberry, apple, and peach. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.; Brennan, R. Introduction to the Rubus Genus. In Raspberry: Breeding, Challenges and Advances; Graham, J., Brennan, R., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead, M.; Weir, A.; Smith, K.; McCallum, S.; Machenzie, K.; Graham, J. Functional markers for red raspberry. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 135, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewers, K.S.; Weber, C.A. The trouble with genetic mapping of raspberry. HortScience 2005, 40, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zorrilla-Fontanesi, Y.; Cabeza, A.; Torres, A.M.; Botella, M.A.; Valpuesta, V.; Monfort, A.; Sanchez-Sevilla, J.F.; Amaya, I. Development and bin mapping of strawberry genic-SSRs in diploid Fragaria and their transferability across the Rosoideae subfamily. Mol. Breed. 2011, 27, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, R.K.; Graner, A.; Sorrells, M.E. Genic microsatellite markers in plants: Features and applications. Trends Biotech. 2005, 23, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.G.; Subbotina, N.M.; Maluchenko, O.P.; Krutovsky, K.V.; Shestibratov, K.A. Assessment of genetic diversity in differently colored raspberry cultivars using SSR markers located in flavonoid biosynthesis genes. Agronomy 2019, 9, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, M.; Salazar, E.; Castillo, J.; Morales, P.; Mura-Jornet, I.; Maldonado, J.; Silva, H.; Carrasco, B. Genetic structure based on EST-SSR: A putative tool for fruit color selection in Japanese plum (Prunus salicina L.) breeding programs. Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakola, L. New insights into the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in fruits. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, H.K.; Kampler, C. Raspberry Breeding. Fruit, Vegetable and Cereal Science and Biotechnology; Isleworth: London, UK, 2011; Volume 5, pp. 44–62. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, W.S.; Lucas, D.C.S.; Neves, K.F.S.; Bertioli, D.J. WebSat—A web software for microsatellite marker development. Bioinformation 2009, 3, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castillo, N.R.F.; Reed, B.M.; Graham, J.; Fernandez-Fernandez, F.; Bassil, N.V. Microsatellite markers for raspberry and blackberry. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 135, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunes, C.F.; Ferreira, J.L.; Nunes-Fernandes, M.C.; de Souza Breves, S.; Generoso, A.L.; Fontes-Soares, B.D.; Carvalho-Dias, M.S.; Pasqual, M.; Borem, A.; de Almeida Cancado, G.M. An improved method for genomic DNA extraction from strawberry leaves. Ciência Rural 2011, 41, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Muse, S.V. PowerMarker: An integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2128–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meirmans, P.G.; Van Tienderen, P.H. GENOTYPE and GENODIVE: Two programs for the analysis of genetic diversity of asexual organisms. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandin, U. PC-ORD version 5: A user-friendly toolbox for ecologists. J. Veg. Sci. 2006, 17, 843–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzban, G.; Herndl, A.; Kolarich, D.; Maghuly, F.; Mansfeld, A.; Hemmer, W.; Katinger, H.; Laimer, M. Identification of four IgE-reactive proteins in raspberry (Rubus ideaeus L.). Mol. Nutr. Food Res 2008, 52, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, N.M.; Grazziotin, A.L.; Ramos, H.C.C.; Pereira, M.G.; Venancio, T.M. Development of a gene-centered SSR atlas as a resource for papaya (Carica papaya) marker-assisted selection and population genetic studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, M.L.C.; Santini, L.; Diniz, A.L.; Munhoz, C.F. Microsatellite markers: What they mean and why they are so useful. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2016, 39, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyant, L.H.-S.; Crespel, L.; Rajapakse, S.; Zhang, L.; Foucher, F. Genetic linkage maps of rose constructed with new microsatellite markers and locating QTL controlling flowering traits. Tree Genet. Genomes 2008, 4, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H.; Ahna, S.G.; Choia, Y.M.; Oha, H.J.; Ahnb, D.C.; Kimb, J.G.; Kanga, J.S.; Choia, Y.W.; Jeong, B.R. Rose (Rosa hybrida L.) EST-derived microsatellite markers and their transferability to strawberry (Fragaria spp.). Sci. Hortic. 2010, 125, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jia, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xie, W. Development and characterization of transcription factor gene-derived microsatellite (TFGM) markers in Medicago truncatula and their transferability in leguminous and non-leguminous species. Molecules 2015, 20, 8759–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sargent, D.J.; Rys, A.; Nier, S.; Simpson, D.W.; Tobutt, K.R. The development and mapping of functional markers in Fragaria and their transferability and potential for mapping in other genera. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 114, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezo, A.B.; Cuevas, E.; Winterhalter, P.; Garcia-Parrilla, M.C.; Troncoso, A.M. Isolation, identification, and antioxidant activity of anthocyanin compounds in Camarosa strawberry. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, S.P.; Nes, A.; Wold, A.-B.; Remberg, S.F.; Aaby, K. Quality and chemical composition of ten red raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) genotypes during three harvest seasons. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Dubos, C.; Lepiniec, L. Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Ning, G.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Jin, H.; Li, P.; Huang, S.; Zhao, J.; Bao, M. Disequilibrium of flavonol synthase and dihydroflavonol-4-reductase expression associated tightly to white vs. red color flower formation in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, D.; Schröder, G.; Schröder, J.; Hrazdina, G. Molecular and biochemical characterization of three aromatic polyketide synthase genes from Rubus idaeus. Plant Mol. Biol. 2001, 46, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin-Wang, K.; Bolitho, K.; Grafton, K.; Kortstee, A.; Karunairetnam, S.; McGhie, T.K.; Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; Allan, A.C. An R2R3 MYB transcription factor associated with regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Rosaceae. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassim, A.; Poette, J.; Paterson, A.; Zait, D.; McCallum, S.; Woodhead, M.; Smith, K.; Hackett, C.; Graham, J. Environmental and seasonal influences on red raspberry anthocyanin antioxidant contents and identification of quantitative traits loci (QTL). Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortora, M.L.; Díaz-Ricci, J.C.; Pedraza, R.O. Protection of strawberry plants (Fragaria ananassa Duch.) against anthracnose disease induced by Azospirillum Bras. Plant Soil 2012, 356, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobes, C.H.; Scheffknecht, S. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci for the Potentilla core group (Rosaceae) using 454 sequencing. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.-A.; Song, J.Y.; Choi, H.-R.; Chung, J.-W.; Jeon, Y.-A.; Lee, J.-R.; Ma, K.-H.; Lee, M.-C. Novel microsatellite markers acquired from Rubus coreanus Miq. and cross-amplification in other Rubus species. Molecules 2015, 20, 6432–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parida, S.K.; Verma, M.; Yadav, S.K.; Ambawat, S.; Das, S.; Garg, R.; Jain, M. Development of genome-wide informative simple sequence repeat markers for large-scale genotyping applications in chickpea and development of web resource. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Walla, J.A.; Zhong, S.; Huang, D.; Dai, W. Development and cross-species/genera transferability of microsatellite markers discovered using 454 genome sequencing in chokecherry (Prunus virginiana L.). Plant Cell Rep 2012, 31, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Gong, C.; Pan, W.; Zhang, D. Development and application of microsatellites in candidate genes related to wood properties in the chinese white poplar (Populus tomentosa Carr.). DNA Res. 2013, 20, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosamia, T.C.; Mishra, G.P.; Thankappan, R.; Dobaria, J.R. Novel and stress relevant EST derived SSR markers developed and validated in peanut. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aaby, K.; Mazur, S.; Nes, A.; Skrede, G. Phenolic compounds in strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch.) fruits: Composition in 27 cultivars and changes during ripening. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaby, K.; Skareta, J.; Røen, D.; Sønstebyc, A. Sensory and instrumental analysis of eight genotypes of red raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) fruits. J. Berry Res. 2019, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leišová-Svobodová, L.; Phillips, J.; Martinussen, I.; Holubec, V. Genetic differentiation of Rubus chamaemorus populations in the Czech Republic and Norway after the last glacial period. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 5701–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostamo, K.; Toljamo, A.; Antonius, K.; Kokko, H.; Karenlampi, S.L. Morphological and molecular identification to secure cultivar maintenance and management of self-sterile Rubus arcticus. Ann. Bot. 2013, 111, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirakawa, H.; Shirasawa, K.; Kosugi, S.; Tashiro, K.; Nakayama, S.; Yamada, M.; Kohara, M.; Watanabe, A.; Kishida, Y.; Fujishiro, T.; et al. Dissection of the octoploid strawberry genome by deep sequencing of the genomes of Fragaria species. DNA Res. 2014, 21, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassil, N.V.; Gunn, M.; Folta, K.M.; Lewers., K.S. Microsatellite markers for Fragaria from ‘Strawberry Festival’ expressed sequence tags. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.; Smith, K.; Woodhead, M.; Russell, J. Development and use of simple sequence repeat SSR markers in Rubus species. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2002, 2, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, F.; Antanaviciute, L.; Govan, C.L.; Sargent, D.J. Development of a multiplexed microsatellite set for fingerprinting red raspberry (Rubus idaeus) germplasm and its transferability to other Rubus species. J. Berry Res. 2011, 1, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stafne, E.T.; Clark, J.R.; Weber, C.A.; Graham, J.; Lewers, K.S. Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers for genetic mapping of raspberry and blackberry. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2005, 130, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, W.C.; Chen, X.; Fang, P.H.; Shi, S.C.; Li, J.J.; Liu, X.T.; Cao, X.Q.; Zhao, N.; Hao, H.Y.; Li, Y.J.; et al. Genomicand transcriptomic sequencing of Rosa hybrida provides microsatellite markers for breeding, flower trait improvement and taxonomy studies. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Huang, C.-H.; Hu, Y.; Wen, J.; Li, S.; Yi, T.; Chen, H.; Xiang, J.; Ma, H. Evolution of Rosaceae fruit types based on nuclear phylogeny in the context of geological times and genome duplication. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 262–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, M.-Y.; Moe, K.T.; Kim, D.-Y.; Rho, I.-R.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.-T.; Won, M.-K.; Chung, J.-W.; Park, Y.-J. Genetic diversity and population structure analysis of strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) using SSR markers. Electron. J. Biotech. 2012, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, M.V.; Wilk, J.A.; Styan, S.M.N.; Craft, K.J.; Jones, K.L.; Feldheim, K.A.; Lewers, K.S.; Ashman, T.L. High variability and disomic segregation of microsatellites in the octoploid Fragaria virginiana Mill. (Rosaceae). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dossett, M.; Bassil, N.V.; Lewers, K.S.; Finn, C.E. Genetic diversity in wild and cultivated black raspberry (Rubus occidentalis L.) evaluated by simple sequence repeat markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2012, 59, 1849–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, A.; Melmaiee, K.; Elavarthi, S.; Julian Jones, J.; Umesh Reddy, U. Characterization of strawberry (Fragaria spp.) accessions by genotyping with SSR markers and phenotyping by leaf antioxidant and trichome analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallarino, J.G.; de Abreu, E.; Lima, F.; Soria, C.; Tong, H.; Pott, D.M.; Willmitzer, L.; Fernie, A.R.; Nikoloski, Z.; Osorio, S. Genetic diversity of strawberry germplasm using metabolomic biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Sevilla, J.F.; Horvath, A.; Botella, M.A.; Gaston, A.; Folta, K.; Kilian, A.; Denoyes, B.; Amaya, I. Diversity arrays technology (DArT) marker platforms for diversity analysis and linkage mapping in a complex crop, the octoploid cultivated strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simlat, M.; Ptak, A.; Kula, A.; Orzeł, A. Assessment of genetic variability among raspberry accessions using molecular markers. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2018, 17, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.K.; Nath, U.K.; Howlader, J.; Bagchi, M.; Natarajan, S.; Kayum, M.A.; Kim, H.-T.; Park, J.-I.; Kang, J.-G.; Nou, I.-S. Exploration and exploitation of novel SSR markers for candidate transcription factor genes in Lilium species. Genes 2018, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kujur, A.; Bajaj, D.; Saxena, M.S.; Tripathi, S.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Gowda, C.L.; Singh, S.; Jain, M.; Tyagi, A.K.; Parida, S.K. Functionally relevant microsatellite markers from chickpea transcription factor genes for efficient genotyping applications and trait association mapping. DNA Res. 2013, 20, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuan, P.A.; Bai, S.; Yaegaki, H.; Tamura, T.; Hihara, S.; Moriguchi, T.; Oda, K. The crucial role of PpMYB10.1 in anthocyanin accumulation in peach and relationships between its allelic type and skin color phenotype. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leoni, C.; Volpicella, M.; Dileo, M.C.; Gattulli, B.A.; Ceci, L.R. Chitinases as food allergens. Molecules 2019, 24, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Shi, W.; Gao, F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G.; Feng, J. Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of the chitinases under cold and osmotic stress in Ammopiptanthus nanus. Genes 2019, 10, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hjernø, K.; Alm, R.; Canbäck, B.; Matthiesen, R.; Trajkovski, K.; Björk, L.; Roespstorff, P.; Emanuelsson, C. Down-regulation of the strawberry Bet v 1-homologous allergen in concert with the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in colorlessstrawberry mutant. Proteomics 2006, 6, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, C.; Hoffmann, T.; Escobar, N.M.; Ludemann, F.; Botella, M.A.; Valpuesta, V.; Schwab, W. The strawberry fruit Fra a allergen functions in flavonoid biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanal, A.; Zander, U.; Munoz, C.; Dupeux, F.; Luque, I.; Botella, M.A.; Schwab, W.; Valpuesta, V.; Marquez, J.A. The strawberry pathogenesis-related 10 (PR-10) Fra a proteins control flavonoid biosynthesis by binding to metabolic intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35322–35332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Species | Specimen | Pedigree | Ploidy | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F. × ananassa | White D | F. virginiana × F. chiloensis | 8x | Sweden |
| Vechnaya Vesna | Grenader-V2 × Rannyaya Plotnaya | 8x | Russia | |
| Girlyanda | Elsanta × Korona | 8x | Russia | |
| Zolushka | Festivalnaya × Senga Sengana | 8x | Russia | |
| Lakomka | Krasavitsa × Korona | 8x | Russia | |
| Lyubava | Solovushka × Geneva | 8x | Russia | |
| Solovushka | Syurpriz Olimpiade × Festivalnaya Romashka | 8x | Russia | |
| Tsaritsa | Venta × Red Gauntlet | 8x | Russia | |
| Honeoye | Vibrant × Holiday | 8x | USA | |
| Korona | Tamella × Induka | 8x | Netherlands | |
| Red Gauntlet | New Jersey 105 × Climax | 8x | UK | |
| Senga Sengana | Sieger × Markee | 8x | Germany | |
| Black Prince | unknown | 8x | unknown | |
| F. × Comarum | Lipstick | Hybrid (F. × ananassa) × Comarum palustre | 7x | Netherlands |
| F. vesca | - | wild strain | 2x | Russia |
| F. viridis | - | 2x | Russia | |
| R. chamaemorus | NyBy | 8x | Finland | |
| R. arcticus | Elpee | 2x | Finland | |
| Mespi | 2x | Finland | ||
| R. × stellarcticus | Anna | Hybrid arctic bramble R. arcticus ssp. stellatus × R. arcticus ssp. arcticus | 2x | Sweden |
| Beata | 2x | Sweden | ||
| Linda | 2x | Sweden | ||
| Sofia | 2x | Sweden | ||
| Astra | 2x | Finland | ||
| Aura | 2x | Finland | ||
| R. idaeus | Babye Leto II | Autumn Bliss × Babye Leto | 2x | Russia |
| Oranzhevoe Chudo | Shapka Monomaha (open pollination) | 2x | Russia | |
| Zheltyj Gigant | Marosejka × Ivanovskaya | 2x | Russia | |
| Zolotaya Osen | 13-39-11 (open pollination) | 2x | Russia | |
| Patritsiya | Marosejka × М102 | 2x | Russia | |
| Gusar | Canby × pollen mix | 2x | Russia | |
| Fenomen | Stolichnaya × Odarka | 2x | Ukraine | |
| Joan J | Terri-Louise × Joan Squire | 2x | UK | |
| Marosejka | 7324/50 × 7331/3 | 2x | Russia | |
| Pingvin | interspecific hybrid | 2x | Russia | |
| Fall Gold | NH 56-1 × (Taylor × R. pungens var. oldhamii) F2 (open pollination) | 2x | USA | |
| Himbo Top | Autumn Bliss × Rafzeter | 2x | Switzerland | |
| Polana | Heritage × Zeva Herbsterne | 2x | Poland | |
| Zhar-Ptitsa | 7-43-2 (open pollination) | 2x | Russia | |
| R. occidentalis | Cumberland | Gregg selfed | 2x | USA |
| Jewel | (Bristol × Dundee) × Dundee | 2x | USA | |
| Blackberry | Brzezina | 90,402 × 89,403 | 4x | Poland |
| Natchez | Ark. 2005 × Ark. 1857 | 4x | USA | |
| Ebony King | unknown | 4x | USA | |
| Hybrid | Boysenberry | complex hybrid | 7x | USA |
| Loganberry | R. ursinus × R. idaeus | 6x | USA | |
| Tayberry | Aurora × SCRI 626/67 | 6x | UK | |
| Buckingham Tayberry | chimeral spineless sport of Tayberry | 6x | UK |
| Location | SSR Motif | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mono | Di | Tri | Tetra | Penta | Hexa | ||
| Upstream | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 17 |
| 5′UTR | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 4 | 16 |
| Exon | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 18 | 11 | 33 |
| Intron | 2 | 9 | 0 | 6 | 17 | 7 | 41 |
| 3′UTR | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 11 |
| Total | 6 | 15 | 5 | 9 | 53 | 30 | 118 |
| Locus | Location | Number of Alleles | Ho | He | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FaF3H01 | 5′UTR | 4 | 0.42 | 0.52 | 0.52 |
| FaFH01 | intron | 5 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.79 |
| FaFS01 | intron/exon | 14 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.89 |
| FaDR01 | upstream | 9 | 0.58 | 0.82 | 0.81 |
| FaLR01 | intron | 4 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.70 |
| FaFG01 | 5′UTR/exon | 8 | 0.74 | 0.72 | 0.71 |
| FaMY01 | intron | 4 | 0.42 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| FaMY02 | intron | 13 | 0.75 | 0.84 | 0.83 |
| RiMY01 | intron | 2 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| RiHL01 | intron | 4 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.59 |
| FaCH02 | exon | 4 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 0.34 |
| FaBG01 | upstream | 9 | 0.68 | 0.82 | 0.81 |
| Mean | 6.7 | 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| Marker | Location | Number of Alleles | Ho | He | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RiG001 | intron | 3 | 0.08 | 0.53 | 0.43 |
| FaFH01 | intron | 5 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 0.51 |
| RcFH01 | intron | 4 | 0.21 | 0.43 | 0.40 |
| FaFS01 | intron/exon | 5 | 0.29 | 0.70 | 0.65 |
| FaLR01 | intron | 3 | 0.04 | 0.34 | 0.29 |
| RiAS01 | exon | 4 | 0.33 | 0.62 | 0.56 |
| RhUF01 | exon | 4 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.34 |
| RiMY01 | intron | 13 | 0.42 | 0.84 | 0.82 |
| RiHL01 | intron | 2 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| FaCH01 | 5′UTR/exon | 3 | 0.50 | 0.64 | 0.57 |
| Mean | 4.60 | 0.23 | 0.51 | 0.46 |
| Genus | Locus | Primer Binding Site Location 1 | Amplification | Locus Location | F. × ananassa | Rubus3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fragaria | Rubus2 | Number of Alleles | Polymorphism | Number of Alleles | Polymorphism | ||||
| Both Binding Sites Located in Exons | |||||||||
| Fragaria | FaFH01 | ex1–ex2 | + | + | in1 | 5 | + | 8 | –/+/+/+/–/+ |
| FaFS01 | ex2–ex3 | + | + | in2 ex3 | 14 | + | 8 | +/–/+/+/–/+ | |
| FaFS02 | ex1–ex1 | + | + | ex1 | 1 | – | 1 | – | |
| FaAR01 | ex4–ex5 | + | + | ex4 in4 | 2 | – | 1 | – | |
| FaTG01 | ex2–ex2 | + | + | ex2 | 1 | – | 3 | –/–/–/+/–/– | |
| Rubus | RiAS01 | ex2–ex2 | + | + | ex2 | 2 | – | 5 | +/–/+/+/+/+ |
| RhUF01 | ex2–ex2 | – | + | ex2 | – | n | 5 | + | |
| RiTT01 | ex–ex | – | + | exon | – | n | 1 | – | |
| One of Binding Sites Located in Exon another in Intron or 5′UTR | |||||||||
| Fragaria | FaMY02 | in2–ex3 | +/– | – | in2 | 14 | + | – | n |
| FaLR01 | ex2–in2 | +/– | –/–/–/+/+ | in2 | 4 | + | 2 | n/n/n/n/+/+ | |
| FaFG01 | 5′UTR–ex1 | + | – | 5′UTR ex1 | 8 | + | – | n | |
| FaAS01 | in–ex2 | + | – | ex2 | 1 | – | – | n | |
| FaCH01 | 5′UTR–ex1 | + | +/–/+/+/+ | 5′UTR ex1 | 2 | – | 3 | +/n/n/+/–/+ | |
| FaCH02 | in–ex2 | + | – | ex2 | 4 | + | – | n | |
| Rubus | RiHL01 | ex1–in | + | + | in | 4 | + | 2 | +/–/–/–/–/– |
| RcFH01 | in2–ex3 | – | + | in2 | – | n | 5 | +/+/–/+/–/+ | |
| RiG001 | in–ex2 | – | +/–/–/–/– | in | – | n | 2 | +/n/n/n/n/n | |
| Both Binding Sites Located in Intron, 5′UTR or Upstream | |||||||||
| Fragaria | FaMY01 | in2–in2 | +/– | – | in2 | 4 | + | – | n |
| FaDR01 | up–5′UTR | +/– | – | up | 9 | + | – | n | |
| FaF3H01 | 5′UTR–5′UTR | + | – | 5′UTR | 4 | + | – | n | |
| FaBG01 | up–up | + | – | up | 9 | + | – | n | |
| One of Binding Sites Located across Exon/Intron Junction | |||||||||
| Rubus | RiMY01 | ex1/in1–ex2 | + | +/+/+/+/– | in1 | 2 | + | 17 | +/–/+/+/+/n |
| RhDR01 | in2–in2/ex3 | – | – | in2 | – | n | – | n | |
| RhDR02 | ex1–in1/ex2 | – | – | in1 | – | n | – | n | |
| RhAR01 | ex5–ex5/in5 | – | – | e5 | – | n | – | n | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lebedev, V.G.; Subbotina, N.M.; Maluchenko, O.P.; Lebedeva, T.N.; Krutovsky, K.V.; Shestibratov, K.A. Transferability and Polymorphism of SSR Markers Located in Flavonoid Pathway Genes in Fragaria and Rubus Species. Genes 2020, 11, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010011
Lebedev VG, Subbotina NM, Maluchenko OP, Lebedeva TN, Krutovsky KV, Shestibratov KA. Transferability and Polymorphism of SSR Markers Located in Flavonoid Pathway Genes in Fragaria and Rubus Species. Genes. 2020; 11(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleLebedev, Vadim G., Natalya M. Subbotina, Oleg P. Maluchenko, Tatyana N. Lebedeva, Konstantin V. Krutovsky, and Konstantin A. Shestibratov. 2020. "Transferability and Polymorphism of SSR Markers Located in Flavonoid Pathway Genes in Fragaria and Rubus Species" Genes 11, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010011
APA StyleLebedev, V. G., Subbotina, N. M., Maluchenko, O. P., Lebedeva, T. N., Krutovsky, K. V., & Shestibratov, K. A. (2020). Transferability and Polymorphism of SSR Markers Located in Flavonoid Pathway Genes in Fragaria and Rubus Species. Genes, 11(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010011






