Distribution and Evolution of Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Gene Clusters in the Ceratocystidaceae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genome Assemblies
2.2. Identification of NRPS Genes and Clusters
2.3. Confirmation of Gene Order and Annotation
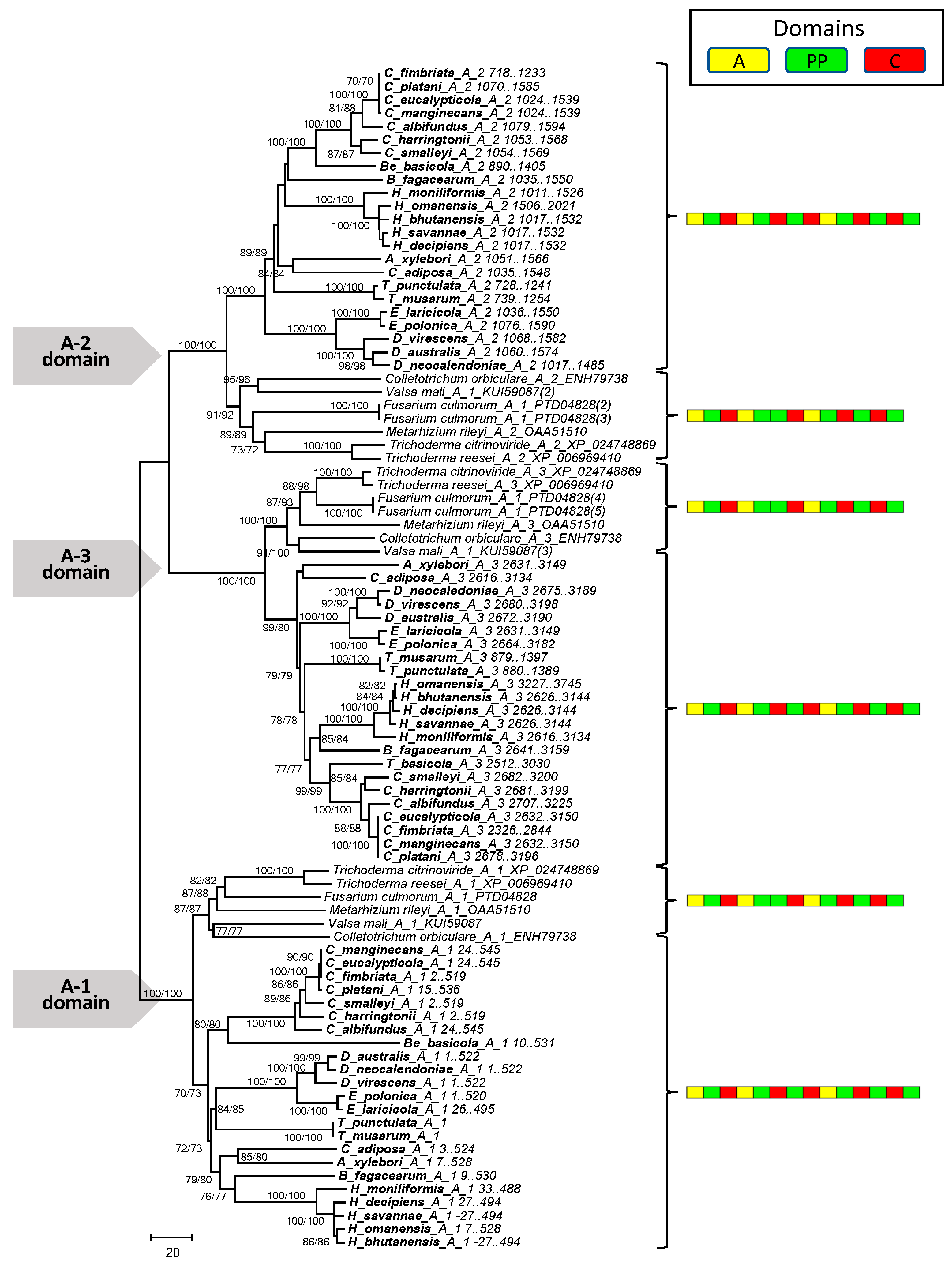
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Mono- and Multimodular NRPS Genes
2.5. Fe–CAS Blue Agar Test
3. Results
3.1. Genome Assemblies
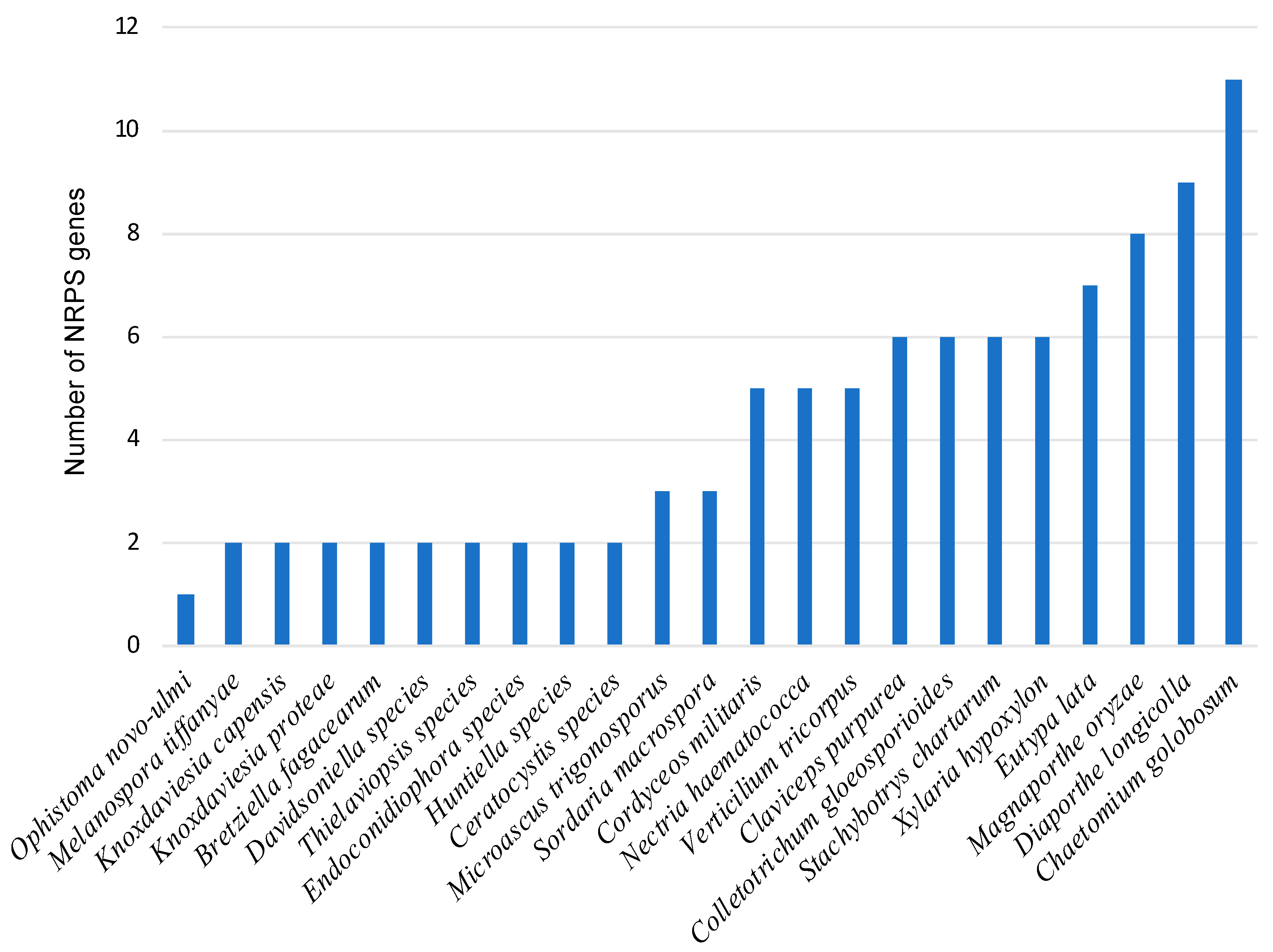
3.2. Identification of NRPS Genes and Clusters
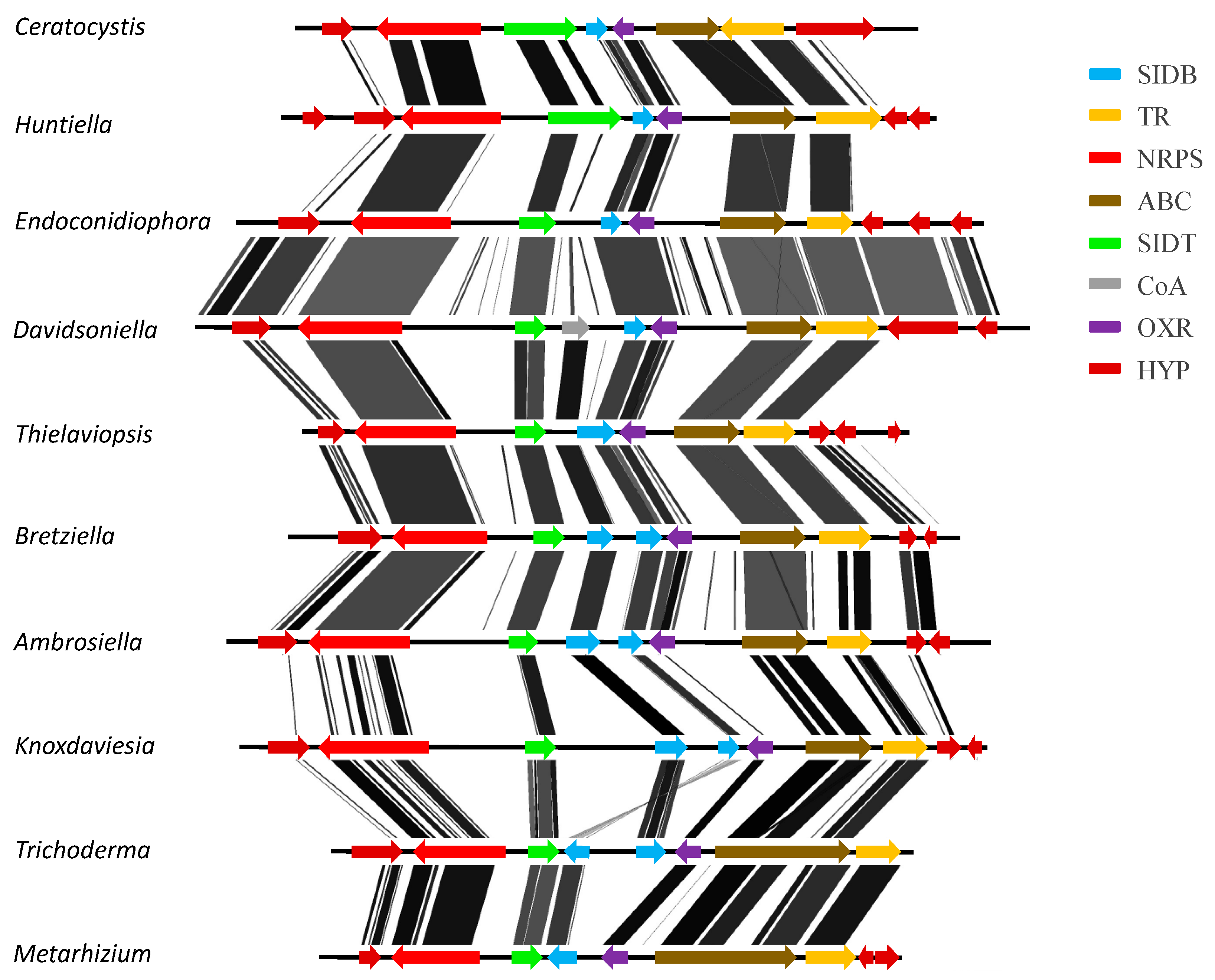
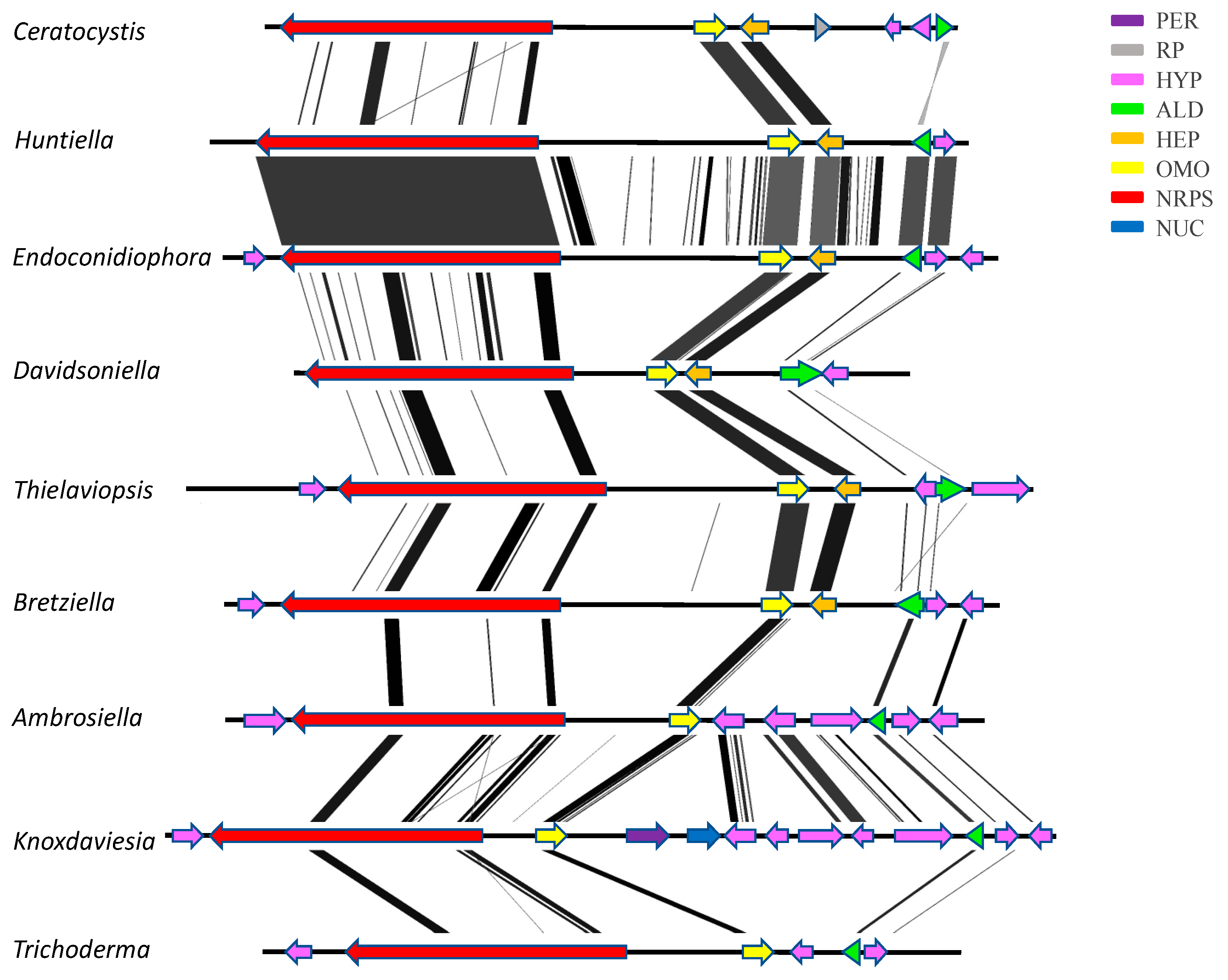
3.3. Confirmation of Gene Order and Annotation
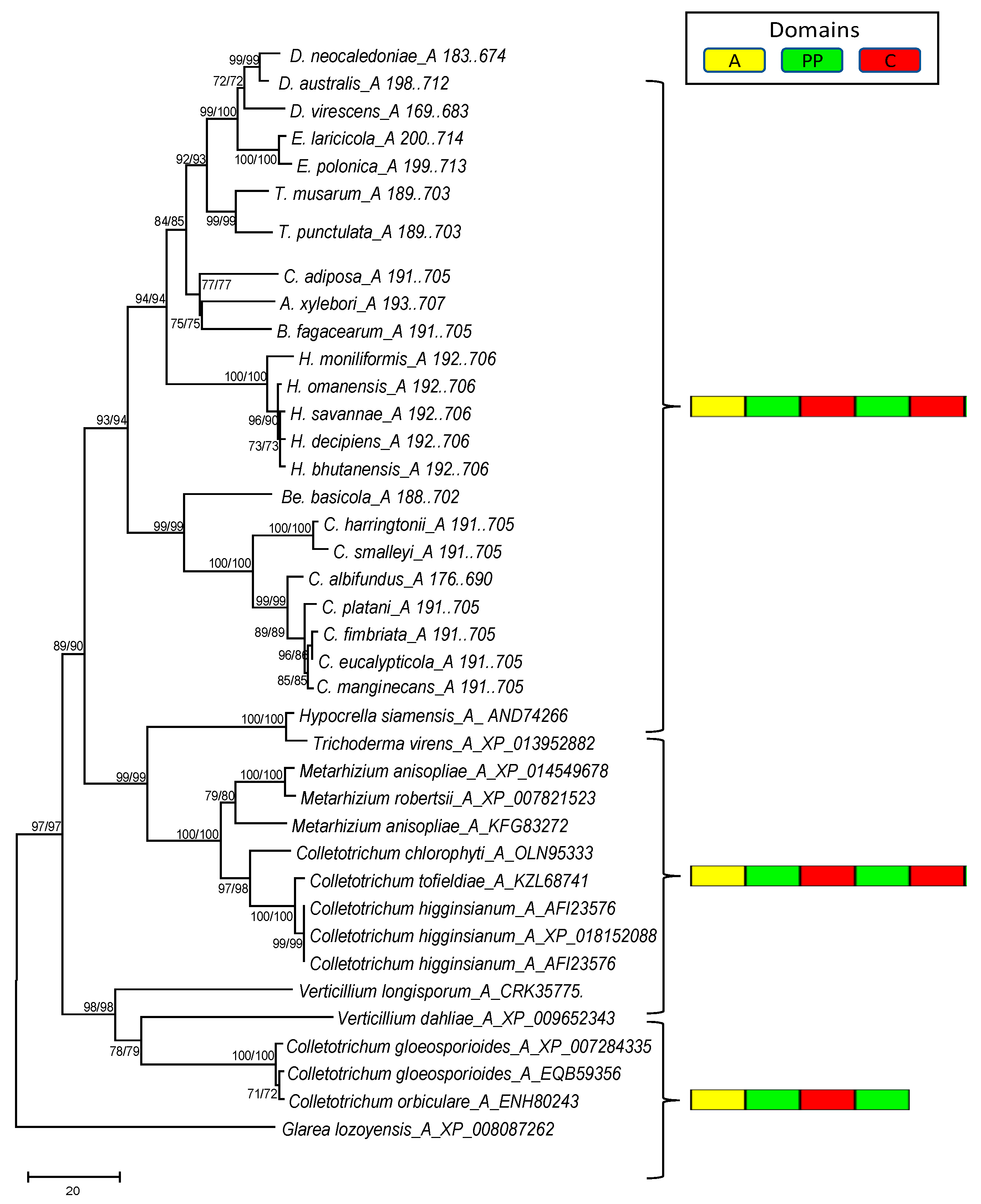
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Mono- and Multimodular NRPS Genes
3.5. Fe–CAS Blue Agar Test
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keller, N.P.; Turner, G.; Bennett, J.W. Fungal secondary metabolism—from biochemistry to genomics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmeister, D.; Keller, N.P. Natural products of filamentous fungi, enzymes, genes, and their regulation. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.T. The chemical versatility of natural-product assembly lines. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 41, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finking, R.; Marahiel, M.A. Biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 58, 453–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caboche, S.; Pupin, M.; Leclère, V.; Fontaine, A.; Jacques, P.; Kucherov, G. NORINE, a database of nonribosomal peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 36, D326–D331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, N.P.; Hohn, T.M. Metabolic pathway gene clusters in filamentous fungi. Fungal Genet. Biol. 1997, 21, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukup, A.A.; Keller, N.P.; Wiemann, P. Enhancing nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis in filamentous fungi. In Nonribosomal Peptide and Polyketide Biosynthesis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Von Döhren, H. Biochemistry and general genetics of nonribosomal peptide synthetases in fungi. In Molecular Biotechnolgy of Fungal Beta-Lactam Antibiotics and Related Peptide Synthetases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 217–264. [Google Scholar]
- Grünewald, J.; Marahiel, M.A. Chemoenzymatic and template-directed synthesis of bioactive macrocyclic peptides. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mootz, H.D.; Schwarzer, D.; Marahiel, M.A. Ways of assembling complex natural products on modular nonribosomal peptide synthetases. ChemBioChem 2002, 3, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, G.H.; Vickery, C.R.; Burkart, M.D. Explorations of catalytic domains in non-ribosomal peptide synthetase enzymology. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 1074–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, T.A.; Ehmann, D.E.; Kohli, R.M.; Marshall, C.G.; Trauger, J.W.; Walsh, C.T. Chain termination steps in nonribosomal peptide synthetase assembly lines, directed acyl-S-enzyme breakdown in antibiotic and siderophore biosynthesis. ChemBioChem 2001, 2, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisch, K. Biosynthesis of natural products by microbial iterative hybrid PKS–NRPS. RSC Adv. 2013, e18228–e18247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galagan, J.E.; Calvo, S.E.; Cuomo, C.; Ma, L.-J.; Wortman, J.R.; Batzoglou, S.; Lee, S.-I.; Baştürkmen, M.; Spevak, C.C.; Clutterbuck, J. Sequencing of Aspergillus nidulans and comparative analysis with A. fumigatus and A. oryzae. Nature 2005, 438, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, M.; Asai, K.; Sano, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kumagai, T.; Terai, G.; Kusumoto, K.-I.; Arima, T.; Akita, O.; Kashiwagi, Y. Genome sequencing and analysis of Aspergillus oryzae. Nature 2005, 438, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Berg, M.A.; Albang, R.; Albermann, K.; Badger, J.H.; Daran, J.-M.; Driessen, A.J.; Garcia-Estrada, C.; Fedorova, N.D.; Harris, D.M.; Heijne, W.H. Genome sequencing and analysis of the filamentous fungus Penicillium chrysogenum. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pel, H.J.; de Winde, J.H.; Archer, D.B.; Dyer, P.S.; Hofmann, G.; Schaap, P.J.; Turner, G.; de Vries, R.P.; Albang, R.; Albermann, K. Genome sequencing and analysis of the versatile cell factory Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nierman, W.C.; Pain, A.; Anderson, M.J.; Wortman, J.R.; Kim, H.S.; Arroyo, J.; Berriman, M.; Abe, K.; Archer, D.B.; Bermejo, C. Genomic sequence of the pathogenic and allergenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature 2005, 438, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, D.; Neville, C.; Doyle, S. Nonribosomal peptide synthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus and other fungi. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiasen, C.; Aahman, J.; Ravnholt, K.; Bjerrum, M.; Grell, M.; Giese, H. Nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NPS) genes in Fusarium graminearum, F. culmorum and F. pseudograminearium and identification of NPS2 as the producer of ferricrocin. Curr. Genet. 2007, 51, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-N.; Kroken, S.; Chou, D.Y.; Robbertse, B.; Yoder, O.; Turgeon, B.G. Functional analysis of all nonribosomal peptide synthetases in Cochliobolus heterostrophus reveals a factor, NPS6, involved in virulence and resistance to oxidative stress. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaldi, N.; Seifuddin, F.T.; Turner, G.; Haft, D.; Nierman, W.C.; Wolfe, K.H.; Fedorova, N.D. SMURF, genomic mapping of fungal secondary metabolite clusters. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2010, 47, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medema, M.H.; Blin, K.; Cimermancic, P.; de Jager, V.; Zakrzewski, P.; Fischbach, M.A.; Weber, T.; Takano, E.; Breitling, R. antiSMASH, rapid identification, annotation and analysis of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters in bacterial and fungal genome sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W339–W346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pöggeler, S.; Wöstemeyer, J. Evolution of Fungi and Fungal-Like Organisms; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Bushley, K.E.; Turgeon, B.G. Phylogenomics reveals subfamilies of fungal nonribosomal peptide synthetases and their evolutionary relationships. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroken, S.; Glass, N.L.; Taylor, J.W.; Yoder, O.; Turgeon, B.G. Phylogenomic analysis of type I polyketide synthase genes in pathogenic and saprobic ascomycetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15670–15675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, I.; Lumbsch, H.T. Ancient horizontal gene transfer from bacteria enhances biosynthetic capabilities of fungi. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beer, Z.W.; Duong, T.; Barnes, I.; Wingfield, B.D.; Wingfield, M.J. Redefining Ceratocystis and allied genera. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 79, 187–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, W.; Duong, T.; Wingfield, B.D.; Wingfield, M.J.; De Beer, Z. A new genus and species for the globally important, multihost root pathogen Thielaviopsis basicola. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremaud, G.; Tabacchi, R. Relationship between the fungus Ceratocystis fimbriata coffea and the canker disease of the coffee tree. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, W.-G.; Sinnwell, V. Isopulegol from liquid cultures of the fungus Ceratocystis coerulescens (Ascomycotina). Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 1987, 42, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loppnau, P.; Tanguay, P.; Breuil, C. Isolation and disruption of the melanin pathway polyketide synthase gene of the softwood deep stain fungus Ceratocystis resinifera. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2004, 41, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, M.; Steenkamp, E.T.; van der Nest, M.A.; Wingfield, B.D. Diversity and evolution of polyketide biosynthesis gene clusters in the Ceratocystidaceae. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, M.; Wingfield, B.D.; Clegg, P.; Wingfield, M.J. Ceratocystis larium sp. nov.; a new species from Styrax benzoin wounds associated with incense harvesting in Indonesia. Persoonia 2009, 22, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza, G.; Upchurch, R.; Brigmon, R.; Whitman, W.; Ulfig, K. Rapid DNA extraction for screening soil filamentous fungi using pcr amplification. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2004, 13, 315–318. [Google Scholar]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO, assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, K.; Wolf, T.; Chevrette, M.; Lu, X.; Schwalen, C.; Kautsar, S.; Suarez Duran, H.; De Los Santos, E.; HU, K.; Nave, M.; et al. antiSMASH 4.0—Improvements in chemistry prediction and gene cluster boundary identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W36–W41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoriev, I.; Nikitin, R.; Haridas, S.; Kuo, A.; Ohm, R.; Otillar, R.; Riley, R.; Salamov, A.; Zhao, X.; Korzeniewski, F.; et al. MycoCosm portal, gearing up for 1000 fungal genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D699–D704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoriev, I.; Cullen, D.; Goodwin, S.; Hibbett, D.; Jeffries, T.; Kubicek, C.; Kuske, C.; Magnuson, J.; Martin, F.; Spatafora, J.; et al. Fueling the future with fungal genomics. Mycology 2011, 2, 192–209. [Google Scholar]
- Stanke, M.; Tzvetkova, A.; Morgenstern, B. AUGUSTUS at EGASP, using EST, protein and genomic alignments for improved gene prediction in the human genome. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdobnov, E.; Apweiler, R. InterProScan—An integration platform for the signature-recognition methods in InterPro. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 847–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, B.; Ravel, J. In aIlico prediction of microbial secondary metabolic pathways from DNA sequence data. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 458, 181–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Lu, S.; Anderson, J.B.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; De Weese-Scott, C.; Fong, J.H.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R. CDD, a Conserved Domain Database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, D225–D229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, C.; Hoof, I.; Weber, T.; Wohlleben, W.; Huson, D.H. Phylogenetic analysis of condensation domains in NRPS sheds light on their functional evolution. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S. Primer3—new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.M.; van der Nest, M.A.; Wilken, P.M.; Wingfield, M.J.; Wingfield, B.D. Pheromone expression reveals putative mechanism of unisexuality in a saprobic ascomycete fungus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, R.A.; Stajich, J.E.; Yamanaka, Y.; Dietrich, F.S.; Steinbach, W.J.; Perfect, J.R. Phylogenomic analysis of non-ribosomal peptide synthetases in the genus Aspergillus. Gene 2006, 383, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT, a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7, molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milagres, A.M.; Machuca, A.; Napoleao, D. Detection of siderophore production from several fungi and bacteria by a modification of chrome azurol S (CAS) agar plate assay. J. Microbiol. Methods 1999, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeilinger, S.; Gruber, S.; Bansal, R.; Mukherjee, P.K. Secondary metabolism in Trichoderma—Chemistry meets genomics. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2016, 30, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushley, K.E.; Ripoll, D.R.; Turgeon, B.G. Module evolution and substrate specificity of fungal nonribosomal peptide synthetases involved in siderophore biosynthesis. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Horwitz, B.A.; Herrera-Estrella, A.; Schmoll, M.; Kenerley, C.M. Trichoderma research in the genome era. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Horwitz, B.A.; Kenerley, C.M. Secondary metabolism in Trichoderma—A genomic perspective. Microbiology 2012, 158, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelmann, G. Importance of siderophores in fungal growth, sporulation and spore germination. In Frontiers in Mycology; Hawksworth, D.L., Ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1991; pp. 49–65. [Google Scholar]
- Neubauer, U.; Nowack, B.; Furrer, G.; Schulin, R. Heavy metal sorption on clay minerals affected by the siderophore desferrioxamine B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2749–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, J. Siderophores, their biochemistry and possible role in the biocontrol of plant pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1986, 24, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renshaw, J.C.; Robson, G.D.; Trinci, A.P.; Wiebe, M.G.; Livens, F.R.; Collison, D.; Taylor, R.J. Fungal siderophores, structures, functions and applications. Mycol. Res. 2002, 106, 1123–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieken, A.; Winkelmann, G. Rhizoferrin, a complexone type siderophore of the mocorales and entomophthorales (Zygomycetes). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1992, 94, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, J.; Knudsen, M.; Hansen, F.; Olesen, C.; Fuertes, P.; Lee, T.; Sondergaard, T.; Pedersen, C.; Brodersen, D.; Giese, H. Fungal NRPS-Dependent Siderophores, from Function to Prediction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kadi, N.; Challis, G. Siderophore biosynthesis, a substrate specificity assay for nonribosomal peptide synthetase-independent siderophore synthetases involving trapping of acyl-adenylate intermediates with hydroxylamine. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 458, 431–457. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, D.; Donzelli, B.; Krasnoff, S.; Keyhani, N. Discovering the secondary metabolite potential encoded within entomopathogenic fungi. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1287–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.M.; Gentil, G.D.; Budde, A.D.; Leong, S.A. Characterization of the Ustilago maydis sid2 gene, encoding a multidomain peptide synthetase in the ferrichrome biosynthetic gene cluster. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 4040–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.G.; Mnich, E.; Nielsen, K.F.; Nielsen, J.B.; Nielsen, M.T.; Mortensen, U.H.; Larsen, T.O.; Patil, K.R. A natural fusion of a cytochrome P450 and a hydrolase is involved in mycophenolic acid biosynthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4908–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oide, S.; Moeder, W.; Krasnoff, S.; Gibson, D.; Haas, H.; Yoshioka, K.; Turgeon, B.G. NPS6, encoding a nonribosomal peptide synthetase involved in siderophore-mediated iron metabolism, is a conserved virulence determinant of plant pathogenic ascomycetes. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2836–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hissen, A.H.; Wan, A.N.; Warwas, M.L.; Pinto, L.J.; Moore, M.M. The Aspergillus fumigatus siderophore biosynthetic gene sidA, encoding L-ornithine N5-oxygenase, is required for virulence. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 5493–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwien, F.; Skrahina, V.; Kasper, L.; Hube, B.; Brunke, S. Metals in fungal virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 42, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hof, C.; Eisfeld, K.; Welzel, K.; Antelo, L.; Foster, A.; Anke, H. Ferricrocin synthesis in Magnaporthe grisea and its role in pathogenicity in rice. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, B.; Budde, A.D.; Leong, S.A. sid1, a gene initiating siderophore biosynthesis in Ustilago maydis, molecular characterization, regulation by iron, and role in phytopathogenicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrettl, M.; Bignell, E.; Kragl, C.; Joechl, C.; Rogers, T.; Arst, H.N.; Haynes, K.; Haas, H. Siderophore biosynthesis but not reductive iron assimilation is essential for Aspergillus fumigatus virulence. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oide, S.; Krasnoff, S.B.; Gibson, D.M.; Turgeon, B.G. Intracellular siderophores are essential for ascomycete sexual development in heterothallic Cochliobolus heterostrophus and homothallic Gibberella zeae. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 1339–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Hurley, J.; Taylor, J.; Puckhaber, L.; Lehner, S.; Druzhinina, I.; Schumacher, R.; Kenerley, C. Ferricrocin, the intracellular siderophore of Trichoderma virens, is involved in growth, conidiation, gliotoxin biosynthesis and induction of systemic resistance in maize. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallner, A.; Blatzer, M.; Schrettl, M.; Sarg, B.; Lindner, H.; Haas, H. Ferricrocin, a siderophore involved in intra-and transcellular iron distribution in Aspergillus fumigatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4194–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwecke, T.; Göttling, K.; Durek, P.; Dueñas, I.; Käufer, N.F.; Zock-Emmenthal, S.; Staub, E.; Neuhof, T.; Dieckmann, R.; von Döhren, H. Nonribosomal peptide synthesis in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and the architectures of ferrichrome-type siderophore synthetases in fungi. Chembiochem 2006, 4, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Species a | Isolate Number b | GenBank Accession Number | BUSCO Completeness Scores c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complete and Single Copy (%) | Complete and Duplicated (%) | Fragmented (%) | Missing (%) | |||
| B. fagacearum | CMW 2656 | MKGJ00000000 | 95.2 | 0 | 3.1 | 1.7 |
| C. adiposa | CMW 2573 | LXGU00000000 | 99.3 | 0 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| C. albifundus | CMW 13980 | JSSU000000000 | 97.6 | 0 | 1.4 | 1 |
| C. eucalypticola | CMW 11536 | LJOA00000000 | 97.9 | 0 | 1.4 | 0.7 |
| C. fimbriata | CMW 15049 | APWK00000000 | 91.0 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 7.6 |
| C. harringtonii | CMW 14789 | MKGM0000000 | 97.9 | 0 | 0.7 | 1.4 |
| C. manginecans | CMW 17570 | JJRZ000000000 | 97.2 | 0.3 | 1.7 | 1.1 |
| C. platani | CF0 | LBBL00000000 | 99.3 | 0 | 0.4 | 0 |
| C. smalleyii | CMW 14800 | NETT01000000 | 99 | 0 | 0.7 | 0.3 |
| D. virescens | CMW 17339 | LJZU000000000 | 97.6 | 0 | 1.4 | 1 |
| E. laricicola | CMW 20928 | LXGT00000000 | 98.9 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.4 |
| E. polonica | CMW 20930 | LXKZ00000000 | 97.6 | 0 | 1.4 | 1 |
| H. bhutanensis | CMW 8217 | MJMS00000000 | 96.2 | 0.3 | 2.1 | 1.7 |
| H. decipiens | CMW 30855 | NETU00000000 | 96.9 | 0.3 | 2.1 | 1 |
| H. moniliformis | CMW 10134 | JMSH00000000 | 94.8 | 0.3 | 3.4 | 1.8 |
| H. omanensis | CMW 11056 | JSUI000000000 | 88.6 | 0.3 | 7.9 | 3.5 |
| H. savannae | CMW 17300 | LCZG00000000 | 96.2 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 1.7 |
| T. musarum | CMW 1546 | LKBB00000000 | 98.6 | 0 | 1.4 | 0 |
| T. punctulata 1 | BPI 893173 | LAEV00000000 | 99.3 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0 |
| T. punctulata 2 | CMW 1032 | MJMR01000000 | 99.7 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0 |
| D. neocaledoniae | CMW 225392 | RHDR00000000 | 96.9 | 0 | 2 | 7 |
| D. australis | CMW 2333 | RHLR00000000 | 95.5 | 0 | 5 | 8 |
| A. xylebori | CBS 110.61 | PCDO00000000 | 98.6 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| K. capensis | CBS 139037 | LNGK00000000 | 99.3 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| K. proteae | CBS 140089 | LNGL00000000 | 97.6 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| Be. basicola | CMW 49352 | PJAC00000000 | 99.0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Species | Growth (days) a | CAS Reaction | CAS-Blue Agar (Colour Change) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B. fagacearum | 14 | +++ | Purple |
| C. fimbriata | 13 | + | Pink |
| H. moniliformis | 7 | ++ | Purple |
| T. punctulata | 5 | ++ | Purplish red |
| D. virescens | 13 | + | Pink |
| E. polonica | 10 | + | Pink |
| C. adiposa | 5 | ++ | Purplish red |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayari, M.; van der Nest, M.A.; Steenkamp, E.T.; Soal, N.C.; Wilken, P.M.; Wingfield, B.D. Distribution and Evolution of Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Gene Clusters in the Ceratocystidaceae. Genes 2019, 10, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10050328
Sayari M, van der Nest MA, Steenkamp ET, Soal NC, Wilken PM, Wingfield BD. Distribution and Evolution of Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Gene Clusters in the Ceratocystidaceae. Genes. 2019; 10(5):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10050328
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayari, Mohammad, Magriet A. van der Nest, Emma T. Steenkamp, Nicole C. Soal, P. Markus Wilken, and Brenda D. Wingfield. 2019. "Distribution and Evolution of Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Gene Clusters in the Ceratocystidaceae" Genes 10, no. 5: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10050328
APA StyleSayari, M., van der Nest, M. A., Steenkamp, E. T., Soal, N. C., Wilken, P. M., & Wingfield, B. D. (2019). Distribution and Evolution of Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Gene Clusters in the Ceratocystidaceae. Genes, 10(5), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10050328





