Identification and Characterization of Salt-Responsive MicroRNAs in Vicia faba by High-Throughput Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions, and Salt Stress Treatments
2.2. sRNA Library Construction and Sequencing
2.3. Data Filtering and Mapping Reads
2.4. Classification of sRNAs
2.5. Predictions of sRNAs
2.6. Analyzing sRNA Expression
2.7. Target Prediction
2.8. Screening the Differentially Expressed sRNAs (DESs)
2.9. GO Enrichment Analysis
2.10. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. sRNA Sequencing
3.2. Annotation of sRNAs and miRNA Identification
3.3. Identification of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
3.4. Target Prediction and Functional Analysis of the miRNAs
4. Discussion
Salt Stress-Responsive miRNAs and Their Targets in Faba Bean
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-W.; Meng, J.; Cui, J.; Luan, Y.-S. Characterization and Function of MicroRNA’s in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Mei, J.; Ren, G. Plant microRNAs: Biogenesis, Homeostasis, and Degradation. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cobb, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. Plant microRNA: a small regulatory molecule with big impact. Dev. Biol. 2006, 289, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, B.R. Viruses and microRNAs: RISCy interactions with serious consequences. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Bartel, B. MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 19–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, A.C.; Vaucheret, H. Functions of microRNAs and related small RNAs in plants. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, S31–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qin, Y.; Duan, H.; Yin, W.; Xia, X. Genome-wide characterization of new and drought stress responsive microRNAs in Populus euphratica. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3765–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trindade, I.; Capitão, C.; Dalmay, T.; Fevereiro, M.P.; Santos, D.M. miR398 and miR408 are up-regulated in response to water deficit in Medicago truncatula. Planta 2010, 231, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Chen, L.; Zhao, M.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, W.H. Identification of drought-responsive microRNAs in Medicago truncatula by genome-wide high-throughput sequencing. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Kong, D.; Duan, M.; Luo, L. Genome-wide identification and analysis of drought-responsive microRNAs in Oryza sativa. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 4157–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Wang, W.X.; Ren, L.; Chen, Q.J.; Mendu, V.; Willcut, B.; Dinkins, R.; Tang, X.; Tang, G. Differential and dynamic regulation of miR398 in response to ABA and salt stress in Populus tremula and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 71, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.H.; Tian, X.; Li, Y.J.; Wu, C.A.; Zheng, C.C. Microarray-based analysis of stress regulated microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA 2008, 14, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkar, R.; Chinnusamy, V.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, J.K. Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Huan, Q.; Chong, K. Deep sequencing of Brachypodium small RNAs at the global genome level identifies microRNAs involved in cold stress response. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkar, R.; Kapoor, A.; Zhu, J.K. Posttranscriptional induction of two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase genes in Arabidopsis is mediated by downregulation of miR398 and important for oxidative stress tolerance. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2051–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licausi, F.; Weits, D.A.; Pant, B.D.; Scheible, W.R.; Geigenberger, P.; van Dongen, J.T. Hypoxia responsive gene expression is mediated by various subsets of transcription factors and miRNAs that are determined by the actual oxygen availability. New Phytol. 2011, 190, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wei, L.; Zou, X.; Tao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y. Submergence-responsive MicroRNAs are potentially involved in the regulation of morphological and metabolic adaptations in maize root cells. Ann. Bot. 2008, 102, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Sun, Y.H.; Shi, R.; Clark, C.; Li, L.; Chiang, V.L. Chiang, novel and mechanical stress responsive microRNAs in Populus trichocarpa that are absent from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2186–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brant, E.J.; Budak, H. Plant small non-coding RNAs and their roles in biotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinocur, B.; Altman, A. Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress: achievements and limitations. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, T.; Shinozaki, K. Research on plant abiotic stress responses in the post-genome era: past, present and future. Plant J. 2010, 61, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, M.; Narusaka, M.; Ishida, J.; Nanjo, T.; Fujita, M.; Oono, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Nakajima, M.; Enju, A.; Sakurai, T.; et al. Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold and high salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant J. 2002, 31, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y. Differential expression of miRNAs in response to salt stress in maize roots. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Li, X. Identification and dynamic regulation of microRNAs involved in salt stress responses in functional soybean nodules by high-throughput sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 2717–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for Transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Xie, Y.; Yan, W. AASRA: An Anchor Alignment-Based Small RNA Annotation Pipeline. bioRxiv 2017, 132928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki, E.P.; Eddy, S.R. Infernal 1.1: 100-fold faster RNA homology searches. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2933–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breakfield, N.W.; Corcoran, D.L.; Petricka, J.J.; Shen, J.; Sae-Seaw, J.; Rubio-Somoza, I.; Weige, D.; Ohler, U.; Benfey, P.N. High-resolution experimental and computational profiling of tissue specific known and novel miRNAs in Arabidopsis. Genome Res. 2001, 22, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Liang, C.; Liu, J.; Xiao, H.; Huang, S.H.; Xu, J.; Li, F. Prediction of piRNAs using transposon interaction and a support vector machine. BMC Bioinformatics 2014, 15, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagla, B.; Aulner, N.; Kelly, P.D.; Song, D.; Volchuk, A.; Zatorski, A.; Shum, D.; Mayer, T.; De Angelis, D.A.; Ouerfelli, O.; et al. Sequence characteristics of functional siRNAs. RNA 2005, 11, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ’t Hoen, P.A.; Ariyurek, Y.; Thygesen, H.H.; Vreugdenhil, E.; Vossen, R.H.; de Menezes, R.X.; Boer, J.M.; van Ommen, G.J.; den Dunnen, J.T. Deep sequencing-based expression analysis shows major advances in robustness, resolution and inter-lab portability over five microarray platforms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.J.; Ma, Y.K.; Chen, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.J. PsRobot: a web-based plant small RNA metaanalysis toolbox. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W22–W28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlgren, N.; Carrington, J.C. miRNA target prediction in plants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 592, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Audic, S.; Claverie, J.M. The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res. 1997, 10, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H. Bonferroni and Sidak corrections for multiple comparisons. In Encyclopedia of Measurement and Statistics; Salkind, N.J., Ed.; Thousand Oaks: Sage, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Kawashima, S.; Okuda, S.; Tokimatsu, T. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D480–D484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D68–D73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrocki, E.P.; Burge, S.W.; Bateman, A.; Daub, J.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Floden, E.W.; Gardner, P.P.; Jones, T.A.; Tate, J.; et al. Rfam 12.0: updates to the RNA families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 43, D130–D138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruszka, K.; Pieczynski, M.; Windels, D.; Bielewicz, D.; Jarmolowski, A.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z.; Vazquez, F. Role of microRNAs and other sRNAs of plants in their changing environments. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 169, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.C.; Wang, L.; Cui, L.C.; Feng, K.W.; Liu, F.Y.; Du, X.H.; Tong, W.; Nie, X.J.; Ji, W.Q.; Weining, S. Global identification of microRNAs and their targets in barley under salinity stress. PLoS ONE 2001, 10, e0137990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnavale-Bottino, M.; Rosario, S.; Grativol, C.; Thiebaut, F.; Rojas, C.A.; Farrineli, L.; Hemerly, A.S.; Ferreira, P.C. High-throughput sequencing of small RNA transcriptome reveals salt stress regulated microRNAs in sugarcane. PLoS ONE 2001, 8, e59423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhang, D.Y.; Qi, X.W.; Ma, B.; Xiang, Z.H.; He, N.J. Identification of the conserved and novel miRNAs in mulberry by high throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 2001, 9, e104409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wu, S.; Van Houten, J.; Wang, Y.; Ding, B.; Fei, Z.J.; Clarke, T.H.; Reed, J.W.; van der Knaap, E. Down-regulation of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTORS 6 and 8 by microRNA 167 leads to floral development defects and female sterility in tomato. J. Exp. Bot. 2001, 65, 2507–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Wall, K.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Carlson, J.E.; Depamphilis, C.W. Large-scale identification of microRNAs from a basal eudicot (Eschscholzia californica) and conservation in flowering plants. Plant J. 2001, 51, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.N.; Zhou, T.; Bo, W.H.; Xu, F.; Wu, R.L. Genome-wide analysis of salt-responsive and novel microRNAs in Populus euphratica by deep sequencing. BMC Genet. 2001, 15, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhotia, N.; Joshi, G.; Bhardwaj, A.R.; Katiyar-Agarwal, S.; Agarwal, M.; Jagannath, A.; Goel, S.; Kumar, A. Identification and characterization of miRNAome in root, stem, leaf and tuber developmental stages of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) by high-throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2001, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, M.; Gustafson, P.; Langridge, P.; Shi, B.J. Differential expression of microRNAs and other small RNAs in barley between water and drought conditions. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2001, 13, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.H.; Tian, Y.M.; Luo, X.J.; Zhou, T.; Huang, Z.P.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, Y.H.; Hou, B.; Sun, D.; Deng, H.Y.; et al. Identification and characterization of microRNAs related to salt stress in broccoli, using high throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis. BMC Plant Biol. 2001, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Noman, A.; Fahad, S.; Aqeel, M.; Ali, U.; Amanullah Anwar, S.; Baloch, S.K.; Zainab, M. MiRNAs: Major modulators for crop growth and development under abiotic stresses. Biotechnol. Lett. 2001, 39, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, O.P.; Meena, N.L.; Sharma, I.; Sharma, P. Differential regulation of microRNAs in response to osmotic, salt and cold stresses in wheat. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2001, 41, 4623–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Bai, X.; Yang, L.A.; Lv, D.K.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, H.; Ji, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, Y.M. Osa-mir393: A salinity and alkaline stress-related microRNA gene. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2001, 38, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, H.; Akpinar, B.A. Plant miRNAs: Biogenesis, organization and origins. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2001, 15, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.R.; Zeng, Y.L.; Yi, X.Y.; Zhao, L.J.; Zhang, Y.F. Small RNA deep sequencing reveals the important role of microRNAs in the halophyte Halostachys caspica. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2001, 13, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandkarimi, H.; Bedre, R.; Solis, J.; Mangu, V.; Baisakh, N. Sequencing and expression analysis of salt-responsive miRNAs and target genes in the halophyte smooth cordgrass (Spartina alternifolia Loisel). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2001, 42, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdogan, G.; Tufekci, E.D.; Uranbey, S.; Unver, T. MiRNA-based drought regulation in wheat. Funct. Integr. Genome 2001, 16, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alptekin, B.; Budak, H. Wheat miRNA ancestors: Evident by transcriptome analysis of A, B, and D genome donors. Funct. Integr. Genome 2001, 17, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shriram, V.; Kumar, V.; Devarumath, R.M.; Khare, T.S.; Wani, S.H. MicroRNAs as potential targets for abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2001, 7, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, M.J.; Terrile, M.C.; Windels, D.; Lombardo, M.C.; Bartoli, C.G.; Vazquez, F.; Estelle, M.; Casalongue, C.A. Mir393 regulation of auxin signaling and redox-related components during acclimation to salinity in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2001, 9, e107678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, K.F.; Wang, R.; Ou, X.J.; Fang, Z.M.; Tian, C.G.; Duan, J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, M.Y. OsTIR1 and osAFB2 down regulation via osmir393 overexpression leads to more tillers, early flowering and less tolerance to salt and drought in rice. PLoS ONE 2001, 7, 364–373. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Sun, Y.F.; Song, N.; Wei, J.P.; Wang, X.J.; Feng, H.; Yin, Z.Y.; Kang, Z.S. MicroRNAs involving in cold, wounding and salt stresses in Triticum aestivum L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 80, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inal, B.; Turktas, M.; Eren, H.; Ilhan, E.; Okay, S.; Atak, M.; Erayman, M.; Unver, T. Genome-wide fungal stress responsive miRNA expression in wheat. Planta 2001, 240, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantar, M.; Lucas, S.J.; Budak, H. MiRNA expression patterns of Triticum dicoccoides in response to shock drought stress. Planta 2001, 233, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



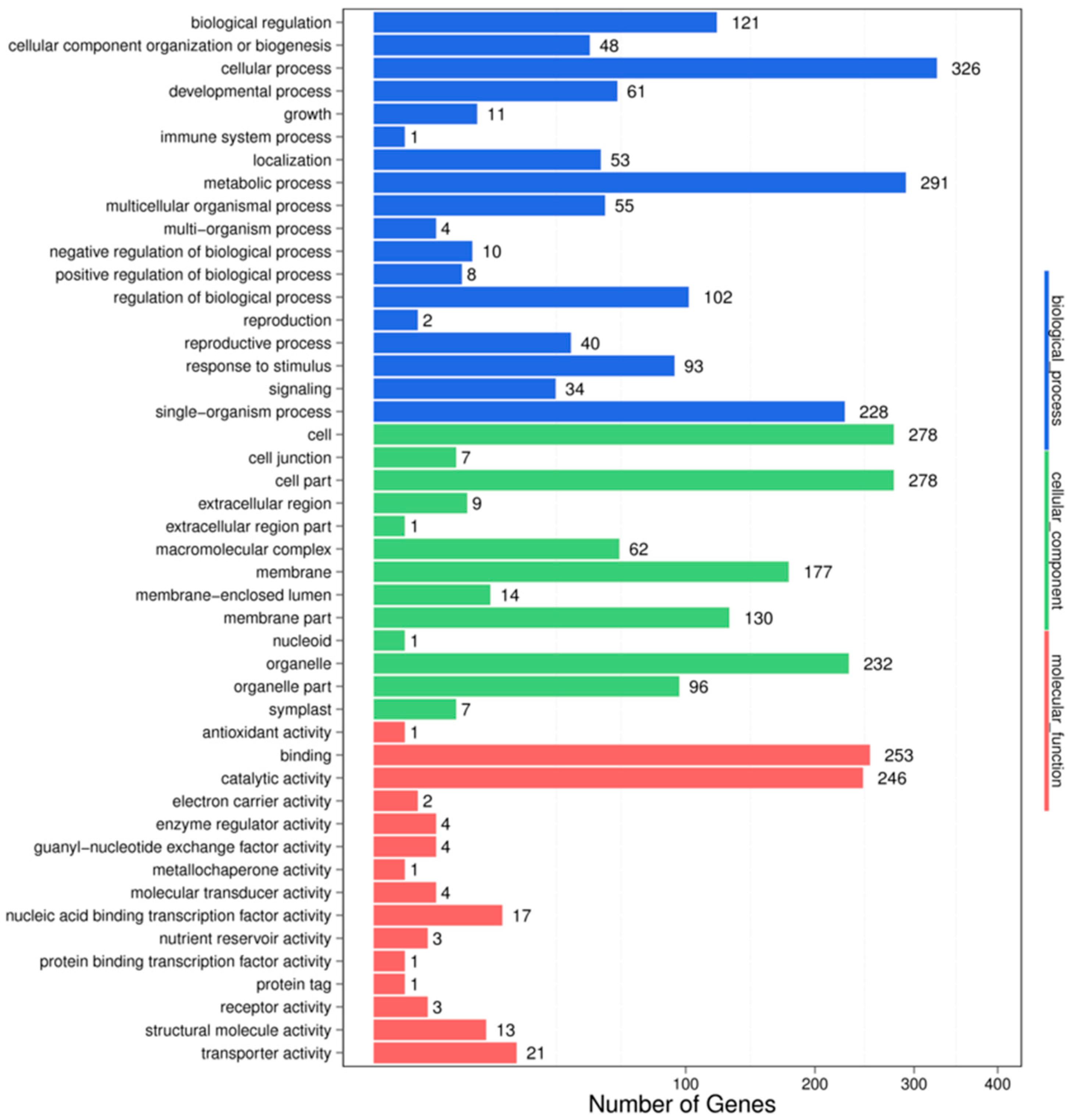

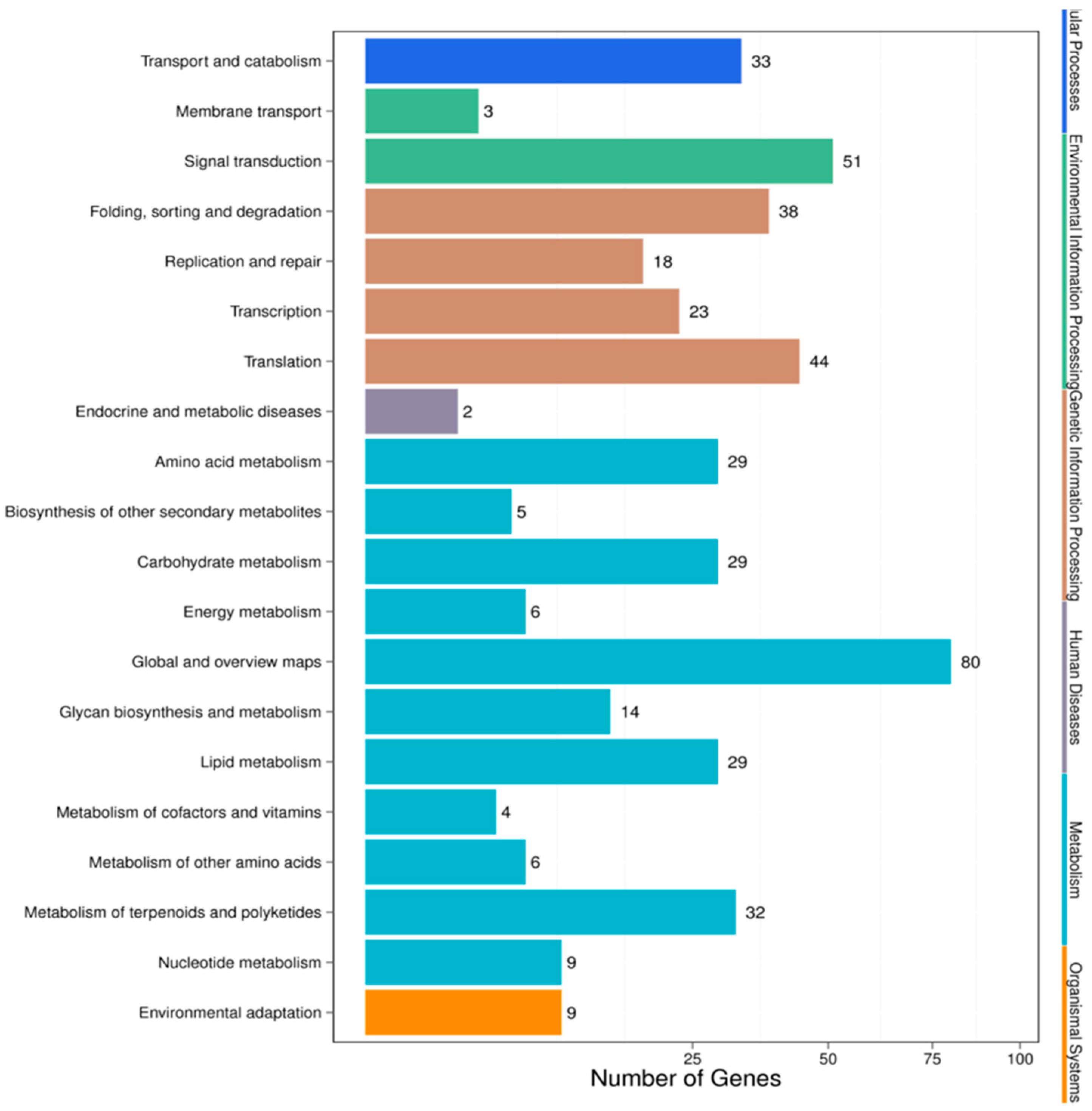
| Sample Name | Sequence Type | Raw Tag Count | Clean Tag Count | Percentage (%) | Number of Mapped Tags | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC-4 | SE50 | 51420111 | 47942551 | 93.24 | 36387118 | 75.9 |
| HSA | SE50 | 43734868 | 40682196 | 93.02 | 26272525 | 64.58 |
| IC-1 | SE50 | 48229628 | 43865674 | 90.95 | 21451106 | 48.9 |
| IS-4 | SE50 | 53763194 | 41563472 | 77.31 | 20568122 | 49.49 |
| Type | HC-4 | HSA | IC-1 | IS-1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | (%) | Count | (%) | Count | (%) | Count | (%) | |
| Total | 47942551 | 100 | 40682196 | 100 | 43865674 | 100 | 41563472 | 100 |
| Intergenic | 9985569 | 20.83 | 10292988 | 25.3 | 9475423 | 21.6 | 8197558 | 19.72 |
| Mature (miRNA) | 3224519 | 6.73 | 1653404 | 4.06 | 6841472 | 15.6 | 5633410 | 13.55 |
| Rfam other sncRNA | 73325 | 0.15 | 94167 | 0.23 | 24135 | 0.06 | 35172 | 0.08 |
| snRNA | 1405 | 0 | 4831 | 0.01 | 2381 | 0.01 | 959 | 0 |
| unmap | 11040957 | 23.03 | 13725210 | 33.74 | 21005681 | 47.89 | 20270917 | 48.77 |
| rRNA | 1773606 | 3.7 | 1100198 | 2.7 | 244021 | 0.56 | 358242 | 0.86 |
| Hairpin | 38 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 80 | 0 | 147 | 0 |
| snoRNA | 30566 | 0.06 | 14138 | 0.03 | 9971 | 0.02 | 6058 | 0.01 |
| Precursor | 27019 | 0.06 | 11116 | 0.03 | 24531 | 0.06 | 40935 | 0.1 |
| Repeat | 21771765 | 45.41 | 13683732 | 33.64 | 6237390 | 14.22 | 7018371 | 16.89 |
| tRNA | 13782 | 0.03 | 102403 | 0.25 | 589 | 0 | 1703 | 0 |
| Sample | Known miRNA Count | Novel miRNA Count | Known piRNA Count | Novel piRNA Count | Known siRNA Count | Novel siRNA Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS-4 | 1301 | 51 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2578 |
| HSA | 1118 | 38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1879 |
| HC-4 | 1018 | 44 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1919 |
| IC-1 | 1465 | 48 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2241 |
| Conserved miRNA Family | DESs in HC-4-vs.-HSA (Sensitive Genotype) | DESs in IC-1-vs.-IS-4 (Tolerant Genotype) | Target Gene Family | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Upregulated Members | Number of Downregulated Members | Number of Upregulated Members | Number of Downregulated Members | ||
| miRNA156 | 20 | 6 | 11 | 7 | Squamosa promoter-binding proteins |
| miRNA157 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | Squamosa promoter-binding proteins |
| miRNA159 | 27 | 8 | 8 | 28 | MYB transcription factors/TCP transcription factors |
| miRNA160 | 4 | 4 | 11 | 43 | Auxin Response factors |
| miRNA162 | 9 | 3 | 8 | 8 | Dicer Like protein/E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF144A-like isoform X1 |
| miRNA164 | 3 | 2 | 12 | 33 | NAC domain protein/NAC transcription factor-like protein |
| miRNA165 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | Homeo domain-Zip transcription factors/homeobox-leucine zipper protein ATHB-14-like/bZIP transcription factor |
| miRNA166 | 39 | 91 | 82 | 80 | Homeobox-leucine zipper protein ATHB-15-like isoform X2/bZIP transcription factor |
| miRNA167 | 38 | 26 | 27 | 31 | Transmembrane protein, putative/translation initiation factor eIF-2B delta subunit |
| miRNA168 | 19 | 13 | 24 | 9 | Argonautes/protamine P1 family protein |
| miRNA169 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4 | HAP2/NFY transcription factors/CCAAT-binding transcription factor |
| miRNA171 | 19 | 14 | 12 | 42 | Scarecrow-like transcription factors/GRAS family transcription regulator |
| miRNA172 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | AP2 domain transcription factors/AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor/myb-like transcription factor family protein |
| miRNA319 | 6 | 3 | 6 | 12 | MYB transcription factors/TCP transcription factors |
| miRNA390 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 5 | TAS3-primary transcripts/LRR receptor-like kinase family protein |
| miRNA391 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | TAS3-primary transcripts/zinc finger CCCH domain protein |
| miRNA393 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 2 | F-Box protein/transport inhibitor response 1 protein/Ubiquitin |
| miRNA394 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | F-Box protein/Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein ZFN-like |
| miRNA396 | 36 | 16 | 31 | 26 | Growth regulating factors/F-box protein interaction domain protein /BZIP transcription factor bZIP80 |
| miRNA397 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | Laccases |
| miRNA398 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 13 | Cu/Zn superoxide dismutases (CSD)/BAG family molecular chaperone regulator-like protein |
| miRNA399 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 4 | Phosphate transporter/ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2/OBP3-responsive protein |
| miRNA408 | 1 | 6 | 16 | 5 | Plantacyanins/uclacyanin-2-like/basic blue-like protein |
| miRNA2111 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 2 | DNA replication factor CDT1-like protein/calcineurin-like phosphoesterase, family protein |
| miRNA482 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| miRNA ID | Count (HC-4) | Count (HSA) | TPM (HC-4) | TPM (HSA) | log2 Ratio (HSA/HC-4) | Regulation Profile (Up/Down) (HSA/HC-4) | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| novel_mir1 | 193 | 869 | 5.12 | 31.31 | 2.612408 | Up | 1.81E-153 | 2.31 × 10−152 |
| novel_mir5 | 24 | 124 | 0.64 | 4.47 | 2.804131 | Up | 3.67E-25 | 2.05 × 10−24 |
| novel_mir6 | 0 | 48 | 0.001 | 1.73 | 10.75656 | Up | 1.12E-18 | 5.58 × 10−18 |
| novel_mir7 | 227 | 1120 | 6.02 | 40.35 | 2.744733 | Up | 1.78E-208 | 2.63 × 10−207 |
| novel_mir9 | 0 | 82 | 0.001 | 2.95 | 11.5265 | Up | 2.42E-31 | 1.47 × 10−30 |
| novel_mir10 | 14 | 894 | 0.37 | 32.21 | 6.44384 | Up | 8.00E-307 | 1.47 × 10−305 |
| novel_mir13 | 33 | 115 | 0.88 | 4.14 | 2.234055 | Up | 2.47E-18 | 1.21 × 10−17 |
| novel_mir16 | 17 | 597 | 0.45 | 21.51 | 5.578939 | Up | 1.75E-194 | 2.51 × 10−193 |
| novel_mir17 | 491 | 794 | 13.03 | 28.61 | 1.134682 | Up | 2.99E-44 | 2.03 × 10−43 |
| novel_mir19 | 39 | 81 | 1.03 | 2.92 | 1.503324 | Up | 3.24E-08 | 1.14 × 10−7 |
| novel_mir22 | 11 | 32 | 0.29 | 1.15 | 1.987509 | Up | 2.35E-05 | 7.14 × 10−5 |
| novel_mir29 | 82 | 180 | 2.18 | 6.49 | 1.57389 | Up | 9.97E-18 | 4.82 × 10−17 |
| novel_mir37 | 492 | 817 | 13.06 | 29.43 | 1.172133 | Up | 6.79E-48 | 4.77 × 10−47 |
| novel_mir38 | 6941 | 74963 | 184.18 | 2700.76 | 3.874177 | Up | 0 | 0 |
| novel_mir39 | 164 | 1013 | 4.35 | 36.5 | 3.068809 | Up | 2.05E-212 | 3.08 × 10−211 |
| novel_mir40 | 31 | 86 | 0.82 | 3.1 | 1.918572 | Up | 1.06E-11 | 4.35 × 10−11 |
| novel_mir41 | 114 | 2010 | 3.02 | 72.42 | 4.583768 | Up | 0 | 0 |
| novel_mir42 | 259 | 1808 | 6.87 | 65.14 | 3.245162 | Up | 0 | 0 |
| novel_mir43 | 50 | 130 | 1.33 | 4.68 | 1.815082 | Up | 6.45E-16 | 3 × 10−15 |
| novel_mir45 | 736 | 2609 | 19.53 | 94 | 2.266969 | Up | 0 | 0 |
| novel_mir46 | 143 | 220 | 3.79 | 7.93 | 1.065123 | Up | 3.38E-12 | 1.41 × 10−11 |
| novel_mir48 | 919 | 1754 | 24.39 | 63.19 | 1.373407 | Up | 9.10E-129 | 1.04 × 10−127 |
| novel_mir8 | 50 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.001 | −10.3772 | Down | 1.20E-12 | 5.13 × 10−12 |
| novel_mir11 | 926 | 75 | 24.57 | 2.7 | −3.18587 | Down | 4.68E-136 | 5.50 × 10−135 |
| novel_mir15 | 35 | 0 | 0.93 | 0.001 | −9.86109 | Down | 4.71E-09 | 1.73 × 10−8 |
| novel_mir20 | 35 | 0 | 0.93 | 0.001 | −9.86109 | Down | 4.71E-09 | 1.74 × 10−8 |
| novel_mir23 | 794 | 252 | 21.07 | 9.08 | −1.21443 | Down | 3.39E-35 | 2.17 × 10−34 |
| novel_mir25 | 59 | 0 | 1.57 | 0.001 | −10.6165 | Down | 8.33E-15 | 3.76 × 10−14 |
| novel_mir27 | 2970 | 65 | 78.81 | 2.34 | −5.0738 | Down | 0 | 0 |
| novel_mir28 | 16 | 0 | 0.42 | 0.001 | −8.71425 | Down | 0.000168 | 0.000477 |
| novel_mir33 | 709 | 173 | 18.81 | 6.23 | −1.5942 | Down | 1.26E-46 | 8.65 × 10−46 |
| novel_mir34 | 479 | 22 | 12.71 | 0.79 | −4.00797 | Down | 1.78E-85 | 1.64 × 10−84 |
| novel_mir36 | 41 | 0 | 1.09 | 0.001 | −10.0901 | Down | 1.72E-10 | 6.84 × 10−10 |
| novel_mir44 | 34 | 0 | 0.9 | 0.001 | −9.81378 | Down | 8.17E-09 | 2.97 × 10−8 |
| novel_mir53 | 230 | 47 | 6.1 | 1.69 | −1.85179 | Down | 1.71E-19 | 8.64 × 10−19 |
| miRNA ID | Count (IC-1) | Count (IS-4) | TPM (IC-1) | TPM (IS-4) | log2 Ratio (IS-4/IC-1) | Regulation Profile (up/down) (IC-1 vs IS-4) | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| novel_mir6 | 44 | 256 | 1.87 | 11.62 | 2.6354999 | Up | 7.82× 10−41 | 4.42 × 10−40 |
| novel_mir8 | 338 | 6850 | 14.38 | 310.9 | 4.434315 | Up | 0 | 0 |
| novel_mir9 | 0 | 207 | 0.001 | 9.4 | 13.198445 | Up | 5.11 × 10−66 | 3.49 × 10−65 |
| novel_mir18 | 0 | 188 | 0.001 | 8.53 | 13.05833 | Up | 5.02 × 10−60 | 3.27 × 10−59 |
| novel_mir19 | 200 | 1538 | 8.51 | 69.81 | 3.0362027 | Up | 3.94 × 10−275 | 5.07 × 10−274 |
| novel_mir22 | 0 | 587 | 0.001 | 26.64 | 14.701306 | Up | 7.53 × 10−186 | 7.83 × 10−185 |
| novel_mir30 | 0 | 200 | 0.001 | 9.08 | 13.148477 | Up | 8.25 × 10−64 | 5.54 × 10−63 |
| novel_mir36 | 163 | 496 | 6.93 | 22.51 | 1.6996388 | Up | 5.04 × 10−45 | 2.99 × 10−44 |
| novel_mir39 | 134 | 453 | 5.7 | 20.56 | 1.8508064 | Up | 2.78 × 10−46 | 1.67 × 10−45 |
| novel_mir42 | 192 | 1707 | 8.17 | 77.48 | 3.245416 | Up | 0 | 0 |
| novel_mir5 | 347 | 663 | 14.76 | 30.09 | 1.0275914 | Up | 2.31 × 10−28 | 1.10 × 10−27 |
| novel_mir13 | 1404 | 298 | 59.72 | 13.53 | −2.1420523 | Down | 2.13 × 10−156 | 1.98 × 10−155 |
| novel_mir14 | 62 | 10 | 2.64 | 0.45 | −2.552541 | Down | 8.44 × 10−10 | 2.72 × 10−9 |
| novel_mir16 | 116 | 42 | 4.93 | 1.91 | −1.368015 | Down | 2.42 × 10−8 | 7.48 × 10−8 |
| novel_mir20 | 254 | 60 | 10.8 | 2.72 | −1.9893528 | Down | 4.41 × 10−27 | 2.07 × 10−26 |
| novel_mir27 | 10812 | 1387 | 459.9 | 62.95 | −2.8690419 | Down | 0 | 0 |
| novel_mir29 | 1387 | 564 | 59 | 25.6 | −1.2045711 | Down | 1.14 × 10−68 | 7.94 × 10−68 |
| novel_mir31 | 245 | 75 | 10.42 | 3.4 | −1.6157486 | Down | 4.83 × 10−20 | 1.98 × 10−19 |
| novel_mir32 | 4098 | 1680 | 174.31 | 76.25 | −1.1928461 | Down | 3.81 × 10−196 | 4.01 × 10−195 |
| novel_mir33 | 1370 | 157 | 58.27 | 7.13 | −3.0307793 | Down | 2.35 × 10−225 | 2.65 × 10−224 |
| novel_mir4 | 165 | 11 | 7.02 | 0.5 | −3.811471 | Down | 1.52 × 10−34 | 7.93 × 10−34 |
| novel_mir40 | 451 | 39 | 19.18 | 1.77 | −3.4377815 | Down | 1.63 × 10−84 | 1.22 × 10−83 |
| novel_mir44 | 240 | 0 | 10.21 | 0.001 | −13.317695 | Down | 1.24 × 10−69 | 8.68 × 10−69 |
| novel_mir46 | 759 | 263 | 32.28 | 11.94 | −1.4348377 | Down | 1.01 × 10−49 | 6.25 × 10−49 |
| novel_mir48 | 6461 | 707 | 274.83 | 32.09 | −3.0983438 | Down | 0 | 0 |
| novel_mir50 | 5351 | 1112 | 227.61 | 50.47 | −2.173066 | Down | 0 | 0 |
| novel_mir52 | 450 | 116 | 19.14 | 5.26 | −1.8634561 | Down | 5.42 × 10−43 | 3.15 × 10−42 |
| novel_mir53 | 871 | 180 | 37.05 | 8.17 | −2.1810656 | Down | 6.75 × 10−100 | 5.38 × 10−99 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzahrani, S.M.; Alaraidh, I.A.; Khan, M.A.; Migdadi, H.M.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Alsahli, A.A. Identification and Characterization of Salt-Responsive MicroRNAs in Vicia faba by High-Throughput Sequencing. Genes 2019, 10, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10040303
Alzahrani SM, Alaraidh IA, Khan MA, Migdadi HM, Alghamdi SS, Alsahli AA. Identification and Characterization of Salt-Responsive MicroRNAs in Vicia faba by High-Throughput Sequencing. Genes. 2019; 10(4):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10040303
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzahrani, Saud M., Ibrahim A. Alaraidh, Muhammad A. Khan, Hussein M. Migdadi, Salem S. Alghamdi, and Abdluaziz A. Alsahli. 2019. "Identification and Characterization of Salt-Responsive MicroRNAs in Vicia faba by High-Throughput Sequencing" Genes 10, no. 4: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10040303
APA StyleAlzahrani, S. M., Alaraidh, I. A., Khan, M. A., Migdadi, H. M., Alghamdi, S. S., & Alsahli, A. A. (2019). Identification and Characterization of Salt-Responsive MicroRNAs in Vicia faba by High-Throughput Sequencing. Genes, 10(4), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10040303







