Genetic Structure and Eco-Geographical Differentiation of Lancea tibetica in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
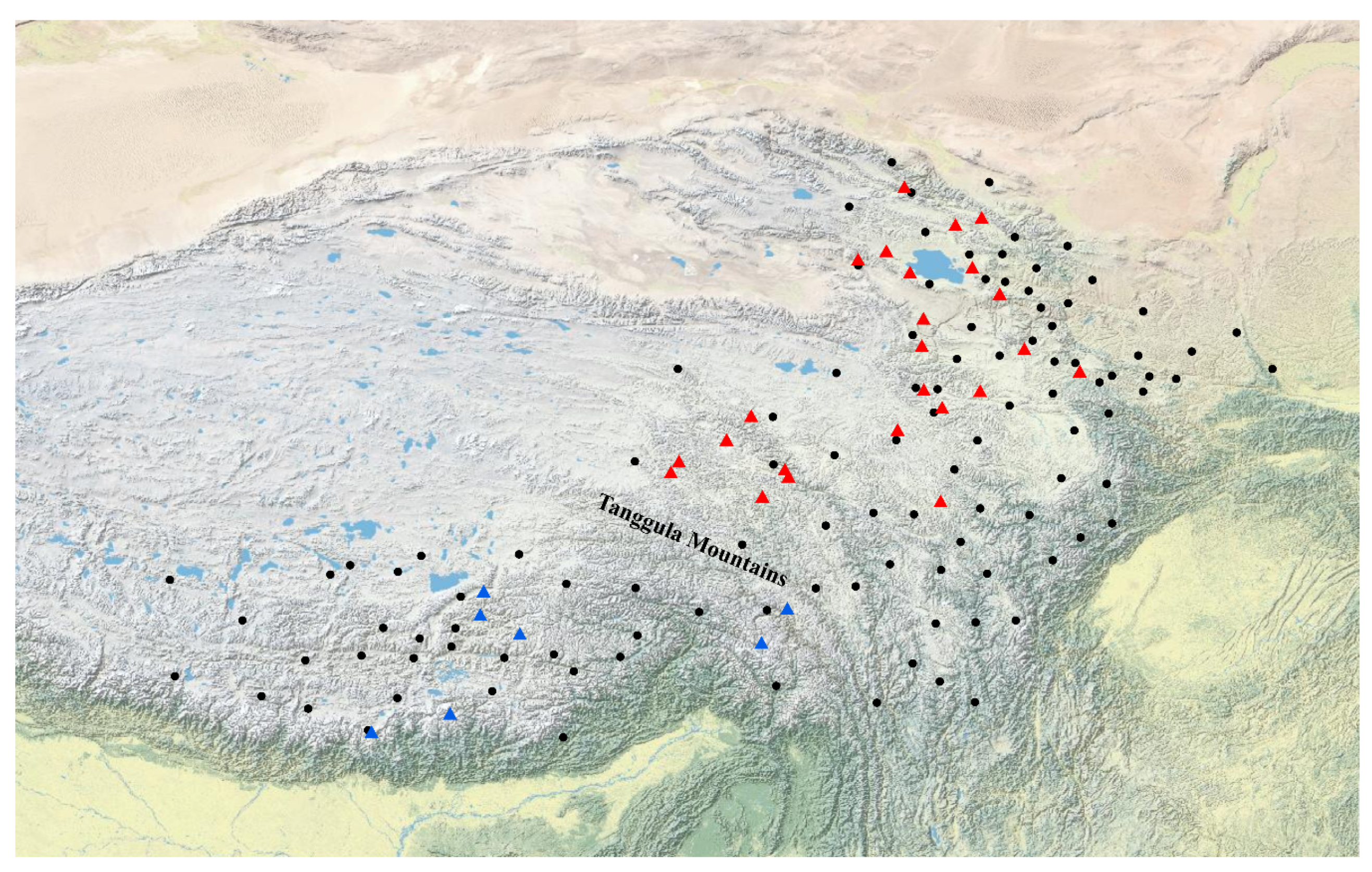
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. DNA Extraction and SSR Amplification
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SSR Markers and Genetic Diversity
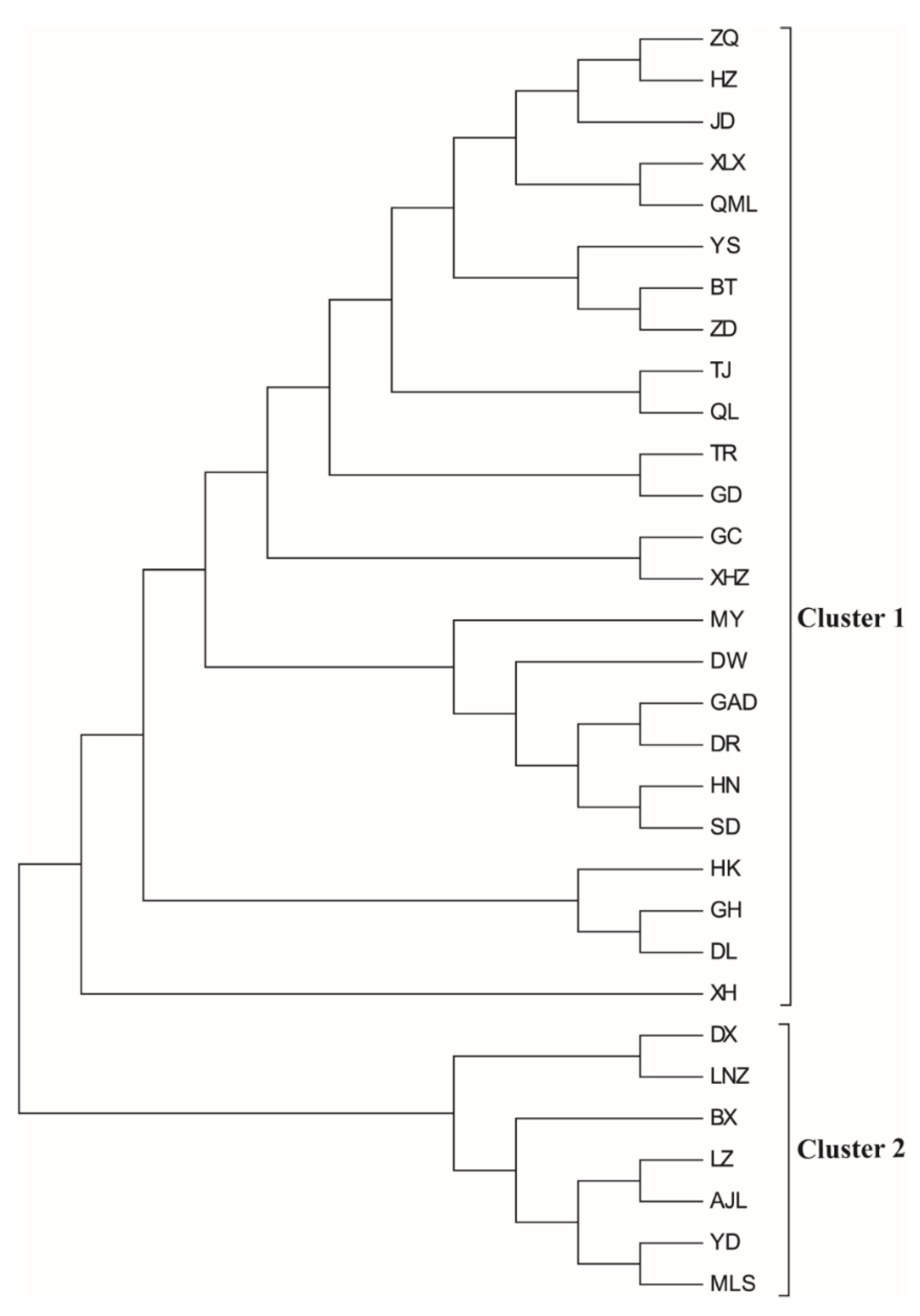
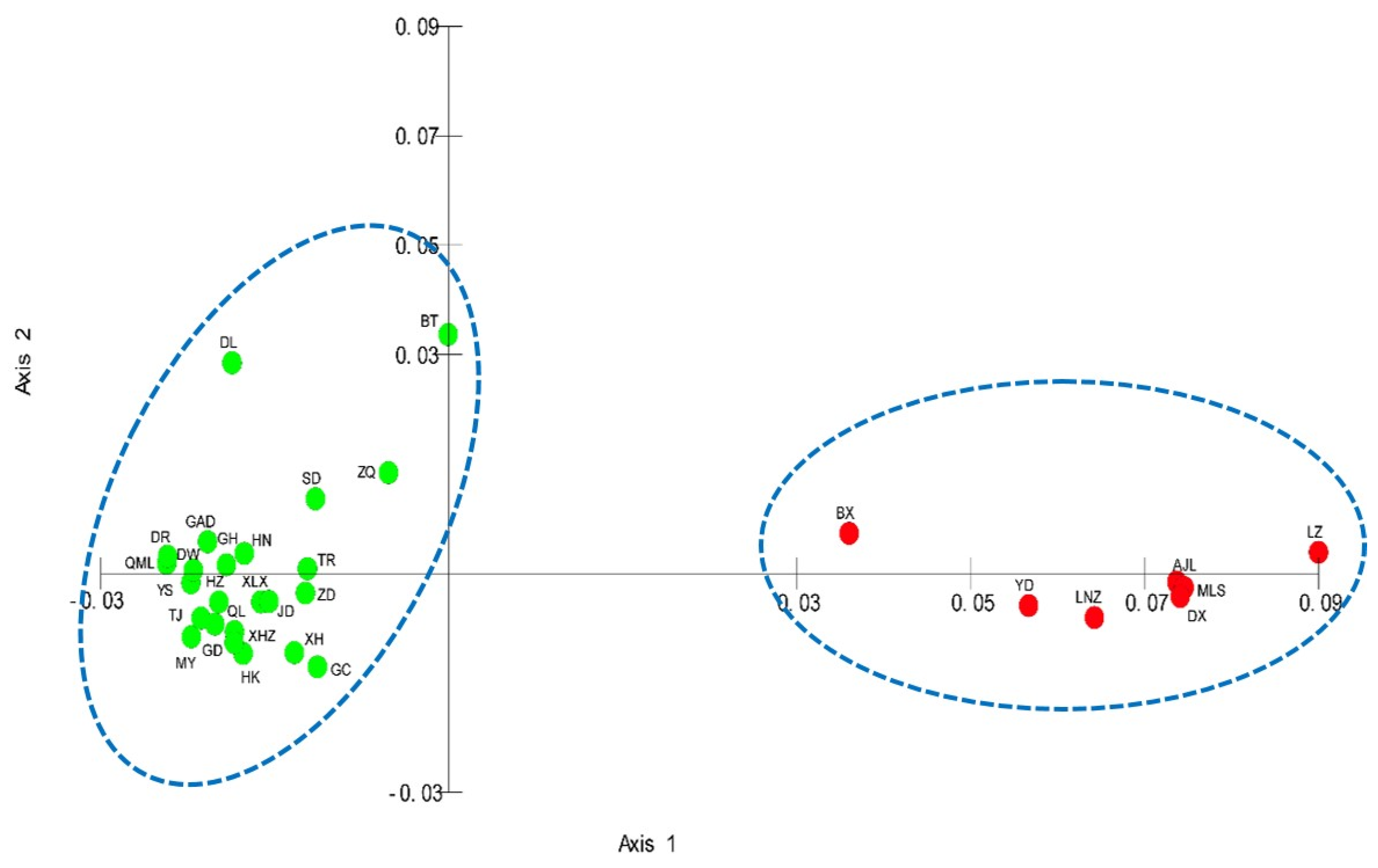
3.2. Population Structure
3.3. Genetic Differentiation
3.4. Genetic Diversity Associated with Geography
4. Discussion
4.1. Genetic Variation
4.2. Genetic Divergence and the Effects of the Tanggula Mountains
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, C.E.; Atchison, G.W. The ubiquity of alpine plant radiations: From the Andes to the Hengduan Mountains. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, R.T.; Matt, L.; Tiina, S.R.; Lewis, G.P.; Klitgaard, B.B.; Hughes, C.E. Contrasting plant diversification histories within the Andean biodiversity hotspot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13783–13787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Da Fonseca, G.A.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Du, J.H.; Li, J.S.; Li, J.Q.; Meng, W. Ecosystem development and biodiversity of Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Tech. Rev. 2017, 35, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bouilhol, P.; Jagoutz, O.; Hanchar, J.M.; Dudas, F.O. Dating the India–Eurasia collision through arc magmatic records. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 366, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagoutz, O.; Royden, L.; Holt, A.F.; Becker, T.W. Anomalously fast convergence of India and Eurasia caused by double subduction. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, R.; Zheng, H.; Clift, P.D. Evolution and variability of the Asian monsoon and its potential linkage with uplift of the Himalaya and Tibetan Plateau. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2016, 3, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.F.; Chen, S.B.; Zhang, J.L.; Hou, Y.H.; Zhou, G.S.; Zhang, X.S. Vascular plant diversity on the roof of the world: Spatial patterns and environmental determinants. J. Syst. Evol. 2013, 51, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, G.; Zhang, F.Q.; Gao, Q.B.; Fu, P.C.; Xing, R.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, H.R.; Chen, S.L. Phylogenetic analyses of Spiraea (Rosaceae) distributed in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and adjacent regions: Insights from molecular data. Plant Syst. Evol. 2016, 302, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Conti, E.; Salamin, N. Phylogeny and biogeography of Primula sect. Armerina: Implications for plant evolution under climate change and the uplift of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Xia, Y.M.; Cannon, C.H.; Kress, W.J.; Li, Q.J. Evolutionary diversification of alpine ginger reflects the early uplift of the Himalayan-Tibetan Plateau and rapid extrusion of Indochina. Gondwana Res. 2016, 32, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, A.; Päckert, M.; Pauls, S.U.; Jähnig, S.C.; Uhl, D.; Michalak, I.; Muellner-Riehl, A.N. The role of the uplift of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau for the evolution of Tibetan biotas. Biol. Rev. 2015, 90, 236–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Zhao, J.Q.; Nie, Z.L.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, H. Evolutionary diversifications of plants on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.S.; Li, Y.F.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.Q. Extensive population expansion of Pedicularis longiflora (Orobanchaceae) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its correlation with the Quaternary climate change. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 17, 5135–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Moeller, M.; Provan, J.; Gao, L.M.; Poudel, R.C.; Li, D.Z. Geological and ecological factors drive cryptic speciation of yews in a biodiversity hotspot. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.P.; Mateo, R.G.; Liu, J.; Suchan, T.; Alvarez, N.; Guisan, A.; Conti, E.; Salamin, N. Genetic consequences of Quaternary climatic oscillations in the Himalayas: Primula tibetica as a case study based on restriction site-associated DNA sequencing. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1500–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.B.; Zhang, Y.L. Advances in phylogeography of alpine plants in the Tibetan Plateau and adjacent regions. Acta Bot. Boreal. Occident. Sin. 2013, 33, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Luo, Y.H.; Li, D.Z.; Gao, L.M. Evolution and maintenance mechanisms of plant diversity in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and adjacent regions: Retrospect and prospect. Biodivers. Sci. 2017, 25, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Yin, H.; Yong, S.; Zhao, J.; Yin, C.; Luo, W.; Dong, Z.; Chen, G.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X.R. Population dynamics of Agriophyllum squarrosum, a pioneer annual plant endemic to mobile sand dunes, in response to global climate change. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.H.; Chen, J.; Zhao, G.F.; Guo, Y.P.; Kou, Y.X.; Ma, Y.Z.; Wang, G.; Ma, X.F. Response of a desert shrub to past geological and climatic change: A phylogeographic study of Reaumuria soongarica (Tamaricaceae) in western China. J. Syst. Evol. 2012, 50, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.B.; Zhang, D.J.; Duan, Y.Z.; Zhang, F.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Fu, P.C.; Chen, S.L. Intraspecific divergences of Rhodiola alsia (Crassulaceae) based on plastid DNA and internal transcribed spacer fragments. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 168, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Y.; Wang, Q.F. Allopatric divergence of Stuckenia filiformis (Potamogetonaceae) on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its comparative phylogeography with S. pectinata in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.Y.; Zheng, D. On the Significance of the Boundary Line-the Cangdisi Nyainqentanglha Range. Geogr. Res. 1985, 4, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Anacker, B.L.; Strauss, S.Y. The geography and ecology of plant speciation: Range overlap and niche divergence in sister species. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20132980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosil, P.; Funk, D.; Ortiz-Barrientos, D. Divergent selection and heterogeneous genomic divergence. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 18, 375–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, D.S.; Feng, J.J.; Jiang, D.C.; Mao, K.S.; Duan, Y.W.; Miehe, G.; Opgenoorth, L. The Quaternary evolutionary history, potential distribution dynamics, and conservation implications for a Qinghai–Tibet Plateau endemic herbaceous perennial, Anisodus tanguticus (Solanaceae). Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 1977–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants, APG IV. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 181, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Raven, P.H. Flora of China: Vol. 18 Scrophulariaceae through Gesneriaceae; Scrophulariaceae through Gesneriaceae; Missouri Botanical Garden: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.C. Flora Tebitan Medicine; Qinghai People’s Publishing House: Xining, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Hao, X.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhu, W.M. Minor furofurano lignans from the Tibetan herb, Lancea tibetica. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.H.; Qian, Z.H.; Rumalla, C.S.; Smillie, T.J.; Khan, I.A. Identification of 11 marker compounds simultaneously in herb Lancea tibetica by using high-performance thin-layer chromatography. JPC 2011, 24, 312–315. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Qian, Z.Z.; Smillie, T.J.; Khan, I.A. Quantitative determination of 10 phenylpropanoid and lignan compounds in Lancea tibetica by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.N.; Zhu, Q.X.; Gao, K.; Yuan, C.S.; Jia, Z.J. Lignan and phenylpropanoid glycosides from Lancea tibetica and their antitumor activity. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H. Study on the chemical constituents of Lancea tibetica Hook F. et Thoms. Acta Bot. Sin. 1985, 27, 402–406. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.Z.; Zhang, F.Q.; Liu, H.R.; Gao, Q.B.; Chen, S.L. Development of SSR markers for a Tibetan medicinal plant, Lancea tibetica (Phrymaceae), based on RAD sequencing. Appl. Plant Sci. 2016, 4, 1600076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small amounts of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- McNeely, J.A.; Miller, K.R.; Reid, W.V.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Werner, T.B. Conserving the World’s Biological Diversity; International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources: Grand, Switzerland, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, M.R.; Jain, S.M. Genetic Diversity and Erosion in Plants; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Deng, G.; Zhai, X.; Long, H.; Tang, Y.; Qiang, X.; Yu, M. Molecular analysis of cultivated naked barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China using SSR markers. Front. Agric. China 2008, 2, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.H.; Lu, Z.X.; Chen, K.; Luukkanen, O.; Korpelainen, H.; Li, C.Y. Population genetic survey of Populus cathayana originating from southeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China based on SSR markers. Silvae Genet. 2005, 54, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Chu, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y. Genetic diversity and population structure of the endangered alpine quillwort Isoetes hypsophila (Isoetaceae) revealed by SSR analysis. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2013, 47, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Shang, Y.; Wang, J.; Jia, Q.; Li, C.; Yang, J. A study of genetic diversity of colored barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) using SSR markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2015, 62, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.X. Genetic variation of isolated Picea balfouriana populations from the southeast of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ann. For. Sci. 2009, 66, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Huang, L. Assessment of genetic diversity and differentiation of Elymus nutans indigenous to Qinghai–Tibet Plateau using simple sequence repeats markers: Revue canadienne de phytotechnie. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 93, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Gao, Q.B.; Zhang, F.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Fu, P.C.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, J.L.; Khan, G.; Chen, S.L. Genetic diversity and population structure of Armillaria luteovirens (Physalacriaceae) in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau revealed by SSR markers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 56, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.C.; Gao, Q.B.; Zhang, F.Q.; Xing, R.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, H.R.; Chen, S.L. Gene flow results in high genetic similarity between Sibiraea (Rosaceae) species in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; You, J.; Qi, D.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Song, Z. Morphological and genetic variation along a North-to-South transect in Stipa purpurea, a dominant grass on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Implications for response to climate change. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, D.; You, J.; Zhou, Y.; Song, Z. The Tanggula Mountains enhance population divergence in Carex moorcroftii: A dominant sedge on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoeckel, S.; Grange, J.; Fernandez-Manjarres, J.; Bilger, I.; Frascaria-Lacoste, N.S. Heterozygote excess in a self-incompatible and partially clonal forest tree species - Prunus avium L. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 15, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.C.; Li, B.Y.; Yi, Z.S.; Zhang, Q.S. The formation and evolution of landforms in the Xizang Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1982, 76–87. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.M.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M. Quaternary tills at the pass of the Tanggula Mountains on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and their geological-environmental significance. Geol. China 2005, 32, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.X.; Yao, T.D.; Tian, L.D. Comparison of summer monsoon precipitation between Northern and Southern slope of Tanggula Mountain over the Tibetan Plateau. Quart. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 11, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.H.; Zhang, B.P. The spatial pattern of monthly air temperature of the Tibetan Plateau and its implications for the geo-ecology pattern of the Plateau. Geogr. Res. 2015, 34, 2084–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.Y. The regionalization of Chinese flora. Acta Bot. Yunnanica 1979, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar]



| Loci | Na | RA | I | Ho | He | Fis | Fst | Fit | PIC | GST | GST’ | Nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT4 | 10 | 9 | 0.6852 | 0.1752 | 0.2760 | 0.0771 | 0.3561 | 0.3740 | 0.2693 | 0.2290 | 0.2924 | 0.4520 |
| LT7 | 3 | 0 | 0.8830 | 0.6674 | 0.5191 | -0.5216 | 0.1303 | -0.2798 | 0.4580 | 0.1081 | 0.2045 | 1.6684 |
| LT9 | 7 | 5 | 0.8299 | 0.4062 | 0.4678 | -0.1183 | 0.2440 | 0.1394 | 0.3984 | 0.2603 | 0.4019 | 0.7746 |
| LT10 | 11 | 9 | 1.0898 | 0.9009 | 0.5817 | -0.7451 | 0.1341 | -0.5420 | 0.5040 | 0.0996 | 0.2128 | 1.6148 |
| LT15 | 5 | 3 | 0.6333 | 0.2412 | 0.3537 | 0.0066 | 0.3141 | 0.3258 | 0.3087 | 0.2912 | 0.3919 | 0.5458 |
| LT16 | 4 | 2 | 0.7875 | 0.9978 | 0.5203 | -0.9328 | 0.0034 | -0.9262 | 0.4052 | 0.0075 | 0.0157 | 72.932 |
| LT25 | 11 | 5 | 1.8425 | 0.5351 | 0.8008 | 0.0490 | 0.2775 | 0.3129 | 0.7761 | 0.2736 | 0.6667 | 0.6507 |
| LT28 | 4 | 1 | 0.7642 | 0.2975 | 0.4400 | -0.0567 | 0.4180 | 0.3850 | 0.3824 | 0.3908 | 0.5387 | 0.3481 |
| Mean | 6.875 | 4.25 | 0.9394 | 0.5277 | 0.4949 | -0.2802 | 0.2215 | -0.0581 | 0.4378 | 0.2075 | 0.3406 | 0.8785 |
| Source of Variation | Degrees of Freedom | Sum of Squares | Variance Components | Percentage of Variation | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (i) total populations | |||||
| Among populations | 30 | 385.473 | 0.38671 | 18.3161 | <0.001 |
| Within populations | 879 | 1497.408 | 1.72461 | 81.6839 | <0.001 |
| (ii) two groups | |||||
| Among groups | 1 | 150.963 | 0.51530 | 20.9305 | <0.001 |
| Among populations within groups | 29 | 234.510 | 0.22204 | 9.0187 | <0.001 |
| Within populations | 879 | 1497.408 | 1.72461 | 70.0508 | <0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, X.; Zhang, F.; Gao, Q.; Xing, R.; Chen, S. Genetic Structure and Eco-Geographical Differentiation of Lancea tibetica in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Genes 2019, 10, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020097
Chi X, Zhang F, Gao Q, Xing R, Chen S. Genetic Structure and Eco-Geographical Differentiation of Lancea tibetica in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Genes. 2019; 10(2):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020097
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Xiaofeng, Faqi Zhang, Qingbo Gao, Rui Xing, and Shilong Chen. 2019. "Genetic Structure and Eco-Geographical Differentiation of Lancea tibetica in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau" Genes 10, no. 2: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020097
APA StyleChi, X., Zhang, F., Gao, Q., Xing, R., & Chen, S. (2019). Genetic Structure and Eco-Geographical Differentiation of Lancea tibetica in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Genes, 10(2), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020097






