Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate: Genome-Wide Association Study in Europeans Identifies a Suggestive Risk Locus at 16p12.1 and Supports SH3PXD2A as a Clefting Susceptibility Gene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. GWAS Patients
2.3. GWAS Controls
2.4. GWAS Genotyping and Quality Control (QC)
2.5. Imputation of GWAS Data
2.6. Genome-Wide Association Analysis
2.7. Replication Analysis for Two Interesting SNVs
2.8. Prioritization of Candidate Genes
2.9. Expression Analysis using SysFACE
3. Results
3.1. SNV-Based Analysis
3.2. Replication of Previously Reported nsCL/P Susceptibility Loci
3.3. Gene-Based Evaluation and Gene-Set Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mangold, E.; Ludwig, K.U.; Nöthen, M.M. Breakthroughs in the genetics of orofacial clefting. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosen, D.; Bille, C.; Petersen, I.; Skytthe, A.; von Hjelmborg, J.B.; Pedersen, J.K.; Murray, J.C.; Christensen, K. Risk of oral clefts in twins. Epidemiology 2011, 22, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimov, F.; Marazita, M.L.; Visel, A.; Cooper, M.E.; Hitchler, M.J.; Rubini, M.; Domann, F.E.; Govil, M.; Christensen, K.; Bille, C.; et al. Disruption of an AP-2alpha binding site in an IRF6 enhancer is associated with cleft lip. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, L.M.; Mansilla, M.A.; Bullard, S.A.; Cooper, M.E.; Busch, T.D.; Machida, J.; Johnson, M.K.; Brauer, D.; Krahn, K.; Daack-Hirsch, S.; et al. FOXE1 association with both isolated cleft lip with or without cleft palate, and isolated cleft palate. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4879–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, A.; Parker, M.M.; Ruczinski, I.; Taub, M.A.; Marazita, M.L.; Murray, J.C.; Mangold, E.; Noethen, M.M.; Ludwig, K.U.; Hetmanski, J.B.; et al. Whole Exome sequencing of distant relatives in multiplex families implicates rare variants in candidate genes for oral clefts. Genetics 2014, 197, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.L.; Cox, T.C.; Uribe, L.M.M.; Zhu, Y.; Richter, C.T.; Nidey, N.; Standley, J.M.; Deng, M.; Blue, E.; Chong, J.X.; et al. Mutations in the Epithelial Cadherin-p120-Catenin Complex Cause Mendelian Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.C.; Lidral, A.C.; McCoy, J.C.; Liu, H.; Cox, L.L.; Zhu, Y.; Anderson, R.D.; Uribe, L.M.M.; Anand, D.; Deng, M.; et al. Mutations in GDF11 and the extracellular antagonist, Follistatin, as a likely cause of Mendelian forms of orofacial clefting in humans. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, S.; Ludwig, K.U.; Reutter, H.; Herms, S.; Steffens, M.; Rubini, M.; Baluardo, C.; Ferrian, M.; de Assis, N.A.; Alblas, M.; et al. Key susceptibility locus for nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate on chromosome 8q24. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.F.A.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Glaberson, W.; Annaiah, K.; Kim, C.E.; Bradfield, J.P.; Glessner, J.T.; Thomas, K.A.; Garris, M.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies a locus for nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate on 8q24. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangold, E.; Ludwig, K.U.; Birnbaum, S.; Baluardo, C.; Ferrian, M.; Herms, S.; Reutter, H.; de Assis, N.A.; Chawa, T.A.; Mattheisen, M.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies two susceptibility loci for nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaty, T.H.; Murray, J.C.; Marazita, M.L.; Munger, R.G.; Ruczinski, I.; Hetmanski, J.B.; Liang, K.Y.; Wu, T.; Murray, T.; Fallin, M.D.; et al. A genome-wide association study of cleft lip with and without cleft palate identifies risk variants near MAFB and ABCA4. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.U.; Mangold, E.; Herms, S.; Nowak, S.; Paul, A.; Becker, J.; Herberz, R.; Alchawa, T.; Böhmer, A.C.; Mattheisen, M.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analyses of nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate indentify six new risk loci. Nat Genet. 2012, 44, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaty, T.H.; Taub, M.A.; Scott, A.F.; Murray, J.C.; Marazita, M.L.; Schwender, H.; Parker, M.M.; Hetmanski, J.B.; Balakrishnan, P.; Mansilla, M.A.; et al. Confirming genes influencing risk to cleft lip with/without cleft palate in a case-parent trio study. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yin, A.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Du, Y.; Wang, M.; Lan, F.; Hu, Z.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a new susceptibility locus for cleft lip with or without a cleft palate. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.U.; Ahmed, S.T.; Böhmer, A.C.; Sangani, N.B.; Varghese, S.; Klamt, J.; Schuenke, H.; Gültepe, P.; Hofmann, A.; Rubini, M.; et al. Meta-analysis Reveals Genome-Wide Significance at 15q13 for Nonsyndromic Clefting of Both the Lip and the Palate, and Functional Analyses Implicate GREM1 As a Plausible Causative Gene. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, E.J.; Carlson, J.C.; Shaffer, J.R.; Feingold, E.; Wehby, G.; Laurie, C.A.; Jain, D.; Laurie, C.C.; Doheny, K.F.; McHenry, T.; et al. A multi-ethnic genome-wide association study identifies novel loci for non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate on 2p24.2, 17q23 and 19q13. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 2862–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zuo, X.; He, M.; Gao, J.; Fu, Y.; Qin, C.; Meng, L.; Wang, W.; Song, Y.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Genome-wide analyses of non-syndromic cleft lip with palate identify 14 novel loci and genetic heterogeneity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostowska, A.; Gaczkowska, A.; Żukowski, K.; Ludwig, K.U.; Hozyasz, K.K.; Wójcicki, P.; Mangold, E.; Böhmer, A.C.; Heilmann-Heimbach, S.; Knapp, M.; et al. Common variants in DLG1 locus are associated with non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.U.; Böhmer, A.C.; Bowes, J.; Nikolic, M.; Ishorst, N.; Wyatt, N.; Hammond, N.L.; Gölz, L.; Thieme, F.; Barth, S.; et al. Imputation of orofacial clefting data identifies novel risk loci and sheds light on the genetic background of cleft lip ± cleft palate and cleft palate only. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, E.J.; Carlson, J.C.; Shaffer, J.R.; Butali, A.; Buxó, C.J.; Castilla, E.E.; Christensen, K.; Deleyiannis, F.W.B.; Leigh Field, L.; Hecht, J.T.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analyses of nonsyndromic orofacial clefts identify novel associations between FOXE1 and all orofacial clefts, and TP63 and cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rooij, I.A.L.M.; van der Zanden, L.F.M.; Bongers, E.M.H.F.; Renkema, K.Y.; Wijers, C.H.W.; Thonissen, M.; Dokter, E.M.J.; Marcelis, C.L.M.; de Blaauw, I.; Wijnen, M.H.W.A.; et al. AGORA, a data- and biobank for birth defects and childhood cancer. Birth Defects Res. Part A-Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2016, 106, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galesloot, T.E.; Vermeulen, S.H.; Swinkels, D.W.; de Vegt, F.; Franke, B.; den Heijer, M.; de Graaf, J.; Verbeek, A.L.M.; Kiemeney, L.A.L.M. Cohort Profile: The Nijmegen Biomedical Study (NBS). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1099–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Manichaikul, A.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Rich, S.S.; Daly, K.; Sale, M.; Chen, W.M. Robust relationship inference in genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2867–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howie, B.; Fuchsberger, C.; Stephens, M.; Marchini, J.; Abecasis, G.R. Fast and accurate genotype imputation in genome-wide association studies through pre-phasing. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, J.; Howie, B. Genotype imputation for genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Martinez, A.; Reutter, H.; Chacon-Camacho, O.; Leon-Cachon, R.B.R.; Munoz-Jimenez, S.G.; Nowak, S.; Becker, J.; Herberz, R.; Ludwig, K.U.; Paredes-Zenteno, M.; et al. Genetic risk factors for nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in a Mesoamerican population: Evidence for IRF6 and variants at 8q24 and 10q25. Birth Defects Res. A. Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2010, 88, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhorae, K.A.; Böhmer, A.C.; Ludwig, K.U.; Esmail, A.H.A.; Al-Hebshi, N.N.; Lippke, B.; Gölz, L.; Nöthen, M.M.; Daratsianos, N.; Knapp, M.; et al. Nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in Arab populations: Genetic analysis of 15 risk loci in a novel case-control sample recruited in Yemen. Birth Defects Res. Part A - Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2014, 100, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Taskesen, E.; Van Bochoven, A.; Posthuma, D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, C.A.; Mooij, J.M.; Heskes, T.; Posthuma, D. MAGMA: Generalized Gene-Set Analysis of GWAS Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, E.J.; Koboldt, D.C.; Kang, C.J.; Ma, L.; Hecht, J.T.; Wehby, G.L.; Christensen, K.; Czeizel, A.E.; Deleyiannis, F.W.-B.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. IRF6 mutation screening in non-syndromic orofacial clefting: Analysis of 1521 families. Clin. Genet. 2016, 90, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butali, A.; Mossey, P.; Adeyemo, W.; Eshete, M.; Gaines, L.; Braimah, R.; Aregbesola, B.; Rigdon, J.; Emeka, C.; Olutayo, J.; et al. Rare functional variants in genome-wide association identified candidate genes for nonsyndromic clefts in the African population. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2014, 164, 2567–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowans, L.J.J.; Adeyemo, W.L.; Eshete, M.; Mossey, P.A.; Busch, T.; Aregbesola, B.; Donkor, P.; Arthur, F.K.N.; Bello, S.A.; Martinez, A.; et al. Association studies and direct DNA sequencing implicate genetic susceptibility loci in the etiology of nonsyndromic orofacial clefts in sub-Saharan African populations. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jugessur, A.; Farlie, P.G.; Kilpatrick, N. The genetics of isolated orofacial clefts: From genotypes to subphenotypes. Oral Dis. 2009, 15, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilderman, A.; VanOudenhove, J.; Kron, J.; Noonan, J.P.; Cotney, J. High-Resolution Epigenomic Atlas of Human Embryonic Craniofacial Development. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, H.V.; Richards, S.M.; Bevan, A.P.; Clayton, S.; Corpas, M.; Rajan, D.; Van Vooren, S.; Moreau, Y.; Pettett, R.M.; Carter, N.P. DECIPHER: Database of Chromosomal Imbalance and Phenotype in Humans Using Ensembl Resources. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, P.; Wolfinger, R.D.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z. Gene set analysis of genome-wide association studies: Methodological issues and perspectives. Genomics 2011, 98, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seals, D.F.; Azucena, E.F.; Pass, I.; Tesfay, L.; Gordon, R.; Woodrow, M.; Resau, J.H.; Courtneidge, S.A. The adaptor protein Tks5/Fish is required for podosome formation and function, and for the protease-driven invasion of cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.A.; Diaz, B.; Bromann, P.A.; Tsai, J.H.; Kawakami, Y.; Maurer, J.; Stewart, R.A.; Izpisúa-Belmonte, J.C.; Courtneidge, S.A. A Src-Tks5 pathway is required for neural crest cell migration during embryonic development. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejudo-Martin, P.; Yuen, A.; Vlahovich, N.; Lock, P.; Courtneidge, S.A.; Díaz, B. Genetic disruption of the Sh3pxd2a gene reveals an essential role in mouse development and the existence of a novel isoform of Tks5. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picollo, A.; Malvezzi, M.; Accardi, A. TMEM16 proteins: Unknown structure and confusing functions. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| LeadSNV_ID 1 | Chromosome | Pos (hg19) | Alleles 2 | Case Frequency A | Control Frequency A | All OR | p-Value 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs36068947 | 1 | 19003293 | G/GC | 0.592 | 0.702 | 1.62 | 1.06 × 10-6 |
| rs11247713 | 1 | 28230494 | A/G | 0.165 | 0.261 | 1.78 | 2.54 × 10-6 |
| rs12404189 | 1 | 81851687 | T/C | 0.951 | 0.899 | 0.46 | 4.48 × 10-6 |
| rs145794647 | 1 | 213880572 | A/G | 0.915 | 0.964 | 2.46 | 3.17 × 10-6 |
| rs1266381 | 1 | 236681990 | A/G | 0.68 | 0.781 | 1.68 | 1.49 × 10-6 |
| rs13429389 | 2 | 2564600 | G/A | 0.713 | 0.807 | 1.68 | 6.34 × 10-6 |
| rs1431903 | 2 | 168468315 | T/C | 0.113 | 0.192 | 1.86 | 8.76 × 10-6 |
| rs112762347 | 5 | 13103319 | G/A | 0.952 | 0.986 | 3.56 | 5.80 × 10-6 |
| rs4868099 | 5 | 170982499 | T/C | 0.156 | 0.089 | 0.53 | 4.29 × 10-6 |
| rs141109174 | 7 | 2926872 | G/GA | 0.924 | 0.856 | 0.49 | 3.95 × 10-6 |
| rs987525 | 8 | 129946154 | C/A | 0.61 | 0.748 | 1.89 | 8.73 × 10-11 |
| rs1535462 | 10 | 102973872 | A/G | 0.623 | 0.518 | 0.65 | 5.69 × 10-6 |
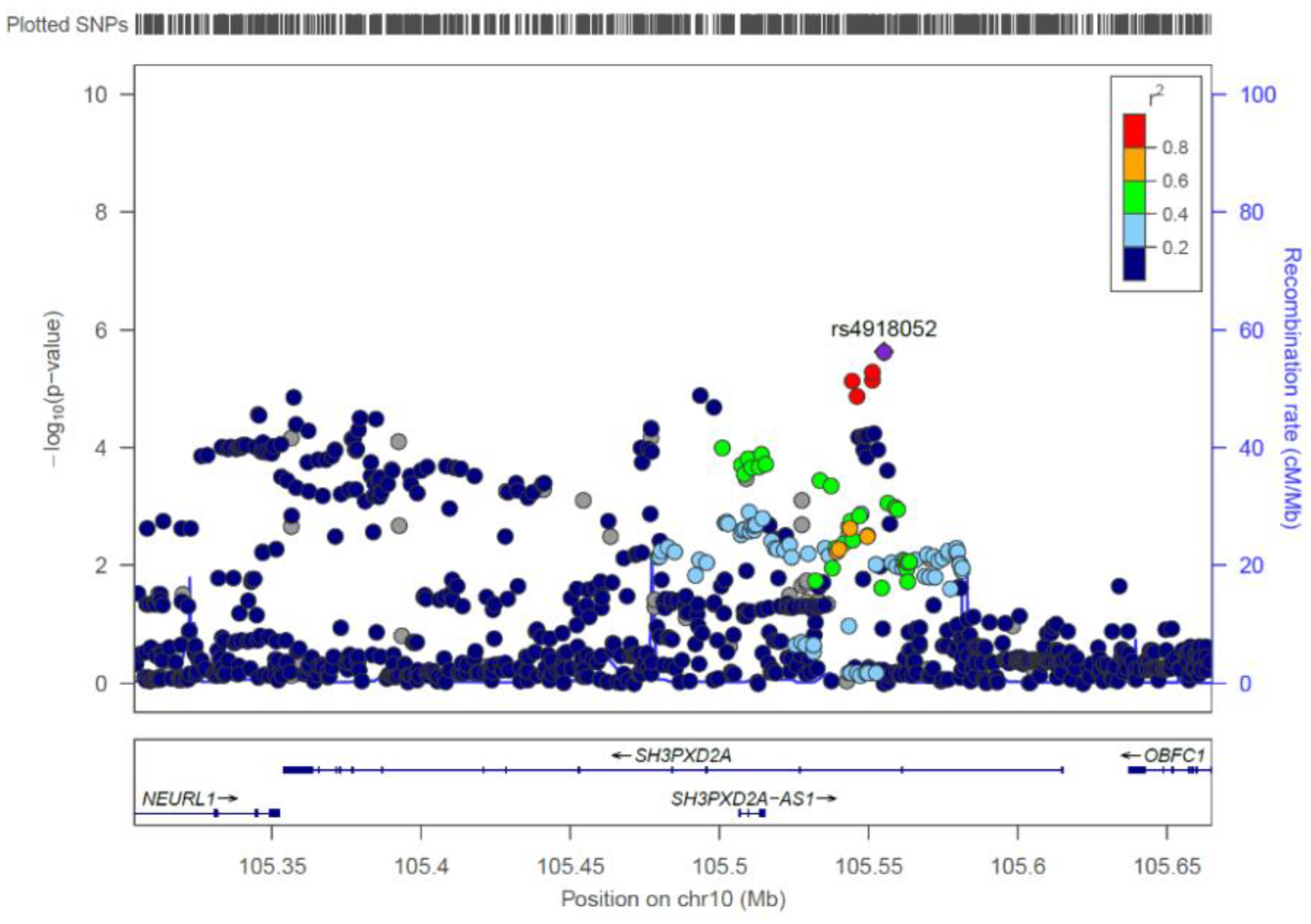
| rs4918052 | 10 | 105555131 | G/A | 0.303 | 0.203 | 0.58 | 2.34 × 10-6 |
| rs17770307 | 10 | 115259535 | G/C | 0.984 | 0.942 | 0.26 | 2.59 × 10-6 |
| rs148248623 | 12 | 23265077 | CA/C | 0.907 | 0.961 | 2.52 | 1.38 × 10-6 |
| rs7980090 | 12 | 67951884 | C/A | 0.908 | 0.958 | 2.28 | 2.35 × 10-6 |
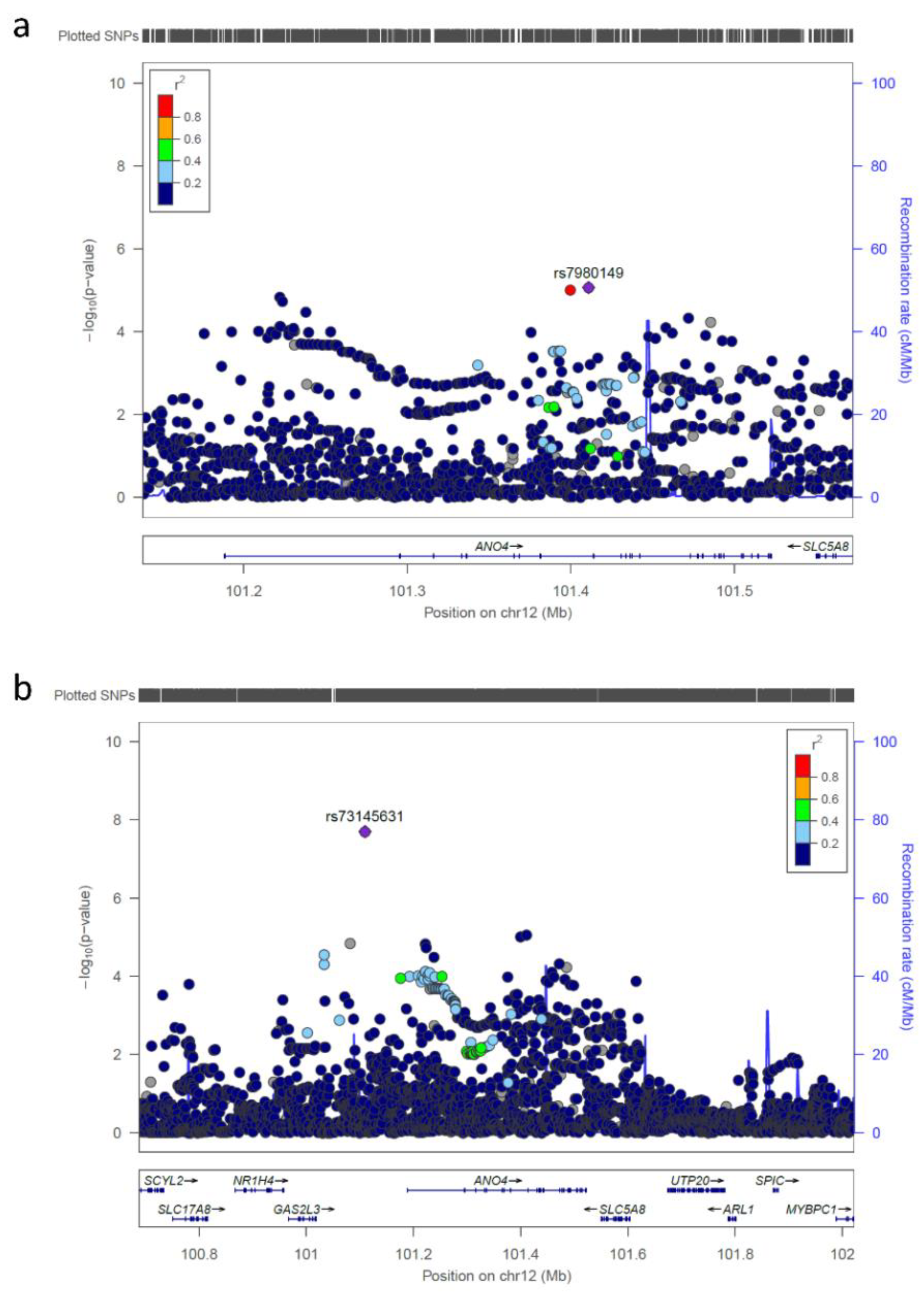
| rs73145631 | 12 | 101109530 | G/A | 0.985 | 0.936 | 0.23 | 1.99 × 10-8 |
| rs56814511 | 12 | 125789014 | C/T | 0.608 | 0.705 | 1.55 | 9.01 × 10-6 |
| rs184467 | 13 | 29622636 | G/T | 0.428 | 0.316 | 0.62 | 1.53 × 10-6 |
| rs10520788 | 15 | 96126414 | T/C | 0.973 | 0.924 | 0.34 | 6.19 × 10-6 |
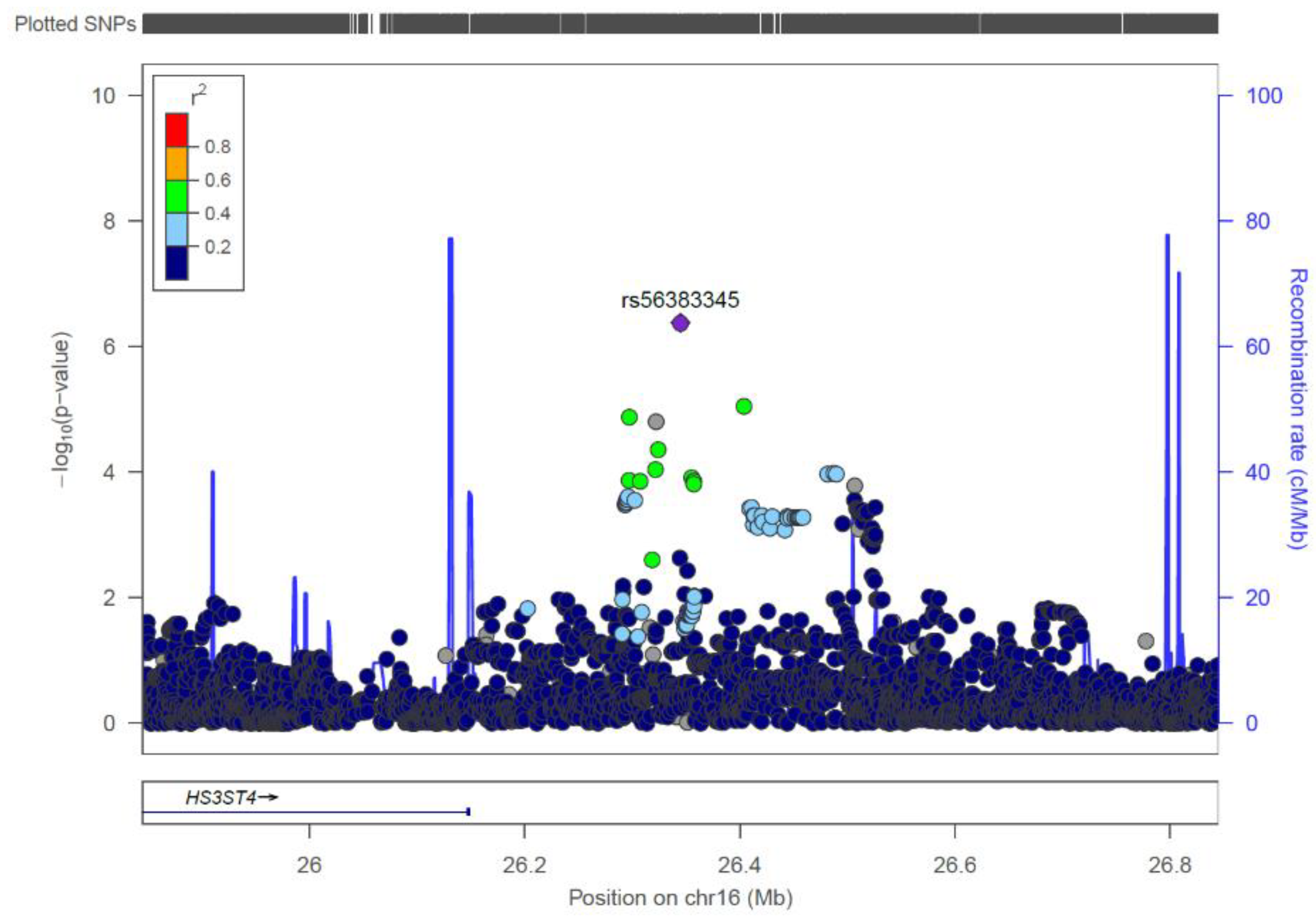
| rs56383345 | 16 | 26344915 | G/C | 0.922 | 0.845 | 0.46 | 4.17 × 10-7 |
| rs11640952 | 16 | 78093932 | G/T | 0.693 | 0.587 | 0.63 | 6.22 × 10-6 |
| rs7215555 | 17 | 29564603 | G/A | 0.231 | 0.331 | 1.64 | 3.28 × 10-6 |
| rs61296704 | 17 | 75721588 | G/A | 0.932 | 0.972 | 2.55 | 8.22 × 10-6 |
| rs73512449 | 19 | 18123050 | G/C | 0.888 | 0.946 | 2.19 | 7.00 × 10-6 |
| SNV-ID | p-Values after Genotyping of SNV in Respective Replication Sample | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNV-ID | Chr. | Pos. (hg19) | Bonn 1 | Mexico 2 | Yemen 3 | All 4 | OR (95% CI) |
| rs73145631 | 12q23.1 | 101109530 | 0.544 | n.a.* | 0.714 | 0.488 | 1.18 (0.74–1.90) |
| rs56383345 | 16p12.1 | 26344915 | 0.027 | 0.577 ** | 0.0099 | 0.00167 | 1.53 (1.17–1.98) |
| Literature Risk Locus 1 | Literature Lead SNV at Respective Locus | Better Dutch/Belgian GWAS lead SNV at Respective Locus | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locus | Original Study | SNV | Pos. (hg19) | p-Value 2 | OR | SNV 3 | Pos (hg19) | p-Value 2,3 | OR |
| 1p36 | Ludwig et al. 2012 [12] | rs742071 | 18979874 | 2.11 × 10-5 | 1.54 | rs36068947 | 19003293 | 1.06272 × 10-6 | 1.62 |
| 1p22 | Beaty et al. 2010 [11] | rs560426 | 94553438 | 0.299446 | 0.90 | rs952499 | 94558425 | 0.0616217 | 0.83 |
| 1q32.1 | Rahimov et al. 2008 [3] | rs642961 | 209989270 | 0.00055997 | 0.69 | - | - | - | - |
| 2p25.1 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs287982 | 9972442 | 0.898877 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - |
| 2p24.2 | Leslie et al. 2016 [16] | rs7552 | 16733928 | 4.84 × 10-5 | 1.52 | rs62122693 | 16734878 | 3.10168 × 10-5 | 1.56 |
| 2p21PKDCC | Ludwig et al. 2017 [19] | rs6740960 | 42181679 | 0.00745325 | 1.28 | rs17029056 | 42158304 | 0.00011259 | 1.52 |
| 2p21THADA | Ludwig et al. 2012 [12] | rs7590268 | 43540125 | 0.13198 | 1.20 | rs6544652 | 43626212 | 0.0881938 | 1.23 |
| 3p11.1 | Ludwig et al. 2012 [12] | rs7632427 | 89534377 | 0.0342897 | 0.81 | rs3792572 | 89456555 | 0.0101378 | 0.77 |
| 3q12.1 | Beaty et al. 2013 [13] | rs793464 | 99626028 | 8.21 × 10-5 | 0.70 | rs9832134 | 99836722 | 4.67043 × 10-5 | 0.66 |
| 3q28 | Leslie et al. 2017 [20] | rs76479869 | 189553372 | 0.00247675 | 1.77 | rs17447439 | 189549423 | 5.67543 × 10-5 | 2.26 |
| 3q29 | Mostowska et al. 2018 [18] | rs338217 | 197026927 | 0.0986085 | 0.85 | rs34099552 | 196799735 | 0.0228988 | 1.27 |
| 4p16.2 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs1907989 | 4818925 | 0.751776 | 1.05 | rs10937893 | 4810491 | 0.649752 | 0.94 |
| 4q28.1 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs908822 | 124906257 | 0.657599 | 0.89 | rs76837304 | 124868111 | 0.532867 | 0.86 |
| 5p12 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs10462065 | 44068846 | 0.258344 | 1.18 | rs139738798 | 44183419 | 0.109377 | 1.26 |
| 8p11.23 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs13317 | 38269514 | 0.774445 | 0.97 | rs75168396 | 38014429 | 0.3038 | 1.11 |
| 8q21 | Ludwig et al. 2012 [12] | rs12543318 | 88868340 | 0.00118317 | 0.73 | - | - | - | - |
| 8q22.1 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs957448 | 95541302 | 0.560023 | 0.94 | rs4442106 | 95609488 | 0.0626976 | 0.83 |
| 8q24 | Birnbaum et al. 2009 [8] | rs987525 | 129946154 | 8.73 × 10-11 | 1.89 | - | - | - | - |
| 9q22.2 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs10908902 | 92224825 | 0.0178356 | 1.31 | rs2031970 | 92204172 | 0.00252225 | 1.41 |
| 9q22.32 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs10512248 | 98259703 | 0.0938744 | 0.84 | rs28591501 | 98278644 | 0.0696448 | 0.82 |
| 9q21.33 | Moreno et al. 2009 [4] | rs3758249 | 100614140 | 0.00519618 | 1.32 | rs7033765 | 100591705 | 0.00127545 | 1.38 |
| 10q25 | Mangold et al. 2010 [10] | rs7078160 | 118827560 | 0.00019291 | 1.60 | rs5788208 | 118836076 | 0.000106433 | 1.63 |
| 12q13.13 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs3741442 | 53346750 | 0.105465 | 0.31 | -4 | -4 | -4 | -4 |
| 12q13.2 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs705704 | 56435412 | 0.0418832 | 1.22 | rs773107 | 56369506 | 0.0210978 | 1.26 |
| 12q21.1 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs2304269 | 72080272 | 0.483316 | 0.86 | rs11178895 | 72089411 | 0.321804 | 0.84 |
| 13q31.1 | Ludwig et al. 2012 [12] | rs8001641 | 80692811 | 0.00268945 | 1.34 | rs11841646 | 80679302 | 0.00135074 | 1.37 |
| 14q22.1 | Ludwig et al. 2017 [19] | rs4901118 | 51856109 | 0.367607 | 1.10 | rs60454187 | 51856566 | 0.279705 | 0.9 |
| 14q22.1 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs7148069 | 51839645 | 0.731853 | 1.03 | - | - | - | - |
| 14q32.13 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs1243572 | 95379499 | 0.343413 | 1.12 | rs1243561 | 95369886 | 0.201146 | 1.16 |
| 15q13 | Ludwig et al. 2016 [15] | rs1258763 | 33050423 | 0.0521438 | 1.19 | rs13329310 | 33052553 | 0.0499003 | 0.83 |
| 15q22.2 | Ludwig et al. 2012 [12] | rs1873147 | 63312632 | 0.469881 | 1.08 | rs12902152 | 63313968 | 0.167601 | 1.19 |
| 15q24 | Ludwig et al. 2017 [19] | rs28689146 | 75005575 | 0.442303 | 1.08 | - | - | - | - |
| 16p13.3 | Sun et al. 2015 [14] | rs8049367 | 3980445 | 0.159099 | 1.13 | rs11076792 | 3968567 | 0.00316807 | 1.33 |
| 17q13.1 | Beaty et al. 2010 [11] | rs9891446 | 8935416 | 0.186388 | 1.14 | - | - | - | - |
| 17q21.32 | Yu et al. 2017 [17] | rs1838105 | 45008935 | 0.00231174 | 0.73 | rs197907 | 44982081 | 0.000282387 | 1.45 |
| 17q22 | Mangold et al. 2010 [10] | rs227727 | 54776955 | 0.180057 | 1.14 | - | - | - | - |
| 17q23.2 | Leslie et al. 2016 [16] | rs1588366 | 61076428 | 0.00901131 | 0.75 | rs72843145 | 61052949 | 0.0057287 | 0.72 |
| 19p13.3 | Ludwig et al. 2017 [19] | rs3746101 | 2050823 | 0.929281 | 0.95 | - | - | - | - |
| 19q12 | Leslie et al. 2016 [16] | rs73039426 | 33520961 | 0.26959 | 1.20 | - | - | - | - |
| 20q12 | Beaty et al. 2010 [11] | rs13041247 | 39269074 | 0.0101081 | 0.77 | rs34753522 | 39278391 | 0.00037345 | 0.69 |
| Chromosome | p-Value 1 | |
|---|---|---|
| SH3PXD2A | 10 | 2.3729 × 10−8 |
| ANO4 | 12 | 1.4588 × 10−7 |
| CMSS1 | 3 | 2.9078 × 10−6 |
| FILIP1L | 3 | 7.1274 × 10−6 |
| CLEC3A | 16 | 1.0871 × 10−5 |
| PAX72 | 1 | 1.9157 × 10−5 |
| CCDC140 | 2 | 4.4909 × 10−5 |
| ESR1 | 6 | 7.1554 × 10−5 |
| IFITM3 | 11 | 8.5273 × 10−5 |
| PANX1 | 11 | 8.7342 × 10−5 |
| BLMH | 17 | 9.5824 × 10−5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Rooij, I.A.; Ludwig, K.U.; Welzenbach, J.; Ishorst, N.; Thonissen, M.; Galesloot, T.E.; Ongkosuwito, E.; Bergé, S.J.; Aldhorae, K.; Rojas-Martinez, A.; et al. Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate: Genome-Wide Association Study in Europeans Identifies a Suggestive Risk Locus at 16p12.1 and Supports SH3PXD2A as a Clefting Susceptibility Gene. Genes 2019, 10, 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121023
van Rooij IA, Ludwig KU, Welzenbach J, Ishorst N, Thonissen M, Galesloot TE, Ongkosuwito E, Bergé SJ, Aldhorae K, Rojas-Martinez A, et al. Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate: Genome-Wide Association Study in Europeans Identifies a Suggestive Risk Locus at 16p12.1 and Supports SH3PXD2A as a Clefting Susceptibility Gene. Genes. 2019; 10(12):1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121023
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Rooij, Iris ALM, Kerstin U Ludwig, Julia Welzenbach, Nina Ishorst, Michelle Thonissen, Tessel E Galesloot, Edwin Ongkosuwito, Stefaan J Bergé, Khalid Aldhorae, Augusto Rojas-Martinez, and et al. 2019. "Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate: Genome-Wide Association Study in Europeans Identifies a Suggestive Risk Locus at 16p12.1 and Supports SH3PXD2A as a Clefting Susceptibility Gene" Genes 10, no. 12: 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121023
APA Stylevan Rooij, I. A., Ludwig, K. U., Welzenbach, J., Ishorst, N., Thonissen, M., Galesloot, T. E., Ongkosuwito, E., Bergé, S. J., Aldhorae, K., Rojas-Martinez, A., Kiemeney, L. A., Vermeesch, J. R., Brunner, H., Roeleveld, N., Devriendt, K., Dormaar, T., Hens, G., Knapp, M., Carels, C., & Mangold, E. (2019). Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate: Genome-Wide Association Study in Europeans Identifies a Suggestive Risk Locus at 16p12.1 and Supports SH3PXD2A as a Clefting Susceptibility Gene. Genes, 10(12), 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121023





