Bioinformatics for Next Generation Sequencing Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. High Throughput Sequencing Technologies
2.1. Roche 454 GenomeSequencer
2.2. Illumina Genome Analyzer
2.3. ABI's SOLiD
2.4. Single Molecule Sequencing
| Roche 454 | Illumina Genome Analyzer | ABI SOLiD | Helicos Heliscope | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequencing method | Pyrosequencing | Reversible dye terminators | Sequencing by ligation | Single Molecule Sequencing |
| Read lengths | 400 bases | 100 bases | 50 bases | 35 bases |
| Sequencing run time | 10 h | 10 days | 11-12 days | 30 days |
| Total bases per run | 500 Mb | 20 Gb | 100 Gb | 35 Gb |
| Error Rate | 0.1% | 1.5% | 4% | 2-7% |
2.5. Paired-end and mate-pair sequencing
3. Methods for alignment, assembly and polymorphism detection
3.1. Alignment
| Program | Author(s) | Website | Platform | Aligned Gbp per CPU day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maq [24] | Li H | http://maq.sourceforge.net/ | Illumina, SOLiD (partial) | ~ 0.2 |
| Bowtie [25] | Langmead B Et, al. | http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/index.shtml | Illumina | ~ 7 |
| SSAHA2 [26] | Ning Z Et, al. | http://www.sanger.ac.uk/resources/software/ssaha2/ | Illumina, SOLiD, 454 | ~ 0.5 |
| BWA [27] | Li H and Durbin R | http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/bwa.shtml | Illumina, SOLiD, 454 | ~ 7 |
| SOAP2 [28] | Li R Et, al. | http://www.sanger.ac.uk/resources/software/ssaha2/ | Illumina | ~ 7 |
3.2. De novo Assembly
3.3. SNP / indel detection
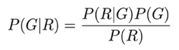
3.4. Alignment / Assembly Viewers
4. Methods for the detection of Structural Variants
| Program | Author(s) | Website | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| EagleView | Huang W and Marth G | http://bioinformatics.bc.edu/marthlab/EagleView | Binary version for Windows, Mac OS X and Linux |
| MapView | Bao H Et, al. | http://202.116.74.148/mapview/l | Binary version for Windows and Linux |
| MaqView | Li H Et, al. | http://maq.sourceforge.net/maqview.shtml | Source Code (C, Java) and Binary version for Linux and Mac OS X |
| Tablet | Milne I Et, al. | http://bioinf.scri.ac.uk/tablet/ | Binary version for Windows, Mac OS X and Linux |
| IGV | Broad Institute | http://www.broadinstitute.org/igv | Binary version for Windows, Mac OS X and Linux |
4.1. PEM-based Methods

4.2. DOC-based Methods
| Program | Author(s) | Website | Detectable Events |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEMer | Korbel J Et, al. | http://sv.gersteinlab.org/pemer/ | basic deletion, basic insertion, basic inversion, linking, linked insertion |
| VariationHunter | Hormozdiari F Et, al. | http://compbio.cs.sfu.ca/strvar.htm | basic deletion, basic insertion, basic inversion, everted duplication |
| MoDIL | Lee S Et, al. | http://compbio.cs.toronto.edu/modil/ | basic deletion, basic insertion |
| BreakDancer | Chen K Et, al. | The software package is available as supplementary information at Nature Methods Online | basic deletion, basic insertion, basic inversion, hanging insertion |
5. Conclusions
References and Notes
- Mitra, R.D.; Church , G.M. In situ localized amplification and contact replication of many individual DNA molecules . Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagalakshmi, U.; Wang, Z.; Waern, K.; Shou, C.; Raha, D.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. The transcriptional landscape of the yeast genome defined by RNA sequencing. Science 2008, 320, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, P.J. ChIP-seq: advantages and challenges of a maturing technology . Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, D.Y.; Getz, G; Jaffe, D.B.; O’Kelly, M.J.T.; Zhao, X; Carter, S.L.; Russ, C.; Nusbaum, C.; Meyerson, M.; Lander, E.S. High-resolution mapping of copy-number alterations with massively parallel sequencing . Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, C.; Kidd, J.M.; Marques-Bonet, T.; Aksay, G.; Antonacci, F.; Hormozdiari, F.; Kitzman, J.O.; Baker, C.; Malig, M.; Mutlu, O.; et al. Personalized copy number and segmental duplication maps using next-generation sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, P.J.; Stephens, P.J.; Pleasance, E.D.; O’Meara, S.; Li, H.; Santarius, T.; Stebbings, L.A.; Leroy, C.; Edkins, S.; et al. Identification of somatically acquired rearrangements in cancer using genome-wide massively parallel paired-end sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyren, P.; Lundin, A. Enzymatic method for continuous monitoring of inorganic pyrophosphate synthesis. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 151, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, E.D. A new method of sequencing DNA. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 174, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 454 Home Page . Available online: http://www.454.com/indecx.asp (accessed on 27 August 2010).
- Fedurco, M.; Romieu, A.; Williams, S.; Lawrence, I.; Turcatti, G. BTA, a novel reagent for DNA attachment on glass and efficient generation of solid-phase amplified DNA colonies . Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcatti, G.; Romieu, A.; Fedurco, M.; Tairi, A.P. A new class of cleavable fluorescent nucleotides: synthesis and optimization as reversible terminators for DNA sequencing by synthesis . Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adessi, C.; Matton, G.; Ayala, G.; Turcatti, G.; Mermod, J.J.; Mayer, P.; Kawashima, E. Solid phase DNA amplification: characterisation of primer attachment and amplification mechanisms . Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solexa Home Page . Available online: http://www.solexa.com/ (accessed on 27 August 2010).
- Shendure, J.; Porreca, G.J.; Reppas, N.B.; Lin, X.; McCutcheon, J.P.; Rosenbaum, A.M.; Wang, M.D.; Zhang, K.; Mitra, R.D.; Church, G.M. Accurate multiplex polony sequencing of an evolved bacterial genome. Science 2005, 309, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKernan, K.; Blanchard, A.; Kotler, L.; Costa, G. Reagents, methods, and libraries for bead-based sequencing . US patent application 20080003571, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Applied Biosystems Home Page . Available online: www3.appliedbiosystems.com/index.htm (accessed on 27 August 2010).
- Jett, J.H.; Keller, R.A.; Martin, J.C.; Marrone, B.L.; Moyzis, R.K.; Ratliff, R.L.; Seitzinger, N.K.; Shera, E.B.; Stewart, C.C. High-speed DNA sequencing: an approach based upon fluorescence detection of single molecules . J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1989, 7, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Helicos Home Page . Available online: http://www.helicosbio.com/ (accessed on 27 August 2010).
- Pushkarev, D.; Neff, N.F.; Quake, S.R. Single-molecule sequencing of an individual human genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzker, M.L. Sequencing technologies – the next generation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, W.J. BLAT--the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 2002, 4, 656–664. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ruan, J.; Durbin, R. Mapping short DNA sequencing reads and calling variants using mapping quality scores. Genome Res. 2008, 11, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome . Genome Biol. 2009, 3, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Cox, A.J.; Mullikin, J.C. SSAHA: a fast search method for large DNA databases. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1725–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 5, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Lam, T.; Yiu, S.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP2: an improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 2009, 15, 1966–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 16, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Homer, N. A survey of sequence alignment algorithms for next-generation sequencing . Brief. Bioinform. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, J.T.; Wong, K.; Jackman, S.D.; Schein, J.E.; Jones, S.J.M.; Birol, I. ABySS: a parallel assembler for short read sequence data. Genome Res. 2009, 6, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.; MacCallum, I.; Kleber, M.; Shlyakhter, I.A.; Belmonte, M.K.; Lander, E.S.; Nusbaum, C.; Jaffe, D.B. ALLPATHS: de novo assembly of whole-genome shotgun microreads. Genome Res. 2008, 5, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, D.; François, P.; Farinelli, L.; Osteras, M.; Schrenzel, J. De novo bacterial genome sequencing: millions of very short reads assembled on a desktop computer. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Birney, E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome. Res. 2008, 5, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP: short oligonucleotide alignment program. Bioinformatics 2008, 5, 713–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevzner, P.A.; Borodovsky, M.Y.; Mironov, A.A. Linguistics of nucleotide sequences. II: Stationary words in genetic texts and the zonal structure of DNA. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1989, 6, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idury, R.M.; Waterman, M.S. A new algorithm for DNA sequence assembly. J. Comput. Biol. 1995, 2, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marth, G.T.; Korf, I.; Yandell, M.D.; Yeh, R.T.; Gu, Z.; Zakeri, H.; Stitziel, N.O.; Hillier, L.; Kwok, P.Y.; Gish, W.R. A general approach to single-nucleotide polymorphism discovery . Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhis, N.; Jones, S.J.M. High quality SNP calling using Illumina data at shallow coverage. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoberman, R.; Dias, J.; Ge, B.; Harmsen, E.; Mayhew, M.; Verlaan, D.J.; Kwan, T.; Dewar, K.; Blanchette, M.; Pastinen, T. A probabilistic approach for SNP discovery in high-throughput human resequencing data. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhis, N.; Butterfield, Y.S.; Ester, M.; Jones, S.J. Slider--maximum use of probability information for alignment of short sequence reads and SNP detection. Bioinformatics 2009, 1, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Marth, G. EagleView: a genome assembly viewer for next-generation sequencing technologies. Genome Res. 2008, 9, 1538–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, R.; Lu, X.; Shi, S. MapView: visualization of short reads alignment on a desktop computer. Bioinformatics 2009, 12, 1554–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, I.; Bayer, M.; Cardle, L.; Shaw, P.; Stephen, G.; Wright, F.; Marshall, D. Tablet—next generation sequence assembly visualization. Bioinformatics 2010, 3, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IGV Software Home Page . Available online: http://www.broadinstitute.org/igv (accessed on 27 August 2010).
- Iafrate, A.J.; Feuk, L.; Rivera, M.N.; Listewnik, M.L.; Donahoe, P.K.; Qi, Y.; Scherer, S.W.; Lee, C. Detection of large-scale variation in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2004, 9, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redon, R.; Ishikawa, S.; Fitch, K.R.; Feuk, L.; Perry, G.H.; Andrews, T.D.; Fiegler, H.; Shapero, M.H.; Carson, A.R.; Wenwei Chen, W.; et al. Global variation in copy number in the human genome. Nature 2006, 7118, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, D.F.; Pinto, D.; Redon, R.; Feuk, L.; Gokcumen, O.; Zhang, Y.; Aerts, J.; Andrews, T.D.; Barnes, C.; Campbell, P.; et al. Origins and functional impact of copy number variation in the human genome. Nature 2010, 7289, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarroll, S.; Kuruvilla, F.; Korn, J.; Cawley, S.; Nemesh, J.; Wysoker, A.; Shapero, M.; de Bakker, P.; Maller, J.; Kirby, A.; et al. Integrated detection and population-genetic analysis of SNPs and copy number variation . Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, G.M.; Zerr, T.; Kidd, J.M.; Eichler, E.E.; Nickerson, D.A. Systematic assessment of copy number variant detection via genome-wide SNP genotyping . Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 1000 Genomes Project Home Page . Available online: http://www.1000genomes.org (accessed on 27 August 2010).
- Dalca, A.V.; Brudno, M. Genome variation discovery with high-throughput sequencing data. Brief. Bioinform. 2010, 11, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olshen, A.B.; Venkatraman, E.S.; Lucito, R.; Wigler, M. Circular binary segmentation for the analysis of array-based DNA copy number data. Biostatistics 2005, 5, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Xuan, Z.; Makarov, V.; Ye, K.; Sebat, J. Sensitive and accurate detection of copy number variants using read depth of coverage. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magi, A.; Benelli, M.; Seungtai Yoon, S.; Torricelli, F. Detecting Common Copy Number Variants in High-Throughput Sequencing Data by using JointSLM algorithm . Nucleic Acids Res. submitted for publication.
- Korbel, J.O.; Abyzov, A.; Mu, X.J.; Carriero, N.; Cayting, P.; Zhang, Z.; Snyder, M.;Gerstein. PEMer: a computational framework with simulation-based error models for inferring genomic structural variants from massive paired-end sequencing data . Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hormozdiari, F.; Alkan, C.; Eichler, E.E.; Sahinalp, S.C. Combinatorial algorithms for structural variation detection in high-throughput sequenced genomes. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Hormozdiari, F.; Alkan, C.; Brudno, M. MoDIL: detecting small indels from clone-end sequencing with mixtures of distributions. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Wallis, J.W.; McLellan, M.D.; Larson, D.E.; Kalicki, J.M.; Pohl, C.S.; McGrath, S.D.; Wendl, M.C.; Zhang, Q.; Locke, D.P.; et al. BreakDancer: an algorithm for high-resolution mapping of genomic structural variation. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tablet Home Page . Available online: http://bioinf.scri.ac.uk/tablet/index.shtml (accessed on 27 August 2010).
- Rdxplorer Home Page . Available online: http://rdxplorer.sourceforge.net/ (accessed on 27 August 2010).
- Seqanswer Home Page . Available online: http://seqanswers.com/ (accessed on 27 August 2010).
- Eid, J.; Fehr, A.; Gray, J.; Luong, K.; Lyle, J.; Otto, G.; Peluso, P.; Rank, D.; Baybayan, P.; Bettman, B.; et al. Real-time DNA sequencing from single polymerase molecules. Science 2009, 5910, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aury, J.; Cruaud, C.; Barbe, V.; Rogier, O.; Mangenot, S.; Samson, G.; Poulain, J.; Anthouard, V.; Scarpelli, C.; Artiguenave, F.; et al. High quality draft sequences for prokaryotic genomes using a mix of new sequencing technologies. BMC Genomics 2008, 9, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, J.A.; Baltrus, D.A.; Nishimura, M.T.; Jeck, W.R.; Jones, C.D.; Dangl, J.L. De novo assembly using low-coverage short read sequence data from the rice pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. oryzae. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Share and Cite
Magi, A.; Benelli, M.; Gozzini, A.; Girolami, F.; Torricelli, F.; Brandi, M.L. Bioinformatics for Next Generation Sequencing Data. Genes 2010, 1, 294-307. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes1020294
Magi A, Benelli M, Gozzini A, Girolami F, Torricelli F, Brandi ML. Bioinformatics for Next Generation Sequencing Data. Genes. 2010; 1(2):294-307. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes1020294
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagi, Alberto, Matteo Benelli, Alessia Gozzini, Francesca Girolami, Francesca Torricelli, and Maria Luisa Brandi. 2010. "Bioinformatics for Next Generation Sequencing Data" Genes 1, no. 2: 294-307. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes1020294
APA StyleMagi, A., Benelli, M., Gozzini, A., Girolami, F., Torricelli, F., & Brandi, M. L. (2010). Bioinformatics for Next Generation Sequencing Data. Genes, 1(2), 294-307. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes1020294






