TRPV4 Inhibition and CRISPR-Cas9 Knockout Reduce Inflammation Induced by Hyperphysiological Stretching in Human Annulus Fibrosus Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human AF Cell Isolation and Culture
2.2. Generation of CRISPR-Cas9 TRPV4 Knockout (KO) Cells
2.3. Cyclic Stretching
2.4. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
2.5. ELISA of Conditioned Medium
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Immunocytochemistry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
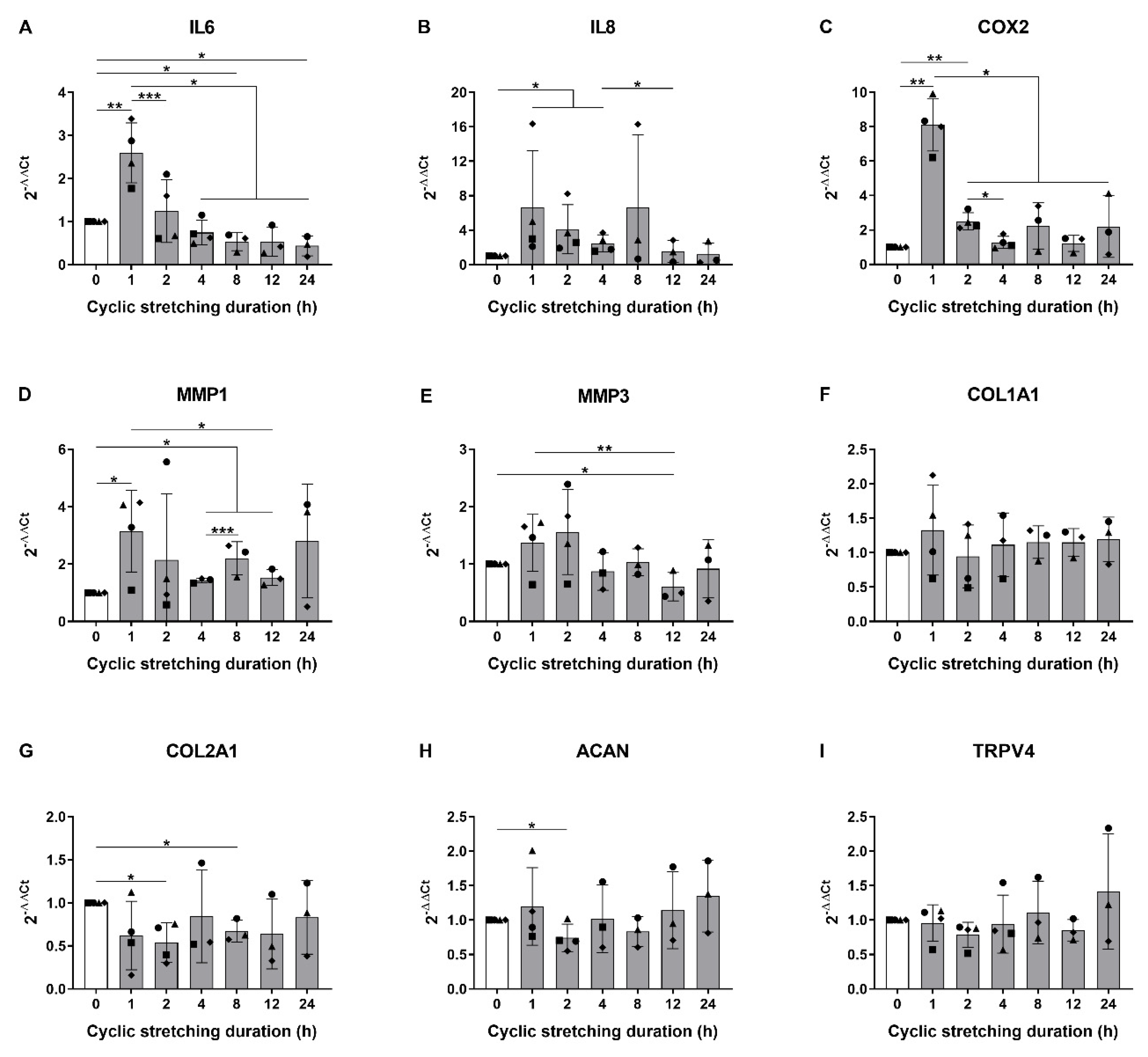
3.1. Hyperphysiological Cyclic Stretching Induces Gene Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators in Human AF Cells
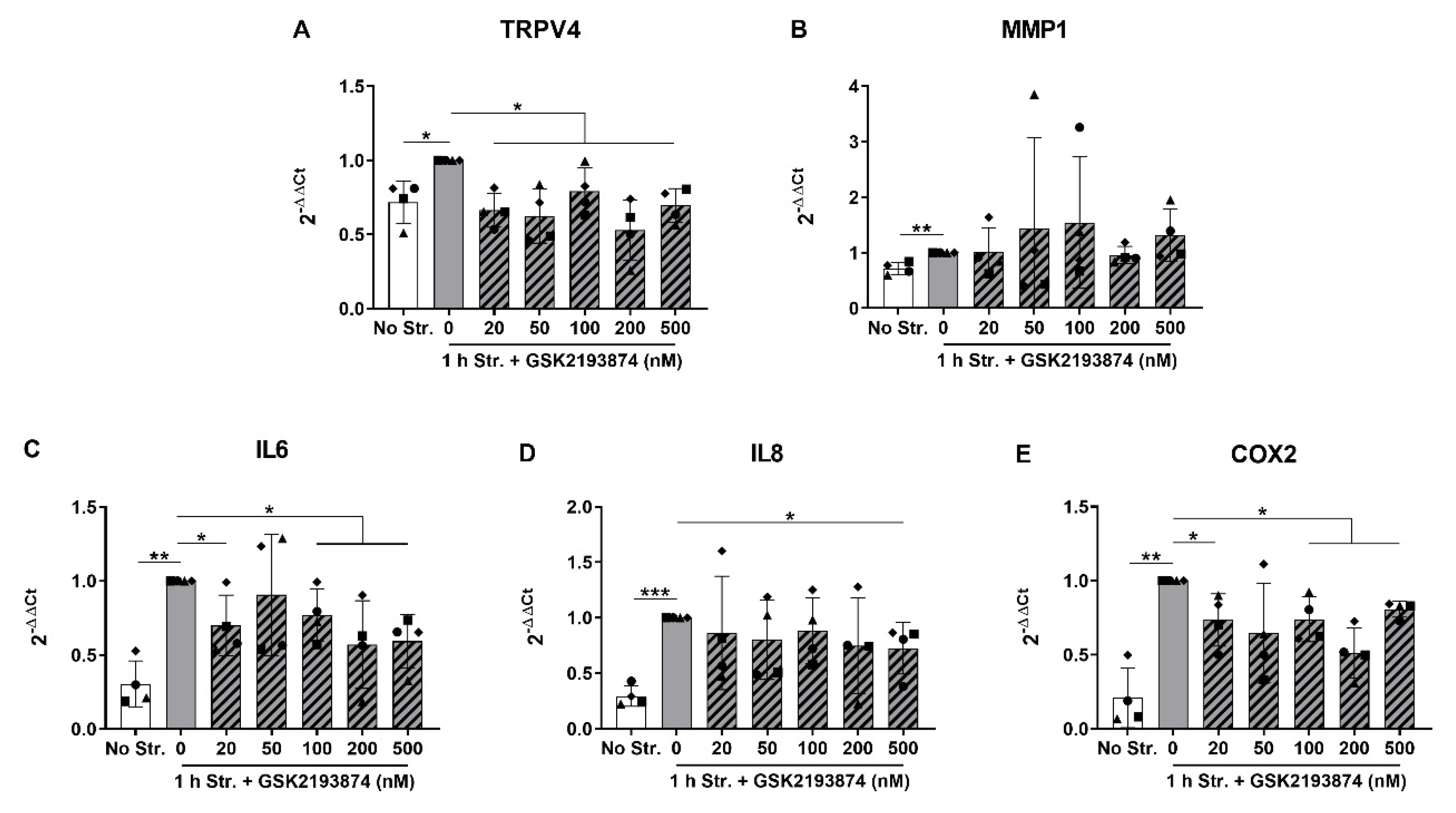
3.2. Pharmacological Inhibition of TRPV4 Reduces Stretch-Induced Gene Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators
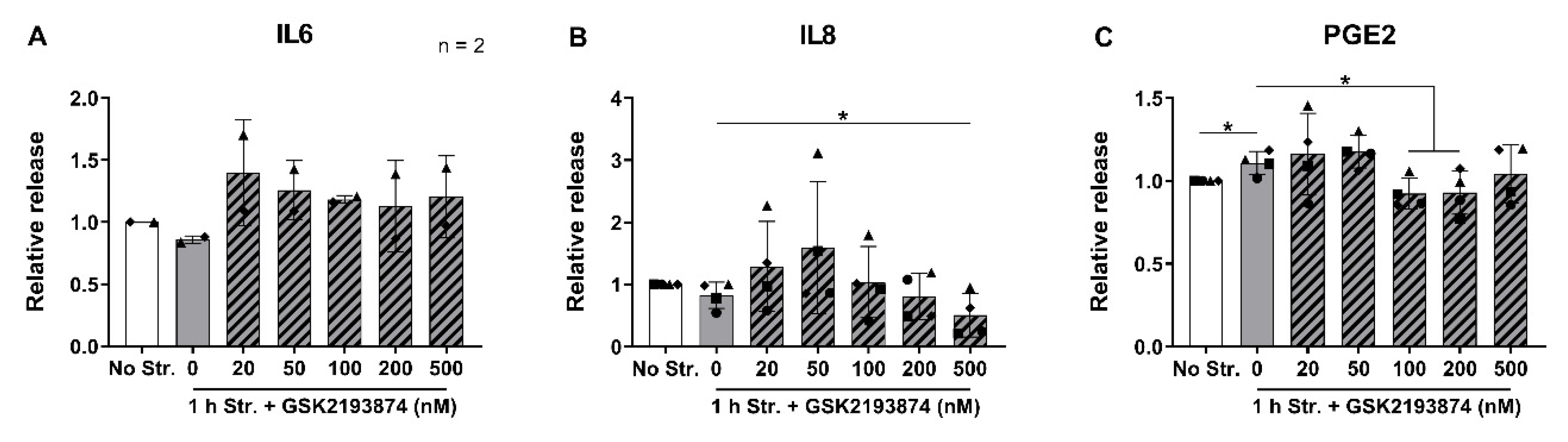
3.3. Pharmacological Inhibition of TRPV4 Downregulates the Release of IL8 and PGE2
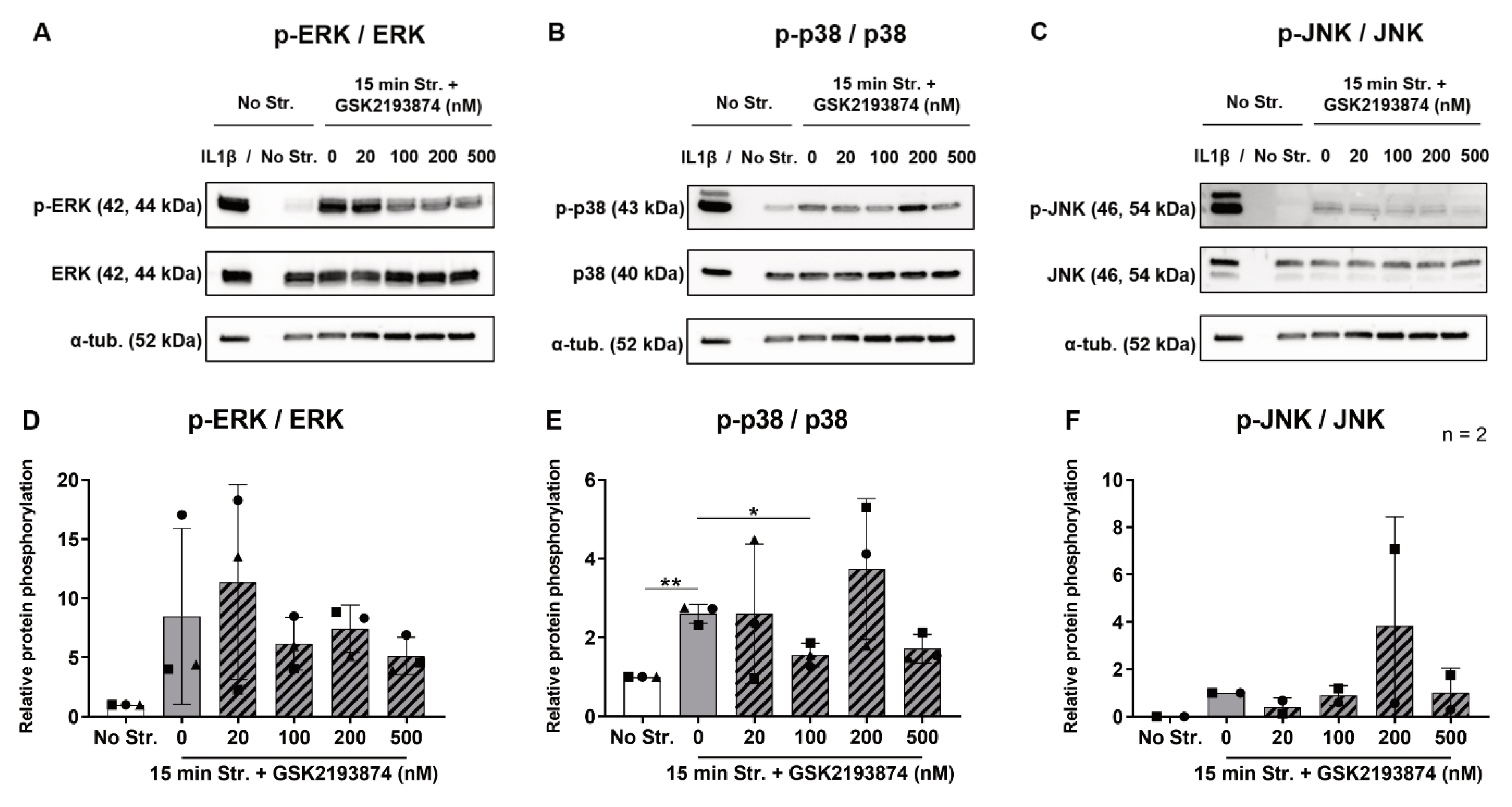
3.4. Pharmacological Inhibition of TRPV4 Reduces Stretch-Induced p38 Phosphorylation
3.5. CRISPR-Cas9 Knocks Out TRPV4 in Human Primary AF Cells
3.6. CRISPR-Cas9 KO of TRPV4 Prevents Stretch-Induced Gene Expression of IL8
3.7. CRISPR-Cas9 KO of TRPV4 Downregulates the Release of IL6 and IL8
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ingber, D.E. Mechanobiology and diseases of mechanotransduction. Ann. Med. 2003, 35, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S. Mechanical stress. In The Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 131, pp. 367–396. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.E.; Hung, C.T.; Sandell, L.J.; Silva, M.J. Musculoskeletal mechanobiology: A new era for MechanoMedicine. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearing, B.V.; Hernandez, P.A.; Setton, L.A.; Chahine, N. Mechanotransduction and cell biomechanics of the intervertebral disc. JOR Spine 2018, 1, e1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.C.W.; Ferguson, S.J.; Gantenbein-Ritter, B. The effects of dynamic loading on the intervertebral disc. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 1796–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.A.; Roughley, P.J. What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine 2006, 31, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergroesen, P.-P.; Kingma, I.; Emanuel, K.; Hoogendoorn, R.; Welting, T.; Van Royen, B.J.; Van Dieën, J.H.; Smit, T.H. Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: A vicious circle. Osteoarthr. Cart. 2015, 23, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhitpanichkul, M.; Torre, O.M.; Gruen, J.; Walter, B.A.; Hecht, A.C.; Iatridis, J.C. Do mechanical strain and TNF-alpha interact to amplify pro-inflammatory cytokine production in human annulus fibrosus cells? J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisherman, R.; Coelho, P.; Phillibert, D.; Wang, D.; Dong, Q.; Vo, N.; Kang, J.; Sowa, J. NF-kappaB signaling pathway in controlling intervertebral disk cell response to inflammatory and mechanical stressors. Phys. Ther. 2016, 96, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagué, F.; Mannion, A.F.; Pellise, F.; Cedraschi, C. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet 2012, 379, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airaksinen, O.; Brox, J.I.; Cedraschi, C.; Hildebrandt, J.; Klaber-Moffett, J.; Kovacs, F.; Mannion, A.F.; Reis, S.; Staal, J.B.; Ursin, H.; et al. Chapter 4. European guidelines for the management of chronic nonspecific low back pain. Eur. Spine J. 2006, 15, S192–S300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, O.M.; Mroz, V.; Bartelstein, M.K.; Huang, A.H.; Iatridis, J.C. Annulus fibrosus cell phenotypes in homeostasis and injury: Implications for regenerative strategies. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1442, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shengjie, W.; Li, J.; Tian, J.; Yu, Z.; Gao, K.; Shao, J.; Li, A.; Xing, S.; Dong, Y.; Li, Z. High amplitude and low frequency cyclic mechanical strain promotes degeneration of human nucleus pulposus cells via the NF-κB p65 pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 7206–7216. [Google Scholar]
- Sowa, G.; Coelho, P.; Vo, N.; Bedison, R.; Chiao, A.; Davies, C.; Studer, R.; Kang, J. Determination of annulus fibrosus cell response to tensile strain as a function of duration, magnitude, and frequency. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, H.; Doita, M.; Nishida, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Sumi, M.; Kurosaka, M. Effects of cyclic mechanical stress on the production of inflammatory agents by nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus derived cells in vitro. Spine 2006, 31, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawri, R.; Rosenzweig, D.H.; Krock, E.; A Ouellet, J.; Stone, L.S.; Quinn, T.M.; Haglund, L. High mechanical strain of primary intervertebral disc cells promotes secretion of inflammatory factors associated with disc degeneration and pain. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratsinis, H.; Papadopoulou, A.; Neidlinger-Wilke, C.; Brayda-Bruno, M.; Wilke, H.-J.; Kletsas, D.; Information, P.E.K.F.C. Cyclic tensile stress of human annulus fibrosus cells induces MAPK activation: Involvement in proinflammatory gene expression. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.M.; McAlexander, M.A.; Bíró, T.; Szallasi, A. Transient receptor potential channels as therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupkova, O.; Zvick, J.; Wuertz-Kozak, K. The role of transient receptor potential channels in joint diseases. Eur. Cells Mater. 2017, 34, 180–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNulty, A.L.; Leddy, H.A.; Liedtke, W.B.; Guilak, F. TRPV4 as a therapeutic target for joint diseases. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2015, 388, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Conor, C.J.; Leddy, H.A.; Benefield, H.C.; Liedtke, W.B.; Guilak, F. TRPV4-mediated mechanotransduction regulates the metabolic response of chondrocytes to dynamic loading. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1316–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Conor, C.J.; Ramalingam, S.; Zelenski, N.A.; Benefield, H.C.; Rigo, I.; Little, D.; Wu, C.-L.; Chen, D.; Liedtke, W.; McNulty, A.L.; et al. Cartilage-specific knockout of the mechanosensory ion channel TRPV4 decreases age-related osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29053. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, B.; Purmessur, D.; Moon, A.; Occhiogrosso, J.; Laudier, D.; Hecht, A.; Iatridis, J. Reduced tissue osmolarity increases TRPV4 expression and pro-inflammatory cytokines in intervertebral disc cells. Eur. Cell Mater. 2016, 32, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Obregon, A.; Cambria, E.; Greutert, H.; Wernas, T.; Hitzl, W.; Egli, M.; Sekiguchi, M.; Boos, N.; Hausmann, O.; Ferguson, S.J.; et al. TRPC6 in simulated microgravity of intervertebral disc cells. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 2621–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska, A.; Touli, E.; Hitzl, W.; Greutert, H.; Ferguson, S.J.; Wuertz-Kozak, K.; Hausmann, O. Inflammaging in cervical and lumbar degenerated intervertebral discs: Analysis of proinflammatory cytokine and TRP channel expression. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowska, A.; Hitzl, W.; Karol, A.; Jaszczuk, P.; Cherif, H.; Haglund, L.; Hausmann, O.N.; Wuertz, K. Differential regulation of TRP channel gene and protein expression by intervertebral disc degeneration and back pain. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameda, T.; Zvick, J.; Vuk, M.; Sadowska, A.; Tam, W.K.; Leung, V.Y.-L.; Bölcskei, K.; Helyes, Z.; Applegate, L.A.; Hausmann, O.; et al. Expression and activity of TRPA1 and TRPV1 in the intervertebral disc: Association with inflammation and matrix remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, Y.; Hino, K.; Bono, H.; Ui-Tei, K. CRISPRdirect: Software for designing CRISPR/Cas guide RNA with reduced off-target sites. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1120–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgens, D.W.; Wainberg, M.; Boyle, E.; Ursu, O.; Araya, C.L.; Tsui, C.K.; Haney, M.S.; Hess, G.T.; Han, K.; Jeng, E.; et al. Genome-scale measurement of off-target activity using Cas9 toxicity in high-throughput screens. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjana, N.E.; Shalem, O.; Zhang, F. Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.A.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Palliser, D.; Mizuno, H.; Yu, E.Y.; An, N.S.; Sabatini, D.M.; Chen, I.S.; Hahn, W.C.; Sharp, P.A.; et al. Lentivirus-delivered stable gene silencing by RNAi in primary cells. RNA 2003, 9, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, T.L. Mechanoflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, S36–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupkova, O.; Cambria, E.; Bešše, L.; Besse, A.; Bowles, R.; Wuertz-Kozak, K. The potential of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing for the study and treatment of intervertebral disc pathologies. JOR Spine 2018, 1, e1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpo, D.J.; Lai, W.S.; Blackshear, P.J. Inflammation: Cytokines and RNA-based regulation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2010, 1, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, B.; Li, X.; Barik, S. Translation control: A multifaceted regulator of inflammatory response. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3311–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.S.; Wang, Y.; Najrana, T.; Priolo, L.M.; Rios, M.; Shaw, S.K.; Sanchez-Esteban, J. Mechanotransduction via TRPV4 regulates inflammation and differentiation in fetal mouse distal lung epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsaki, A.; Tanuma, S.I.; Tsukimoto, M. TRPV4 channel-regulated ATP release contributes to gamma-irradiation-induced production of IL-6 and IL-8 in epidermal keratinocytes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Pan, Y.; Guo, S.; Sun, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L. The roles of mechanosensitive ion channels and associated downstream MAPK signaling pathways in PDLC mechanotransduction. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, M.N.; Leddy, H.A.; Votta, B.J.; Kumar, S.; Levy, D.S.; Lipshutz, D.B.; Lee, S.H.; Liedtke, W.; Guilak, F. Functional characterization of TRPV4 as an osmotically sensitive ion channel in porcine articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3028–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.-J.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Z.-Z.; Huai, J.; Teng, Y.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, S.-W. Effect of TRPV4-p38 MAPK pathway on neuropathic pain in rats with chronic compression of the dorsal root ganglion. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6978923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzute, T.; He, F.; Zhang, X.; Pei, M. Impact of Wnt signals on human intervertebral disc cell regeneration. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 3196–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhang, N.; Ginley-Hidinger, M.; Berrett, K.C.; Gertz, J.; Lawrence, B.; Bowles, R.D.; Bowles, R.D. Lentiviral CRISPR epigenome editing of inflammatory receptors as a gene therapy strategy for disc degeneration. Hum. Gene Ther. 2019, 30, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorneloe, K.S.; Cheung, M.; Bao, W.; Alsaid, H.; Lenhard, S.; Jian, M.-Y.; Costell, M.; Maniscalco-Hauk, K.; Krawiec, J.A.; Olzinski, A.; et al. An orally active TRPV4 channel blocker prevents and resolves pulmonary edema induced by heart failure. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 159ra148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Li, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, N.; Qian, C.; Ding, D.; Wang, B.-B.; Chen, L.; Guo, K.-F.; Fu, D.; et al. Blockage of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalick, L.; Erfinanda, L.; Weichelt, U.; Van Der Giet, M.; Liedtke, W.; Kuebler, W.M. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 and serum glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 are critical mediators of lung injury in overventilated mice in vivo. Anesthesiology 2017, 126, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.; Skrdla, P.; Schroyer, R.; Kumar, S.; Fernando, D.; Oughton, A.; Norton, N.; Sprecher, D.L.; Cheriyan, J. Clinical pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of a novel, first-in-class TRPV4 ion channel inhibitor, GSK2798745, in healthy and heart failure subjects. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2019, 19, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setton, L.A.; Chen, J. Cell mechanics and mechanobiology in the intervertebral disc. Spine 2004, 29, 2710–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.T.; Alipui, D.O.; Sison, C.P.; Bloom, O.; Quraishi, S.; Overby, M.C.; Levine, M.; Chahine, N.O. Serum levels of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 vary based on diagnoses in individuals with lumbar intervertebral disc diseases. Arthritis Res. 2016, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.N.; Jacobsen, H.E.; Khan, J.; Filippi, C.G.; Levine, M.; Lehman, R.A.; Riew, K.D.; Lenke, L.G.; Chahine, N. Inflammatory biomarkers of low back pain and disc degeneration: A review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1410, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Bao, J.-P.; Yang, S.; Hong, X.; Liu, L.; Xie, X.-H.; Wu, X.-T. A cohort study comparing the serum levels of pro- or anti-inflammatory cytokines in patients with lumbar radicular pain and healthy subjects. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.D.; Stefanovic-Racic, M.; McIntyre, L.A.; Georgescu, H.I.; Evans, C.H. Toward a biochemical understanding of human intervertebral disc degeneration and herniation. Contributions of nitric oxide, interleukins, prostaglandin E2, and matrix metalloproteinases. Spine 1997, 22, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, H.; Saura, R.; Doita, M.; Kurosaka, M.; Mizuno, K. The role of cyclooxygenase-2 in lumbar disc herniation. Spine 2002, 27, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.D.; Georgescu, H.I.; McIntyre-Larkin, L.; Stefanovic-Racic, M.; Evans, C.H. Herniated cervical intervertebral discs spontaneously produce matrix metalloproteinases, nitric oxide, interleukin-6, and prostaglandin E2. Spine 1995, 20, 2373–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuertz, K.; Vo, N.; Kletsas, D.; Boos, N. Inflammatory and catabolic signalling in intervertebral discs: The roles of NF-kappaB and MAP kinases. Eur. Cell Mater. 2012, 23, 103–119, discussion 119–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henckaerts, E.; Linden, R.M. Adeno-associated virus: A key to the human genome? Future Virol. 2010, 5, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
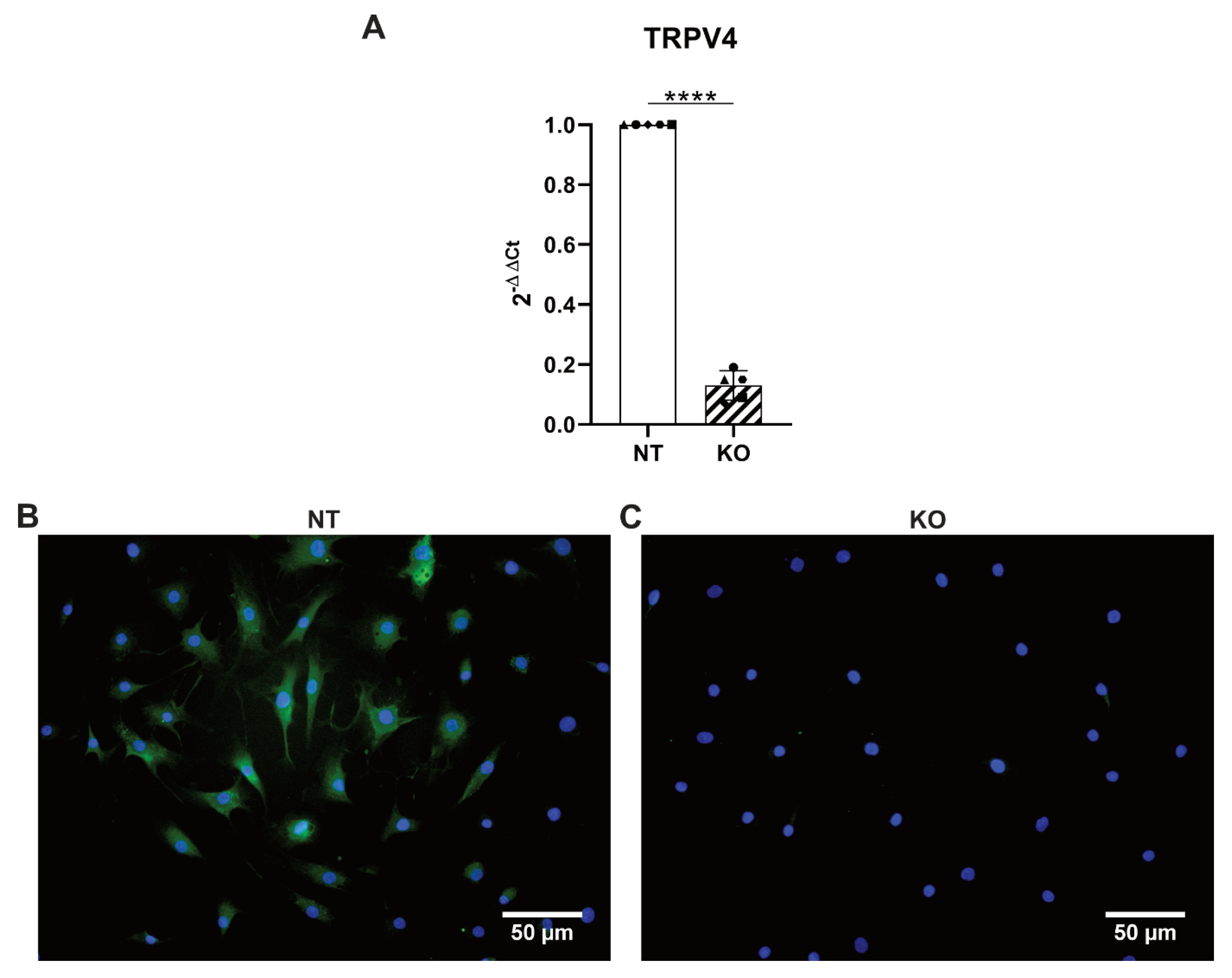
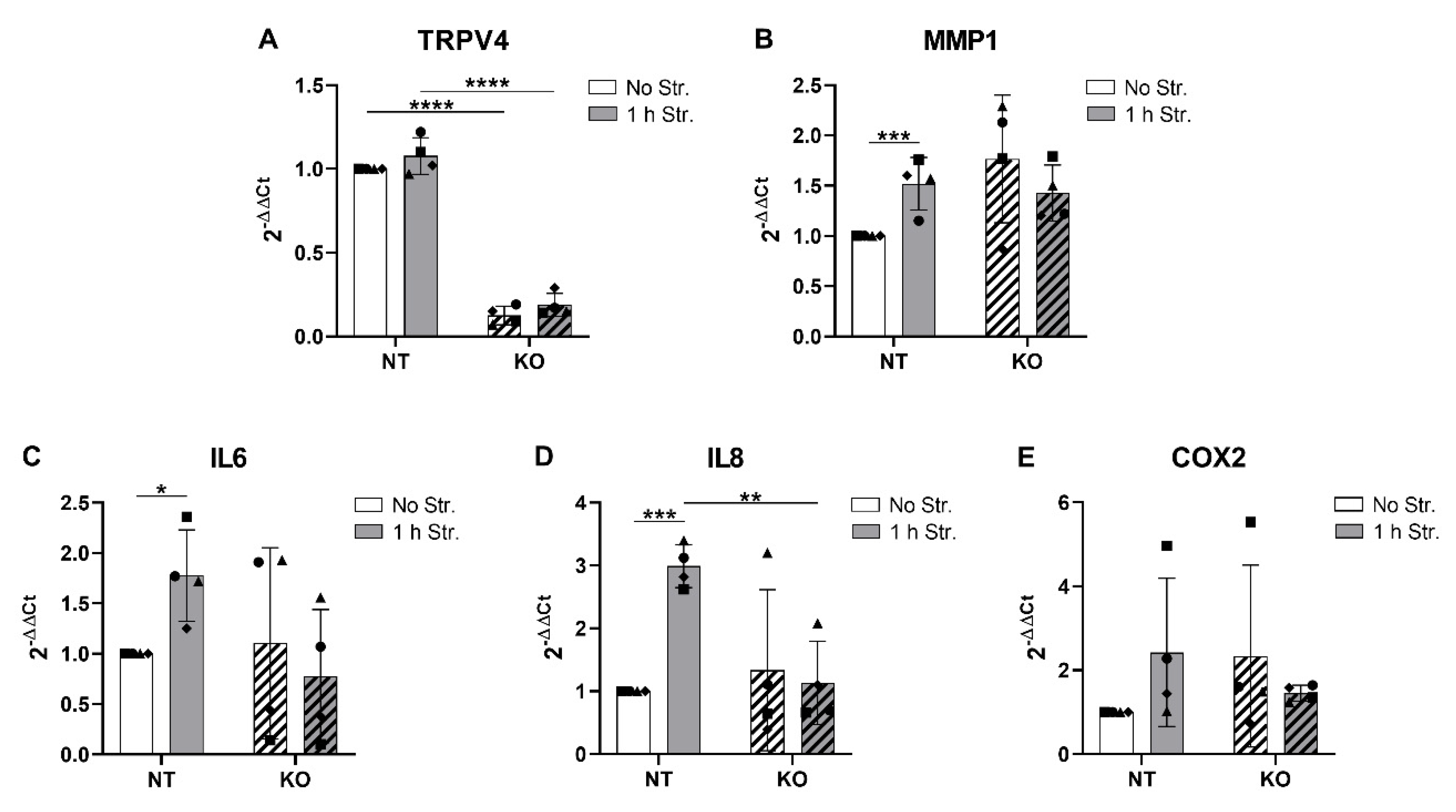
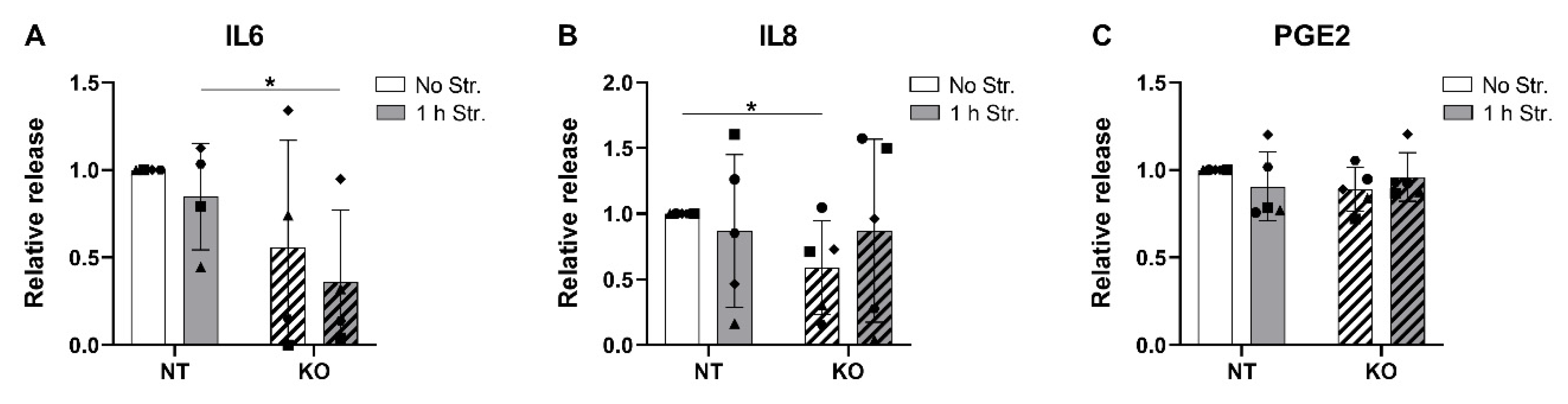
| N° | Age | Sex | Diagnosis | Disc Level | Pfirrmann Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 74 | M | Herniation | L4/5 | 3 |
| 2 | 71 | M | Herniation | L4/5 | 3 |
| 3 | 76 | F | DDD | L5/S1 | 4 |
| 4 | 56 | F | DDD | C6/7 | 3 |
| 5 | 40 | F | Herniation | C5/6 | 2 |
| 6 | 52 | F | Herniation | L4/5 | 3 |
| 7 | 15 | M | DDD | L4/5 | 4 |
| 8 | 75 | F | DDD | L3/4 | 3 |
| 9 | 46 | M | Herniation | L4/5 | 4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cambria, E.; Arlt, M.J.E.; Wandel, S.; Krupkova, O.; Hitzl, W.; Passini, F.S.; Hausmann, O.N.; Snedeker, J.G.; Ferguson, S.J.; Wuertz-Kozak, K. TRPV4 Inhibition and CRISPR-Cas9 Knockout Reduce Inflammation Induced by Hyperphysiological Stretching in Human Annulus Fibrosus Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071736
Cambria E, Arlt MJE, Wandel S, Krupkova O, Hitzl W, Passini FS, Hausmann ON, Snedeker JG, Ferguson SJ, Wuertz-Kozak K. TRPV4 Inhibition and CRISPR-Cas9 Knockout Reduce Inflammation Induced by Hyperphysiological Stretching in Human Annulus Fibrosus Cells. Cells. 2020; 9(7):1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071736
Chicago/Turabian StyleCambria, Elena, Matthias J. E. Arlt, Sandra Wandel, Olga Krupkova, Wolfgang Hitzl, Fabian S. Passini, Oliver N. Hausmann, Jess G. Snedeker, Stephen J. Ferguson, and Karin Wuertz-Kozak. 2020. "TRPV4 Inhibition and CRISPR-Cas9 Knockout Reduce Inflammation Induced by Hyperphysiological Stretching in Human Annulus Fibrosus Cells" Cells 9, no. 7: 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071736
APA StyleCambria, E., Arlt, M. J. E., Wandel, S., Krupkova, O., Hitzl, W., Passini, F. S., Hausmann, O. N., Snedeker, J. G., Ferguson, S. J., & Wuertz-Kozak, K. (2020). TRPV4 Inhibition and CRISPR-Cas9 Knockout Reduce Inflammation Induced by Hyperphysiological Stretching in Human Annulus Fibrosus Cells. Cells, 9(7), 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071736






