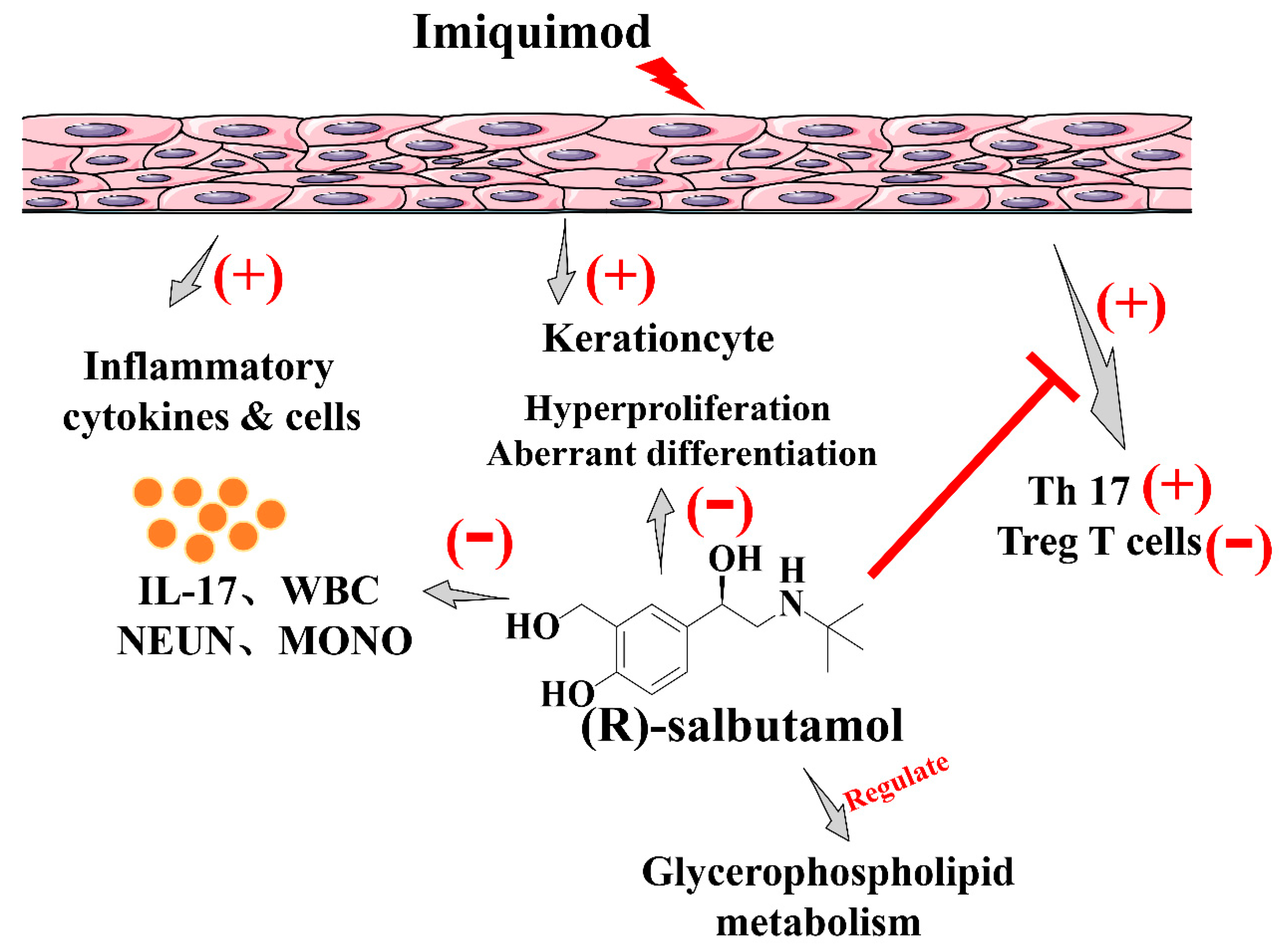
(R)-Salbutamol Improves Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Dermatitis by Regulating the Th17/Tregs Balance and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
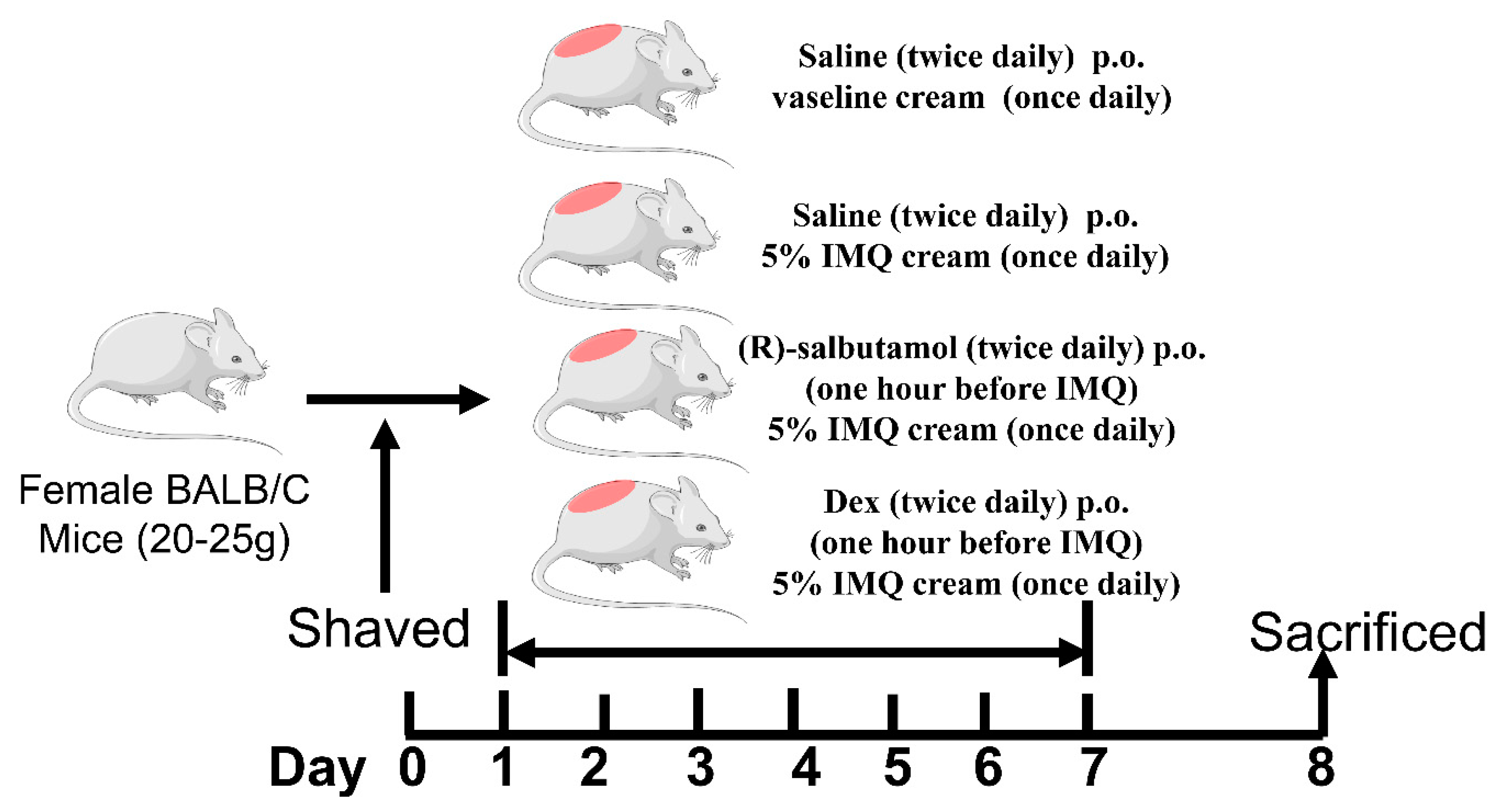
2.2. Mice Treatments
2.3. Evaluating the Severity of Skin Inflammation
2.4. Histopathological Examination
2.5. Hematological Analysis
2.6. IL-17 ELISA
2.7. Intracellular Staining and Flow Cytometry
2.8. Metabolomic Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
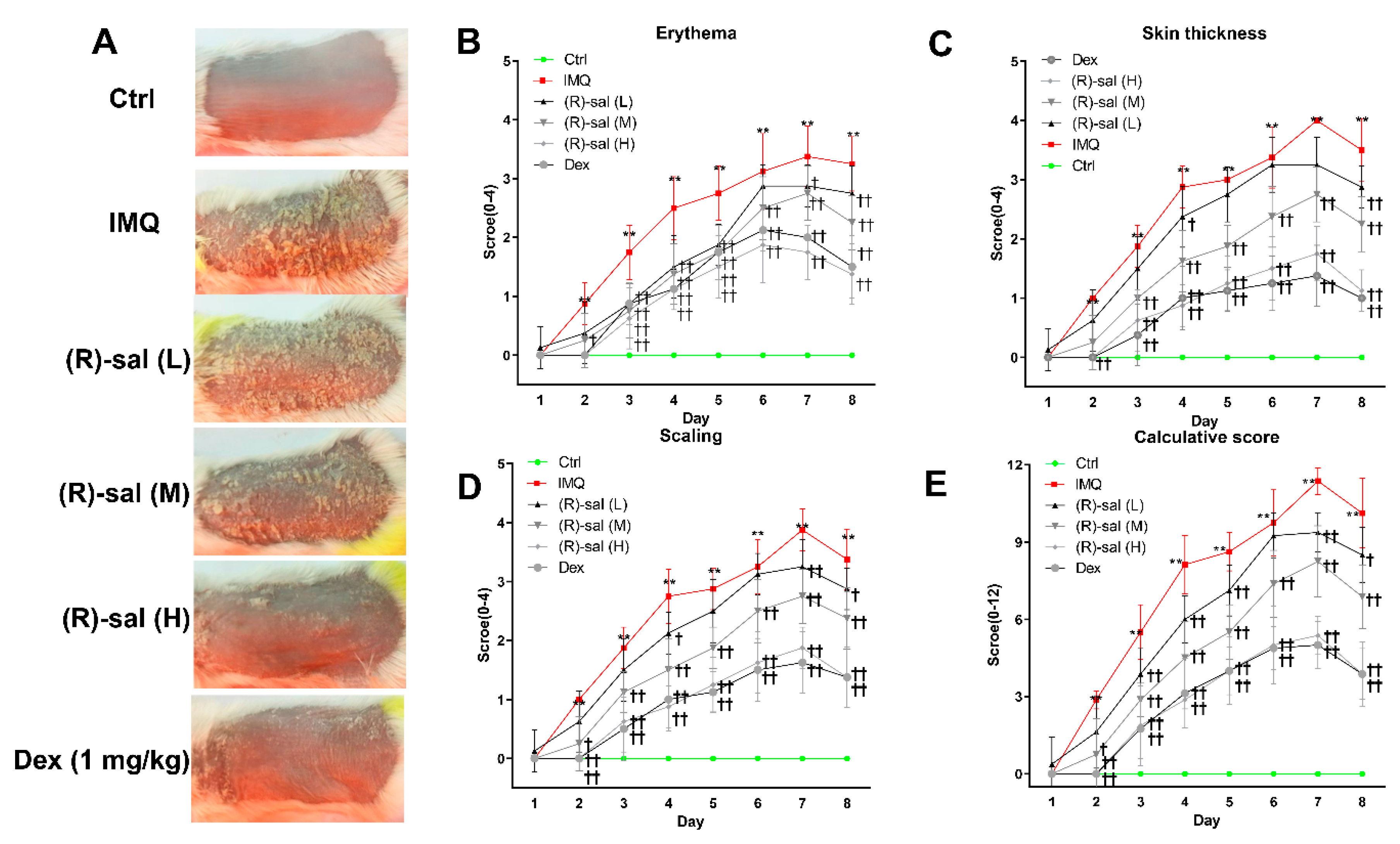
3.1. (R)-Salbutamol Alleviates Psoriatic Dermatiti
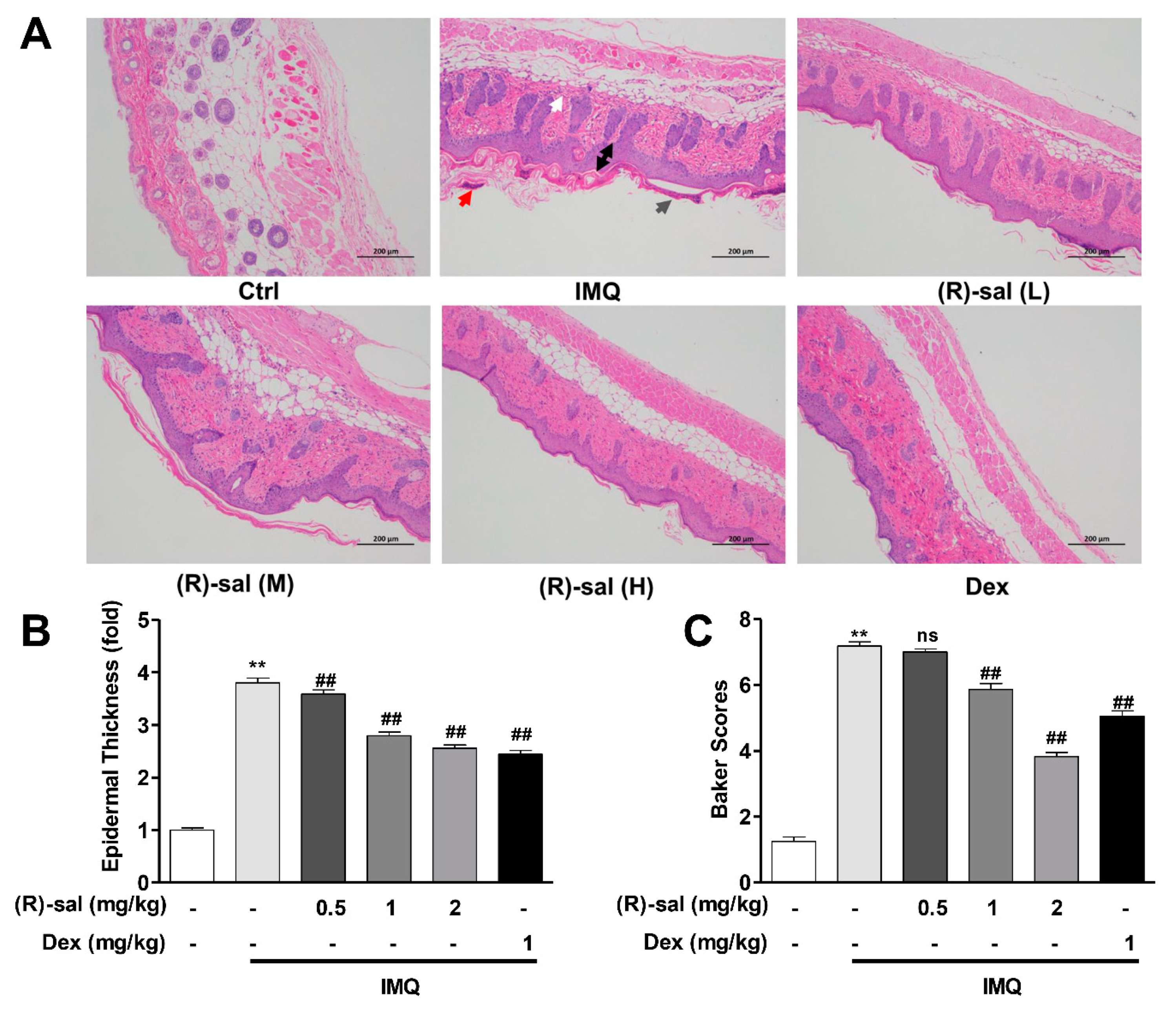
3.2. (R)-Salbutamol Alleviates the Pathology Changes Alterations Caused by IMQ on Mice Skin
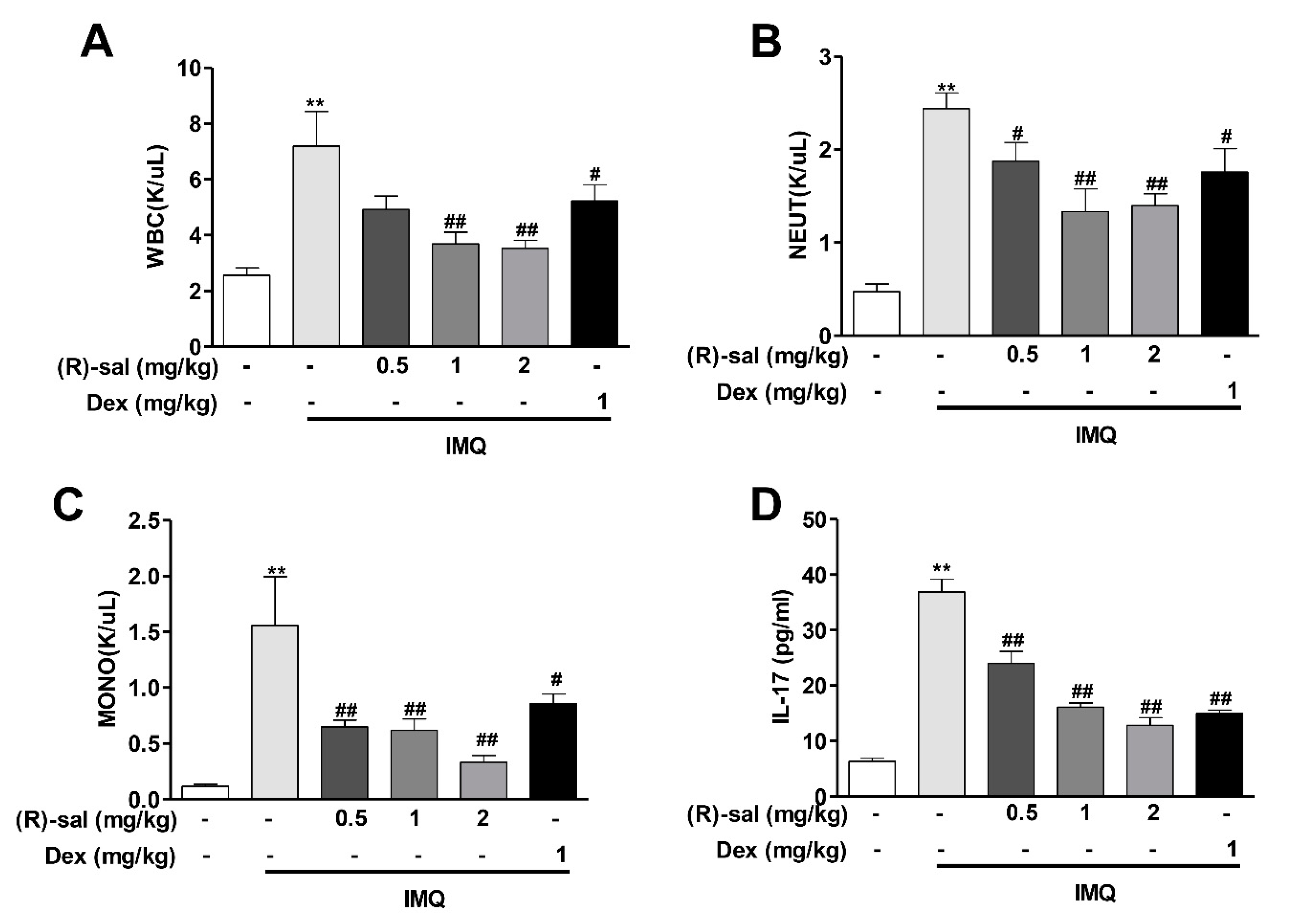
3.3. Effect of (R)-Salbutamol on Haematological Parameters of IMQ-Induced Mouse Psoriasis
3.4. (R)-Salbutamol Reduced IL-17 Secretion in Mice Plasma
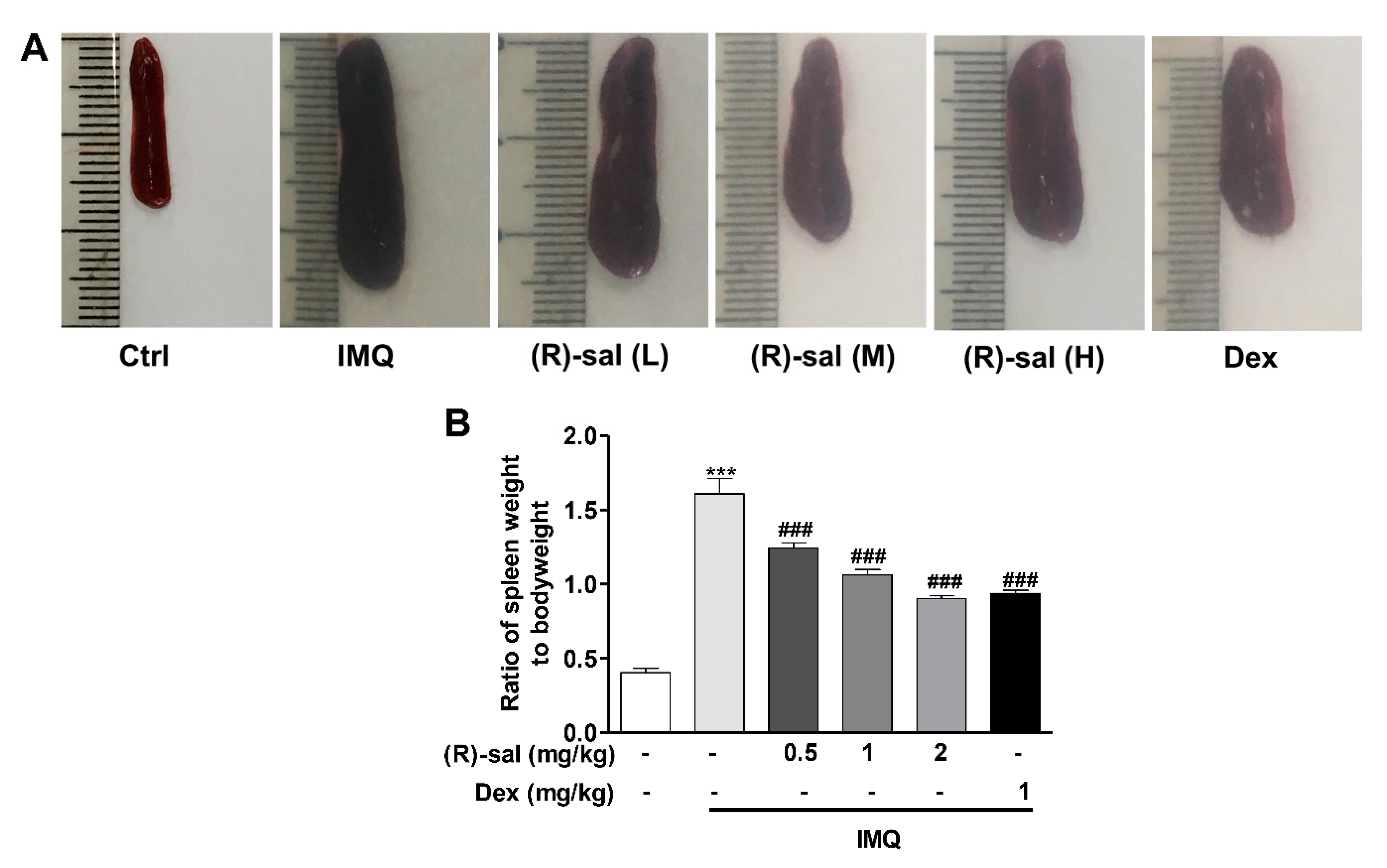
3.5. Effect of (R)-Salbutamol Treatment on the Ratio of Spleen Weight to Body Weight
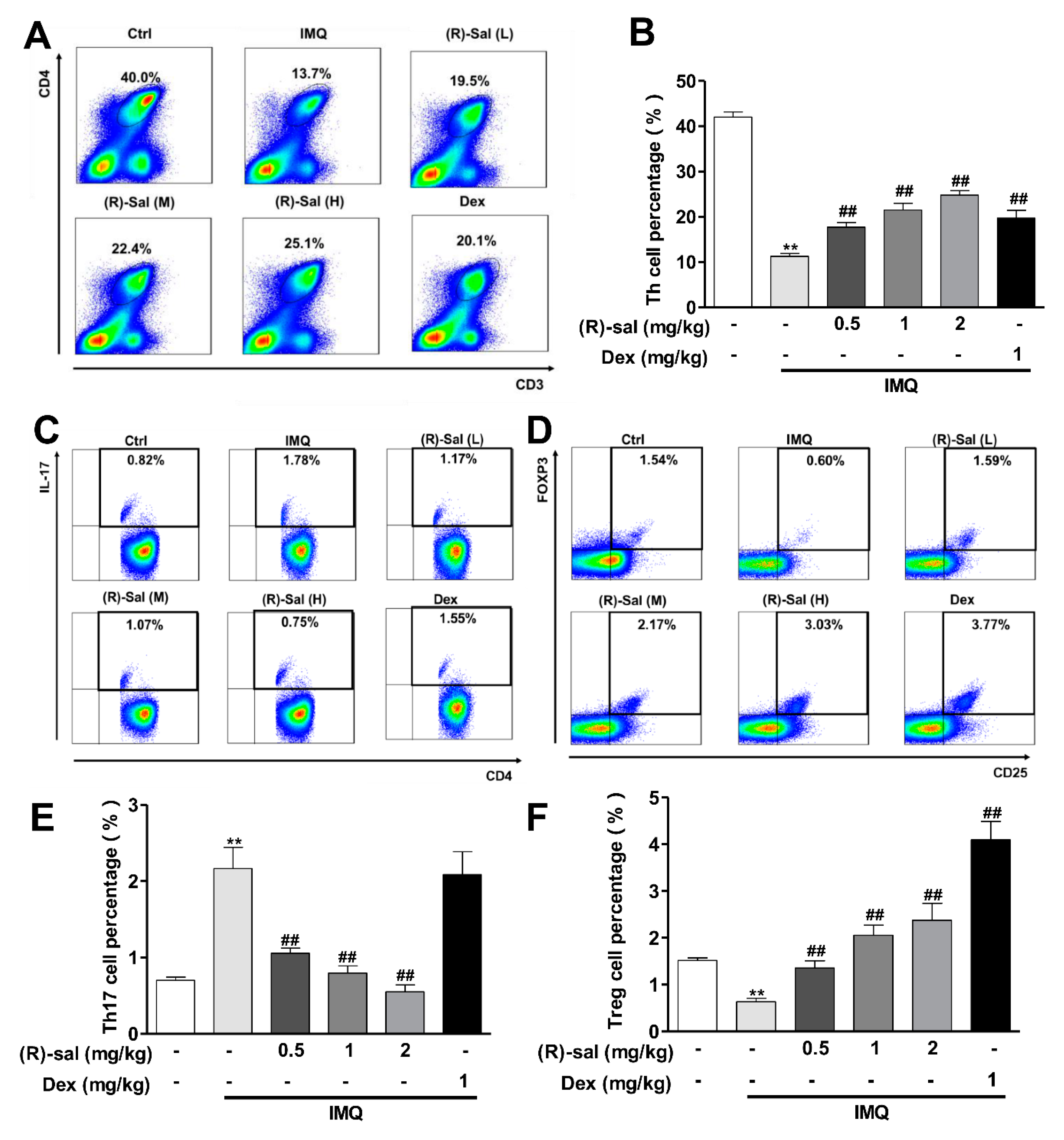
3.6. (R)-Salbutamol Immune-Regulates the Number of CD3+CD4+ T Cells in Mice Treated with IMQ
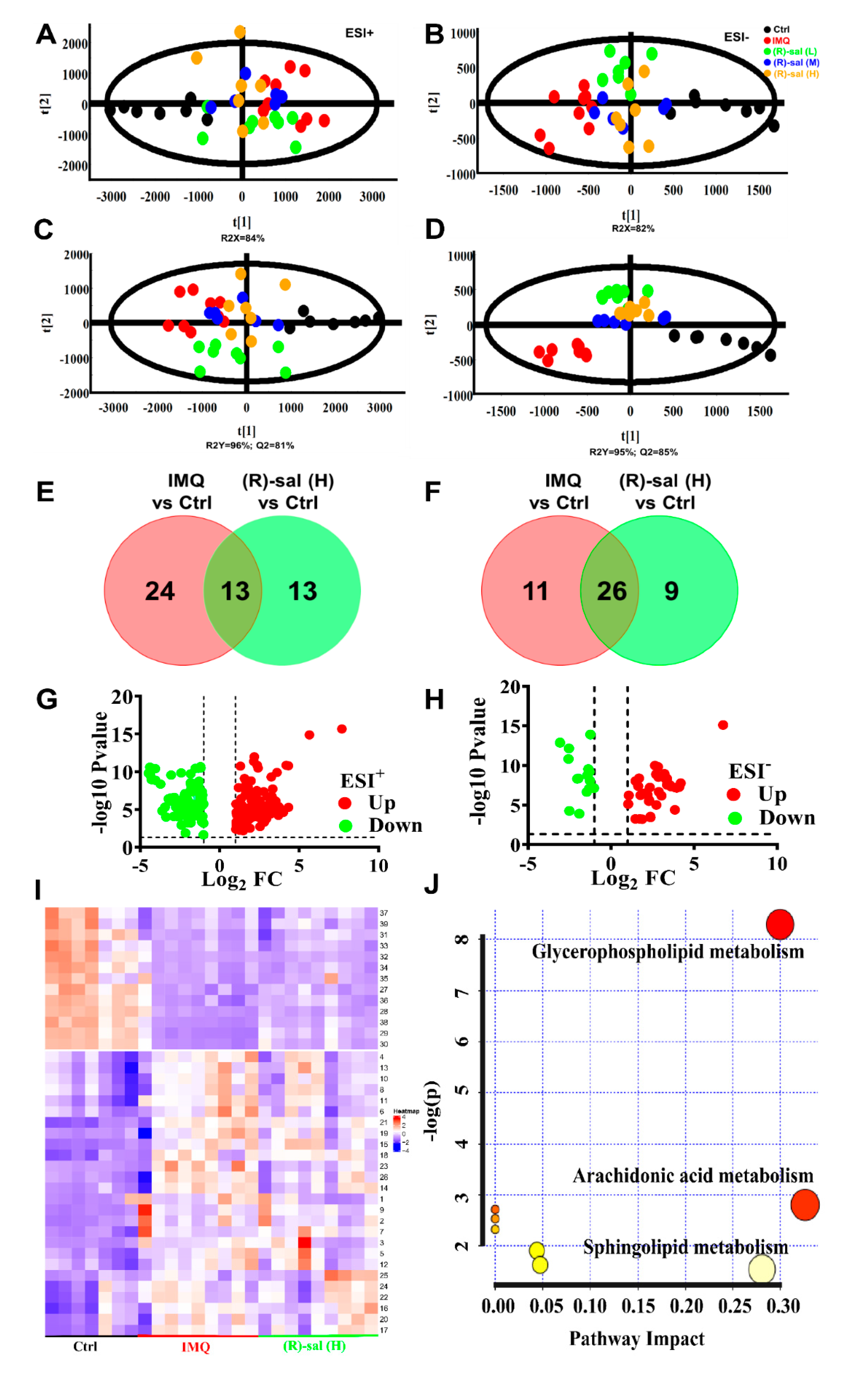
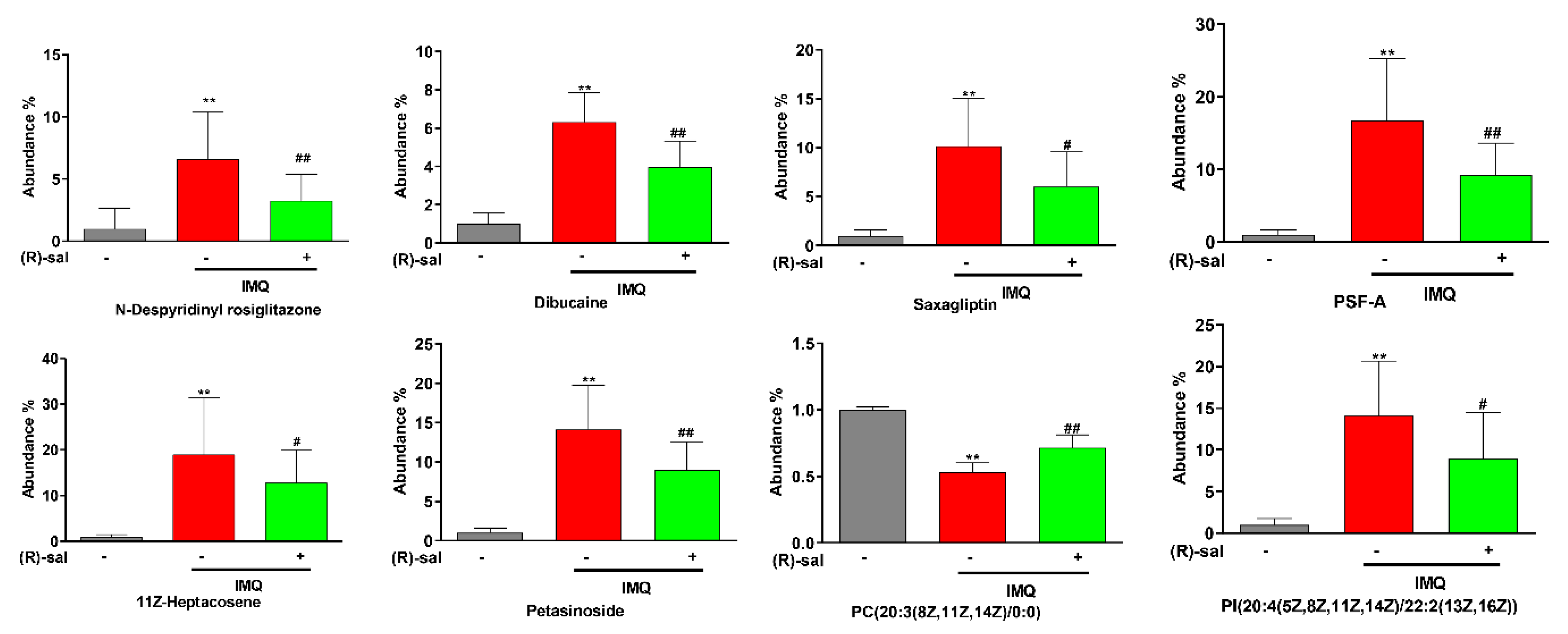
3.7. The Influence of (R)-Salbutamol on Metabolic Effects of IMQ Treatment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiang, C.C.; Cheng, W.J.; Korinek, M.; Lin, C.Y.; Hwang, T.L. Neutrophils in Psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, M.S.; Diamond, A.; Russell, A.; Jameson, J.M. Human αβ and γδ T Cells in Skin Immunity and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traidl, C.; Jugert, F.; Krieg, T.; Merk, H.; Hunzelmann, N. Inhibition of allergic contact dermatitis to DNCB but not to oxazolone in interleukin-4-deficient mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 112, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschoal, R.S.; Silva, D.A.; Cardili, R.N.; Souza, C.D.S. Metabolic syndrome, C-reactive protein and cardiovascular risk in psoriasis patients: A cross-sectional study. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2018, 93, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, Y.R.; Herbosa, C.M.; Rogers, A.T.; Huang, A.; Kwatra, S.G.; Cohen, B.; Anadkat, M.J.; Silverberg, J.I. Psoriasis and Mortality in the US: Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E.M.J. Stressed skin-a molecular psychosomatic update on stress-causes and effects in dermatologic diseases. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2016, 14, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mease, P.J.; Menter, M.A. Quality-of-life issues in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Outcome measures and therapies from a dermatological perspective. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, 685–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, J.; Wu, H.X.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Q.T.; Wu, Y.J.; Zhou, P.; Yang, X.D.; Yu, J.; Wei, W. Total glucosides of paeony inhibit the inflammatory responses of mice with allergic contact dermatitis by restoring the balanced secretion of pro-/anti-inflammatory cytokines. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 24, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, I.; Sandrock, I.; Mrowietz, U. Interleukin-17 cytokines: Effectors and targets in psoriasis-A breakthrough in understanding and treatment. J. Exp. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalekar, L.A.; Rosenblum, M.D. Regulatory T cells in inflammatory skin disease: From mice to humans. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesne, J.; Braza, F.; Mahay, G.; Brouard, S.; Aronica, M.; Magnan, A. IL-17 in severe asthma. Where do we stand? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinschen, M.M.; Ivanisevic, J.; Giera, M.; Siuzdak, G. Identification of bioactive metabolites using activity metabolomics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheelock, C.E.; Wheelock, A.M.; Kawashima, S.; Diez, D.; Kanehisa, M.; van Erk, M.; Kleemann, R.; Haeggstrom, J.Z.; Goto, S. Systems biology approaches and pathway tools for investigating cardiovascular disease. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, E.; Wilson, I.D.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic phenotyping in health and disease. Cell 2008, 134, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, A.-H.; Miao, J.-H.; Sun, H.; Han, Y.; Yan, G.-L.; Wu, F.-F.; Wang, X.-J. Metabolomics biotechnology, applications, and future trends: A systematic review. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 37245–37257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabonomics and its role in drug development and disease diagnosis. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2004, 4, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueharaguchi, Y.; Honda, T.; Kusuba, N.; Hanakawa, S.; Adachi, A.; Sawada, Y.; Otsuka, A.; Kitoh, A.; Dainichi, T.; Egawa, G.; et al. Thromboxane A2 facilitates IL-17A production from Vgamma4(+) gammadelta T cells and promotes psoriatic dermatitis in mice. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 680–683.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J. Identifying biomarkers in human psoriasis: Revealed by a systems metabolomics approach. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazargani, Y.T.; de Boer, A.; Leufkens, H.G.; Mantel-Teeuwisse, A.K. Essential medicines for COPD and asthma in low and middle-income countries. Thorax 2014, 69, 1149–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Tsutsui, M.; Kishida, T.; Souma, S.; Kuroda1, J.; Yoshida, T. Salbutamol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in rat peritoneal macrophages. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 35, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemec, G.B.; Ullman, S.; Goodfield, M.; Bygum, A.; Olesen, A.B.; Berth-Jones, J.; Nyberg, F.; Cramers, M.; Faergemann, J.; Andersen, P.; et al. A randomized controlled trial of R-salbutamol for topical treatment of discoid lupus erythematosus. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, W.; Frischauf, A.M.; Aberger, F. An old friend with new skills: Imiquimod as novel inhibitor of Hedgehog signaling in basal cell carcinoma. Oncoscience 2014, 1, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.P.; et al. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulmer, C.Z.; Jones, C.M.; Yost, R.A.; Garrett, T.J.; Bowden, J.A. Optimization of Folch, Bligh-Dyer, and Matyash Sample-to Extraction Solvent Ratios for Human Plasma-Based Lipidomics Studies. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, Q.; Hu, C.; Yu, D.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, G. Development of a High Coverage Pseudotargeted Lipidomics Method Based on Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; Wilson, I.D.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling procedures for urine using UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gika, H.G.; Macpherson, E.; Theodoridis, G.A.; Wilson, I.D. Evaluation of the repeatability of ultra-performance liquid chromatography-TOF-MS for global metabolic profiling of human urine samples. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2008, 871, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeckling, C.D.; Prenni, J.E. Stacked Injections of Biphasic Extractions for Improved Metabolomic Coverage and Sample Throughput. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattozzi, C.; Salvi, M.; D’Epiro, S.; Giancristoforo, S.; Macaluso, L.; Luci, C.; Lal, K.; Calvieri, S.; Richetta, A.G. Importance of regulatory T cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: Review of the literature. Dermatology 2013, 227, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vida, G.; Pena, G.; Kanashiro, A.; Thompson-Bonilla Mdel, R.; Palange, D.; Deitch, E.A.; Ulloa, L. beta2-Adrenoreceptors of regulatory lymphocytes are essential for vagal neuromodulation of the innate immune system. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 4476–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beng, H.; Su, H.; Wang, S.; Kuai, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, F.; Tan, W. Differential effects of inhaled R- and S-terbutaline in ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 73, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Tan, K.S.; Ser, H.L.; Tan, L.T.; Lee, L.H.; Tan, W. Effect of (R)-salbutamol on the switch of phenotype and metabolic pattern in LPS-induced macrophage cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzkeser, H.; Cadirci, E.; Halici, Z.; Odabasoglu, F.; Polat, B.; Yuksel, T.N.; Ozaltin, S.; Atalay, F. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of salbutamol on acute and chronic models of inflammation in rats: Involvement of an antioxidant mechanism. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 438912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteleone, G.; Pallone, F.; MacDonald, T.T.; Chimenti, S.; Costanzo, A. Psoriasis: From pathogenesis to novel therapeutic approaches. Clin. Sci. 2011, 120, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, J.C. Autoimmune aspects of psoriasis: Heritability and autoantigens. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, J.E.; Chan, T.C.; Krueger, J.G. Psoriasis pathogenesis and the development of novel targeted immune therapies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Gupta, S. TLR1/2, TLR7, and TLR9 signals directly activate human peripheral blood naive and memory B cell subsets to produce cytokines, chemokines, and hematopoietic growth factors. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedoszytko, B.; Sokolowska-Wojdylo, M.; Ruckemann-Dziurdzinska, K.; Roszkiewicz, J.; Nowicki, R.J. Chemokines and cytokines network in the pathogenesis of the inflammatory skin diseases: Atopic dermatitis, psoriasis and skin mastocytosis. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2014, 31, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Lu, C.; Liang, C.L.; Qiu, F.; Han, L.; Dai, Z. Esculetin Ameliorates Psoriasis-Like Skin Disease in Mice by Inducing CD4(+)Foxp3(+) Regulatory T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Fleming, C.; Yan, J. New insights of T cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2012, 9, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, M.; Miossec, P. Th17 and regulatory T cell balance in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haak, S.G.G.; Becher, B. Th17 cells in autoimmune disease: Changing the verdict. Immunotherapy 2009, 1, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littman, D.R.; Rudensky, A.Y. Th17 and regulatory T cells in mediating and restraining inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbi, J.; Pardoll, D.; Pan, F. Metabolic control of the Treg/Th17 axis. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 252, 52–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wei, Q. Quercitrin extracted from Tartary buckwheat alleviates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis in mice by inhibiting the Th17 cell response. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Soma, T.; Takaku, Y.; Nakagome, K.; Hagiwara, K.; Kanazawa, M.; Nagata, M. Salbutamol modulates the balance of Th1 and Th2 cytokines by mononuclear cells from allergic asthmatics. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 152, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S.A. Enhanced histopathology of the spleen. Toxicol. Pathol. 2006, 34, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, A.; Michalak-Stoma, A.; Chodorowska, G.; Szepietowski, J.C. Lipid disturbances in psoriasis: An update. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottas, A.; Fishman, D.; Okas, T.L.; Kingo, K.; Soomets, U. The metabolic analysis of psoriasis identifies the associated metabolites while providing computational models for the monitoring of the disease. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hishikawa, D.; Hashidate, T.; Shimizu, T.; Shindou, H. Diversity and function of membrane glycerophospholipids generated by the remodeling pathway in mammalian cells. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, T.; Golfier, S.; Tabeling, C.; Rabel, K.; Graler, M.H.; Witzenrath, M.; Lipp, M. Sphingosine-1-phospate receptor 4 (S1P(4)) deficiency profoundly affects dendritic cell function and TH17-cell differentiation in a murine model. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 4024–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, A.; Robson, S. Beyond ecto-nucleotidase: CD39 defines human Th17 cells with CD161. Purinergic Signal. 2015, 11, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.H.; Cho, K.A.; Hahn, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Woo, S.Y.; Ryu, K.H.; Park, W.J.; Park, J.W. Inhibiting Sphingosine Kinase 2 Derived-sphingosine-1-phosphate Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Disease via Blocking Th17 Differentiation of Naive CD4 T Lymphocytes in Mice. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Tan, W. (R)-Salbutamol Improves Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Dermatitis by Regulating the Th17/Tregs Balance and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism. Cells 2020, 9, 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020511
Liu F, Wang S, Liu B, Wang Y, Tan W. (R)-Salbutamol Improves Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Dermatitis by Regulating the Th17/Tregs Balance and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism. Cells. 2020; 9(2):511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020511
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Fei, Shanping Wang, Bo Liu, Yukun Wang, and Wen Tan. 2020. "(R)-Salbutamol Improves Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Dermatitis by Regulating the Th17/Tregs Balance and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism" Cells 9, no. 2: 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020511
APA StyleLiu, F., Wang, S., Liu, B., Wang, Y., & Tan, W. (2020). (R)-Salbutamol Improves Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Dermatitis by Regulating the Th17/Tregs Balance and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism. Cells, 9(2), 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020511



