Expression of the microRNA-200 Family, microRNA-205, and Markers of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition as Predictors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection over Esophagectomy in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining of EMT Markers in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Samples
3. Expression Analysis of miR-200 Family Members and miR-205 in FFPE Samples
4. Statistics
5. Results
Cohort Description
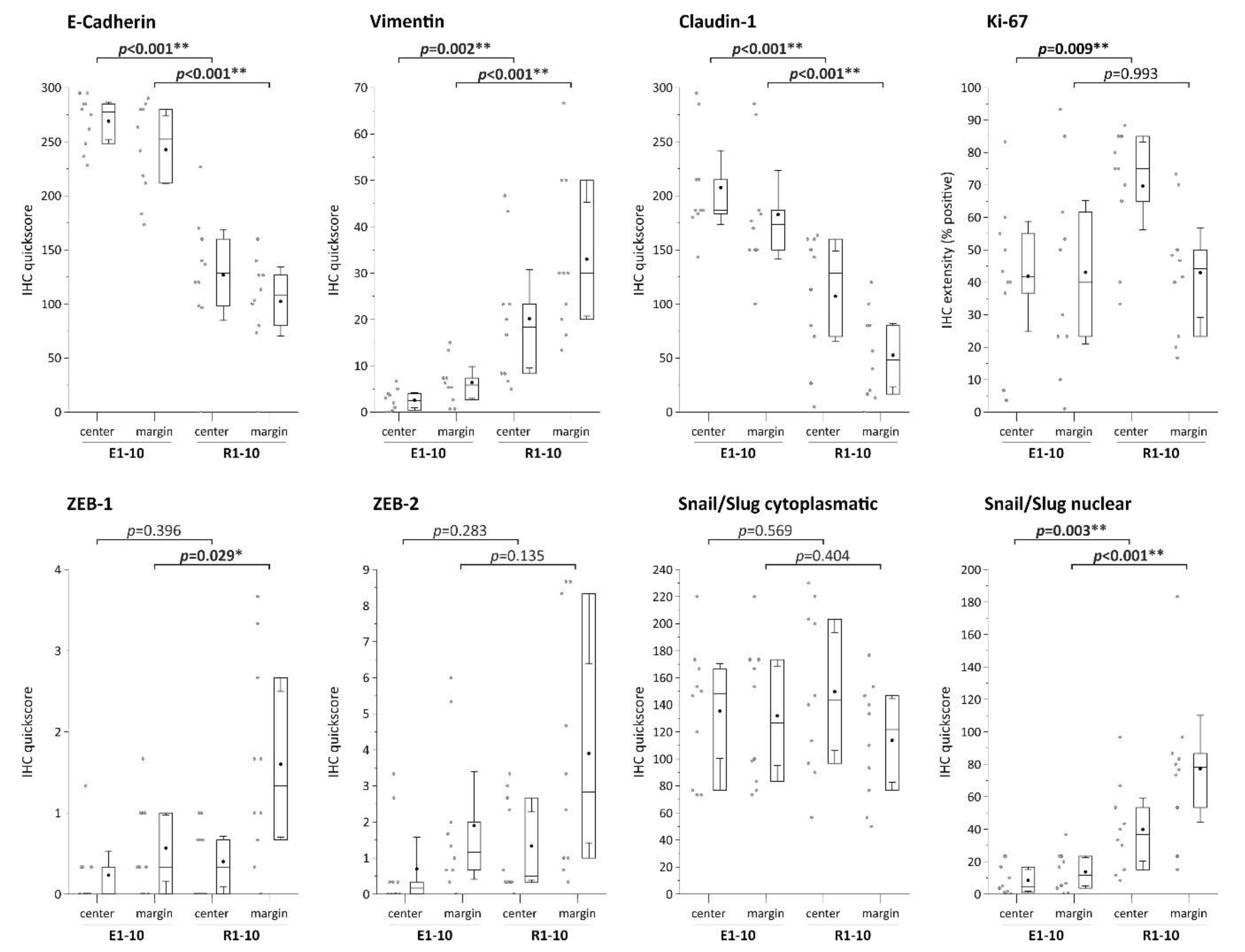
6. Expression Pattern of EMT Markers in Localized (ESD) and Regional (Surgically Resected) Invasive EACs
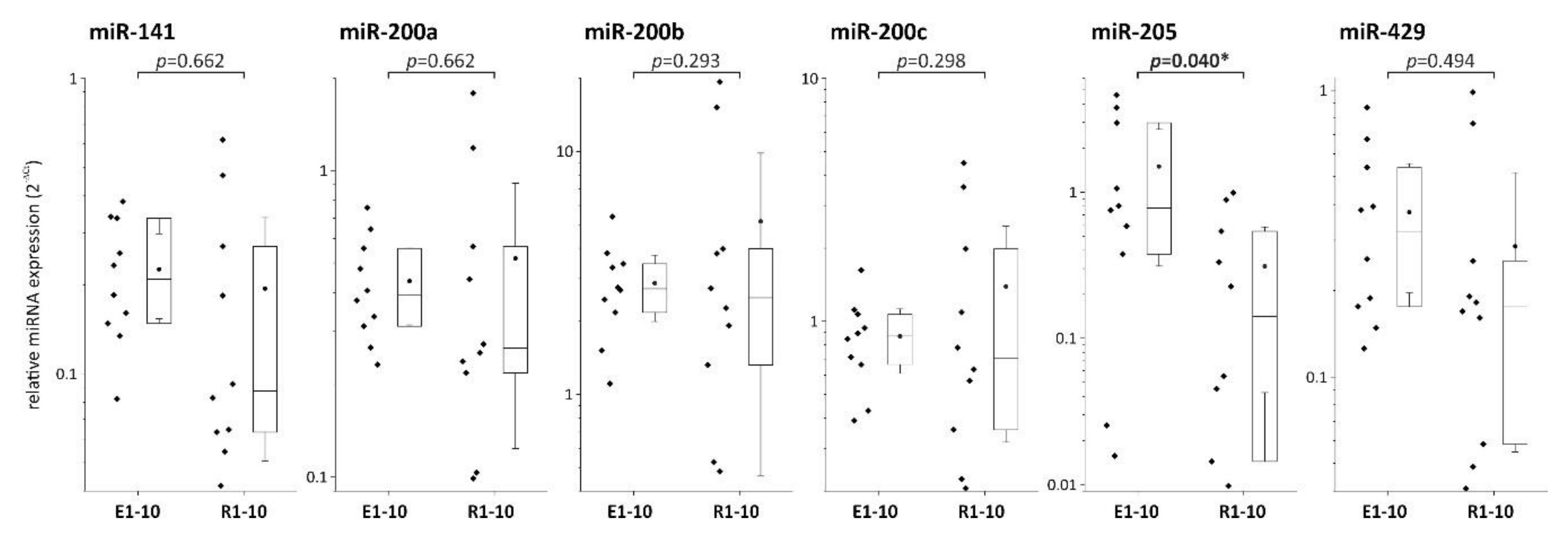
7. Expression of miRNA Family Members in Localized (ESD) and Regional (Surgically Resected) Invasive EACs
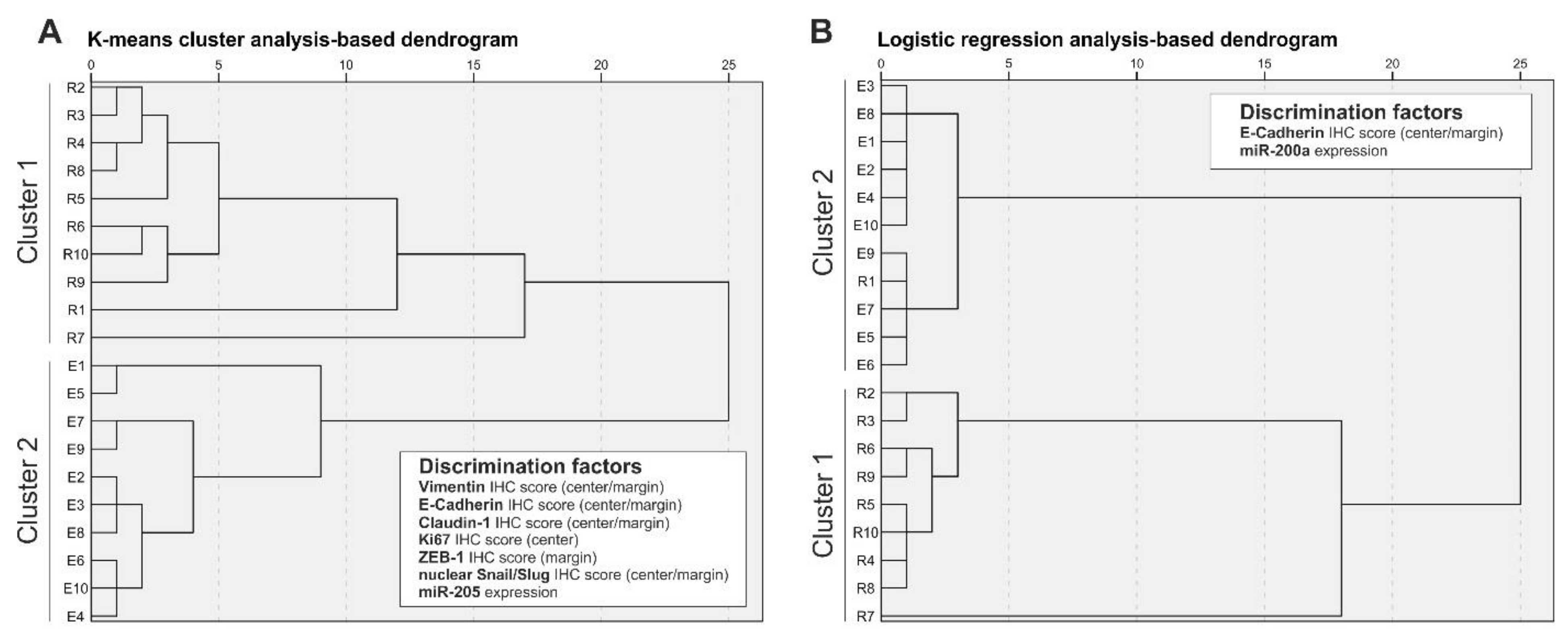
8. Correlation and Discriminative Power of EMT Markers and miRNAs
9. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Who Classification of Tumours Editorial. Digestive System Tumours (World Health Organization Classification of Tumours, Band 1); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, R.; Hainaut, P. The multidisciplinary management of gastrointestinal cancer. Epidemiology of oesophagogastric cancer. Best Pract Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 21, 921–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagergren, J.; Smyth, E.; Cunningham, D.; Lagergren, P. Oesophageal cancer. Lancet 2017, 390, 2383–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, B.; Abdelfatah, M.M.; Othman, M.O. Endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for early stage esophageal cancer. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 6, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incarbone, R.; Bonavina, L.; Saino, G.; Bona, D.; Peracchia, A. Outcome of esophageal adenocarcinoma detected during endoscopic biopsy surveillance for Barrett’s esophagus. Surg. Endosc. 2002, 16, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.M.; Zhang, X.Q.; Chen, M.; Huang, S.L.; Zou, X.P. Endoscopic submucosal dissection vs. endoscopic mucosal resection for superficial esophageal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5540–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Singh, V.; Fleischer, D.E.; Sharma, V.K. A comparison of endoscopic treatment and surgery in early esophageal cancer: An analysis of surveillance epidemiology and end results data. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1340–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszewski, W.J. Endoscopic methods in the treatment of early-stage esophageal cancer. Wideochir Inne. Tech. Maloinwazyjne 2014, 9, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Roh, Y.H.; Lee, Y.C. Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early stage esophagogastric junction cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isomoto, H.; Yamaguchi, N.; Minami, H.; Nakao, K. Management of complications associated with endoscopic submucosal dissection/endoscopic mucosal resection for esophageal cancer. Dig. Endosc. 2013, 25 (Suppl. 1), 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepass, U.; Truong, K.; Godt, D.; Ikura, M.; Peifer, M. Cadherins in embryonic and neural morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev. Cell. 2008, 14, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medici, D.; Hay, E.D.; Olsen, B.R. Snail and Slug promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition through beta-catenin-T-cell factor-4-dependent expression of transforming growth factor-beta3. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2008, 19, 4875–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansieau, S.; Bastid, J.; Doreau, A.; Morel, A.P.; Bouchet, B.P.; Thomas, C.; Fauvet, F.; Puisieux, I.; Doglioni, C.; Piccinin, S.; et al. Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a collateral effect of tumor-promoting inactivation of premature senescence. Cancer Cell. 2008, 14, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Gaur, A.B.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigner, K.; Dampier, B.; Descovich, L.; Mikula, M.; Sultan, A.; Schreiber, M.; Mikulits, W.; Brabletz, T.; Strand, D.; Obrist, P.; et al. The transcription factor ZEB1 (deltaEF1) promotes tumour cell dedifferentiation by repressing master regulators of epithelial polarity. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6979–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbas, R.; Mayr, C.; Klieser, E.; Fuereder, J.; Bach, D.; Stattner, S.; Primavesi, F.; Jaeger, T.; Stanzer, S.; Ress, A.L.; et al. Relevance of MicroRNA200 Family and MicroRNA205 for Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Clinical Outcome in Biliary Tract Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestens, C.; Siersema, P.D.; Offerhaus, G.J.; van Baal, J.W. BMP4 Signaling Is Able to Induce an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Like Phenotype in Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma through Induction of SNAIL2. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.; Mesquita, M.; Dias Pereira, A.; Bettencourt-Dias, M.; Chaves, P.; Pereira-Leal, J.B. CYR61 and TAZ Upregulation and Focal Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition May Be Early Predictors of Barrett’s Esophagus Malignant Progression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, Y.; Wu, T.T.; Wang, K.K. Epithelial mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells in esophageal adenocarcinoma originating from Barrett’s esophagus. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Lam, A.K. Current perspectives of mi-RNA in oesophageal adenocarcinoma: Roles in predicting carcinogenesis, progression and values in clinical management. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 98, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.M.; Watson, D.I.; Leong, M.P.; Mayne, G.C.; Michael, M.Z.; Wijnhoven, B.P.; Hussey, D.J. miR-200 family expression is downregulated upon neoplastic progression of Barrett’s esophagus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, K.; Liao, L.D.; Li, L.Y.; Du, Z.P.; Wu, B.L.; Wu, J.Y.; Xu, X.E.; Zeng, F.M.; Chen, B.; et al. miR-200b suppresses invasiveness and modulates the cytoskeletal and adhesive machinery in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting Kindlin-2. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamano, R.; Miyata, H.; Yamasaki, M.; Kurokawa, Y.; Hara, J.; Moon, J.H.; Nakajima, K.; Takiguchi, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Mori, M.; et al. Overexpression of miR-200c induces chemoresistance in esophageal cancers mediated through activation of the Akt signaling pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3029–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.J.; Craig, M.P.; Agrawal, S.; Kadakia, M. microRNA involvement in the onset and progression of Barrett’s esophagus: A systematic review. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8179–8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Gao, Y.M.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, Y.B.; Zhao, Z.G.; Yang, K. MicroRNAs as oncogenes or tumour suppressors in oesophageal cancer: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Cell Prolif. 2014, 47, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezova, R.; Kovarikova, A.; Srovnal, J.; Zemanova, M.; Harustiak, T.; Ehrmann, J.; Hajduch, M.; Sachlova, M.; Svoboda, M.; Slaby, O. MiR-205 functions as a tumor suppressor in adenocarcinoma and an oncogene in squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 8007–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detre, S.; Saclani Jotti, G.; Dowsett, M. A “quickscore” method for immunohistochemical semiquantitation: Validation for oestrogen receptor in breast carcinomas. J. Clin. Pathol. 1995, 48, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittekind, C. TNM Klassifikation maligner Tumoren, 8th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Pech, O.; May, A.; Rabenstein, T.; Ell, C. Endoscopic resection of early oesophageal cancer. Gut 2007, 56, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskens, C.J.; Westerterp, M.; Lagarde, S.M.; Bergman, J.J.; ten Kate, F.J.; van Lanschot, J.J. Prediction of appropriateness of local endoscopic treatment for high-grade dysplasia and early adenocarcinoma by EUS and histopathologic features. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004, 60, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, M.J.; Ruurda, J.P.; Lolkema, M.P.; Sitarz, R.; Ten Kate, F.J.; van Hillegersberg, R. The role of biological markers of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in oesophageal adenocarcinoma, an immunohistochemical study. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 68, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbing, E.A.; van der Zalm, A.P.; Steins, A.; Creemers, A.; Hermsen, S.; Rentenaar, R.; Klein, M.; Waasdorp, C.; Hooijer, G.K.J.; Meijer, S.L.; et al. Stromal-derived interleukin 6 drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and therapy resistance in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2237–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jethwa, P.; Naqvi, M.; Hardy, R.G.; Hotchin, N.A.; Roberts, S.; Spychal, R.; Tselepis, C. Overexpression of Slug is associated with malignant progression of esophageal adenocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Bing, Z.; Yan, P.; Li, R.; Wang, C.; Sun, X.; Yang, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K. Integrative data mining and meta-analysis to investigate the prognostic role of microRNA-200 family in various human malignant neoplasms: A consideration on heterogeneity. Gene 2019, 716, 144025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Alshareef, A.; Wu, C.; Li, S.; Jiao, J.W.; Cao, H.H.; Lai, R.; Xu, L.Y.; Li, E.M. Loss of miR-200b promotes invasion via activating the Kindlin-2/integrin beta1/AKT pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: An E-cadherin-independent mechanism. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 28949–28960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaby, O.; Srovnal, J.; Radova, L.; Gregar, J.; Juracek, J.; Luzna, P.; Svoboda, M.; Hajduch, M.; Ehrmann, J. Dynamic changes in microRNA expression profiles reflect progression of Barrett’s esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassan, M.; Volinia, S.; Palatini, J.; Pizzi, M.; Fernandez-Cymering, C.; Balistreri, M.; Realdon, S.; Battaglia, G.; Souza, R.; Odze, R.D.; et al. MicroRNA Expression Profiling in the Histological Subtypes of Barrett’s Metaplasia. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2013, 4, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ajani, J.A.; Gu, J.; Chang, D.W.; Tan, W.; Hildebrandt, M.A.; Huang, M.; Wang, K.K.; Hawk, E. MicroRNA expression signatures during malignant progression from Barrett’s esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2013, 6, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordick, F.; Mariette, C.; Haustermans, K.; Obermannova, R.; Arnold, D.; Committee, E.G. Oesophageal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, v50–v57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

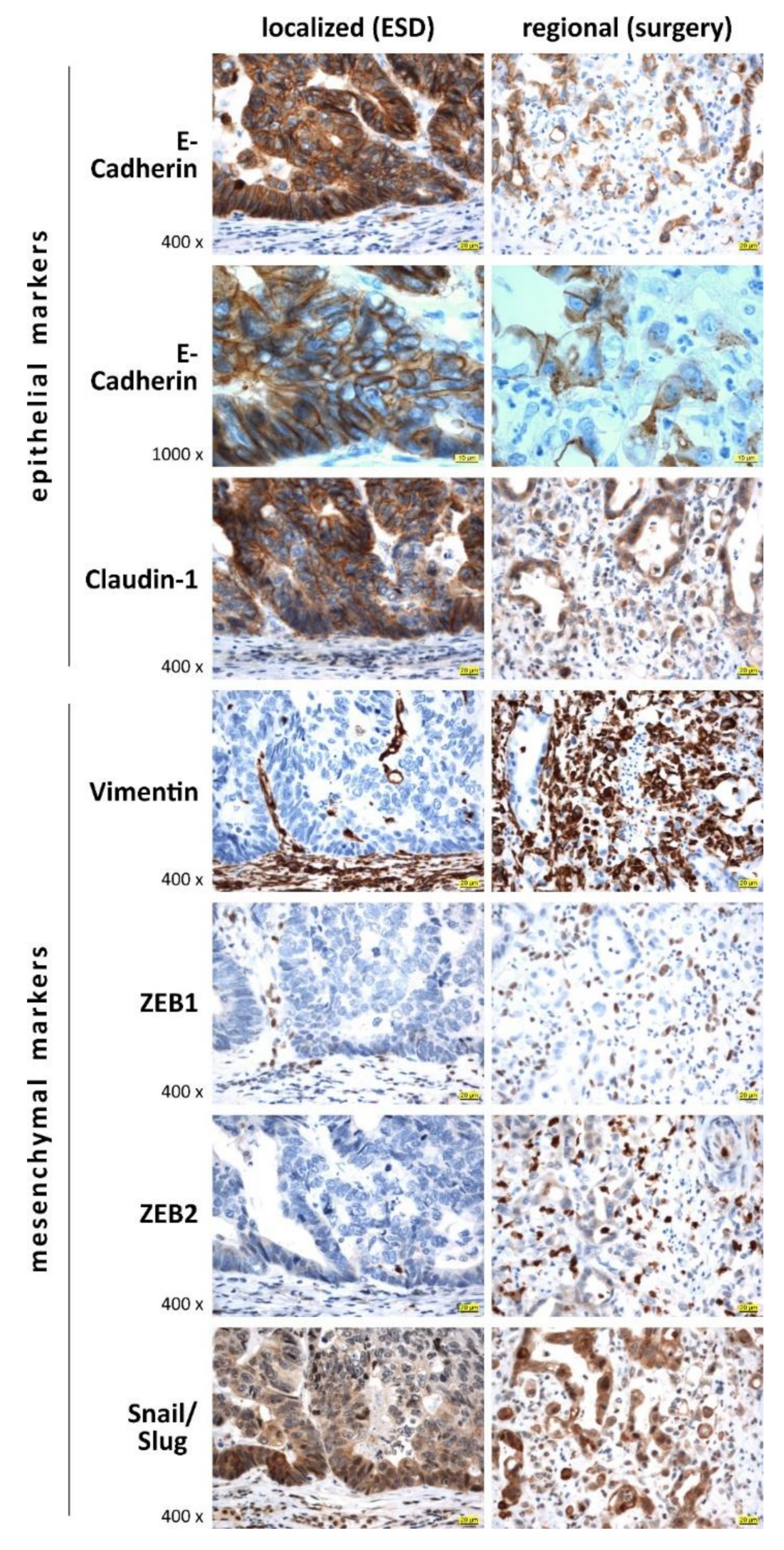


| Antibody | Vendor a | Catalog No. | Species | Clone | Pretreatment | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Claudin-1 | a | 51-9000 | Rabbit polyclonal | n.a. | High pH | 1:200 |
| E-cadherin | b | 790-4497 | Mouse monoclonal | 36 | High pH | Ready-to-use |
| Ki67 | b | 790-4286 | Rabbit monoclonal | 30-9 | High pH | Ready-to-use |
| P53 | b | 760-2542 | Mouse monoclonal | Bp53-11 | High pH | Ready-to-use |
| SNAIL/SLUG | c | ab224731 | Mouse monoclonal | CL3700 | High pH | 1:50 |
| Vimentin | b | 790-2917 | Mouse monoclonal | V9 | High pH | Ready-to-use |
| ZEB1 | c | ab203829 | Rabbit monoclonal | EPR17375 | Low pH | 1:50 |
| ZEB2 | c | ab230561 | Rabbit monoclonal | EPR21246 | Low pH | 1:500 |
| ID | Max. Tumor Size (mm) | Grading [G1-G3] | T | N | No. of Lymph Nodes a | UICC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| endoscopic resection (ESD) | ||||||
| E1 | 2.4 | 2 | 1a (m2) | cN0 | n.a. | IA |
| E2 | 3.7 | 2 | 1a (m2) | cN0 | n.a. | IA |
| E3 | 4.3 | 2 | 1a (m3) | cN0 | n.a. | IA |
| E4 | 5.1 | 1 | 1a (m2) | cN0 | n.a. | IA |
| E5 | 16.2 | 2 | 1a (m3) | cN0 | n.a. | IA |
| E6 | 8.1 | 1 | 1a (m2) | cN0 | n.a. | IA |
| E7 | 13.2 | 2 | 1a (m3) | cN0 | n.a. | IA |
| E8 | 8.3 | 2 | 1a (m2) | cN0 | n.a. | IA |
| E9 | 7.2 | 2 | 1a (m3) | cN0 | n.a. | IA |
| E10 | 5.1 | 1 | 1a (m1) | cN0 | n.a. | IA |
| esophagectomy(surgery) | ||||||
| R1 | 30 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 20/20 | IVA |
| R2 | 35 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2/21 | IIIB |
| R3 | 20 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 8/55 | IIIB |
| R4 | 30 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 18/24 | IVA |
| R5 | 45 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 6/12 | IIIB |
| R6 | 28 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4/12 | IIIB |
| R7 | 28 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4/10 | IIIB |
| R8 | 76 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 6/49 | IIIB |
| R9 | 33 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 12/38 | IVA |
| R10 | 50 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 22/37 | IVA |
| Factor | IHC Mean Scores | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | |||
| 1 | 2 | ||
| Vimentin score (center) | 20.17 | 2.57 | 0.002 |
| Vimentin score (margin) | 33.00 | 6.40 | <0.001 |
| E-cadherin score (center) | 126.83 | 269.00 | <0.001 |
| E-cadherin score (margin) | 102.33 | 242.67 | <0.001 |
| Claudin-1 (center) | 107.17 | 207.67 | 0.001 |
| Claudin-1 (margin) | 52.67 | 182.67 | <0.001 |
| p53 (center) | 170.67 | 122.50 | 0.370 |
| p53 (margin) | 158.03 | 131.40 | 0.628 |
| Ki67 (center) | 69.67 | 41.87 | 0.009 |
| Ki67 (margin) ZEB1 (center) | 43.00 | 43.10 | 0.993 |
| 0.40 | 0.23 | 0.396 | |
| ZEB1 (margin) | 1.60 | 0.57 | 0.029 |
| ZEB2 (center) | 1.33 | 0.70 | 0.283 |
| ZEB2 (margin) | 3.90 | 1.90 | 0.135 |
| Snail/Slug cytoplasmic (center) | 149.67 | 135.33 | 0.569 |
| Snail/Slug cytoplasmic (margin) | 113.67 | 131.83 | 0.404 |
| Slug/Snail nuclear (center) | 39.83 | 8.47 | 0.003 |
| Slug/Snail nuclear (margin) | 77.17 | 13.67 | 0.001 |
| miR-141 | 0.194 | 0.226 | 0.662 |
| miR-200a | 0.517 | 0.436 | 0.662 |
| miR-200b | 5.154 | 2.869 | 0.293 |
| miR-200c | 1.390 | 0.867 | 0.298 |
| miR-205 | 0.310 | 1.498 | 0.040 |
| miR-429 | 0.285 | 0.375 | 0.494 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neureiter, D.; Mayr, C.; Winkelmann, P.; Neumayer, B.; Klieser, E.; Wagner, A.; Hufnagl, C.; Emmanuel, K.; Holzinger, J.; Koch, O.; et al. Expression of the microRNA-200 Family, microRNA-205, and Markers of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition as Predictors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection over Esophagectomy in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Single-Center Experience. Cells 2020, 9, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020486
Neureiter D, Mayr C, Winkelmann P, Neumayer B, Klieser E, Wagner A, Hufnagl C, Emmanuel K, Holzinger J, Koch O, et al. Expression of the microRNA-200 Family, microRNA-205, and Markers of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition as Predictors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection over Esophagectomy in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Single-Center Experience. Cells. 2020; 9(2):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020486
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeureiter, Daniel, Christian Mayr, Paul Winkelmann, Bettina Neumayer, Eckhard Klieser, Andrej Wagner, Clemens Hufnagl, Klaus Emmanuel, Josef Holzinger, Oliver Koch, and et al. 2020. "Expression of the microRNA-200 Family, microRNA-205, and Markers of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition as Predictors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection over Esophagectomy in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Single-Center Experience" Cells 9, no. 2: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020486
APA StyleNeureiter, D., Mayr, C., Winkelmann, P., Neumayer, B., Klieser, E., Wagner, A., Hufnagl, C., Emmanuel, K., Holzinger, J., Koch, O., Kiesslich, T., & Varga, M. (2020). Expression of the microRNA-200 Family, microRNA-205, and Markers of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition as Predictors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection over Esophagectomy in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Single-Center Experience. Cells, 9(2), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020486





