The miR-28-5p Targetome Discovery Identified SREBF2 as One of the Mediators of the miR-28-5p Tumor Suppressor Activity in Prostate Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Culture Conditions
2.2. Transfection
2.3. Cell Proliferation
2.4. Survival Assay
2.5. Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay
2.6. Wound Healing Assay
2.7. Transwell Assay
2.8. miRNA Pull Out Assay
2.9. Targets Identification by Next Generation Sequencings (NGS)
2.10. NGS Data Analysis
2.11. Bioinformatics Analyses
2.12. Bioinformatics Analyses Related to miRNA Pull Out Assay
2.13. Quantification of miRNAs and mRNAs (qRT-PCR)
2.14. Western Blot Analysis
2.15. Vectors Construction
2.16. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.17. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
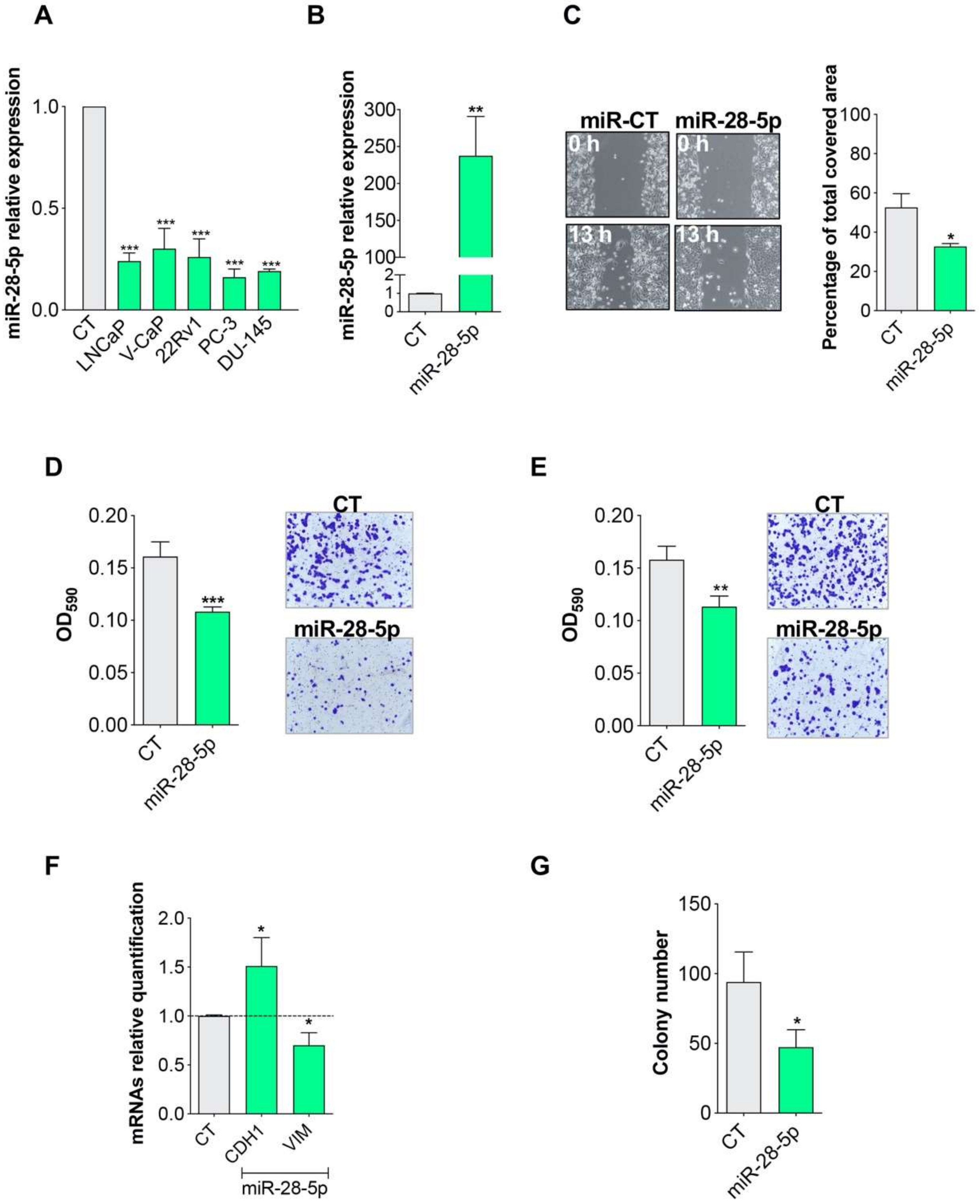
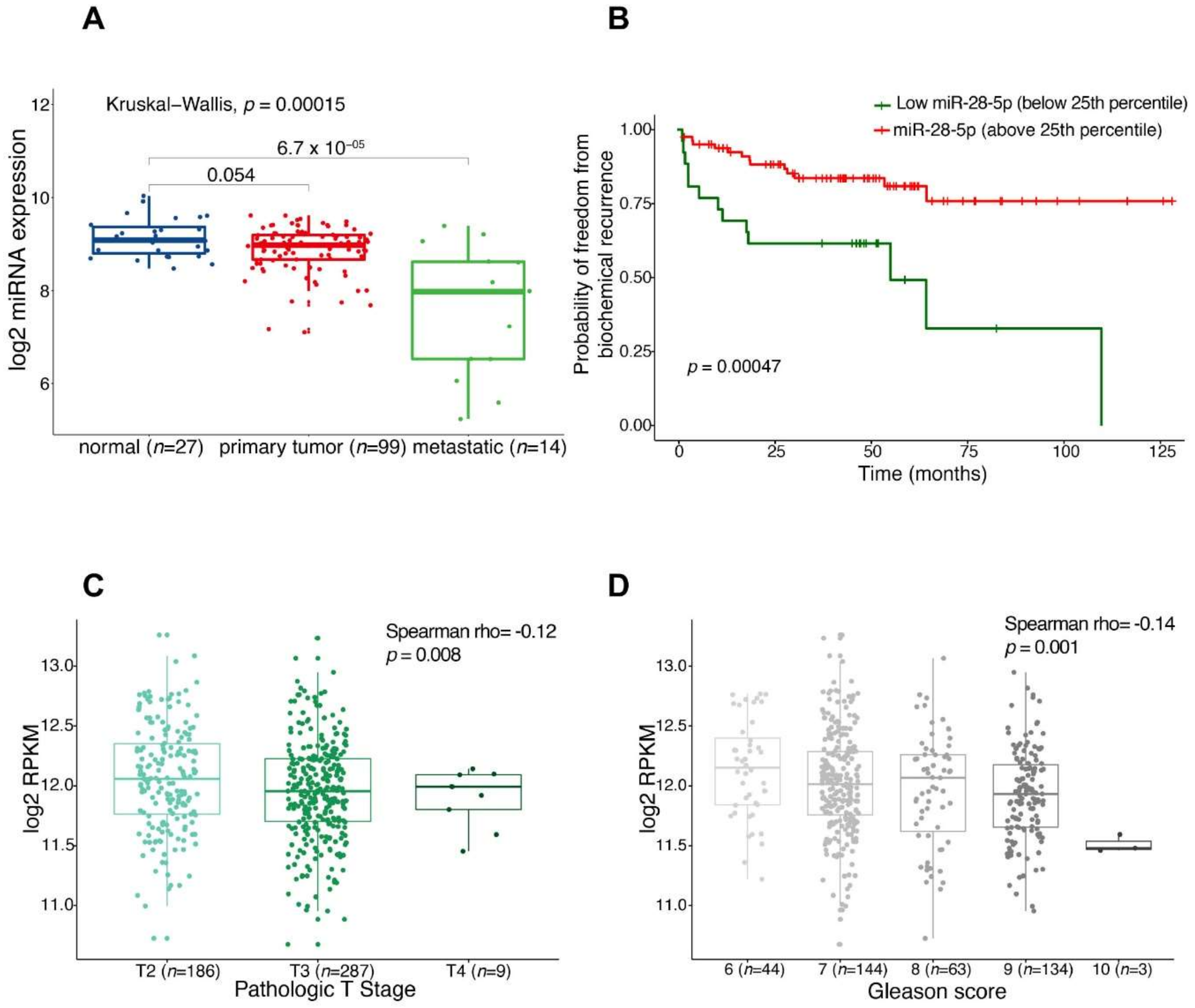
3.1. miR-28-5p Showed Antitumor Effects in PCa
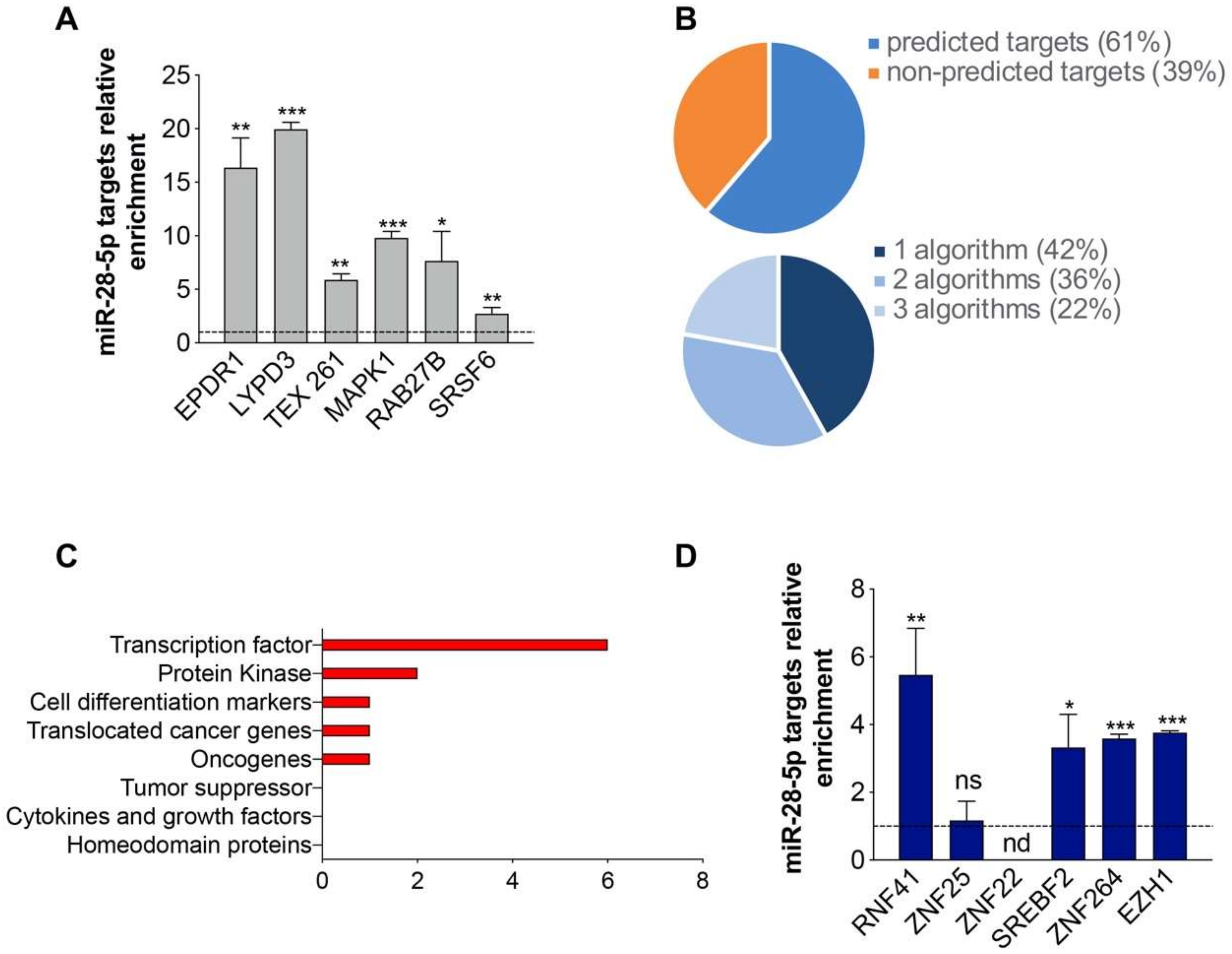
3.2. Identification of miR-28-5p/Targetome
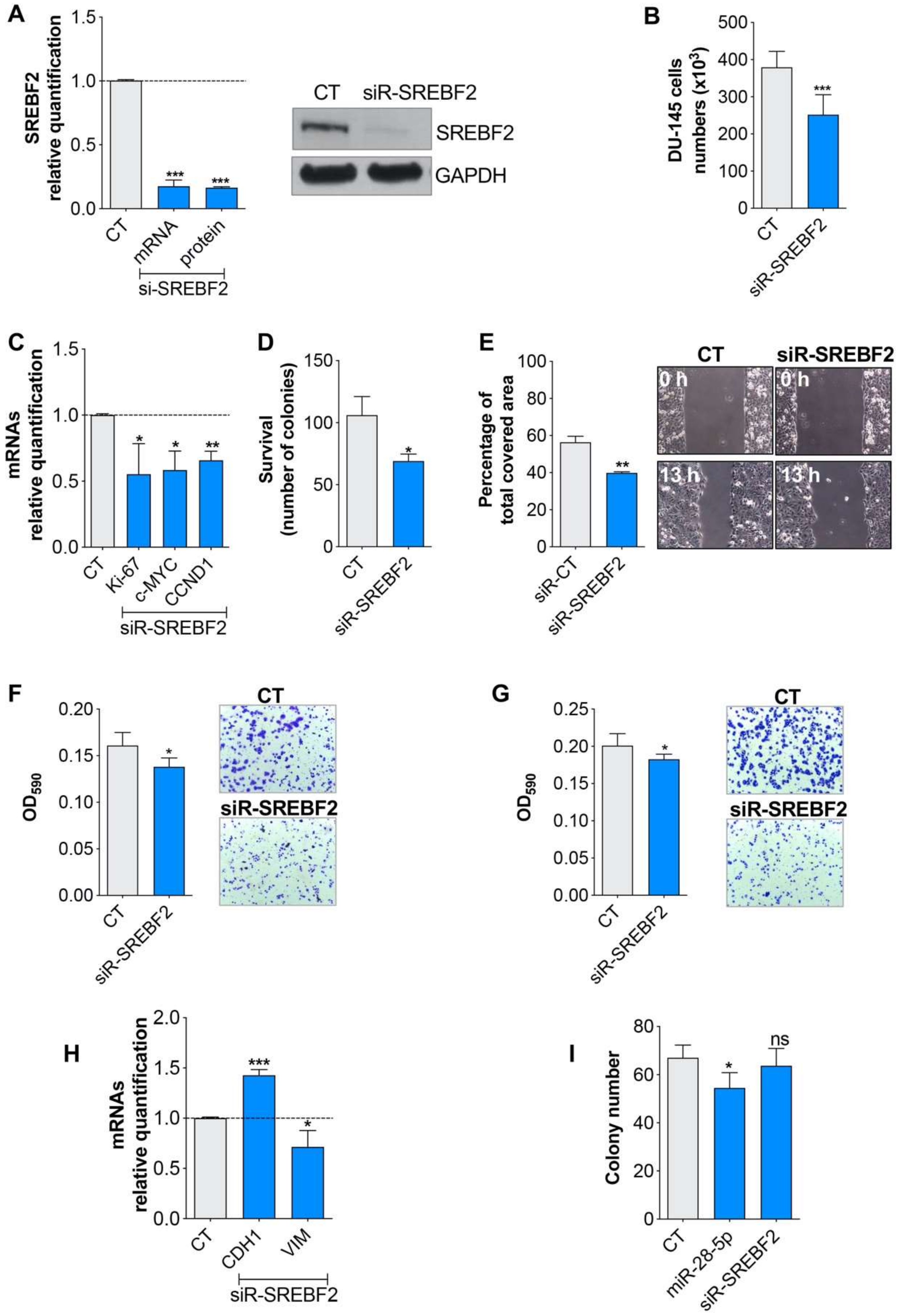
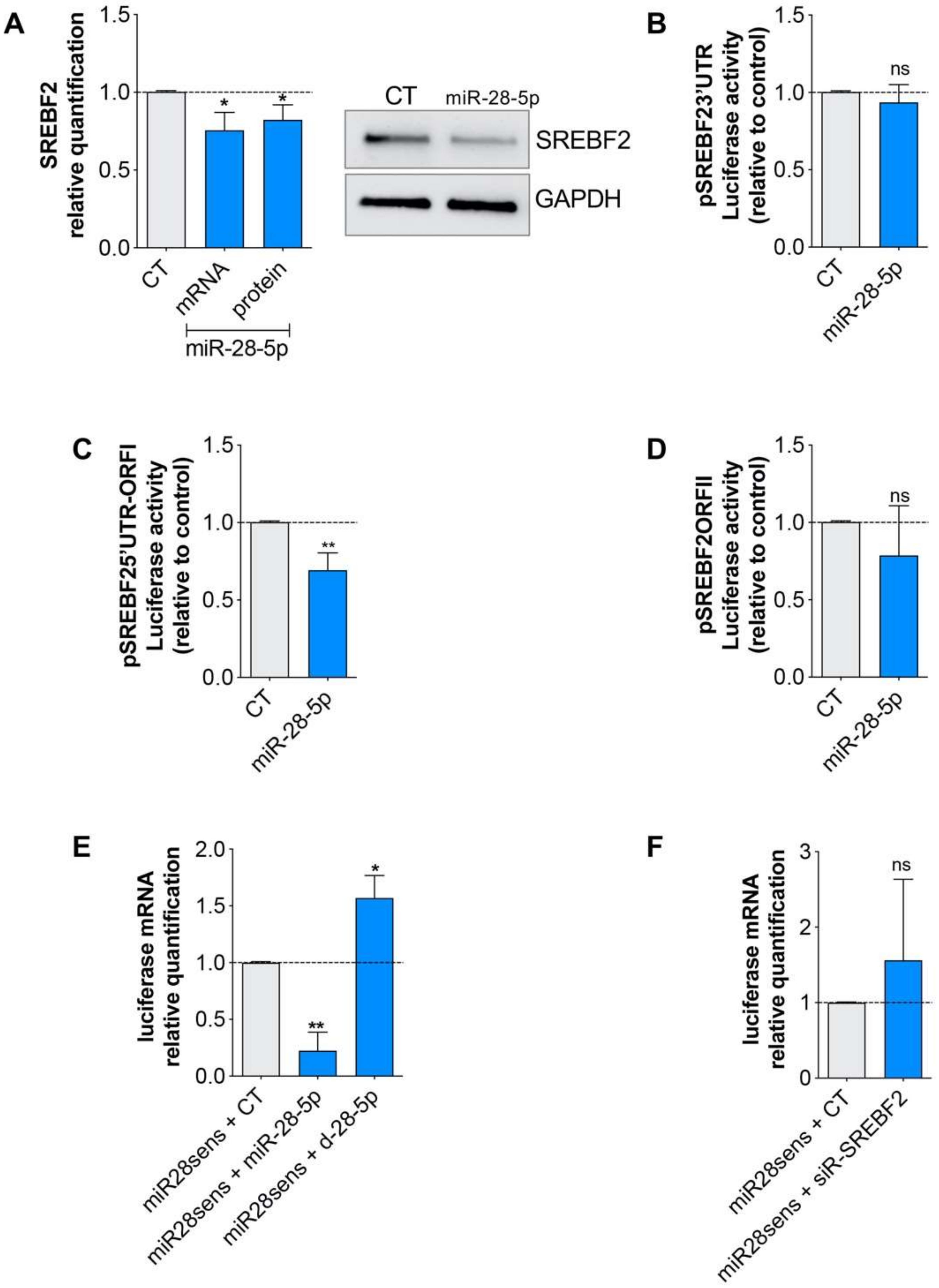
3.3. miR-28-5p Directly Regulated SREBF2 Expression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, X.; Teng, F. Down-regulated miR-28-5p in human hepatocellular carcinoma correlated with tumor proliferation and migration by targeting insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). Mol. Cell Biochem. 2015, 408, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, C.; Yang, Q.; Ding, M.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Ge, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C. miR-28-5p acts as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma for multiple antitumor effects by targeting RAP1B. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 73888–73902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Setty, M.; Holmes, A.B.; Maute, R.L.; Leslie, C.S.; Mussolin, L.; Rosolen, A.; Dalla-Favera, R.; Basso, K. MicroRNA 28 controls cell proliferation and is down-regulated in B-cell lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8185–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.I.; Nicoloso, M.S.; Zeng, L.; Ivan, C.; Spizzo, R.; Gafa, R.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, X.; Vannini, I.; Fanini, F.; et al. Strand-specific miR-28-5p and miR-28-3p have distinct effects in colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Chen, M.; Shen, Z.; Wang, R.; Fang, X.; Song, B. LncRNA-UCA1 modulates progression of colon cancer through regulating the miR-28-5p/HOXB3 axis. J. Cell Biochem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Gong, B.; Huang, H.; Xing, Y.; Liu, F. MicroRNA-28-5p inhibits the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by suppressing AKT phosphorylation. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9777–9785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.L.; Hu, Z.Q.; Zhou, Z.J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Fan, J.; Huang, X.W.; Zhou, J. miR-28-5p-IL-34-macrophage feedback loop modulates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1560–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.N.; Maqbool, R.; Parray, F.Q.; Ul Hussain, M. Triose-phosphate isomerase is a novel target of miR-22 and miR-28, with implications in tumorigenesis. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 8919–8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Ling, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Xu, B.; Guan, H.; et al. LncRNA CCAT1 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by interacting with DDX5 and miR-28-5p. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Berti, G.; Russo, F.; Evangelista, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Rainaldi, G. The miRNA Pull Out Assay as a Method to Validate the miR-28-5p Targets Identified in Other Tumor Contexts in Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 5214806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.W.; Zang, J.B.; Mele, A.; Darnell, R.B. Argonaute HITS-CLIP decodes microRNA-mRNA interaction maps. Nature 2009, 460, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, M.; Landthaler, M.; Burger, L.; Khorshid, M.; Hausser, J.; Berninger, P.; Rothballer, A.; Ascano, M., Jr.; Jungkamp, A.C.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Transcriptome-wide identification of RNA-binding protein and microRNA target sites by PAR-CLIP. Cell 2010, 141, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungkamp, A.C.; Stoeckius, M.; Mecenas, D.; Grun, D.; Mastrobuoni, G.; Kempa, S.; Rajewsky, N. In vivo and transcriptome-wide identification of RNA binding protein target sites. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helwak, A.; Kudla, G.; Dudnakova, T.; Tollervey, D. Mapping the human miRNA interactome by CLASH reveals frequent noncanonical binding. Cell 2013, 153, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orom, U.A.; Lund, A.H. Isolation of microRNA targets using biotinylated synthetic microRNAs. Methods 2007, 43, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patella, F.; Leucci, E.; Evangelista, M.; Parker, B.; Wen, J.; Mercatanti, A.; Rizzo, M.; Chiavacci, E.; Lund, A.H.; Rainaldi, G. MiR-492 impairs the angiogenic potential of endothelial cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Berti, G.; Russo, F.; Fazio, S.; Evangelista, M.; D’Aurizio, R.; Pellegrini, M.; Rainaldi, G. Discovering the miR-26a-5p Targetome in Prostate Cancer Cells. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2729–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taylor, B.S.; Schultz, N.; Hieronymus, H.; Gopalan, A.; Xiao, Y.; Carver, B.S.; Arora, V.K.; Kaushik, P.; Cerami, E.; Reva, B.; et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broad Institute TCGA Genome Data Analysis Center. Correlation between Mirseq Expression and Clinical Features; Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertesz, M.; Iovino, N.; Unnerstall, U.; Gaul, U.; Segal, E. The role of site accessibility in microRNA target recognition. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, K.C.; Huynh, T.; Tay, Y.; Ang, Y.S.; Tam, W.L.; Thomson, A.M.; Lim, B.; Rigoutsos, I. A pattern-based method for the identification of MicroRNA binding sites and their corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell 2006, 126, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, J.; Rehmsmeier, M. RNAhybrid: microRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W451–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, J.B.; Li, Q.; Shigemura, K.; Chung, L.W.; Huang, W.C. SREBP-2 promotes stem cell-like properties and metastasis by transcriptional activation of c-Myc in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 12869–12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wu, S.; Ding, J.; Lin, J.; Wei, L.; Gu, J.; He, X. MicroRNA-181a modulates gene expression of zinc finger family members by directly targeting their coding regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 7211–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, J.R.; Yario, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. Target mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the 5’ UTR as in the 3’ UTR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9667–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, N.; Shi, H.; Zhao, S.; Yao, S.; Shen, H. miR-28-5p promotes the development and progression of ovarian cancer through inhibition of N4BP1. Int. J. Oncol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.; Shan, X.; Zhou, X.; Qi, L.W.; Wu, L.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, H.; et al. A novel serum microRNA signature to screen esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilting, S.M.; Snijders, P.J.; Verlaat, W.; Jaspers, A.; van de Wiel, M.A.; van Wieringen, W.N.; Meijer, G.A.; Kenter, G.G.; Yi, Y.; le Sage, C.; et al. Altered microRNA expression associated with chromosomal changes contributes to cervical carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2013, 32, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; He, K.; Guo, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Huang, K.; Yang, D.; Wu, L.; Deng, Y.; Luo, X.; et al. SSRP1 promotes colorectal cancer progression and is negatively regulated by miR-28-5p. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3118–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolome-Izquierdo, N.; de Yebenes, V.G.; Alvarez-Prado, A.F.; Mur, S.M.; Lopez Del Olmo, J.A.; Roa, S.; Vazquez, J.; Ramiro, A.R. miR-28 regulates the germinal center reaction and blocks tumor growth in preclinical models of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2017, 129, 2408–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimano, H. Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs): Transcriptional regulators of lipid synthetic genes. Prog. Lipid Res. 2001, 40, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, S.L.; Sobel, R.; Whitmore, T.G.; Akbari, M.; Bradley, D.R.; Gleave, M.E.; Nelson, C.C. Dysregulation of sterol response element-binding proteins and downstream effectors in prostate cancer during progression to androgen independence. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Sampieri, K.; Clohessy, J.G.; Mendez, L.; Gonzalez-Billalabeitia, E.; Liu, X.S.; Lee, Y.R.; Fung, J.; Katon, J.M.; et al. An aberrant SREBP-dependent lipogenic program promotes metastatic prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.T.; Hu, P.; Huang, W.C. Fatostatin displays high antitumor activity in prostate cancer by blocking SREBP-regulated metabolic pathways and androgen receptor signaling. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardot, M.; Pecquet, C.; Boukour, S.; Knoops, L.; Ferrant, A.; Vainchenker, W.; Giraudier, S.; Constantinescu, S.N. miR-28 is a thrombopoietin receptor targeting microRNA detected in a fraction of myeloproliferative neoplasm patient platelets. Blood 2010, 116, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Chang, H.R.; Baek, D. Rules for functional microRNA targeting. BMB Rep. 2017, 50, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duursma, A.M.; Kedde, M.; Schrier, M.; le Sage, C.; Agami, R. miR-148 targets human DNMT3b protein coding region. RNA 2008, 14, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elcheva, I.; Goswami, S.; Noubissi, F.K.; Spiegelman, V.S. CRD-BP protects the coding region of betaTrCP1 mRNA from miR-183-mediated degradation. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.; Zhang, J.; Thomson, A.M.; Lim, B.; Rigoutsos, I. MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature 2008, 455, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fazio, S.; Berti, G.; Russo, F.; Evangelista, M.; D’Aurizio, R.; Mercatanti, A.; Pellegrini, M.; Rizzo, M. The miR-28-5p Targetome Discovery Identified SREBF2 as One of the Mediators of the miR-28-5p Tumor Suppressor Activity in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020354
Fazio S, Berti G, Russo F, Evangelista M, D’Aurizio R, Mercatanti A, Pellegrini M, Rizzo M. The miR-28-5p Targetome Discovery Identified SREBF2 as One of the Mediators of the miR-28-5p Tumor Suppressor Activity in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cells. 2020; 9(2):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020354
Chicago/Turabian StyleFazio, Sofia, Gabriele Berti, Francesco Russo, Monica Evangelista, Romina D’Aurizio, Alberto Mercatanti, Marco Pellegrini, and Milena Rizzo. 2020. "The miR-28-5p Targetome Discovery Identified SREBF2 as One of the Mediators of the miR-28-5p Tumor Suppressor Activity in Prostate Cancer Cells" Cells 9, no. 2: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020354
APA StyleFazio, S., Berti, G., Russo, F., Evangelista, M., D’Aurizio, R., Mercatanti, A., Pellegrini, M., & Rizzo, M. (2020). The miR-28-5p Targetome Discovery Identified SREBF2 as One of the Mediators of the miR-28-5p Tumor Suppressor Activity in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cells, 9(2), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020354




