Epigenetic Silencing of Tumor Suppressor miR-124 Directly Supports STAT3 Activation in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Samples, Cell Lines, and Treatments
2.2. DNA Methylation Status of the miR-124 Promoter in CTCL Cell Lines and Patients
2.3. Expression Analysis of miR-124 by qRT–PCR
2.4. Lentiviral Transfection
2.5. Microarray Expression Profiles
2.6. Gene Ontology Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
2.7. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
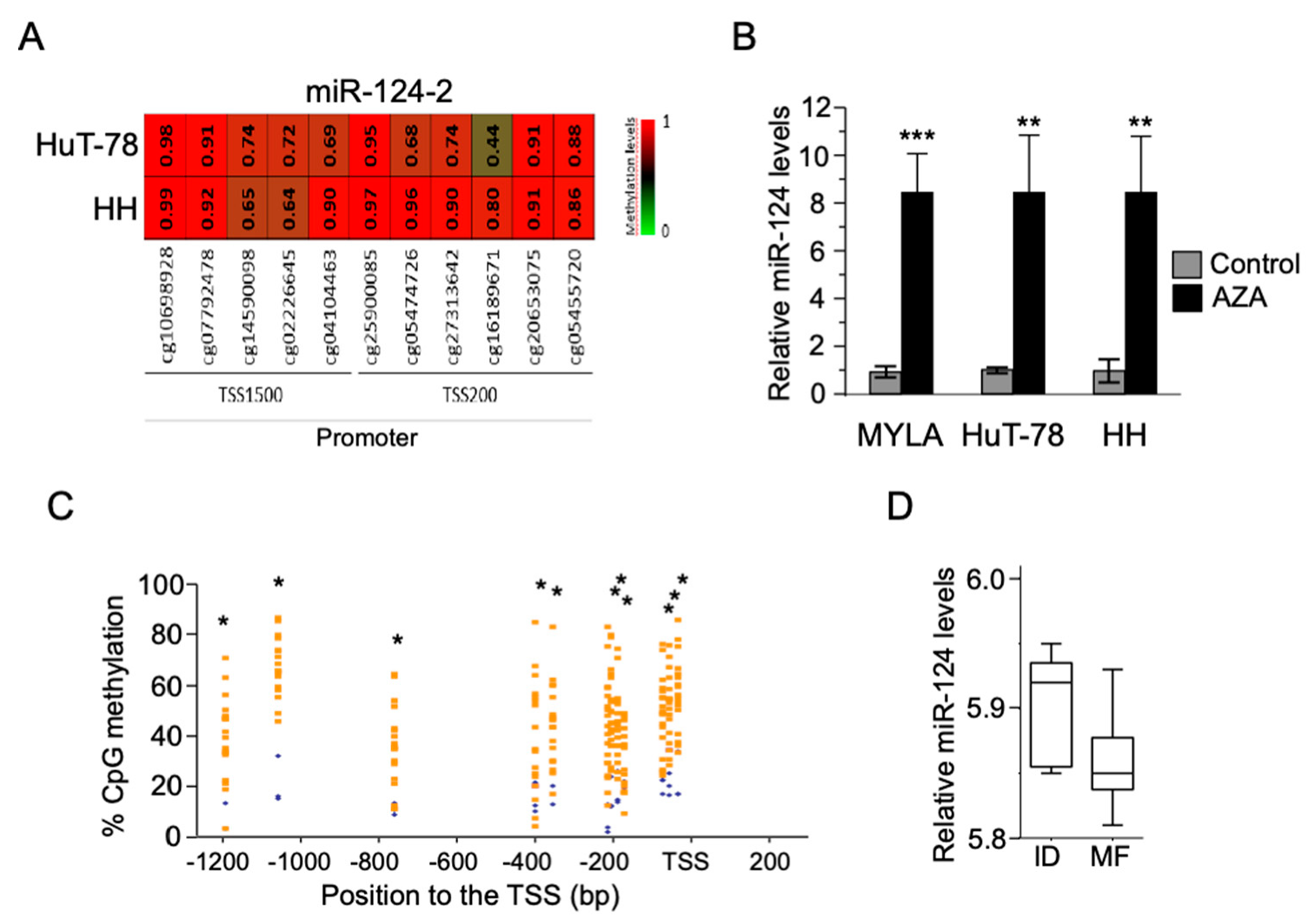
3.1. Silencing of miR-124 as a Consequence of Its Promoter Hypermethylation in Both CTCL Cell Lines and MF Tumor Samples
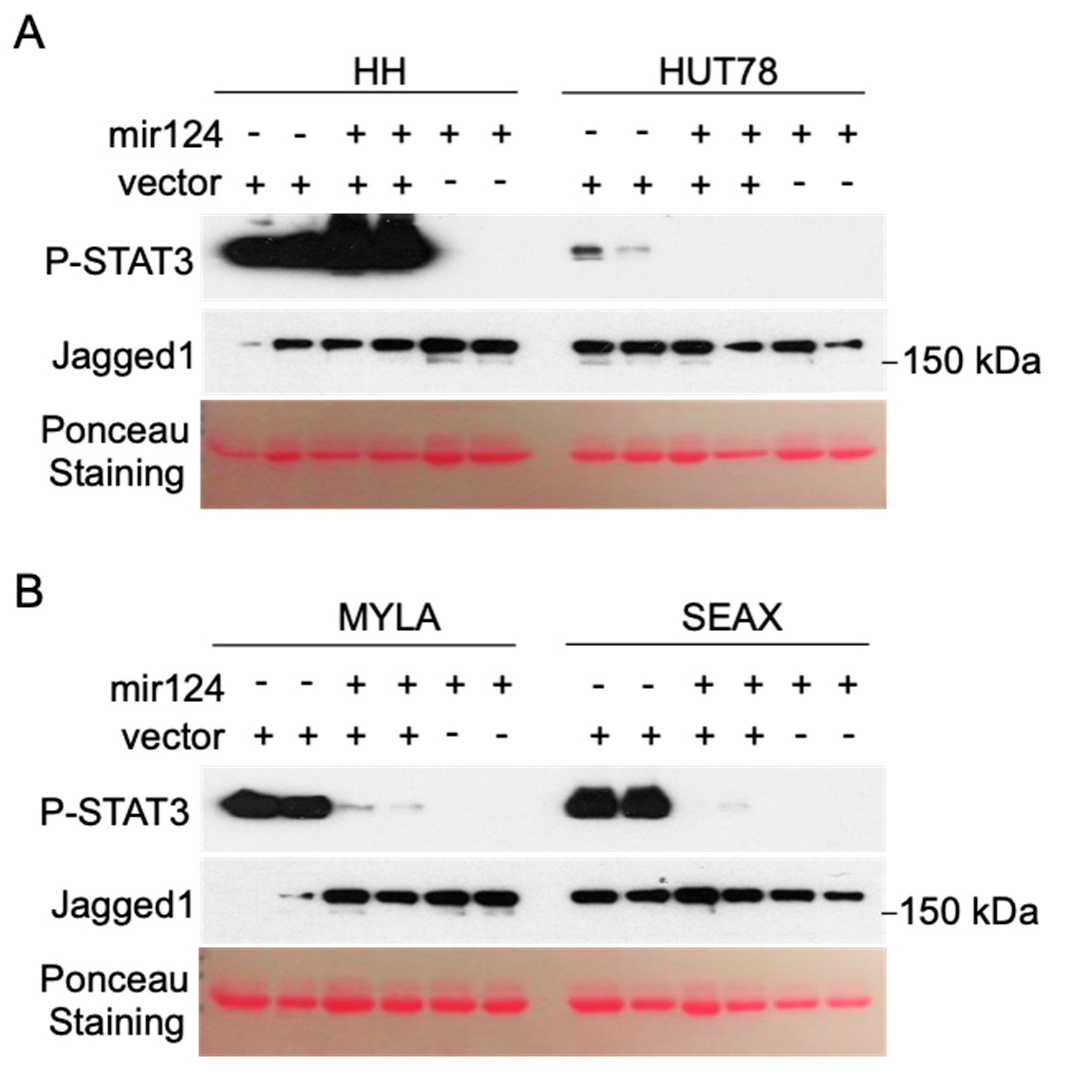
3.2. Hypermethylation of the miR-124 Promoter in CTCL Cells Leads to miR-124 Silencing and Increased STAT3 Levels
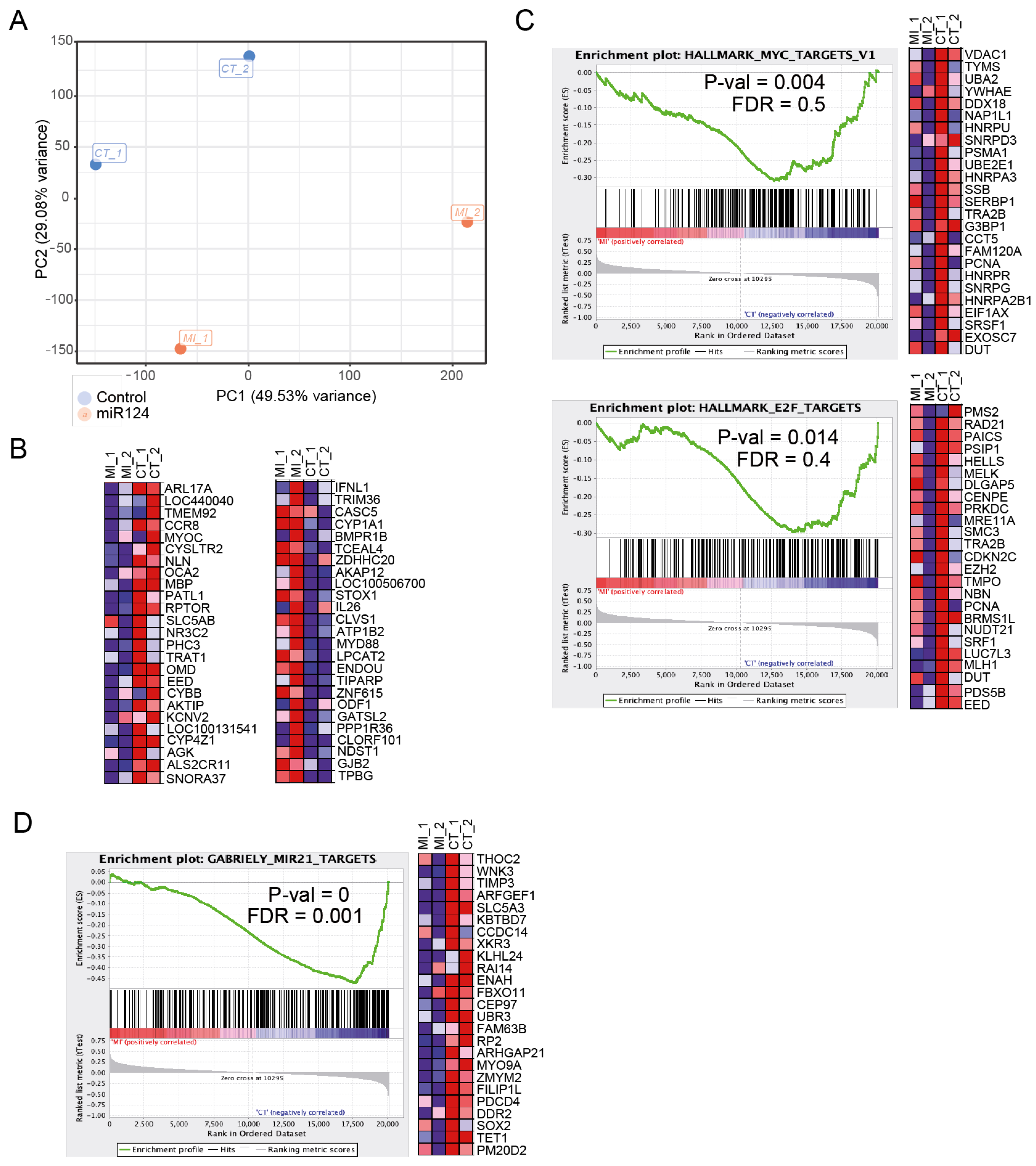
3.3. Ectopic miR-124 Expression in CTCL Cells Imposes an Altered Gene Expression Profile
3.4. CTCL Cells Carrying STAT3 Activation Are Highly Sensitive to Pharmacologic JAK/STAT Inhibition
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.; Goh, G.; Walradt, T.; Hong, B.S.; Bunick, C.G.; Chen, K.; Bjornson, R.D.; Maman, Y.; Wang, T.; Tordoff, J.; et al. Genomic landscape of cutaneous T cell lymphoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.C.D.; Abate, F.; Khiabanian, H.; Martinez-Escala, E.; Guitart, J.; Tensen, C.P.; Vermeer, M.H.; Rabadan, R.; Ferrando, A.; Palomero, T. The mutational landscape of cutaneous T cell lymphoma and Sezary syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiel, M.J.; Sahasrabuddhe, A.A.; Rolland, D.C.; Velusamy, T.; Chung, F.; Schaller, M.; Bailey, N.G.; Betz, B.L.; Miranda, R.N.; Porcu, P.; et al. Genomic analyses reveal recurrent mutations in epigenetic modifiers and the JAK-STAT pathway in Sezary syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGirt, L.Y.; Jia, P.; Baerenwald, D.A.; Duszynski, R.J.; Dahlman, K.B.; Zic, J.A.; Zwerner, J.P.; Hucks, D.; Dave, U.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing reveals oncogenic mutations in mycosis fungoides. Blood 2015, 126, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.; Gonzalez-Rincon, J.; Onaindia, A.; Almaraz, C.; Garcia-Diaz, N.; Pisonero, H.; Curiel-Olmo, S.; Gomez, S.; Cereceda, L.; Madureira, R.; et al. Mutated JAK kinases and deregulated STAT activity are potential therapeutic targets in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2015, 100, e450–e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Rabionet, R.; Espinet, B.; Zapata, L.; Puiggros, A.; Melero, C.; Puig, A.; Sarria-Trujillo, Y.; Ossowski, S.; Garcia-Muret, M.P.; et al. Identification of Gene Mutations and Fusion Genes in Patients with Sezary Syndrome. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungewickell, A.; Bhaduri, A.; Rios, E.; Reuter, J.; Lee, C.S.; Mah, A.; Zehnder, A.; Ohgami, R.; Kulkarni, S.; Armstrong, R.; et al. Genomic analysis of mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome identifies recurrent alterations in TNFR2. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaque, J.P.; Gomez-Lopez, G.; Monsalvez, V.; Varela, I.; Martinez, N.; Perez, C.; Dominguez, O.; Grana, O.; Rodriguez-Peralto, J.L.; Rodriguez-Pinilla, S.M.; et al. PLCG1 mutations in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Blood 2014, 123, 2034–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ni, X.; Covington, K.R.; Yang, B.Y.; Shiu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xi, L.; Meng, Q.; Langridge, T.; Drummond, J.; et al. Genomic profiling of Sezary syndrome identifies alterations of key T cell signaling and differentiation genes. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C.; Mondéjar, R.; García-Díaz, N.; Cereceda, L.; León, A.; Montes, S.; Vian, C.D.; Paredes, M.G.P.; González-Morán, A.; de Miguel, V.A.; et al. Advanced-stage mycosis fungoides: Role of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, nuclear factor-κB and nuclear factor of activated T cells pathways. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumeen, S.; Girardi, M. Insights into the Molecular and Cellular Underpinnings of Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2020, 93, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seffens, A.; Herrera, A.; Tegla, C.; Buus, T.B.; Hymes, K.B.; Ødum, N.; Geskin, L.J.; Koralov, S.B. STAT3 Dysregulation in Mature T and NK Cell Lymphomas. Cancers 2019, 11, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.; Kershaw, N.J.; Babon, J.J. The molecular details of cytokine signaling via the JAK/STAT pathway. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1984–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabile, H.; Scarno, G.; Fionda, C.; Gismondi, A.; Santoni, A.; Gadina, M.; Sciume, G. JAK/STAT signaling in regulation of innate lymphoid cells: The gods before the guardians. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 286, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netchiporouk, E.; Litvinov, I.V.; Moreau, L.; Gilbert, M.; Sasseville, D.; Duvic, M. Deregulation in STAT signaling is important for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) pathogenesis and cancer progression. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3331–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Fits, L.; Out-Luiting, J.J.; Tensen, C.P.; Zoutman, W.H.; Vermeer, M.H. Exploring the IL-21-STAT3 axis as therapeutic target for Sezary syndrome. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2639–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Fits, L.; Out-Luiting, J.J.; van Leeuwen, M.A.; Samsom, J.N.; Willemze, R.; Tensen, C.P.; Vermeer, M.H. Autocrine IL-21 stimulation is involved in the maintenance of constitutive STAT3 activation in Sezary syndrome. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Fits, L.; van Kester, M.S.; Qin, Y.; Out-Luiting, J.J.; Smit, F.; Zoutman, W.H.; Willemze, R.; Tensen, C.P.; Vermeer, M.H. MicroRNA-21 expression in CD4+ T cells is regulated by STAT3 and is pathologically involved in Sezary syndrome. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieyra-Garcia, P.A.; Wei, T.; Naym, D.G.; Fredholm, S.; Fink-Puches, R.; Cerroni, L.; Odum, N.; O’Malley, J.T.; Gniadecki, R.; Wolf, P. STAT3/5-Dependent IL9 Overexpression Contributes to Neoplastic Cell Survival in Mycosis Fungoides. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3328–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kester, M.S.; Out-Luiting, J.J.; Borne, P.A.V.; Willemze, R.; Tensen, C.P.; Vermeer, M.H. Cucurbitacin I inhibits Stat3 and induces apoptosis in Sezary cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, K.W.; Kaltoft, K.; Mikkelsen, G.; Nielsen, M.; Zhang, Q.; Geisler, C.; Nissen, M.H.; Röpke, C.; Wasik, M.A.; Ødum, N. Consti-tutive Stat3-activation in Sezary syndrome: Tyr-phostin AG-490 inhibits Stat3-activation, interleu-kin-2 receptor expression and growth of aleukemic Sezary cell line. Leukemia 2001, 15, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.; Kaltoft, K.; Nordahl, M.; Röpke, C.; Geisler, C.; Mustelin, T.; Dobson, P.; Svejgaard, A.; Ødum, N. Constitu-tive activation of a slowly migrating isoform of Stat3 in mycosis fungoides: Tyrphostin AG490inhibits Stat3 activation and growth of MF tumorcell lines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6764–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Hwang, S.T. A Microbiota-Dependent, STAT3-Driven Mouse Model of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, T.; He, W.; Shen, Y.; Liu, X.; Hong, K.; Cao, Q. miR-124 functions as a tumor suppressor in the endometrial carcinoma cell line HEC-1B partly by suppressing STAT3. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 388, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yue, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K. MicroRNA-124 suppresses growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting STAT3. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, G.; Han, Y.; Song, P.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liang, P. miR-124 regulates STAT3-mediated cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis in bladder cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5875–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhao, N.; Hui, L.; Song, M.; Miao, Z.W.; Jiang, X.J. MicroRNA-124-3p inhibits the growth and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by targeting STAT3. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, F.; Sandoval, J.; Diaz-Lagares, A.; Garcia, R.; D’Altri, T.; Gonzalez, J.; Alegre, V.; Servitje, O.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Stefansson, O.A.; et al. Notch1 Pathway Activation Results from the Epigenetic Abrogation of Notch-Related MicroRNAs in Mycosis Fungoides. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 3144–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemze, R.; Cerroni, L.; Kempf, W.; Berti, E.; Facchetti, F.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Jaffe, E.S. The 2018 update of the WHO-EORTC classification for primary cutaneous lymphomas. Blood 2019, 133, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irizarry, R.A.; Bolstad, B.M.; Collin, F.; Cope, L.M.; Hobbs, B.; Speed, T.P. Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe level data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettenhall, J.M.; Smyth, G.K. limmaGUI: A graphical user interface for linear modeling of microarray data. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3705–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, J.; Díaz-Lagares, A.; Salgado, R.; Servitje, O.; Climent, F.; Ortiz-Romero, P.L.; Pérez-Ferriols, A.; Garcia-Muret, M.P.; Estrach, T.; Garcia, M.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiling and DNA methylation signature for deregulated microRNA in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsheshet, Y.; Wildbaum, G.; Levy, E.; Vitenshtein, A.; Akinseye, C.; Griggs, J.; Lira, S.A.; Karin, N. CCR8(+)FOXp3(+) Treg cells as master drivers of immune regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6086–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshii, T.; Kasada, A.; Hatakeyama, T.; Ohtani, M.; Tadokoro, Y.; Naka, K.; Ikenoue, T.; Ikawa, T.; Kawamoto, H.; Fehling, H.J.; et al. Loss of mTOR complex 1 induces developmental blockage in early T-lymphopoiesis and eradicates T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3805–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Z.X.; Jin, M.; Peterson, L.F.; Bernard, D.; Saiya-Cork, K.; Yildiz, M.; Wang, S.; Kaminski, M.S.; Chang, A.E.; Klionsky, D.J.; et al. Recurrent Mutations in the MTOR Regulator RRAGC in Follicular Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5383–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvinov, I.V.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Thibault, P.; Gangar, P.; Moreau, L.; Watters, A.K.; Netchiporouk, E.; Pehr, K.; Prieto, V.G.; Rahme, E.; et al. Gene expression analysis in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas (CTCL) highlights disease heterogeneity and potential diagnostic and prognostic indicators. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1306618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolach, B.; Ash, S.; Gavrieli, R.; Stark, B.; Yaniv, I.; Roos, D. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease and a novel mutation in CYBB: First report. Am. J. Hematol. 2005, 80, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Aggan, H.; Farahat, N.; el Deeb, N.; Zeid, A.; El-Shendidi, A. Peripheral blood and hepatic Toll-like receptor 7 expression and interferon lambda 1 levels in chronic hepatitis C: Relation to virus replication and liver injury. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, A.C.; Aram, B.B.; Jiang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhou, G.; Jefcoate, C.R.; Couroucli, X.I.; Lingappan, K.; Moorthy, B. Mice Lacking the Cytochrome P450 1B1 Gene Are Less Susceptible to Hyperoxic Lung Injury Than Wild Type. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 165, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvaisier, M.; Delneste, Y.; Jeanvoine, H.; Preisser, L.; Blanchard, S.; Garo, E.; Hoppe, E.; Barre, B.; Audran, M.; Bouvard, B.; et al. IL-26 is overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis and induces proinflammatory cytokine production and Th17 cell generation. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurer, L.; Reber, P.; Schaffner, T.; Buchler, M.W.; Buri, C.; Kappeler, A.; Walz, A.; Friess, H.; Mueller, C. Differential expression of chemokines in normal pancreas and in chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, M.; Ni, J.; Feng, P.; Dixit, V.M. IRAK (Pelle) family member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as proximal mediators of IL-1 signaling. Science 1997, 278, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.H.; Liang, Y.Y.; Liang, M.; Zhai, W.; Lin, X. Direct Interaction of c-Myc with Smad2 and Smad3 to Inhibit TGF-beta-Mediated Induction of the CDK Inhibitor p15(Ink4B). Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriely, G.; Wurdinger, T.; Kesari, S.; Esau, C.C.; Burchard, J.; Linsley, P.S.; Krichevsky, A.M. MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 5369–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, V.H.; Clemmensen, O.J.; Nielsen, O.; Wasik, M.; Lovato, P.; Brender, C.; Eriksen, K.W.; Woetmann, A.; Kaestel, C.G.; Nissen, M.H.; et al. In vivo activation of STAT3 in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Evidence for an antiapoptotic function of STAT3. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, I.; Gorunova, L.; Spetalen, S.; Bassarova, A.; Beiske, K.; Micci, F.; Heim, S. Fusion of the genes ataxin 2 like, ATXN2L, and Janus kinase 2, JAK2, in cutaneous CD4 positive T-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 103775–103784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willerslev-Olsen, A.; Krejsgaard, T.; Lindahl, L.M.; Litvinov, I.V.; Fredholm, S.; Petersen, D.L.; Nastasi, C.; Gniadecki, R.; Mongan, N.P.; Sasseville, D.; et al. Staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) stimulates STAT3 activation and IL-17 expression in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2016, 127, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S.; Kitadate, A.; Ito, M.; Abe, F.; Nara, M.; Watanabe, A.; Takahashi, N.; Miyagaki, T.; Sugaya, M.; Tagawa, H. Disruption of CCL20-CCR6 interaction inhibits metastasis of advanced cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13563–13574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsky, W.E.; Choi, J. Genetics of Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma: From Bench to Bedside. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2016, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swider, A.; Siegel, R.; Eskdale, J.; Gallagher, G. Regulation of interferon lambda-1 (IFNL1/IFN-lambda1/IL-29) expression in human colon epithelial cells. Cytokine 2014, 65, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Gu, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, X. IL-26 promotes the proliferation and survival of human gastric cancer cells by regulating the balance of STAT1 and STAT3 activation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kester, M.S.; Tensen, C.P.; Vermeer, M.H.; Dijkman, R.; Mulder, A.A.; Szuhai, K.; Willemze, R.; van Doorn, R. Cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma NOS show distinct chromosomal alterations and differential expression of chemokine receptors and apoptosis regulators. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, S.; Nakatani, Y.; Takezaki, T.; Hide, T.; Yamashita, D.; Ohtsu, N.; Ohnishi, T.; Terasaka, S.; Houkin, K.; Kondo, T. Ceacam1L Modulates STAT3 Signaling to Control the Proliferation of Glioblastoma-Initiating Cells. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4224–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.S.; Shiue, L.H.; Duvic, M.; Pandya, A.; Cruz, P.D., Jr.; Ariizumi, K. Sezary syndrome cells overexpress syndecan-4 bearing distinct heparan sulfate moieties that suppress T-cell activation by binding DC-HIL and trapping TGF-beta on the cell surface. Blood 2011, 117, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Gadalla, R.; El-Ghonaimy, E.A.; Samir, O.; Mohamed, H.T.; Hassan, H.; Greve, B.; El-Shinawi, M.; Mohamed, M.M.; Gotte, M. Syndecan-1 is a novel molecular marker for triple negative inflammatory breast cancer and modulates the cancer stem cell phenotype via the IL-6/STAT3, Notch and EGFR signaling pathways. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.A.; Louissaint, A., Jr.; Wenzel, A.; Yang, J.; Martinez-Escala, M.E.; Moy, A.P.; Morgan, E.A.; Paxton, C.N.; Hong, B.; Andersen, E.F.; et al. Genomic Analyses Identify Recurrent Alterations in Immune Evasion Genes in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma, Leg Type. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, M.H.; van Doorn, R.; Dijkman, R.; Mao, X.; Whittaker, S.; Vader, P.C.v.; Gerritsen, M.J.; Geerts, M.L.; Gellrich, S.; Soderberg, O.; et al. Novel and highly recurrent chromosomal alterations in Sezary syndrome. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2689–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Kim, N.Y.; Yu, L.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, I.K.; Yang, D.H.; Lee, J.J.; Shin, M.H.; Park, K.S.; Choi, J.S.; et al. Polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing genes and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2009, 84, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, R.; Toll, A.; Espinet, B.; Gonzalez-Roca, E.; Barranco, C.L.; Serrano, S.; Sole, F.; Pujol, R.M. Analysis of cytogenetic abnormalities in squamous cell carcinoma by array comparative genomic hybridization. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2008, 99, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Colmenero, L.; González, J.; Sandoval, J.; Guillén, Y.; Diaz-Lagares, A.; Andrades, E.; Iglesias, A.; Nonell, L.; Pujol, R.M.; Bigas, A.; et al. Epigenetic Silencing of Tumor Suppressor miR-124 Directly Supports STAT3 Activation in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Cells 2020, 9, 2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122692
García-Colmenero L, González J, Sandoval J, Guillén Y, Diaz-Lagares A, Andrades E, Iglesias A, Nonell L, Pujol RM, Bigas A, et al. Epigenetic Silencing of Tumor Suppressor miR-124 Directly Supports STAT3 Activation in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Cells. 2020; 9(12):2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122692
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Colmenero, Lidia, Jéssica González, Juan Sandoval, Yolanda Guillén, Angel Diaz-Lagares, Evelyn Andrades, Arnau Iglesias, Lara Nonell, Ramon Maria Pujol, Anna Bigas, and et al. 2020. "Epigenetic Silencing of Tumor Suppressor miR-124 Directly Supports STAT3 Activation in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma" Cells 9, no. 12: 2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122692
APA StyleGarcía-Colmenero, L., González, J., Sandoval, J., Guillén, Y., Diaz-Lagares, A., Andrades, E., Iglesias, A., Nonell, L., Pujol, R. M., Bigas, A., Espinosa, L., & Gallardo, F. (2020). Epigenetic Silencing of Tumor Suppressor miR-124 Directly Supports STAT3 Activation in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Cells, 9(12), 2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122692





