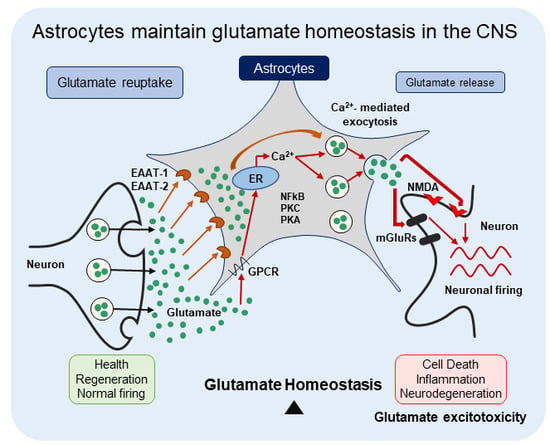
Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and Release
Abstract
1. Introduction
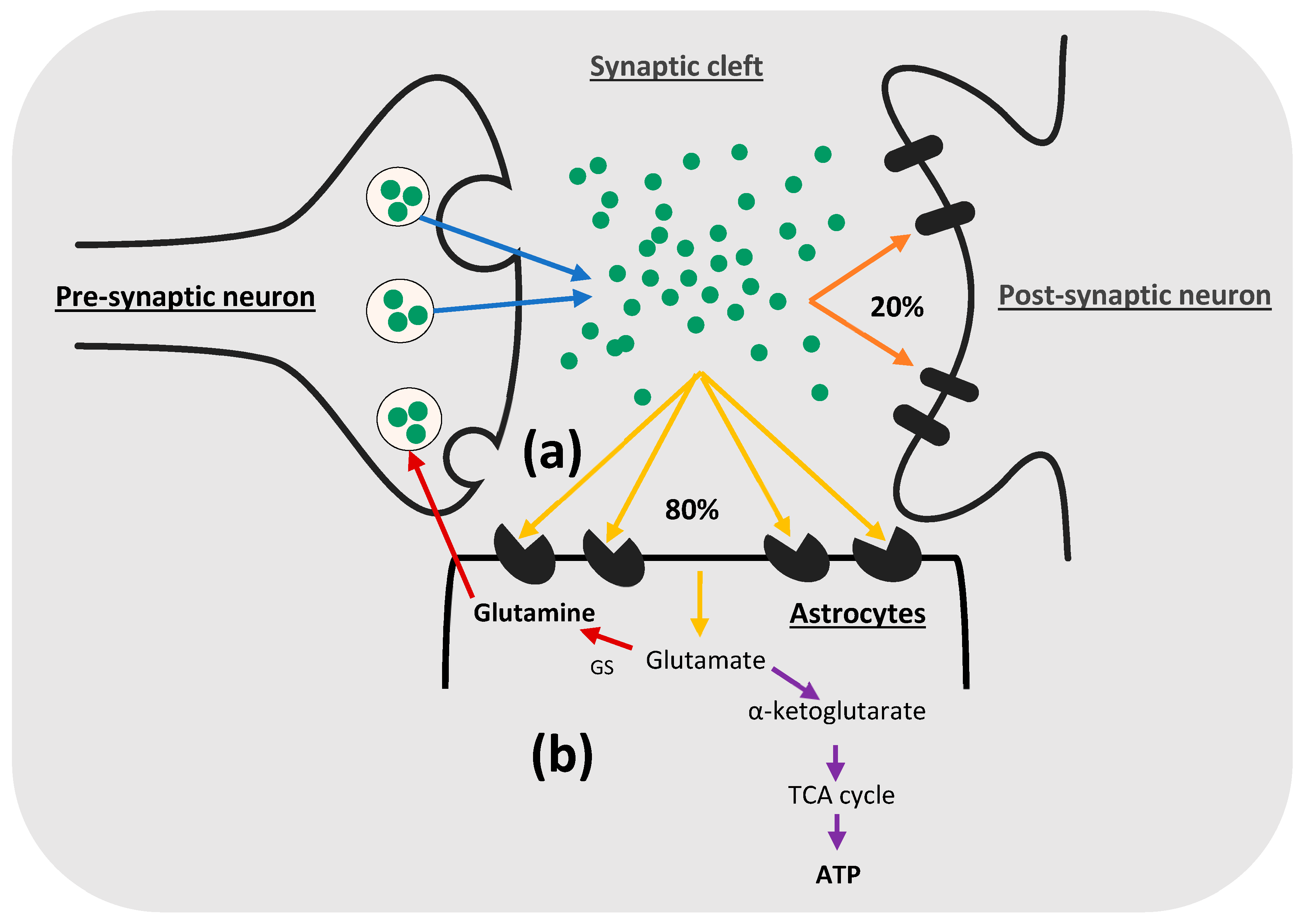
2. Glutamate Uptake in the CNS
2.1. Glutamate Uptake Transporters
2.1.1. Na+-Independent Glutamate Uptake Transporters
2.1.2. Na+-Dependent Glutamate Uptake Transporters
2.2. Expression Profile of EAAT-1 and EAAT-2
2.3. EAAT-2 and EAAT-1 in Astrocytes Play the Major Role in Glutamate Uptake in the CNS
2.4. Mechanism of Glutamate Uptake by EAATs
2.5. Metabolism of Glutamate in Astrocytes
2.6. EAAT-1 and EAAT-2 Regulation of Expression
2.6.1. Transcriptional and Translational Modifications
2.6.2. Post-Translational Modifications and Regulation of the Transporter Activity
3. Glutamate Release by Astrocytes
3.1. Physiological Role of Astroglial Glutamate Release
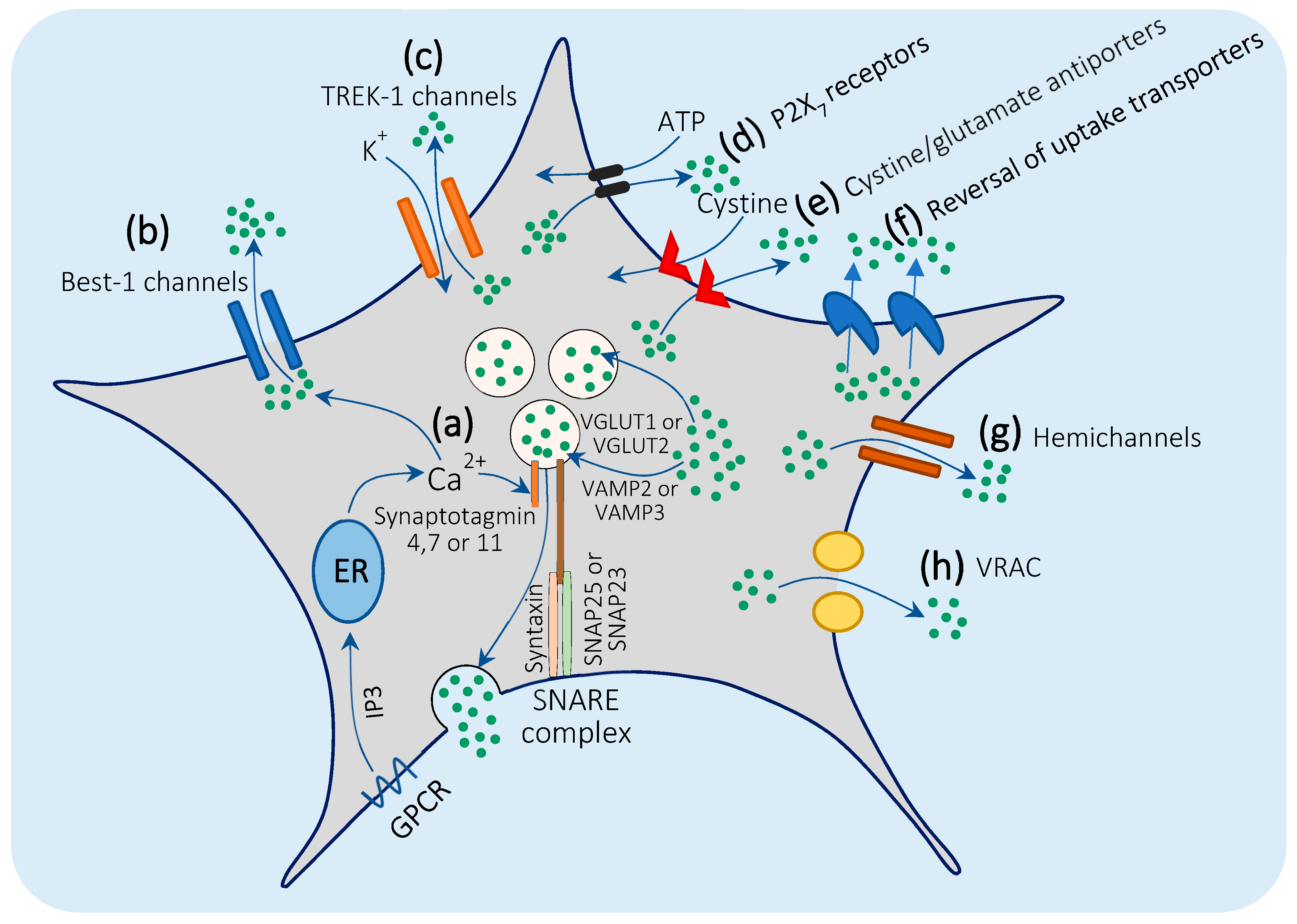
3.2. Mechanisms of Glutamate Release by Astrocytes
3.2.1. Ca2+-Mediated Exocytosis
3.2.2. Bestrophin-1 and TREK-1 Channel-Mediated Glutamate Release.
3.2.3. Glutamate Release through P2X7 Receptors
3.2.4. Cystine/Glutamate Antiporters
3.2.5. Reversal of Glutamate Uptake Transporters
3.2.6. Gap Junction Hemichannels
3.2.7. Volume-Regulated Anion Channels (VRACs)
3.3. An Issue of Debate Shrouds Astroglial Glutamate Release
4. Dysregulation of Astrocytic Glutamate Uptake and/or Release Leads to CNS Disorders
5. Mechanism of Glutamate Excitotoxicity
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, C.; Aloisi, F.; Meinl, E. Astrocytes are active players in cerebral innate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, D.; Johnston, G. Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergebnisse der Physiol. Rev. Physiol. 1974, 69, 97–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonnum, F. Glutamate: A Neurotransmitter in Mammalian Brain. J. Neurochem. 1984, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z. Molecular mechanisms of excitotoxicity and their relevance to pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.M.; Swanson, R.A. Astrocyte glutamate transport: Review of properties, regulation, and physiological functions. Glia 2000. [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, N.B.; Attwell, D. Do astrocytes really exocytose neurotransmitters? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarkey, E.B.; Parpura, V. Mechanisms of glutamate release from astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehre, K.P.; Danbolt, N.C. The number of glutamate transporter subtype molecules at glutamatergic synapses: Chemical and stereological quantification in young adult rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 8751–8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulenburg, V.; Gomeza, J. Neurotransmitter transporters expressed in glial cells as regulators of synapse function. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 63, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, C.R.; Ziemens, D.; Untiet, V.; Fahlke, C. Molecular and cellular physiology of sodium-dependent glutamate transporters. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 136, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Bannai, S. Uptake of glutamate and cysteine in C-6 glioma cells and in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 1990, 55, 2091–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.J.; Chang, Y.F.; Schwarcz, R.; Brookes, N. Characterization of l-alpha-aminoadipic acid transport in cultured rat astrocytes. Brain Res. 1996, 741, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Hashimoto, H.; Matsuda, T.; Baba, A. l-lactate inhibits l-cystine/l-glutamate exchange transport and decreases glutathione content in rat cultured astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 59, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, D.; Fontana, A. Involvement of the cystine transport system xc- in the macrophage-induced glutamate-dependent cytotoxicity to neurons. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 3578–3585. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, S.; Ishita, S.; Sugawara, K.; Mawatari, K. Cystine/glutamate antiporter expression in retinal Müller glial cells: Implications for DL-alpha-aminoadipate toxicity. Neuroscience 1993, 57, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.C.; Rothstein, J.D.; Sontheimer, H. Compromised glutamate transport in human glioma cells: Reduction-mislocalization of sodium-dependent glutamate transporters and enhanced activity of cystine-glutamate exchange. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10767–10777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashidharan, P.; Plaitakis, A. Cloning and characterization of a glutamate transporter cDNA from human cerebellum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1216, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashidharan, P.; Wittenberg, I.; Plaitakis, A. Molecular cloning of human brain glutamate/aspartate transporter II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1191, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, T.; Schulte, S.; Hofmann, K.; Stoffel, W. Structure, expression, and functional analysis of a Na(+)-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter from rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10955–10959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, G.; Danbolt, N.C.; Bjørås, M.; Zhang, Y.; Bendahan, A.; Eide, L.; Koepsell, H.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Seeberg, E.; Kanner, B.I. Cloning and expression of a rat brain l-glutamate transporter. Nature 1992, 360, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, Y.; Hediger, M.A. Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature 1992, 360, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairman, W.A.; Vandenberg, R.J.; Arriza, J.L.; Kavanaught, M.P.; Amara, S.G. An excitatory amino-acid transporter with properties of a ligand-gated chloride channel. Nature 1995, 375, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriza, J.L.; Eliasof, S.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Amara, S.G. Excitatory amino acid transporter 5, a retinal glutamate transporter coupled to a chloride conductance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4155–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gegelashvili, G.; Schousboe, A. High affinity glutamate transporters: Regulation of expression and activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 52, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöckner, U.; Storck, T.; Conradt, M.; Stoffel, W. Functional properties and substrate specificity of the cloned L-glutamate/L-aspartate transporter GLAST-1 from rat brain expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 5759–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerangue, N.; Arriza, J.L.; Amara, S.G.; Kavanaugh, M.P. Differential modulation of human glutamate transporter subtypes by arachidonic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 6433–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriza, J.L.; Fairman, W.A.; Wadiche, J.I.; Murdoch, G.H.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Amara, S.G. Functional comparisons of three glutamate transporter subtypes cloned from human motor cortex. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 5559–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owe, S.G.; Marcaggi, P.; Attwell, D. The ionic stoichiometry of the GLAST glutamate transporter in salamander retinal glia. J. Physiol. 2006, 577, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Yamada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Ikenaka, K.; Wada, K.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y. Glutamate transporter GLAST is expressed in the radial glia-astrocyte lineage of developing mouse spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 9212–9219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Martin, L.; Levey, A.I.; Dykes-Hoberg, M.; Jin, L.; Wu, D.; Nash, N.; Kuncl, R.W. Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron 1994, 13, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, F.A.; Lehre, K.P.; van Lookeren Campagne, M.; Ottersen, O.P.; Danbolt, N.C.; Storm-Mathisen, J. Glutamate transporters in glial plasma membranes: Highly differentiated localizations revealed by quantitative ultrastructural immunocytochemistry. Neuron 1995, 15, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayasu, Y.; Iino, M.; Takatsuru, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Ozawa, S. Functions of glutamate transporters in cerebellar Purkinje cell synapses. Acta Physiol. 2009, 197, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouiche, A.; Rauen, T. Coincidence of L-glutamate/L-aspartate transporter (GLAST) and glutamine synthetase (GS) immunoreactions in retinal glia: Evidence for coupling of GLAST and GS in transmitter clearance. J. Neurosci. Res. 1995, 42, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehre, K.P.; Davanger, S.; Danbolt, N.C. Localization of the glutamate transporter protein GLAST in rat retina. Brain Res. 1997, 744, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, U.V.; Hediger, M.A. Distribution of the glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT-1 in rat circumventricular organs, meninges, and dorsal root ganglia. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 421, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, D.N.; Lehre, K.P. Immunocytochemical Localization of a High-affinity Glutamate-Aspartate Transporter, GLAST, in the Rat and Guinea-pig Cochlea. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takumi, Y.; Matsubara, A.; Danbolt, N.; Laake, J.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Usami, S.; Shinkawa, H.; Ottersen, O. Discrete cellular and subcellular localization of glutamine synthetase and the glutamate transporter GLAST in the rat vestibular end organ. Neuroscience 1997, 79, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowatzki, E.; Cheng, N.; Hiel, H.; Yi, E.; Tanaka, K.; Ellis-Davies, G.C.R.; Rothstein, J.D.; Bergles, D.E. The Glutamate-Aspartate Transporter GLAST Mediates Glutamate Uptake at Inner Hair Cell Afferent Synapses in the Mammalian Cochlea. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7659–7664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.; Asan, E.; Püschel, B.; Kugler, P. Cellular and regional distribution of the glutamate transporter GLAST in the CNS of rats: Nonradioactive in situ hybridization and comparative immunocytochemistry. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Hashimoto, H.; Kitanaka, J.; Sawada, M.; Suzumura, A.; Marunouchi, T.; Baba, A. Expression of glutamate transporters in cultured glial cells. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 188, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domercq, M.; Matute, C. Expression of glutamate transporters in the adult bovine corpus callosum. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1999, 67, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullensvang, K.; Lehre, K.P.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Danbolt, N.C. Differential Developmental Expression of the Two Rat Brain Glutamate Transporter Proteins GLAST and GLT. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, A.E.; Durry, S.; Aida, T.; Stock, M.C.; Rüther, U.; Tanaka, K.; Rose, C.R.; Kafitz, K.W. Laminar and subcellular heterogeneity of GLAST and GLT-1 immunoreactivity in the developing postnatal mouse hippocampus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 204–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, A.; Rothstein, J.D.; Martin, L.J. Glutamate transporter protein subtypes are expressed differentially during rat CNS development. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 8363–8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachez, C.; Danbolt, N.C.; Récasens, M. Transient expression of the glial glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT in hippocampal neurons in primary culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 59, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks-Kayal, A.R.; Munir, M.; Jin, H.; Robinson, M.B. The glutamate transporter, GLT-1, is expressed in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurochem. Int. 1998, 33, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennerick, S.; Dhond, R.P.; Benz, A.; Xu, W.; Rothstein, J.D.; Danbolt, N.C.; Isenberg, K.E.; Zorumski, C.F. Neuronal expression of the glutamate transporter GLT-1 in hippocampal microcultures. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 4490–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Shibata, T.; Nagashima, M.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y. Glutamate transporter GLT-1 is transiently localized on growing axons of the mouse spinal cord before establishing astrocytic expression. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 5706–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Brambrink, A.M.; Lehmann, C.; Portera-Cailliau, C.; Koehler, R.; Rothstein, J.; Traystman, R.J. Hypoxia?ischemia causes abnormalities in glutamate transporters and death of astroglia and neurons in newborn striatum. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 42, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaki, C.; Okada, R.; Mitani, A.; Fukaya, M.; Yamasaki, M.; Fujihara, Y.; Shirakawa, T.; Tanaka, K.; Watanabe, M. Glutamate Transporters Regulate Lesion-Induced Plasticity in the Developing Somatosensory Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 4995–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benediktsson, A.M.; Marrs, G.S.; Tu, J.C.; Worley, P.F.; Rothstein, J.D.; Bergles, D.E.; Dailey, M.E. Neuronal activity regulates glutamate transporter dynamics in developing astrocytes. Glia 2012, 60, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, A.; Barbaresi, P.; Reimer, R.; Edwards, R.; Conti, F. The glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 is localized both in the vicinity of and at distance from axon terminals in the rat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience 2001, 108, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitry-Yamate, C.L.; Vutskits, L.; Rauen, T. Neuronal-induced and glutamate-dependent activation of glial glutamate transporter function. J. Neurochem. 2002, 82, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Sutherland, M.L. Glutamate Transporter Cluster Formation in Astrocytic Processes Regulates Glutamate Uptake Activity. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6301–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Otsubo, Y.; Yatani, Y.; Shirakawa, H.; Kaneko, S. Mechanisms of substrate transport-induced clustering of a glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in astroglial-neuronal cultures. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, R.A.; Liu, J.; Miller, J.W.; Rothstein, J.D.; Farrell, K.; Stein, B.A.; Longuemare, M.C. Neuronal regulation of glutamate transporter subtype expression in astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlag, B.D.; Vondrasek, J.R.; Munir, M.; Kalandadze, A.; Zelenaia, O.A.; Rothstein, J.D.; Robinson, M.B. Regulation of the glial Na+-dependent glutamate transporters by cyclic AMP analogs and neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, P.A.; Aizenman, E. Hundred-fold increase in neuronal vulnerability to glutamate toxicity in astrocyte-poor cultures of rat cerebral cortex. Neurosci. Lett. 1989, 103, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennerick, S.; Zorumski, C.F. Glial contributions to excitatory neurotransmission in cultured hippocampal cells. Nature 1994, 368, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergles, D.E.; Jahr, C.E. Synaptic activation of glutamate transporters in hippocampal astrocytes. Neuron 1997, 19, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Nakamura, T.; Nidaira, T.; Nakamura, K.; Ooashi, N.; Ito, E.; Watase, K.; Tanaka, K.; Wada, K.; Kudo, Y.; et al. Optical detection of synaptically induced glutamate transport in hippocampal slices. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 2580–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.A.; Barbour, B. Currents evoked in Bergmann glial cells by parallel fibre stimulation in rat cerebellar slices. J. Physiol. 1997, 502, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergles, D.E.; Dzubay, J.A.; Jahr, C.E. Glutamate transporter currents in bergmann glial cells follow the time course of extrasynaptic glutamate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14821–14825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergles, D.E.; Jahr, C.E. Glial contribution to glutamate uptake at Schaffer collateral-commissural synapses in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 7709–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Dykes-Hoberg, M.; Pardo, C.A.; Bristol, L.A.; Jin, L.; Kuncl, R.W.; Kanai, Y.; Hediger, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Schielke, J.P.; et al. Knockout of Glutamate Transporters Reveals a Major Role for Astroglial Transport in Excitotoxicity and Clearance of Glutamate. Neuron 1996, 16, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Watase, K.; Manabe, T.; Yamada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Takahashi, K.; Iwama, H.; Nishikawa, T.; Ichihara, N.; Kikuchi, T.; et al. Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science 1997, 276, 1699–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petr, G.T.; Sun, Y.; Frederick, N.M.; Zhou, Y.; Dhamne, S.C.; Hameed, M.Q.; Miranda, C.; Bedoya, E.A.; Fischer, K.D.; Armsen, W.; et al. Conditional Deletion of the Glutamate Transporter GLT-1 Reveals That Astrocytic GLT-1 Protects against Fatal Epilepsy While Neuronal GLT-1 Contributes Significantly to Glutamate Uptake into Synaptosomes. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 5187–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watase, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Kano, M.; Yamada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Inoue, Y.; Okuyama, S.; Sakagawa, T.; Ogawa, S.; Kawashima, N.; et al. Motor discoordination and increased susceptibility to cerebellar injury in GLAST mutant mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peghini, P.; Janzen, J.; Stoffel, W. Glutamate transporter EAAC-1-deficient mice develop dicarboxylic aminoaciduria and behavioral abnormalities but no neurodegeneration. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 3822–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Bergles, D.E. Glutamate transporters bring competition to the synapse. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2004, 14, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.B.; Dowling, J.E. A glutamate-activated chloride current in cone-driven ON bipolar cells of the white perch retina. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 3852–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otis, T.S.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Jahr, C.E. Postsynaptic glutamate transport at the climbing fiber-Purkinje cell synapse. Science 1997, 277, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.R.; Ransom, B.R. Intracellular sodium homeostasis in rat hippocampal astrocytes. J. Physiol. 1996, 491, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, I.A.; Deas, J.; Erecińska, M. Ion homeostasis in brain cells: Differences in intracellular ion responses to energy limitation between cultured neurons and glial cells. Neuroscience 1997, 78, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.R.; Waxman, S.G.; Ransom, B.R. Effects of glucose deprivation, chemical hypoxia, and simulated ischemia on Na+ homeostasis in rat spinal cord astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3554–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuemare, M.C.; Rose, C.R.; Farrell, K.; Ransom, B.R.; Waxman, S.G.; Swanson, R.A. K(+)-induced reversal of astrocyte glutamate uptake is limited by compensatory changes in intracellular Na+. Neuroscience 1999, 93, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.C.; Schousboe, A.; Hertz, L. Metabolic fate of 14C-labeled glutamate in astrocytes in primary cultures. J. Neurochem. 1982, 39, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinelli, S.E.; Nicklas, W.J. Glutamate metabolism in rat cortical astrocyte cultures. J. Neurochem. 1992, 58, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.C.; Sonnewald, U.; Huang, X.; Stevenson, J.; Zielke, H.R. Exogenous glutamate concentration regulates the metabolic fate of glutamate in astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnewald, U.; Westergaard, N.; Schousboe, A. Glutamate transport and metabolism in astrocytes. Glia 1997, 21, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, L.; Dringen, R.; Schousboe, A.; Robinson, S.R. Astrocytes: Glutamate producers for neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 57, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergles, D.E.; Diamond, J.S.; Jahr, C.E. Clearance of glutamate inside the synapse and beyond. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1999, 9, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, L.K.; Schousboe, A.; Waagepetersen, H.S. The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: Aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schousboe, A.; Sarup, A.; Bak, L.K.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Larsson, O.M. Role of astrocytic transport processes in glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, H.; Drejer, J.; Schousboe, A.; Diemer, N.H. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J. Neurochem. 1984, 43, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erecińska, M.; Silver, I.A. Metabolism and role of glutamate in mammalian brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 1990, 35, 245–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerangue, N.; Kavanaugh, M.P. Flux coupling in a neuronal glutamate transporter. Nature 1996, 383, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, L.M.; Warr, O.; Attwell, D. Stoichiometry of the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 expressed inducibly in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line selected for low endogenous Na+-dependent glutamate uptake. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 9620–9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, C.L.; Kimelberg, H.K. Excitatory amino acids directly depolarize rat brain astrocytes in primary culture. Nature 1984, 311, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadiche, J.I.; Amara, S.G.; Kavanaugh, M.P. Ion fluxes associated with excitatory amino acid transport. Neuron 1995, 15, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairman, W.A.; Sonders, M.S.; Murdoch, G.H.; Amara, S.G. Arachidonic acid elicits a substrate-gated proton current associated with the glutamate transporter EAAT4. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untiet, V.; Kovermann, P.; Gerkau, N.J.; Gensch, T.; Rose, C.R.; Fahlke, C. Glutamate transporter-associated anion channels adjust intracellular chloride concentrations during glial maturation. Glia 2017, 65, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibson, N.R.; Dhankhar, A.; Mason, G.F.; Rothman, D.L.; Behar, K.L.; Shulman, R.G. Stoichiometric coupling of brain glucose metabolism and glutamatergic neuronal activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, L.; Magistretti, P.J. Glutamate uptake stimulates Na+,K+-ATPase activity in astrocytes via activation of a distinct subunit highly sensitive to ouabain. J. Neurochem. 1997, 69, 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatton, J.-Y.; Marquet, P.; Magistretti, P.J. A quantitative analysis of l -glutamate-regulated Na + dynamics in mouse cortical astrocytes: Implications for cellular bioenergetics. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 3843–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, L.; Magistretti, P.J. Glutamate uptake into astrocytes stimulates aerobic glycolysis: A mechanism coupling neuronal activity to glucose utilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10625–10629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardinelli, Y.; Magistretti, P.J.; Chatton, J.-Y. Astrocytes generate Na+-mediated metabolic waves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14937–14942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistretti, P.J.; Chatton, J.-Y. Relationship between l-glutamate-regulated intracellular Na+ dynamics and ATP hydrolysis in astrocytes. J. Neural Transm. 2005, 112, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaman, I.; Bélanger, M.; Magistretti, P.J. Astrocyte–neuron metabolic relationships: For better and for worse. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatton, J.-Y.; Magistretti, P.J.; Barros, L.F. Sodium signaling and astrocyte energy metabolism. Glia 2016, 64, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waniewski, R.A.; Martin, D.L. Exogenous glutamate is metabolized to glutamine and exported by rat primary astrocyte cultures. J. Neurochem. 1986, 47, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Hernandez, A.; Bell, K.P.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine synthetase: Glial localization in brain. Science 1977, 195, 1356–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammer, W. Glutamine synthetase in the central nervous system is not confined to astrocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 1990, 26, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, F.A.; Reimer, R.J.; Krizaj, D.; Barber, D.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Copenhagen, D.R.; Edwards, R.H. Molecular Analysis of System N Suggests Novel Physiological Roles in Nitrogen Metabolism and Synaptic Transmission. Cell 1999, 99, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröer, S.; Brookes, N. Transfer of glutamine between astrocytes and neurons. J. Neurochem. 2001, 77, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröer, A.; Albers, A.; Setiawan, I.; Edwards, R.H.; Chaudhry, F.A.; Lang, F.; Wagner, C.A.; Bröer, S. Regulation of the glutamine transporter SN1 by extracellular pH and intracellular sodium ions. J. Physiol. 2002, 539, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.J.; McDonald, J.M.; Gelbard, A.S.; Gledhill, R.F.; Duffy, T.E. The metabolic fate of 13N-labeled ammonia in rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 4982–4992. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, A.J.L.; Lai, J.C.K. Cerebral ammonia metabolism in normal and hyperammonemic rats. Neurochem. Pathol. 1987, 6, 67–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcaggi, P.; Coles, J.A. Ammonium in nervous tissue: Transport across cell membranes, fluxes from neurons to glial cells, and role in signalling. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 64, 157–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, J.; Zielińska, M.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine as a mediator of ammonia neurotoxicity: A critical appraisal. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama Rao, K.V.; Jayakumar, A.R.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine in the pathogenesis of acute hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.C.; Stridh, M.H.; McNair, L.F.; Sonnewald, U.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Schousboe, A. Glutamate oxidation in astrocytes: Roles of glutamate dehydrogenase and aminotransferases. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 94, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.C. Glutamate Pays Its Own Way in Astrocytes. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2013, 4, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi-Castañeda, D.; Suárez-Pozos, E.; Ortega, A. Regulation of Glutamate Transporter Expression in Glial Cells. In Advances in Neurobiology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 16, pp. 199–224. [Google Scholar]
- Sattler, R.; Rothstein, J.D. Regulation and dysregulation of glutamate transporters. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 277–303. [Google Scholar]
- Gegelashvili, G.; Civenni, G.; Racagni, G.; Danbolt, N.C.; Schousboe, I.; Schousboe, A. Glutamate receptor agonists up-regulate glutamate transporter GLAST in astrocytes. Neuroreport 1996, 8, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Anderson, C.M.; Stein, B.A.; Swanson, R.A. Glutamate induces rapid upregulation of astrocyte glutamate transport and cell-surface expression of GLAST. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10193–10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gegelashvili, G.; Dehnes, Y.; Danbolt, N.C.; Schousboe, A. The high-affinity glutamate transporters GLT1, GLAST, and EAAT4 are regulated via different signalling mechanisms. Neurochem. Int. 2000, 37, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronica, E.; Gorter, J.A.; Ijlst-Keizers, H.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Yankaya, B.; Leenstra, S.; Troost, D. Expression and functional role of mGluR3 and mGluR5 in human astrocytes and glioma cells: Opposite regulation of glutamate transporter proteins. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 2106–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; You, J.-R.; Wei, K.-C.; Gean, P.-W. Stimulating ERK/PI3K/NFκB signaling pathways upon activation of mGluR2/3 restores OGD-induced impairment in glutamate clearance in astrocytes. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 39, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Bayghen, E.; Espinoza-Rojo, M.; Ortega, A. Glutamate down-regulates GLAST expression through AMPA receptors in Bergmann glial cells. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 115, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bayghen, E.; Ortega, A. Glutamate-dependent transcriptional regulation of GLAST: Role of PKC. J. Neurochem. 2004, 91, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apricò, K.; Beart, P.M.; Crawford, D.; O’Shea, R.D. Binding and transport of [3H](2S,4R)- 4-methylglutamate, a new ligand for glutamate transporters, demonstrate labeling of EAAT1 in cultured murine astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 75, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, M.; Lane, M.; Krizman, E.; Sattler, R.; Rothstein, J.D.; Robinson, M.B. The transcription factor Pax6 contributes to the induction of GLT-1 expression in astrocytes through an interaction with a distal enhancer element. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenaia, O.; Schlag, B.D.; Gochenauer, G.E.; Ganel, R.; Song, W.; Beesley, J.S.; Grinspan, J.B.; Rothstein, J.D.; Robinson, M.B. Epidermal growth factor receptor agonists increase expression of glutamate transporter GLT-1 in astrocytes through pathways dependent on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and transcription factor NF-kappaB. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiel, M.; Maucher, T.; Rozyczka, J.; Bayatti, N.; Engele, J. Regulation of glial glutamate transporter expression by growth factors. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 183, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiel, M.; Engele, J. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP), a neuron-derived peptide regulating glial glutamate transport and metabolism. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3596–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Ikegaya, Y.; Matsuura, S.; Kanai, Y.; Endou, H.; Matsuki, N. Transient upregulation of the glial glutamate transporter GLAST in response to fibroblast growth factor, insulin-like growth factor and epidermal growth factor in cultured astrocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3717–3725. [Google Scholar]
- Bonde, C.; Sarup, A.; Schousboe, A.; Gegelashvili, G.; Noraberg, J.; Zimmer, J. GDNF pre-treatment aggravates neuronal cell loss in oxygen-glucose deprived hippocampal slice cultures: A possible effect of glutamate transporter up-regulation. Neurochem. Int. 2003, 43, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, P.; Webb, A.; Zerguine, A.; Choi, J.; Son, D.-S.; Lee, E. Mechanism of raloxifene-induced upregulation of glutamate transporters in rat primary astrocytes. Glia 2014, 62, 1270–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-S.Y.; Sidoryk, M.; Jiang, H.; Yin, Z.; Aschner, M. Estrogen and tamoxifen reverse manganese-induced glutamate transporter impairment in astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, P.; Webb, A.; Smith, K.; Lee, K.; Son, D.-S.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. cAMP Response Element-binding Protein (CREB) and Nuclear Factor κB Mediate the Tamoxifen-induced Up-regulation of Glutamate Transporter 1 (GLT-1) in Rat Astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 28975–28986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Sidoryk-Wêgrzynowicz, M.; Wang, N.; Webb, A.; Son, D.-S.; Lee, K.; Aschner, M. GPR30 Regulates Glutamate Transporter GLT-1 Expression in Rat Primary Astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26817–26828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zschocke, J.; Bayatti, N.; Clement, A.M.; Witan, H.; Figiel, M.; Engele, J.; Behl, C. Differential Promotion of Glutamate Transporter Expression and Function by Glucocorticoids in Astrocytes from Various Brain Regions. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 34924–34932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poblete-Naredo, I.; Angulo, C.; Hernández-Kelly, L.; López-Bayghen, E.; Aguilera, J.; Ortega, A. Insulin-dependent regulation of GLAST/EAAT1 in Bergmann glial cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 451, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizzo, M.E.; Frizzo, J.K.; Amadio, S.; Rodrigues, J.M.; Perry, M.L.; Bernardi, G.; Volonté, C. Extracellular adenosine triphosphate induces glutamate transporter-1 expression in hippocampus. Hippocampus 2007, 17, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lee, M.R.; Kim, T.; Johng, S.; Rohrback, S.; Kang, N.; Choi, D.-S. Regulation of ethanol-sensitive EAAT2 expression through adenosine A1 receptor in astrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 406, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.-W.; Nguyen, K.T.D.; Pow, D.V.; Knight, T.; Buljan, V.; Bennett, M.R.; Balcar, V.J. Distribution of Glutamate Transporter GLAST in Membranes of Cultured Astrocytes in the Presence of Glutamate Transport Substrates and ATP. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozyczka, J.; Figiel, M.; Engele, J. Endothelins negatively regulate glial glutamate transporter expression. Brain Pathol. 2004, 14, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Grammas, P. Endothelin-1 is Elevated in Alzheimer’s Disease Brain Microvessels and is Neuroprotective. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 21, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, V.I.; Rozanski, V.E.; Beyer, C.; Küppers, E. Dopamine Regulates the Expression of the Glutamate Transporter GLT1 but Not GLAST in Developing Striatal Astrocytes. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2009, 39, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.-J.; Her, L.-S.; Liaw, H.-J.; Chen, M.-C.; Tzeng, S.-F. Retinoic acid mediates the expression of glutamate transporter-1 in rat astrocytes through genomic RXR action and non-genomic protein kinase C signaling pathway. J. Neurochem. 2012, 121, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, T.; Magnus, T.; Jung, S. Autoantigen specific T cells inhibit glutamate uptake in astrocytes by decreasing expression of astrocytic glutamate transporter GLAST: A mechanism mediated by tumor necrosis factor-α. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1878–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitcheran, R.; Gupta, P.; Fisher, P.B.; Baldwin, A.S. Positive and negative regulation of EAAT2 by NF-κB: A role for N-myc in TNFα-controlled repression. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, P.; Webb, A.; Smith, K.; Johnson, J.; Lee, K.; Son, D.-S.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. Yin Yang 1 Is a Repressor of Glutamate Transporter EAAT2, and It Mediates Manganese-Induced Decrease of EAAT2 Expression in Astrocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torp, R.; Lekieffre, D.; Levy, L.M.; Haug, F.M.; Danbolt, N.C.; Meldrum, B.S.; Ottersen, O.P. Reduced postischemic expression of a glial glutamate transporter, GLT1, in the rat hippocampus. Exp. Brain Res. 1995, 103, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, M.; Li, P.; Mangin, J.-M.; Huntsman, M.; Gallo, V. Chronic Perinatal Hypoxia Reduces Glutamate-Aspartate Transporter Function in Astrocytes through the Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 17864–17871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Guo, B.; Liu, G.; Wang, B.; Wang, W.; Gao, G.; Qin, H.; Wu, S. FGF2 alleviates PTSD symptoms in rats by restoring GLAST function in astrocytes via the JAK/STAT pathway. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradt, M.; Storck, T.; Stoffel, W. Localization of N-glycosylation sites and functional role of the carbohydrate units of GLAST-1, a cloned rat brain L-glutamate/L-aspartate transporter. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 229, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raunser, S.; Haase, W.; Bostina, M.; Parcej, D.N.; Kühlbrandt, W. High-yield Expression, Reconstitution and Structure of the Recombinant, Fully Functional Glutamate Transporter GLT-1 from Rattus norvegicus. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 351, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butchbach, M.E.R.; Tian, G.; Guo, H.; Lin, C.G. Association of Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters, Especially EAAT2, with Cholesterol-rich Lipid Raft Microdomains. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 34388–34396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado, M.; Bendahan, A.; Zafra, F.; Danbolt, N.C.; Aragón, C.; Giménez, C.; Kanner, B.I. Phosphorylation and modulation of brain glutamate transporters by protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 27313–27317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Zelenaia, O.; Correale, D.; Rothstein, J.D.; Robinson, M.B. Expression of the GLT-1 subtype of Na+-dependent glutamate transporter: Pharmacological characterization and lack of regulation by protein kinase C. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalandadze, A.; Wu, Y.; Robinson, M.B. Protein Kinase C Activation Decreases Cell Surface Expression of the GLT-1 Subtype of Glutamate Transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 45741–45750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.I.; Susarla, B.T.S.; Robinson, M.B. Evidence that protein kinase Cα interacts with and regulates the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1. J. Neurochem. 2005, 94, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GUILLET, B.; VELLY, L.; CANOLLE, B.; MASMEJEAN, F.; NIEOULLON, A.; PISANO, P. Differential regulation by protein kinases of activity and cell surface expression of glutamate transporters in neuron-enriched cultures. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 46, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conradt, M.; Stoffel, W. Inhibition of the high-affinity brain glutamate transporter GLAST-1 via direct phosphorylation. J. Neurochem. 1997, 68, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.I.; López-Colom, A.M.; Ortega, A. Sodium-dependent glutamate transport in Müller glial cells: Regulation by phorbol esters. Brain Res. 1999, 831, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.I.; Ortega, A. Regulation of the Na+-dependent high affinity glutamate/aspartate transporter in cultured Bergmann glia by phorbol esters. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 50, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susarla, B.T.S.; Seal, R.P.; Zelenaia, O.; Watson, D.J.; Wolfe, J.H.; Amara, S.G.; Robinson, M.B. Differential regulation of GLAST immunoreactivity and activity by protein kinase C: Evidence for modification of amino and carboxyl termini. J. Neurochem. 2004, 91, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundy, D.F.; McBean, G.J. Pre-incubation of synaptosomes with arachidonic acid potentiates inhibition of [3H]D-aspartate transport. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 291, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, C.; Mennini, T. Arachidonic Acid Inhibits3h-Glutamate Uptake with Different Potencies in Rodent Central Nervous System Regions Expressing Different Transporter Subtypes. Pharmacol. Res. 1997, 35, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volterra, A.; Trotti, D.; Cassutti, P.; Tromba, C.; Salvaggio, A.; Melcangi, R.C.; Racagni, G. High sensitivity of glutamate uptake to extracellular free arachidonic acid levels in rat cortical synaptosomes and astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 1992, 59, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masliah, E.; Hansen, L.; Alford, M.; Deteresa, R.; Mallory, M. Deficient glutamate tranport is associated with neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 40, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegaya, Y.; Matsuura, S.; Ueno, S.; Baba, A.; Yamada, M.K.; Nishiyama, N.; Matsuki, N. β-Amyloid Enhances Glial Glutamate Uptake Activity and Attenuates Synaptic Efficacy. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32180–32186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volterra, A.; Trotti, D.; Floridi, S.; Racagni, G. Reactive oxygen species inhibit high-affinity glutamate uptake: Molecular mechanism and neuropathological implications. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 738, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, O.; Horn, T.F.; Yu, N.; Gruol, D.L.; Bloom, F.E. Inhibition of astrocyte glutamate uptake by reactive oxygen species: Role of antioxidant enzymes. Mol. Med. 1997, 3, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotti, D.; Rizzini, B.L.; Rossi, D.; Haugeto, O.; Racagni, G.; Danbolt, N.C.; Volterra, A. Neuronal and glial glutamate transporters possess an SH-based redox regulatory mechanism. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, D.J.; Dixit, S.; Warner, T.A.; Kennard, J.A.; Scharf, D.A.; Kessler, E.S.; Moore, L.M.; Consoli, D.C.; Bown, C.W.; Eugene, A.J.; et al. Altered glutamate clearance in ascorbate deficient mice increases seizure susceptibility and contributes to cognitive impairment in APP/PSEN1 mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 71, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornell-Bell, A.H.; Finkbeiner, S.M.; Cooper, M.S.; Smith, S.J. Glutamate induces calcium waves in cultured astrocytes: Long-range glial signaling. Science 1990, 247, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpura, V.; Basarsky, T.A.; Liu, F.; Jeftinija, K.; Jeftinija, S.; Haydon, P.G. Glutamate-mediated astrocyte–neuron signalling. Nature 1994, 369, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedergaard, M. Direct signaling from astrocytes to neurons in cultures of mammalian brain cells. Science 1994, 263, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasti, L.; Volterra, A.; Pozzan, T.; Carmignoto, G. Intracellular calcium oscillations in astrocytes: A highly plastic, bidirectional form of communication between neurons and astrocytes in situ. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 7817–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezzi, P.; Carmignoto, G.; Pasti, L.; Vesce, S.; Rossi, D.; Rizzini, B.L.; Pozzan, T.; Volterra, A. Prostaglandins stimulate calcium-dependent glutamate release in astrocytes. Nature 1998, 391, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangršič, T.; Potokar, M.; Stenovec, M.; Kreft, M.; Fabbretti, E.; Nistri, A.; Pryazhnikov, E.; Khiroug, L.; Giniatullin, R.; Zorec, R. Exocytotic Release of ATP from Cultured Astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 28749–28758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Ye, C.; Ge, W.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, C.; Poo, M.; Duan, S. ATP released by astrocytes mediates glutamatergic activity-dependent heterosynaptic suppression. Neuron 2003, 40, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Meur, K.; Mendizabal-Zubiaga, J.; Grandes, P.; Audinat, E. GABA release by hippocampal astrocytes. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; McGeer, E.G.; McGeer, P.L. Mechanisms of GABA release from human astrocytes. Glia 2011, 59, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.-E.; Jo, S.; Woo, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, T.; Kim, D.; Lee, C.J. The amount of astrocytic GABA positively correlates with the degree of tonic inhibition in hippocampal CA1 and cerebellum. Mol. Brain 2011, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothet, J.-P.; Pollegioni, L.; Ouanounou, G.; Martineau, M.; Fossier, P.; Baux, G. Glutamate receptor activation triggers a calcium-dependent and SNARE protein-dependent release of the gliotransmitter D-serine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5606–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Kamiya, T.; Tsuboi, T. Gliotransmitter Release from Astrocytes: Functional, Developmental, and Pathological Implications in the Brain. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parri, H.R.; Gould, T.M.; Crunelli, V. Spontaneous astrocytic Ca2+ oscillations in situ drive NMDAR-mediated neuronal excitation. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellin, T.; Pascual, O.; Gobbo, S.; Pozzan, T.; Haydon, P.G.; Carmignoto, G. Neuronal Synchrony Mediated by Astrocytic Glutamate through Activation of Extrasynaptic NMDA Receptors. Neuron 2004, 43, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, M.C.; Kozlov, A.S.; Charpak, S.; Audinat, E. Glutamate Released from Glial Cells Synchronizes Neuronal Activity in the Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6920–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ascenzo, M.; Fellin, T.; Terunuma, M.; Revilla-Sanchez, R.; Meaney, D.F.; Auberson, Y.P.; Moss, S.J.; Haydon, P.G. mGluR5 stimulates gliotransmission in the nucleus accumbens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Jiang, L.; Goldman, S.A.; Nedergaard, M. Astrocyte-mediated potentiation of inhibitory synaptic transmission. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Blomstrand, F.; Hanse, E. Astrocytes play a critical role in transient heterosynaptic depression in the rat hippocampal CA1 region. J. Physiol. 2007, 585, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, G.; Araque, A. Properties of Synaptically Evoked Astrocyte Calcium Signal Reveal Synaptic Information Processing by Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2192–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araque, A.; Sanzgiri, R.P.; Parpura, V.; Haydon, P.G. Calcium elevation in astrocytes causes an NMDA receptor-dependent increase in the frequency of miniature synaptic currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 6822–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiacco, T.A.; McCarthy, K.D. Intracellular Astrocyte Calcium Waves In Situ Increase the Frequency of Spontaneous AMPA Receptor Currents in CA1 Pyramidal Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourdain, P.; Bergersen, L.H.; Bhaukaurally, K.; Bezzi, P.; Santello, M.; Domercq, M.; Matute, C.; Tonello, F.; Gundersen, V.; Volterra, A. Glutamate exocytosis from astrocytes controls synaptic strength. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, G.; Araque, A. Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses. Science 2007, 317, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezzi, P.; Gundersen, V.; Galbete, J.L.; Seifert, G.; Steinhäuser, C.; Pilati, E.; Volterra, A. Astrocytes contain a vesicular compartment that is competent for regulated exocytosis of glutamate. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, L.-H.; Zhou, Z. “Kiss-and-Run” Glutamate Secretion in Cultured and Freshly Isolated Rat Hippocampal Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 9236–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montana, V.; Ni, Y.; Sunjara, V.; Hua, X.; Parpura, V. Vesicular Glutamate Transporter-Dependent Glutamate Release from Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2633–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasti, L.; Zonta, M.; Pozzan, T.; Vicini, S.; Carmignoto, G. Cytosolic calcium oscillations in astrocytes may regulate exocytotic release of glutamate. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque, A.; Li, N.; Doyle, R.T.; Haydon, P.G. SNARE protein-dependent glutamate release from astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpura, V.; Zorec, R. Gliotransmission: Exocytotic release from astrocytes. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 63, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, R.; Scheller, R.H. SNAREs—Engines for membrane fusion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpura, V.; Liu, F.; Brethorst, S.; Jeftinija, K.; Jeftinija, S.; Haydon, P.G. Alpha-latrotoxin stimulates glutamate release from cortical astrocytes in cell culture. FEBS Lett. 1995, 360, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maienschein, V.; Marxen, M.; Volknandt, W.; Zimmermann, H. A plethora of presynaptic proteins associated with ATP-storing organelles in cultured astrocytes. Glia 1999, 26, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, R.; Perraut, M.; Chasserot-Golaz, S.; Galli, T.; Aunis, D.; Langley, K.; Grant, N.J. Cultured glial cells express the SNAP-25 analogue SNAP-23. Glia 1999, 27, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fukuda, M.; Van Bockstaele, E.; Pascual, O.; Haydon, P.G. Synaptotagmin IV regulates glial glutamate release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9441–9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, I.M.; Ranjan, R.; Schwarz, T.L. Synaptotagmins I and IV promote transmitter release independently of Ca2+ binding in the C2A domain. Nature 2002, 418, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-T.; Lu, J.-C.; Bai, J.; Chang, P.Y.; Martin, T.F.J.; Chapman, E.R.; Jackson, M.B. Different domains of synaptotagmin control the choice between kiss-and-run and full fusion. Nature 2003, 424, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, S.; Han, W.; Butz, S.; Liu, X.; Fernández-Chacón, R.; Lao, Y.; Südhof, T.C. Synaptotagmin VII as a plasma membrane Ca(2+) sensor in exocytosis. Neuron 2001, 30, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpura, V.; Haydon, P.G. Physiological astrocytic calcium levels stimulate glutamate release to modulate adjacent neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8629–8634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, R.C.; Parpura, V. Mitochondria modulate Ca2+-dependent glutamate release from rat cortical astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9682–9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Malarkey, E.B.; Sunjara, V.; Rosenwald, S.E.; Li, W.; Parpura, V. Ca2+-dependent glutamate release involves two classes of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ stores in astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 76, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, D.H.; Han, K.-S.; Shim, J.W.; Yoon, B.-E.; Kim, E.; Bae, J.Y.; Oh, S.-J.; Hwang, E.M.; Marmorstein, A.D.; Bae, Y.C.; et al. TREK-1 and Best1 Channels Mediate Fast and Slow Glutamate Release in Astrocytes upon GPCR Activation. Cell 2012, 151, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.-S.; Woo, J.; Park, H.; Yoon, B.-J.; Choi, S.; Lee, C.J. Channel-mediated astrocytic glutamate release via Bestrophin-1 targets synaptic NMDARs. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Prussia, A.; Yu, K.; Cui, Y.; Hartzell, H.C. Regulation of Bestrophin Cl Channels by Calcium: Role of the C Terminus. J. Gen. Physiol. 2008, 132, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virginio, C.; MacKenzie, A.; Rassendren, F.A.; North, R.A.; Surprenant, A. Pore dilation of neuronal P2X receptor channels. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Anderson, C.M.; Keung, E.C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Swanson, R.A. P2X7 receptor-mediated release of excitatory amino acids from astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warr, O.; Takahashi, M.; Attwell, D. Modulation of extracellular glutamate concentration in rat brain slices by cystine-glutamate exchange. J. Physiol. 1999, 514 Pt 3, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.A.; Xi, Z.-X.; Shen, H.; Swanson, C.J.; Kalivas, P.W. The origin and neuronal function of in vivo nonsynaptic glutamate. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9134–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, M.M.; McFarland, K.; Melendez, R.I.; Kalivas, P.W.; Seamans, J.K. Cystine/glutamate exchange regulates metabotropic glutamate receptor presynaptic inhibition of excitatory transmission and vulnerability to cocaine seeking. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6389–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezzi, P.; Domercq, M.; Brambilla, L.; Galli, R.; Schols, D.; De Clercq, E.; Vescovi, A.; Bagetta, G.; Kollias, G.; Meldolesi, J.; et al. CXCR4-activated astrocyte glutamate release via TNFα: Amplification by microglia triggers neurotoxicity. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.J.; Oshima, T.; Attwell, D. Glutamate release in severe brain ischaemia is mainly by reversed uptake. Nature 2000, 403, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.-C.; Wyeth, M.S.; Baltan-Tekkok, S.; Ransom, B.R. Functional hemichannels in astrocytes: A novel mechanism of glutamate release. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 3588–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.J.; Macvicar, B.A. Connexin and pannexin hemichannels of neurons and astrocytes. Channels (Austin) 2008, 2, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimelberg, H.K.; Goderie, S.K.; Higman, S.; Pang, S.; Waniewski, R.A. Swelling-induced release of glutamate, aspartate, and taurine from astrocyte cultures. J. Neurosci. 1990, 10, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, Y.; Feustel, P.J.; Keller, R.W.; Tranmer, B.I.; Kimelberg, H.K. Inhibition of ischemia-induced glutamate release in rat striatum by dihydrokinate and an anion channel blocker. Stroke 1999, 30, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, E.R.; Kimelberg, H.K. Role of calcium in astrocyte volume regulation and in the release of ions and amino acids. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongin, A.A.; Kimelberg, H.K. ATP regulates anion channel-mediated organic osmolyte release from cultured rat astrocytes via multiple Ca2+-sensitive mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2005, 288, C204–C213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, T.; Kang, J.; Jaiswal, J.K.; Simon, S.M.; Lin, J.H.-C.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Dienel, G.; Zielke, H.R.; et al. Receptor-mediated glutamate release from volume sensitive channels in astrocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16466–16471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiacco, T.A.; McCarthy, K.D. Multiple Lines of Evidence Indicate That Gliotransmission Does Not Occur under Physiological Conditions. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlender, D.A.; Savtchouk, I.; Volterra, A. What do we know about gliotransmitter release from astrocytes? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramham, C.R.; Torp, R.; Zhang, N.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Ottersen, O.P. Distribution of glutamate-like immunoreactivity in excitatory hippocampal pathways: A semiquantitative electron microscopic study in rats. Neuroscience 1990, 39, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barres, B.A. The Mystery and Magic of Glia: A Perspective on Their Roles in Health and Disease. Neuron 2008, 60, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Landeghem, F.K.H.; Weiss, T.; Oehmichen, M.; Deimling, A. Von Decreased Expression of Glutamate Transporters in Astrocytes after Human Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2006, 23, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesce, S.; Bezzi, P.; Rossi, D.; Meldolesi, J.; Volterra, A. HIV-1 gp120 glycoprotein affects the astrocyte control of extracellular glutamate by both inhibiting the uptake and stimulating the release of the amino acid. FEBS Lett. 1997, 411, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, A.L.; Robinson, M.B. The role of glutamate transporters in neurodegenerative diseases and potential opportunities for intervention. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 51, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Van Kammen, M.; Levey, A.I.; Martin, L.J.; Kuncl, R.W. Selective loss of glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 38, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothstein, J.D.; Patel, S.; Regan, M.R.; Haenggeli, C.; Huang, Y.H.; Bergles, D.E.; Jin, L.; Dykes Hoberg, M.; Vidensky, S.; Chung, D.S.; et al. β-Lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature 2005, 433, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Foster, J.B.; Lin, C.L.G. Glutamate transporter EAAT2: Regulation, function, and potential as a therapeutic target for neurological and psychiatric disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, D.; Werner, P.; Raine, C.S. Glutamate excitotoxicity in a model of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, P.; Pitt, D.; Raine, C.S. Multiple sclerosis: Altered glutamate homeostasis in lesions correlates with oligodendrocyte and axonal damage. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waubant, E.; Maghzi, A.-H.; Revirajan, N.; Spain, R.; Julian, L.; Mowry, E.M.; Marcus, J.; Liu, S.; Jin, C.; Green, A.; et al. A randomized controlled phase II trial of riluzole in early multiple sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillis, J.W.; O’Regan, M.H. Mechanisms of glutamate and aspartate release in the ischemic rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1996, 730, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewer, C.; Gameiro, A.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, Z.; Braams, S.; Rauen, T. Glutamate forward and reverse transport: From molecular mechanism to transporter-mediated release after ischemia. IUBMB Life 2008, 60, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.; Kafitz, K.W.; Roderigo, C.; Rose, C.R. Ammonium-evoked alterations in intracellular sodium and pH reduce glial glutamate transport activity. Glia 2009, 57, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechtholt-Gompf, A.J.; Walther, H.V.; Adams, M.A.; Carlezon, W.A.; Ongür, D.; Cohen, B.M.; Cohen, B.M. Blockade of astrocytic glutamate uptake in rats induces signs of anhedonia and impaired spatial memory. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, E.; Miller, A.H.; Sanacora, G. Inflammation, Glutamate and Glia: A Trio of Trouble in Mood Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanacora, G.; Kendell, S.F.; Levin, Y.; Simen, A.A.; Fenton, L.R.; Coric, V.; Krystal, J.H. Preliminary Evidence of Riluzole Efficacy in Antidepressant-Treated Patients with Residual Depressive Symptoms. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarate, C.A.; Payne, J.L.; Quiroz, J.; Sporn, J.; Denicoff, K.K.; Luckenbaugh, D.; Charney, D.S.; Manji, H.K. An Open-Label Trial of Riluzole in Patients With Treatment-Resistant Major Depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, Z. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of excitotoxic neuronal death. Apoptosis 2010, 15, 1382–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danysz, W.; Parsons, C.G. The NMDA receptor antagonist memantine as a symptomatological and neuroprotective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease: Preclinical evidence. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2003, 18, S23–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndountse, L.T.; Chan, H.M. Role of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors in polychlorinated biphenyl mediated neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 184, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAN, M.; RAYMOND, L. N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor function and excitotoxicity in Huntington’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 272–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Damme, P.; Bogaert, E.; Dewil, M.; Hersmus, N.; Kiraly, D.; Scheveneels, W.; Bockx, I.; Braeken, D.; Verpoorten, N.; Verhoeven, K.; et al. Astrocytes regulate GluR2 expression in motor neurons and their vulnerability to excitotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14825–14830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, R.; Liang, Z.-Q.; Wu, J.-C.; Zhang, X.-D.; Gu, Z.-L.; Qin, Z.-H. An autophagic mechanism is involved in apoptotic death of rat striatal neurons induced by the non-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor agonist kainic acid. Autophagy 2008, 4, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, Z.-L.; Cao, Y.; Liang, Z.-Q.; Han, R.; Bennett, M.C.; Qin, Z.-H. Lysosomal enzyme cathepsin B is involved in kainic acid-induced excitotoxicity in rat striatum. Brain Res. 2006, 1071, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, L.K. CALCIUM: A Role for Neuroproduction and Sustained Adaptation. Mol. Interv. 2006, 6, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.G.; Pathan, N.; Ethell, I.M.; Krajewski, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Shibasaki, F.; McKeon, F.; Bobo, T.; Franke, T.F.; Reed, J.C. Ca2+-induced apoptosis through calcineurin dephosphorylation of BAD. Science 1999, 284, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, R.A. A “protease activation cascade” in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 924, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.K. Calpain and caspase: Can you tell the difference? Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.; Lenart, B.; Kintner, D.B.; Sun, D. Na-K-Cl cotransporter contributes to glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 5061–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Olney, J.W.; Lukasiewicz, P.D.; Almli, T.; Romano, C. Ca2+-independent excitotoxic neurodegeneration in isolated retina, an intact neural net: A role for Cl− and inhibitory transmitters. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, D.G. Mitochondrial dysfunction and glutamate excitotoxicity studied in primary neuronal cultures. Curr. Mol. Med. 2004, 4, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, T.; Farooqui, A.A. Aging: An important factor for the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2009, 130, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, S.A.; Choi, Y.-B.; Pan, Z.-H.; Lei, S.Z.; Chen, H.-S.V.; Sucher, N.J.; Loscalzo, J.; Singel, D.J.; Stamler, J.S. A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective and neurodestructive effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature 1993, 364, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, M.; Omote, K.; Ninomiya, T. Direct evidence for the role of nitric oxide on the glutamate-induced neuronal death in cultured cortical neurons. Brain Res. 1998, 780, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchen, M.R. Roles of mitochondria in health and disease. Diabetes 2004, 53 (Suppl. 1), S96–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrenius, S. Mitochondrial regulation of apoptotic cell death. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 149, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izrael, M.; Slutsky, S.G.; Admoni, T.; Cohen, L.; Granit, A.; Hasson, A.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Krush Paker, L.; Kuperstein, G.; Lavon, N.; et al. Safety and efficacy of human embryonic stem cell-derived astrocytes following intrathecal transplantation in SOD1G93A and NSG animal models. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbeito, L. Astrocyte-based cell therapy: New hope for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients? Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmoud, S.; Gharagozloo, M.; Simard, C.; Gris, D. Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and Release. Cells 2019, 8, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020184
Mahmoud S, Gharagozloo M, Simard C, Gris D. Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and Release. Cells. 2019; 8(2):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020184
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmoud, Shaimaa, Marjan Gharagozloo, Camille Simard, and Denis Gris. 2019. "Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and Release" Cells 8, no. 2: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020184
APA StyleMahmoud, S., Gharagozloo, M., Simard, C., & Gris, D. (2019). Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and Release. Cells, 8(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020184