The Emerging Role of Gβ Subunits in Human Genetic Diseases
Abstract
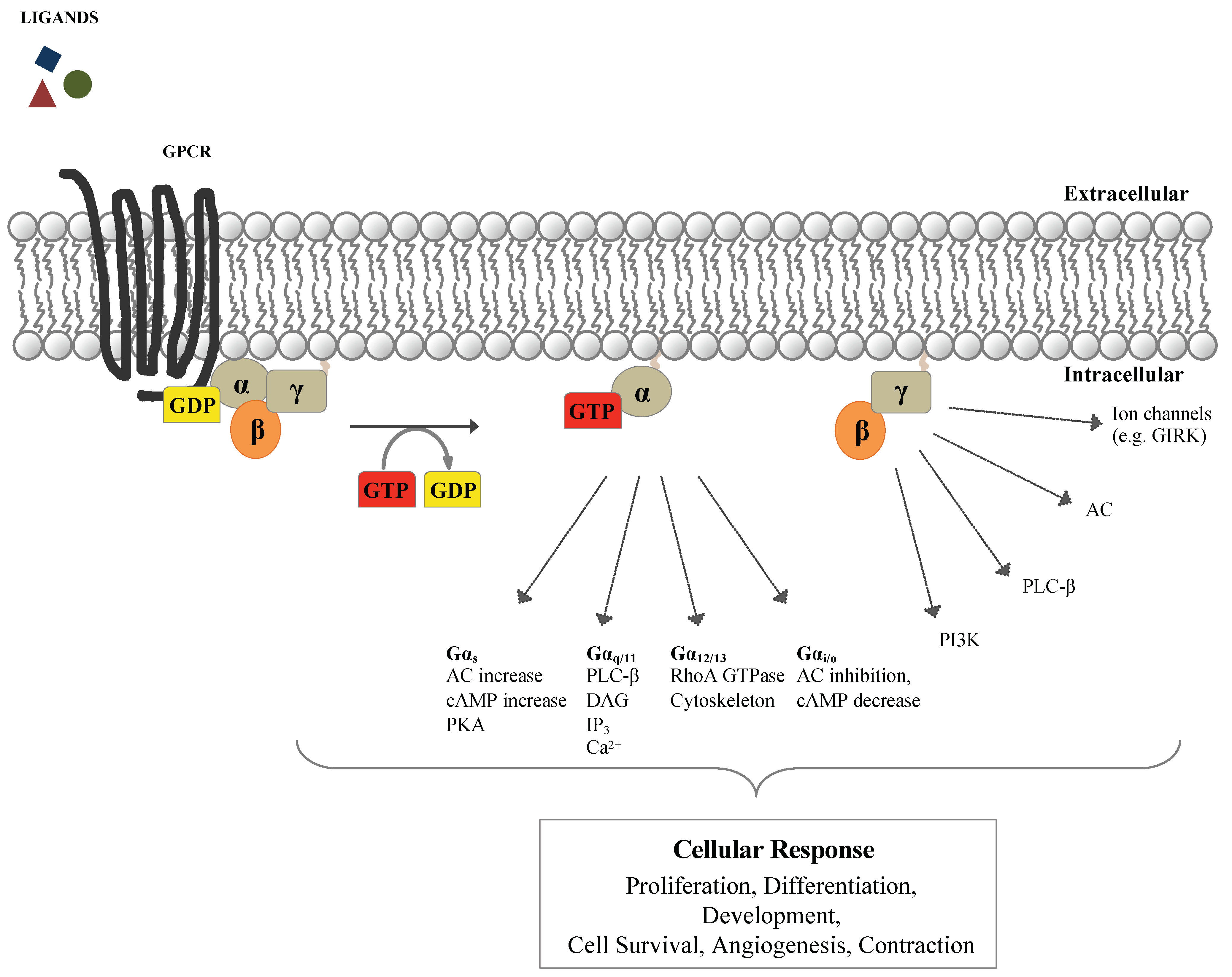
1. G-Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) and Heterotrimeric G-Proteins
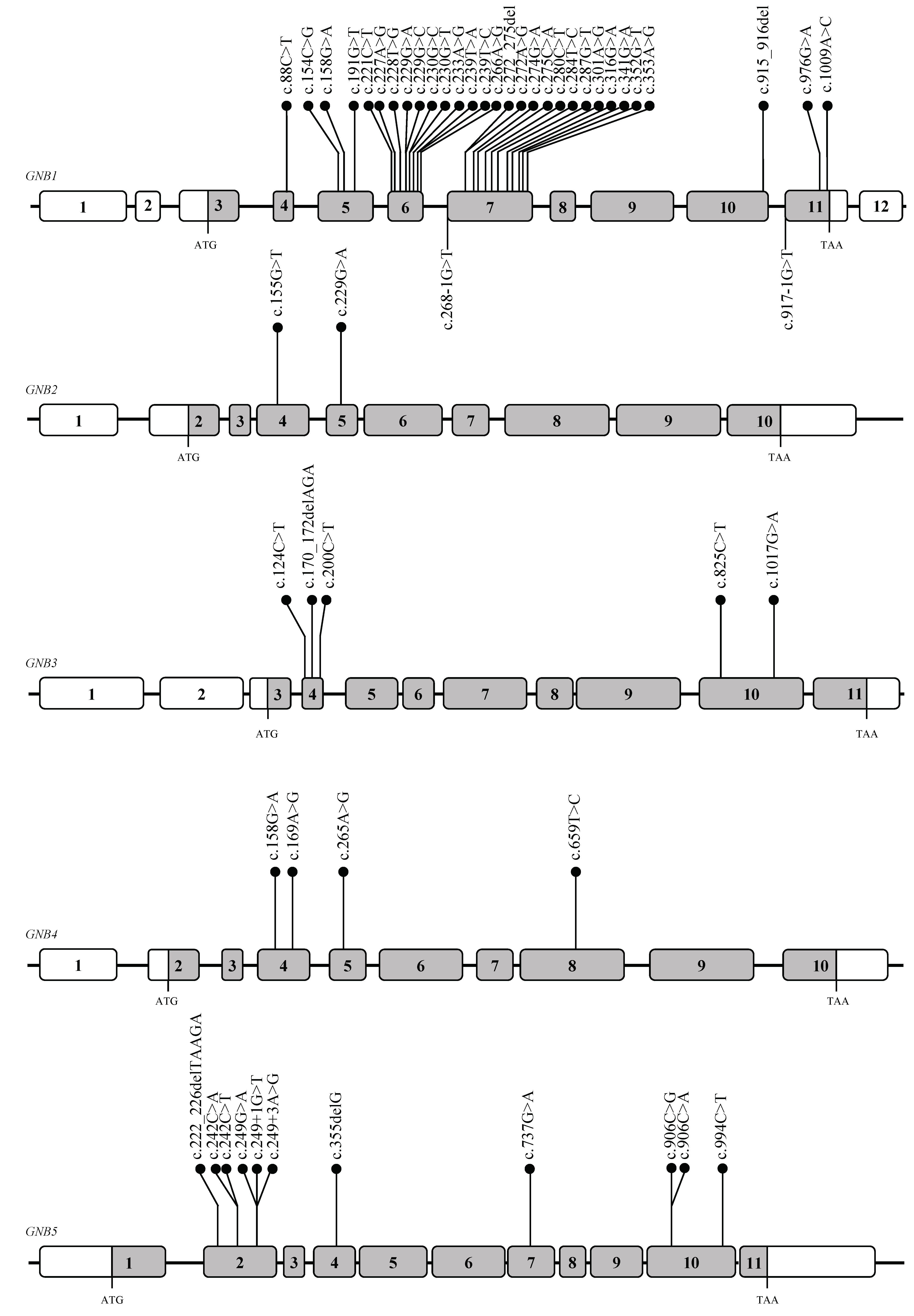
2. Gβ Subunits: Genes and Proteins Structure
3. Gβ proteins and Human Diseases
3.1. G Protein Subunit Beta 1 (GNB1, Gβ1)
3.2. G Protein Subunit Beta 2 (GNB2, Gβ2)
3.3. G Protein Subunit Beta 3 (GNB3, Gβ3)
3.4. G Protein Subunit Beta (GNB4, Gβ4)
3.5. G Protein Subunit Beta (GNB5, Gβ5)
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fredriksson, R.; Lagerstrom, M.C.; Lundin, L.G.; Schioth, H.B. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol. Pharm. 2003, 63, 1256–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamato, D.; Burch, M.L.; Osman, N.; Zheng, W.; Little, P.J. Therapeutic implications of endothelin and thrombin G-protein-coupled receptor transactivation of tyrosine and serine/threonine kinase cell surface receptors. J. Pharm. 2013, 65, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, P.G.; Ramos, M.L.S.; Amaro, A.J.; Dias, R.A.; Vieira, S.I. Gi/o-Protein coupled receptors in the aging brain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagerstrom, M.C.; Schioth, H.B. Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, K.L.; Premont, R.T.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, A.G. G proteins: Transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 615–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smrcka, A.V. G protein βγ subunits: Central mediators of G protein-coupled receptor signaling. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2191–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.; Audo, I.; Tavares, E.; Maynes, J.T.; Tumber, A.; Wright, T.; Li, S.; Michiels, C.; Consortium, G.N.B.; Condroyer, C.; et al. Biallelic mutations in GNB3 cause a unique form of autosomal-recessive congenital stationary night blindness. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 98, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Watson, A.J.; Aragay, A.M.; Slepak, V.Z.; Simon, M.I. A novel form of the G protein β subunit Gβ5 is specifically expressed in the vertebrate retina. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 28154–28160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.M.; Sleno, R.; Gora, S.; Zylbergold, P.; Laverdure, J.P.; Labbe, J.C.; Miller, G.J.; Hebert, T.E. The expanding roles of Gβγ subunits in G protein-coupled receptor signaling and drug action. Pharm. Rev. 2013, 65, 545–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupre, D.J.; Robitaille, M.; Rebois, R.V.; Hebert, T.E. The role of Gβγ subunits in the organization, assembly, and function of GPCR signaling complexes. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2009, 49, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robishaw, J.D.; Berlot, C.H. Translating G protein subunit diversity into functional specificity. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzi, M.; Charest, P.G.; Angers, S.; Rousseau, G.; Kohout, T.; Bouvier, M.; Pineyro, G. Β-arrestin-mediated activation of MAPK by inverse agonists reveals distinct active conformations for G protein-coupled receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11406–11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudin, Y.; Rohacs, T. Inhibitory Gi/O-coupled receptors in somatosensory neurons: Potential therapeutic targets for novel analgesics. Mol. Pain 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopal, S.; Kim, J.; Ahn, S.; Craig, S.; Lam, C.M.; Gerard, N.P.; Gerard, C.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Β-arrestin- but not G protein-mediated signaling by the “decoy” receptor CXCR7. PNAS Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2010, 107, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, D.M.; Rasmussen, S.G.; Kobilka, B.K. The structure and function of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 2009, 459, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobles, M.; Benians, A.; Tinker, A. Heterotrimeric G proteins precouple with G protein-coupled receptors in living cells. PNAS Proc. Natl Acad Sci. 2005, 102, 18706–18711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, G.; Kostenis, E. Heterotrimeric G-proteins: A short history. Br. J. Pharm. 2006, 147, S46–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepler, J.R.; Berman, D.M.; Gilman, A.G.; Kozasa, T. RGS4 and GAIP are GTPase-activating proteins for Gqα and block activation of phospholipase Cβ by γ-thio-GTP-Gqα. PNAS Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1997, 94, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozasa, T.; Jiang, X.; Hart, M.J.; Sternweis, P.M.; Singer, W.D.; Gilman, A.G.; Bollag, G.; Sternweis, P.C. P115 RhoGEF, a GTPase activating protein for Gα12 and Gα13. Science 1998, 280, 2109–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, T.W.; Fields, T.A.; Casey, P.J.; Peralta, E.G. RGS10 is a selective activator of Gαi GTPase activity. Nature 1996, 383, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, D.M.; Wilkie, T.M.; Gilman, A.G. GAIP and RGS4 are GTPase-activating proteins for the Gi subfamily of G protein α subunits. Cell 1996, 86, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, L.; Zheng, B.; Fischer, T.; Elenko, E.; Farquhar, M.G. The regulator of G protein signaling family. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2000, 40, 235–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neer, E.J. Heterotrimeric G proteins: Organizers of transmembrane signals. Cell 1995, 80, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, G.B.; Gautam, N. The G protein subunit gene families. Genomics 1999, 62, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindorfer, M.A.; Myung, C.S.; Savino, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Khazan, R.; Garrison, J.C. Differential activity of the G protein β5γ2 subunit at receptors and effectors. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 34429–34436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, N.; Downes, G.B.; Yan, K.; Kisselev, O. The G-protein βγ complex. Cell Signal. 1998, 10, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, A.C.; Gray, A.J.; Hunter, J.M.; Willardson, B.M. Role of molecular chaperones in G protein β5/regulator of G protein signaling dimer assembly and G protein βγ dimer specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 16386–16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.J.; Katz, A.; Simon, M.I. A fifth member of the mammalian G-protein β-subunit family. Expression in brain and activation of the β2 isotype of phospholipase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 22150–22156. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Roberts, R. WD-repeat proteins: Structure characteristics, biological function, and their involvement in human diseases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 2085–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondek, J.; Bohm, A.; Lambright, D.G.; Hamm, H.E.; Sigler, P.B. Crystal structure of a G-protein βγ dimer at 2.1A resolution. Nature 1996, 379, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, B.P.; Pandey, S. WD40 repeat proteins: Signalling scaffold with diverse functions. Protein J. 2018, 37, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, B.; Braschi, B.; Gray, K.A.; Seal, R.L.; Tweedie, S.; Bruford, E.A. Genenames.org: the HGNC and VGNC resources in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D619–D625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinrucke, S.; Lohmann, K.; Domingo, A.; Rolfs, A.; Baumer, T.; Spiegler, J.; Hartmann, C.; Munchau, A. Novel GNB1 missense mutation in a patient with generalized dystonia, hypotonia, and intellectual disability. Neurol. Genet. 2016, 2, e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, W.; Ikemoto, S.; Togashi, N.; Miyabayashi, T.; Nakajima, E.; Hamano, S.I.; Shibuya, M.; Sato, R.; Takezawa, Y.; Okubo, Y.; et al. Phenotype-genotype correlations in patients with GNB1 gene variants, including the first three reported Japanese patients to exhibit spastic diplegia, dyskinetic quadriplegia, and infantile spasms. Brain Dev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, M.; Lai, A.H.; Ting, T.W.; Tan, A.M.; Foo, R.; Jamuar, S.; Tan, E.C. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a child with a de novo germline gnb1 mutation. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2017, 173, 550–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovski, S.; Kury, S.; Myers, C.T.; Anyane-Yeboa, K.; Cogne, B.; Bialer, M.; Xia, F.; Hemati, P.; Riviello, J.; Mehaffey, M.; et al. Germline de novo mutations in GNB1 cause severe neurodevelopmental disability, hypotonia, and seizures. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 98, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.F.; Morales-Briceno, H.; Barwick, K.; Lewis, J.; Sanchis-Juan, A.; Raymond, F.L.; Stewart, K.; Waugh, M.C.; Mahant, N.; Kurian, M.A.; et al. Myoclonus-dystonia caused by GNB1 mutation responsive to deep brain stimulation. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1079–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, K.; Masuho, I.; Patil, D.N.; Baumann, H.; Hebert, E.; Steinrucke, S.; Trujillano, D.; Skamangas, N.K.; Dobricic, V.; Huning, I.; et al. Novel GNB1 mutations disrupt assembly and function of G protein heterotrimers and cause global developmental delay in humans. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemati, P.; Revah-Politi, A.; Bassan, H.; Petrovski, S.; Bilancia, C.G.; Ramsey, K.; Griffin, N.G.; Bier, L.; Cho, M.T.; Rosello, M.; et al. Refining the phenotype associated with GNB1 mutations: Clinical data on 18 newly identified patients and review of the literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2018, 176, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczaluba, K.; Biernacka, A.; Szymanska, K.; Gasperowicz, P.; Kosinska, J.; Rydzanicz, M.; Ploski, R. Novel GNB1 de novo mutation in a patient with neurodevelopmental disorder and cutaneous mastocytosis: Clinical report and literature review. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2018, 61, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, J.A.; Crolla, J.A.; Tomkins, S.; Bader, P.; Morrow, B.; Gorski, J.; Troxell, R.; Forster-Gibson, C.; Cilliers, D.; Hislop, R.G.; et al. Refinement of causative genes in monosomy 1p36 through clinical and molecular cytogenetic characterization of small interstitial deletions. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2010, 152A, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, L.G.; Lupski, J.R. Molecular mechanisms for constitutional chromosomal rearrangements in humans. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2000, 34, 297–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okae, H.; Iwakura, Y. Neural tube defects and impaired neural progenitor cell proliferation in Gβ1-deficient mice. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, C.E.; Skiba, N.P.; Bae, H.; Daaka, Y.; Reuveny, E.; Shekter, L.R.; Rosal, R.; Weng, G.; Yang, C.S.; Iyengar, R.; et al. Molecular basis for interactions of G protein βγ subunits with effectors. Science 1998, 280, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallmeyer, B.; Kuss, J.; Kotthoff, S.; Zumhagen, S.; Vowinkel, K.; Rinne, S.; Matschke, L.A.; Friedrich, C.; Schulze-Bahr, E.; Rust, S.; et al. A mutation in the G-protein gene GNB2 causes familial sinus node and atrioventricular conduction dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, e33–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whorton, M.R.; MacKinnon, R. X-ray structure of the mammalian GIRK2-βγ G-protein complex. Nature 2013, 498, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrmann, J.; Meister, M.; Maguire, C.T.; Martins, D.C.; Hammer, P.E.; Neer, E.J.; Berul, C.I.; Mende, U. Impaired parasympathetic heart rate control in mice with a reduction of functional G protein βγ-subunits. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2002, 282, H445–H456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Logothetis, D.E.; Kurachi, Y.; Galper, J.; Neer, E.J.; Clapham, D.E. The βγ subunits of GTP-binding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart. Nature 1987, 325, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, J.; Stallmeyer, B.; Goldstein, M.; Rinne, S.; Pees, C.; Zumhagen, S.; Seebohm, G.; Decher, N.; Pott, L.; Kienitz, M.C.; et al. Familial sinus node disease caused by a gain of GIRK (G-protein activated inwardly rectifying K+ channel) channel function. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2019, 12, e002238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, M.E.; Flenniken, A.M.; Ji, X.; Teboul, L.; Wong, M.D.; White, J.K.; Meehan, T.F.; Weninger, W.J.; Westerberg, H.; Adissu, H.; et al. High-throughput discovery of novel developmental phenotypes. Nature 2016, 537, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, T.; Hiraide, T.; Yamoto, K.; Nakashima, M.; Kawai, T.; Yanagi, K.; Ogata, T.; Saitsu, H. Exome reports A de novo GNB2 variant associated with global developmental delay, intellectual disability, and dysmorphic features. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 103804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, W.; Ye, D.; Mersch, K.; Xu, H.; Chen, S.; Lin, F. Gβ1 is required for neutrophil migration in zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2017, 428, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuse, N.; Hisata, K.; Katzen, A.L.; Matsuzaki, F. Heterotrimeric G proteins regulate daughter cell size asymmetry in Drosophila neuroblast divisions. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmer, F.; Moorman, C.; van der Linden, A.M.; Kuijk, E.; van den Berghe, P.V.; Kamath, R.S.; Fraser, A.G.; Ahringer, J.; Plasterk, R.H. Genome-wide RNAi of C. elegans using the hypersensitive rrf-3 strain reveals novel gene functions. PLoS Biol. 2003, 1, E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubaj Price, M.; Hurd, D.D. WormBase: A model organism database. Med. Ref. Serv. Q 2019, 38, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Sun, Z.; Guo, A.; Song, L.S.; Grobe, J.L.; Chen, S. Ablation of the GNB3 gene in mice does not affect body weight, metabolism or blood pressure, but causes bradycardia. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 2514–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ozdemir, A.C.; Wynn, G.M.; Vester, A.; Weitzmann, M.N.; Neigh, G.N.; Srinivasan, S.; Rudd, M.K. GNB3 overexpression causes obesity and metabolic syndrome. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldlust, I.S.; Hermetz, K.E.; Catalano, L.M.; Barfield, R.T.; Cozad, R.; Wynn, G.; Ozdemir, A.C.; Conneely, K.N.; Mulle, J.G.; Dharamrup, S.; et al. Mouse model implicates GNB3 duplication in a childhood obesity syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013, 110, 14990–14994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagman, D.; Callado-Perez, A.; Franzen, I.E.; Larhammar, D.; Abalo, X.M. Transducin duplicates in the zebrafish retina and pineal complex: Differential specialisation after the teleost tetraploidisation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Levay, K.; Chanturiya, T.; Dvoriantchikova, G.; Anderson, K.L.; Bianco, S.D.; Ueta, C.B.; Molano, R.D.; Pileggi, A.; Gurevich, E.V.; et al. Targeted deletion of one or two copies of the G protein β subunit Gβ5 gene has distinct effects on body weight and behavior in mice. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3949–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Pandey, M.; Seigneur, E.M.; Panicker, L.M.; Koo, L.; Schwartz, O.M.; Chen, W.; Chen, C.K.; Simonds, W.F. Knockout of G protein β5 impairs brain development and causes multiple neurologic abnormalities in mice. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Ge, S.; Collins, V.E.; Haynes, C.L.; Renner, K.J.; Meisel, R.L.; Lujan, R.; Martemyanov, K.A. Gβ5-RGS complexes are gatekeepers of hyperactivity involved in control of multiple neurotransmitter systems. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2012, 219, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.K.; Eversole-Cire, P.; Zhang, H.; Mancino, V.; Chen, Y.J.; He, W.; Wensel, T.G.; Simon, M.I. Instability of GGL domain-containing RGS proteins in mice lacking the G protein β-subunit Gβ5. PNAS Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 6604–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodder, E.M.; De Nittis, P.; Koopman, C.D.; Wiszniewski, W.; Moura de Souza, C.F.; Lahrouchi, N.; Guex, N.; Napolioni, V.; Tessadori, F.; Beekman, L.; et al. GNB5 mutations cause an autosomal-recessive multisystem syndrome with sinus bradycardia and cognitive disability. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurmond, J.; Goodman, J.L.; Strelets, V.B.; Attrill, H.; Gramates, L.S.; Marygold, S.J.; Matthews, B.B.; Millburn, G.; Antonazzo, G.; Trovisco, V.; et al. FlyBase 2.0: The next generation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D759–D765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robatzek, M.; Niacaris, T.; Steger, K.; Avery, L.; Thomas, J.H. Eat-11 encodes GPB-2, a Gβ5 ortholog that interacts with Goα and Gqα to regulate C. elegans behavior. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arno, G.; Holder, G.E.; Chakarova, C.; Kohl, S.; Pontikos, N.; Fiorentino, A.; Plagnol, V.; Cheetham, M.E.; Hardcastle, A.J.; Webster, A.R.; et al. Recessive retinopathy consequent on mutant G-protein β subunit 3 (GNB3). JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 924–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.G.; Becker, D.; Jagannathan, V.; Goldstein, O.; Santana, E.; Carlin, K.; Sudharsan, R.; Leeb, T.; Nishizawa, Y.; Kondo, M.; et al. Genome-wide association study and whole-genome sequencing identify a deletion in LRIT3 associated with canine congenital stationary night blindness. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitz, C.; Robson, A.G.; Audo, I. Congenital stationary night blindness: An analysis and update of genotype-phenotype correlations and pathogenic mechanisms. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 45, 58–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchey, E.R.; Bongini, R.E.; Code, K.A.; Zelinka, C.; Petersen-Jones, S.; Fischer, A.J. The pattern of expression of guanine nucleotide-binding protein β3 in the retina is conserved across vertebrate species. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1376–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.H.; Lieberman, B.S.; Yamane, H.K.; Bok, D.; Fung, B.K. A third form of the G protein β subunit. 1. Immunochemical identification and localization to cone photoreceptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 24776–24781. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.W.; Robishaw, J.D.; Levine, M.A.; Yau, K.W. Retinal rods and cones have distinct G protein β and γ subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1992, 89, 10882–10886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikonov, S.S.; Lyubarsky, A.; Fina, M.E.; Nikonova, E.S.; Sengupta, A.; Chinniah, C.; Ding, X.Q.; Smith, R.G.; Pugh, E.N., Jr.; Vardi, N.; et al. Cones respond to light in the absence of transducin β subunit. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 5182–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhingra, A.; Ramakrishnan, H.; Neinstein, A.; Fina, M.E.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Chung, D.C.; Lyubarsky, A.; Vardi, N. Gβ3 is required for normal light ON responses and synaptic maintenance. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 11343–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tummala, H.; Ali, M.; Getty, P.; Hocking, P.M.; Burt, D.W.; Inglehearn, C.F.; Lester, D.H. Mutation in the guanine nucleotide-binding protein β-3 causes retinal degeneration and embryonic mortality in chickens. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 4714–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siffert, W.; Rosskopf, D.; Siffert, G.; Busch, S.; Moritz, A.; Erbel, R.; Sharma, A.M.; Ritz, E.; Wichmann, H.E.; Jakobs, K.H.; et al. Association of a human G-protein β3 subunit variant with hypertension. Nat. Genet. 1998, 18, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.C.; Reis, R.P.D.; Pereira, A.; Borges, S.; Gouveia, S.; Spinola, A.; Freitas, A.I.; Guerra, G.; Gois, T.; Rodrigues, M.; et al. The genetic variant C825T of the β3 subunit of G protein is associated with hypertension in a Portuguese population. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2018, 37, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.L.; Zheng, J.Z.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Su, J.; Li, B. Association of G-protein β3 subunit C825T polymorphism with essential hypertension: Evidence from 63,729 subjects. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2017, 31, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengstenberg, C.; Schunkert, H.; Mayer, B.; Doring, A.; Lowel, H.; Hense, H.W.; Fischer, M.; Riegger, G.A.; Holmer, S.R. Association between a polymorphism in the G protein β3 subunit gene (GNB3) with arterial hypertension but not with myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 49, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moselhy, S.S.; Alhetari, Y.A.; Iyer, A.; Huwait, E.A.; Al-Ghamdi, M.A.; Al-Ghamdi, S.; Balamash, K.S.; Basuni, A.A.; Alama, M.N.; Kumosani, T.A.; et al. Analysis of SNPs of MC4R, GNB3 and FTO gene polymorphism in obese Saudi subjects. Afr. Health Sci. 2017, 17, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rizvi, S.; Raza, S.T.; Rahman, Q.; Mahdi, F. Role of GNB3, NET, KCNJ11, TCF7L2 and GRL genes single nucleotide polymorphism in the risk prediction of type 2 diabetes mellitus. 3 Biotech. 2016, 6, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.S.; Chang, H.H.; Huang, C.C.; Lee, C.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Huang, S.Y.; Yang, Y.K.; Lu, R.B. A longitudinal study of the association between the GNB3 C825T polymorphism and metabolic disturbance in bipolar II patients treated with valproate. Pharm. J. 2017, 17, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prystupa, L.N.; Moiseyenko, I.O.; Garbuzova, V.Y.; Kmyta, V.V.; Dudchenko, I.A. Association of metabolic syndrome components with the genotypes of the C825T polymorphism in the G protein β3-subunit gene (GNB3). Wiadomosci Lekarskie 2018, 71, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Fang, D.; Qiu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhu, X.; He, J.; Pan, H.; et al. GNB3 and CREB1 gene polymorphisms combined with negative life events increase susceptibility to major depression in a Chinese Han population. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zill, P.; Baghai, T.C.; Zwanzger, P.; Schule, C.; Minov, C.; Riedel, M.; Neumeier, K.; Rupprecht, R.; Bondy, B. Evidence for an association between a G-protein β3-gene variant with depression and response to antidepressant treatment. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 1893–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.J.; Cho, C.H.; Kim, L.; Lee, H.J. Association of G-protein β3 subunit C825T polymorphism with seasonal variations in mood and behavior. Psychiatry Investig. 2018, 15, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Z.; You, H.Y.; Zhu, Z.H.; Wen, Z.D.; Xu, H.Y.; Chen, B.C.; Chen, Z.J.; Huang, Q.K. The C825T polymorphism of the G-protein β3 gene as a risk factor for functional dyspepsia: A meta-analysis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pr. 2016, 2016, 5037254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, K.; Kourikou, A.; Gazouli, M.; Karamanolis, G.P.; Dimitriadis, G.D. Functional dyspepsia susceptibility is related to CD14, GNB3, MIF, and TRPV1 gene polymorphisms in the Greek population. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.C.; Doris, P.A.; Folsom, A.R.; Nieto, F.J.; Boerwinkle, E. G-protein β3 subunit and α-adducin polymorphisms and risk of subclinical and clinical stroke. Stroke 2001, 32, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, K.; Song, Y.; Hui, R.; Huang, X. The 825C/T polymorphism of G-protein β3 subunit gene and risk of ischaemic stroke. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2005, 19, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreieck, J.; Dostal, S.; von Beckerath, N.; Wacker, A.; Flory, M.; Weyerbrock, S.; Koch, W.; Schomig, A.; Schmitt, C. C825T polymorphism of the G-protein β3 subunit gene and atrial fibrillation: Association of the TT genotype with a reduced risk for atrial fibrillation. Am. Heart J. 2004, 148, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Hua, Q. Association of G-protein β3 subunit gene C825T polymorphism with cardiac and cerebrovascular events in Chinese hypertensive patients. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2017, 39, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eba, A.; Raza, S.T.; Abbas, M.; Rizvi, S.; Rajput, M.; Mahdi, F. Association of SDF1β (G801A) and GNB3 (C825T) polymorphisms with the incidence and severity of coronary artery disease. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 76, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, R.; Tanaka, H.; Takitani, K.; Kajiura, M.; Okamoto, N.; Kanbara, Y.; Tamai, H. GNB3 C825T polymorphism is associated with postural tachycardia syndrome in children. Pediatr. Int. 2012, 54, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, U.H.; Moebus, S.; Mohlenkamp, S.; Kalsch, H.; Bauer, M.; Lehmann, N.; Nothen, M.; Muhleisen, T.W.; Stang, A.; Erbel, R.; et al. GNB3 gene 825 TT variant predicts hard coronary events in the population-based Heinz Nixdorf Recall study. Atherosclerosis 2014, 237, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wascher, T.C.; Paulweber, B.; Malaimare, L.; Stadlmayr, A.; Iglseder, B.; Schmoelzer, I.; Renner, W. Associations of a human G protein β3 subunit dimorphism with insulin resistance and carotid atherosclerosis. Stroke 2003, 34, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiglia, E.; Tikhonoff, V.; Boschetti, G.; Bascelli, A.; Saugo, M.; Guglielmi, G.; Caffi, S.; Rigoni, G.; Giordano, N.; Grasselli, C.; et al. The C825T GNB3 polymorphism, independent of blood pressure, predicts cerebrovascular risk at a population level. Am. J. Hypertens. 2012, 25, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, C.S.; Varela, M.C.; de Castro, C.I.E.; Otto, P.A.; Perez, A.B.A.; Lourenco, C.M.; Kim, C.A.; Bertola, D.R.; Kok, F.; Garcia-Alonso, L.; et al. Chromosomal microarray analysis in the genetic evaluation of 279 patients with syndromic obesity. Mol. Cytogenet. 2018, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, B.W.; Huang, Y.H.; Tsai, P.C.; Huang, C.C.; Pan, H.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Chien, H.J.; Liu, T.T.; Chang, M.H.; Lin, K.P.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies GNB4 mutations as a cause of dominant intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 92, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassuthova, P.; Safka Brozkova, D.; Neupauerova, J.; Krutova, M.; Mazanec, R.; Seeman, P. Confirmation of the GNB4 gene as causal for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease by a novel de novo mutation in a Czech patient. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2017, 27, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, S.; Morikawa, T.; Fujioka, R.; Noda, K.; Kosaka, K.; Taniwaki, T.; Shibata, H. A novel missense variant (Gln220Arg) of GNB4 encoding guanine nucleotide-binding protein, subunit β-4 in a Japanese family with autosomal dominant motor and sensory neuropathy. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 60, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, M.A.; Posner, B.A.; Sprang, S.R. Structural basis of activity and subunit recognition in G protein heterotrimers. Structure 1998, 6, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, R.; Bohm, A.; Sigler, P.B. Crystal structure at 2.4 angstroms resolution of the complex of transducin βγ and its regulator, phosducin. Cell 1996, 87, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.M.; Min, A.; Gora, S.; Houranieh, G.M.; Campden, R.; Robitaille, M.; Trieu, P.; Petrin, D.; Jacobi, A.M.; Behlke, M.A.; et al. Gβ4γ1 as a modulator of M3 muscarinic receptor signalling and novel roles of Gβ1 subunits in the modulation of cellular signalling. Cell Signal. 2015, 27, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, N.J.; Greener, I.D.; Tellez, J.O.; Inada, S.; Musa, H.; Molenaar, P.; Difrancesco, D.; Baruscotti, M.; Longhi, R.; Anderson, R.H.; et al. Molecular architecture of the human sinus node: Insights into the function of the cardiac pacemaker. Circulation 2009, 119, 1562–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Velasco, V.; Ikeda, S.R.; Puhl, H.L. Cloning, tissue distribution, and functional expression of the human G protein β4-subunit. Physiol. Genom. 2002, 8, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, B.K.; Duan, Y.; Fan, Y.; Schoneberg, T.; Ehlich, A.; Lenka, N.; Viatchenko-Karpinski, S.; Pott, L.; Hescheler, J.; Fakler, B. Differential subunit composition of the G protein-activated inward-rectifier potassium channel during cardiac development. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 114, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosskopf, D.; Nikula, C.; Manthey, I.; Joisten, M.; Frey, U.; Kohnen, S.; Siffert, W. The human G protein β4 subunit: Gene structure, expression, Gγ and effector interaction. FEBS Lett. 2003, 544, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- den Hoed, M.; Eijgelsheim, M.; Esko, T.; Brundel, B.J.; Peal, D.S.; Evans, D.M.; Nolte, I.M.; Segre, A.V.; Holm, H.; Handsaker, R.E.; et al. Identification of heart rate-associated loci and their effects on cardiac conduction and rhythm disorders. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolock, E.M.; Ilyushkina, I.A.; Ghazalpour, A.; Gerloff, J.; Murashev, A.N.; Lusis, A.J.; Korshunov, V.A. Genetic locus on mouse chromosome 7 controls elevated heart rate. Physiol. Genom. 2012, 44, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, D.N.; Rangarajan, E.S.; Novick, S.J.; Pascal, B.D.; Kojetin, D.J.; Griffin, P.R.; Izard, T.; Martemyanov, K.A. Structural organization of a major neuronal G protein regulator, the RGS7-Gβ5-R7BP complex. eLIFE 2018, 7, e42150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Masuho, I.; Brand, C.; Dessauer, C.W.; Martemyanov, K.A. The complex of G protein regulator RGS9-2 and Gβ5 controls sensitization and signaling kinetics of type 5 adenylyl cyclase in the striatum. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Witherow, D.S.; Slepak, V.Z. A novel kind of G protein heterodimer: The G β5-RGS complex. Recept. Channels 2003, 9, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Blazquez, P.; Rodriguez-Diaz, M.; Lopez-Fando, A.; Rodriguez-Munoz, M.; Garzon, J. The Gβ5 subunit that associates with the R7 subfamily of RGS proteins regulates mu-opioid effects. Neuropharmacology 2003, 45, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nini, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Pandey, M.; Panicker, L.M.; Simonds, W.F. Expression of the Gβ5/R7-RGS protein complex in pituitary and pancreatic islet cells. Endocrine 2012, 42, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sondek, J.; Siderovski, D.P. Gγ-like (GGL) domains: New frontiers in G-protein signaling and β-propeller scaffolding. Biochem. Pharm. 2001, 61, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Allen, K.L.; Kourrich, S.; Colon-Saez, J.; Thomas, M.J.; Wickman, K.; Martemyanov, K.A. Gβ5 recruits R7 RGS proteins to GIRK channels to regulate the timing of neuronal inhibitory signaling. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Tumber, A.; Maynes, J.; Tavares, E.; Kannu, P.; Heon, E.; Vincent, A. Unique retinal signaling defect in GNB5-related disease. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poke, G.; King, C.; Muir, A.; de Valles-Ibanez, G.; Germano, M.; Moura de Souza, C.F.; Fung, J.; Chung, B.; Fung, C.W.; Mignot, C.; et al. The epileptology of GNB5 encephalopathy. Epilepsia 2019, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malerba, N.; Towner, S.; Keating, K.; Squeo, G.M.; Wilson, W.; Merla, G. A NGS-targeted autism/ID Panel reveals compound heterozygous GNB5 variants in a novel patient. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, H.; Cohen, J.; De Nittis, P.; Fatemi, A.; McClellan, R.; Goldstein, A.; Malerba, N.; Guex, N.; Reymond, A.; Merla, G. Intellectual developmental disorder with cardiac arrhythmia syndrome in a child with compound heterozygous GNB5 variants. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 1254–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkdogan, D.; Usluer, S.; Akalin, F.; Agyuz, U.; Aslan, E.S. Familial early infantile epileptic encephalopathy and cardiac conduction disorder: A rare cause of SUDEP in infancy. Seizure 2017, 50, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseldin, H.E.; Masuho, I.; Alenizi, A.; Alyamani, S.; Patil, D.N.; Ibrahim, N.; Martemyanov, K.A.; Alkuraya, F.S. GNB5 mutation causes a novel neuropsychiatric disorder featuring attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, severely impaired language development and normal cognition. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerman, C.C.; Mengarelli, I.; Koopman, C.D.; Wilders, R.; van Amersfoorth, S.C.; Bakker, D.; Wolswinkel, R.; Hababa, M.; de Boer, T.P.; Guan, K.; et al. Genetic variation in GNB5 causes bradycardia by augmenting the cholinergic response via increased acetylcholine-activated potassium current (IK,ACh). Dis. Model. Mech. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krispel, C.M.; Chen, C.K.; Simon, M.I.; Burns, M.E. Novel form of adaptation in mouse retinal rods speeds recovery of phototransduction. J. Gen. Physiol. 2003, 122, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Zallocchi, M.; Wang, W.; Chen, C.K.; Palczewski, K.; Delimont, D.; Cosgrove, D.; Peng, Y.W. Light-induced translocation of RGS9-1 and Gβ5L in mouse rod photoreceptors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Dallman, R.; Henderson, S.; Chen, C.K. Gβ5 is required for normal light responses and morphology of retinal ON-bipolar cells. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 14199–14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, K.; Xie, X.; Marron Fernandez de Velasco, E.; Anderson, A.; Martemyanov, K.A.; Wickman, K.; Tolkacheva, E.G. Correction: The influences of the M2R-GIRK4-RGS6 dependent parasympathetic pathway on electrophysiological properties of the mouse heart. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posokhova, E.; Wydeven, N.; Allen, K.L.; Wickman, K.; Martemyanov, K.A. RGS6/Gβ5 complex accelerates IKACh gating kinetics in atrial myocytes and modulates parasympathetic regulation of heart rate. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, B.; Stewart, A.; Yang, J.; Loo, L.; Sheff, D.; Shepherd, A.J.; Mohapatra, D.P.; Fisher, R.A. Regulator of G protein signaling 6 (RGS6) protein ensures coordination of motor movement by modulating GABAB receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4972–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Name (HGNC) | Description | Ensembl ID | RefSeq ID | Ensembl Transcript ID | Transcritp Length (bp) | Protein length (aa) | Uniprot | Cytogenetic Location | Genomic Coordinates (GRCh38, from Ensembl) | Strand | Nr. of Exons | Nr. of Coding Exons | MIM ID | Phenotype MIM Number(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNB1 | G protein subunit beta 1 | ENSG00000078369.18 | NM_002074 | ENST00000378609.9 | 3163 | 340 | P62873 | 1p36.33 | 1:1,785,285-1,891,117 | reverse strand | 12 | 9 | *139380 | #616973 |
| GNB2 | G protein subunit beta 2 | ENSG00000172354.10 | NM_005273 | ENST00000303210.9 | 1664 | 340 | Q6FHM2 | 7q22.1 | 7:100,673,567-100,679,174 | forward strand | 10 | 9 | *139390 | - |
| GNB3 | G protein subunit beta 3 | ENSG00000111664.10 | NM_002075 | ENST00000229264.7 | 1923 | 340 | P16520 | 12p13.31 | 12:6,840,211-6,847,393 | forward strand | 11 | 9 | *139130 | #617024 |
| GNB4 | G protein subunit beta 4 | ENSG00000114450.10 | NM_021629 | ENST00000232564.8 | 6315 | 340 | Q9HAV0 | 3q26.33 | 3:179,396,088-179,451,476 | reverse strand | 10 | 9 | *610863 | #615185 |
| GNB5 | G protein subunit beta 5 | ENSG00000069966.18 | NM_006578 | ENST00000358784.11 | 1735 | 353 | O14775 | 15q21.2 | 15:52,122,206-52,180,001 | reverse strand | 11 | 11 | *604447 | #617173, #617182 |
| Gene Name (HGNC) | Annotated Terms in Animal Models | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. Musculus | Zebrafish | D. Melanogaster | C. elegans | |
| GNB1 | (Gnb1): abnormal brain morphology and size (KO) [52] | (gnb1a/gnb1b): altered regulation of neutrophil migrations and posterior lateral line neuromast primordium migration (KD) [54] | (CG10545): abnormal spindle size (KD and overexpression) [55] | (gpb1): essential for embryo development (50–80% embryonic lethality); uncoordinated phenotype in surviving adult worms; functions in establishment of mitotic spindle orientation; expressed in alimentary system, body wall musculature, epithelial system, nervous system and reproductive organs (KD) [56,57] |
| GNB2 | (Gnb2): abnormal behavioral response to light, increased heart rate, shortened PQ interval, shortened RR interval, shortened ST segment (KO) [52] | NA | ||
| GNB3 | (Gnb3): abnormal eye electrophysiology, mild bradycardia (KO); weight gain (Dup) [58,59,60] | (gnb3a): expressed throughout development; (gnb3b) expressed in the cones of the dorsal and medial retina (KD) [61] | ||
| GNB4 | (Gnb4): enlarged heart and spleen (KO) [52] | NA | ||
| GNB5 | (Gnb5): pre-weaning lethality with incomplete penetrance, decreased body size, slow post-natal weigh gain and abnormal vision (KO); increased body weight, adiposity, insulin resistance and liver steatosis (HET) [62,63,64,65] | (gnb5a/gnb5b): abnormal heart contraction, optokinetic behavior and swimming behavior (KO) [66] | (CG10763): pain responsive defective (KD) [67] | (gpb-2): behavioral defects, e.g., delayed egg laying, locomotion, and pharingeal pumping (KO and overexpression) [68] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malerba, N.; De Nittis, P.; Merla, G. The Emerging Role of Gβ Subunits in Human Genetic Diseases. Cells 2019, 8, 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121567
Malerba N, De Nittis P, Merla G. The Emerging Role of Gβ Subunits in Human Genetic Diseases. Cells. 2019; 8(12):1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121567
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalerba, Natascia, Pasquelena De Nittis, and Giuseppe Merla. 2019. "The Emerging Role of Gβ Subunits in Human Genetic Diseases" Cells 8, no. 12: 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121567
APA StyleMalerba, N., De Nittis, P., & Merla, G. (2019). The Emerging Role of Gβ Subunits in Human Genetic Diseases. Cells, 8(12), 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121567






