The Many Roles of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Hepatic Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Liver as Target of Chronic Injury and Fibrosis
3. Cell Adhesion Molecules—General Aspects and their Function in Classical Cell Recruitment
4. Adhesion Molecules in Cell–ECM Interaction
5. Adhesion Molecules in Cell–Cell Interaction
6. Selectins
7. Integrins
7.1. β1-Integrins
7.2. β2-Integrins
7.3. αV-Integrins
8. Cadherins
9. Immunoglobulin Superfamily of Adhesion Molecules
9.1. ICAMs
9.2. VCAMs
9.3. PECAM-1
9.4. NCAM
9.5. JAMs
9.6. Nectins and Nectin-Like Receptors
10. Non-Classical Adhesion Molecules
10.1. VAP-1
10.2. MAdCAM-1
10.3. Stabilins
11. Adhesion Molecules as Hepatic Fibrosis Markers and as Therapeutic Targets
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guillot, A.; Tacke, F. Liver Macrophages: Old Dogmas and New Insights. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, D.M. Long-Term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1676–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Urbani, S.; Bradfield, P.F.; Lee, B.P.; Imhof, B.A. Vascular and Epithelial Junctions: A Barrier for Leucocyte Migration. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalor, P.F.; Adams, D.H. The Liver: A Model of Organ-Specific Lymphocyte Recruitment. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2002, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, Y.H.; Adams, D.H. The Role of Chemokines in the Recruitment of Lymphocytes to the Liver. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weninger, W.; Biro, M.; Jain, R. Leukocyte Migration in the Interstitial Space of Non-Lymphoid Organs. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Gea, V.; Friedman, S.L. Pathogenesis of Liver Fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 425–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Friedman, S.L.; Aloman, C. Hepatic Fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 25, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaskou, E.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Gershwin, M.E. Mechanisms of Tissue Injury in Autoimmune Liver Diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2014, 36, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicoro, A.; Ramachandran, P.; Iredale, J.P.; Fallowfield, J.A. Liver Fibrosis and Repair: Immune Regulation of Wound Healing in a Solid Organ. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, P.; Iredale, J.P. Liver Fibrosis: A Bidirectional Model of Fibrogenesis and Resolution. QJM An Int. J. Med. 2012, 105, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchers, A.T.; Shimoda, S.; Bowlus, C.; Keen, C.L.; Gershwin, M.E. Lymphocyte Recruitment and Homing to the Liver in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2009, 31, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.Y.; Kubes, P. Leukocyte Adhesion in the Liver: Distinct Adhesion Paradigm from other Organs. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.A.; Kisseleva, T.; Scholten, D.; Paik, Y.H.; Iwaisako, K.; Inokuchi, S.; Schnabl, B.; Seki, E.; De Minicis, S.; Oesterreicher, C.; et al. Origin of Myofibroblasts in Liver Fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2012, 5, S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L. Hepatic Stellate Cells: Protean, Multifunctional, and Enigmatic Cells of the Liver. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 125–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressner, A.M.; Weiskirchen, R. Modern Pathogenetic Concepts of Liver Fibrosis Suggest Stellate Cells and TGF-Beta as Major Players and Therapeutic Targets. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2006, 10, 76–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingberg, F.; Chow, M.L.; Koehler, A.; Boo, S.; Buscemi, L.; Quinn, T.M.; Costell, M.; Alman, B.A.; Genot, E.; Hinz, B. Prestress in the Extracellular Matrix Sensitizes Latent TGF-Beta1 for Activation. J. Cell Biol 2014, 207, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingberg, F.; Hinz, B.; White, E.S. The Myofibroblast Matrix: Implications for Tissue Repair and Fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2013, 229, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Wallace, M.C.; Friedman, S.L. Pathobiology of Liver Fibrosis: A Translational Success Story. Gut 2015, 64, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricescu, A.R.; Jones, E.Y. Immunoglobulin Superfamily Cell Adhesion Molecules: Zippers and Signals. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, B.; Georgiou, M. Dynamics of Adherens Junctions in Epithelial Establishment, Maintenance, and Remodeling. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, U.; Dejana, E. Adhesion Molecule Signalling: Not Always a Sticky Business. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citi, S.; Guerrera, D.; Spadaro, D.; Shah, J. Epithelial Junctions and Rho Family GTPases: The Zonular Signalosome. Small GTPases 2014, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejana, E. Endothelial Cell-Cell Junctions: Happy Together. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjunpaa, H.; Llort Asens, M.; Guenther, C.; Fagerholm, S.C. Cell Adhesion Molecules and Their Roles and Regulation in the Immune and Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Bidirectional, Allosteric Signaling Machines. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L. Signal Transduction by Cell Adhesion Receptors and the Cytoskeleton: Functions of Integrins, Cadherins, Selectins, and Immunoglobulin-Superfamily Members. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002, 42, 283–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannecoeck, R.; Serruys, D.; Benmeridja, L.; Delanghe, J.R.; Van Geel, N.; Speeckaert, R.; Speeckaert, M.M. Vascular Adhesion Protein-1: Role in Human Pathology and Application as a Biomarker. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 52, 284–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, D.A.; Shetty, S. The Role of Stabilin-1 in Lymphocyte Trafficking and Macrophage Scavenging in the Liver Microenvironment. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinisch, W.; Hung, K.; Hassan-Zahraee, M.; Cataldi, F. Targeting Endothelial Ligands: ICAM-1/Alicaforsen, MAdCAM-1. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, S669–S677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmi, M.; Jalkanen, S. VAP-1: An Adhesin and an Enzyme. Trends. Immunol. 2001, 22, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, C.J.; Adams, D.H. Hepatic Consequences of Vascular Adhesion Protein-1 Expression. J. Neural. Transm. 2011, 118, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejana, E. The Transcellular Railway: Insights into Leukocyte Diapedesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsdal, M.A.; Manon-Jensen, T.; Genovese, F.; Kristensen, J.H.; Nielsen, M.J.; Sand, J.M.; Hansen, N.U.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; Bager, C.L.; Krag, A.; et al. Novel Insights into the Function and Dynamics of Extracellular Matrix in Liver Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G807–G830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.O. Cell-Matrix Adhesion in Vascular Development. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treyer, A.; Musch, A. Hepatocyte Polarity. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 243–287. [Google Scholar]
- Thabut, D.; Shah, V. Intrahepatic Angiogenesis and Sinusoidal Remodeling in Chronic Liver Disease: New Targets for the Treatment of Portal Hypertension? J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, S.S.; Gaudio, E.; Miller, T.; Alvaro, D.; Alpini, G. Cholangiocyte Proliferation and Liver fibrosis. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2009, 11, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, G.D.; Sadahiro, T.; Noh, S.I.; Wang, H.; Talavera, D.; Wang, H.; Vierling, J.M.; Klein, A.S. Interaction of CD44 and Hyaluronic acid Enhances Biliary Epithelial Proliferation in Cholestatic Livers. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G305–G312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baer, H.U.; Friess, H.; Abou-Shady, M.; Berberat, P.; Zimmermann, A.; Gold, L.I.; Korc, M.; Buchler, M.W. Transforming Growth Factor Betas and Their Receptors in Human Liver Cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1998, 10, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dietz, H.C. One Integrin to Rule Them All? Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 288fs221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, D. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Interactions in Fibrosis and Repair. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Activation by Epithelial Cells and Fibroblasts. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2015, 12, S21–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, K.P.; Kitto, L.J.; Henderson, N.C. Alphav Integrins: Key Regulators of Tissue Fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Mi, L.; Walz, T.; Springer, T.A. Latent TGF-Beta Structure and Activation. Nature 2011, 474, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, F.A.; Contreras-Ruiz, L.; Masli, S. Thrombospondin-1-Dependent Immune Regulation by Transforming Growth Factor-Beta2-Exposed Antigen-Presenting Cells. Immunology 2015, 146, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Bowen, W.C.; Li, G.; Demetris, A.J.; Michalopoulos, G.K.; Wu, T. Cytosolic Phospholipase A2alpha and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Signaling Pathway Counteracts Transforming Growth Factor Beta-Mediated Inhibition of Primary and Transformed Hepatocyte Growth. Hepatology 2010, 52, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, T.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Kogure, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Takagi, H.; Mori, M.; Kojima, I. Transforming Growth Factor Beta and Activin Tonically Inhibit DNA Synthesis in the Rat Liver. Hepatology 2001, 34, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjabi, S.; Zenewicz, L.A.; Kamanaka, M.; Flavell, R.A. Anti-Inflammatory and Pro-Inflammatory Roles of TGF-Beta, IL-10, and IL-22 in Immunity and Autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, J.J.; Fenton, T.M.; Czajkowska, B.I.; Klementowicz, J.E.; Travis, M.A. Regulation of TGFbeta in the Immune System: An Emerging Role for Integrins and Dendritic Cells. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCuskey, R.S. The Hepatic Microvascular System in Health and its Response to Toxicants. Anat. Rec. 2008, 291, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Semela, D.; Iredale, J.; Shah, V.H. Sinusoidal Remodeling and Angiogenesis: A New Function for the Liver-Specific Pericyte? Hepatology 2007, 45, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, R.D.; Kanel, G.C.; Gaarde, W.A.; Deleve, L.D. Role of Differentiation of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in Progression and Regression of Hepatic Fibrosis in Rats. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soon, R.K., Jr.; Yee, H.F., Jr. Stellate Cell Contraction: Role, Regulation, and Potential Therapeutic Target. Clin. Liver Dis. 2008, 12, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulon, S.; Heindryckx, F.; Geerts, A.; Van Steenkiste, C.; Colle, I.; Van Vlierberghe, H. Angiogenesis in Chronic Liver Disease and Its Complications. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; D’Amico, G.; Hodivala-Dilke, K.M.; Reynolds, L.E. Integrins: The Keys to Unlocking Angiogenesis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinken, M.; Papeleu, P.; Snykers, S.; De Rop, E.; Henkens, T.; Chipman, J.K.; Rogiers, V.; Vanhaecke, T. Involvement of Cell Junctions in Hepatocyte Culture Functionality. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchini, C.; Amicone, L.; Alonzi, T.; Marchetti, A.; Mancone, C.; Tripodi, M. Molecular Mechanisms Controlling the Phenotype and the EMT/MET Dynamics of Hepatocyte. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munker, S.; Wu, Y.L.; Ding, H.G.; Liebe, R.; Weng, H.L. Can a Fibrotic Liver Afford Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition? World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4661–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Diehl, A.M. Evidence for and Against Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition in the Liver. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G881–G890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiari, S. Selectin-Mediated Leukocyte Trafficking During the Development of Autoimmune Disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivetic, A.; Hoskins Green, H.L.; Hart, S.J. L-Selectin: A Major Regulator of Leukocyte Adhesion, Migration and Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnaar, R.L. Glycobiology Simplified: Diverse Roles of Glycan Recognition in Inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertola, A.; Park, O.; Gao, B. Chronic plus Binge Ethanol Feeding Synergistically Induces Neutrophil Infiltration and Liver Injury in Mice: A Critical Role for E-Selectin. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dold, S.; Laschke, M.W.; Zhau, Y.; Schilling, M.; Menger, M.D.; Jeppsson, B.; Thorlacius, H. P-Selectin Glycoprotein Ligand-1-Mediated Leukocyte Recruitment Regulates Hepatocellular Damage in Acute Obstructive Cholestasis in Mice. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klintman, D.; Schramm, R.; Menger, M.D.; Thorlacius, H. Leukocyte Recruitment in Hepatic Injury: Selectin-Mediated Leukocyte Rolling is a Prerequisite for CD18-Dependent Firm Adhesion. J. Hepatol. 2002, 36, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolachala, V.L.; Palle, S.; Shen, M.; Feng, A.; Shayakhmetov, D.; Gupta, N.A. Loss of L-Selectin-Guided CD8(+), But not CD4(+), Cells Protects Against Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in a Steatotic Liver. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1258–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Johnston, B.; Lee, S.S.; Bullard, D.C.; Smith, C.W.; Beaudet, A.L.; Kubes, P. A Minimal Role for Selectins in the Recruitment of Leukocytes into the Inflamed Liver Microvasculature. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2782–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Hesse, M.; Sandler, N.G.; Kaviratne, M.; Hoffmann, K.F.; Chiaramonte, M.G.; Reiman, R.; Cheever, A.W.; Sypek, J.P.; Mentink-Kane, M.M. P-Selectin Suppresses Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice by Regulating Interferon Gamma and the IL-13 Decoy Receptor. Hepatology 2004, 39, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.H.; Hubscher, S.G.; Fisher, N.C.; Williams, A.; Robinson, M. Expression of E-Selectin and E-Selectin Ligands in Human Liver Inflammation. Hepatology 1996, 24, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalor, P.F.; Lai, W.K.; Curbishley, S.M.; Shetty, S.; Adams, D.H. Human Hepatic Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells Can be Distinguished by Expression of Phenotypic Markers Related to Their Specialised Functions in Vivo. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5429–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFoya, B.; Munroe, J.A.; Miyamoto, A.; Detweiler, M.A.; Crow, J.J.; Gazdik, T.; Albig, A.R. Beyond the Matrix: The Many Non-ECM Ligands for Integrins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuppan, D.; Ruehl, M.; Somasundaram, R.; Hahn, E.G. Matrix as a Modulator of Hepatic Fibrogenesis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2001, 21, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H. Cellular Adhesion Molecules: Regulation and Functional Significance in the Pathogenesis of Liver Diseases. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, G602–G611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodali, P.; Wu, P.; Lahiji, P.A.; Brown, E.J.; Maher, J.J. ANIT Toxicity Toward Mouse Hepatocytes in Vivo is Mediated Primarily by Neutrophils Via CD18. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 291, G355–G363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Nussenzweig, R.S.; Romero, P.; Zavala, F. The in Vivo Cytotoxic Activity of CD8+ T Cell Clones Correlates with Their Levels of Expression of Adhesion Molecules. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 175, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejjari, M.; Couvelard, A.; Mosnier, J.F.; Moreau, A.; Feldmann, G.; Degott, C.; Marcellin, P.; Scoazec, J.Y. Integrin Up-Regulation in Chronic Liver Disease: Relationship with Inflammation and Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis C. J. Pathol. 2001, 195, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, Y.; Patsenker, E.; Stickel, F.; Zaks, J.; Bhaskar, K.R.; Niedobitek, G.; Kolb, A.; Friess, H.; Schuppan, D. Integrin Alphavbeta6 is a Marker of the Progression of Biliary and Portal Liver Fibrosis and a Novel Target for Antifibrotic Therapies. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitroulis, I.; Alexaki, V.I.; Kourtzelis, I.; Ziogas, A.; Hajishengallis, G.; Chavakis, T. Leukocyte Integrins: Role in Leukocyte Recruitment and as Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 147, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Van Seventer, G.A.; Horgan, K.J.; Shaw, S. Roles of Adhesion Molecules in T-Cell Recognition: Fundamental Similarities Between Four Integrins on Resting Human T Cells (LFA-1, VLA-4, VLA-5, VLA-6) in Expression, Binding, and Costimulation. Immunol. Rev. 1990, 114, 109–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afford, S.C.; Humphreys, E.H.; Reid, D.T.; Russell, C.L.; Banz, V.M.; Oo, Y.; Vo, T.; Jenne, C.; Adams, D.H.; Eksteen, B. Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 Expression by Biliary Epithelium Promotes Persistence of Inflammation by Inhibiting Effector T-Cell Apoptosis. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1932–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpes, R.; Van Den Oord, J.J.; Desmet, V.J. Distribution of the VLA Family of Integrins in Normal and Pathological Human Liver Tissue. Gastroenterology 1991, 101, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.J.; Puranen, S.; Johnson, M.S.; Heino, J. The Collagen Receptor Subfamily of the Integrins. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeltz, C.; Gullberg, D. The Integrin-Collagen Connection-A Glue for Tissue Repair? J. Cell. Sci. 2016, 129, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.; Pritchett, J.; Llewellyn, J.; Mullan, A.F.; Athwal, V.S.; Dobie, R.; Harvey, E.; Zeef, L.; Farrow, S.; Streuli, C.; et al. PAK Proteins and YAP-1 Signalling Downstream of Integrin Beta-1 in Myofibroblasts Promote Liver Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.; Nakagawa, S.; Yazdani, S.; van Baarlen, J.; Venkatesh, A.; Koh, A.P.; Song, W.M.; Goossens, N.; Watanabe, H.; Beasley, M.B.; et al. Integrin alpha 11 in the Regulation of the Myofibroblast Phenotype: Implications for Fibrotic Diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eble, J.A. Collagen-Binding Integrins as Pharmaceutical Targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, J.D.; Byron, A.; Humphries, M.J. Integrin Ligands at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 3901–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaout, M.A. Biology and Structure of Leukocyte Beta 2 Integrins and Their Role in Inflammation. F1000Res 2016, 5, F1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Ley, K. Leukocyte Arrest: Biomechanics and Molecular Mechanisms of Beta2 Integrin Activation. Biorheology 2015, 52, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasiuk, A.; Zak, J.; Maciorkowska, E.; Panasiuk, B.; Prokopowicz, D. Expression of Beta2-Integrin on Leukocytes in Liver Cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 6193–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malissen, B. Dancing the Immunological Two-Step. Science 1999, 285, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondino, A.; Khoruts, A.; Jenkins, M.K. The Anatomy of T-Cell Activation and Tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, S.Y.; Dustin, M.L. T-Cell Activation: A Multidimensional Signaling Network. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2002, 14, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.K.; Kelleher, D. Not Just an Adhesion Molecule: LFA-1 Contact Tunes the T Lymphocyte Program. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingren, A.G.; Parra, E.; Varga, M.; Kalland, T.; Sjogren, H.O.; Hedlund, G.; Dohlsten, M. T Cell Activation Pathways: B7, LFA-3, and ICAM-1 Shape Unique T Cell Profiles. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 37, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, N.C.; Arnold, T.D.; Katamura, Y.; Giacomini, M.M.; Rodriguez, J.D.; McCarty, J.H.; Pellicoro, A.; Raschperger, E.; Betsholtz, C.; Ruminski, P.G.; et al. Targeting of Alphav Integrin Identifies a Core Molecular Pathway that Regulates Fibrosis in Several Organs. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, N.I.; Jo, H.; Chen, C.; Tsujino, K.; Arnold, T.D.; DeGrado, W.F.; Sheppard, D. The Alphavbeta1 Integrin Plays a Critical in Vivo Role in Tissue Fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 288ra279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Murphy, F.R.; Gehdu, N.; Zhang, J.; Iredale, J.P.; Benyon, R.C. Engagement of Alphavbeta3 Integrin Regulates Proliferation and Apoptosis of Hepatic Stellate Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 23996–24006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhanna, N.; Doron, S.; Wald, O.; Horani, A.; Eid, A.; Pappo, O.; Friedman, S.L.; Safadi, R. Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells After Phagocytosis of Lymphocytes: A Novel Pathway of Fibrogenesis. Hepatology 2008, 48, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbay, A.; Taimr, P.; Torok, N.; Higuchi, H.; Friedman, S.; Gores, G.J. Apoptotic Body Engulfment by a Human Stellate Cell Line is Profibrogenic. Lab. Invest. 2003, 83, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, S.S.; Jiang, J.X.; Wu, J.; Halsted, C.; Friedman, S.L.; Zern, M.A.; Torok, N.J. Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Bodies by Hepatic Stellate Cells Induces NADPH Oxidase and is Associated with Liver Fibrosis in Vivo. Hepatology 2006, 43, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsenker, E.; Popov, Y.; Stickel, F.; Schneider, V.; Ledermann, M.; Sagesser, H.; Niedobitek, G.; Goodman, S.L.; Schuppan, D. Pharmacological Inhibition of Integrin Alphavbeta3 Aggravates Experimental Liver Fibrosis and Suppresses Hepatic Angiogenesis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogten, J.M.; Drixler, T.A.; Te Velde, E.A.; Schipper, M.E.; Van Vroonhoven, T.J.; Voest, E.E.; Borel Rinkes, I.H. Angiostatin Inhibits Experimental Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2004, 19, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiji, H.; Kuriyama, S.; Yoshii, J.; Ikenaka, Y.; Noguchi, R.; Hicklin, D.J.; Wu, Y.; Yanase, K.; Namisaki, T.; Yamazaki, M.; et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Receptor Interaction is a Prerequisite for Murine Hepatic Fibrogenesis. Gut 2003, 52, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, L.E.; Wyder, L.; Lively, J.C.; Taverna, D.; Robinson, S.D.; Huang, X.; Sheppard, D.; Hynes, R.O.; Hodivala-Dilke, K.M. Enhanced Pathological Angiogenesis in Mice Lacking Beta3 Integrin or Beta3 and Beta5 Integrins. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuss, J.M.; Gallo, J.; DeLisser, H.M.; Klimanskaya, I.V.; Folkesson, H.G.; Pittet, J.F.; Nishimura, S.L.; Aldape, K.; Landers, D.V.; Carpenter, W.; et al. Expression of the Beta 6 Integrin Subunit in Development, Neoplasia and Tissue Repair Suggests a Role in Epithelial Remodeling. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 2241–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.W.; Ikenaga, N.; Liu, S.B.; Sverdlov, D.Y.; Vaid, K.A.; Dixit, R.; Weinreb, P.H.; Violette, S.; Sheppard, D.; Schuppan, D.; et al. Integrin Alphavbeta6 Critically Regulates Hepatic Progenitor Cell Function and Promotes Ductular Reaction, Fibrosis, and Tumorigenesis. Hepatology 2016, 63, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsenker, E.; Popov, Y.; Stickel, F.; Jonczyk, A.; Goodman, S.L.; Schuppan, D. Inhibition of Integrin Alphavbeta6 on Cholangiocytes Blocks Transforming Growth FACTOR-Beta Activation and Retards Biliary Fibrosis Progression. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, L.; Robinson, P.M.; Jorgensen, M.; Oh, S.H.; Brown, A.R.; Weinreb, P.H.; Trinh, T.L.; Yianni, P.; Liu, C.; Leask, A.; et al. Connective Tissue Growth Factor and Integrin Alphavbeta6: A New Pair of Regulators Critical for duCtular Reaction and Biliary Fibrosis in Mice. Hepatology 2015, 61, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, S.N.; Matchett, K.P.; Taylor, R.S.; Huang, K.; Li, J.T.; Saeteurn, K.; Donnelly, M.C.; Simpson, E.E.M.; Pollack, J.L.; Atakilit, A.; et al. Loss of Integrin Alphavbeta8 in Murine Hepatocytes Accelerates Liver Regeneration. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, M.; Yap, A.S. Classical Cadherin Adhesion Molecules: Coordinating Cell Adhesion, Signaling and the Cytoskeleton. J. Mol. Histol. 2004, 35, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, I.S.; Hulpiau, P.; Saeys, Y.; Van Roy, F. Evolution and Diversity of Cadherins and Catenins. Exp. Cell. Res. 2017, 358, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartsock, A.; Nelson, W.J. Adherens and Tight Junctions: Structure, Function and Connections to the Actin Cytoskeleton. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.D.; Chen, C.P.; Bahna, F.; Honig, B.; Shapiro, L. Cadherin-Mediated Cell-Cell Adhesion: Sticking Together as a Family. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003, 13, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomayor, M.; Gaudet, R.; Corey, D.P. Sorting Out a Promiscuous Superfamily: Towards Cadherin Connectomics. Trends. Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delva, E.; Tucker, D.K.; Kowalczyk, A.P. The Desmosome. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a002543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Pradhan-Sundd, T.; Poddar, M.; Singh, S.; Kikuchi, A.; Stolz, D.B.; Shou, W.; Li, Z.; Nejak-Bowen, K.N.; Monga, S.P. Mice with Hepatic Loss of the Desmosomal Protein Gamma-Catenin Are Prone to Cholestatic Injury and Chemical Carcinogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 3274–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robenek, H.; Herwig, J.; Themann, H. The Morphologic Characteristics of Intercellular Junctions Between Normal Human Liver Cells and Cells from Patients with Extrahepatic Cholestasis. Am. J. Pathol. 1980, 100, 93–114. [Google Scholar]
- Monga, S.P. Role and Regulation of Beta-Catenin Signaling During Physiological Liver Growth. Gene Expr. 2014, 16, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monga, S.P. Beta-Catenin Signaling and Roles in Liver Homeostasis, Injury, and Tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1294–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, H.; Hikiba, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Font-Burgada, J.; Sakamoto, K.; Hayakawa, Y.; Taniguchi, K.; Umemura, A.; Kinoshita, H.; Sakitani, K.; et al. Loss of Liver E-cadherin Induces Sclerosing Cholangitis and Promotes Carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hengel, J.; Van Den Broeke, C.; Pieters, T.; Libbrecht, L.; Hofmann, I.; van Roy, F. Inactivation of p120 Catenin in Mice Disturbs Intrahepatic Bile Duct Development and Aggravates Liver Carcinogenesis. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 95, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Krijger, M.; Wildenberg, M.E.; De Jonge, W.J.; Ponsioen, C.Y. Return to Sender: Lymphocyte Trafficking Mechanisms as Contributors to Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartland, S.N.; Murphy, F.; Aucott, R.L.; Abergel, A.; Zhou, X.; Waung, J.; Patel, N.; Bradshaw, C.; Collins, J.; Mann, D.; et al. Active Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Promotes Apoptosis of Hepatic Stellate Cells Via the Cleavage of Cellular N-Cadherin. Liver Int. 2009, 29, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, F.; Waung, J.; Collins, J.; Arthur, M.J.; Nagase, H.; Mann, D.; Benyon, R.C.; Iredale, J.P. N-Cadherin Cleavage During Activated Hepatic Stellate Cell Apoptosis is Inhibited by Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1. Comp. Hepatol. 2004, 3, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cho, I.J.; Kim, Y.W.; Han, C.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Anderson, R.A.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, S.J.; Kim, S.G. E-Cadherin Antagonizes Transforming Growth Factor Beta1 Gene Induction in Hepatic Stellate Cells by Inhibiting RhoA-Dependent Smad3 Phosphorylation. Hepatology 2010, 52, 2053–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Geraud, C.; Evdokimov, K.; Straub, B.K.; Peitsch, W.K.; Demory, A.; Dorflinger, Y.; Schledzewski, K.; Schmieder, A.; Schemmer, P.; Augustin, H.G.; et al. Unique Cell Type-Specific Junctional Complexes in Vascular Endothelium of Human and Rat Liver Sinusoids. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Tamura, S.; Nammo, T.; Fukui, K.; Kiso, S.; Nagafuchi, A. Development of Complementary Expression Patterns of E-And N-Cadherin in the Mouse Liver. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.; Johnson, J.L.; Jackson, C.L.; White, S.J.; George, S.J. MMP-7 Mediates Cleavage of N-Cadherin and Promotes Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.K. Integrins and Cadherins as Therapeutic Targets in Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, D.J.; Wu, M.; Le, T.T.; Cho, S.H.; Brenner, M.B.; Blackburn, M.R.; Agarwal, S.K. Cadherin-11 Contributes to Pulmonary Fibrosis: Potential Role in TGF-Beta Production and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodyga, M.; Cambridge, E.; Karvonen, H.M.; Pakshir, P.; Wu, B.; Boo, S.; Kiebalo, M.; Kaarteenaho, R.; Glogauer, M.; Kapoor, M.; et al. Cadherin-11-Mediated Adhesion of Macrophages to Myofibroblasts Establishes a Profibrotic Niche of Active TGF-Beta. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaao3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Row, S.; Liu, Y.; Alimperti, S.; Agarwal, S.K.; Andreadis, S.T. Cadherin-11 is a Novel Regulator of Extracellular Matrix Synthesis and Tissue Mechanics. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 2950–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedroza, M.; To, S.; Smith, J.; Agarwal, S.K. Cadherin-11 Contributes to Liver Fibrosis Induced By Carbon Tetrachloride. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Pan, R.; Shen, X.; Nie, Y.; Wu, Y. CDH11 Promotes Liver Fibrosis Via Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 508, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, A.K.; Rothlein, R. Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1) Expression and Cell Signaling Cascades. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebuck, K.A.; Finnegan, A. Regulation of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (CD54) Gene Expression. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 66, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.H.; Hubscher, S.G.; Shaw, J.; Johnson, G.D.; Babbs, C.; Rothlein, R.; Neuberger, J.M. Increased Expression of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 on Bile Ducts in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Hepatology 1991, 14, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.H.; Mainolfi, E.; Burra, P.; Neuberger, J.M.; Ayres, R.; Elias, E.; Rothlein, R. Detection of Circulating Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 in Chronic Liver Diseases. Hepatology 1992, 16, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, S.; Fleming, K.; Chapman, R. Adhesion Molecule Expression in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Primary Biliary Cirrhosis. Gut 1995, 36, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubscher, S.G.; Adams, D.H. ICAM-1 Expression in Normal liver. J. Clin. Pathol. 1991, 44, 438–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyck, R.; Enzmann, G. The Physiological Roles of ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 in Neutrophil Migration into Tissues. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2015, 22, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellerbrand, C.; Wang, S.C.; Tsukamoto, H.; Brenner, D.A.; Rippe, R.A. Expression of Intracellular Adhesion Molecule 1 by Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells. Hepatology 1996, 24, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.C.; Hung, C.H.; Lu, L.; Qian, S. Hepatic Immune Tolerance Induced by Hepatic Stellate Cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11887–11892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodfin, A.; Voisin, M.B.; Nourshargh, S. PECAM-1: A Multi-Functional Molecule in Inflammation and Vascular Biology. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 2514–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertkiatmongkol, P.; Liao, D.; Mei, H.; Hu, Y.; Newman, P.J. Endothelial Functions of Platelet/Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (CD31). Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2016, 23, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelli-Berg, F.M.; Clement, M.; Mauro, C.; Caligiuri, G. An Immunologist’s Guide to CD31 Function in T-Cells. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 2343–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privratsky, J.R.; Newman, D.K.; Newman, P.J. PECAM-1: Conflicts of Interest in Inflammation. Life Sci. 2010, 87, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chosay, J.G.; Fisher, M.A.; Farhood, A.; Ready, K.A.; Dunn, C.J.; Jaeschke, H. Role of PECAM-1 (CD31) in Neutrophil Transmigration in Murine Models of Liver and Peritoneal Inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, G776–G782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, A.C.; Stolz, D.B.; Ross, M.A.; Hernandez-Zavala, A.; Soucy, N.V.; Klei, L.R.; Barchowsky, A. Arsenic Stimulates Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell Capillarization and Vessel Remodeling in Mouse Liver. Hepatology 2007, 45, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintermann, E.; Bayer, M.; Ehser, J.; Aurrand-Lions, M.; Pfeilschifter, J.M.; Imhof, B.A.; Christen, U. Murine Junctional Adhesion Molecules JAM-B and JAM-C Mediate Endothelial and Stellate Cell Interactions during Hepatic Fibrosis. Cell Adh. Migr. 2016, 10, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, K.; Lindhorst, A.; Tron, K.; Ramadori, G.; Saile, B. Decrease of PECAM-1-Gene-Expression Induced by Proinflammatory Cytokines IFN-Gamma and IFN-Alpha is Reversed by TGF-Beta in Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells and Hepatic Mononuclear Phagocytes. BMC Physiol. 2008, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvelard, A.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Feldmann, G. Expression of Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix Adhesion Proteins by Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in the Normal and Cirrhotic Human Liver. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 738–752. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, R.; Boylan, B.; Gruman, L.; Newman, P.J.; North, P.E.; Newman, D.K. The Proinflammatory Phenotype of PECAM-1-Deficient Mice Results in Atherogenic Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G1205–G1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, I.A.; Malik, G.; Strobel, P.; Wilting, J. Development of A New Mouse Model for Intrahepatic Cholangiocellular Carcinoma: Accelerating Functions of Pecam-1. Cancers 2019, 11, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, P.; Sjostrom, M.; Soderberg, C.; Kinnman, N.; Stal, P.; Hultcrantz, R. Attenuated Liver Fibrosis after Bile Duct Ligation and Defective Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation in Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Knockout Mice. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libbrecht, L.; Cassiman, D.; Desmet, V.; Roskams, T. Expression of Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule in Human Liver Development and in Congenital and Acquired Liver Diseases. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 116, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiman, D.; Libbrecht, L.; Desmet, V.; Denef, C.; Roskams, T. Hepatic Stellate Cell/Myofibroblast Subpopulations in Fibrotic Human and Rat Livers. J. Hepatol. 2002, 36, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Urbani, S.; Bradfield, P.F.; Imhof, B.A. Tight Junction Dynamics: The Role of Junctional Adhesion Molecules (JAMs). Cell Tissue. Res. 2014, 355, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Fraemohs, L.; Dejana, E. The Role of Junctional Adhesion Molecules in Vascular Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Stankovic, M.; Lee, B.P.; Aurrand-Lions, M.; Hahn, C.N.; Lu, Y.; Imhof, B.A.; Vadas, M.A.; Gamble, J.R. JAM-C Induces Endothelial Cell Permeability Through its Association and Regulation of {beta}3 Integrins. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebnet, K.; Suzuki, A.; Ohno, S.; Vestweber, D. Junctional Adhesion Molecules (JAMs): More Molecules with Dual Functions? J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintermann, E.; Bayer, M.; Conti, C.B.; Fuchs, S.; Fausther, M.; Leung, P.S.; Aurrand-Lions, M.; Taubert, R.; Pfeilschifter, J.M.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; et al. Junctional Adhesion Molecules JAM-B and JAM-C Promote Autoimmune-Mediated Liver Fibrosis in Mice. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 91, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, C.M.; Gottardi, C.J. Molecular Components of the Adherens Junction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh-Horikawa, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Takahashi, K.; Miyahara, M.; Nishimura, M.; Tachibana, K.; Mizoguchi, A.; Takai, Y. Nectin-3, a New Member of Immunoglobulin-Like Cell Adhesion Molecules That Shows Homophilic and Heterophilic Cell-Cell Adhesion Activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10291–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, B.M.; Thompson, N.L.; Hixson, D.C. Tightly Regulated Induction of the Adhesion Molecule Necl-5/CD155 During Rat Liver Regeneration and Acute Liver Injury. Hepatology 2006, 43, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Nishikawa, Y.; Ohnuma, K.; Ohnuma, I.; Koma, Y.; Sato, A.; Enomoto, K.; Tsujimura, T.; Yokozaki, H. SgIGSF is a Novel Biliary-Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Mediating Duct/Ductule Development. Hepatology 2007, 45, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.J.; Tickle, J.; Vesterhus, M.N.; Eddowes, P.J.; Bruns, T.; Vainio, J.; Parker, R.; Smith, D.; Liaskou, E.; Thorbjornsen, L.W.; et al. Vascular Adhesion Protein-1 is Elevated in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis, is Predictive of Clinical Outcome and Facilitates Recruitment of Gut-Tropic Lymphocytes to Liver in a Substrate-Dependent Manner. Gut 2018, 67, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonder, C.S.; Norman, M.U.; Swain, M.G.; Zbytnuik, L.D.; Yamanouchi, J.; Santamaria, P.; Ajuebor, M.; Salmi, M.; Jalkanen, S.; Kubes, P. Rules of Recruitment for Th1 and Th2 Lymphocytes in Inflamed Liver: A Role for Alpha-4 Integrin and Vascular Adhesion Protein-1. Immunity 2005, 23, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, C.J.; Shepherd, E.L.; Claridge, L.C.; Rantakari, P.; Curbishley, S.M.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Hubscher, S.G.; Reynolds, G.M.; Aalto, K.; Anstee, Q.M.; et al. Vascular Adhesion Protein-1 Promotes Liver Inflammation and Drives Hepatic Fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2015, 125, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurkijarvi, R.; Adams, D.H.; Leino, R.; Mottonen, T.; Jalkanen, S.; Salmi, M. Circulating form of Human Vascular Adhesion Protein-1 (VAP-1): Increased Serum Levels in Inflammatory Liver Diseases. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hillan, K.J.; Hagler, K.E.; MacSween, R.N.; Ryan, A.M.; Renz, M.E.; Chiu, H.H.; Ferrier, R.K.; Bird, G.L.; Dhillon, A.P.; Ferrell, L.D.; et al. Expression of the Mucosal Vascular Addressin, MAdCAM-1, in Inflammatory Liver Disease. Liver 1999, 19, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drescher, H.K.; Schippers, A.; Clahsen, T.; Sahin, H.; Noels, H.; Hornef, M.; Wagner, N.; Trautwein, C.; Streetz, K.L.; Kroy, D.C. Beta7-Integrin and MAdCAM-1 Play Opposing Roles During the Development of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.; Weston, C.J.; Oo, Y.H.; Westerlund, N.; Stamataki, Z.; Youster, J.; Hubscher, S.G.; Salmi, M.; Jalkanen, S.; Lalor, P.F.; et al. Common Lymphatic Endothelial and Vascular Endothelial Receptor-1 Mediates the Transmigration of Regulatory T Cells Across Human Hepatic Sinusoidal Endothelium. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4147–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantakari, P.; Patten, D.A.; Valtonen, J.; Karikoski, M.; Gerke, H.; Dawes, H.; Laurila, J.; Ohlmeier, S.; Elima, K.; Hubscher, S.G.; et al. Stabilin-1 Expression Defines a Subset of Macrophages That Mediate Tissue Homeostasis and Prevent Fibrosis in Chronic Liver Injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9298–9303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douds, A.C.; Lim, A.G.; Jazrawi, R.P.; Finlayson, C.; Maxwell, J.D. Serum Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 in Alcoholic Liver Disease and Its Relationship with Histological Disease Severity. J. Hepatol. 1997, 26, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplanski, G.; Farnarier, C.; Payan, M.J.; Bongrand, P.; Durand, J.M. Increased Levels of Soluble Adhesion Molecules in the Serum of Patients with Hepatitis C. Correlation with Cytokine Concentrations and Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1997, 42, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefere, S.; Van de Velde, F.; Devisscher, L.; Bekaert, M.; Raevens, S.; Verhelst, X.; Van Nieuwenhove, Y.; Praet, M.; Hoorens, A.; Van Steenkiste, C.; et al. Serum Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Predicts Significant Liver Fibrosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.G.; Jazrawi, R.P.; Levy, J.H.; Petroni, M.L.; Douds, A.C.; Maxwell, J.D.; Northfield, T.C. Soluble E-Selectin and Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 1995, 22, 416–422. [Google Scholar]
- Zohrens, G.; Armbrust, T.; Pirzer, U.; Meyer Zum Buschenfelde, K.H.; Ramadori, G. Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Concentration in Sera of Patients with Acute and Chronic Liver Disease: Relationship to Disease Activity and Cirrhosis. Hepatology 1993, 18, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexiou, D.; Karayiannakis, A.J.; Syrigos, K.N.; Zbar, A.; Sekara, E.; Michail, P.; Rosenberg, T.; Diamantis, T. Clinical Significance of Serum Levels of E-Selectin, Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1, and Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 in Gastric Cancer Patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perabo, F.; Sharma, S.; Gierer, R.; Wirger, A.; Fimmers, R.; Steiner, G.; Adam, M.; Schultze-Seemann, W. Circulating Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1), Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and E-Selectin in Urological Malignancies. Indian J. Cancer 2001, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khodabandehlou, K.; Masehi-Lano, J.J.; Poon, C.; Wang, J.; Chung, E.J. Targeting Cell Adhesion Molecules with Nanoparticles Using in Vivo and Flow-Based in Vitro Models of Atherosclerosis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich-Rust, M.; Rosenberg, W.; Parkes, J.; Herrmann, E.; Zeuzem, S.; Sarrazin, C. Comparison of ELF, FibroTest and FibroScan for the Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Song, Z.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, C.; Tu, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Lu, W. Molecular Imaging of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activity by Visualization of Hepatic Integrin Alphavbeta3 Expression with SPECT in Rat. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yan, H.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Wu, J.; Wu, S.; Rao, S.; Gao, X.; Jin, Q. Non-Invasively Differentiating Extent of Liver Fibrosis by Visualizing Hepatic Integrin Alphavbeta3 Expression with an MRI Modality in Mice. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, P.; Iredale, J.P.; Fallowfield, J.A. Resolution of Liver Fibrosis: Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Relevance. Semin. Liver Dis. 2015, 35, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.J.; Friedman, S.L.; Lee, Y.A. Antifibrotic Therapies: Where Are We Now? Semin. Liver Dis. 2016, 36, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iredale, J.P.; Pellicoro, A.; Fallowfield, J.A. Liver Fibrosis: Understanding the Dynamics of Bidirectional Wound Repair to Inform the Design of Markers and Therapies. Dig. Dis. 2017, 35, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppan, D.; Ashfaq-Khan, M.; Yang, A.T.; Kim, Y.O. Liver Fibrosis: Direct Antifibrotic Agents and Targeted Therapies. Matrix Biol. 2018, 68, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuppan, D.; Kim, Y.O. Evolving Therapies for Liver Fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 1887–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torok, N.J.; Dranoff, J.A.; Schuppan, D.; Friedman, S.L. Strategies and Endpoints of Antifibrotic Drug Trials: Summary and Recommendations from the AASLD Emerging Trends Conference, Chicago, June 2014. Hepatology 2015, 62, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trautwein, C.; Friedman, S.L.; Schuppan, D.; Pinzani, M. Hepatic Fibrosis: Concept to Treatment. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S15–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartneck, M.; Warzecha, K.T.; Tacke, F. Therapeutic Targeting of Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis by Nanomedicine. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2014, 3, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Violatto, M.B.; Casarin, E.; Talamini, L.; Russo, L.; Baldan, S.; Tondello, C.; Messmer, M.; Hintermann, E.; Rossi, A.; Passoni, A.; et al. Dexamethasone Conjugation to Biodegradable Avidin-Nucleic-Acid-Nano-Assemblies Promotes Selective Liver Targeting and Improves Therapeutic Efficacy in an Autoimmune Hepatitis Murine Model. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 4410–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndtz, K.; Corrigan, M.; Rowe, A.; Kirkham, A.; Barton, D.; Fox, R.P.; Llewellyn, L.; Athwal, A.; Wilkhu, M.; Chen, Y.Y.; et al. Investigating the Safety and Activity of the Use of BTT1023 (Timolumab), in the Treatment of Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (BUTEO): A Single-Arm, Two-Stage, Open-Label, Multi-Centre, Phase Ii Clinical Trial Protocol. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e015081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Gan-Schreier, H.; Goeppert, B.; Chamulitrat, W.; Stremmel, W.; Pathil, A. Bivalent Ligand UDCA-LPE Inhibits Pro-Fibrogenic Integrin Signalling by Inducing Lipid Raft-Mediated Internalization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hou, Y.; Ji, G.; Song, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dai, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Targeted Delivery of the RGD-Labeled Biodegradable Polymersomes Loaded with the Hydrophilic Drug Oxymatrine on Cultured Hepatic Stellate Cells and Liver Fibrosis in Rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 52, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.L.; Pan, H.; Lu, W.Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.Y. Cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp Peptide-Labeled Liposomes for Targeting Drug Therapy of Hepatic Fibrosis in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenne, C.N.; Kubes, P. Immune Surveillance by the Liver. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
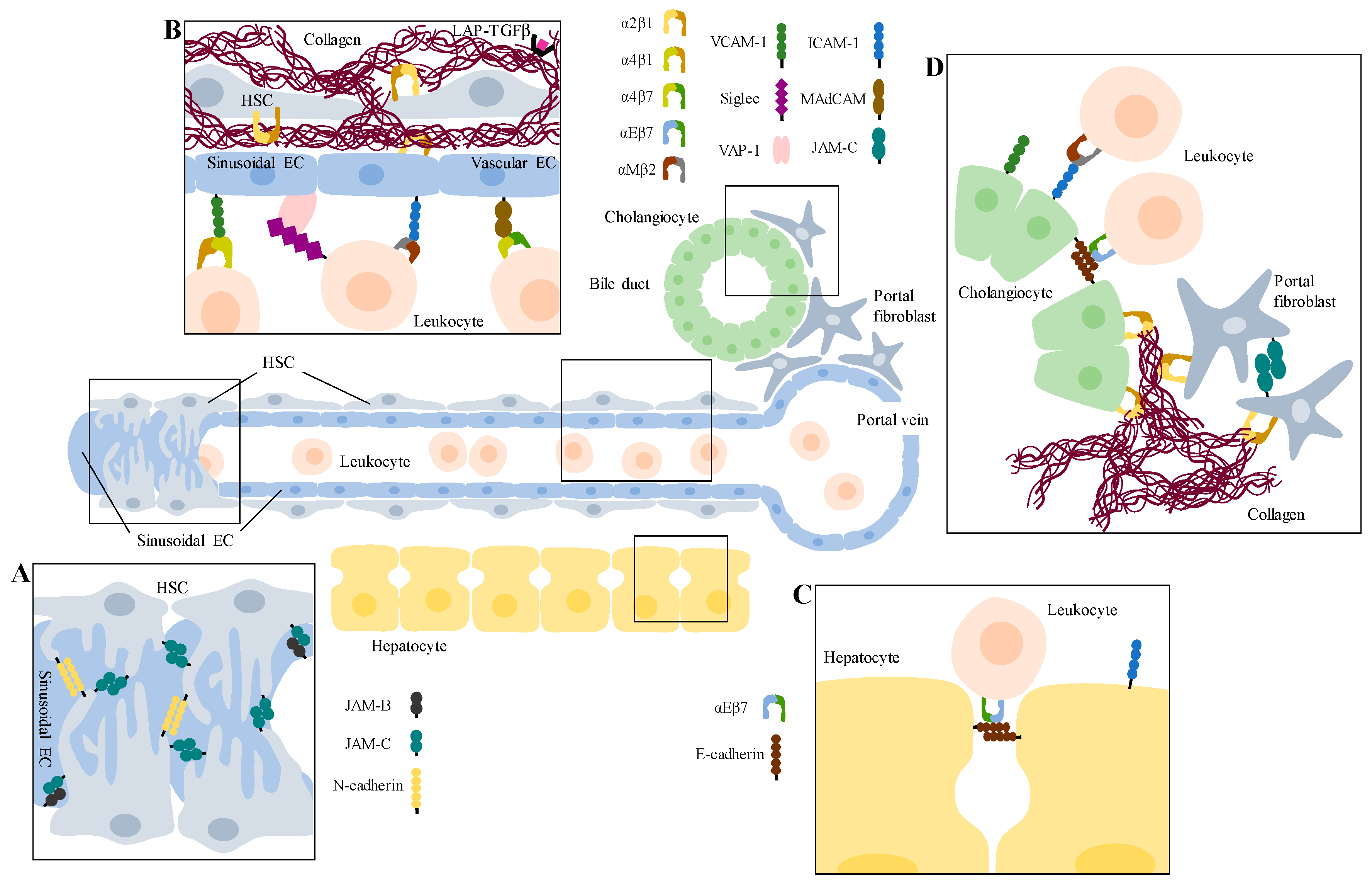
| Adhesion Molecule | Adhesion Molecule Expressing Resident and Immigrated Liver Cell Type | ECM Ligand and Counter-Receptor | Counter-receptor Expressing Resident and Immigrated Liver Cell Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selectins E-selectin P-selectin L-selectin | vEC vEC, P T | PSGL-1 PSGL-1 MECA-79, MAdCAM-1 | LC LC EC |
| Integrins α1β1 (VLA-1) α2β1 (VLA-2) α3β1 (VLA-3) α4β1 (VLA-4) α5β1 (VLA-5) α6β1 (VLA-6) α11β1 αLβ2 (LFA-1) αMβ2 (Mac-1) αXβ2 (p150,95) αDβ2 αVβ1 αVβ3 αVβ5 αVβ6 αVβ8 α4β7 αEβ7 | sEC, vEC, H, HSC C, sEC, vEC, periportal H, HSC C, vEC, H sEC, LC C, sEC, vEC, H, HSC C, vEC, H HSC LC LC LC LC HSC EC, HSC EC, HSC C, H H, HSC T T, D | CL, LN CL, LN LN FN, JAM-B, MAdCAM-1, VCAM-1 FN LN CL ICAMs, JAM-A ICAM, JAM-C ICAM, JAM-C ICAM, VCAM FN, LAP-TGFβ FN, TN, VN, LAP-TGFβ, JAM-A, JAM-C VN, LAP-TGFβ FN, TN, LAP-TGFβ VN, LAP-TGFβ FN, MAdCAM-1, VCAM-1 E-cadherin | C, EC, H, HSC EC, EpC, HSC, LC EC, EpC, HSC EC, C, H, HSC EC, C, H, HSC EC, C, H, HSC EC C, H, HSC |
| Adhesion Molecule | Adhesion Molecule Expressing Resident and Immigrated Liver Cell Type | Counter-Receptor | Counter-Receptor Expressing Resident and Immigrated Liver Cell Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cadherins | |||
| Desmoglein Desmocollin VE-cadherin E-cadherin N-cadherin Cadherin-11 | EpC EpC EC C, periportal H, HSC H, HSC H, HSC, M | Desmoglein, Desmocollin Desmocollin, Desmoglein VE-cadherin E-cadherin, [αEβ7, KLRG1] N-cadherin Cadherin-11 | EpC EpC EC C, periportal H, HSC, [T, D, NK] H, HSC H, HSC, M |
| IgCAMs | |||
| ICAM-1 VCAM-1 PECAM-1 NCAM JAM-A JAM-B JAM-C | C, EC, H, HSC C, EC, HSC EC, LC C, HSC, PF EC, EpC, LC, P mouse sEC and vEC C, sEC, vEC, HSC, PF, SM human LC | ICAM-1, β2 integrins like αLβ2 VCAM-1, α4β1 PECAM-1, [αVβ3] NCAM JAM-A, αLβ2, αVβ3 JAM-C, JAM-B, [α4β1] JAM-B, JAM-C, [αMβ2, αXβ2, αVβ2] | EC, C, H, HSC, LC EC, C, HSC, LC EC, [T] C, HSC, PF EC, EpC, P, LC mouse sEC and vEC, [LC] C, sEC, vEC, HSC, PF, SM, [LC] |
| Non-classical | |||
| VAP-1 MAdCAM-1 Stabilin-1 | vEC, sEC, HSC vEC sEC, vEC | Siglec-9, Siglec-10 α4β1, α4β7, L-selectin αLβ2 | LC T Treg, B |
| Liver Cell | Interaction Type | Functions/Effects | CAM Group Involved |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSC | HSC/ECM | Induction of TGFβ release Coordination of fibrogenic activation and perpetuation Perception of ECM composition Support of fibrotic ECM synthesis Coordination of motility and contractility | Integrins |
| HSC/HSC | Contribution to fibrogenic activation and survival Coordination of contractility and motility | Cadherins, IgCAMs | |
| HSC/sEC | Vessel wall stabilization and diameter control Support of fibrosis-associated neovascularization | IgCAMs | |
| HSC/T cell | HSC activation after phagocytosis of T cells | IgCAM (ICAM-1) | |
| sEC | sEC/ECM | Coordination of capillarization, proliferation and motility Support of fibrosis-associated neovascularization | Integrins |
| sEC/sEC | Contribution to tissue integrity, cell polarity, functionality Coordination of motility and neovascularization | Cadherins, IgCAMs | |
| sEC/HSC | sECs influence HSCs rather by soluble factors than direct cell-cell contact | IgCAMs | |
| sEC/leukocyte | Leukocyte recruitment | Integrins, cadherins, IgCAMs, non-classical CAMs | |
| EpC | EpC/ECM | Coordination of polarity, homeostasis, proliferation Coordination of motility | Integrins |
| EpC/EpC | Contribution to tissue integrity, cell polarity, proliferation and functionality Coordination of motility | Cadherins, IgCAMs | |
| EpC/leukocyte | Leukocyte recruitment, support of leukocyte survival | Integrins, cadherins, IgCAMs |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hintermann, E.; Christen, U. The Many Roles of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Hepatic Fibrosis. Cells 2019, 8, 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121503
Hintermann E, Christen U. The Many Roles of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Hepatic Fibrosis. Cells. 2019; 8(12):1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121503
Chicago/Turabian StyleHintermann, Edith, and Urs Christen. 2019. "The Many Roles of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Hepatic Fibrosis" Cells 8, no. 12: 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121503
APA StyleHintermann, E., & Christen, U. (2019). The Many Roles of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Hepatic Fibrosis. Cells, 8(12), 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121503





