Very Long-Chain C24:1 Ceramide Is Increased in Serum Extracellular Vesicles with Aging and Can Induce Senescence in Bone-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Serum Samples, EV Isolation, and EV Characterization
2.2. Lipidomic Analysis of Serum EVs
2.3. In Vitro Studies of Exosome Uptake
2.4. Loading of C24:1 Ceramide into Exosomes and Analysis of Cell Senescence
2.5. Real-Time PCR Analysis of Sphingomyelinase Expression
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
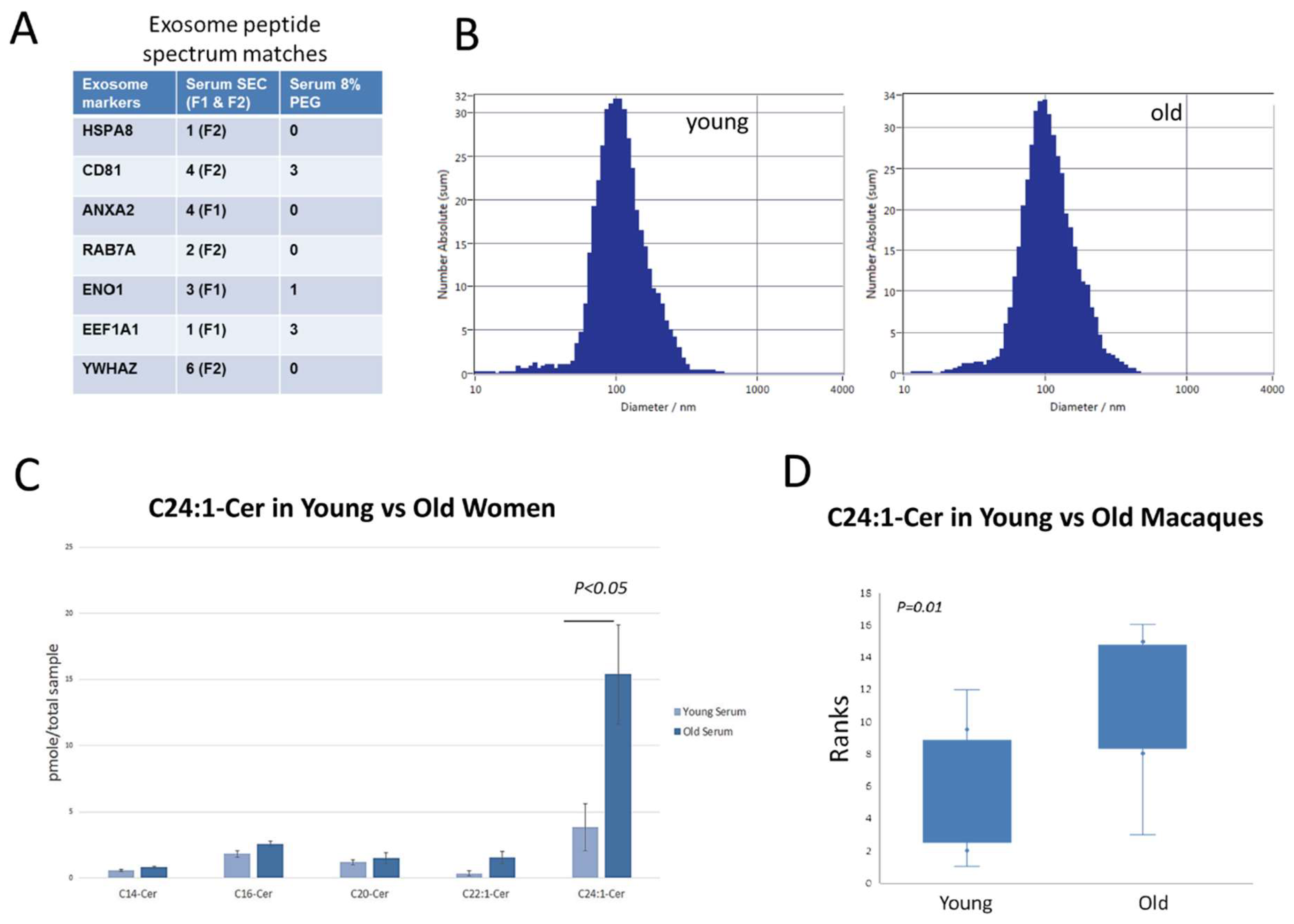
3.1. C24:1 Ceramide Is Increased with Age in Extracellular Vesicles from Older Human Subjects and Non-Human Primates
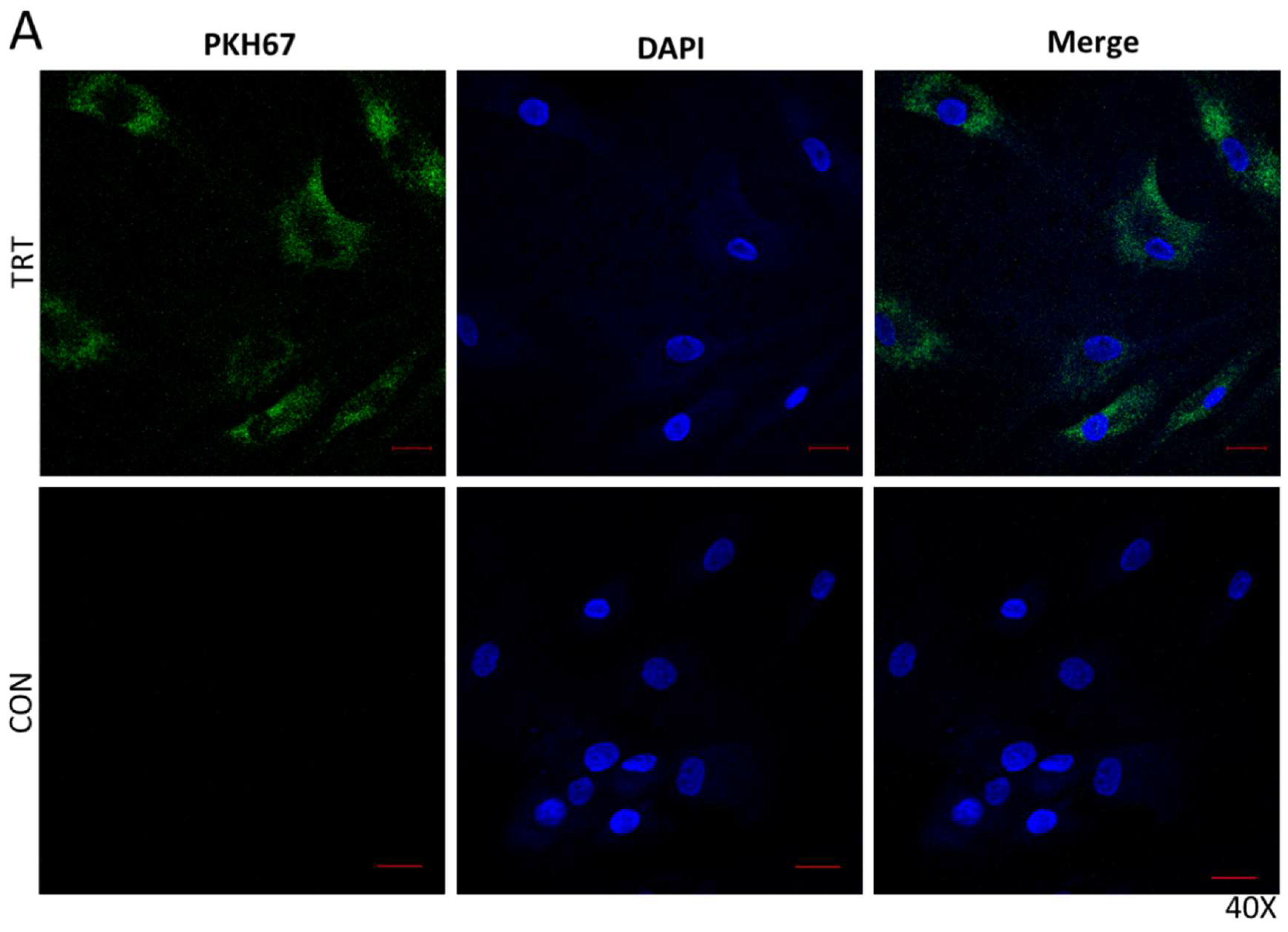
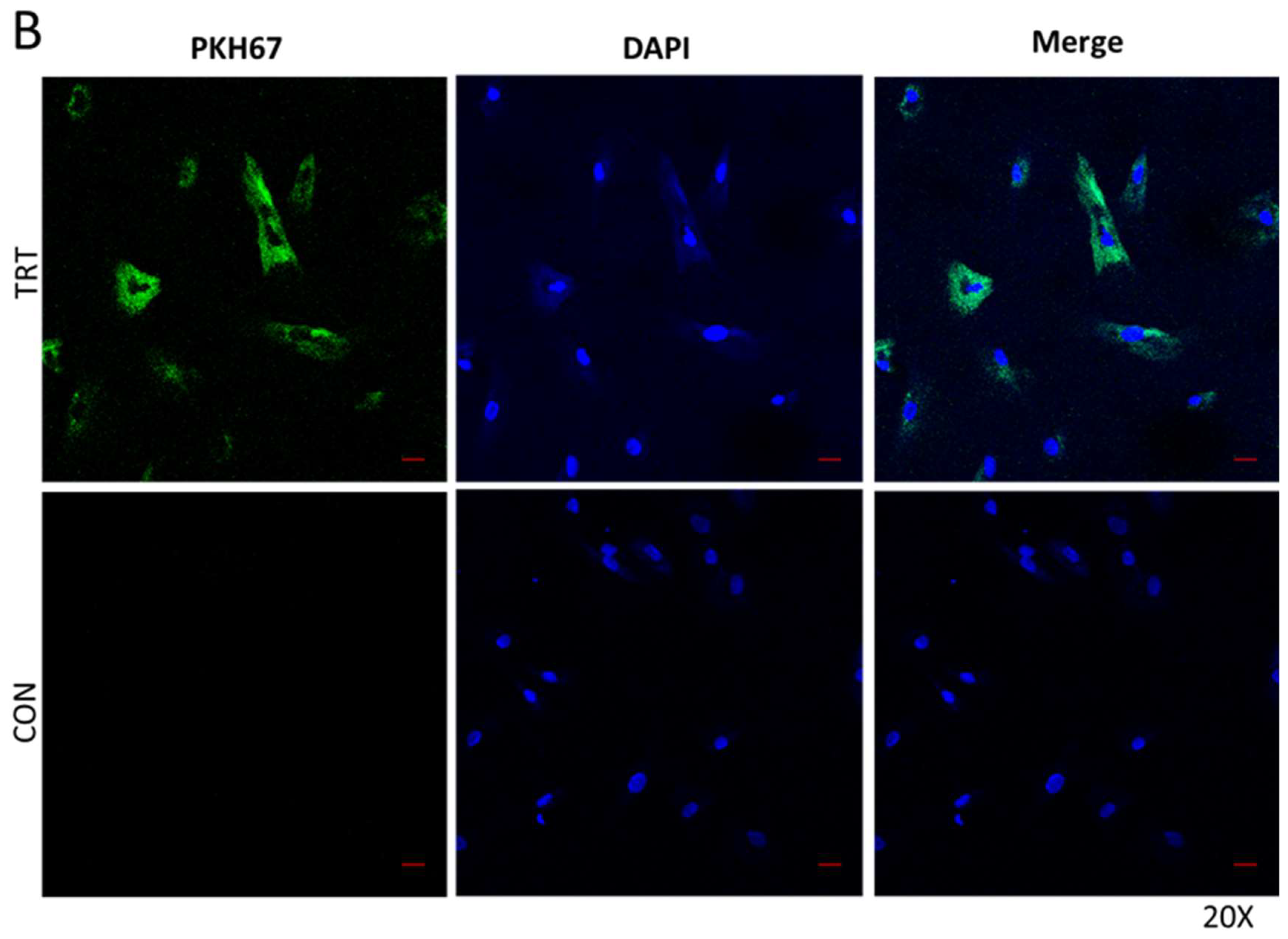
3.2. Serum EVS Are Endocytosed by Bone Marrow Stem Cells
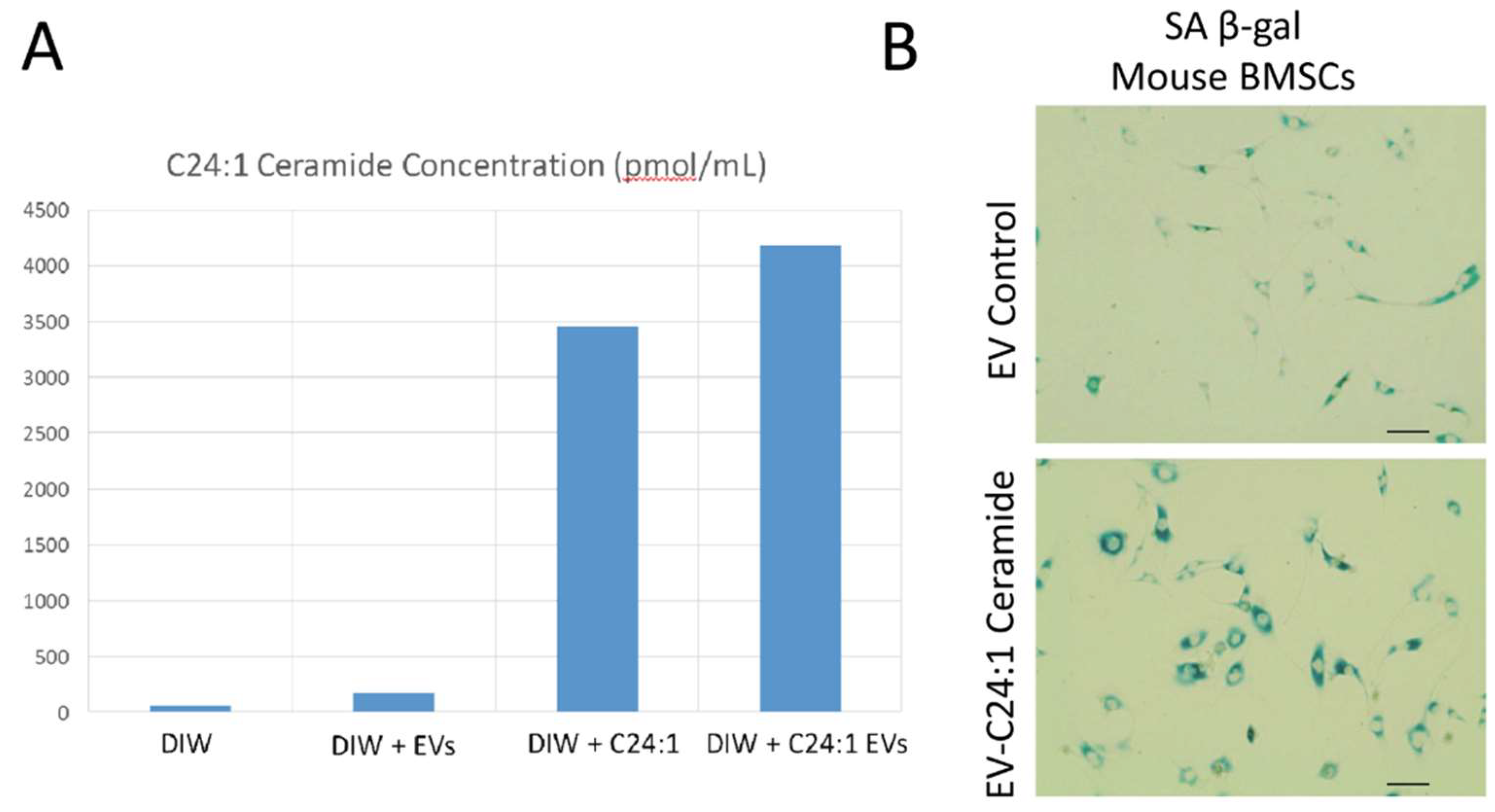
3.3. Young EVs Loaded with C24:1 Ceramide Can Induce Cell Senescence
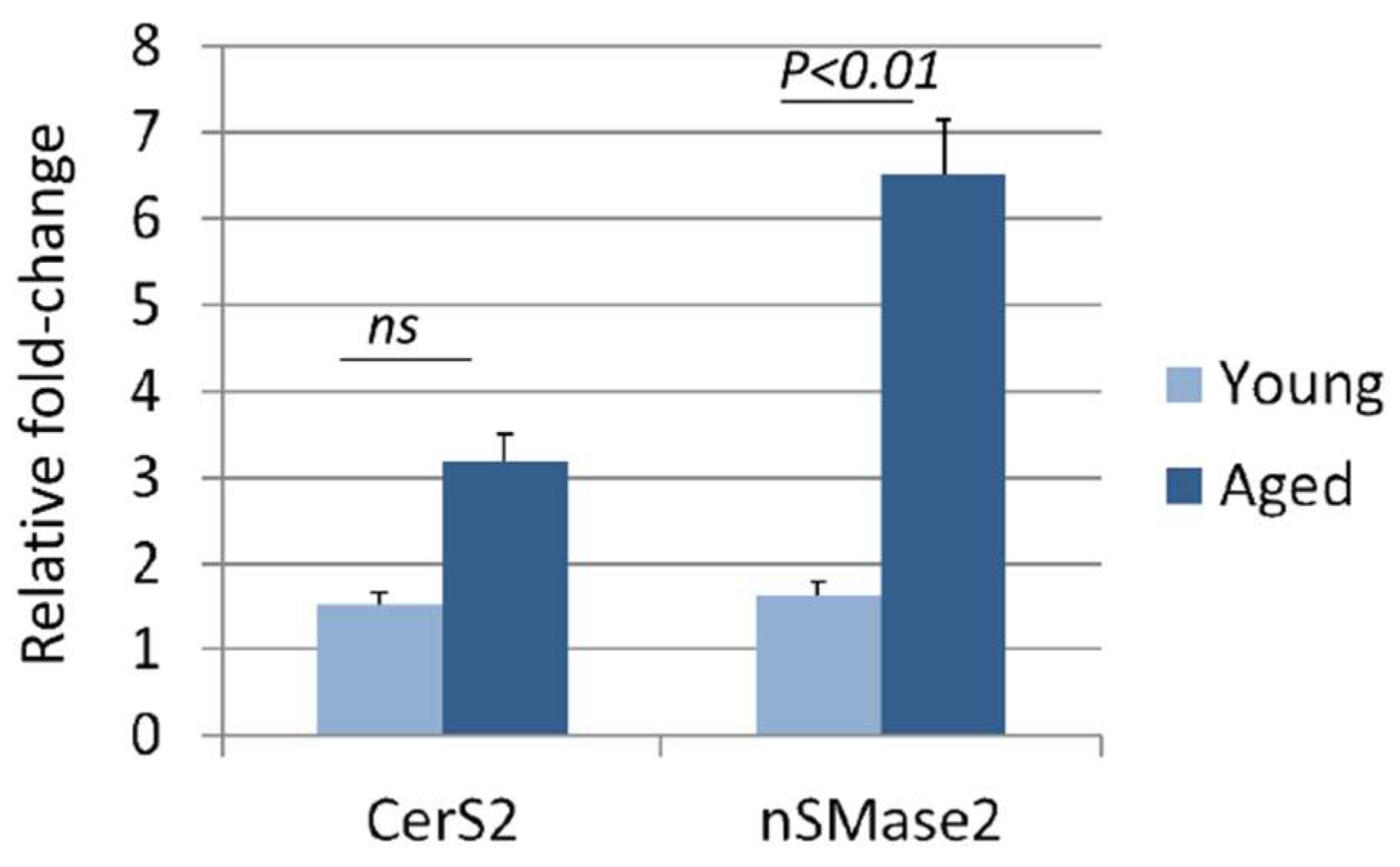
3.4. Aging Increases Sphingomyelinase Activity in the Liver
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gray, S.L.; Anderson, M.L.; Hubbard, R.A. Frailty and incident dementia. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loskutova, N.; Honea, R.A.; Vidoni, E.D.; Brooks, W.M.; Burns, J.M. Bone density and brain atrophy in early Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2009, 18, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villeda, S.A.; Plambeck, K.E.; Middeldorp, J.; Castellano, J.M.; Mosher, K.I.; Luo, J.; Smith, L.K.; Bieri, G.; Lin, K.; Berdnik, D.; et al. Young blood reverses age-related impairments in cognitive function and synaptic plasticity in mice. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villeda, S.A.; Luo, J.; Mosher, K.I.; Zou, B.; Britschgi, M.; Bieri, G.; Stan, T.M.; Fainberg, N.; Ding, Z.; Eggel, A.; et al. The aging systemic milieu negatively regulates neurogenesis and cognitive function. Nature 2011, 477, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathivanan, S.; Ji, H.; Simpson, R. Exosomes: Extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar]
- Camussi, G.; Deregibus, M.C.; Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Fonsato, V.; Tetta, C. Exosome/microvesicle-mediated epigenetic reprogramming of cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 1, 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Haraszti, R.; Didiot, M.C.; Sapp, E.; Leszyk, J.; Shaffer, S.A.; Rockwell, H.E.; Gao, F.; Narain, N.R.; DiFiglia, M.; Kiebish, M.A.; et al. High-resolution proteomic and lipidomic analysis of exosomes and microvesicles from different cell sources. J. Extracellular Vesicles 2016, 5, 32570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Dinkins, M.; He, Q.; Zhu, G.; Poirier, C.; Campbell, A.; Mayer-Proschel, M.; Bieberich, E. Astrocytes secrete exosomes enriched with proapoptotic ceramide and prostate apoptosis response 4 (PAR-4): Potential mechanism of apoptosis induction in Alzheimer disease (AD). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21384–21395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, R.G.; Mattson, M.P. Sphingomyelin and ceramide as regulators of development and lifespan. Mech. Aging Dev. 2001, 122, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podbielska, M.; Szulc, Z.; Kurowska, E.; Hogan, E.L.; Bielawski, J.; Bielawska, A.; Bhat, N.R. Cytokine-induced release of ceramide-enriched exosomes as a mediator of cell death signaling in an oligodendrogloma cell line. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 2028–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venable, M.; Lee, Y.J.; Smyth, M.J.; Bielawska, A.; Obeid, L.M. Role of ceramide in cellular senescence. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 30701–30708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Silva, J.; Dasgupta, S.; Bieberich, E. Long-chain ceramide is elevated in presenilin 1 (PS1M146V) mouse brain and induces apoptosis in PS1 astrocytes. Glia 2008, 56, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorczynski, R.M.; Erin, N.; Zhu, F. Serum-derived exosomes from mice with highly metastatic breast cancer transfer increased metastatic capacity to a poorly metastatic tumor. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Pochampally, R.; Watabe, K.; Lu, Z.; Mo, Y. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-10b promotes cell invasion in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkins, M.; Enasko, J.; Hernandez, C.; Wang, G.; Kong, J.; Helwa, I.; Liu, Y.; Terry, A.V., Jr.; Bieberich, E. Neutral sphingomyelinase-2 deficiency ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease pathology and improves cognition in the 5XFAD mouse. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 8653–8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkins, M.; Dasgupta, S.; Wang, G.; Zhu, G.; Bieberich, E. Exosome reduction in vivo is associated with lower amyloid plaque load in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightle, S.; Tosheva, R.; Lee, A.; Queen-Baker, J.; Boyanovsky, B.; Shedlofsky, S.; Nikolova-Karakashian, M. Elevation of ceramide in serum lipoproteins during acute phase response in humans and mice: Role of serine-palmitoyl transferase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 419, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Miyashita, Y.; Kumagai, Y.; Kojo, S. Change in liver and plasma ceramides during D-galactosamine-induced acute hepatic injury by LC-MS/MS. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 4061–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightle, S.A.; Oakley, J.I.; Nikolova-Karakashian, M.N. Activation of sphingolipid turnover and chronic generation of ceramide and sphingosine in liver during aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2000, 120, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Castillo, S.S.; Goldkorn, T. nSMase2 activation and trafficking are modulated by oxidative stress to induce apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 344, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Corbacho, M.J.; Canals, D.; Adada, M.; Liu, M.; Senkal, C.E.; Yi, J.K.; Mao, C.; Luberto, C.; Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα)-induced ceramide generation via ceramide synthases regulates loss of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and programmed cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 25356–25373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brack, A.S.; Bildsoe, H.; Hughes, S.M. Evidence that satellite cell decrement contributes to preferential decline in nuclear number from large fibres during murine age-related muscle atrophy. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4813–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ou, G.; Hamrick, M.W.; Hill, W.; Borke, J.; Wenger, K.; Chutkan, N.; Yu, J.; Mi, Q.S.; Isales, C.M.; et al. Age-related changes in the osteogenic differentiation potential of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2008, 23, 118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.; Dukes, A.; Drewry, M.; Helwa, I.; Johnson, M.H.; Isales, C.M.; Hill, W.D.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Fulzele, S.; et al. MicroRNA-183-5p increases with age in bone-derived extracellular vesicles, suppresses bone marrow stromal (stem) cell proliferation, and induces stem cell senescence. Tissue Eng. Part A 2017, 23, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, B.A.; Liao, X.; Moore, K.S.; Southard, A.; Roddy, P.; Ji, R.; Szulc, Z.; Bielawska, A.; Schulze, P.C.; Cowart, L.A. Lipotoxic very-long-chain ceramides cause mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and cell death in cardiomyocytes. FASEB J 2018, 32, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.; Akashi, H.; Drosatos, K.; Liao, X.; Jiang, H.; Kennel, P.J.; Brunjes, D.L.; Castillero, E.; Zhang, X.; Deng, L.Y.; et al. Increased de novo ceramide synthesis and accumulation in failing myocardium. JCI Insight 2017, 2, 82922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helwa, I.; Cai, J.; Drewry, M.D.; Zimmerman, A.; Dinkins, M.B.; Khaled, M.L.; Seremwe, M.; Dismuke, W.M.; Bieberich, E.; Stamer, W.D.; et al. A comparative study of serum exosome isolation using differential ultracentrifugation and three commercial reagents. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, M.S.; Hurwitz, S.N.; Meckes, D.G. ExtraPEG: A polyethylene glycol-based method for enrichment of extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamez-Velero, A.; Monguió-Tortajada, M.; Carreras-Planella, L.; Franquesa, M.; Beyer, K.; Borràs, F.E. Size-exclusion chromatography-based isolation minimally alters extracellular vesicles’ characteristics compared to precipitating agents. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böing, A.; van der Pol, E.; Grootemaat, A.; Coumans, F.A.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Single-step isolation of extracellular vesicles by size-exclusion chromatography. J. Extracellular Vesicles 2014, 3, 23430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, J.; Lee, Y.; Vader, P.; Mäger, I.; Johansson, H.J.; Heusermann, W.; Wiklander, O.P.; Hällbrink, M.; Seow, Y.7; Bultema, J.J.; et al. Ultrafiltration with size-exclusion liquid chromatography fo high yield isolation of extracellular vesicles preserving intact biophysical and functional properties. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowser, M.; Herberg, S.; Arounleut, P.; Shi, X.; Fulzele, S.; Hill, W.D.; Isales, C.M.; Hamrick, M.W. Effects of the activin A-myostatin-follistatin system on aging bone and muscle progenitor cells. Exp. Gerontol. 2013, 48, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulzele, S.; Chothe, P.; Sangani, R.; Chutkan, N.; Hamrick, M.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Prasad, P.D.; Zakhary, I.; Bowser, M.; Isales, C.M.; et al. Sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter SVCT2: Expression and function in bone marrow stromal cells and in osteogenesis. Stem Cell Res. 2013, 10, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesini, N.; Hannun, Y.A. Acid and neutral sphingomyelinases: Roles and mechanisms of regulation. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laviad, E.L.; Albee, L.; Pankova-Kholmyansky, I.; Epstein, S.; Park, H.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Futerman, A.H. Characterization of ceramide synthase 2: Tissue distribution, substrate specificity, and inhibition by sphingosine-1-phosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 5677–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, M.; Futerman, A. Mammalian ceramide synthases. Life 2010, 62, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.; Bandaru, V.; Haughey, N.J.; Xia, J.; Fried, L.P.; Yasar, S.; Albert, M.; Varma, V.; Harris, G.; Schneider, E.B.; et al. Serum ceramides increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease: The Women’s Health and Aging Study II. Neurology 2012, 79, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennberg, A.; Schafer, M.J.; LeBrasseur, N.; Savica, R.; Bui, H.H.; Hagen, C.E.; Hollman, J.H.; Petersen, R.C.; Mielke, M.M. Plasma sphingolipids are associated with gait parameters in the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Y.; Miao, H.; Cheng, X.-L.; Wei, F. Lipidomics: Novel insight into the biochemical mechanisms of lipid metabolism and dysregulation-associated disease. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2015, 240, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitan, E.; Green, J.; Bodogai, M.; Mode, N.A.; Bæk, R.; Jørgensen, M.M.; Freeman, D.W.; Witwer, K.W.; Zonderman, A.B.; Biragyn, A.; et al. Age-related changes in plasma extracellular vesicle characteristics and internalization by leukocytes. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, E.; Yang, A.; Simonsick, E.; Chia, C.W.; Zoli, M.; Haughey, N.J.; Mielke, M.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Coen, P.M. Circulating ceramides are inversely associated with cardiorespiratory fitness in participants aged 54-96 years from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Toledo, E.; Hruby, A.; Rosner, B.A.; Willett, W.C.; Sun, Q.; Razquin, C.; Zheng, Y.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; et al. Plasma ceramides, Mediterranean Diet, and incident cardiovascular diseases in the PREDIMED Trial. Circulation 2017, 135, 2028–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke, M.; Bandaru, V.; Haughey, N.; Rabins, P.V.; Lyketsos, C.G.; Carlson, M. Serum sphingomyelins and ceramides are early predictors of memory impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutler, R.G.; Thompson, K.W.; Camandola, S.; Mack, K.T.; Mattson, M.P. Sphingolipid metabolism regulates development and lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 143–144, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouz, R.; Khoury, R.; Blachnio-Zabielska, A.; Turban, S.; Loiseau, N.; Lipina, C.; Stretton, C.; Bourron, O.; Ferré, P.; Foufelle, F.; et al. Characterising the inhibitory actions of ceramide upon insulin signaling in different skeletal muscle cell models: A mechanistic insight. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, G.; Peralta, E.; Rosales, K.; Wong, S.Y.; Siskind, L.J.; Edinger, A.L. Ceramide starves cells to death by downregulating nutrient transporter proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17402–17407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyde, R.; Hajduch, E.; Powell, D.J.; Taylor, P.; Hundal, H.S. Ceramide down-regulates system A amino acid transport and protein synthesis in rat skeletal muscle cells. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, Y.; Kita, S.; Koyama, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Takeda, H.; Takahashi, M.; Fujishima, Y.; Nagao, H.; Masuda, S.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Adiponectin/T-cadherin system enhances exosome biogenesis and decreases cellular ceramides by exosomal release. JCI Insight 2018, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Cacabelos, R.; Sanpedro, C.; García-Fantini, M.; Aleixandre, M. Serum TNF alpha levels are increased and correlate negatively with free IGF-1 in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershler, W.B.; Keller, E.T. Age-associated increased interleukin-6 gene expression, late-life diseases, and frailty. Annu. Rev. Med. 2000, 51, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagiola, U.; Cossarizza, A.; Scala, E.; Fanales-Belasio, E.; Ortolani, C.; Cozzi, E.; Monti, D.; Franceschi, C.; Paganelli, R. Increased cytokine production in mononuclear cells of healthy elderly people. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 2375–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkute, K.; Karakashian, A.; Giltiay, N.; Dobierzewska, A.; Nikolova-Karakashian, M.N. Aging in rat causes hepatic hyperresponsiveness to interleukin-1 beta which is mediated by neutral sphingomyelinase-2. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figuera-Losada, M.; Stathis, M.; Dorskind, J.M.; Thomas, A.G.; Bandaru, V.V.; Yoo, S.W.; Westwood, N.J.; Rogers, G.W.; McArthur, J.C.; Haughey, N.J.; et al. Cambinol, a novel inhibitor of neutral sphingomyelinase 2 shows neuroprotective properties. PLoS ONE 2014, 10, e0124481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khayrullin, A.; Krishnan, P.; Martinez-Nater, L.; Mendhe, B.; Fulzele, S.; Liu, Y.; Mattison, J.A.; Hamrick, M.W. Very Long-Chain C24:1 Ceramide Is Increased in Serum Extracellular Vesicles with Aging and Can Induce Senescence in Bone-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells 2019, 8, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010037
Khayrullin A, Krishnan P, Martinez-Nater L, Mendhe B, Fulzele S, Liu Y, Mattison JA, Hamrick MW. Very Long-Chain C24:1 Ceramide Is Increased in Serum Extracellular Vesicles with Aging and Can Induce Senescence in Bone-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells. 2019; 8(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhayrullin, Andrew, Priyanka Krishnan, Luis Martinez-Nater, Bharati Mendhe, Sadanand Fulzele, Yutao Liu, Julie A. Mattison, and Mark W. Hamrick. 2019. "Very Long-Chain C24:1 Ceramide Is Increased in Serum Extracellular Vesicles with Aging and Can Induce Senescence in Bone-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells" Cells 8, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010037
APA StyleKhayrullin, A., Krishnan, P., Martinez-Nater, L., Mendhe, B., Fulzele, S., Liu, Y., Mattison, J. A., & Hamrick, M. W. (2019). Very Long-Chain C24:1 Ceramide Is Increased in Serum Extracellular Vesicles with Aging and Can Induce Senescence in Bone-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells, 8(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010037




