TRPC3 as a Target of Novel Therapeutic Interventions
Abstract
:1. Introduction to TRPC3
2. Potential Role of TRPC3 in Human Disease
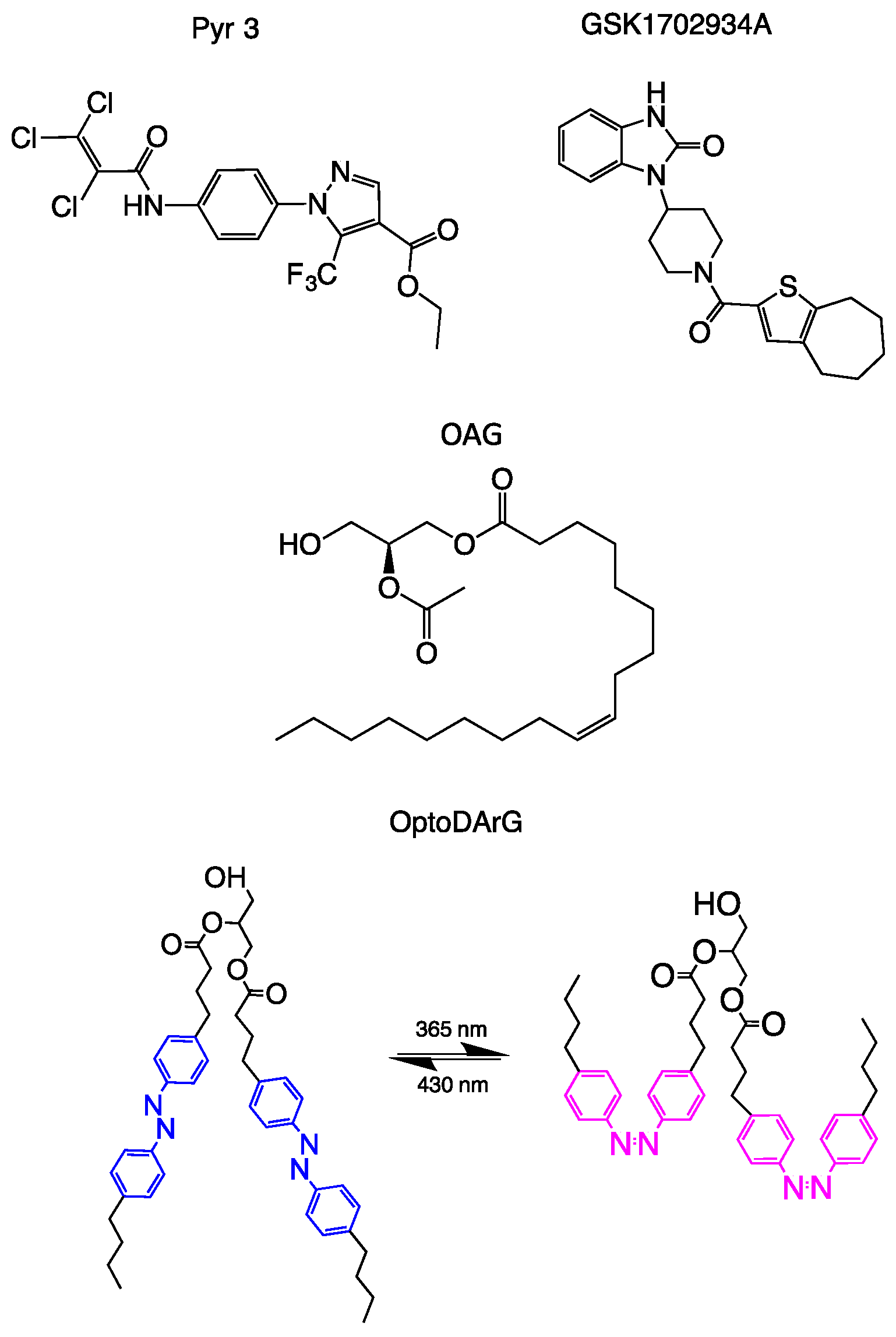
3. Pharmacological Inhibitors
4. Endogenous and Synthetic Channel Activators
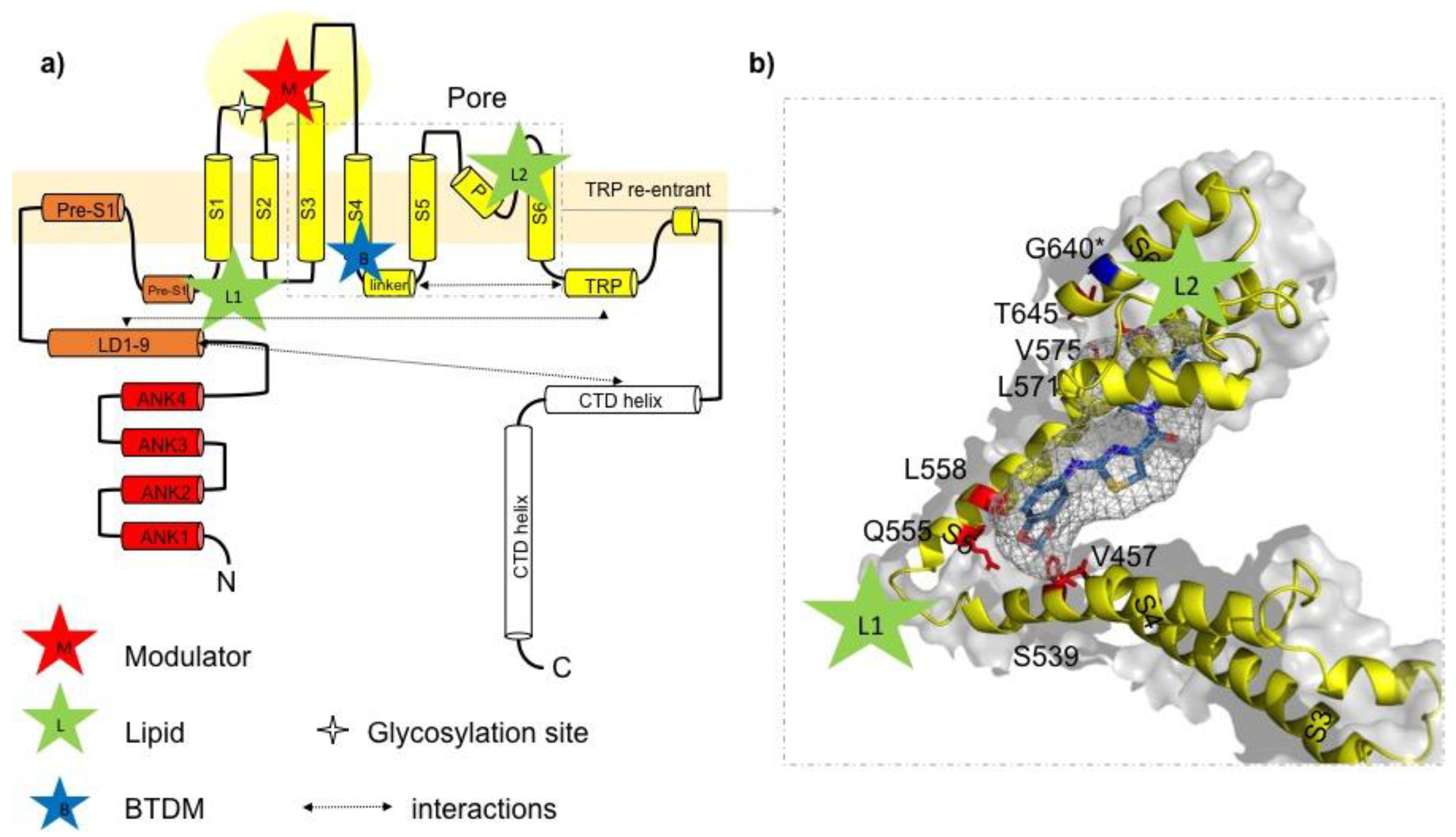
5. New Insights into the Ligand Binding Domains in TRPC3
6. TRPC3 Photopharmacology—A Therapeutic Perspective
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Minke, B.; Cook, B. TRP channel proteins and signal transduction. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 429–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Jiang, M.; Peyton, M.; Boulay, G.; Hurst, R.; Stefani, E.; Birnbaumer, L. Trp, a novel mammalian gene family essential for agonist-activated capacitative Ca2+ entry. Cell 1996, 85, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodova, B.; Groschner, K. Mechanisms of lipid regulation and lipid gating in TRPC channels. Cell Calcium 2016, 59, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storch, U.; Forst, A.-L.; Pardatscher, F.; Erdogmus, S.; Philipp, M.; Gregoritza, M.; Mederos y Schnitzler, M.; Gudermann, T. Dynamic NHERF interaction with TRPC4/5 proteins is required for channel gating by diacylglycerol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E37–E46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, T.; Obukhov, A.G.; Schaefer, M.; Harteneck, C.; Gudermann, T.; Schultz, G. Direct activation of human TRPC6 and TRPC3 channels by diacylglycerol. Nature 1999, 397, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, B.; Zholos, A.; Sydorenko, V.; Roudbaraki, M.; Lehen’kyi, V.; Bordat, P.; Prevarskaya, N.; Skryma, R. TRPC7 is a Receptor-Operated DAG-Activated Channel in Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1982–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Choi, W.; Sun, W.; Du, J.; Lu, W. Structure of the human lipid-gated cation channel TRPC3. eLife 2018, 7, e36852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Q.; Guo, W.; Zheng, L.; Wu, J.-X.; Liu, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L. Structure of the receptor-activated human TRPC6 and TRPC3 ion channels. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenegger, M.; Stockner, T.; Poteser, M.; Schleifer, H.; Platzer, D.; Romanin, C.; Groschner, K. A novel homology model of TRPC3 reveals allosteric coupling between gate and selectivity filter. Cell Calcium 2013, 54, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, G.; Wedel, B.J.; Aziz, O.; Trebak, M.; Putney, J.W., Jr. The mammalian TRPC cation channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2004, 1742, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Bu, J.; Shen, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G. Targeting Transient Receptor Potential Canonical Channels for Diseases of the Nervous System. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, G.; Lievremont, J.P.; Bird, G.S.J.; Putney, J.W. Human Trp3 forms both inositol trisphosphate receptor-dependent and receptor-independent store-operated cation channels in DT40 avian B lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11777–11782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trebak, M.; Bird, G.S.J.; McKay, R.R.; Putney, J.W., Jr. Comparison of Human TRPC3 Channels in Receptor-activated and Store-operated Modes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 21617–21623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenegger, M.; Tiapko, O.; Svobodova, B.; Stockner, T.; Glasnov, T.N.; Schreibmayer, W.; Platzer, D.; Cruz, G.G.; Krenn, S.; Schober, R. An optically controlled probe identifies lipid-gating fenestrations within the TRPC3 channel. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, H.-X.; Shen, K.; Cao, W.; Li, X.-Q. Canonical Transient Receptor Potential Channels and Their Link with Cardio/Cerebro-Vascular Diseases. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2017, 25, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poteser, M.; Graziani, A.; Eder, P.; Yates, A.; Mächler, H.; Romanin, C.; Groschner, K. Identification of a rare subset of adipose tissue-resident progenitor cells, which express CD133 and TRPC3 as a VEGF-regulated Ca2+ entry channel. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 2696–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.B.; Webb, S.E.; Yue, J.; Moreau, M.; Leclerc, C.; Miller, A.L. TRPC3 is required for the survival, pluripotency and neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs). Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.S.; Xu, X.Z.; Montell, C. Activation of a TRPC3-dependent cation current through the neurotrophin BDNF. Neuron 1999, 24, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facemire, C.S.; Mohler, P.J.; Arendshorst, W.J. Expression and relative abundance of short transient receptor potential channels in the rat renal microcirculation. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2004, 286, F546–F551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, P.; Probst, D.; Rosker, C.; Poteser, M.; Wolinski, H.; Kohlwein, S.D.; Romanin, C.; Groschner, K. Phospholipase C-dependent control of cardiac calcium homeostasis involves a TRPC3-NCX1 signaling complex. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 73, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosker, C.; Graziani, A.; Lukas, M.; Eder, P.; Zhu, M.X.; Romanin, C.; Groschner, K. Ca2+ signaling by TRPC3 involves Na+ entry and local coupling to the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 13696–13704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doleschal, B.; Primessnig, U.; Wolkart, G.; Wolf, S.; Schernthaner, M.; Lichtenegger, M.; Glasnov, T.N.; Kappe, C.O.; Mayer, B.; Antoons, G.; et al. TRPC3 contributes to regulation of cardiac contractility and arrhythmogenesis by dynamic interaction with NCX. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 106, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenegger, M.; Groschner, K. TRPC3: A multifunctional signaling molecule. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2014, 222, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riccio, A.; Medhurst, A.D.; Mattei, C.; Kelsell, R.E.; Calver, A.R.; Randall, A.D.; Benham, C.D.; Pangalos, M.N. mRNA distribution analysis of human TRPC family in CNS and peripheral tissues. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2002, 109, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, E.W.; Hood, D.B.; Papst, P.J.; Chapo, J.A.; Minobe, W.; Bristow, M.R.; Olson, E.N.; McKinsey, T.A. Canonical Transient Receptor Potential Channels Promote Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy through Activation of Calcineurin Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 33487–33496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onohara, N.; Nishida, M.; Inoue, R.; Kobayashi, H.; Sumimoto, H.; Sato, Y.; Mori, Y.; Nagao, T.; Kurose, H. TRPC3 and TRPC6 are essential for angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 5305–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poteser, M.; Schleifer, H.; Lichtenegger, M.; Schernthaner, M.; Stockner, T.; Kappe, C.O.; Glasnov, T.N.; Romanin, C.; Groschner, K. PKC-dependent coupling of calcium permeation through transient receptor potential canonical 3 (TRPC3) to calcineurin signaling in HL-1 myocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10556–10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harada, M.; Luo, X.; Qi, X.Y.; Tadevosyan, A.; Maguy, A.; Ordog, B.; Ledoux, J.; Kato, T.; Naud, P.; Voigt, N.; et al. Transient Receptor Potential Canonical-3 Channel-Dependent Fibroblast Regulation in Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2012, 126, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numaga-Tomita, T.; Kitajima, N.; Kuroda, T.; Nishimura, A.; Miyano, K.; Yasuda, S.; Kuwahara, K.; Sato, Y.; Ide, T.; Birnbaumer, L.; et al. TRPC3-GEF-H1 axis mediates pressure overload-induced cardiac fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thodeti, C.K.; Paruchuri, S.; Meszaros, J.G. A TRP to cardiac fibroblast differentiation. Channels 2014, 7, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groschner, K.; Hingel, S.; Lintschinger, B.; Balzer, M.; Romanin, C.; Zhu, X.; Schreibmayer, W. Trp proteins form store-operated cation channels in human vascular endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1998, 437, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yip, H.; Chan, W.-Y.; Leung, P.-C.; Kwan, H.-Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Michel, V.; Yew, D.T.-W.; Yao, X. Expression of TRPC homologs in endothelial cells and smooth muscle layers of human arteries. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 122, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senadheera, S.; Kim, Y.; Grayson, T.H.; Toemoe, S.; Kochukov, M.Y.; Abramowitz, J.; Housley, G.D.; Bertrand, R.L.; Chadha, P.S.; Bertrand, P.P.; et al. Transient receptor potential canonical type 3 channels facilitate endothelium-derived hyperpolarization-mediated resistance artery vasodilator activity. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.-H.; He, G.-W.; Xue, H.-M.; Yao, X.-Q.; Liu, X.-C.; Underwood, M.J.; Yang, Q. TRPC3 channel contributes to nitric oxide release: Significance during normoxia and hypoxia–reoxygenation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 91, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, A.; Mederos y Schnitzler, M.; Gollasch, M.; Gross, V.; Storch, U.; Dubrovska, G.; Obst, M.; Yildirim, E.; Salanova, B.; Kalwa, H.; et al. Increased vascular smooth muscle contractility in TRPC6-/- mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 6980–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, S.; Schernthaner, M.; Maechler, H.; Kappe, C.O.; Glasnov, T.N.; Hoefler, G.; Braune, M.; Wittchow, E.; Groschner, K. A TRPC3 blocker, ethyl-1-(4-(2,3,3-trichloroacrylamide)phenyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate (Pyr3), prevents stent-induced arterial remodeling. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 344, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, J.; Konnerth, A. Mechanisms of metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated synaptic signalling in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Acta Physiol. 2009, 195, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, E.B.E.; Oliver, P.L.; Glitsch, M.D.; Banks, G.T.; Achilli, F.; Hardy, A.; Nolan, P.M.; Fisher, E.M.C.; Davies, K.E. A point mutation in TRPC3 causes abnormal Purkinje cell development and cerebellar ataxia in moonwalker mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6706–6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fogel, B.L.; Hanson, S.M.; Becker, E.B.E. Do mutations in the murine ataxia gene TRPC3 cause cerebellar ataxia in humans? Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuner, S.M.; Wilmott, L.A.; Hope, K.A.; Hoffmann, B.; Chong, J.A.; Abramowitz, J.; Birnbaumer, L.; O’Connell, K.M.; Tryba, A.K.; Greene, A.S.; et al. TRPC3 channels critically regulate hippocampal excitability and contextual fear memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 281, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.; Torres, A.; Ma, H.T.; Holowka, D.; Baird, B. Ca2+ Waves Initiate Antigen-Stimulated Ca2+ Responses in Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6478–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanger, C.M.; Hoth, M.; Crabtree, G.R.; Lewis, R.S. Characterization of T cell mutants with defects in capacitative calcium entry: Genetic evidence for the physiological roles of CRAC channels. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 131, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipp, S.; Strauss, B.; Hirnet, D.; Wissenbach, U.; Méry, L.; Flockerzi, V.; Hoth, M. TRPC3 Mediates T-cell Receptor-dependent Calcium Entry in Human T-lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 26629–26638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wenning, A.S.; Neblung, K.; Strauss, B.; Wolfs, M.-J.; Sappok, A.; Hoth, M.; Schwarz, E.C. TRP expression pattern and the functional importance of TRPC3 in primary human T-cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardini, M.; Fiorio Pla, A.; Prevarskaya, N.; Gkika, D. Human transient receptor potential (TRP) channel expression profiling in carcinogenesis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2015, 59, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oda, K.; Umemura, M.; Nakakaji, R.; Tanaka, R.; Sato, I.; Nagasako, A.; Oyamada, C.; Baljinnyam, E.; Katsumata, M.; Xie, L.-H.; et al. Transient receptor potential cation 3 channel regulates melanoma proliferation and migration. J. Physiol. Sci. 2017, 67, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.-N.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Daskoulidou, N.; Fan, H.; Qu, J.-M.; Xu, S.-Z. Involvement of TRPC channels in lung cancer cell differentiation and the correlation analysis in human non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-M.; Heo, K.; Choi, J.; Kim, K.; An, W. The histone variant MacroH2A regulates Ca2+ influx through TRPC3 and TRPC6 channels. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.L.; Cao, Q.; Zhou, K.C.; Feng, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Z. Transient receptor potential channel C3 contributes to the progression of human ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2009, 28, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aydar, E.; Yeo, S.; Djamgoz, M.; Palmer, C. Abnormal expression, localization and interaction of canonical transient receptor potential ion channels in human breast cancer cell lines and tissues: A potential target for breast cancer diagnosis and therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2009, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, K.; Rainer, P.P.; Lee, D.I.; Hao, S.; Bedja, D.; Birnbaumer, L.; Cingolani, O.H.; Kass, D.A. Hyperactive Adverse Mechanical Stress Responses in Dystrophic Heart Are Coupled to Transient Receptor Potential Canonical 6 and Blocked by cGMP-Protein Kinase G Modulation. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lintschinger, B.; Balzer-Geldsetzer, M.; Baskaran, T.; Graier, W.F.; Romanin, C.; Zhu, M.X.; Groschner, K. Coassembly of Trp1 and Trp3 proteins generates diacylglycerol- and Ca2+-sensitive cation channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 27799–27805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strübing, C.; Krapivinsky, G.; Krapivinsky, L.; Clapham, D.E. Formation of Novel TRPC Channels by Complex Subunit Interactions in Embryonic Brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39014–39019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poteser, M.; Graziani, A.; Rosker, C.; Eder, P.; Derler, I.; Kahr, H.; Zhu, M.X.; Romanin, C.; Groschner, K. TRPC3 and TRPC4 associate to form a redox-sensitive cation channel. Evidence for expression of native TRPC3-TRPC4 heteromeric channels in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 13588–13595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Jiang, M.; Birnbaumer, L. Receptor-activated Ca2+ influx via human Trp3 stably expressed in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells. Evidence for a non-capacitative Ca2+ entry. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamouchi, M.; Philipp, S.; Flockerzi, V.; Wissenbach, U.; Mamin, A.; Raeymaekers, L.; Eggermont, J.; Droogmans, G.; Nilius, B. Properties of heterologously expressed hTRP3 channels in bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J. Physiol. 1999, 2, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, J.; Ohga, K.; Yoshino, T.; Takezawa, R.; Ichikawa, A.; Kubota, H.; Yamada, T. A Pyrazole Derivative, YM-58483, Potently Inhibits Store-Operated Sustained Ca2+ Influx and IL-2 Production in T Lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4441–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitt, C.; Strauss, B.; Schwarz, E.C.; Spaeth, N.; Rast, G.; Hatzelmann, A.; Hoth, M. Potent Inhibition of Ca2+ Release-activated Ca2+ Channels and T-lymphocyte Activation by the Pyrazole Derivative BTPJ. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12427–12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.-P.; Hewavitharana, T.; Soboloff, J.; Spassova, M.A.; Gill, D.L. A functional link between store-operated and TRPC channels revealed by the 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)pyrazole derivative, BTP. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10997–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyonaka, S.; Kato, K.; Nishida, M.; Mio, K.; Numaga, T.; Sawaguchi, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Wakamori, M.; Mori, E.; Numata, T.; et al. Selective and direct inhibition of TRPC3 channels underlies biological activities of a pyrazole compound. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5400–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schleifer, H.; Doleschal, B.; Lichtenegger, M.; Oppenrieder, R.; Derler, I.; Frischauf, I.; Glasnov, T.N.; Kappe, C.O.; Romanin, C.; Groschner, K. Novel pyrazole compounds for pharmacological discrimination between receptor-operated and store-operated Ca2+ entry pathways. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1712–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washburn, D.G.; Holt, D.A.; Dodson, J.; McAtee, J.J.; Terrell, L.R.; Barton, L.; Manns, S.; Waszkiewicz, A.; Pritchard, C.; Gillie, D.J.; et al. The discovery of potent blockers of the canonical transient receptor channels, TRPC3 and TRPC6, based on an anilino-thiazole pharmacophore. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4979–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, K.; Rainer, P.P.; Shalkey Hahn, V.; Lee, D.I.; Jo, S.H.; Andersen, A.; Liu, T.; Xu, X.; Willette, R.N.; Lepore, J.J.; et al. Combined TRPC3 and TRPC6 blockade by selective small-molecule or genetic deletion inhibits pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miehe, S.; Kleemann, H.-W.; Struebing, C. Use of Norgestimate as a Selective Inhibitor of Trpc3, Trpc6 and Trpc7 Ion Channels-European Patent Office-ep 2205247 B1use of Norgestimate as a Selective Inhibitor of Trpc3, Trpc6 and Trpc7 Ion Channels-European Patent Office-EP 2205247 B1 [Internet]. European Patent Office, 2013. Available online: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/41/64/8c/b98422f55179fa/EP2205247B1.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2018).
- Maier, T.; Follmann, M.; Hessler, G.; Kleemann, H.-W.; Hachtel, S.; Fuchs, B.; Weissmann, N.; Linz, W.; Schmidt, T.; Löhn, M.; et al. Discovery and pharmacological characterization of a novel potent inhibitor of diacylglycerol-sensitive TRPC cation channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3650–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemonnier, L.; Trebak, M.; Putney, J.W., Jr. Complex regulation of the TRPC3, 6 and 7 channel subfamily by diacylglycerol and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Cell Calcium 2008, 43, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graziani, A.; Rosker, C.; Kohlwein, S.D.; Zhu, M.X.; Romanin, C.; Sattler, W.; Groschner, K.; Poteser, M. Cellular cholesterol controls TRPC3 function: Evidence from a novel dominant-negative knockdown strategy. Biochem. J. 2006, 396, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, J.T.; Lemonnier, L.; Vazquez, G.; Bird, G.S.; Putney, J.W. Dissociation of regulated trafficking of TRPC3 channels to the plasma membrane from their activation by phospholipase C. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 11712–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, A.; Mederos y Schnitzler, M.; Emmel, J.; Kalwa, H.; Hofmann, T.; Gudermann, T. N-Linked Protein Glycosylation Is a Major Determinant for Basal TRPC3 and TRPC6 Channel Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 47842–47852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Lozinskaya, I.; Costell, M.; Lin, Z.; Ball, J.A.; Bernard, R.; Behm, D.J.; Marino, J.P.; Schnackenberg, C.G. Characterization of Small Molecule TRPC3 and TRPC6 agonist and Antagonists. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 454a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, C.; Ding, M.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Du, J.; Miller, M.; Tian, J.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Wen, M.; et al. Pyrazolopyrimidines as Potent Stimulators for Transient Receptor Potential Canonical 3/6/7 Channels. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4680–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutas, A.; Birnbaumer, L.; Yellen, G. Metabolism Regulates the Spontaneous Firing of Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata Neurons via K ATPand Nonselective Cation Channels. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 16336–16347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehrentz, T.; Schönberger, M.; Trauner, D. Optochemical genetics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 12156–12182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadler, A.; Reither, G.; Feng, S.; Stein, F.; Reither, S.; Müller, R.; Schultz, C. The fatty acid composition of diacylglycerols determines local signaling patterns. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 6330–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiapko, O.; Bacsa, B.; la Cruz de, G.G.; Glasnov, T.; Groschner, K. Optopharmacological control of TRPC channels by coumarin-caged lipids is associated with a phototoxic membrane effect. Sci. China Life Sci. 2016, 59, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leinders-Zufall, T.; Storch, U.; Bleymehl, K.; Schnitzler, M.M.Y.; Frank, J.A.; Konrad, D.B.; Trauner, D.; Gudermann, T.; Zufall, F. PhoDAGs Enable Optical Control of Diacylglycerol- Sensitive Transient Receptor Potential Channels. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 215–223.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J.A.; Moroni, M.; Moshourab, R.; Sumser, M.; Lewin, G.R.; Trauner, D. Photoswitchable fatty acids enable optical control of TRPV. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J.A.; Yushchenko, D.A.; Hodson, D.J.; Lipstein, N.; Nagpal, J.; Rutter, G.A.; Rhee, J.-S.; Gottschalk, A.; Brose, N.; Schultz, C.; et al. Photoswitchable diacylglycerols enable optical control of protein kinase C. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tiapko, O.; Groschner, K. TRPC3 as a Target of Novel Therapeutic Interventions. Cells 2018, 7, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070083
Tiapko O, Groschner K. TRPC3 as a Target of Novel Therapeutic Interventions. Cells. 2018; 7(7):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070083
Chicago/Turabian StyleTiapko, Oleksandra, and Klaus Groschner. 2018. "TRPC3 as a Target of Novel Therapeutic Interventions" Cells 7, no. 7: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070083
APA StyleTiapko, O., & Groschner, K. (2018). TRPC3 as a Target of Novel Therapeutic Interventions. Cells, 7(7), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7070083





