Real-Time Imaging of Retinal Ganglion Cell Apoptosis
Abstract
1. The Cellular Basis of Glaucomatous Degeneration
1.1. Background to Glaucoma
1.2. Visual Pathway in Glaucoma
1.3. Cellular Events in Glaucoma
2. Annexin A5 as a Marker of Cells Undergoing Apoptosis
2.1. Apoptosis
2.2. Annexin and Apoptosis
2.3. Uses of Annexin
2.4. Other Methods for Imaging Apoptosis
3. Single-Cell Resolution Imaging of the Retina
3.1. Imaging the Eye
3.2. Retinal Cell Imaging
4. Imaging Retinal Ganglion Cells
4.1. The Challenge of Imaging Retinal Ganglion Cells
4.2. DARC Technology
4.3. Experimental Studies with DARC
4.4. DARC as an Outcome Measure
5. The Use of DARC Imaging in Humans
5.1. Phase 1 DARC Study
5.2. DARC as a Surrogate for Neurodegeneration
5.3. Potential of DARC in Glaucoma Diagnosis
5.4. Current Outcome Measures in Glaucoma
5.5. DARC as an Exploratory Outcome Measure in Glaucoma
6. DARC—Next Steps
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kerrigan, L.A.; Zack, D.J.; Quigley, H.A.; Smith, S.D.; Pease, M.E. Tunel-positive ganglion cells in human primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1997, 115, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okisaka, S.; Murakami, A.; Mizukawa, A.; Ito, J. Apoptosis in retinal ganglion cell decrease in human glaucomatous eyes. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 1997, 41, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Kyung, H.; Shim, S.H.; Azarbod, P.; Caprioli, J. Location of initial visual field defects in glaucoma and their modes of deterioration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 7956–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, Y.C.; Li, X.; Wong, T.Y.; Quigley, H.A.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C.Y. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Aung, T.; Medeiros, F.A. The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: A review. JAMA 2014, 311, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kass, M.A.; Heuer, D.K.; Higginbotham, E.J.; Johnson, C.A.; Keltner, J.L.; Miller, J.P.; Parrish, R.K.; Wilson, M.R.; Gordon, M.O. The ocular hypertension treatment study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, W.; Guo, L.; Cordeiro, M.F. Neuroprotection in glaucoma: Drug-based approaches. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2008, 85, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, K.; Shibata-Germanos, S.; Pahlitzsch, M.; Cordeiro, M.F. Current perspective of neuroprotection and glaucoma. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2015, 9, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsunoda, S. Chapter 54—Organization of photoreceptor signaling complexes a2-bradshaw, ralph A. In Handbook of Cell Signaling, 2nd ed.; Dennis, E.A., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 373–377. [Google Scholar]
- Quigley, H.A.; McKinnon, S.J.; Zack, D.J.; Pease, M.E.; Kerrigan-Baumrind, L.A.; Kerrigan, D.F.; Mitchell, R.S. Retrograde axonal transport of BDNF in retinal ganglion cells is blocked by acute IOP elevation in rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 3460–3466. [Google Scholar]
- Quigley, H.A.; Addicks, E.M.; Green, W.R.; Maumenee, A.E. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. II. The site of injury and susceptibility to damage. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1981, 99, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calkins, D.J. Critical pathogenic events underlying progression of neurodegeneration in glaucoma. Prog. Retin. Eye. Res. 2012, 31, 702–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flammer, J. The vascular concept of glaucoma. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1994, 38, S3–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.F.; Wyllie, A.H.; Currie, A.R. Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br. J. Cancer 1972, 26, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankenberg, F.G.; Norfray, J.F. Multimodality molecular imaging of apoptosis in oncology. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majno, G.; Joris, I. Apoptosis, oncosis, and necrosis. An overview of cell death. Am. J. Pathol. 1995, 146, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wyllie, A.H.; Beattie, G.J.; Hargreaves, A.D. Chromatin changes in apoptosis. Histochem. J. 1981, 13, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyrylkova, K.; Kyryachenko, S.; Leid, M.; Kioussi, C. Detection of apoptosis by tunel assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 887, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bergsbaken, T.; Fink, S.L.; Cookson, B.T. Pyroptosis: Host cell death and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantz, S.; Ducharme, A.; Sawyer, D.; Rohde, L.E.; Kobzik, L.; Fukazawa, R.; Tracey, D.; Allen, H.; Lee, R.T.; Kelly, R.A. Targeted deletion of caspase-1 reduces early mortality and left ventricular dilatation following myocardial infarction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2003, 35, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.N.; Berry, M.; Logan, A.; Blanch, R.J.; Ahmed, Z. Caspases in retinal ganglion cell death and axon regeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 3, 17032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, H.A. Neuronal death in glaucoma. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 1999, 18, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour-Robaey, S.; Clarke, D.B.; Wang, Y.C.; Bray, G.M.; Aguayo, A.J. Effects of ocular injury and administration of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on survival and regrowth of axotomized retinal ganglion cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1632–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellerino, A.; Carroll, P.; Thoenen, H.; Barde, Y.A. Reduced size of retinal ganglion cell axons and hypomyelination in mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, E.B.; Zurakowski, D.; Schumer, R.A.; Podos, S.M.; Lipton, S.A. Elevated glutamate levels in the vitreous body of humans and monkeys with glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1996, 114, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, D.E.; Garcia, G.A.; Dreyer, E.B.; Zurakowski, D.; Franco-Bourland, R.E. Vitreous body glutamate concentration in dogs with glaucoma. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1997, 58, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Honkanen, R.A.; Baruah, S.; Zimmerman, M.B.; Khanna, C.L.; Weaver, Y.K.; Narkiewicz, J.; Waziri, R.; Gehrs, K.M.; Weingeist, T.A.; Boldt, H.C.; et al. Vitreous amino acid concentrations in patients with glaucoma undergoing vitrectomy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2003, 121, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levkovitch-Verbin, H.; Martin, K.R.; Quigley, H.A.; Baumrind, L.A.; Pease, M.E.; Valenta, D. Measurement of amino acid levels in the vitreous humor of rats after chronic intraocular pressure elevation or optic nerve transection. J. Glaucoma 2002, 11, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wamsley, S.; Gabelt, B.T.; Dahl, D.B.; Case, G.L.; Sherwood, R.W.; May, C.A.; Hernandez, M.R.; Kaufman, P.L. Vitreous glutamate concentration and axon loss in monkeys with experimental glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2005, 123, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, N.N.; Ugarte, M.; Chao, M.; Chidlow, G.; Bae, J.H.; Wood, J.P.; Nash, M.S. Neuroprotection in relation to retinal ischemia and relevance to glaucoma. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1999, 43 (Suppl. 1), S102–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.R.; Levkovitch-Verbin, H.; Valenta, D.; Baumrind, L.; Pease, M.E.; Quigley, H.A. Retinal glutamate transporter changes in experimental glaucoma and after optic nerve transection in the rat. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 2236–2243. [Google Scholar]
- Tatton, W.G.; Chalmers-Redman, R.M.; Sud, A.; Podos, S.M.; Mittag, T.W. Maintaining mitochondrial membrane impermeability. An opportunity for new therapy in glaucoma? Surv. Ophthalmol. 2001, 45 (Suppl. 3), S277–S283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzotti, A.; Bagnis, A.; Sacca, S.C. The role of oxidative stress in glaucoma. Mutat. Res. 2006, 612, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieck, J. The pathogenesis of glaucoma in the interplay with the immune system. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 2393–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezel, G. The immune response in glaucoma: A perspective on the roles of oxidative stress. Exp. Eye Res. 2011, 93, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flammer, J.; Konieczka, K.; Flammer, A.J.F. The primary vascular dysregulation syndrome: Implications for eye diseases. EPMA J. 2013, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irnaten, M.; Barry, R.C.; Quill, B.; Clark, A.F.; Harvey, B.J.; O’Brien, C.J. Activation of stretch-activated channels and maxi-k+ channels by membrane stress of human lamina cribrosa cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddineni, P.; Kasetti, R.B.; Zode, G.S. Methods for analyzing endoplasmic reticulum stress in the trabecular meshwork of glaucoma models. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1695, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Obulesu, M.; Lakshmi, M.J. Apoptosis in alzheimer’s disease: An understanding of the physiology, pathology and therapeutic avenues. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 2301–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bano, D.; Zanetti, F.; Mende, Y.; Nicotera, P. Neurodegenerative processes in huntington’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venderova, K.; Park, D.S. Programmed cell death in parkinson’s disease. In Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, D.S.; Kung, A.L.; Kieran, M.W. Anti-apoptosis mechanisms in malignant gliomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, D.; McNiff, J.M.; Li, F.; Altieri, D.C. Expression and targeting of the apoptosis inhibitor, survivin, in human melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archana, M.; Bastian; Yogesh, T.L.; Kumaraswamy, K.L. Various methods available for detection of apoptotic cells—A review. Ind. J. Cancer 2013, 50, 274–283. [Google Scholar]
- Creutz, C.E.; Hira, J.K.; Gee, V.E.; Eaton, J.M. Protection of the membrane permeability barrier by annexins. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 9966–9983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghislat, G.; Aguado, C.; Knecht, E. Annexin A5 stimulates autophagy and inhibits endocytosis. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo-Marie, F. Annexin v and phospholipid metabolism. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1999, 37, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Jang, J.H.; Choi, E.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, E.J.; Jung, I.D.; Han, H.D.; Wu, T.C.; Hung, C.F.; Kang, T.H.; et al. Annexin A5 increases survival in murine sepsis model by inhibiting hmgb1-mediated pro-inflammation and coagulation. Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, A.; Frostegard, J. Annexin A5 multitasking: A potentially novel antiatherothrombotic agent? Drug News Perspect. 2007, 20, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meers, P.; Mealy, T. Calcium-dependent annexin v binding to phospholipids: Stoichiometry, specificity, and the role of negative charge. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 11711–11721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daleke, D.L. Phospholipid flippases. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, R.A.; Williamson, P. Phosphatidylserine, a death knell. Cell Death Differ. 2001, 8, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoven, B.; Schlegel, R.A.; Williamson, P. Mechanisms of phosphatidylserine exposure, a phagocyte recognition signal, on apoptotic t lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 1597–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadok, V.A.; Voelker, D.R.; Campbell, P.A.; Cohen, J.J.; Bratton, D.L.; Henson, P.M. Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bratton, D.L.; Fadok, V.A.; Richter, D.A.; Kailey, J.M.; Guthrie, L.A.; Henson, P.M. Appearance of phosphatidylserine on apoptotic cells requires calcium-mediated nonspecific flip-flop and is enhanced by loss of the aminophospholipid translocase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 26159–26165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankins, H.M.; Baldridge, R.D.; Xu, P.; Graham, T.R. Role of flippases, scramblases and transfer proteins in phosphatidylserine subcellular distribution. Traffic 2015, 16, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovsky, A.; Schellenberger, E.; Josephson, L.; Weissleder, R.; Bogdanov, A., Jr. Near-infrared fluorescent imaging of tumor apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hofstra, L.; Liem, I.H.; Dumont, E.A.; Boersma, H.H.; van Heerde, W.L.; Doevendans, P.A.; De Muinck, E.; Wellens, H.J.; Kemerink, G.J.; Reutelingsperger, C.P.; et al. Visualisation of cell death in vivo in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 2000, 356, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimister, P.W.; Hofstra, L.; Liem, I.H.; Boersma, H.H.; Kemerink, G.; Reutelingsperger, C.P.; Heidendal, G.A. In vivo detection of cell death in the area at risk in acute myocardial infarction. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 44, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Narula, J.; Acio, E.R.; Narula, N.; Samuels, L.E.; Fyfe, B.; Wood, D.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Raghunath, P.N.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Kelly, C.; et al. Annexin-v imaging for noninvasive detection of cardiac allograft rejection. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofstra, L.; Dumont, E.A.; Thimister, P.W.; Heidendal, G.A.; DeBruine, A.P.; Elenbaas, T.W.; Boersma, H.H.; van Heerde, W.L.; Reutelingsperger, C.P. In vivo detection of apoptosis in an intracardiac tumor. JAMA 2001, 285, 1841–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhocine, T.; Steinmetz, N.; Hustinx, R.; Bartsch, P.; Jerusalem, G.; Seidel, L.; Rigo, P.; Green, A. Increased uptake of the apoptosis-imaging agent 99mTc recombinant human annexin V in human tumors after one course of chemotherapy as a predictor of tumor response and patient prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kartachova, M.; Haas, R.L.; Olmos, R.A.; Hoebers, F.J.; van Zandwijk, N.; Verheij, M. In vivo imaging of apoptosis by 99mTc-annexin V scintigraphy: Visual analysis in relation to treatment response. Radiother. Oncol. 2004, 72, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeersch, H.; Ham, H.; Rottey, S.; Lahorte, C.; Corsetti, F.; Dierckx, R.; Steinmetz, N.; Van de Wiele, C. Intraobserver, interobserver, and day-to-day reproducibility of quantitative 99mTc-hynic annexin-v imaging in head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2004, 19, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kietselaer, B.L.; Reutelingsperger, C.P.; Heidendal, G.A.; Daemen, M.J.; Mess, W.H.; Hofstra, L.; Narula, J. Noninvasive detection of plaque instability with use of radiolabeled annexin A5 in patients with carotid-artery atherosclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1472–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Brande, J.M.; Koehler, T.C.; Zelinkova, Z.; Bennink, R.J.; te Velde, A.A.; ten Cate, F.J.; van Deventer, S.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Hommes, D.W. Prediction of antitumour necrosis factor clinical efficacy by real-time visualisation of apoptosis in patients with crohn’s disease. Gut 2007, 56, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloya, R.; Shirvan, A.; Grimberg, H.; Reshef, A.; Levin, G.; Kidron, D.; Cohen, A.; Ziv, I. Molecular imaging of cell death in vivo by a novel small molecule probe. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 2089–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickson, J.; Ackler, S.; Klaubert, D.; Bouska, J.; Ellis, P.; Foster, K.; Oleksijew, A.; Rodriguez, L.; Schlessinger, S.; Wang, B.; et al. Noninvasive molecular imaging of apoptosis in vivo using a modified firefly luciferase substrate, Z-DEVD-aminoluciferin. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, R.J.; Williams, B.W.; Bischof, J.C.; Olin, M.; Johnson, G.L.; Lee, B.W. Use of a fluorescently labeled poly-caspase inhibitor for in vivo detection of apoptosis related to vascular-targeting agent arsenic trioxide for cancer therapy. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 6, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivannan, A.; Sharp, P.F.; Phillips, R.P.; Forrester, J.V. Digital fundus imaging using a scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Physiol. Meas. 1993, 14, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, L.M.; Deleon-Ortega, J.; Sakata, V.; Girkin, C.A. Optical coherence tomography of the retina and optic nerve—a review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 37, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pircher, M.; Zawadzki, R.J. Review of adaptive optics OCT (AO-OCT): Principles and applications for retinal imaging [invited]. Biomed. Opt. Expr. 2017, 8, 2536–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Li, N.; Kang, J.; He, Y.; Chen, X.M. Adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy in fundus imaging, a review and update. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 10, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Williams, D.R.; Miller, D.T. Imaging photoreceptors in the living eye with adaptive optics. In Basic and Clinical Applications of Vision Science: The Professor Jay m. Enoch Festschrift Volume; Lakshminarayanan, V., Ed.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Roorda, A.; Williams, D.R. The arrangement of the three cone classes in the living human eye. Nature 1999, 397, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubra, A.; Sulai, Y.; Norris, J.L.; Cooper, R.F.; Dubis, A.M.; Williams, D.R.; Carroll, J. Noninvasive imaging of the human rod photoreceptor mosaic using a confocal adaptive optics scanning ophthalmoscope. Biomed. Opt. Exp. 2011, 2, 1864–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scoles, D.; Sulai, Y.N.; Dubra, A. In vivo dark-field imaging of the retinal pigment epithelium cell mosaic. Biomed. Opt. Exp. 2013, 4, 1710–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chui, T.Y.; Gast, T.J.; Burns, S.A. Imaging of vascular wall fine structure in the human retina using adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 7115–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arichika, S.; Uji, A.; Hangai, M.; Ooto, S.; Yoshimura, N. Noninvasive and direct monitoring of erythrocyte aggregates in human retinal microvasculature using adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 4394–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfing, J.I.; Chung, M.; Carroll, J.; Roorda, A.; Williams, D.R. High-resolution retinal imaging of cone-rod dystrophy. Ophthalmology 2006, 113, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Rivero, E.B.; Clark, M.E.; Witherspoon, C.D.; Spaide, R.F.; Girkin, C.A.; Owsley, C.; Curcio, C.A. Photoreceptor perturbation around subretinal drusenoid deposits as revealed by adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 158, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, J.; Krivosic, V.; Paques, M.; Tadayoni, R.; Gaudric, A. Cone density loss on adaptive optics in early macular telangiectasia type 2. Retina 2016, 36, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debellemaniere, G.; Flores, M.; Tumahai, P.; Meillat, M.; Bidaut Garnier, M.; Delbosc, B.; Saleh, M. Assessment of parafoveal cone density in patients taking hydroxychloroquine in the absence of clinically documented retinal toxicity. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, e534–e540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Soliman, M.K.; Hanout, M.; Sadiq, M.A.; Sarwar, S.; Jack, L.S.; Do, D.V.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Sepah, Y.J. Adaptive optics imaging of retinal photoreceptors overlying lesions in white dot syndrome and its functional correlation. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 160, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errera, M.H.; Coisy, S.; Fardeau, C.; Sahel, J.A.; Kallel, S.; Westcott, M.; Bodaghi, B.; Paques, M. Retinal vasculitis imaging by adaptive optics. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 1311–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Kurokawa, K.; Zhang, F.; Lee, J.J.; Miller, D.T. Imaging and quantifying ganglion cells and other transparent neurons in the living human retina. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12803–12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwerth, R.S.; Vilupuru, A.S.; Rangaswamy, N.V.; Smith, E.L., 3rd. The relationship between nerve fiber layer and perimetry measurements. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.R.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, W.; Knighton, R.W. Reflectance decreases before thickness changes in the retinal nerve fiber layer in glaucomatous retinas. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 6737–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, D.C.; Chen, M.F.; Lee, D.; Epstein, B.; Alhadeff, P.; Rosen, R.B.; Ritch, R.; Dubra, A.; Chui, T.Y. Confocal adaptive optics imaging of peripapillary nerve fiber bundles: Implications for glaucomatous damage seen on circumpapillary oct scans. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Williams, D.R.; Palczewska, G.; Palczewski, K.; Hunter, J.J. Two-photon autofluorescence imaging reveals cellular structures throughout the retina of the living primate eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, M.F.; Normando, E.M.; Cardoso, M.J.; Miodragovic, S.; Jeylani, S.; Davis, B.M.; Guo, L.; Ourselin, S.; A’Hern, R.; Bloom, P.A. Real-time imaging of single neuronal cell apoptosis in patients with glaucoma. Brain 2017, 140, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthy, R.S.; Lyon, A.T.; Rabb, M.F.; Spaide, R.F.; Yannuzzi, L.A.; Jampol, L.M. Idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy of the macula. Ophthalmology 1998, 105, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanga, P.E.; Lim, J.I.; Hamilton, P. Indocyanine green angiography in chorioretinal diseases: Indications and interpretation: An evidence-based update. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, R.H.; Hughes, G.W.; Delori, F.C. Confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Appl. Opt. 1987, 26, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, R.H.; Hughes, G.W.; Pomerantzeff, O. Flying spot TV ophthalmoscope. Appl. Opt. 1980, 19, 2991–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsner, A.E.; Burns, S.A.; Hughes, G.W.; Webb, R.H. Reflectometry with a scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Appl. Opt. 1992, 31, 3697–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modat, M.; Cash, D.M.; Daga, P.; Winston, G.P.; Duncan, J.S.; Ourselin, S. Global image registration using a symmetric block-matching approach. J. Med. Imaging 2014, 1, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modat, M.; Ridgway, G.R.; Taylor, Z.A.; Lehmann, M.; Barnes, J.; Hawkes, D.J.; Fox, N.C.; Ourselin, S. Fast free-form deformation using graphics processing units. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2010, 98, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, E.B.; Fox, N.C. Correction of differential intensity inhomogeneity in longitudinal MR images. Neuroimage 2004, 23, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelli, R. Template Matching Techniques in Computer Vision: Theory and Practice; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; p. 338. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, J.C.; Moore, C.G.; Deppmeier, L.M.; Gold, B.G.; Meshul, C.K.; Johnson, E.C. A rat model of chronic pressure-induced optic nerve damage. Exp. Eye Res. 1997, 64, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levkovitch-Verbin, H.; Quigley, H.A.; Martin, K.R.; Zack, D.J.; Pease, M.E.; Valenta, D.F. A model to study differences between primary and secondary degeneration of retinal ganglion cells in rats by partial optic nerve transection. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 3388–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.Y.; Wie, M.B.; Gwag, B.J.; Sensi, S.L.; Canzoniero, L.M.; Demaro, J.; Csernansky, C.; Choi, D.W. Staurosporine-induced neuronal apoptosis. Exp. Neurol. 1995, 135, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, M.F.; Guo, L.; Luong, V.; Harding, G.; Wang, W.; Jones, H.E.; Moss, S.E.; Sillito, A.M.; Fitzke, F.W. Real-time imaging of single nerve cell apoptosis in retinal neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13352–13356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bove, J.; Perier, C. Neurotoxin-based models of parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2012, 211, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrie, S.C.; Cheung, W.; Guo, L.; Barber, A.J.; Singh, R.S.J.; Gardner, T.W.; Cordeiro, M.F. Diabetic retinal neurodegeneration: In vivo imaging of retinal ganglion cell apoptosis in the Ins2Akita/J mouse. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 4924. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Moss, S.E.; Alexander, R.A.; Ali, R.R.; Fitzke, F.W.; Cordeiro, M.F. Retinal ganglion cell apoptosis in glaucoma is related to intraocular pressure and iop-induced effects on extracellular matrix. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Salt, T.E.; Maass, A.; Luong, V.; Moss, S.E.; Fitzke, F.W.; Cordeiro, M.F. Assessment of neuroprotective effects of glutamate modulation on glaucoma-related retinal ganglion cell apoptosis in vivo. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Salt, T.E.; Luong, V.; Wood, N.; Cheung, W.; Maass, A.; Ferrari, G.; Russo-Marie, F.; Sillito, A.M.; Cheetham, M.E.; et al. Targeting amyloid-beta in glaucoma treatment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13444–13449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz-Valckenberg, S.; Guo, L.; Maass, A.; Cheung, W.; Vugler, A.; Moss, S.E.; Munro, P.M.; Fitzke, F.W.; Cordeiro, M.F. Real-time in vivo imaging of retinal cell apoptosis after laser exposure. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 2773–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz-Valckenberg, S.; Guo, L.; Cheung, W.; Moss, S.E.; Fitzke, F.W.; Cordeiro, M.F. [In vivo imaging of retinal cell apoptosis following acute light exposure]. Ophthalmologe 2010, 107, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, M.F.; Guo, L.; Coxon, K.M.; Duggan, J.; Nizari, S.; Normando, E.M.; Sensi, S.L.; Sillito, A.M.; Fitzke, F.W.; Salt, T.E.; et al. Imaging multiple phases of neurodegeneration: A novel approach to assessing cell death in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normando, E.M.; Tilley, M.; Guo, L.; Cordeiro, M.F. Imaging in dry AMD. In Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 10, pp. e35–e41. [Google Scholar]
- xSalt, T.E.; Nizari, S.; Cordeiro, M.F.; Russ, H.; Danysz, W. Effect of the abeta aggregation modulator MRZ-99030 on retinal damage in an animal model of glaucoma. Neurotox. Res. 2014, 26, 440–446. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Davis, B.; Nizari, S.; Normando, E.M.; Shi, H.; Galvao, J.; Turner, L.; Shi, J.; Clements, M.; Parrinello, S.; et al. Direct optic nerve sheath (dons) application of schwann cells prolongs retinal ganglion cell survival in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvao, J.; Elvas, F.; Martins, T.; Cordeiro, M.F.; Ambrosio, A.F.; Santiago, A.R. Adenosine A3 receptor activation is neuroprotective against retinal neurodegeneration. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 140, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normando, E.M.; Davis, B.M.; De Groef, L.; Nizari, S.; Turner, L.A.; Ravindran, N.; Pahlitzsch, M.; Brenton, J.; Malaguarnera, G.; Guo, L.; et al. The retina as an early biomarker of neurodegeneration in a rotenone-induced model of parkinson’s disease: Evidence for a neuroprotective effect of rosiglitazone in the eye and brain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizari, S.; Guo, L.; Davis, B.M.; Normando, E.M.; Galvao, J.; Turner, L.A.; Bizrah, M.; Dehabadi, M.; Tian, K.; Cordeiro, M.F. Non-amyloidogenic effects of alpha2 adrenergic agonists: Implications for brimonidine-mediated neuroprotection. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.M.; Tian, K.; Pahlitzsch, M.; Brenton, J.; Ravindran, N.; Butt, G.; Malaguarnera, G.; Normando, E.M.; Guo, L.; Cordeiro, M.F. Topical coenzyme Q10 demonstrates mitochondrial-mediated neuroprotection in a rodent model of ocular hypertension. Mitochondrion 2017, 36, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Egea, M.A.; Davis, B.M.; Guo, L.; Espina, M.; Silva, A.M.; Calpena, A.C.; Souto, E.M.B.; Ravindran, N.; Ettcheto, M.; et al. Memantine-loaded pegylated biodegradable nanoparticles for the treatment of glaucoma. Small 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naskar, R.; Wissing, M.; Thanos, S. Detection of early neuron degeneration and accompanying microglial responses in the retina of a rat model of glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 2962–2968. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Fernandez, E.; Sanchez-Gomez, M.V.; Perez-Samartin, A.; Arellano, R.O.; Matute, C. A3 adenosine receptors mediate oligodendrocyte death and ischemic damage to optic nerve. Glia 2014, 62, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, M.O.; Beiser, J.A.; Brandt, J.D.; Heuer, D.K.; Higginbotham, E.J.; Johnson, C.A.; Keltner, J.L.; Miller, J.P.; Parrish, R.K., 2nd; Wilson, M.R.; et al. The ocular hypertension treatment study: Baseline factors that predict the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, F.A.; Weinreb, R.N. Is corneal thickness an independent risk factor for glaucoma? Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, B.; Heijl, A. Sita fast, a new rapid perimetric threshold test. Description of methods and evaluation in patients with manifest and suspect glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 1998, 76, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, B.; Heijl, A.; Olsson, J. Evaluation of a new threshold visual field strategy, sita, in normal subjects. Swedish interactive thresholding algorithm. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 1998, 76, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birt, C.M.; Shin, D.H.; Samudrala, V.; Hughes, B.A.; Kim, C.; Lee, D. Analysis of reliability indices from humphrey visual field tests in an urban glaucoma population. Ophthalmology 1997, 104, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, S.K.; Demirel, S.; Johnson, C.A. Is there evidence for continued learning over multiple years in perimetry? Optom. Vis. Sci. 2008, 85, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moraes, C.G.; Hood, D.C.; Thenappan, A.; Girkin, C.A.; Medeiros, F.A.; Weinreb, R.N.; Zangwill, L.M.; Liebmann, J.M. 24-2 visual fields miss central defects shown on 10-2 tests in glaucoma suspects, ocular hypertensives, and early glaucoma. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, B.C.; Garway-Heath, D.F.; Goni, F.J.; Rossetti, L.; Bengtsson, B.; Viswanathan, A.C.; Heijl, A. Practical recommendations for measuring rates of visual field change in glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 92, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garway-Heath, D.F.; Crabb, D.P.; Bunce, C.; Lascaratos, G.; Amalfitano, F.; Anand, N.; Azuara-Blanco, A.; Bourne, R.R.; Broadway, D.C.; Cunliffe, I.A.; et al. Latanoprost for open-angle glaucoma (UKGTS): A randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, F.A.; Lisboa, R.; Weinreb, R.N.; Liebmann, J.M.; Girkin, C.; Zangwill, L.M. Retinal ganglion cell count estimates associated with early development of visual field defects in glaucoma. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijl, A.; Leske, M.C.; Bengtsson, B.; Hyman, L.; Bengtsson, B.; Hussein, M.; Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial, G. Reduction of intraocular pressure and glaucoma progression: Results from the early manifest glaucoma trial. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, R.; Zangwill, L.; Briscoe, D.; Dagan, M.; Yagev, R.; Yassur, Y. Diurnal intraocular pressure variations: An analysis of 690 diurnal curves. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1992, 76, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Mathai, M.; Kelly, S.P.; Kwartz, J.; Henson, D.; McLeod, D. Relationship between corneal thickness and measured intraocular pressure in a general ophthalmology clinic. Ophthalmology 1999, 106, 2154–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, K.N.; Gurses-Ozden, R.; Liebmann, J.M.; Ritch, R. Attempted eyelid closure affects intraocular pressure measurement in open-angle glaucoma patients. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 134, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risner, D.; Ehrlich, R.; Kheradiya, N.S.; Siesky, B.; McCranor, L.; Harris, A. Effects of exercise on intraocular pressure and ocular blood flow: A review. J. Glaucoma 2009, 18, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarkkanen, A.; Leikola, J. Postural variations of the intraocular pressure as measured with the mackay-marg tonometer. Acta Ophthalmol. 1967, 45, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, J.; Hong, S.; Kim, C.Y.; Seong, G.J. Instability of 24-hour intraocular pressure fluctuation in healthy young subjects: A prospective, cross-sectional study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2014, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussel, I.I.; Wollstein, G.; Schuman, J.S. Oct for glaucoma diagnosis, screening and detection of glaucoma progression. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98 (Suppl. 2), 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, D.T.; Ushida, M.; Battistella, R.; Dorairaj, S.; Prata, T.S. Neurophthalmological conditions mimicking glaucomatous optic neuropathy: Analysis of the most common causes of misdiagnosis. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, E.M.; Zangwill, L.M.; Crowston, J.G.; Weinreb, R.N. Optic disk size and glaucoma. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2007, 52, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takkar, B.; Venkatesh, P.; Agarwal, D.; Kumar, A. Optic disc coloboma with pit treated as glaucoma: Diagnostic utility of ultrasound and swept source optical coherence tomography. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Lin, C.; Weinreb, R.N.; Lai, G.; Chiu, V.; Leung, C.K. Risk of visual field progression in glaucoma patients with progressive retinal nerve fiber layer thinning: A 5-year prospective study. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenthal, E.Z.; Horani, A.; Sasikumar, R.; Garudadri, C.; Udaykumar, A.; Thomas, R. Correlating structure with function in end-stage glaucoma. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging 2006, 37, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, M.F.; Migdal, C.; Bloom, P.; Fitzke, F.W.; Moss, S.E. Imaging apoptosis in the eye. Eye 2011, 25, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirooka, K.; Izumibata, S.; Ukegawa, K.; Nitta, E.; Tsujikawa, A. Estimating the rate of retinal ganglion cell loss to detect glaucoma progression: An observational cohort study. Medicine 2016, 95, e4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
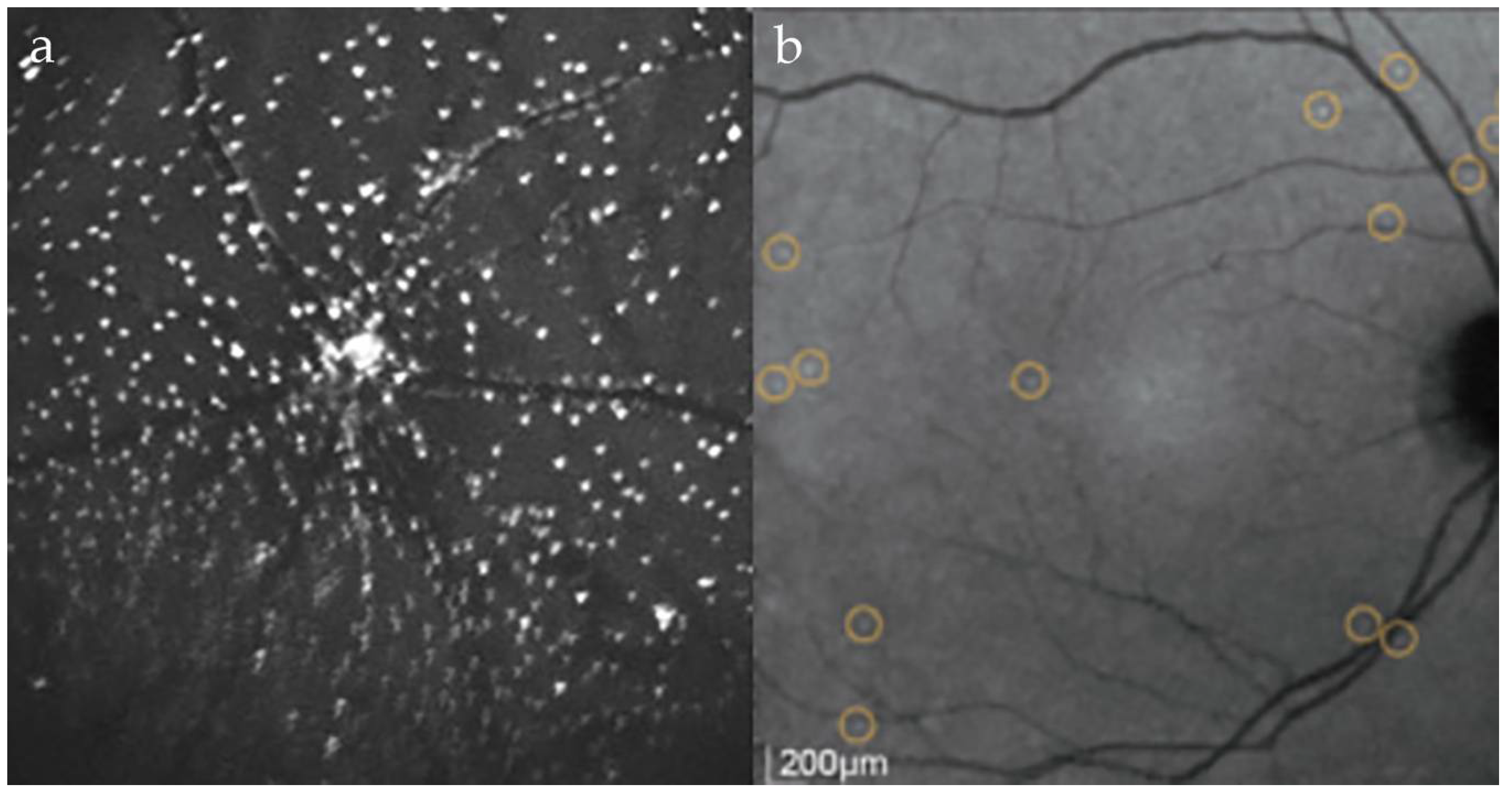
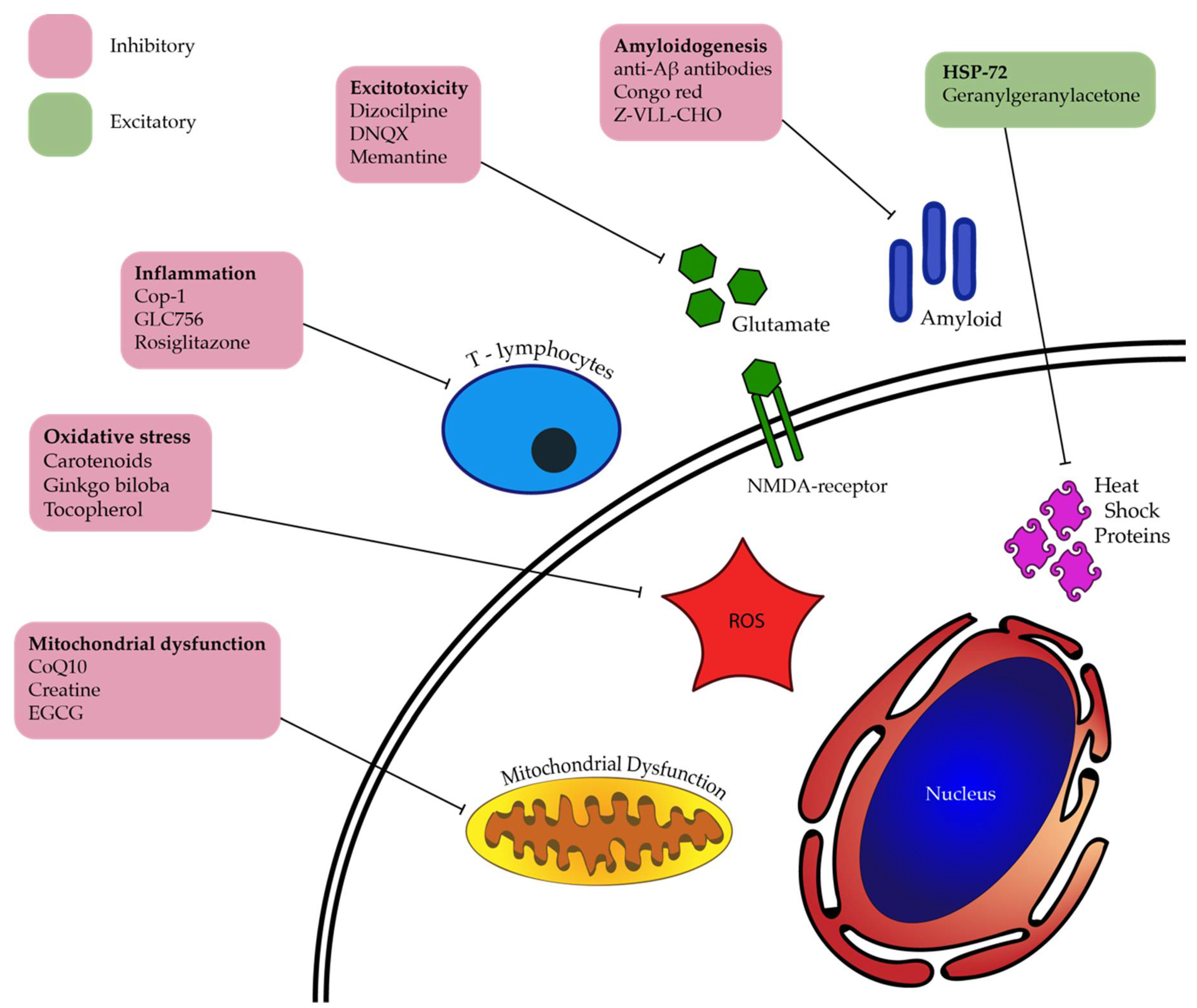
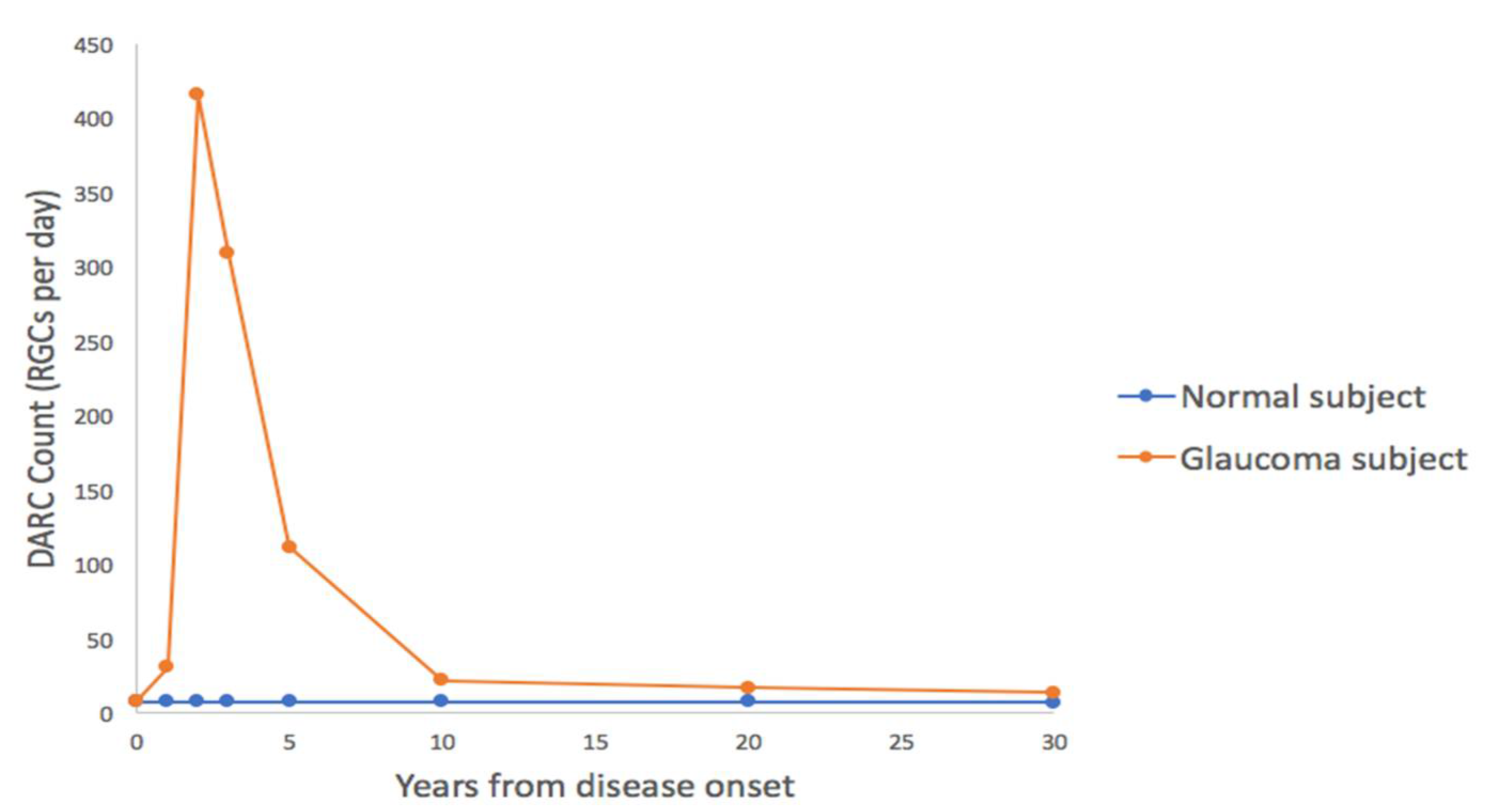
| Focus of Study | Model | Finding | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proof of concept | Rat | First retinal cell apoptosis imaging with DARC in vivo. Histological validation of the DARC technique confirms apoptosing RGCs. | [104] |
| IOP (Pathogenesis) | Rat | RGC apoptosis is strongly correlated with elevated IOP, and changes to the extra-cellular matrix induced by raised IOP. | [107] |
| NMDA receptor antagonism (Treatment) | Rat | Demonstration of a staurosporine-induced rat ocular hypertension model in testing neuroprotective strategies. Broad-spectrum NMDA receptor antagonist MK801 is a more effective neuroprotector than NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonist ifenprodil, especially when combined with group II mGluR agonist LY354740. | [108] |
| Beta-amyloid (Pathogenesis) | Rat | Beta-amyloid, implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, co-localizes with apoptosing retinal ganglion cells, and induces RGC apoptosis in a time and dose-dependent manner. | [109] |
| Diabetic retinopathy (Pathogenesis) | Mouse | RGC apoptosis was significantly higher in transgenic diabetic mice at eight weeks of age when compared to normal controls, suggesting DARC may be useful in early detection of diabetic retinopathy. | [106] |
| Laser exposure (Pathogenesis) | Rat | First use of DARC to image inner nuclear layer apoptosis after laser treatment with frequency-doubled Nd:YAG retinal laser. Increasing duration and power of laser led to more inner retinal layer involvement, with dose-dependent correlation of laser exposure and DARC spot density, along with lesion area and elevation. | [110] |
| Light damage (Pathogenesis) | Rat | In vivo demonstration of outer nuclear layer apoptosis in response to blue light exposure. Histological analysis confirmed photoreceptor death. | [111] |
| Proof of concept | Rat | Spectrally distinct fluorescent markers were used to monitor both early and late apoptosis and necrosis in individual cells, in real-time. | [112] |
| Dry AMD (Pathogenesis) | Mouse | Identification of photoreceptor apoptosis in dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD). | [113] |
| Amyloid-beta (Treatment) | Rat | A dose-dependent neuroprotective effect from systemic injections of the amyloid-beta aggregation modulator MRZ-99030. | [114] |
| DONS (Treatment) | Rat | A novel method of direct optic nerve sheath (DONS) delivery of Schwann cells in a partial optic nerve transection model of secondary degeneration is protective against RGC apoptosis, compared to intravitreal delivery. | [115] |
| Adenosine A3 agonists (Treatment) | Rat | 2-Cl-IB-MECA, a selective adenosine A3 agonist, is neuroprotective in vitro and in vivo. | [116] |
| Rosiglitazone (Treatment) | Rat | DARC used to demonstrate retinal changes in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. An enhanced neuroprotective effect against rotenone-induced damage was seen with liposome-encapsulated rosiglitazone. | [117] |
| Brimonidine (Treatment) | Rat | IOP-independent neuroprotective effect of alpha2 adrenergic receptor agonists (α2ARAs) brimonidine and clonidine. | [118] |
| Coenzyme Q10 (Treatment) | Rat | Topical coenzyme Q10 has a significant neuroprotective effect in a surgically-induced ocular hypertension model of glaucoma. | [119] |
| Proof of concept | Human | Intravenous ANX776 is a safe way to monitor rates of RGC apoptosis in humans using DARC imaging. A significant difference in DARC count was seen between progressing glaucoma patients and healthy controls. | [91] |
| Memantine (Treatment) | Rat | Memantine is an NMDA receptor antagonist, used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Topical memantine-loaded PLGA-PEG nanoparticles significantly reduced RGC loss in an experimental glaucoma model. | [120] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yap, T.E.; Donna, P.; Almonte, M.T.; Cordeiro, M.F. Real-Time Imaging of Retinal Ganglion Cell Apoptosis. Cells 2018, 7, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7060060
Yap TE, Donna P, Almonte MT, Cordeiro MF. Real-Time Imaging of Retinal Ganglion Cell Apoptosis. Cells. 2018; 7(6):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7060060
Chicago/Turabian StyleYap, Timothy E., Piero Donna, Melanie T. Almonte, and Maria Francesca Cordeiro. 2018. "Real-Time Imaging of Retinal Ganglion Cell Apoptosis" Cells 7, no. 6: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7060060
APA StyleYap, T. E., Donna, P., Almonte, M. T., & Cordeiro, M. F. (2018). Real-Time Imaging of Retinal Ganglion Cell Apoptosis. Cells, 7(6), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7060060





