Systems Biology as an Integrated Platform for Bioinformatics, Systems Synthetic Biology, and Systems Metabolic Engineering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
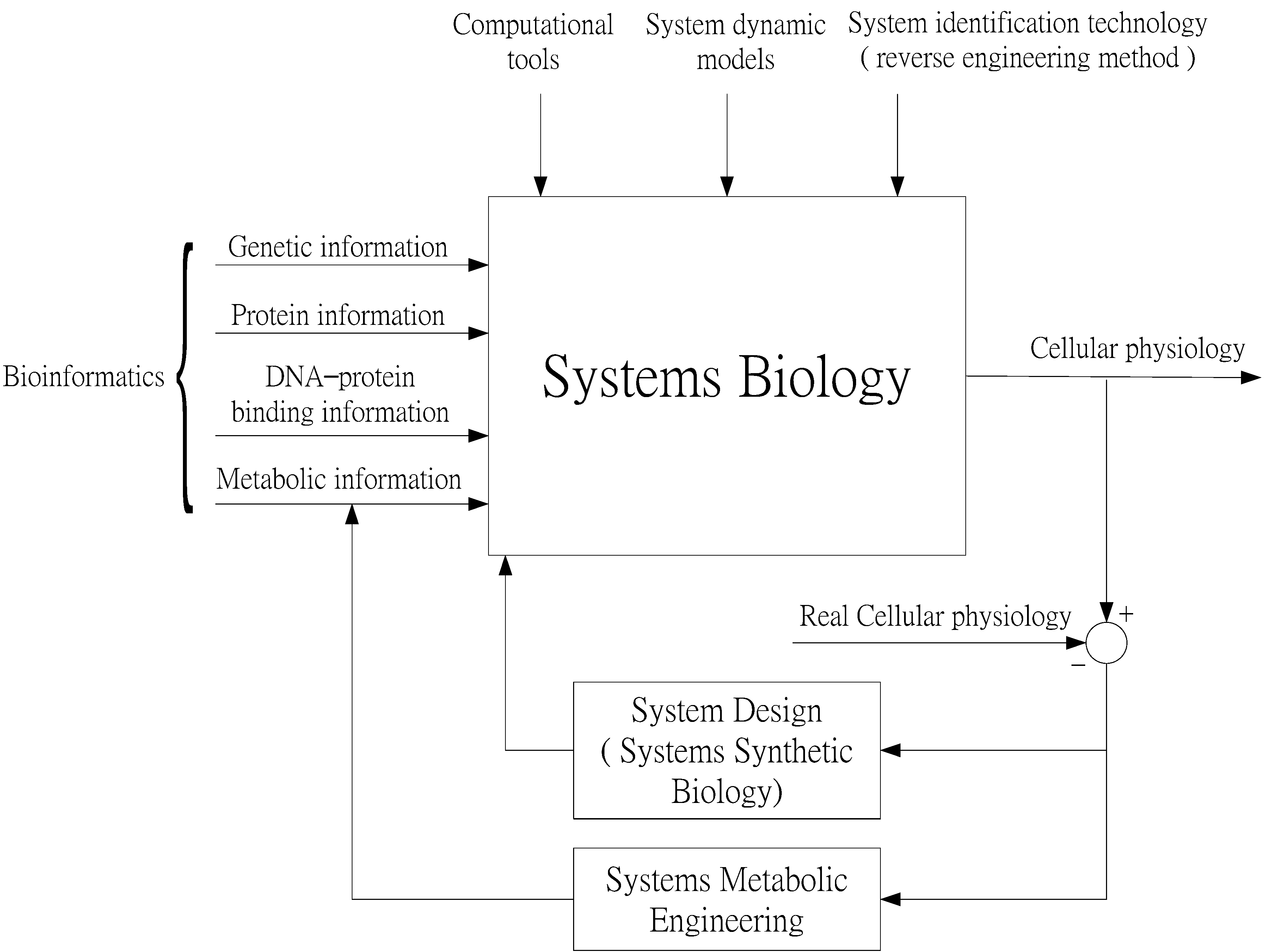
2. Systems Biology Approach to GRNs and PPI Networks via Bioinformatics Methodology
2.1. Construction of GRNs via Microarray Data


2.2. Construction of PPI Networks


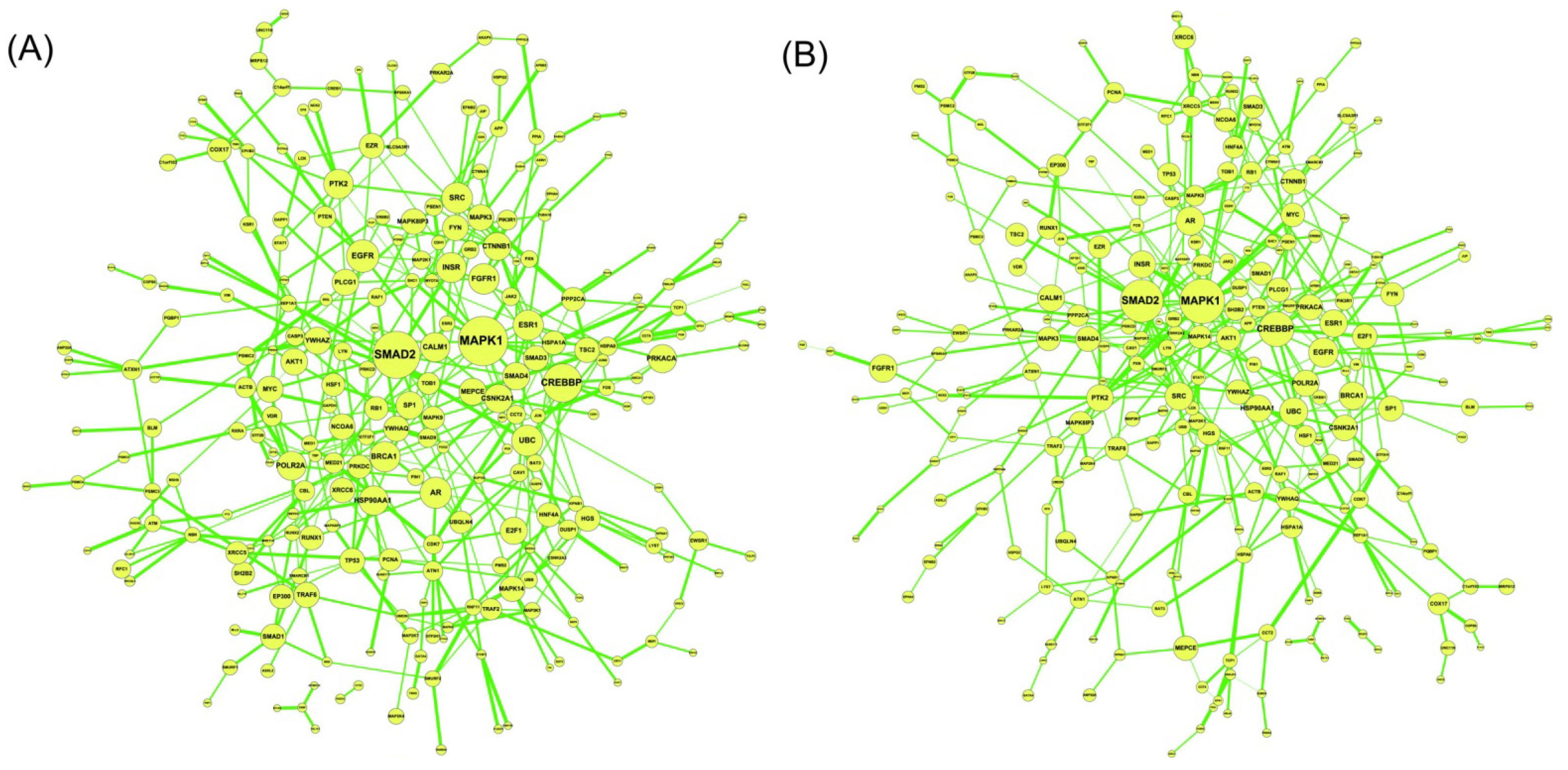
2.3. Construction of Integrated GRN and PPI Cellular Networks



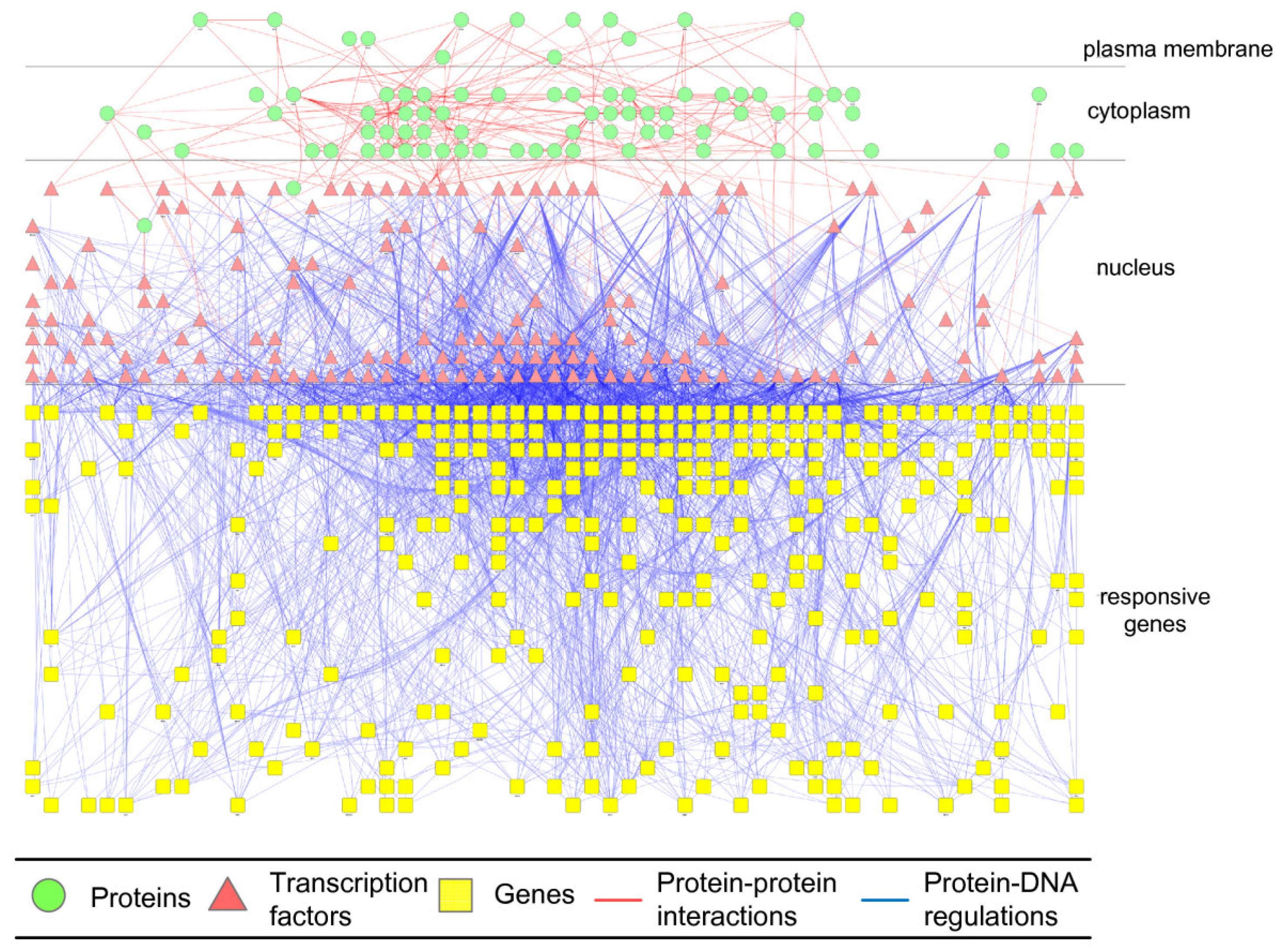
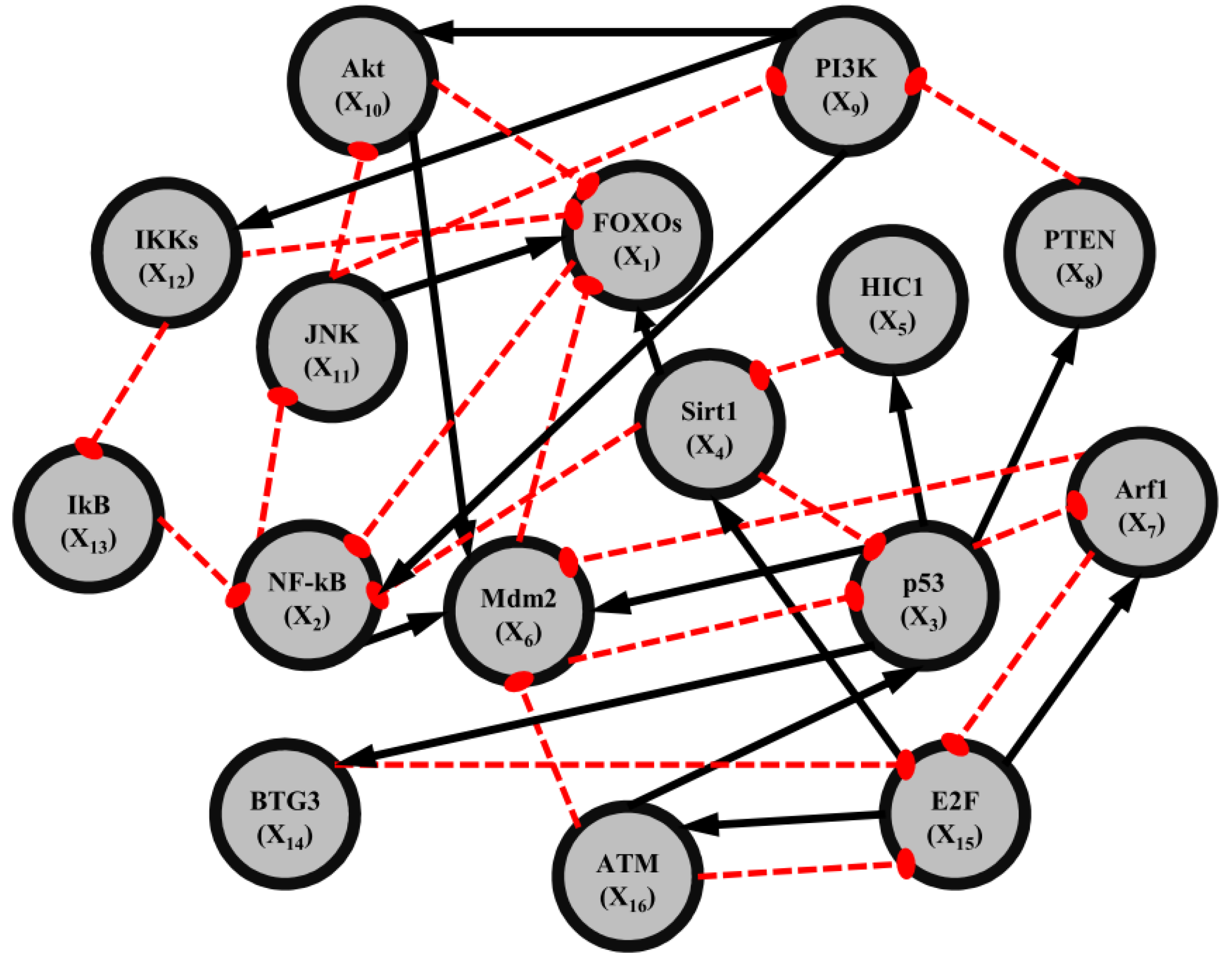
2.4. Network Robustness and Sensitivity Estimation via Microarray Data Using a Systems Biology Approach


 denotes the estimated basal level of the i-th gene. n(t) denotes the model residual and measurement noise. The steady state xs of x(t) is obtained as t→∞:
denotes the estimated basal level of the i-th gene. n(t) denotes the model residual and measurement noise. The steady state xs of x(t) is obtained as t→∞:

 (t) + xs. This shift allows the following shifted dynamic system to be achieved by subtracting Equation (2.7) from Equation (2.8) [34]:
(t) + xs. This shift allows the following shifted dynamic system to be achieved by subtracting Equation (2.7) from Equation (2.8) [34]:

 (t) ≡ 0. In the following, its network robustness (tolerance to intrinsic network perturbation) is tested. Suppose the linear GRN suffers from intrinsic molecular perturbations mainly due to process noise, thermal fluctuation, or genetic mutations. The interactive matrix  is then perturbed as Â(1 + η), where η denotes the ratio of intrinsic perturbation. That is, the corresponding additional system perturbation is Δ = η [80]. A GRN with intrinsic perturbation can then be represented by
(t) ≡ 0. In the following, its network robustness (tolerance to intrinsic network perturbation) is tested. Suppose the linear GRN suffers from intrinsic molecular perturbations mainly due to process noise, thermal fluctuation, or genetic mutations. The interactive matrix  is then perturbed as Â(1 + η), where η denotes the ratio of intrinsic perturbation. That is, the corresponding additional system perturbation is Δ = η [80]. A GRN with intrinsic perturbation can then be represented by

 ) =
) =  T(t)P
T(t)P  (t) > 0, with V(0) = 0 for a positive symmetric matrix, P = PT > 0. The perturbative GRN in Equation (2.10) is robustly stable if ΔV(
(t) > 0, with V(0) = 0 for a positive symmetric matrix, P = PT > 0. The perturbative GRN in Equation (2.10) is robustly stable if ΔV(  ) = V(
) = V(  (t+1)) − V(
(t+1)) − V(  (t)) ≤ 0, i.e., the energy of the gene network is not increased by intrinsic perturbations [79]. Based on this idea of robust stability, if the following inequality has a positive definite solution P = PT > 0 [34],
(t)) ≤ 0, i.e., the energy of the gene network is not increased by intrinsic perturbations [79]. Based on this idea of robust stability, if the following inequality has a positive definite solution P = PT > 0 [34],






| Tissue | Young | Aged | CR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thymas | |||
| η° | 0.2310 | 0.3750 | 0.2050 |
| δ° | 1.1653 | 0.9463 | 1.2279 |
| Spinal Cord | |||
| η° | 0.2410 | 0.6270 | 0.1400 |
| δ° | 1.1630 | 0.9367 | 1.2645 |
| Eye | |||
| η° | 0.1600 | 0.2910 | |
| δ° | 1.2376 | 0.8798 |
2.5. Network-Based Biomarker Determination via Sample Microarray Data Using a Systems Biology Approach





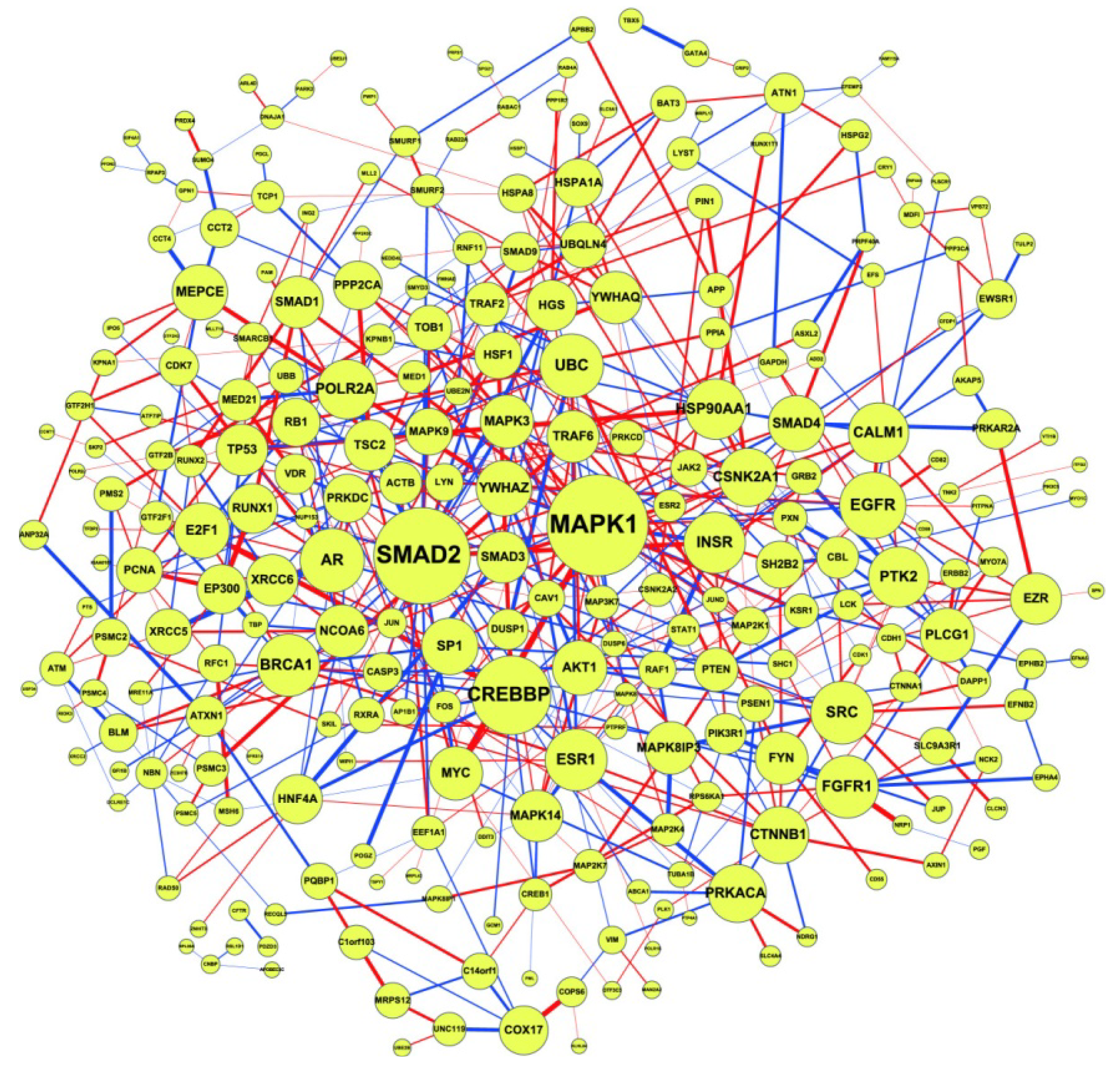
2.6. On the Network Robustness and Filtering Ability versus Molecular Noise in GRNs Using a Stochastic System Approach



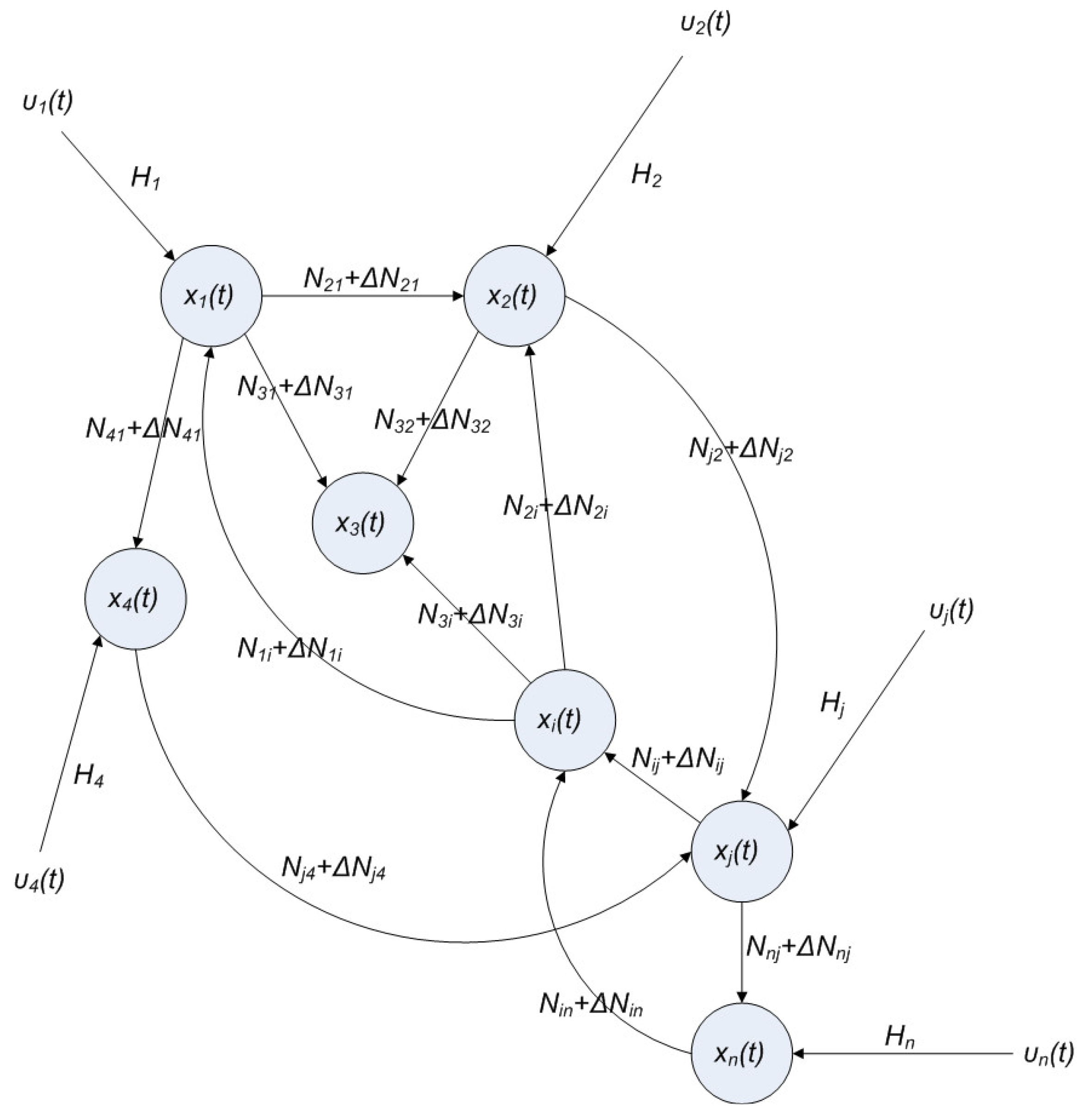


















 hi(z) = 1, and dx = (Nix + Hiv)dt + Mixdω is the i-th local linearized GRN.
hi(z) = 1, and dx = (Nix + Hiv)dt + Mixdω is the i-th local linearized GRN.
3. Systems Synthetic Biology
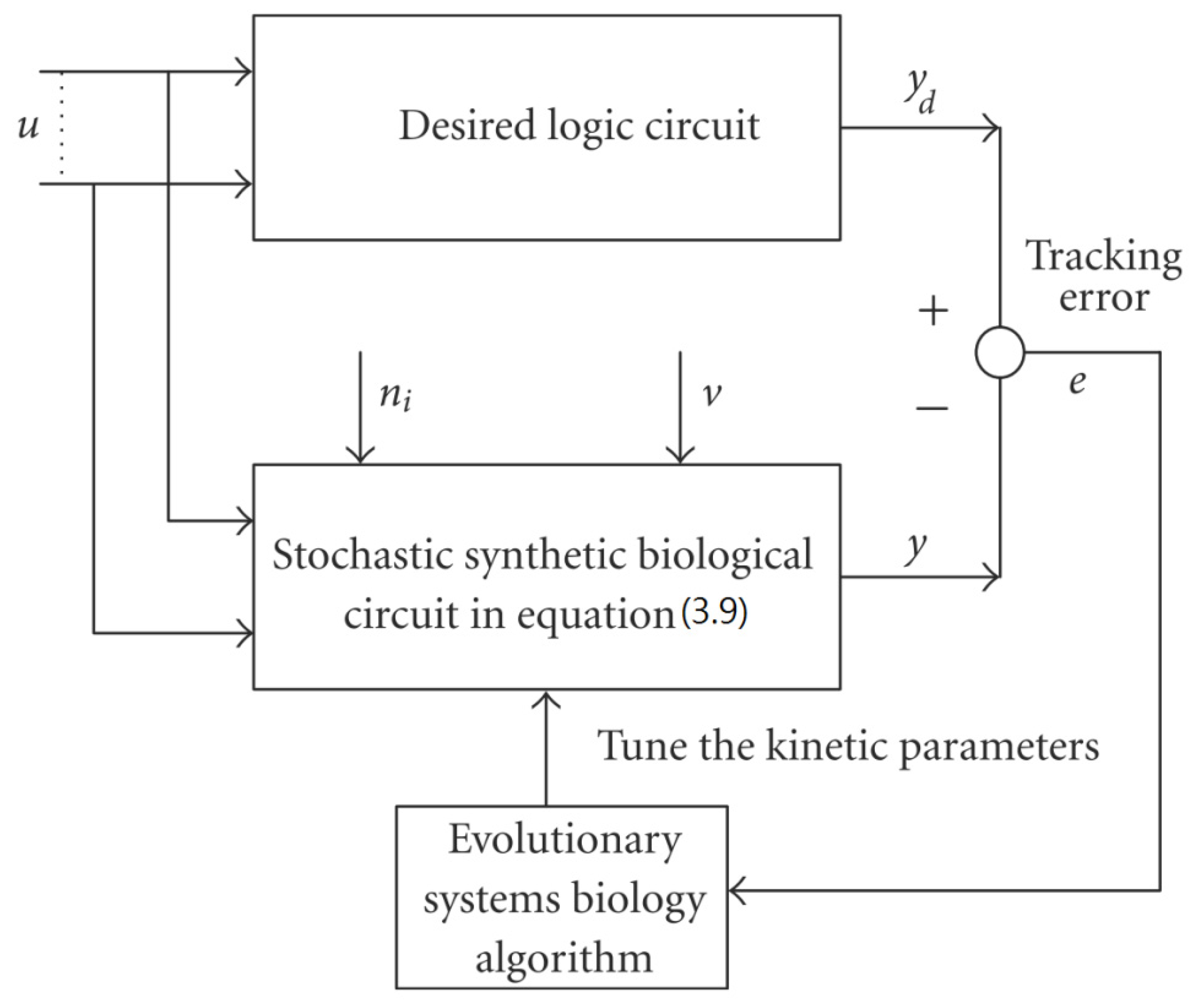
3.1. Design of Specifications-Based Systems Synthetic Biology











 = x – xd. The following shifted stochastic synthetic genetic system is then derived [79]:
= x – xd. The following shifted stochastic synthetic genetic system is then derived [79]:

 = 0 of the stochastic system in Equation (3.9) is at the desired steady state xd of the original stochastic system in Equation (3.7). N ∈ [N1,N2] is then specified to tolerate the stochastic parameter fluctuation
= 0 of the stochastic system in Equation (3.9) is at the desired steady state xd of the original stochastic system in Equation (3.7). N ∈ [N1,N2] is then specified to tolerate the stochastic parameter fluctuation  Migi(
Migi(  + xd)dWi and efficiently attenuate the environmental disturbance v to the prescribed level
+ xd)dWi and efficiently attenuate the environmental disturbance v to the prescribed level

 ) > 0
) > 0

 →0 or x→xd in probability, i.e., design specification (iii) is achieved.
→0 or x→xd in probability, i.e., design specification (iii) is achieved. ) > 0 using a systematic method. If all global linearizations are bound by a polytope consisting of M vertices
) > 0 using a systematic method. If all global linearizations are bound by a polytope consisting of M vertices

 (t) of the shifted gene network in Equation (3.9) can be represented by the convex combination of M linearized gene networks as
(t) of the shifted gene network in Equation (3.9) can be represented by the convex combination of M linearized gene networks as

 ) satisfies 0 ≤ αj(
) satisfies 0 ≤ αj(  ) ≤ 1 and ∑i = 1M αj(
) ≤ 1 and ∑i = 1M αj(  ) = 1. The trajectory of the nonlinear stochastic synthetic gene network in Equation (3.9) could thus be represented by the interpolated synthetic gene network in Equation (3.13). This yields the following result.
) = 1. The trajectory of the nonlinear stochastic synthetic gene network in Equation (3.9) could thus be represented by the interpolated synthetic gene network in Equation (3.13). This yields the following result.
 (0) of the synthetic gene network (3.9) in the host cell, the following minimax design has also been considered to reset the uncertainty of ν(t) and
(0) of the synthetic gene network (3.9) in the host cell, the following minimax design has also been considered to reset the uncertainty of ν(t) and  (0) in vivo [52]. ν(t) and
(0) in vivo [52]. ν(t) and  (0) are considered players maximizing their effects on regulation error
(0) are considered players maximizing their effects on regulation error  (t) when the kinetic parameters are specified as another player minimizing the effects of v and
(t) when the kinetic parameters are specified as another player minimizing the effects of v and  (0) on
(0) on  (t).
(t). 





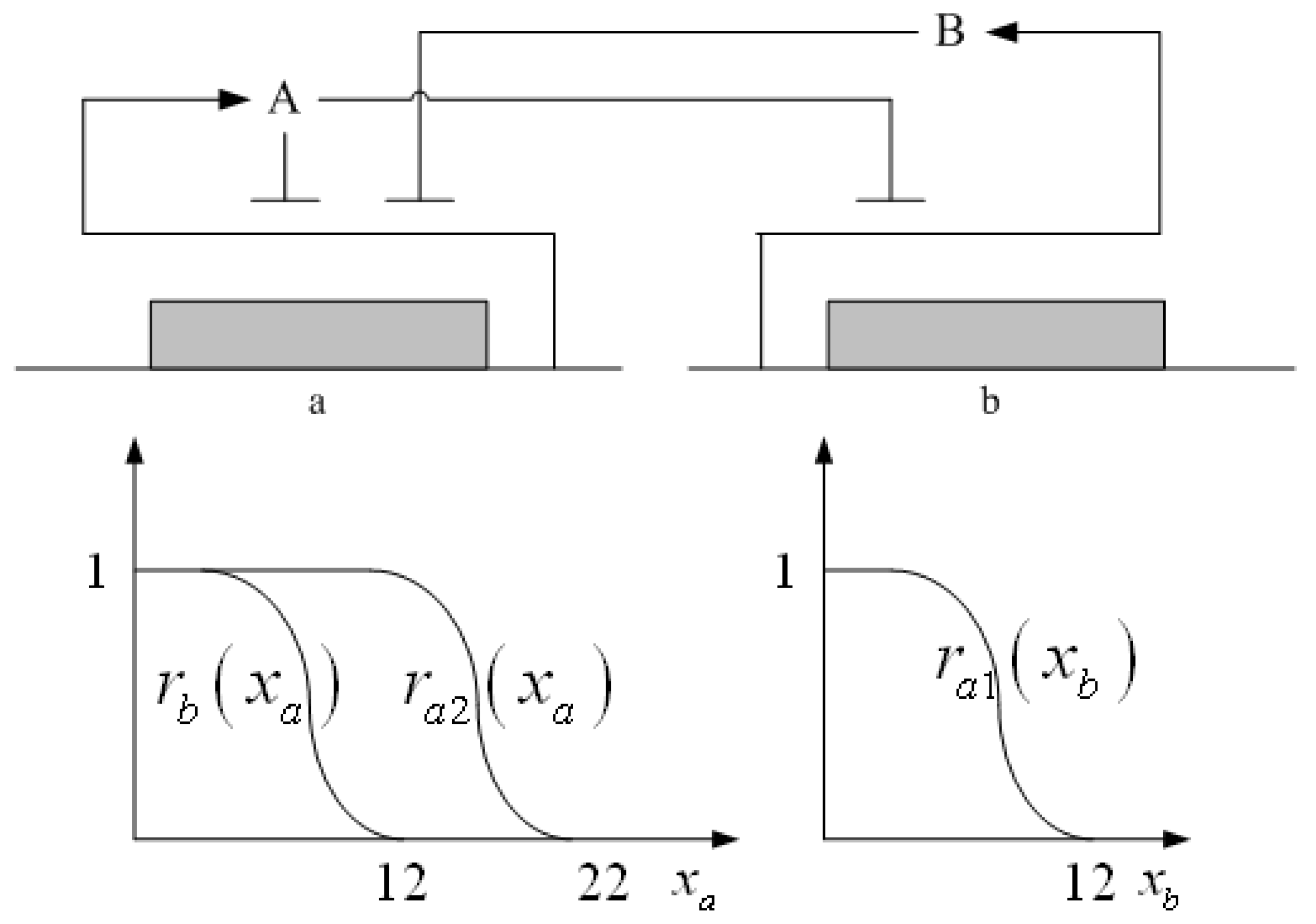
3.2. Robust Synthetic Gene Network Design via Library-Based Search Methods



| TetR-regulated promoter library (LibTetR) | LacI-regulated promoter library (LibLacI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Promoter | Promoter activity | Promoter | Promoter activity | ||
| cs | cr | cs | cr | ||
| T0 | 2121 | 0.1724 | L0 | 1657.5 | 0.3018 |
| T1 | 1604 | 0.7576 | L1 | 923.97 | 0.2567 |
| T2 | 1376.6 | 0.1936 | L2 | 860.87 | 0.2244 |
| T3 | 1169.8 | 0.4672 | L3 | 674.92 | 1.9189 |
| T4 | 974.52 | 0.0753 | L4 | 651.58 | 1.1680 |
| T5 | 942.77 | 0.2281 | L5 | 570.07 | 3.5062 |
| T6 | 967.17 | 0.1493 | L6 | 527.83 | 0.5497 |
| T7 | 738.57 | 0.0702 | L7 | 323.45 | 0.1248 |
| T8 | 641.74 | 0.7135 | L8 | 327.77 | 0.1772 |
| T9 | 564.24 | 0.2620 | L9 | 309.74 | 0.5439 |
| T10 | 501.35 | 0.0756 | L10 | 298.35 | 0.1146 |
| T11 | 469.35 | 0.0788 | L11 | 250.16 | 0.1326 |
| T12 | 466.16 | 0.1636 | L12 | 248.03 | 0.1171 |
| T13 | 356.88 | 0.0927 | L13 | 239.32 | 0.1010 |
| T14 | 348.95 | 0.1483 | L14 | 190.2 | 0.0959 |
| T15 | 274.79 | 0.1067 | L15 | 163.84 | 0.4813 |
| T16 | 250.04 | 0.0857 | L16 | 166.42 | 0.0989 |
| T17 | 188.77 | 0.1366 | L17 | 131.63 | 0.1190 |
| T18 | 119.57 | 0.0753 | L18 | 108.96 | 0.0903 |
| T19 | 111.57 | 0.1185 | L19 | 101.89 | 0.0982 |
| T20 | 70.909 | 0.1606 | L20 | 85.673 | 0.2174 |
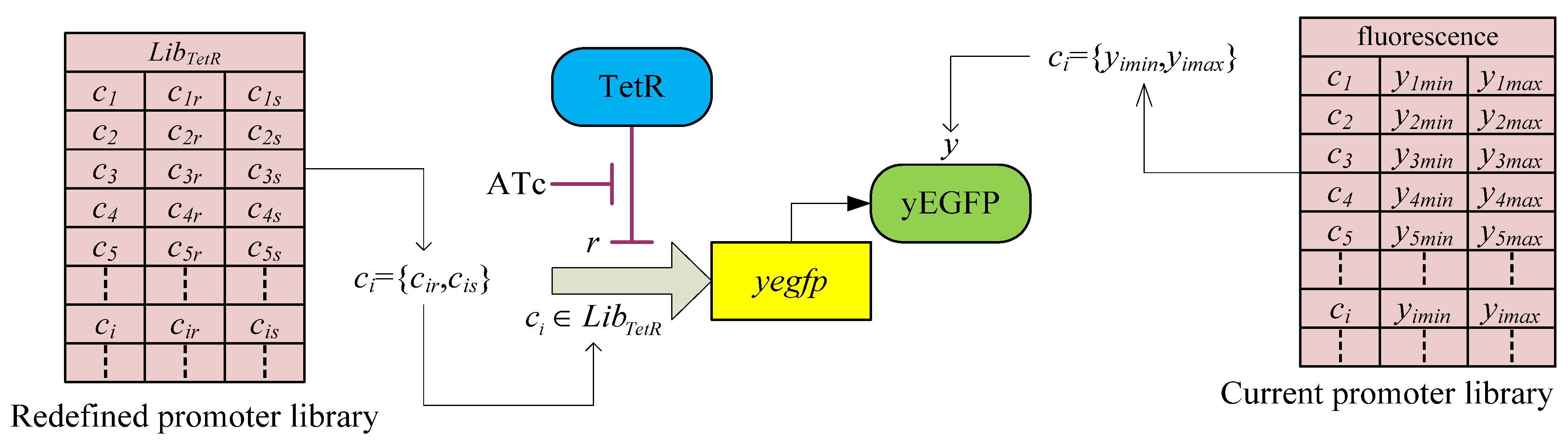


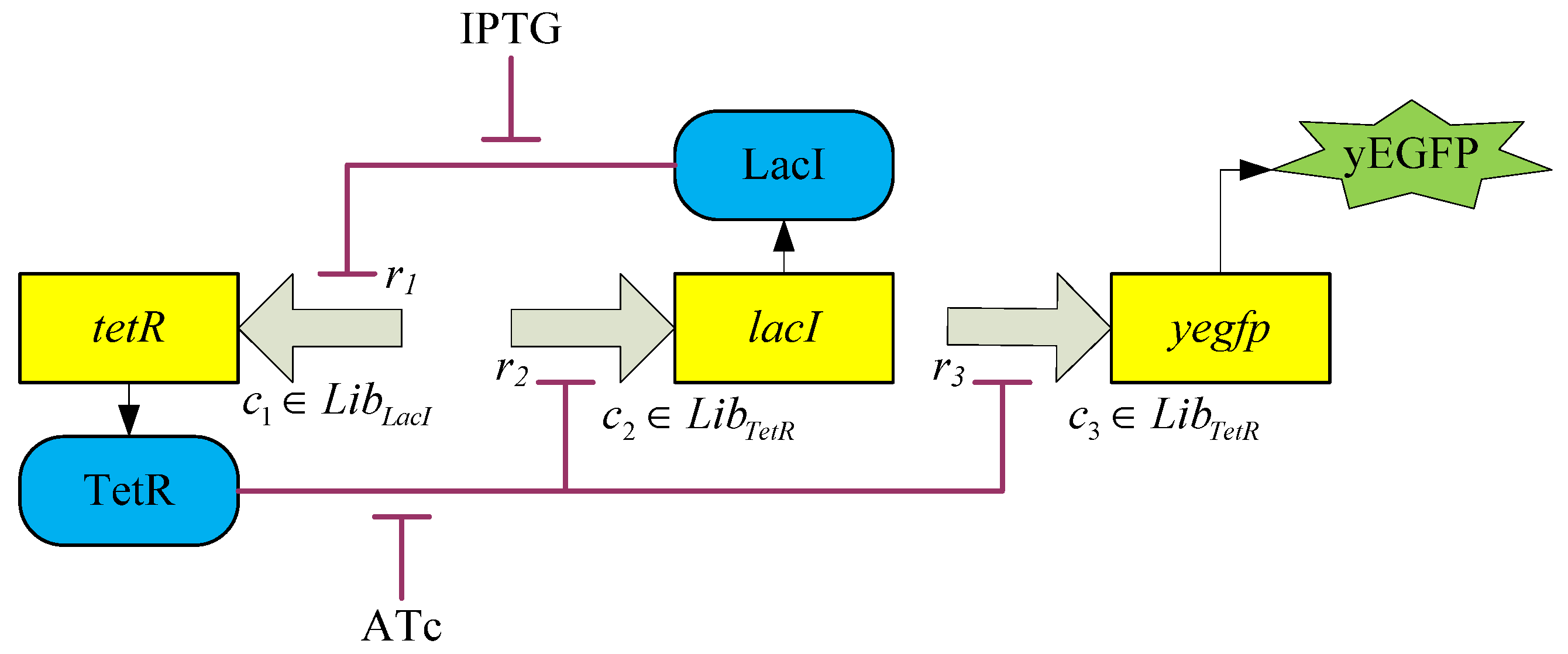
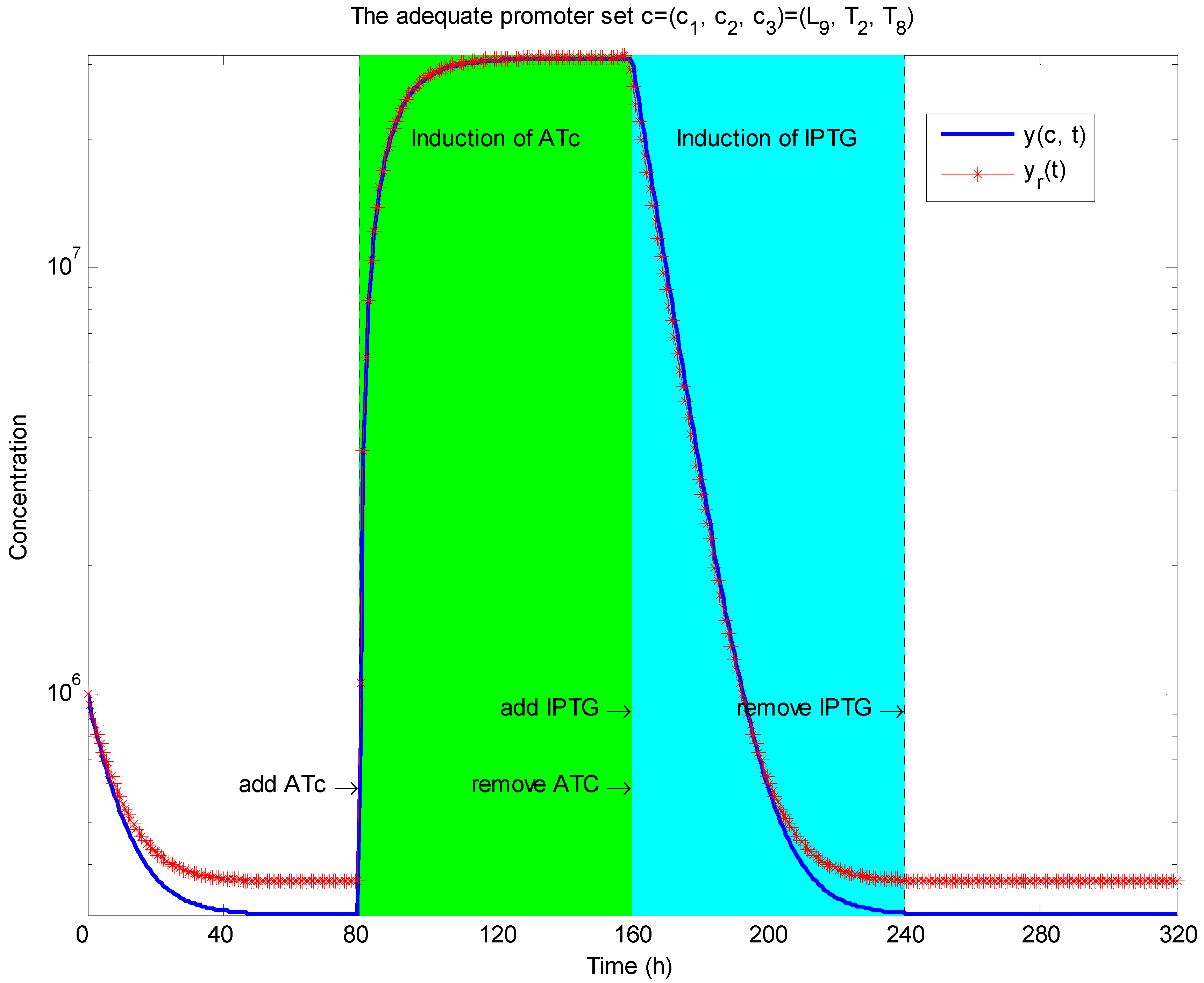
4. Systems Metabolic Engineering

4.1. Robust Biochemical Circuit Design in Metabolic Networks
















 denotes a new biochemical control circuit with Xk regulating the production of Xi by the kinetic parameter fik.
denotes a new biochemical control circuit with Xk regulating the production of Xi by the kinetic parameter fik.  denotes a new biochemical control circuit with Xk regulating the degradation of Xi by the kinetic parameter lik. The choice of regulating objects, Xk and Xi, and the specification of the kinetic parameters, fik and lik, are designed according to the feasibility of biochemical circuit linkage to achieve a desired robustness to tolerate ΔAD within the prescribed range of kinetic parameter perturbations in a metabolic network. Since fik and lik represent the elasticities of the corresponding enzymes in the designed control circuits, the implementation of control circuits is heavily dependent on the elasticity specification of these enzymes.
denotes a new biochemical control circuit with Xk regulating the degradation of Xi by the kinetic parameter lik. The choice of regulating objects, Xk and Xi, and the specification of the kinetic parameters, fik and lik, are designed according to the feasibility of biochemical circuit linkage to achieve a desired robustness to tolerate ΔAD within the prescribed range of kinetic parameter perturbations in a metabolic network. Since fik and lik represent the elasticities of the corresponding enzymes in the designed control circuits, the implementation of control circuits is heavily dependent on the elasticity specification of these enzymes.



4.2. Multipurpose Circuit Control Design of Metabolic Networks







4.3. Robust Control Circuit Design of Stochastic Dynamic Metabolic Networks


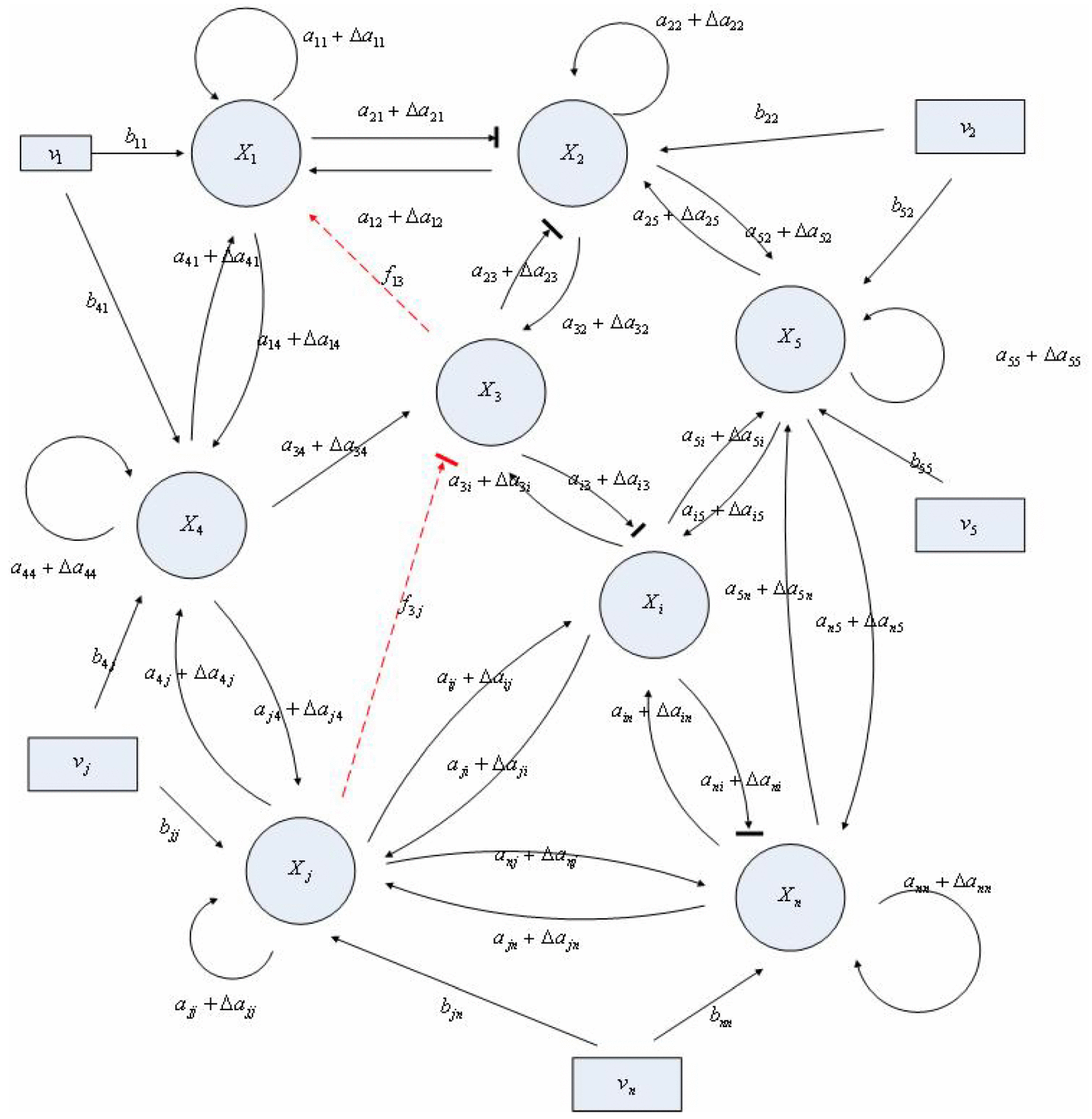

 Aini(t) denotes the intrinsic parameter fluctuations due to an L random fluctuation source (e.g., thermal fluctuation, alternative splicing, molecular diffusion, etc.), and ni(t) denotes the i-th random noise with the statistics E[ni(t)] = 0 and E[ni2(t)] = σi2, i = 1,⋯, L. ν(t) denotes the environmental disturbance.
Aini(t) denotes the intrinsic parameter fluctuations due to an L random fluctuation source (e.g., thermal fluctuation, alternative splicing, molecular diffusion, etc.), and ni(t) denotes the i-th random noise with the statistics E[ni(t)] = 0 and E[ni2(t)] = σi2, i = 1,⋯, L. ν(t) denotes the environmental disturbance.













 αj(X)AjX(t),
αj(X)AjX(t),  GjX(t), and
GjX(t), and  AijX(t), respectively. In this situation, the following robust chemical circuit design for a metabolic network with a prescribed noise attenuation level ρP is derived.
AijX(t), respectively. In this situation, the following robust chemical circuit design for a metabolic network with a prescribed noise attenuation level ρP is derived.

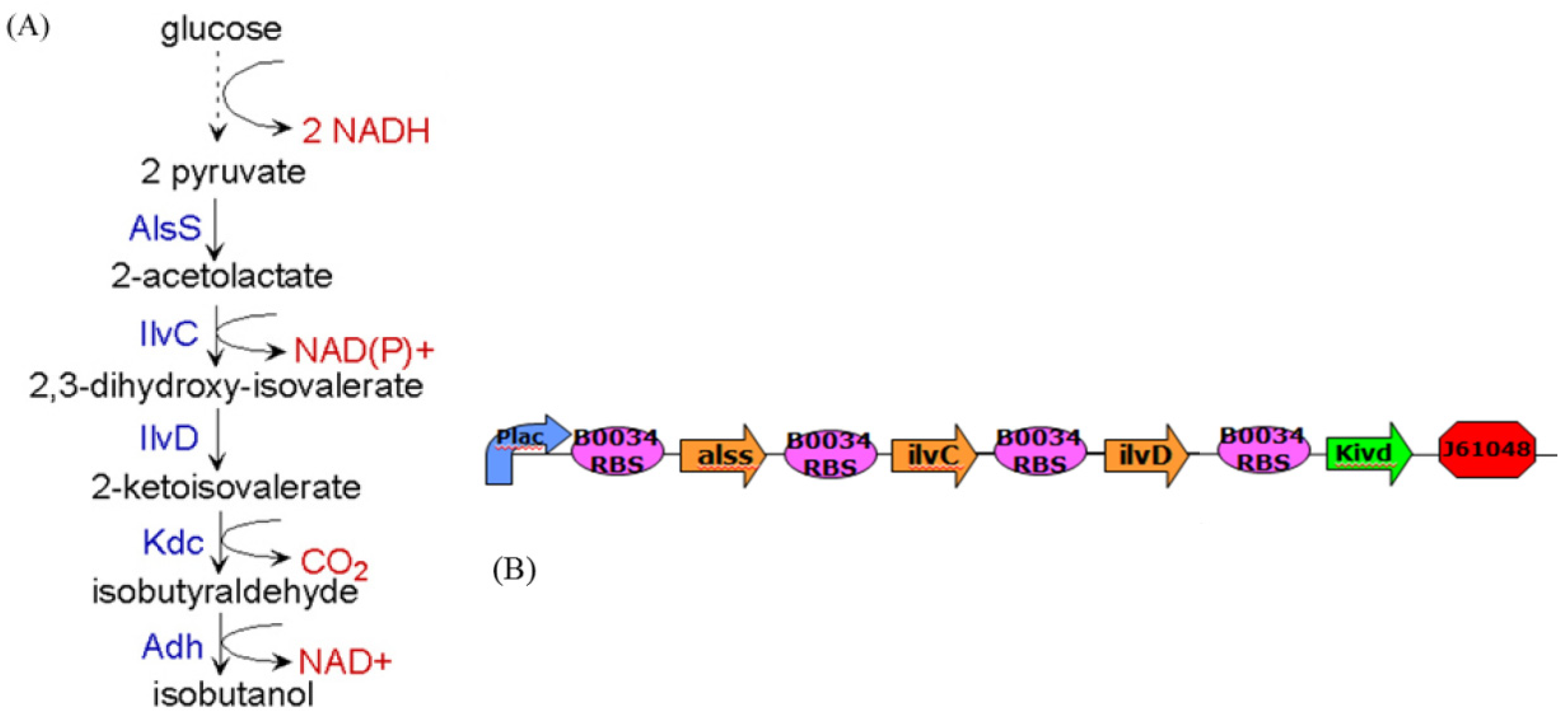
5. Future Challenges in Systems Biology
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joyce, A.R.; Palsson, B.O. The model organism as a system: integrating 'omics' data sets. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Bio. 2006, 7, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ideker, T.; Bafna, V.; Lemberger, T. Integrating scientific cultures. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 105–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, H.Y.; Lee, E.; Liu, Y.T.; Lee, D.; Ideker, T. Network-based classification of breast cancer metastasis. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 140–157. [Google Scholar]
- Oti, M.; Snel, B.; Huynen, M.A.; Brunner, H.G. Predicting disease genes using protein-protein interactions. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri, S.; Navarro, J.D.; Amanchy, R.; Kristiansen, T.Z.; Jonnalagadda, C.K.; Surendranath, V.; Niranjan, V.; Muthusamy, B.; Gandhi, T.K.B.; Gronborg, M.; et al. Development of human protein reference database as an initial platform for approaching systems biology in humans. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Jin, G.X.; Zhang, X.S.; Chen, L.N. Discovering functions and revealing mechanisms at molecular level from biological networks. Proteomics 2007, 7, 2856–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voit, E.O. Computational Analysis of Biochemical Systems: a Practical Guide for Biochemists and Molecular Biologists; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA,, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.S.; Wu, C.C. On the calculation of signal transduction ability of signaling transduction pathways in intracellular communication: systematic approach. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Opinon—Cancer as a robust system: Implications for anticancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelling, J.; Sauer, U.; Szallasi, Z.; Doyle, F.J.; Doyle, J. Robustness of cellular functions. Cell 2004, 118, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, J.D.; Xiao, W.Z.; Leek, J.T.; Tompkins, R.G.; Davis, R.W. Significance analysis of time course microarray experiments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12837–12842. [Google Scholar]
- Cherry, J.M.; Adler, C.; Ball, C.; Chervitz, S.A.; Dwight, S.S.; Hester, E.T.; Jia, Y.K.; Juvik, G.; Roe, T.; Schroeder, M.; et al. SGD, Saccharomyces genome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasch, A.P.; Spellman, P.T.; Kao, C.M.; Carmel-Harel, O.; Eisen, M.B.; Storz, G.; Botstein, D.; Brown, P.O. Genomic expression programs in the response of yeast cells to environmental changes. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2000, 11, 4241–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbison, C.T.; Gordon, D.B.; Lee, T.I.; Rinaldi, N.J.; Macisaac, K.D.; Danford, T.W.; Hannett, N.M.; Tagne, J.B.; Reynolds, D.B.; Yoo, J.; et al. Transcriptional regulatory code of a eukaryotic genome. Nature 2004, 431, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.C.; Monteiro, P.; Jain, P.; Tenreiro, S.; Fernandes, A.R.; Mira, N.P.; Alenquer, M.; Freitas, A.T.; Oliveira, A.L.; Sa-Correia, I. The YEASTRACT database, a tool for the analysis of transcription regulatory associations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D446–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, C.; Breitkreutz, B.J.; Reguly, T.; Boucher, L.; Breitkreutz, A.; Tyers, M. BioGRID, a general repository for interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D535–D539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology, Tool for the unification of biology. The gene ontology consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Lee, H.C.; Lin, T.Y.; Li, W.H.; Chen, B.S. Quantitative characterization of the transcriptional regulatory network in the yeast cell cycle. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1914–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Wang, Y.C.; Wu, W.S.; Li, W.H. A new measure of the robustness of biochemical networks. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2698–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.C.; Li, C.W.; Chen, B.S. Quantitative inference of dynamic regulatory pathways via microarray data. BMC Bioinf. 2005, 6, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.H.; Lee, H.C.; Li, W.H.; Chen, B.S. Dynamic modeling of cis-regulatory circuits and gene expression prediction via cross-gene identification. BMC Bioinf. 2005, 6, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, B.S. Identification of transcription factor cooperativity via stochastic system model. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2276–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.S.; Li, W.H.; Chen, B.S. Computational reconstruction of transcriptional regulatory modules of the yeast cell cycle. BMC Bioinf. 2006, 7, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.S.; Li, W.H.; Chen, B.S. Identifying regulatory targets of cell cycle transcription factors using gene expression and ChIP-chip data. BMC Bioinf. 2007, 8, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Wang, Y.C. On the attenuation and amplification of molecular noise in genetic regulatory networks. BMC Bioinf. 2006, 7, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-S.; Li, C.-W. Analysing microarray data in drug discovery using systems biology. Expert Opin. Drug Discovery 2007, 2, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Wu, W.S.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, W.H. On the Robust Circuit Design Schemes of Biochemical Networks, Steady-State Approach. IEEE T Biomed. Circ. S 2007, 1, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Chen, P.W. Robust Engineered Circuit Design Principles for Stochastic Biochemical Networks With Parameter Uncertainties and Disturbances. IEEE T Biomed. Circ. S 2008, 2, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Lin, Y.P. A unifying mathematical framework for genetic robustness, environmental robustness, network robustness and their trade-off on phenotype robustness in biological networks Part I, Gene regulatory networks in systems and evolutionary biology. Evol. Bioinform 2013, 9, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Lin, Y.P. A Unifying mathematical framework for genetic robustness, environmental robustness, Network robustness and their tradeoff on phenotype robustness in biological networks Part II, Ecological networks. Evol. Bioinform 2013, 9, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Huang, S.H.; Lan, C.Y.; Chen, B.S. Prediction of phenotype-associated genes via a cellular network approach, a candida albicans infection case study. PloS One 2012, 7, e35339. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, Z.Y.; Chuang, Y.J.; Chao, C.C.; Liu, F.C.; Lan, C.Y.; Chen, B.S. Identification of infection- and defense-related genes via a dynamic host-pathogen interaction network using a candida albicans -zebrafish infection model. J. Innate Immun. 2013, 5, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.T.; Chen, B.S. New measurement methods of network robustness and response ability via microarray data. PloS One 2013, 8, e55230. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, C.T.; Chen, B.S. On the Increase in Network Robustness and Decrease in Network Response Ability During the Aging Process, A Systems Biology Approach via Microarray Data. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2013, 10, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csete, M.E.; Doyle, J.C. Reverse engineering of biological complexity. Science 2002, 295, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, H.U.; Lee, S.Y. Systems metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for L-threonine production. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 149. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, H.U. Application of systems biology for bioprocess development. Trends Biotechnol 2008, 26, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Chang, Y.T.; Wang, Y.C. Robust H infinity-stabilization design in gene networks under stochastic molecular noises, fuzzy-interpolation approach. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern B Cybern 2008, 38, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.H.; Chen, B.S. Construction of a cancer-perturbed protein-protein interaction network for discovery of apoptosis drug targets. BMC Syst. Biol. 2008, 2, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Chang, C.H.; Chuang, Y.J. Robust model matching control of immune systems under environmental disturbances, Dynamic game approach. J. Theor. Biol. 2008, 253, 824–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Yang, S.K.; Lan, C.Y.; Chuang, Y.J. A systems biology approach to construct the gene regulatory network of systemic inflammation via microarray and databases mining. BMC Med. Genomics 2008, 1, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Chen, P.W. On the estimation of robustness and filtering ability of dynamic biochemical networks under process delays, internal parametric perturbations and external disturbances. Math. Biosci. 2009, 222, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Lan, C.Y.; Hsieh, W.P.; Murillo, L.A.; Agabian, N.; Chen, B.S. Global screening of potential Candida albicans biofilm-related transcription factors via network comparison. BMC Bioinf. 2010, 11, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Chen, B.S. Identifying Functional Mechanisms of Gene and Protein Regulatory Networks in Response to a Broader Range of Environmental Stresses. Comp. Funct. Genom. 2010, 2010, 408705. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, T.S.; Cantor, C.R.; Collins, J.J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli. Nature 2000, 403, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elowitz, M.B.; Leibler, S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators. Nature 2000, 403, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasty, J.; McMillen, D.; Collins, J.J. Engineered gene circuits. Nature 2002, 420, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, R.; Weiss, R. Advances in synthetic biology, on the path from prototypes to applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endy, D. Foundations for engineering biology. Nature 2005, 438, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdams, H.H.; Arkin, A. It’s a noisy business! Genetic regulation at the nanomolar scale. Trends Genet. 1999, 15, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batt, G.; Yordanov, B.; Weiss, R.; Belta, C. Robustness analysis and tuning of synthetic gene networks. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2415–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Chang, C.H.; Lee, H.C. Robust synthetic biology design, stochastic game theory approach. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Wu, C.H. A systematic design method for robust synthetic biology to satisfy design specifications. BMC Syst. Biol. 2009, 3, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Chen, P.W. GA-based Design Algorithms for the Robust Synthetic Genetic Oscillators with Prescribed Amplitude, Period and Phase. Gene Regul. Syst. Bio. 2010, 4, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Wu, C.H. Robust optimal reference-tracking design method for stochastic synthetic biology systems, T-S fuzzy approach. IEEE T. Fuzzy Syst. 2010, 18, 1144–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Zhang, W.H.; Chen, B.S. Multiobjective H-2/H-infinity synthetic gene network design based on promoter libraries. Math. Biosci. 2011, 233, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Lee, H.C.; Chen, B.S. Robust synthetic gene network design via library-based search method. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2700–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Hsu, C.Y.; Liou, J.J. Robust design of biological circuits, Evolutionary systems biology approach. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 30423. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.S.; Lin, Y.P. A unifying mathematical framework for genetic robustness, Environmental robustness, Network robustness and their trade-offs on phenotype robustness in biological networks. Part III, Synthetic gene networks in synthetic biology. Evol. Bioinform 2013, 9, 87–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Hsu, C.Y. Robust synchronization control scheme of a population of nonlinear stochastic synthetic genetic oscillators under intrinsic and extrinsic molecular noise via quorum sensing. BMC Systems Biology 2012, 6, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Jeong, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S. Metabolite essentiality elucidates robustness of Escherichia coli metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13638–13642. [Google Scholar]
- Segre, D.; Vitkup, D.; Church, G.M. Analysis of optimality in natural and perturbed metabolic networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15112–15117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, D.; Copeland, W.B.; Sleight, S.C.; Sauro, H.M. Mathematical modeling and synthetic biology. Drug Discovery Today 2008, 5, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Iverson, A.G.; Grayburn, W.S. Engineering a native homoethanol pathway in Escherichia coli B for ethanol production. Biotechnol. Lett. 2008, 30, 335–342. [Google Scholar]
- Shlomi, T.; Eisenberg, Y.; Sharan, R.; Ruppin, E. A genome-scale computational study of the interplay between transcriptional regulation and metabolism. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshidi, N.; Palsson, B.O. Formulating genome-scale kinetic models in the post-genome era. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008, 4, 171–186. [Google Scholar]
- Bonneau, R.; Facciotti, M.T.; Reiss, D.J.; Schmid, A.K.; Pan, M.; Kaur, A.; Thorsson, V.; Shannon, P.; Johnson, M.H.; Bare, J.C.; et al. A predictive model for transcriptional control of physiology in a free living cell. Cell 2007, 131, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuepfer, L.; Sauer, U.; Parrilo, P.A. Efficient classification of complete parameter regions based on semidefinite programming. BMC Bioinf. 2007, 8, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.W.; Hsu, B.D.; Chen, B.S. Constructing gene regulatory networks for long term photosynthetic light acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Bioinf. 2011, 12, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Chen, B.S. A network-based biomarker approach for molecular investigation and diagnosis of lung cancer. BMC Med. Genomics 2011, 4, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Chen, B.S. Integrated cellular network of transcription regulations and protein-protein interactions. BMC Syst. Biol. 2010, 4, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiue, E.; Prather, K.L.J. Synthetic biology devices as tools for metabolic engineering. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 65, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Zhang, W.H. Stochastic H(2)/H(infinity) control with state-dependent noise. IEEE T Automat. Contr. 2004, 49, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Chen, B.S.; Tseng, C.S. Robust H-infinity filtering for nonlinear stochastic systems. IEEE T Signal. Proces. 2005, 53, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Chen, B.S. State feedback H(infinity) control for a class of nonlinear stochastic systems. Siam J. Control. Optim 2006, 44, 1973–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.R.; Marton, M.J.; Jones, A.R.; Roberts, C.J.; Stoughton, R.; Armour, C.D.; Bennett, H.A.; Coffey, E.; Dai, H.Y.; He, Y.D.D.; et al. Functional discovery via a compendium of expression profiles. Cell 2000, 102, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, R. System Modeling & Identification; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.W.; Chu, Y.H.; Chen, B.S. Construction and clarification of dynamic gene regulatory network of cancer cell cycle via microarray data. Cancer Informatics 2006, 2, 223–241. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.P. Linear Matrix Inequalities in System and Control Theory; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kitano, H. Biological robustness. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Chen, W.H.; Wu, H.L. Robust H-2/H-infinity global linearization filter design for nonlinear stochastic systems. IEEE T Circuits-I 2009, 56, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Lee, T.S.; Feng, J.H. A nonlinear H-Infinity control design in robotic systems under parameter perturbation and external disturbance. Int J. Control. 1994, 59, 439–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Tseng, C.S.; Uang, H.J. Mixed H-2/H-infinity fuzzy output feedback control design for nonlinear dynamic systems, An LMI approach. IEEE T. Fuzzy Syst. 2000, 8, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, J.; Cookson, S.; Bennett, M.R.; Mather, W.H.; Tsimring, L.S.; Hasty, J. A fast, robust and tunable synthetic gene oscillator. Nature 2008, 456, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigges, M.; Marquez-Lago, T.T.; Stelling, J.; Fussenegger, M. A tunable synthetic mammalian oscillator. Nature 2009, 457, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Gerchman, Y.; Collins, C.H.; Arnold, F.H.; Weiss, R. A synthetic multicellular system for programmed pattern formation. Nature 2005, 434, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.Y.; Choi, Y.S.; Ma, W.; Pomerening, J.R.; Tang, C.; Ferrell, J.E., Jr. Robust, Tunable biological oscillations from interlinked positive and negative feedback loops. Science 2008, 321, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alon, U. An Introduction to Systems Biology, Design Principles of Biological Circuits; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, T.; Wang, X.; Collins, J.J. Diversity-based, Model-guided construction of synthetic gene networks with predicted functions. Nat. Biotechnol 2009, 27, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragon-Palomino, O.; Danino, T.; Selimkhanov, J.; Tsimring, L.; Hasty, J. Entrainment of a Population of Synthetic Genetic Oscillators. Science 2011, 333, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Matsuoka, Y.; Asai, Y.; Hsin, K.Y.; Kitano, H. Software for systems biology, from tools to integrated platforms. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 821–832. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, K.Y.; Wang, F.S. Evolutionary optimization with data collocation for reverse engineering of biological networks. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Tseng, C.S.; Uang, H.J. Robustness design of nonlinear dynamic systems via fuzzy linear control. IEEE T. Fuzzy Syst. 1999, 7, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Computational systems biology. Nature 2002, 420, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.-S.; Wu, C.-C. Systems Biology as an Integrated Platform for Bioinformatics, Systems Synthetic Biology, and Systems Metabolic Engineering. Cells 2013, 2, 635-688. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells2040635
Chen B-S, Wu C-C. Systems Biology as an Integrated Platform for Bioinformatics, Systems Synthetic Biology, and Systems Metabolic Engineering. Cells. 2013; 2(4):635-688. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells2040635
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Bor-Sen, and Chia-Chou Wu. 2013. "Systems Biology as an Integrated Platform for Bioinformatics, Systems Synthetic Biology, and Systems Metabolic Engineering" Cells 2, no. 4: 635-688. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells2040635
APA StyleChen, B.-S., & Wu, C.-C. (2013). Systems Biology as an Integrated Platform for Bioinformatics, Systems Synthetic Biology, and Systems Metabolic Engineering. Cells, 2(4), 635-688. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells2040635




