DUSP5 Downregulation in Nucleus Accumbens Core Correlates with Cocaine-Induced Maladaptive Synaptic Plasticity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Housing and Surgery
2.2. Drugs and Reagents Used
2.3. Self-Administration (SA), Extinction, and Reinstatement
2.4. Quantification of Dendritic Spine Morphology and Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Statistics
2.6. Methods of Phillips and Tuscher et al., 2023 [29]
2.6.1. Behavioral Procedures
2.6.2. Single-Nucleus Isolation and snRNA-Seq
2.6.3. Differential Expression and Functional Analyses
- Gini coefficient calculations to assess transcriptional specificity.
- Rank–rank hypergeometric overlap (RRHO) to quantify transcriptomic similarity across conditions.
- Gene ontology analyses via g:Profiler using Benjamini–Hochberg correction.
2.6.4. Cross-Species Conservation Analysis
2.6.5. Tissue Preparation and RNAscope Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
2.6.6. Image Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DUSPs mRNA Levels Changes in D1-MSN in NAcore Isolated from Non-Contingent Saline- and Cocaine-Injected Rats
3.2. Cocaine-Treatment Decreased DUSP5 Immunoreactivity in NAcore MSNs
3.3. DUSP5 Immunoreactivity in NAcore MSN Correlates with Active Lever Presses During Reinstatement
3.4. Enhanced Synaptic Plasticity in NAcore MSNs During Cue-Induced Reinstatement
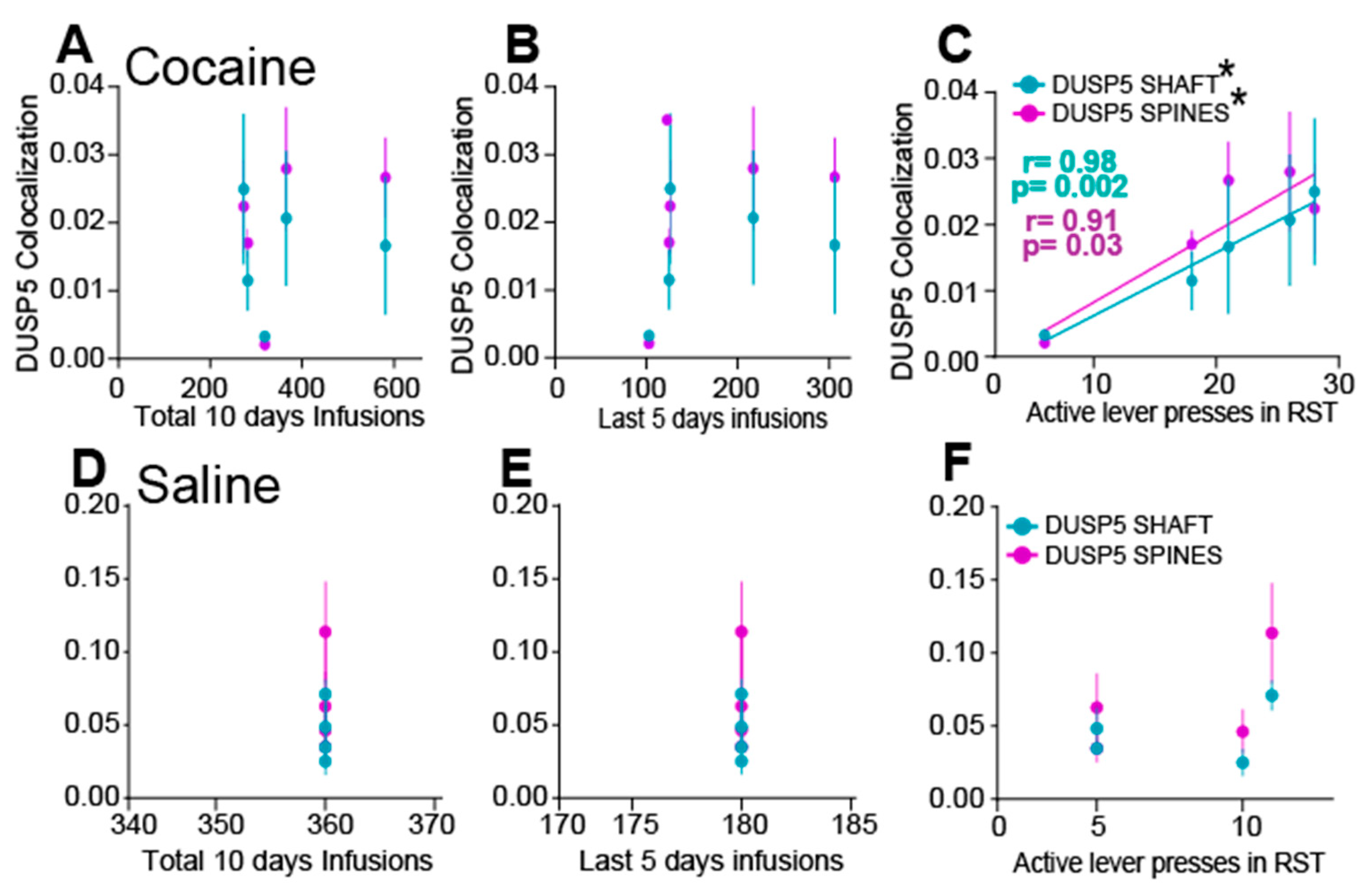
3.5. Cocaine Disrupts the Correlation Between DUSP5 Immunoreactivity and Synaptic Plasticity Markers in NAcore MSNs
4. Discussion
4.1. Dynamic Regulation of DUSP5 Across the Addiction Cycle
4.2. DUSP5 Deficiency Correlates with Cocaine-Seeking Behavior
4.3. Mechanistic Insights: DUSP5
4.4. Limitations of the Interpretation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, J.; Shover, C.L. Charting the fourth wave: Geographic, temporal, race/ethnicity and demographic trends in polysubstance fentanyl overdose deaths in the United States, 2010–2021. Addiction 2023, 118, 2477–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccarone, D. The rise of illicit fentanyls, stimulants and the fourth wave of the opioid overdose crisis. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2021, 34, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, N.; Beletsky, L.; Ciccarone, D. Opioid Crisis: No Easy Fix to Its Social and Economic Determinants. Am. J. Public Health 2018, 108, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Blanco, C. Substance use disorders: A comprehensive update of classification, epidemiology, neurobiology, clinical aspects, treatment and prevention. World Psychiatry 2023, 22, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Keller, C.; Kupchik, Y.M.; Gipson, C.D.; Brown, R.M.; Spencer, S.; Bollati, F.; Esparza, M.A.; Roberts-Wolfe, D.J.; Heinsbroek, J.A.; Bobadilla, A.C.; et al. Glutamatergic mechanisms of comorbidity between acute stress and cocaine self-administration. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, A.E. Ventral striatal control of appetitive motivation: Role in ingestive behavior and reward-related learning. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 27, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scofield, M.D.; Heinsbroek, J.A.; Gipson, C.D.; Kupchik, Y.M.; Spencer, S.; Smith, A.C.W.; Roberts-Wolfe, D.; Kalivas, P.W. The Nucleus Accumbens: Mechanisms of Addiction across Drug Classes Reflect the Importance of Glutamate Homeostasis. Pharmacol. Rev. 2016, 68, 816–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerfen, C.R.; Surmeier, D.J. Modulation of striatal projection systems by dopamine. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 441–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Garcia, T.R.; Garcia-Keller, C.; Penaloza, T.; Richie, C.T.; Pickel, J.; Hope, B.T.; Harvey, B.K.; Kalivas, P.W.; Heinsbroek, J.A. Ventral Pallidum Is the Primary Target for Accumbens D1 Projections Driving Cocaine Seeking. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gipson, C.D.; Kupchik, Y.M.; Shen, H.; Reissner, K.J.; Thomas, C.A.; Kalivas, P.W. Relapse induced by cues predicting cocaine depends on rapid, transient synaptic potentiation. Neuron 2013, 77, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Salgado, J.M.; Ostroff, L.; Helton, T.D.; Robinson, C.G.; Harris, K.M.; Ehlers, M.D. Plasticity-induced growth of dendritic spines by exocytic trafficking from recycling endosomes. Neuron 2006, 52, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, W.C.; Hill, T.C.; Zito, K. Synapse-specific and size-dependent mechanisms of spine structural plasticity accompanying synaptic weakening. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E305–E312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, R.; Satoh, R.; Takasaki, T. ERK: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer. ERK-Dependent Apoptosis as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, J.L.; Worlikar, S.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr.; Shapiro, P.; Fletcher, S. Small-molecule inhibitors of the ERK signaling pathway: Towards novel anticancer therapeutics. ChemMedChem 2011, 6, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, A.; Sweeney, N.L.; Bongard, R.D.; Syrlybaeva, R.; Gupta, A.; Del Carpio, E.; Talipov, M.R.; Garcia-Keller, C.; Crans, D.C.; Ramchandran, R.; et al. Structural and kinetic characterization of DUSP5 with a Di-phosphorylated tripeptide substrate from the ERK activation loop. Front. Chem. Biol. 2024, 3, 1385560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntz-Melcavage, K.L.; Brucklacher, R.M.; Grigson, P.S.; Freeman, W.M.; Vrana, K.E. Gene expression changes following extinction testing in a heroin behavioral incubation model. BMC Neurosci. 2009, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleman, M.; Chapy, H.; Cisternino, S.; Courtin, C.; Smirnova, M.; Schlatter, J.; Chiadmi, F.; Scherrmann, J.M.; Noble, F.; Marie-Claire, C. Impact of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier on the uptake of heroin and its main metabolites: Behavioral effects and consequences on the transcriptional responses and reinforcing properties. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 3139–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujike, H.; Takaki, M.; Kodama, M.; Kuroda, S. Gene expression related to synaptogenesis, neuritogenesis, and MAP kinase in behavioral sensitization to psychostimulants. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 965, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, M.; Ujike, H.; Kodama, M.; Takehisa, Y.; Nakata, K.; Kuroda, S. Two kinds of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatases, MKP-1 and MKP-3, are differentially activated by acute and chronic methamphetamine treatment in the rat brain. J. Neurochem. 2001, 79, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Dang, W.; Wang, R.; Sun, M.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L. Dual-specificity phosphatase 15 (DUSP15) in the nucleus accumbens is a novel negative regulator of morphine-associated contextual memory. Addict. Biol. 2021, 26, e12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.A.; Ji, F.; Yuferov, V.; Ho, A.; He, C.; Ott, J.; Kreek, M.J. Genome-wide association study identifies genes that may contribute to risk for developing heroin addiction. Psychiatr. Genet. 2010, 20, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutty, R.G.; Talipov, M.R.; Bongard, R.D.; Lipinski, R.A.J.; Sweeney, N.L.; Sem, D.S.; Rathore, R.; Ramchandran, R. Dual Specificity Phosphatase 5-Substrate Interaction: A Mechanistic Perspective. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 7, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talipov, M.R.; Nayak, J.; Lepley, M.; Bongard, R.D.; Sem, D.S.; Ramchandran, R.; Rathore, R. Critical Role of the Secondary Binding Pocket in Modulating the Enzymatic Activity of DUSP5 toward Phosphorylated ERKs. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 6187–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, I.S.; Krate, J.; Schrauwen, I.; Corneveaux, J.J.; Serrano, G.E.; Sue, L.; Beach, T.G.; Huentelman, M.J. Whole transcriptome profiling of the human hippocampus suggests an involvement of the KIBRA rs17070145 polymorphism in differential activation of the MAPK signaling pathway. Hippocampus 2017, 27, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protein Atlas Version 25.0: Noviembre, 11 2025, Protein Atlas Version 1.1. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000138166-DUSP5/brain/hippocampal%2Bformation?utm (accessed on 11 November 2025).
- Garcia-Keller, C.; Neuhofer, D.; Bobadilla, A.-C.; Spencer, S.; Chioma, V.C.; Monforton, C.; Kalivas, P.W. Extracellular Matrix Signaling Through β3 Integrin Mediates Cocaine Cue-Induced Transient Synaptic Plasticity and Relapse. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 86, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Keller, C.; Scofield, M.D.; Neuhofer, D.; Varanasi, S.; Reeves, M.T.; Hughes, B.; Anderson, E.; Richie, C.T.; Mejias-Aponte, C.; Pickel, J.; et al. Relapse-Associated Transient Synaptic Potentiation Requires Integrin-Mediated Activation of Focal Adhesion Kinase and Cofilin in D1-Expressing Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 8463–8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiki, R.M.; Cornbrooks, R.G.; Magami, K.; Greige, A.; Snyder, K.K.; Wood, D.J.; Herrington, M.C.; Mace, P.; Blidy, K.; Koike, N.; et al. A long noncoding eRNA forms R-loops to shape emotional experience-induced behavioral adaptation. Science 2024, 386, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.A., III; Tuscher, J.J.; Fitzgerald, N.D.; Wan, E.; Zipperly, M.E.; Duke, C.G.; Ianov, L.; Day, J.J. Distinct subpopulations of D1 medium spiny neurons exhibit unique transcriptional responsiveness to cocaine. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 125, 103849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S.; Garcia-Keller, C.; Roberts-Wolfe, D.; Heinsbroek, J.A.; Mulvaney, M.; Sorrell, A.; Kalivas, P.W. Cocaine Use Reverses Striatal Plasticity Produced During Cocaine Seeking. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gipson, C.D.; Reissner, K.J.; Kupchik, Y.M.; Smith, A.C.W.; Stankeviciute, N.; Hensley-Simon, M.E.; Kalivas, P.W. Reinstatement of nicotine seeking is mediated by glutamatergic plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9124–9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobadilla, A.C.; Heinsbroek, J.A.; Gipson, C.D.; Griffin, W.C.; Fowler, C.D.; Kenny, P.J.; Kalivas, P.W. Corticostriatal plasticity, neuronal ensembles, and regulation of drug-seeking behavior. Prog. Brain Res. 2017, 235, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borczyk, M.; Sliwinska, M.A.; Caly, A.; Bernas, T.; Radwanska, K. Neuronal plasticity affects correlation between the size of dendritic spine and its postsynaptic density. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotulainen, P.; Hoogenraad, C.C. Actin in dendritic spines: Connecting dynamics to function. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.W.; Gipson, C.D.; Huits, M.; Kalivas, P.W. Prelimbic cortex and ventral tegmental area modulate synaptic plasticity differentially in nucleus accumbens during cocaine-reinstated drug seeking. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.E.; Kolb, B. Structural plasticity associated with exposure to drugs of abuse. Neuropharmacology 2004, 47, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, S.J.; Dietz, D.M.; Dumitriu, D.; Morrison, J.H.; Malenka, R.C.; Nestler, E.J. The addicted synapse: Mechanisms of synaptic and structural plasticity in nucleus accumbens. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S. Regulation of actin filament dynamics by actin depolymerizing factor/cofilin and actin-interacting protein 1: New blades for twisted filaments. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 13363–13370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciello, F.; Battistoni, M.; Martini, S.; Simone, C.; Pastore, F.; Sollazzo, R.; Grassi, C.; Ripoli, C. Role of LIMK1-cofilin-actin axis in dendritic spine dynamics in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, M.B. ADF/cofilin: A crucial regulator of synapse physiology and behavior. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3521–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
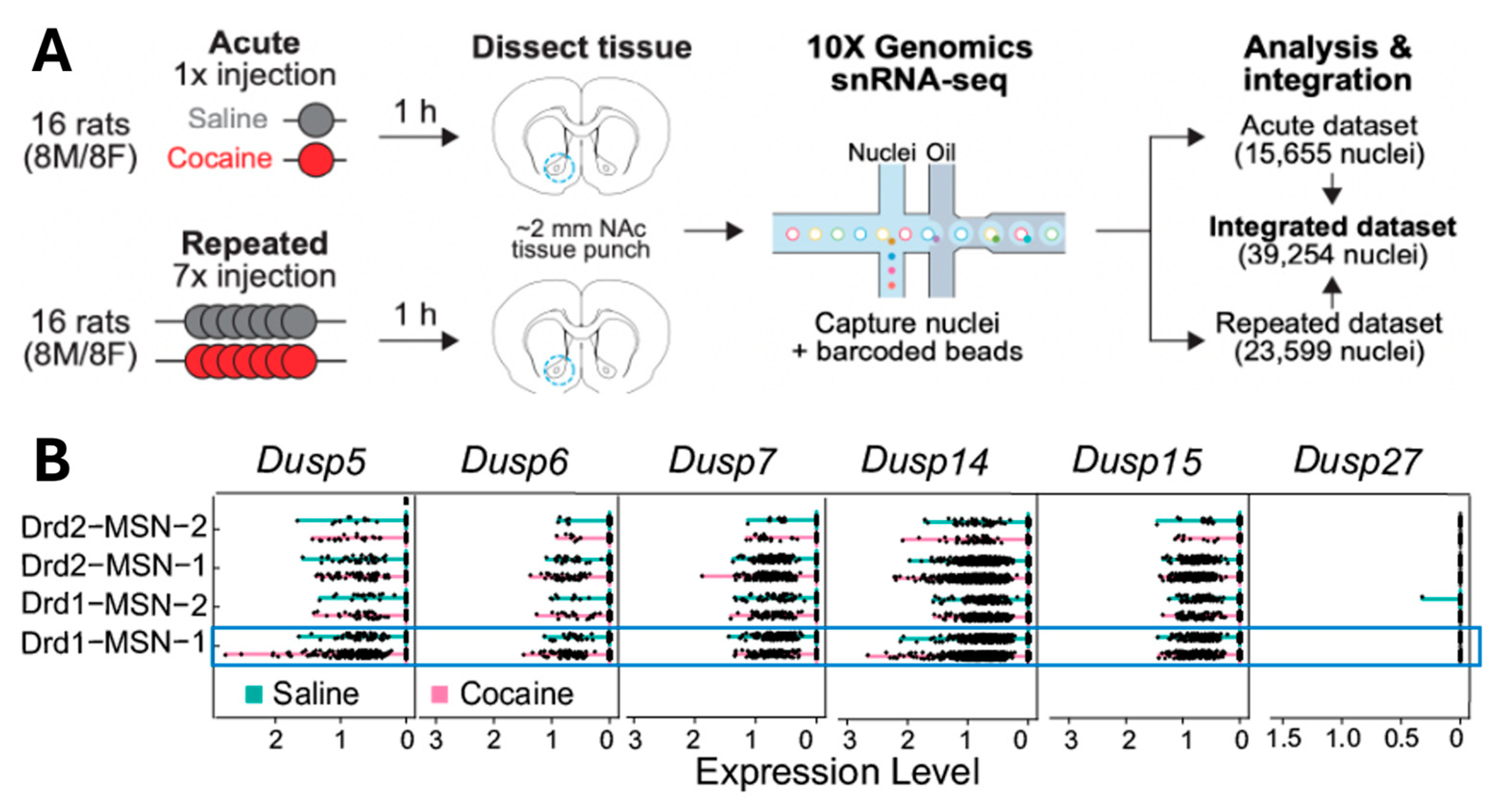



| Gene | Condition | p-Value | p-adj | log2 Fold Change | Significant? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dusp5 | Acute cocaine | <0.00001 | 0.0003 | 2.778 | Yes |
| Repeated cocaine | 0.509 | 0.997 | 0.416 | No | |
| Dusp6 | Acute cocaine | 0.001 | N/A | 2.837 | No |
| Repeated cocaine | 0.747 | 0.997 | −0.303 | No | |
| Dusp7 | Acute cocaine | 0.093 | 0.961 | −0.908 | No |
| Repeated cocaine | 0.998 | 0.997 | 0.006 | No | |
| Dusp14 | Acute cocaine | 0.018 | 0.474 | 0.758 | No |
| Repeated cocaine | 0.495 | 0.997 | 0.181 | No | |
| Dusp15 | Acute cocaine | 0.819 | 0.983 | −0.115 | No |
| Repeated cocaine | 0.766 | 0.997 | 0.123 | No | |
| Limk1 | Acute cocaine | 0.742 | 0.983 | −0.162 | No |
| Repeated cocaine | 0.741 | 0.997 | 0.179 | No | |
| Limk2 | Acute cocaine | 0.278 | 0.983 | −0.271 | No |
| Repeated cocaine | 0.572 | 0.997 | −0.125 | No | |
| Mapk1 | Acute cocaine | 0.741 | 0.983 | −0.044 | No |
| Repeated cocaine | 0.609 | 0.997 | −0.059 | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Taborda-Bejarano, J.P.; Meyerink, M.; Crans, D.C.; Ramchandran, R.; Garcia-Keller, C. DUSP5 Downregulation in Nucleus Accumbens Core Correlates with Cocaine-Induced Maladaptive Synaptic Plasticity. Cells 2026, 15, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells15010032
Taborda-Bejarano JP, Meyerink M, Crans DC, Ramchandran R, Garcia-Keller C. DUSP5 Downregulation in Nucleus Accumbens Core Correlates with Cocaine-Induced Maladaptive Synaptic Plasticity. Cells. 2026; 15(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells15010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaborda-Bejarano, Juan Pablo, Michael Meyerink, Debbie C. Crans, Ramani Ramchandran, and Constanza Garcia-Keller. 2026. "DUSP5 Downregulation in Nucleus Accumbens Core Correlates with Cocaine-Induced Maladaptive Synaptic Plasticity" Cells 15, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells15010032
APA StyleTaborda-Bejarano, J. P., Meyerink, M., Crans, D. C., Ramchandran, R., & Garcia-Keller, C. (2026). DUSP5 Downregulation in Nucleus Accumbens Core Correlates with Cocaine-Induced Maladaptive Synaptic Plasticity. Cells, 15(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells15010032









