ALKBH5 Improves the Epithelial Cell Tight Junctions to Inhibit Escherichia coli-Induced Mastitis
Abstract
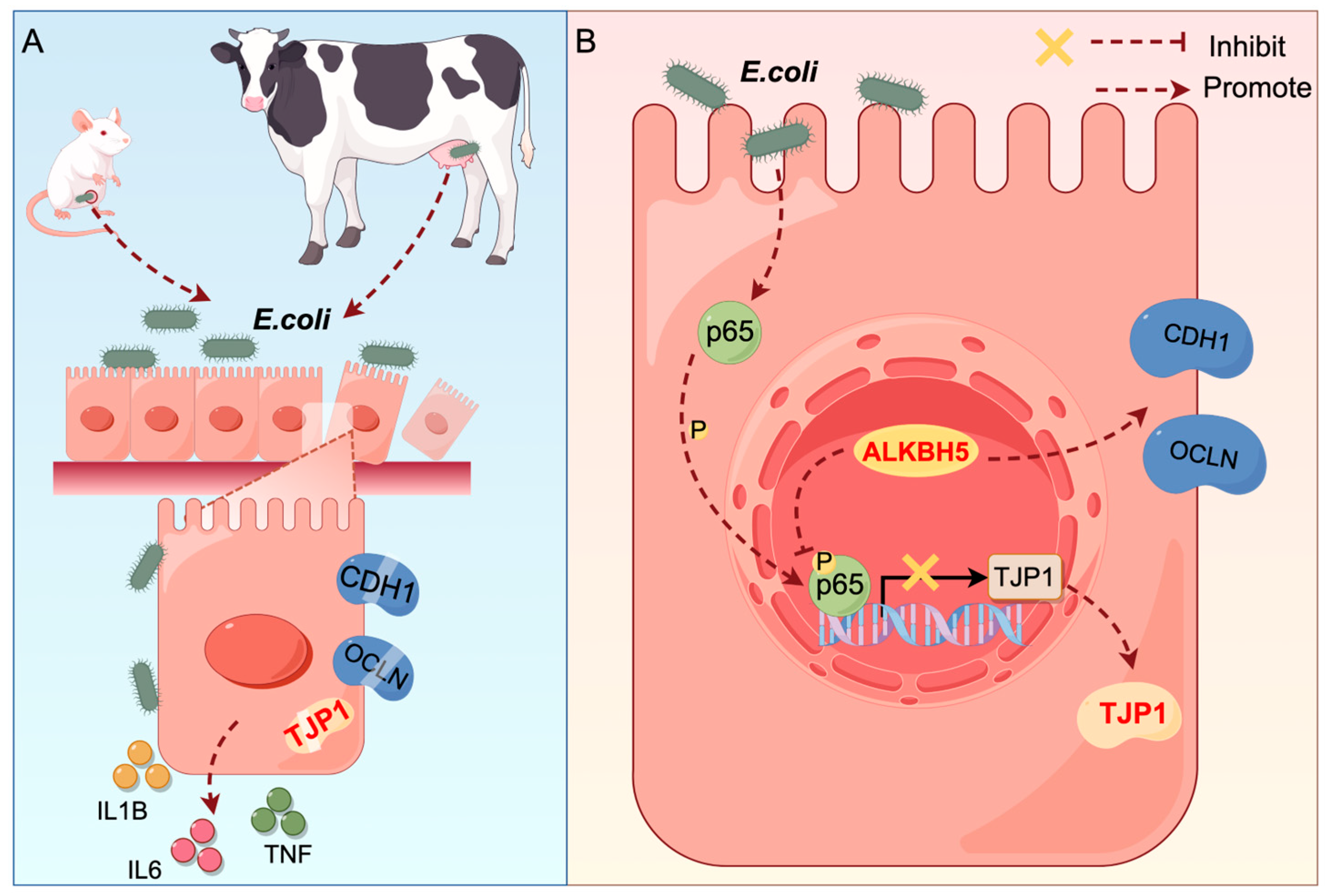
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line, Bacteria, and Mouse
2.2. Gene Knockdown
2.3. Cell Adhesion Assay
2.4. CHIP
2.5. Dual-Luciferase Assay
2.6. Molecular Docking Analysis
2.7. Mouse Mastitis Model Construction
2.8. Mouse Live Imaging
2.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.10. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.11. HE and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining
2.12. RT-qPCR
2.13. Western Blot
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
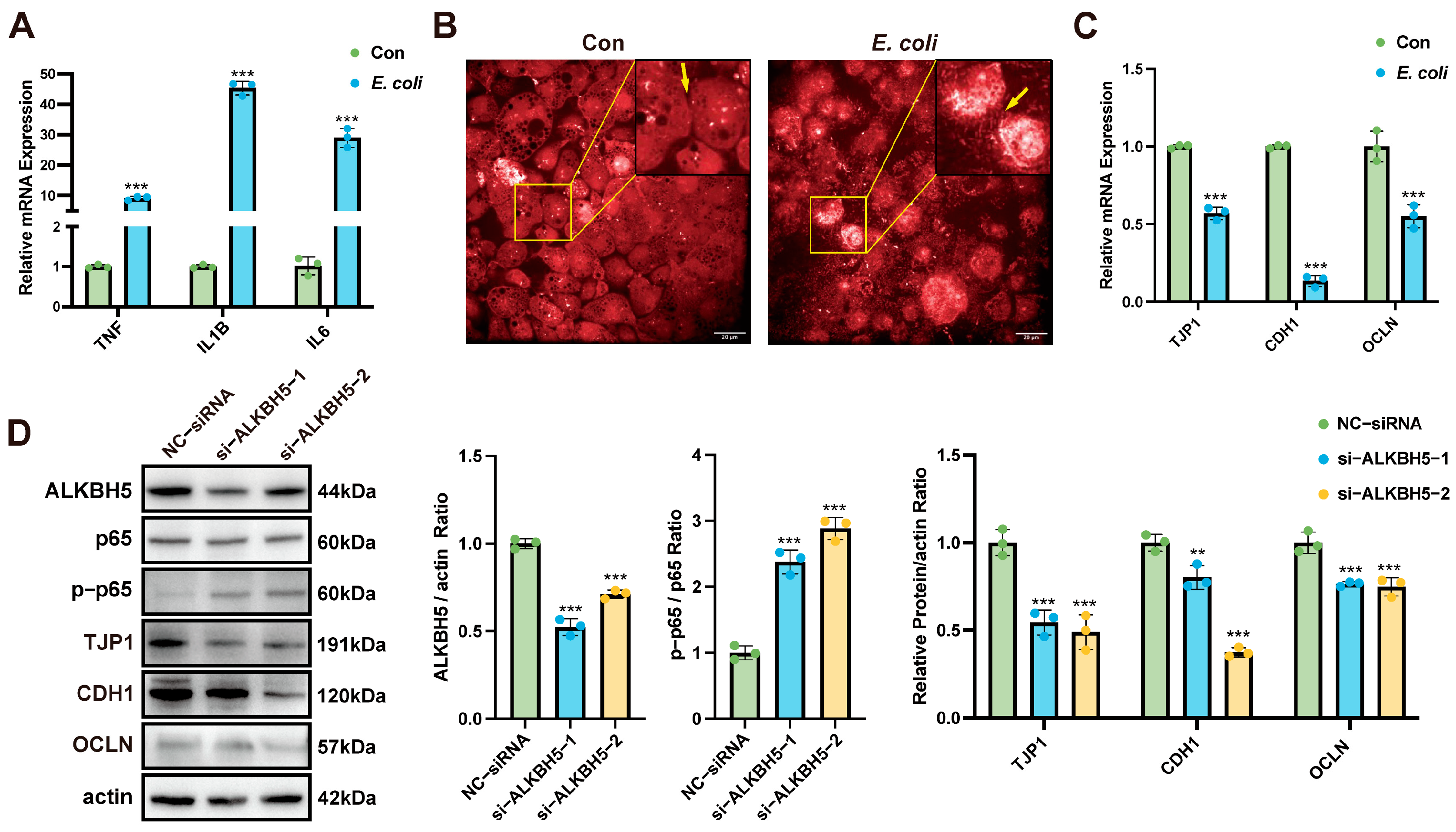
3.1. ALKBH5 Inhibits E. coli-Induced Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cell Tight Junction Disruption
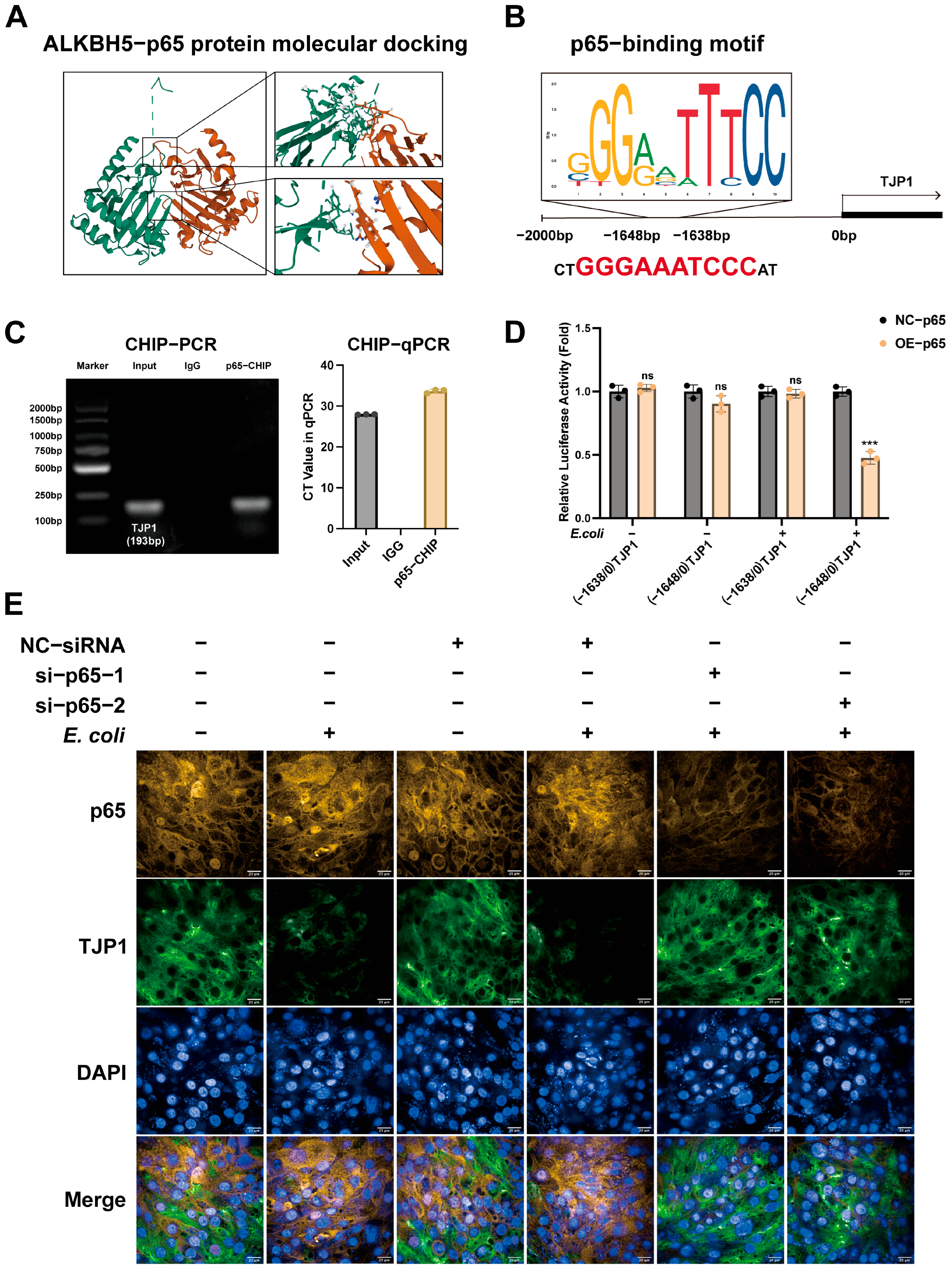
3.2. ALKBH5 Mediates p65 to Promote TJP1 Expression
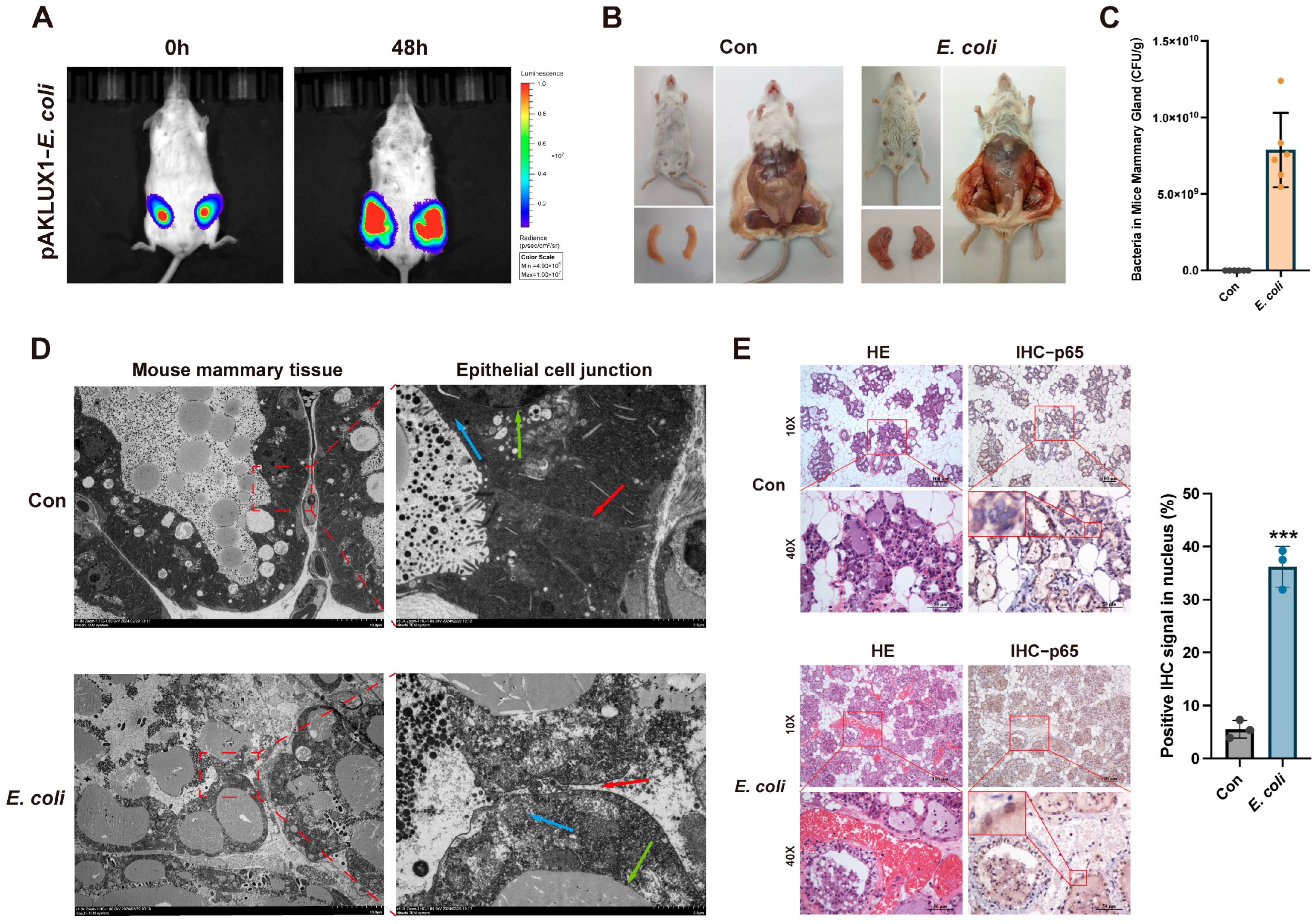
3.3. E. coli Induces Mouse Mastitis and Disrupts Epithelial Cell Tight Junctions
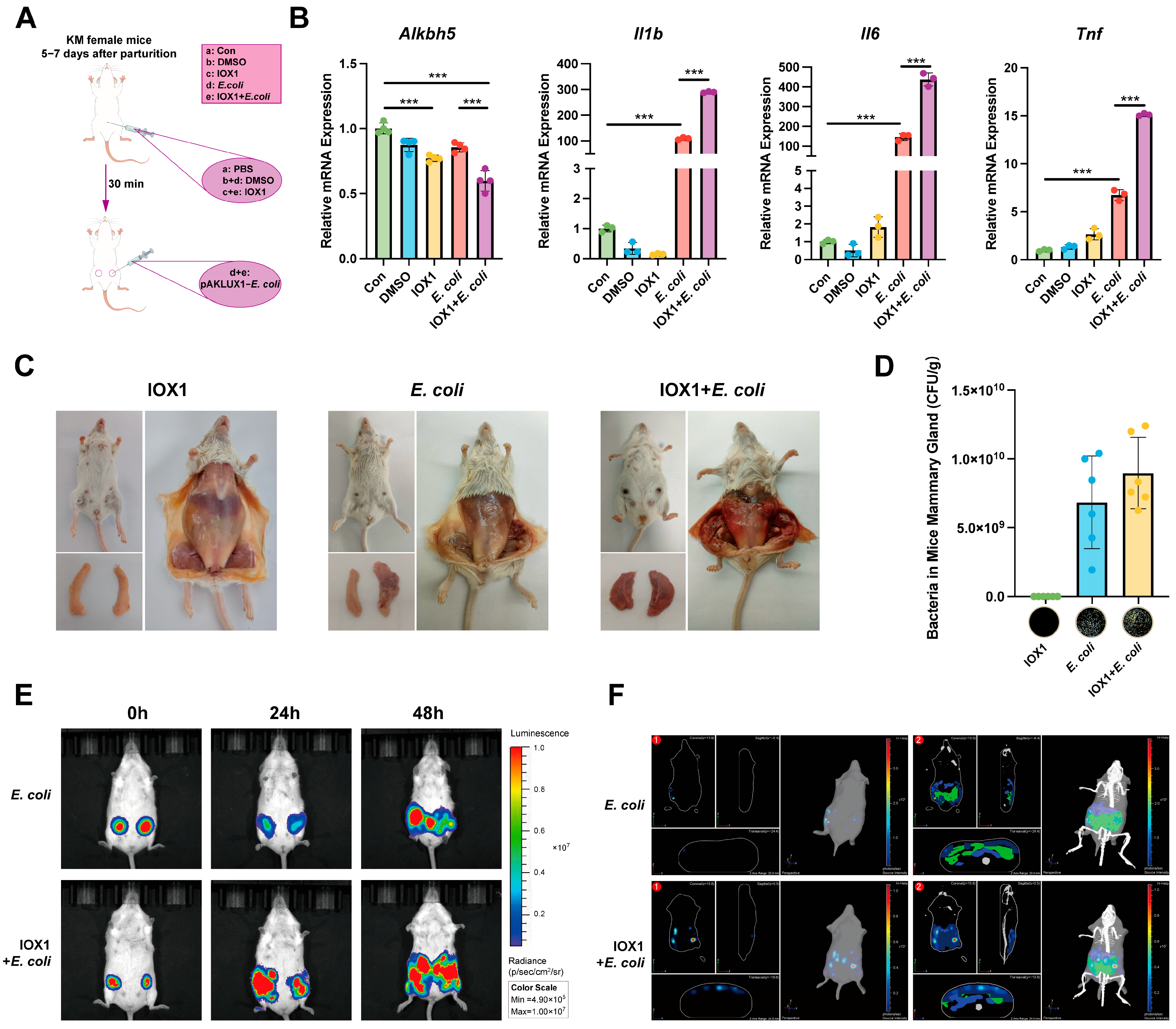
3.4. Inhibition of ALKBH5 Aggravates Mastitis
3.5. Inhibition of ALKBH5 Aggravates Epithelial Cell Tight Junctions Disruption
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| ALKBH5 | AlkB Homolog 5 |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-B |
| M6A | N6-methyladenosine |
| TJP1 | tight junction protein 1 |
| CDH1 | cadherin 1 |
| OCLN | occluding |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| IL1B | interleukin 1 beta |
| IL6 | interleukin 6 |
| ACTB | actin beta |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscope |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IF | Immunofluorescence |
| CHIP | Chromatin Immunoprecipitation |
References
- Huma, Z.I.; Sharma, N.; Kour, S.; Lee, S.J. Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of Bovine Mastitis Milk Origin Bacteria and Linkage of Intramammary Infection with Milk Quality. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 885134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharun, K.; Dhama, K.; Tiwari, R.; Gugjoo, M.B.; Yatoo, M.I.; Patel, S.K.; Pathak, M.; Karthik, K.; Khurana, S.K.; Singh, R.; et al. Advances in therapeutic and managemental approaches of bovine mastitis: A comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 2021, 41, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Ubaldo, A.L.; Rivero-Perez, N.; Valladares-Carranza, B.; Velázquez-Ordoñez, V.; Delgadillo-Ruiz, L.; Zaragoza-Bastida, A. Bovine mastitis, a worldwide impact disease: Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and viable alternative approaches. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2023, 21, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, Z.; Shi, X.; Guo, A.; Hu, C. N6-methyladenosine-modified lncRNA in Staphylococcus aureus-injured bovine mammary epithelial cells. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, V.; McClure, J.; Léger, D.; Dufour, S.; Sheldon, A.; Scholl, D.; Barkema, H. Antimicrobial use on Canadian dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyra, V.G.; Pol, M.; Pastorino, F.; Herrero, A. Quantification of antimicrobial usage in dairy cows and preweaned calves in Argentina. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 122, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.; Piepers, S.; Supré, K.; Dewulf, J.; De Vliegher, S. Quantification of antimicrobial consumption in adult cattle on dairy herds in Flanders, Belgium, and associations with udder health, milk quality, and production performance. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2118–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordillo, L.M. Mammary Gland Immunobiology and Resistance to Mastitis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2018, 34, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelwagen, K.; Singh, K. The Role of Tight Junctions in Mammary Gland Function. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2013, 19, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo-Boyso, J.; Valdez-Alarcón, J.J.; Cajero-Juárez, M.; Ochoa-Zarzosa, A.; López-Meza, J.E.; Bravo-Patiño, A.; Baizabal-Aguirre, V.M. Innate immune response of bovine mammary gland to pathogenic bacteria responsible for mastitis. J. Infect. 2007, 54, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albelda, S.M.; Smith, C.W.; Ward, P.A. Adhesion molecules and inflammatory injury. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, S.; Huo, L.; Ding, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Lv, C.; Wu, H.; et al. Deoxynivalenol exposure inhibits biosynthesis of milk fat and protein by impairing tight junction in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ao, C. Ethanol Extract of Artemisia Annua Prevents LPS-Induced Inflammation and Blood–Milk Barrier Disruption in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Animals 2022, 12, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminsky, L.W.; Al-Sadi, R.; Ma, T.Y. IL-1β and the Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Barrier. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 767456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Duan, H. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer metabolism. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, B.; Nie, Z.; Duan, L.; Xiong, Q.; Jin, Z.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y. The role of m6A modification in the biological functions and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lin, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Qi, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. ALKBH5 Stabilized N6-Methyladenosine-Modified LOC4191 to Suppress E. coli-Induced Apoptosis. Cells 2023, 12, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Yan, H.; Hou, Y.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, E.; He, J.; Cai, Z. RNA demethylase ALKBH5 in cancer: From mechanisms to therapeutic potential. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Gu, Q.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.A. The biological function of m6A demethylase ALKBH5 and its role in human disease. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 347. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Song, R.; Zhao, L.; Lu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhan, X.; Lu, F.; Yang, J.; Niu, Y.; Cao, X. m6A demethylase ALKBH5 is required for antibacterial innate defense by intrinsic motivation of neutrophil migration. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; You, Y.; Lu, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, P.; Liu, L.; Xu, H.; Niu, Y.; Cao, X. N6-methyladenosine RNA modification-mediated cellular metabolism rewiring inhibits viral replication. Science 2019, 365, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Lin, C.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, H.; Yin, Y.; Wang, C.; Tang, X.; Song, T.; Guo, A.; Chen, Y.; et al. Transcriptome Profiling of m6A mRNA Modification in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells Treated with Escherichia coli. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aik, W.; Scotti, J.S.; Choi, H.; Gong, L.; Demetriades, M.; Schofield, C.J.; McDonough, M.A. Structure of human RNA N6-methyladenine demethylase ALKBH5 provides insights into its mechanisms of nucleic acid recognition and demethylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 4741–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Hu, X.; Qiu, M.; Bao, L.; Wu, K.; Meng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, L.; Duan, S.; He, Y.; et al. Sialic acid exacerbates gut dysbiosis-associated mastitis through the microbiota-gut-mammary axis by fueling gut microbiota disruption. Microbiome 2023, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, F.B.; Cunha, P.; Jensen, K.; Glass, E.J.; Foucras, G.; Robert-Granié, C.; Rupp, R.; Rainard, P. Differential response of bovine mammary epithelial cells to Staphylococcus aureus or Escherichia coli agonists of the innate immune system. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M.; Liang, G.; Beaudoin, F.; Zhao, X.; Guan, L.L. Transcriptome microRNA profiling of bovine mammary epithelial cells challenged with Escherichia coli or Staphylococcus aureusbacteria reveals pathogen directed microRNA expression profiles. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, J.; Koczan, D.; Yang, W.; Nürnberg, G.; Repsilber, D.; Schuberth, H.-J.; Park, Z.; Maqbool, N.; Molenaar, A.; Seyfert, H.-M. Assessment of the immune capacity of mammary epithelial cells: Comparison with mammary tissue after challenge with Escherichia coli. Vet. Res. 2009, 40, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, R.M.; Schwertz, C.I.; de Cecco, B.S.; Panziera, W.; De Lorenzo, C.; Heck, L.C.; Snel, G.G.M.; Lopes, B.C.; da Silva, F.S.; Pavarini, S.P.; et al. Pathological and microbiological characterization of mastitis in dairy cows. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaatout, N. An overview on mastitis-associated Escherichia coli: Pathogenicity, host immunity and the use of alternative therapies. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 256, 126960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballou, M.A. GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT SYMPOSIUM: Inflammation: Role in the etiology and pathophysiology of clinical mastitis in dairy cows1. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasig, I.E.; Bellmann, C.; Cording, J.; del Vecchio, G.; Zwanziger, D.; Huber, O.; Haseloff, R.F. Occludin Protein Family: Oxidative Stress and Reducing Conditions. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1195–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mariscal, L.; Quirós, M.; Díaz-Coránguez, M. ZO Proteins and Redox-Dependent Processes. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1235–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corps, K.N.; Roth, T.L.; McGavern, D.B. Inflammation and Neuroprotection in Traumatic Brain Injury. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raby, K.L.; Michaeloudes, C.; Tonkin, J.; Chung, K.F.; Bhavsar, P.K. Mechanisms of airway epithelial injury and abnormal repair in asthma and COPD. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1201658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Wang, S.; Nagpal, R.; Wang, B.; Jain, S.; Razazan, A.; Mishra, S.P.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Kavanagh, K.; et al. A human-origin probiotic cocktail ameliorates aging-related leaky gut and inflammation via modulating the microbiota/taurine/tight junction axis. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 5, e132055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittekindt, O.H. Tight junctions in pulmonary epithelia during lung inflammation. Pflüg. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2017, 469, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, D.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Han, Y.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Electroacupuncture restores intestinal mucosal barrier through TLR4/NF-κB p65 pathway in functional dyspepsia-like rats. Anat. Rec. 2023, 306, 2927–2938. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Zhu, Y.; Le, G. Tetramethylpyrazine Alleviates Tight Junction Disruption of Bronchial Mucosal Epithelial Cells Caused by Interleukin-17 via Inhibiting Nuclear Factor-κB-p65/Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Signaling Pathway. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2021, 41, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, S. Lactobacillus casei Zhang Counteracts Blood-Milk Barrier Disruption and Moderates the Inflammatory Response in Escherichia coli-Induced Mastitis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 675492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, A.M.M.; Ko, E.K.; Huang, S.; Pacella, G.; Kuprasertkul, N.; D’souza, C.A.; Hueros, R.A.R.; Shen, H.; Stoute, J.; Elashal, H.; et al. Mettl3-catalyzed m6 A regulates histone modifier and modification expression in self-renewing somatic tissue. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, C.; Yang, K.; Gao, R.; Cao, Y.; Liang, L.; Chen, A.; Zu, S.; Rong, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Inhibition of ALKBH5 attenuates I/R-induced renal injury in male mice by promoting Ccl28 m6A modification and in-creasing Treg recruitment. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.-X.; Zhu, H.-J.; Zhang, Y.-R.; Wang, J.-N.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Q.-C.; Ji, J.-D.; Jiang, C.; Yuan, S.-T.; Chen, X.; et al. ALKBH5 causes retinal pigment epithelium anomalies and choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration via the AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Song, R.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhan, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, X. The RNA m6A demethylase ALKBH5 drives emergency granulopoiesis and neutrophil mobilization by upregulating G-CSFR expression. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 21, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zou, Y.; Copland, D.A.; Schewitz-Bowers, L.P.; Li, Y.; Lait, P.J.; Stimpson, M.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, S.; Liang, J.; et al. Epigenetic drug screen identified IOX1 as an inhibitor of Th17-mediated inflammation through targeting TET2. EBioMedicine 2022, 86, 104333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Shen, F.; Meng, Y. Lysine demethylase KDM3A alleviates hyperoxia-induced bronchopulmonary dysplasia in mice by promoting ETS1 expression. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 435, 113945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-C. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Xu, H.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Hu, Y.; Guo, A.; Hu, C. ALKBH5 Improves the Epithelial Cell Tight Junctions to Inhibit Escherichia coli-Induced Mastitis. Cells 2025, 14, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070521
Wu X, Xu H, Peng Y, Zhang R, Hu Y, Guo A, Hu C. ALKBH5 Improves the Epithelial Cell Tight Junctions to Inhibit Escherichia coli-Induced Mastitis. Cells. 2025; 14(7):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070521
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xuan, Haojun Xu, Yongchong Peng, Ruikai Zhang, Yanjun Hu, Aizhen Guo, and Changmin Hu. 2025. "ALKBH5 Improves the Epithelial Cell Tight Junctions to Inhibit Escherichia coli-Induced Mastitis" Cells 14, no. 7: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070521
APA StyleWu, X., Xu, H., Peng, Y., Zhang, R., Hu, Y., Guo, A., & Hu, C. (2025). ALKBH5 Improves the Epithelial Cell Tight Junctions to Inhibit Escherichia coli-Induced Mastitis. Cells, 14(7), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070521






